Most cited
- Page Path
- HOME > BROWSE ARTICLES > Most cited
From articles published in Endocrinology and Metabolism during the past two years (2022 ~ ).
Review Article
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Homeostatic Regulation of Glucose Metabolism by the Central Nervous System
- Jong Han Choi, Min-Seon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):9-25. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1364

- 5,511 View
- 355 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Evidence for involvement of the central nervous system (CNS) in the regulation of glucose metabolism dates back to the 19th century, although the majority of the research on glucose metabolism has focused on the peripheral metabolic organs. Due to recent advances in neuroscience, it has now become clear that the CNS is indeed vital for maintaining glucose homeostasis. To achieve normoglycemia, specific populations of neurons and glia in the hypothalamus sense changes in the blood concentrations of glucose and of glucoregulatory hormones such as insulin, leptin, glucagon-like peptide 1, and glucagon. This information is integrated and transmitted to other areas of the brain where it eventually modulates various processes in glucose metabolism (i.e., hepatic glucose production, glucose uptake in the brown adipose tissue and skeletal muscle, pancreatic insulin and glucagon secretion, renal glucose reabsorption, etc.). Errors in these processes lead to hyper- or hypoglycemia. We here review the current understanding of the brain regulation of glucose metabolism.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sympathetic nerve-enteroendocrine L cell communication modulates GLP-1 release, brain glucose utilization, and cognitive function
Wenran Ren, Jianhui Chen, Wenjing Wang, Qingqing Li, Xia Yin, Guanglei Zhuang, Hong Zhou, Wenwen Zeng
Neuron.2024; 112(6): 972. CrossRef - Hypothalamic astrocyte NAD+ salvage pathway mediates the coupling of dietary fat overconsumption in a mouse model of obesity
Jae Woo Park, Se Eun Park, Wuhyun Koh, Won Hee Jang, Jong Han Choi, Eun Roh, Gil Myoung Kang, Seong Jun Kim, Hyo Sun Lim, Chae Beom Park, So Yeon Jeong, Sang Yun Moon, Chan Hee Lee, Sang Yeob Kim, Hyung Jin Choi, Se Hee Min, C. Justin Lee, Min-Seon Kim
Nature Communications.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of metformin and electrical pulses in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells
Praveen Sahu, Ignacio G. Camarillo, Raji Sundararajan
Exploration of Targeted Anti-tumor Therapy.2024; 5(1): 54. CrossRef - Redox imbalance and metabolic defects in the context of Alzheimer disease
Fabio Di Domenico, Chiara Lanzillotta, Marzia Perluigi
FEBS Letters.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity-associated microglial inflammatory activation paradoxically improves glucose tolerance
John D. Douglass, Kelly M. Ness, Martin Valdearcos, Alice Wyse-Jackson, Mauricio D. Dorfman, Jeremy M. Frey, Rachael D. Fasnacht, Olivia D. Santiago, Anzela Niraula, Jineta Banerjee, Megan Robblee, Suneil K. Koliwad, Joshua P. Thaler
Cell Metabolism.2023; 35(9): 1613. CrossRef - Phenotypic screening using waveform analysis of synchronized calcium oscillations in primary cortical cultures
Richi Sakaguchi, Saki Nakamura, Hiroyuki Iha, Masaki Tanaka, Ming Tatt Lee
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(4): e0271782. CrossRef - Effects of Escitalopram on the Functional Neural Circuits in an Animal Model of Adolescent Depression
Se Jong Oh, Namhun Lee, Kyung Rok Nam, Kyung Jun Kang, Sang Jin Han, Jae Yong Choi
Molecular Imaging and Biology.2023; 25(4): 735. CrossRef - A Survey of Deep Learning for Alzheimer’s Disease
Qinghua Zhou, Jiaji Wang, Xiang Yu, Shuihua Wang, Yudong Zhang
Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction.2023; 5(2): 611. CrossRef - Potassium channels in behavioral brain disorders. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential: A narrative review
Kazi Asraful Alam, Pernille Svalastoga, Aurora Martinez, Jeffrey Colm Glennon, Jan Haavik
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews.2023; 152: 105301. CrossRef - Knockout of Nur77 Leads to Amino Acid, Lipid, and Glucose Metabolism Disorders in Zebrafish
Yang Xu, Juanjuan Tian, Qi Kang, Hang Yuan, Chengdong Liu, Zhehui Li, Jie Liu, Mingyu Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the POMC System on Glucose Homeostasis and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Obesity and Diabetes
Dan Yang, Xintong Hou, Guimei Yang, Mengnan Li, Jian Zhang, Minmin Han, Yi Zhang, Yunfeng Liu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 2939. CrossRef
- Sympathetic nerve-enteroendocrine L cell communication modulates GLP-1 release, brain glucose utilization, and cognitive function

Original Articles
- Thyroid
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Recent Changes in the Incidence of Thyroid Cancer in Korea between 2005 and 2018: Analysis of Korean National Data
- Yun Mi Choi, Jiwoo Lee, Mi Kyung Kwak, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Won Bae Kim, Won Gu Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(5):791-799. Published online October 11, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1533
- 2,767 View
- 193 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
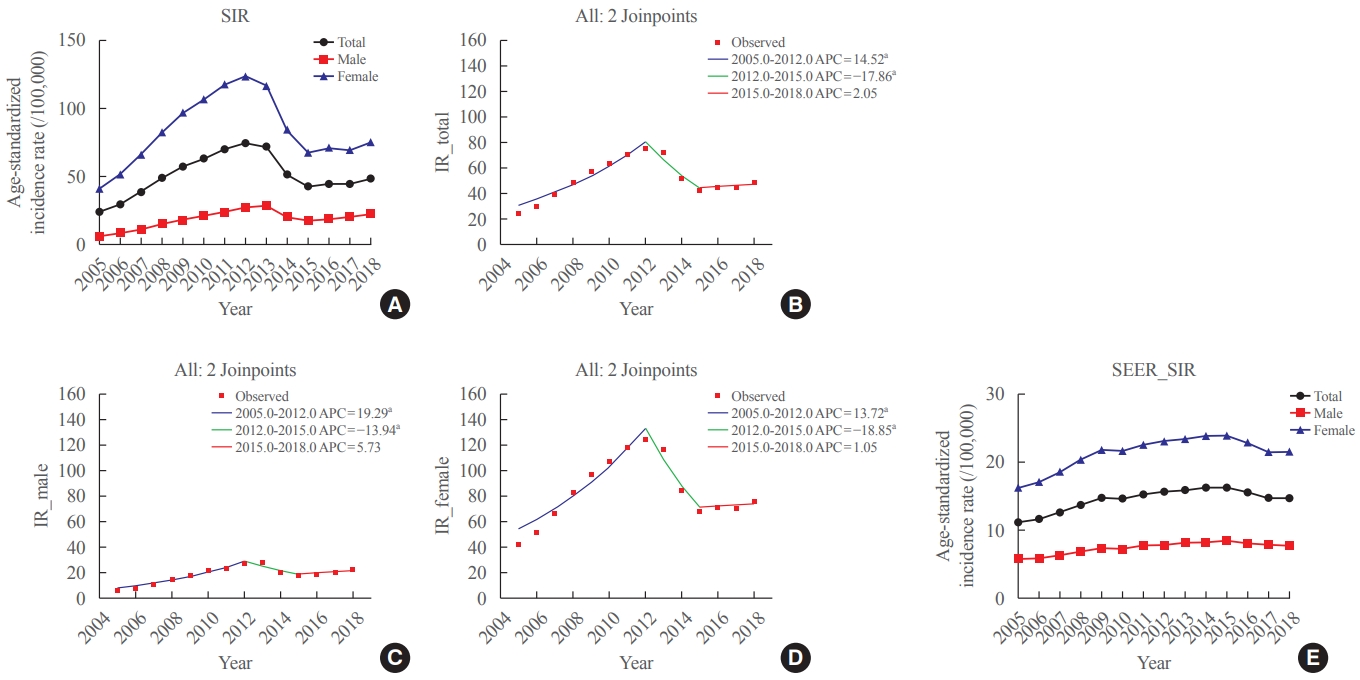
In this study, we evaluated the recent changes in the standardized, age-specific, stage-specific incidence rates (IRs) of thyroid cancer in Korea and compared them with the incidence data reported by the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program.
Methods
The analysis was conducted using the incidence data (2005 to 2018) from the Statistics Korea and Korea Central Cancer Registry.
Results
The age-standardized IR (SIR) of thyroid cancer increased from 24.09 per 100,000 in 2005 to 74.83 in 2012 (annual percent change [APC], 14.5). From 2012 to 2015, the SIR decreased to 42.52 (APC, –17.9) and then remained stable until 2018 (APC, 2.1). This trend was similar in both men and women. Regarding age-specific IRs, the IRs for ages of 30 years and older showed a trend similar to that of the SIR; however, for ages below 30 years, no significant reduction was observed from the vertex of IR in 2015. Regarding stage-specific IRs, the increase was more prominent in those with regional disease (APC, 17.4) than in those with localized disease until 2012; then, the IR decreased until 2015 (APC, –16.1). The average APC from 2005 to 2018 increased in men, those under the age of 30 years, and those with regional disease.
Conclusion
The SIR in Korea peaked in 2012 and decreased until 2015 and then remained stable until 2018. However, in young individuals under the age of 30 years, the IR did not significantly decrease but tended to increase again. In terms of stage-specific IRs, the sharpest increase was seen among those with regional disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of postoperative pain between transoral and conventional thyroidectomy: a propensity score-matched analysis
Min Kyu Park, Van Cuong Nguyen, Eugene Kim, Chang Myeon Song, Yong Bae Ji, Jin Hyeok Jeong, Kyung Tae
Surgical Endoscopy.2024; 38(3): 1512. CrossRef - Contents analysis of thyroid cancer-related information uploaded to YouTube by physicians in Korea: endorsing thyroid cancer screening, potentially leading to overdiagnosis
EunKyo Kang, HyoRim Ju, Soojeong Kim, Juyoung Choi
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Bilateral axillo-breast approach robotic total thyroidectomy without isthmectomy: a case report
Hyeji Kim, Hyeonuk Hwang, Hyungju Kwon
The Ewha Medical Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Consumption of Iodine-Rich Foods and Thyroid Cancer Prevalence: Findings from a Large Population-Based Study
Yu-Jin Kwon, Hye-Sun Lee, Sang-Wook Kang, Ji-Won Lee
Nutrients.2024; 16(7): 1041. CrossRef - Cancer and Mortality Risks of Graves’ Disease in South Korea Based on National Data from 2010 to 2019
Young Ju Choi, Kyungdo Han, Won Kyoung Cho, Min Ho Jung, Byung-Kyu Suh
Clinical Epidemiology.2023; Volume 15: 535. CrossRef - Survival Comparison of Incidentally Found versus Clinically Detected Thyroid Cancers: An Analysis of a Nationwide Cohort Study
Shinje Moon, Eun Kyung Lee, Hoonsung Choi, Sue K. Park, Young Joo Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 81. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to metabolic syndrome increases thyroid cancer risk in young adults: a population-based cohort study
Jinyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(4): 526. CrossRef - Cost-Effectiveness of Active Surveillance Compared to Early Surgery of Small Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Retrospective Study on a Korean Population
Han-Sang Baek, Jeonghoon Ha, Kwangsoon Kim, Jaseong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim, Sungju Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Chulmin Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Changes in the Mortality Rates of Thyroid Cancer in Korea: Analysis of Korean National Data from 1985 to 2020
Yun Mi Choi, Min-Ju Kim, Jiwoo Lee, Mi Kyung Kwak, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Won Bae Kim, Won Gu Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 588. CrossRef - Age and Post-Lobectomy Recurrence after Endoscopic or Robotic Thyroid Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study of 2348 Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Patients
Jin-Seong Cho, Yong-Min Na, Hee Kyung Kim
Cancers.2023; 15(23): 5506. CrossRef
- Comparison of postoperative pain between transoral and conventional thyroidectomy: a propensity score-matched analysis

- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
- Decreased Serum Level of Sclerostin in Older Adults with Sarcopenia
- Seong Hee Ahn, Hee-Won Jung, Eunju Lee, Ji Yeon Baek, Il-Young Jang, So Jeong Park, Jin Young Lee, Eunah Choi, Yun Sun Lee, Seongbin Hong, Beom-Jun Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):487-496. Published online May 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1428
- 3,144 View
- 141 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
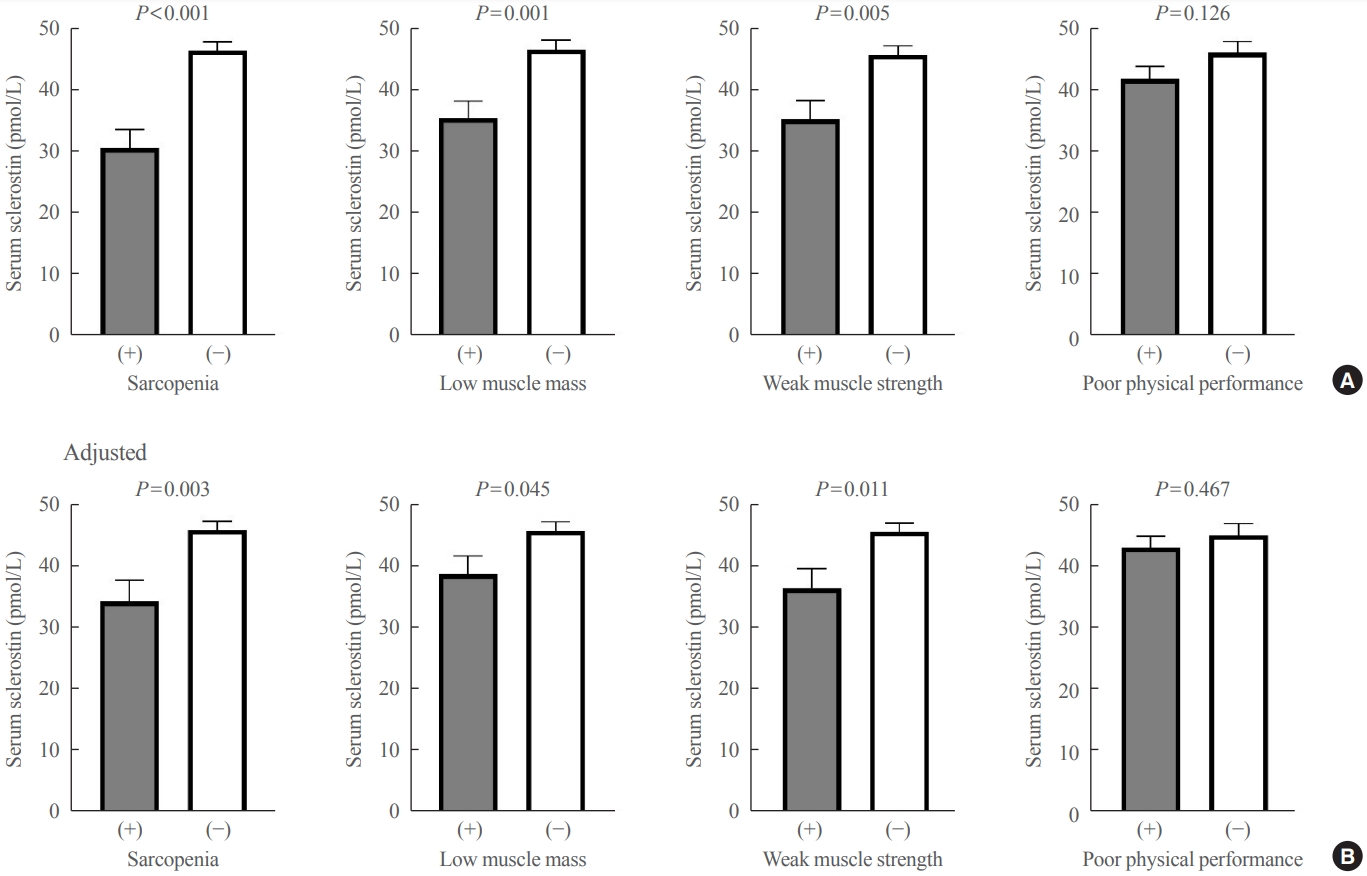
Although muscles and bones interact with each other through various secretory factors, the role of sclerostin, an osteocyte-secreted factor, on muscle metabolism has not been well studied. We investigated the levels of serum sclerostin in Korean older adults with sarcopenia.
Methods
Blood samples were collected from 129 participants who underwent evaluation of muscle mass and function in an outpatient geriatric clinic of a teaching hospital. Sarcopenia and related parameters were determined using cutoff values for the Asian population. Serum sclerostin levels were measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Results
The mean age of the participants was 69.6 years, and 20 participants (15.5%) were classified as having sarcopenia. After adjusting for age, sex, and body mass index, serum sclerostin levels were significantly lower in participants with sarcopenia, low muscle mass, or weak muscle strength (P=0.003 to 0.045). Serum sclerostin levels were positively associated with skeletal muscle index and grip strength after adjusting for confounders (P=0.001 and P=0.003), whereas sarcopenic phenotype score showed a negative association (P=0.006). These increases in muscle mass and strength were also dose dependent as serum sclerostin levels increased (P for trends=0.003 and P for trends=0.015). Higher serum sclerostin levels were associated with lower odds ratio (ORs) for sarcopenia, low muscle mass, and weak muscle strength after adjusting for confounders (OR, 0.27 to 0.50; P<0.001 to 0.025).
Conclusion
Higher serum sclerostin levels were associated with a lower risk of sarcopenia, low muscle mass, and weak muscle strength in Korean older adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mechanism and physical activities in bone-skeletal muscle crosstalk
Zhonghan Zhao, Kai Yan, Qiao Guan, Qiang Guo, Can Zhao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Musculoskeletal disorders and coronary artery disease —promising molecular markers: literature review
Viktoria N. Karetnikova, Anastasiya G. Neeshpapa, Evgenia I. Carpova, Olga L. Barbarash
CardioSomatics.2024; 15(1): 55. CrossRef - Determinants of bone mass in older adults with normal- and overweight derived from the crosstalk with muscle and adipose tissue
Carina O. Walowski, Catrin Herpich, Janna Enderle, Wiebke Braun, Marcus Both, Mario Hasler, Manfred J. Müller, Kristina Norman, Anja Bosy-Westphal
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of the Osteocyte in Musculoskeletal Disease
Anika Shimonty, Lynda F. Bonewald, Fabrizio Pin
Current Osteoporosis Reports.2023; 21(3): 303. CrossRef - The role of sclerostin in lipid and glucose metabolism disorders
Hewen Jiang, Dijie Li, Ying Han, Nanxi Li, Xiaohui Tao, Jin Liu, Zongkang Zhang, Yuanyuan Yu, Luyao Wang, Sifan Yu, Ning Zhang, Huan Xiao, Xin Yang, Yihao Zhang, Ge Zhang, Bao-Ting Zhang
Biochemical Pharmacology.2023; 215: 115694. CrossRef - Cytokines and exosomal miRNAs in skeletal muscle–adipose crosstalk
Liu Guo, Menchus Quan, Weijun Pang, Yulong Yin, Fengna Li
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 34(10): 666. CrossRef - Sclerostin: clinical insights in muscle–bone crosstalk
Antimo Moretti, Giovanni Iolascon
Journal of International Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-sclerostin antibodies: a new frontier in fragility fractures treatment
Giovanni Iolascon, Sara Liguori, Marco Paoletta, Giuseppe Toro, Antimo Moretti
Therapeutic Advances in Musculoskeletal Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sclerostin as a Putative Myokine in Sarcopenia
Hyon-Seung Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 430. CrossRef - Organokines, Sarcopenia, and Metabolic Repercussions: The Vicious Cycle and the Interplay with Exercise
Giulia Minniti, Letícia Maria Pescinini-Salzedas, Guilherme Almeida dos Santos Minniti, Lucas Fornari Laurindo, Sandra Maria Barbalho, Renata Vargas Sinatora, Lance Alan Sloan, Rafael Santos de Argollo Haber, Adriano Cressoni Araújo, Karina Quesada, Jesse
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(21): 13452. CrossRef
- Mechanism and physical activities in bone-skeletal muscle crosstalk

- Adrenal Gland
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Epidemiology and Long-Term Adverse Outcomes in Korean Patients with Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: A Nationwide Study
- Jung Hee Kim, Sunkyu Choi, Young Ah Lee, Juneyoung Lee, Sin Gon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):138-147. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1328

- 3,334 View
- 148 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Previous studies on the epidemiology and complications of congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) were conducted in Western countries and in children/adolescents. We aimed to explore the epidemiology of CAH, as well as the risk of comorbidities and mortality, in a Korean nationwide case-control study.
Methods
CAH patients (n=2,840) were included between 2002 and 2017 from the National Health Insurance Service database and the Rare Intractable Disease program. CAH patients were compared, at a 1:10 ratio, with age-, sex-, and index year-matched controls (n=28,400).
Results
The point prevalence of CAH patients in Korea was 1 in 18,745 persons in 2017. The annual incidence rate declined between 2003 and 2017 from 3.25 to 0.41 per 100,000 persons. CAH patients were at elevated risk for cardiovascular disease (odds ratio [OR], 1.6; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.4 to 1.9), stroke (OR, 1.7; 95% CI, 1.3 to 2.0), diabetes mellitus (OR, 2.8; 95% CI, 2.6 to 3.1), dyslipidemia (OR, 2.4; 95% CI, 2.2 to 2.6), and psychiatric disorders (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.3 to 1.6). Fracture risk increased in CAH patients aged over 40 years (OR, 1.4; 95% CI, 1.1 to 1.7). CAH patients were at higher risk of mortality than controls (hazard ratio, 1.6; 95% CI, 1.3 to 2.0).
Conclusion
Our nationwide study showed a recent decline in the incidence of CAH and an elevated risk for cardiovascular, metabolic, skeletal, and psychiatric disorders in CAH patients. Lifelong management for comorbidity risk is a crucial component of treating CAH patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictors of Cardiovascular Morbidities in Adults With 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Suranut Charoensri, Richard J Auchus
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(3): e1133. CrossRef - Анализ распространенности и заболеваемости надпочечниковой недостаточностью в мире
М. Ю. Юкина, Н. Ф. Нуралиева, Е. А. Трошина
Ateroscleroz.2023; 18(4): 426. CrossRef - Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - Long-term cardiometabolic morbidity in young adults with classic 21-hydroxylase deficiency congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Beatrice Righi, Salma R. Ali, Jillian Bryce, Jeremy W. Tomlinson, Walter Bonfig, Federico Baronio, Eduardo C. Costa, Guilherme Guaragna-Filho, Guy T’Sjoen, Martine Cools, Renata Markosyan, Tania A. S. S. Bachega, Mirela C. Miranda, Violeta Iotova, Henrik
Endocrine.2023; 80(3): 630. CrossRef - Serum steroid profile captures metabolic phenotypes in adults with classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Chang Ho Ahn, Jaeyoon Shim, Han Na Jang, Young Ah Lee, Sang-Won Lee, Man Ho Choi, Jung Hee Kim
The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.2023; 234: 106374. CrossRef - Long‐term health consequences of congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Riccardo Pofi, Xiaochen Ji, Nils P. Krone, Jeremy W. Tomlinson
Clinical Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hyperandrogenism and Cardiometabolic Risk in Pre- and Postmenopausal Women—What Is the Evidence?
Angelica Lindén Hirschberg
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Multiplexed Serum Steroid Profiling Reveals Metabolic Signatures of Subtypes in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Jaeyoon Shim, Chang Ho Ahn, Seung Shin Park, Jongsung Noh, Chaelin Lee, Sang Won Lee, Jung Hee Kim, Man Ho Choi
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Outcomes of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Anna Nordenström, Svetlana Lajic, Henrik Falhammar
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 587. CrossRef
- Predictors of Cardiovascular Morbidities in Adults With 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
- Han-sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Jin Yu, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Jeonghoon Ha, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Dong-Jun Lim, Hun-Sung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(4):641-651. Published online August 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1501
- 6,162 View
- 165 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
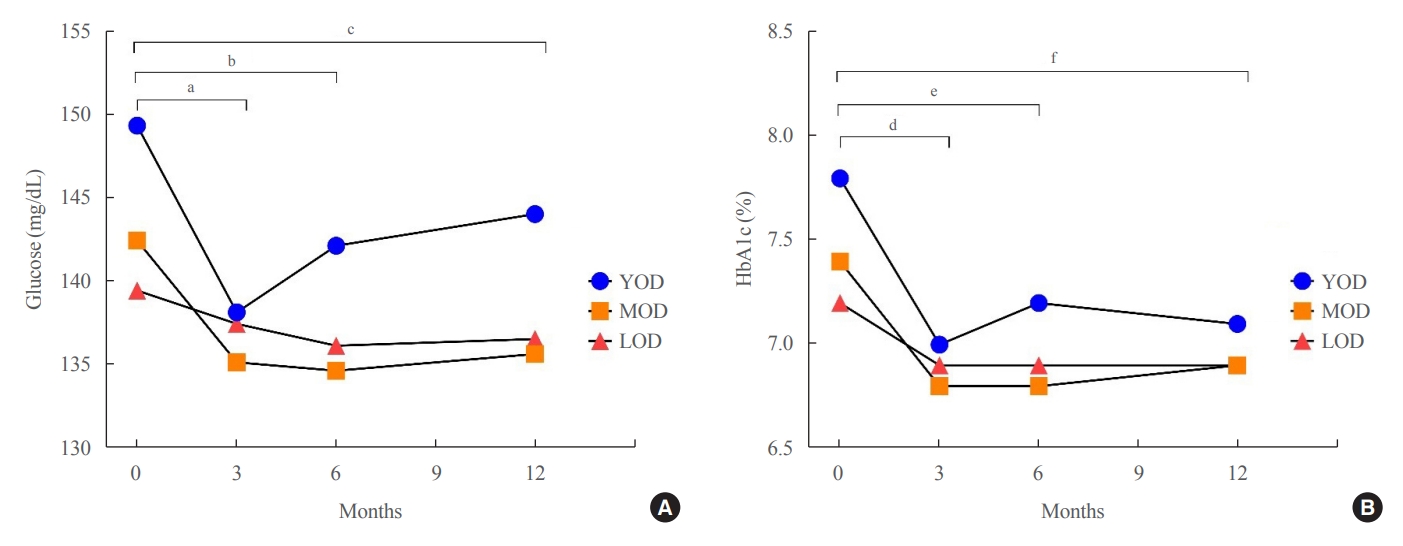
The prevalence of young-onset diabetes (YOD) has been increasing worldwide. As the incidence of YOD increases, it is necessary to determine the characteristics of YOD and the factors that influence its development and associated complications.
Methods
In this retrospective study, we recruited patients who were diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus between June 2001 and December 2021 at a tertiary hospital. The study population was categorized according to age: YOD (age <40 years), middle-age-onset diabetes (MOD, 40≤ age <65 years), and late-onset diabetes (LOD, age ≥65 years). We examined trends in glycemic control by analyzing fasting glucose levels during the first year in each age group. A Cox proportional-hazards model was used to determine the relative risk of developing complications according to glycemic control trends.
Results
The fasting glucose level at the time of diagnosis was highest in the YOD group (YOD 149±65 mg/dL; MOD 143±54 mg/dL; and LOD 140±55 mg/dL; p=0.009). In the YOD group, glucose levels decreased at 3 months, but increased by 12 months. YOD patients and those with poor glycemic control in the first year were at a higher risk of developing complications, whereas the risk in patients with LOD was not statistically significant.
Conclusion
YOD patients had higher glucose levels at diagnosis, and their glycemic control was poorly maintained. As poor glycemic control can influence the development of complications, especially in young patients, intensive treatment is necessary for patients with YOD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Increased risk of incident mental disorders in adults with new-onset type 1 diabetes diagnosed after the age of 19: A nationwide cohort study
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, So Hyun Cho, Rosa Oh, Ji Yoon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism.2024; 50(1): 101505. CrossRef - Association between age at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality risks: A nationwide population-based study
Da Hea Seo, Mina Kim, Young Ju Suh, Yongin Cho, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, So Hun Kim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 208: 111098. CrossRef - Impact of diabetes distress on glycemic control and diabetic complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hye-Sun Park, Yongin Cho, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, Young Ju Suh, Suk Chon, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Kwan Woo Lee, So Hun Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Early onset type 2 diabetes mellitus: an update
Myrsini Strati, Melpomeni Moustaki, Theodora Psaltopoulou, Andromachi Vryonidou, Stavroula A. Paschou
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Complications and Treatment of Early-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Fahimeh Soheilipour, Naghmeh Abbasi Kasbi, Mahshid Imankhan, Delaram Eskandari
International Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2022;37:641-51, Han-sang Baek et al.)
Han-sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Jin Yu, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Jeonghoon Ha, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Dong-Jun Lim, Hun-Sung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 945. CrossRef -
ISPAD
Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2022: Management of the child, adolescent, and young adult with diabetes in limited resource settings
Anju Virmani, Stuart J. Brink, Angela Middlehurst, Fauzia Mohsin, Franco Giraudo, Archana Sarda, Sana Ajmal, Julia E. von Oettingen, Kuben Pillay, Supawadee Likitmaskul, Luis Eduardo Calliari, Maria E. Craig
Pediatric Diabetes.2022; 23(8): 1529. CrossRef - Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2022;37:641-51, Han-sang Baek et al.)
May Thu Hla Aye, Sajid Adhi Raja, Vui Heng Chong
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 943. CrossRef
- Increased risk of incident mental disorders in adults with new-onset type 1 diabetes diagnosed after the age of 19: A nationwide cohort study

- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
- Real-World Safety and Effectiveness of Denosumab in Patients with Osteoporosis: A Prospective, Observational Study in South Korea
- Yumie Rhee, Dong-Gune Chang, Jeonghoon Ha, Sooa Kim, Yusun Lee, Euna Jo, Jung-Min Koh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):497-505. Published online June 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1427

- 5,363 View
- 267 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The efficacy and safety of denosumab have been established in a phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial in Korean postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. This postmarketing surveillance study was aimed to investigate the safety and effectiveness of denosumab in Korean real-world clinical practice.
Methods
Patients with osteoporosis who had received denosumab per the Korean approved indications in the postmarketing setting between September 2014 and September 2019 were enrolled. The primary endpoint was the incidence of adverse events (AEs) and adverse drug reactions (ADRs). The secondary endpoint was the percent change from baseline in bone mineral density (BMD) of the lumbar spine, total hip, and femoral neck.
Results
Of the 3,221 patients enrolled, 3,185 were included in the safety analysis set; 2,973 (93.3%) were female, and the mean± standard deviation (SD) age was 68.9±9.9 years. The mean±SD study period was 350.0±71.4 days. AEs, fatal AEs, and ADRs occurred in 19.3%, 0.8%, and 1.6%, respectively. The most frequent AEs, occurring in >0.5% of patients, were dizziness (0.7%), arthralgia (0.7%), back pain (0.6%), and myalgia (0.6%). Hypocalcemia occurred in 0.3% of patients. There were no cases of osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical femoral fracture. Mean±SD percent change from baseline in BMD of the lumbar spine, total hip, and femoral neck was 7.3%±23.6%, 3.6%±31.4%, and 3.2%±10.7%, respectively.
Conclusion
The safety and effectiveness of denosumab in Korean patients with osteoporosis in this study were comparable with those in the Korean randomized controlled trial, with no new safety findings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of denosumab-induced hypocalcemia: a retrospective observational study of patients routinely monitored with ionized calcium post-injection
Anna Spångeus, Johan Rydetun, Mischa Woisetschläger
Osteoporosis International.2024; 35(1): 173. CrossRef - Cost-consequence analysis of continuous denosumab therapy for osteoporosis treatment in South Korea
Seungju Cha, Minjeong Sohn, Hyowon Yang, Eric J. Yeh, Ki-Hyun Baek, Jeonghoon Ha, Hyemin Ku
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Denosumab and the Risk of Diabetes in Patients Treated for Osteoporosis
Huei-Kai Huang, Albert Tzu-Ming Chuang, Tzu-Chi Liao, Shih-Chieh Shao, Peter Pin-Sung Liu, Yu-Kang Tu, Edward Chia-Cheng Lai
JAMA Network Open.2024; 7(2): e2354734. CrossRef - Adverse Effects of Denosumab in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A 20-Year Retrospective Single-Center Observation Study in Central Taiwan
Tsung-Yin Tsai, Zi-Hong You, Shang-Feng Tsai, Ming-Ju Wu, Tung-Min Yu, Ya-Wen Chuang, Yung-Chieh Lin, Ya-Lian Deng, Chiann-Yi Hsu, Cheng-Hsu Chen
Transplantation Proceedings.2023; 55(4): 837. CrossRef - Persistence with Denosumab in Male Osteoporosis Patients: A Real-World, Non-Interventional Multicenter Study
Chaiho Jeong, Jeongmin Lee, Jinyoung Kim, Jeonghoon Ha, Kwanhoon Jo, Yejee Lim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Tae-Seo Sohn, Ki-Ho Song, Moo Il Kang, Ki-Hyun Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 260. CrossRef - Effect of Denosumab on Bone Density in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: A Comparison with and without Calcium Supplementation in Patients on Standard Diets in Korea
Chaiho Jeong, Jinyoung Kim, Jeongmin Lee, Yejee Lim, Dong-Jun Lim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Jeonghoon Ha
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(21): 6904. CrossRef - Denosumab
Reactions Weekly.2022; 1919(1): 221. CrossRef - Denosumab, an effective osteoporosis treatment option for men
Sung Hye Kong
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2022; 37(5): 947. CrossRef
- Prevalence of denosumab-induced hypocalcemia: a retrospective observational study of patients routinely monitored with ionized calcium post-injection

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Associations of Phthalate Metabolites and Bisphenol A Levels with Obesity in Children: The Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) 2015 to 2017
- Moon Young Seo, Shinje Moon, Shin-Hye Kim, Mi Jung Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):249-260. Published online April 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1235
- 5,704 View
- 151 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
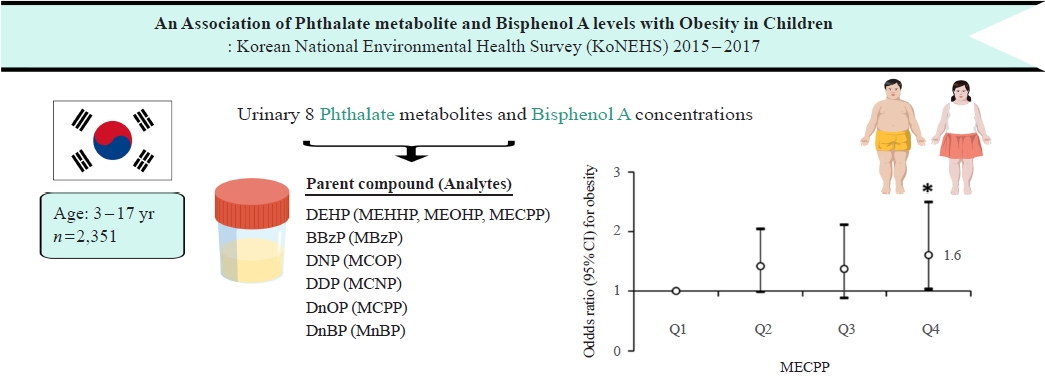
Phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA) are synthetic chemicals widely used in daily life. This study investigated urinary phthalate and BPA levels in Korean children and their associations with obesity. Methods: A total of 2,351 children aged 3 to 17 years who participated in the Korean National Environmental Health Survey 2015 to 2017 were included. Urinary dilution was corrected using covariate-adjusted standardization (CAS). We examined the geometric mean (GM) concentrations of urinary phthalate metabolites, including di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) metabolites (mono [2-ethyl-5-hydroxyhexyl] phthalate, mono [2-ethyl-5-oxohexyl] phthalate, and mono [2-ethyl-5-carboxypentyl] phthalate [MECPP]), mono-benzyl-phthalate (MBzP), mono (carboxyoctyl) phthalate (MCOP), mono (carboxy-isononyl) phthalate (MCNP), mono (3-carboxypropyl) phthalate, and mono-n-butyl-phthalate (MnBP), and BPA. We also analyzed the odds ratio (OR) for obesity according to the quartiles of each analyte. Results: The urinary GM levels of DEHP metabolites and MnBP were notably higher among Korean children than among American, Canadian, and German children. The CAS-applied GM concentrations of most analytes, except for MBzP, MCOP, and MCNP, were higher in children aged 3 to 5 years than in those aged 6 to 17 years. The OR for obesity in the highest quartile of MECPP was significantly higher than in the lowest quartile after adjusting for covariates. However, the other phthalate metabolites and BPA were not significantly associated with obesity. Conclusion: The concentrations of urinary DEHP metabolites and MnBP were higher in Korean children than in children in Western countries. Urinary MECPP exposure, but not other phthalates or BPA, showed a positive association with obesity in Korean children. Further studies are required to elucidate the causal relationships. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diethyl phthalate, a plasticizer, induces adipocyte inflammation and apoptosis in mice after long‐term dietary administration
Shirsha Mondal, Soumyadeep Basu, Songita Ghosh, Suktara Guria, Sutapa Mukherjee
Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nontargeted metabolomic evidence for antagonism between tetracycline and its resistance bacteria underlying their obesogenic effects on Caenorhabditis elegans
Zhuo Li, Di Wu, Zhenyang Yu, Changzheng Cui, Daqiang Yin
Science of The Total Environment.2023; 859: 160223. CrossRef - Prospective association between phthalate exposure in childhood and liver function in adolescence: the Ewha Birth and Growth Cohort Study
Seonhwa Lee, Hye Ah Lee, Bohyun Park, Hyejin Han, Young Sun Hong, Eun Hee Ha, Hyesook Park
Environmental Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bisphenol A substitutes and childhood obesity at 7 years: a cross-sectional study in Shandong, China
Minyan Chen, Cheng Lv, Shanyu Zhang, Lap Ah Tse, Xinyu Hong, Xi Liu, Yu Ding, Ping Xiao, Ying Tian, Yu Gao
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2023; 30(29): 73174. CrossRef - Association between Di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease among US adults: Mediation analysis of body mass index and waist circumference in the NHANES
Youming He, Jun Zou, Ting Hong, Dan Feng
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2023; 179: 113968. CrossRef - Association between phthalate exposure and obesity risk: A meta-analysis of observational studies
Qian Wu, Gang Li, Chen-Yang Zhao, Xiao-Lin Na, Yun-Bo Zhang
Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology.2023; 102: 104240. CrossRef - Levels of Bisphenol A and its analogs in nails, saliva, and urine of children: a case control study
Yolanda Gálvez-Ontiveros, Inmaculada Moscoso-Ruiz, Vega Almazán Fernández de Bobadilla, Celia Monteagudo, Rafael Giménez-Martínez, Lourdes Rodrigo, Alberto Zafra-Gómez, Ana Rivas
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Nontargeted Metabolomic Evidence for Antagonism between Tetracycline and its Resistance Bacteria Underlying Their Obesogenic Effects on Caenorhabditis Elegans
Zhuo Li, Zhenyang Yu, Changzheng Cui, Daqiang Yin
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Diethyl phthalate, a plasticizer, induces adipocyte inflammation and apoptosis in mice after long‐term dietary administration

Review Articles
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
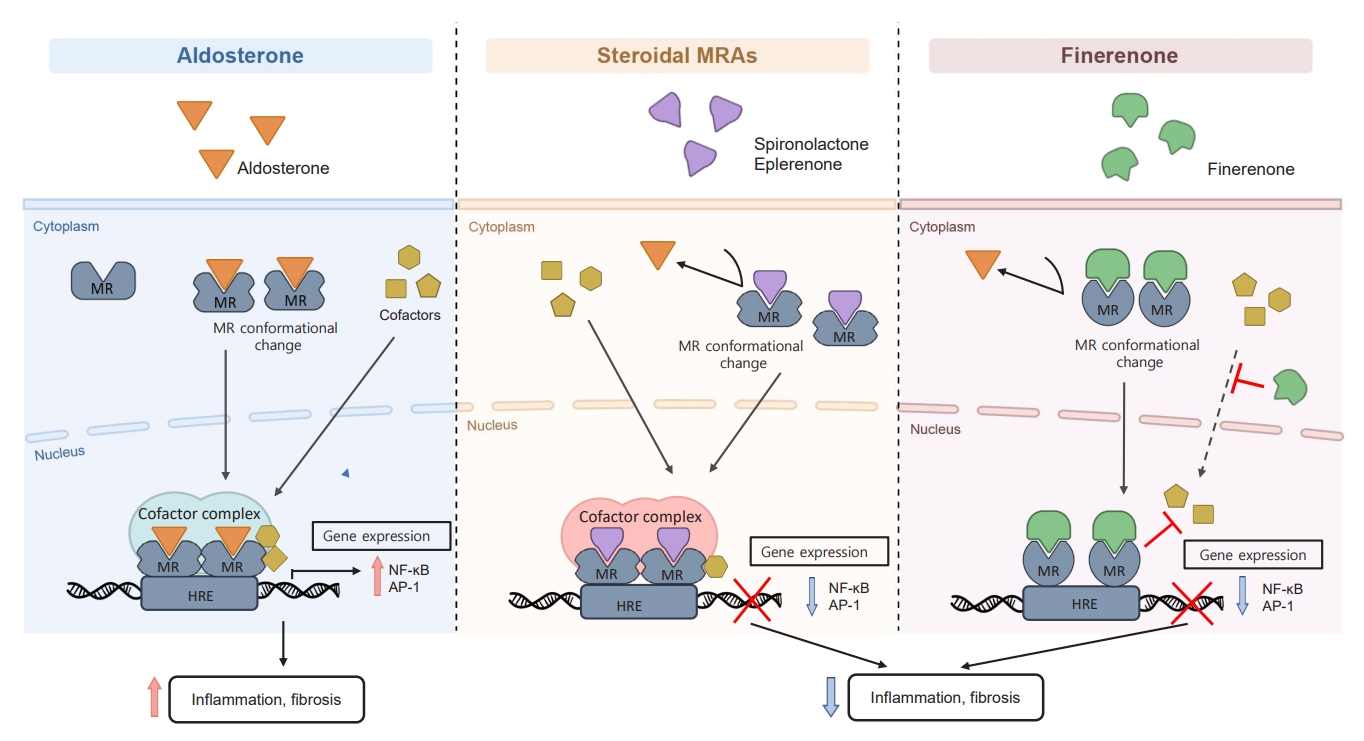
- Renal Protection of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist, Finerenone, in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Dong-Lim Kim, Seung-Eun Lee, Nan Hee Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):43-55. Published online February 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1629
- 5,539 View
- 762 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the most common cause of end-stage renal disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). CKD increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases; therefore, its prevention and treatment are important. The prevention of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) can be achieved through intensive glycemic control and blood pressure management. Additionally, DKD treatment aims to reduce albuminuria and improve kidney function. In patients with T2DM, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors, sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists can delay the progression of DKD. Hence, there is a need for novel treatments that can effectively suppress DKD progression. Finerenone is a first-in-class nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist with clinically proven efficacy in improving albuminuria, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and risk of cardiovascular events in early and advanced DKD. Therefore, finerenone is a promising treatment option to delay DKD progression. This article reviews the mechanism of renal effects and major clinical outcomes of finerenone in DKD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Neue Antihypertensiva im Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosteron-System
Markus van der Giet
CardioVasc.2024; 24(1): 33. CrossRef -
Chicoric acid
advanced PAQR3 ubiquitination to ameliorate ferroptosis in diabetes nephropathy through the relieving of the interaction between PAQR3 and P110α pathway
Weiwei Zhang, Yong Liu, Jiajun Zhou, Teng Qiu, Haitang Xie, Zhichen Pu
Clinical and Experimental Hypertension.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endothelial CXCR2 deficiency attenuates renal inflammation and glycocalyx shedding through NF-κB signaling in diabetic kidney disease
Siyuan Cui, Xin Chen, Jiayu Li, Wei Wang, Deqi Meng, Shenglong Zhu, Shiwei Shen
Cell Communication and Signaling.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular Targets of Novel Therapeutics for Diabetic Kidney Disease: A New Era of Nephroprotection
Alessio Mazzieri, Francesca Porcellati, Francesca Timio, Gianpaolo Reboldi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3969. CrossRef - Epigenetic modification in diabetic kidney disease
Zhe Liu, Jiahui Liu, Wanning Wang, Xingna An, Ling Luo, Dehai Yu, Weixia Sun
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel Approaches in Chronic Renal Failure without Renal Replacement Therapy: A Review
Sandra Martínez-Hernández, Martín Muñoz-Ortega, Manuel Ávila-Blanco, Mariana Medina-Pizaño, Javier Ventura-Juárez
Biomedicines.2023; 11(10): 2828. CrossRef - Finerenone and other future therapeutic options for Alport syndrome
Helen Pearce, Holly Mabillard
Journal of Rare Diseases.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Neue Antihypertensiva im Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosteron-System

- Thyroid
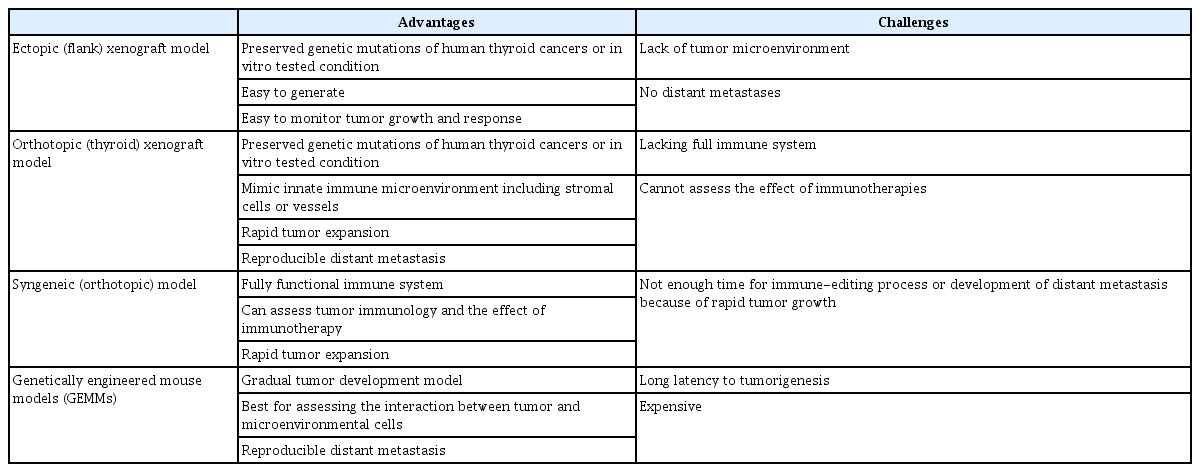
- Preclinical Models of Follicular Cell-Derived Thyroid Cancer: An Overview from Cancer Cell Lines to Mouse Models
- Min Ji Jeon, Bryan R. Haugen
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):830-838. Published online December 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1636
- 2,380 View
- 196 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The overall prognosis of thyroid cancer is excellent, but some patients have grossly invasive disease and distant metastases with limited responses to systemic therapies. Thus, relevant preclinical models are needed to investigate thyroid cancer biology and novel treatments. Different preclinical models have recently emerged with advances in thyroid cancer genetics, mouse modeling and new cell lines. Choosing the appropriate model according to the research question is crucial to studying thyroid cancer. This review will discuss the current preclinical models frequently used in thyroid cancer research, from cell lines to mouse models, and future perspectives on patient-derived and humanized preclinical models in this field.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advancements of 3D bioprinting in regenerative medicine: Exploring cell sources for organ fabrication
Yue Ma, Bo Deng, Runbang He, Pengyu Huang
Heliyon.2024; 10(3): e24593. CrossRef - Strategies to investigate migration and metastases in thyroid cancer
Daniel M. Chopyk, Priya H. Dedhia
Current Opinion in Endocrine and Metabolic Research.2024; 34: 100502. CrossRef - Mouse Models to Examine Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Pathogenesis: Recent Updates
Hye Choi, Kwangsoon Kim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(13): 11138. CrossRef - Modeling the tumor microenvironment of anaplastic thyroid cancer: an orthotopic tumor model in C57BL/6 mice
Zhen Xu, Hyo Shik Shin, Yoo Hyung Kim, Seong Yun Ha, Jae-Kyung Won, Su-jin Kim, Young Joo Park, Sareh Parangi, Sun Wook Cho, Kyu Eun Lee
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Patient-derived tumor models: a suitable tool for preclinical studies on esophageal cancer
Fan Liang, Hongyan Xu, Hongwei Cheng, Yabo Zhao, Junhe Zhang
Cancer Gene Therapy.2023; 30(11): 1443. CrossRef - Mechanistic Insights of Thyroid Cancer Progression
Luis Javier Leandro-García, Iñigo Landa
Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances of Osteosarcoma Models for Drug Discovery and Precision Medicine
Linyun Tan, Yitian Wang, Xin Hu, Guifeng Du, Xiaodi Tang, Li Min
Biomolecules.2023; 13(9): 1362. CrossRef
- Advancements of 3D bioprinting in regenerative medicine: Exploring cell sources for organ fabrication

Original Articles
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
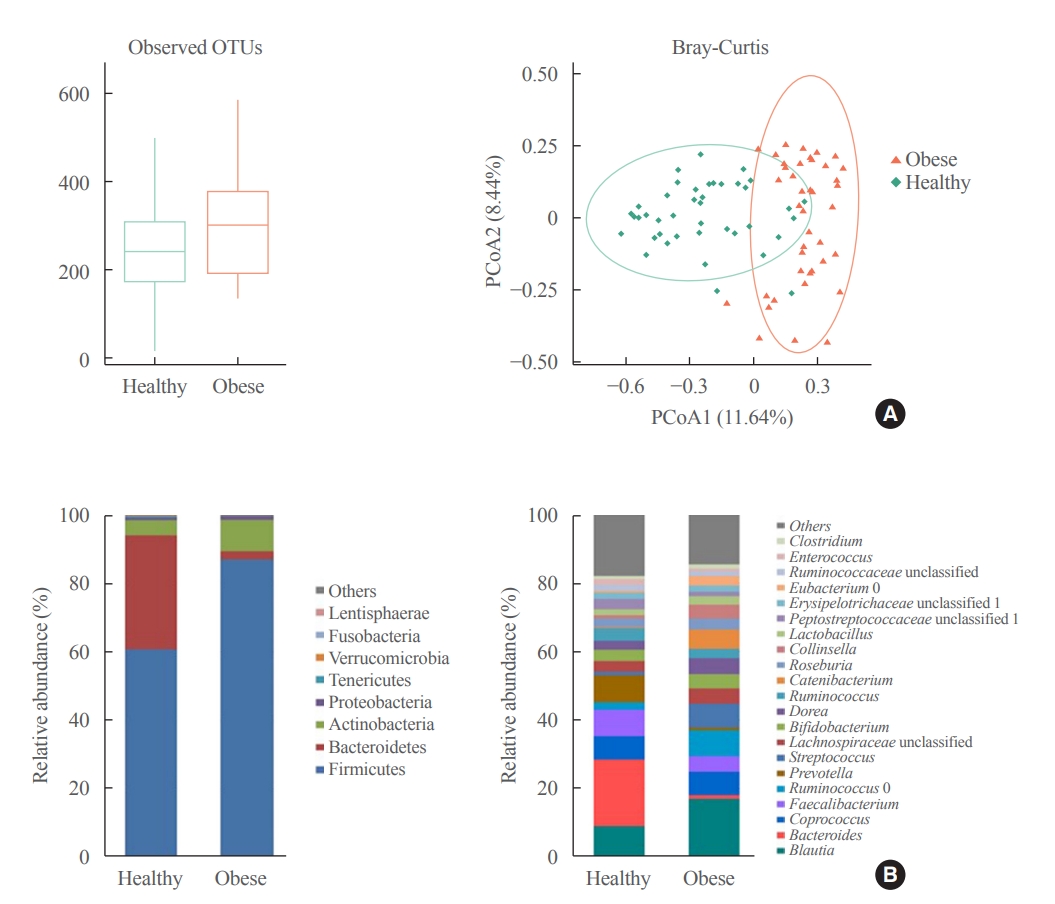
- Association between the Blautia/Bacteroides Ratio and Altered Body Mass Index after Bariatric Surgery
- Yoonhong Kim, Dooheon Son, Bu Kyung Kim, Ki Hyun Kim, Kyung Won Seo, Kyoungwon Jung, Seun Ja Park, Sanghyun Lim, Jae Hyun Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):475-486. Published online June 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1481
- Correction in: Endocrinol Metab 2022;37(4):701
- 3,143 View
- 123 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Current evidence support that the gut microbiota plays a potential role in obesity. Bariatric surgery can reduce excess weight and decrease the risk of life-threatening weight-related health problems and may also influence gut microbiota. In this study, we aimed to investigate the changes in gut microbiota before and after bariatric surgery and evaluate the association of the gut microbial shift and altered body mass index (BMI) after bariatric surgery.
Methods
Between January 2019 and July 2020, stools from 58 patients scheduled for bariatric surgery were collected. Six months after bariatric surgery, stools from 22 of these patients were re-collected, and the changes in gut microbiota before and after bariatric surgery were evaluated. In addition, the differences in gut microbiota between patients with severe obesity (BMI >35 kg/m2, n=42) and healthy volunteers with normal BMI (18.8 to 22.8 kg/m2, n=41) were investigated.
Results
The gut microbiota of patients who underwent bariatric surgery showed increased α-diversity and differed β-diversity compared with those before surgery. Interestingly, Blautia was decreased and Bacteriodes was increased at the genus level after bariatric surgery. Further, the Blautia/Bacteroides ratio showed a positive correlation with BMI. To validate these results, we compared the gut microbiota from severely obese patients with high BMI with those from healthy volunteers and demonstrated that the Blautia/Bacteroides ratio correlated positively with BMI.
Conclusion
In the gut microbial analysis of patients who underwent bariatric surgery, we presented that the Blautia/Bacteroides ratio had changed after bariatric surgery and showed a positive correlation with BMI. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Modulation of the gut microbiome and Firmicutes phylum reduction by a nutraceutical blend in the obesity mouse model and overweight humans: A double‐blind clinical trial
Victor Nehmi‐Filho, Jessica Alves de Freitas, Lucas Augusto Franco, Roberta Cristina Martins, José Antônio Orellana Turri, Aline Boveto Santamarina, Joyce Vanessa da Silva Fonseca, Ester Cerdeira Sabino, Bruna Carvalho Moraes, Erica Souza, Gilson Masahiro
Food Science & Nutrition.2024; 12(4): 2436. CrossRef - Natural emulsifiers lecithins preserve gut microbiota diversity in relation with specific faecal lipids in high fat-fed mice
Chloé Robert, Armelle Penhoat, Leslie Couëdelo, Magali Monnoye, Dominique Rainteau, Emmanuelle Meugnier, Sofia Bary, Hélène Abrous, Emmanuelle Loizon, Pranvera Krasniqi, Stéphanie Chanon, Aurélie Vieille-Marchiset, François Caillet, Sabine Danthine, Huber
Journal of Functional Foods.2023; 105: 105540. CrossRef - Effects and action mechanisms of lotus leaf (Nelumbo nucifera) ethanol extract on gut microbes and obesity in high-fat diet-fed rats
Zhang Yanan, Ma Lu, Zhang Lu, Huo Jinhai, Wang Weiming
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - First characterization of the intestinal microbiota in healthy Tunisian adults using 16S rRNA gene sequencing
Ahlem Mahjoub Khachroub, Magali Monnoye, Nour Elhouda Bouhlel, Sana Azaiez, Maha Ben Fredj, Wejdene Mansour, Philippe Gérard
FEMS Microbiology Letters.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gut microbiota and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Boyeon Kim, Bukyung Kim
Kosin Medical Journal.2023; 38(3): 169. CrossRef - Obésité et risque cardiovasculaire : le rôle de la chirurgie bariatrique dans la modulation du microbiote intestinal
Davide Masi, Mickael Massicard, Karine Clément
Nutrition Clinique et Métabolisme.2023; 37(2): 2S8. CrossRef - The Related Metabolic Diseases and Treatments of Obesity
Ming Yang, Shuai Liu, Chunye Zhang
Healthcare.2022; 10(9): 1616. CrossRef
- Modulation of the gut microbiome and Firmicutes phylum reduction by a nutraceutical blend in the obesity mouse model and overweight humans: A double‐blind clinical trial

- Thyroid
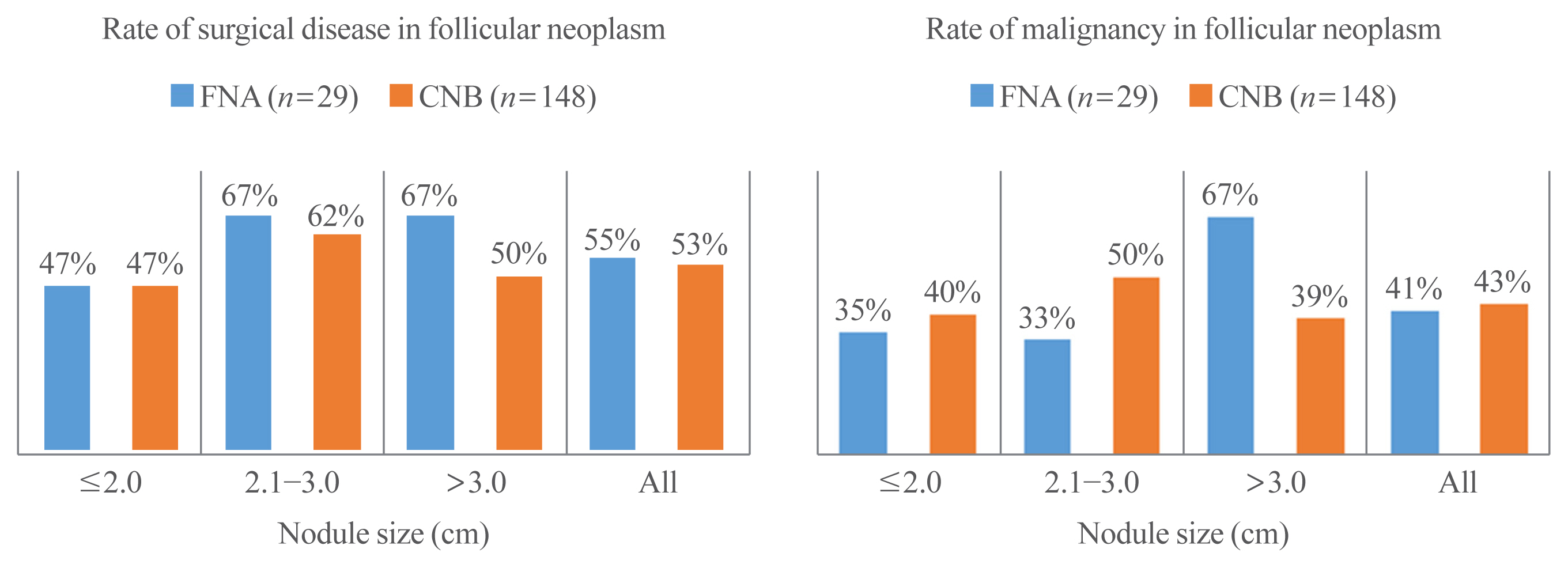
- Diagnostic Performance of Thyroid Core Needle Biopsy Using the Revised Reporting System: Comparison with Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
- Kwangsoon Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim, So Lyung Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):159-169. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1299
- 3,853 View
- 161 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We aim to validate the diagnostic performance of thyroid core needle biopsy (CNB) for diagnosing malignancy in clinical settings to align with the changes made in recently updated thyroid CNB guidelines.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 1,381 thyroid CNB and 2,223 fine needle aspiration (FNA) samples. The FNA and CNB slides were interpreted according to the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology and updated practice guidelines for thyroid CNB, respectively.
Results
Compared to FNA, CNB showed lower rates of inconclusive results: categories I (2.8% vs. 11.2%) and III (1.2% vs. 6.2%), and higher rates of categories II (60.9% vs. 50.4%) and IV (17.5% vs. 2.0%). The upper and lower bounds of the risk of malignancy (ROM) for category IV of CNB were 43.2% and 26.6%, respectively. The CNB subcategory IVb with nuclear atypia had a higher ROM than the subcategory without nuclear atypia (40%–62% vs. 23%–36%). In histologically confirmed cases, there was no significant difference in the diagnostic performance between CNB and FNA for malignancy. However, neoplastic diseases were more frequently detected by CNB than by FNA (88.8% vs. 77.6%, P=0.046). In category IV, there was no difference in unnecessary surgery rate between CNB and FNA (4.7% vs. 6.9%, P=0.6361).
Conclusion
Thyroid CNB decreased the rate of inconclusive results and showed a higher category IV diagnostic rate than FNA. The revised guidelines for thyroid CNB proved to be an excellent reporting system for assessing thyroid nodules. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Examining the impact of several factors including COVID‐19 on thyroid fine‐needle aspiration biopsy
Muzaffer Serdar Deniz, Merve Dindar
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2024; 52(1): 42. CrossRef - Consensus SFE-AFCE-SFMN 2022 sur la prise en charge des nodules thyroïdiens : intérêt et place de la cytologie thyroïdienne
Myriam Decaussin-Petrucci, Beatrix Cochand Priollet, Emannuelle Leteurtre, Frédérique Albarel, Françoise Borson-Chazot
Annales de Pathologie.2024; 44(1): 20. CrossRef - A comparative analysis of core needle biopsy and repeat fine needle aspiration in patients with inconclusive initial cytology of thyroid nodules
Xuejiao Su, Can Yue, Wanting Yang, Buyun Ma
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Preoperative Risk Stratification of Follicular-patterned Thyroid Lesions on Core Needle Biopsy by Histologic Subtyping and RAS Variant-specific Immunohistochemistry
Meejeong Kim, Sora Jeon, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(2): 247. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Patients with Thyroid Nodules
Young Joo Park, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Soo Hwan Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Seung-Kuk Baek, So Won Oh, Min Kyoung Lee, Sang-Woo Lee, Young Ah Lee, Yong Sang Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Leehi Joo, Yuh-Seog Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2023; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - Reevaluating diagnostic categories and associated malignancy risks in thyroid core needle biopsy
Chan Kwon Jung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(4): 208. CrossRef - A Matched-Pair Analysis of Nuclear Morphologic Features Between Core Needle Biopsy and Surgical Specimen in Thyroid Tumors Using a Deep Learning Model
Faridul Haq, Andrey Bychkov, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2022; 33(4): 472. CrossRef
- Examining the impact of several factors including COVID‐19 on thyroid fine‐needle aspiration biopsy

Review Article
- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
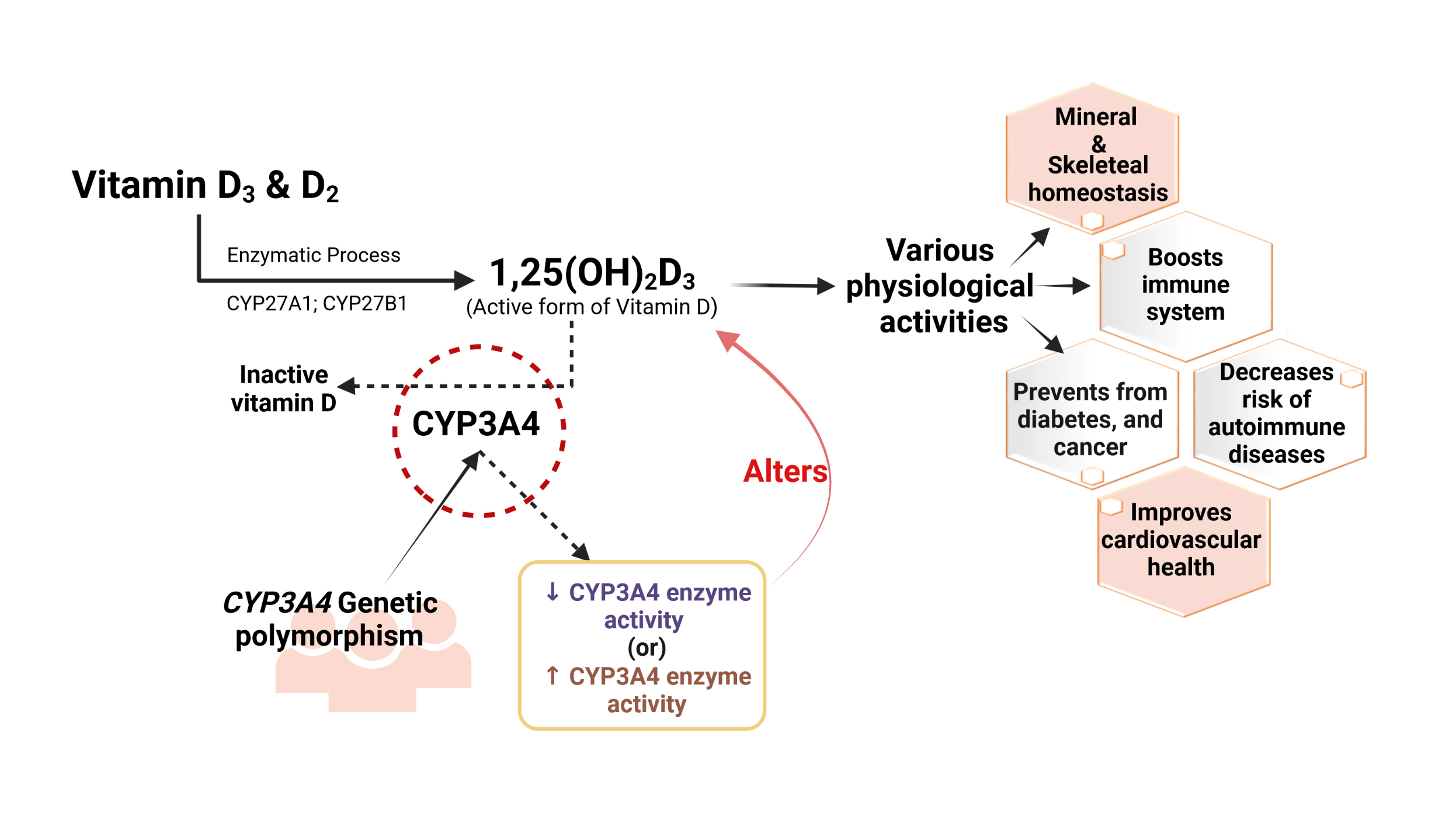
- Interplay of Vitamin D and CYP3A4 Polymorphisms in Endocrine Disorders and Cancer
- Siva Swapna Kasarla, Vannuruswamy Garikapati, Yashwant Kumar, Sujatha Dodoala
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):392-407. Published online June 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1349
- 5,341 View
- 198 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Vitamin D has received considerable optimistic attention as a potentially important factor in many pathological states over the past few decades. However, the proportion of the active form of vitamin D metabolites responsible for biological activity is highly questionable in disease states due to flexible alterations in the enzymes responsible for their metabolism. For instance, CYP3A4 plays a crucial role in the biotransformation of vitamin D and other drug substances. Food-drug and/or drug-drug interactions, the disease state, genetic polymorphism, age, sex, diet, and environmental factors all influence CYP3A4 activity. Genetic polymorphisms in CYP450-encoding genes have received considerable attention in the past few decades due to their extensive impact on the pharmacokinetic and dynamic properties of drugs and endogenous substances. In this review, we focused on CYP3A4 polymorphisms and their interplay with vitamin D metabolism and summarized the role of vitamin D in calcium homeostasis, bone diseases, diabetes, cancer, other diseases, and drug substances. We also reviewed clinical observations pertaining to CYP3A4 polymorphisms among the aforementioned disease conditions. In addition, we highlighted the future perspectives of studying the pharmacogenetics of CYP3A4, which may have potential clinical significance for developing novel diagnostic genetic markers that will ascertain disease risk and progression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Revealing the association between vitamin D metabolic pathway gene variants and lung cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohamed I. Elsalahaty, Samar Sami Alkafaas, Aya O. Bashir, Khaled A. El-Tarabily, Mohamed T. El-Saadony, Eman H. Yousef
Frontiers in Genetics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Vitamin D in Melanoma: Potential Role of Cytochrome P450 Enzymes
Mohamed Ben-Eltriki, Erysa J. Gayle, Jhoanne M. Paras, Louisa Nyame-Addo, Manik Chhabra, Subrata Deb
Life.2024; 14(4): 510. CrossRef - Heat stress as a potential risk factor for vitamin D deficiency
Martina Balducci, Letizia Pruccoli, Andrea Tarozzi
Medical Hypotheses.2023; 176: 111085. CrossRef - Association and Haplotype Analysis of the PON1, ITGB3 and CYP3A4 Genes, Strong Candidates for Familial Coronary Artery Disease Susceptibility
Faruk SAYDAM, İrfan DEĞİRMENCİ, Alparslan BİRDANE, Cansu ÖZBAYER, Taner ULUS, Mahmut ÖZDEMİR, Necmi ATA, Hasan Veysi GÜNEŞ
Online Türk Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2023; 8(1): 81. CrossRef - Association of flame retardants, polybrominated diethyl ethers (PBDEs), with vitamin D in female subjects
Alexandra E. Butler, Edwina Brennan, Daniel S. Drage, Thozhukat Sathyapalan, Stephen L. Atkin
Chemosphere.2023; 338: 139488. CrossRef - Genetic variations of CYP3A4 on the metabolism of itraconazole in vitro
Sai-li Xie, Xiayan Zhu, Nanyong Gao, Qianmeng Lin, Chaojie Chen, Yun-jun Yang, Jian-ping Cai, Guo-xin Hu, Ren-ai Xu
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2023; 181: 114101. CrossRef
- Revealing the association between vitamin D metabolic pathway gene variants and lung cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis

Original Articles
- Adrenal Gland
- Adrenal Morphology as an Indicator of Long-Term Disease Control in Adults with Classic 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency
- Taek Min Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Han Na Jang, Man Ho Choi, Jeong Yeon Cho, Sang Youn Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):124-137. Published online February 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1278

- 4,243 View
- 125 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Monitoring adults with classical 21-hydroxylase deficiency (21OHD) is challenging due to variation in clinical and laboratory settings. Moreover, guidelines for adrenal imaging in 21OHD are not yet available. We evaluated the relationship between adrenal morphology and disease control status in classical 21OHD.
Methods
This retrospective, cross-sectional study included 90 adult 21OHD patients and 270 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. We assessed adrenal volume, width, and tumor presence using abdominal computed tomography and evaluated correlations of adrenal volume and width with hormonal status. We investigated the diagnostic performance of adrenal volume and width for identifying well-controlled status in 21OHD patients (17α-hydroxyprogesterone [17-OHP] <10 ng/mL).
Results
The adrenal morphology of 21OHD patients showed hypertrophy (45.6%), normal size (42.2%), and hypotrophy (12.2%). Adrenal tumors were detected in 12 patients (13.3%). The adrenal volume and width of 21OHD patients were significantly larger than those of controls (18.2±12.2 mL vs. 7.1±2.0 mL, 4.7±1.9 mm vs. 3.3±0.5 mm, P<0.001 for both). The 17-OHP and androstenedione levels were highest in patients with adrenal hypertrophy, followed by those with normal adrenal glands and adrenal hypotrophy (P<0.05 for both). Adrenal volume and width correlated positively with adrenocorticotropic hormone, 17-OHP, 11β-hydroxytestosterone, progesterone sulfate, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in both sexes (r=0.33–0.95, P<0.05 for all). For identifying well-controlled patients, the optimal cut-off values of adrenal volume and width were 10.7 mL and 4 mm, respectively (area under the curve, 0.82–0.88; P<0.001 for both).
Conclusion
Adrenal volume and width may be reliable quantitative parameters for monitoring patients with classical 21OHD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Long‐term health consequences of congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Riccardo Pofi, Xiaochen Ji, Nils P. Krone, Jeremy W. Tomlinson
Clinical Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Landscape of Adrenal Tumours in Patients with Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Mara Carsote, Ana-Maria Gheorghe, Claudiu Nistor, Alexandra-Ioana Trandafir, Oana-Claudia Sima, Anca-Pati Cucu, Adrian Ciuche, Eugenia Petrova, Adina Ghemigian
Biomedicines.2023; 11(11): 3081. CrossRef - Multiplexed Serum Steroid Profiling Reveals Metabolic Signatures of Subtypes in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Jaeyoon Shim, Chang Ho Ahn, Seung Shin Park, Jongsung Noh, Chaelin Lee, Sang Won Lee, Jung Hee Kim, Man Ho Choi
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Outcomes of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Anna Nordenström, Svetlana Lajic, Henrik Falhammar
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 587. CrossRef - Congenital adrenal hyperplasia in patients with adrenal tumors: a population-based case–control study
F. Sahlander, J. Patrova, B. Mannheimer, J. D. Lindh, H. Falhammar
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2022; 46(3): 559. CrossRef - Fully automatic volume measurement of the adrenal gland on CT using deep learning to classify adrenal hyperplasia
Taek Min Kim, Seung Jae Choi, Ji Yeon Ko, Sungwan Kim, Chang Wook Jeong, Jeong Yeon Cho, Sang Youn Kim, Young-Gon Kim
European Radiology.2022; 33(6): 4292. CrossRef
- Long‐term health consequences of congenital adrenal hyperplasia

- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
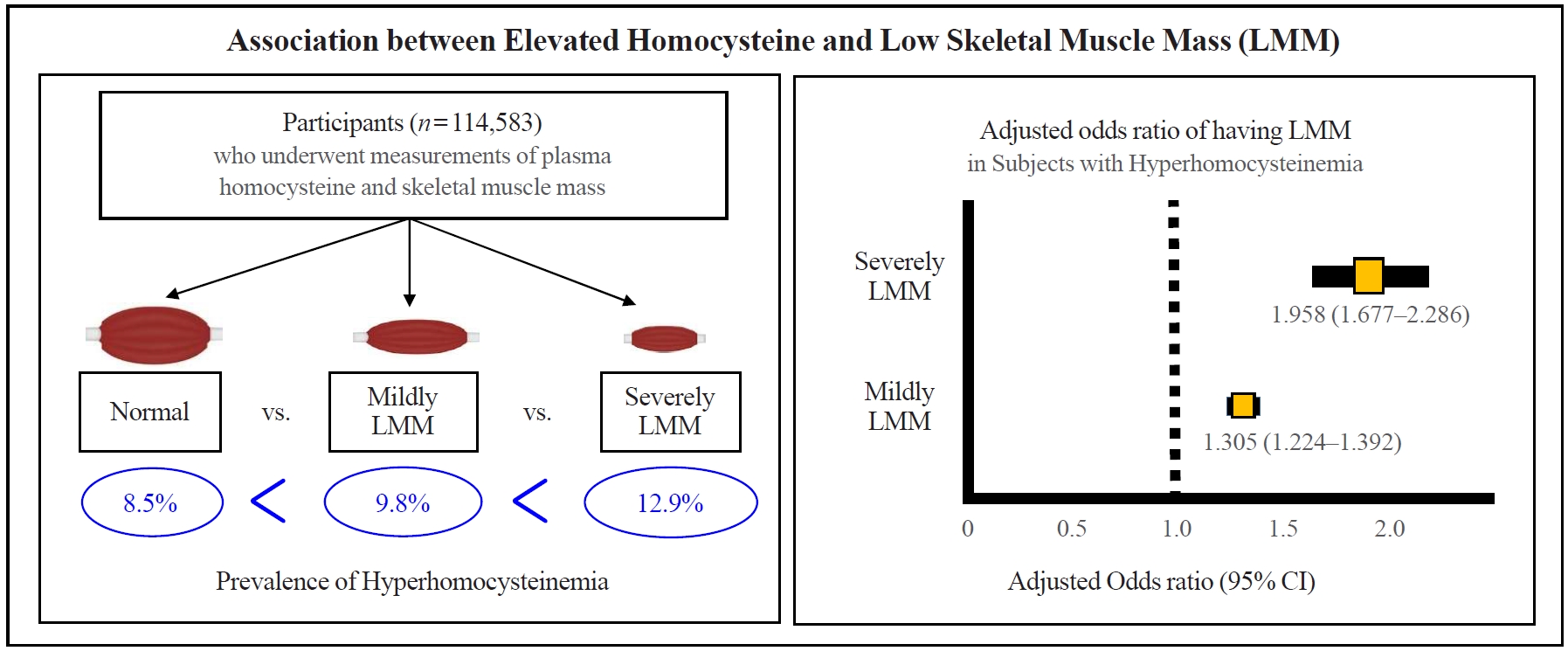
- Association between Elevated Plasma Homocysteine and Low Skeletal Muscle Mass in Asymptomatic Adults
- Jae-Hyeong Choi, Jin-Woo Seo, Mi-Yeon Lee, Yong-Taek Lee, Kyung Jae Yoon, Chul-Hyun Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):333-343. Published online February 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1202
- 7,917 View
- 187 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Homocysteine has been drawing attention with a closed linkage with skeletal muscle. However, the association of hyperhomocysteinemia with decreased skeletal muscle mass remains unclear. We aimed to investigate the association of hyperhomocysteinemia with low skeletal muscle mass (LMM) in asymptomatic adults.
Methods
This was a cross-sectional study of 114,583 community-dwelling adults without cancer, stroke, or cardiovascular diseases who underwent measurements of plasma homocysteine and body composition analysis from 2012 to 2018. Hyperhomocysteinemia was defined as >15 μmol/L. Skeletal muscle mass index (SMI) was calculated based on appendicular muscle mass (kg)/height (m)2. Participants were classified into three groups based on SMI: “normal,” “mildly low,” and “severely low.”
Results
The prevalence of hyperhomocysteinemia was the highest in subjects with severely LMM (12.9%), followed by those with mildly LMM (9.8%), and those with normal muscle mass (8.5%) (P for trend <0.001). In a multivariable logistic regression model, hyperhomocysteinemia was significantly associated with having a mildly LMM (odds ratio [OR], 1.305; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.224 to 1.392) and severely LMM (OR, 1.958; 95% CI, 1.667 to 2.286), respectively. One unit increment of log-transformed homocysteine was associated with 1.360 and 2.169 times higher risk of having mildly LMM and severely LMM, respectively.
Conclusion
We demonstrated that elevated homocysteine has an independent association with LMM in asymptomatic adults, supporting that hyperhomocysteinemia itself can be a risk for decline in skeletal musculature. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The role of the mitochondrial trans-sulfuration in cerebro-cardio renal dysfunction during trisomy down syndrome
Sathnur Pushpakumar, Mahavir Singh, Utpal Sen, N. Tyagi, Suresh C. Tyagi
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2024; 479(4): 825. CrossRef - Association of vitamins B1 and B2 intake with early-onset sarcopenia in the general adult population of the US: a cross-sectional study of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
Sha Yang, Zhenyu Dong, Jiaqi Zhao, Lijia Yuan, Yao Xiao, Xing Luo, Zhuyang Zhao, Xia Kang, Kanglai Tang, Ming Chen, Liu Feng
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Triglyceride-Glucose Index with the Risk of Hyperhomocysteinemia Among Chinese Male Bus Drivers: A Longitudinal Study
Juan Xiong, Yanxia Wu, Lingling Huang, Xujuan Zheng
International Journal of General Medicine.2023; Volume 16: 2857. CrossRef - Relationship between hyperhomocysteinemia and coexisting obesity with low skeletal muscle mass in asymptomatic adult population
Tae Kyung Yoo, Hye Chang Rhim, Yong-Taek Lee, Kyung Jae Yoon, Chul-Hyun Park
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Causal effects of homocysteine levels on the components of sarcopenia: A two-sample mendelian randomization study
Hongwei Yu, Gan Luo, Tianwei Sun, Qiong Tang
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between serum homocysteine and sarcopenia among hospitalized older Chinese adults: a cross-sectional study
Bing Lu, Lingyu Shen, Haiqiong Zhu, Ling Xi, Wei Wang, Xiaojun Ouyang
BMC Geriatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- The role of the mitochondrial trans-sulfuration in cerebro-cardio renal dysfunction during trisomy down syndrome

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Triglyceride-Glucose Index Predicts Future Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases: A 16-Year Follow-up in a Prospective, Community-Dwelling Cohort Study
- Joon Ho Moon, Yongkang Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Jae Hoon Moon, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi, Nam H. Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):406-417. Published online August 3, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1703

- 2,654 View
- 165 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
While the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index is a measure of insulin resistance, its association with cardiovascular disease (CVD) has not been well elucidated. We evaluated the TyG index for prediction of CVDs in a prospective large communitybased cohort.
Methods
Individuals 40 to 70 years old were prospectively followed for a median 15.6 years. The TyG index was calculated as the Ln [fasting triglycerides (mg/dL)×fasting glucose (mg/dL)/2]. CVDs included any acute myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease or cerebrovascular disease. We used a Cox proportional hazards model to estimate CVD risks according to quartiles of the TyG index and plotted the receiver operating characteristics curve for the incident CVD.
Results
Among 8,511 subjects (age 51.9±8.8 years; 47.5% males), 931 (10.9%) had incident CVDs during the follow-up. After adjustment for age, sex, body mass index, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, total cholesterol, smoking, alcohol, exercise, and C-reactive protein, subjects in the highest TyG quartile had 36% increased risk of incident CVD compared with the lowest TyG quartile (hazard ratio, 1.36; 95% confidence interval, 1.10 to 1.68). Carotid plaque, assessed by ultrasonography was more frequent in subjects in the higher quartile of TyG index (P for trend=0.049 in men and P for trend <0.001 in women). The TyG index had a higher predictive power for CVDs than the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) (area under the curve, 0.578 for TyG and 0.543 for HOMA-IR). Adding TyG index on diabetes or hypertension alone gave sounder predictability for CVDs.
Conclusion
The TyG index is independently associated with future CVDs in 16 years of follow-up in large, prospective Korean cohort. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Construction and validation of a nomogram for predicting diabetes remission at 3 months after bariatric surgery in patients with obesity combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Kaisheng Yuan, Bing Wu, Ruiqi Zeng, Fuqing Zhou, Ruixiang Hu, Cunchuan Wang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(1): 169. CrossRef - Association between the triglyceride glucose index and chronic total coronary occlusion: A cross-sectional study from southwest China
Kaiyong Xiao, Huili Cao, Bin Yang, Zhe Xv, Lian Xiao, Jianping Wang, Shuiqing Ni, Hui Feng, Zhongwei He, Lei Xv, Juan Li, Dongmei Xv
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024; 34(4): 850. CrossRef - The association between TyG and all-cause/non-cardiovascular mortality in general patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus is modified by age: results from the cohort study of NHANES 1999–2018
Younan Yao, Bo Wang, Tian Geng, Jiyan Chen, Wan Chen, Liwen Li
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index predicts type 2 diabetes mellitus more effectively than oral glucose tolerance test-derived insulin sensitivity and secretion markers
Min Jin Lee, Ji Hyun Bae, Ah Reum Khang, Dongwon Yi, Mi Sook Yun, Yang Ho Kang
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111640. CrossRef - Evaluation of the novel three lipid indices for predicting five- and ten-year incidence of cardiovascular disease: findings from Kerman coronary artery disease risk factors study (KERCADRS)
Alireza Jafari, Hamid Najafipour, Mitra Shadkam, Sina Aminizadeh
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Construction and validation of a nomogram for predicting diabetes remission at 3 months after bariatric surgery in patients with obesity combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



