Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Thyroid
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Risk of Subsequent Primary Cancers in Thyroid Cancer Survivors according to the Dose of Levothyroxine: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- Min-Su Kim, Jang Won Lee, Min Kyung Hyun, Young Shin Song
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(2):288-299. Published online March 4, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1815
- 1,416 View
- 44 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
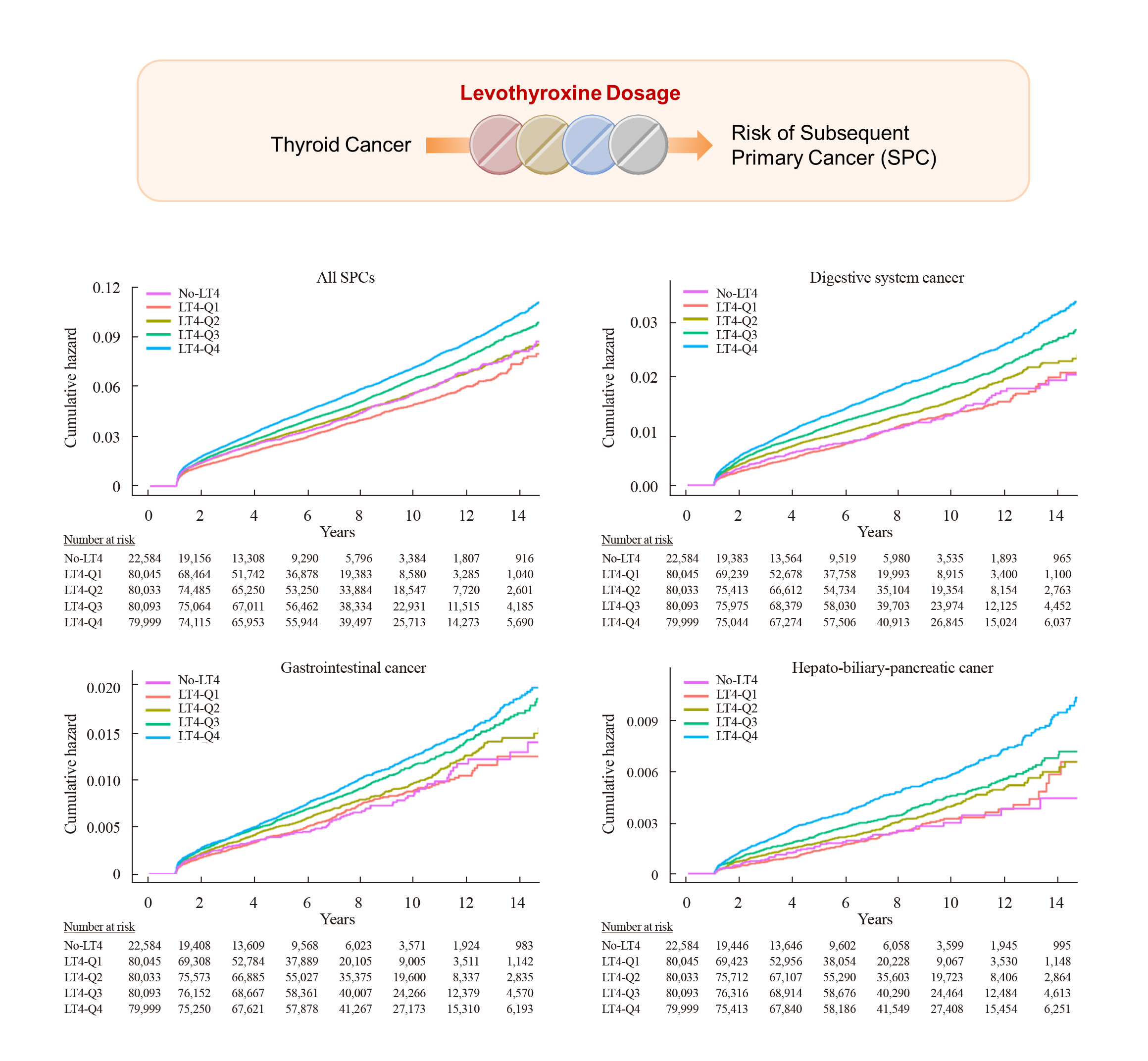
Current research has not investigated the effect of thyroid-stimulating hormone suppression therapy with levothyroxine on the risk for developing subsequent primary cancers (SPCs). This study aimed to investigate the association between levothyroxine dosage and the risk for SPCs in thyroid cancer patients.
Methods
We conducted a nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study form Korean National Health Insurance database. This cohort included 342,920 thyroid cancer patients between 2004 and 2018. Patients were divided into the non-levothyroxine and the levothyroxine groups, the latter consisting of four dosage subgroups according to quartiles. Cox proportional hazard models were performed to evaluate the risk for SPCs by adjusting for variables including cumulative doses of radioactive iodine (RAI) therapy.
Results
A total of 17,410 SPC cases were observed over a median 7.3 years of follow-up. The high-dose levothyroxine subgroups (Q3 and Q4) had a higher risk for SPC (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 1.14 and 1.27; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.05–1.24 and 1.17– 1.37; respectively) compared to the non-levothyroxine group. In particular, the adjusted HR of stomach (1.31), colorectal (1.60), liver and biliary tract (1.95), and pancreatic (2.48) cancers were increased in the Q4 subgroup. We consistently observed a positive association between high levothyroxine dosage per body weight and risk of SPCs, even after adjusting for various confounding variables. Moreover, similar results were identified in the stratified analyses according to thyroidectomy type and RAI therapy, as well as in a subgroup analysis of patients with good adherence.
Conclusion
High-dose levothyroxine use was associated with increased risk of SPCs among thyroid cancer patients regardless of RAI therapy.

- Thyroid
- Management of Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Focus on Proven Health Effects in the 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines
- Eu Jeong Ku, Won Sang Yoo, Hyun Kyung Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):381-391. Published online August 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1778

- 3,105 View
- 462 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) is characterized by elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and normal free thyroxine levels. The Korean Thyroid Association recently issued a guideline for managing SCH, which emphasizes Korean-specific TSH diagnostic criteria and highlights the health benefits of levothyroxine (LT4) treatment. A serum TSH level of 6.8 mIU/L is presented as the reference value for diagnosing SCH. SCH can be classified as mild (TSH 6.8 to 10.0 mIU/L) or severe (TSH >10.0 mIU/L), and patients can be categorized as adults (age <70 years) or elderly (age ≥70 years), depending on the health effects of LT4 treatment. An initial increase in serum TSH levels should be reassessed with a subsequent measurement, including a thyroid peroxidase antibody test, preferably 2 to 3 months after the initial assessment. While LT4 treatment is not generally recommended for mild SCH in adults, it is necessary for severe SCH in patients with underlying coronary artery disease or heart failure and it may be considered for those with concurrent dyslipidemia. Conversely, LT4 treatment is generally not recommended for elderly patients, regardless of SCH severity. For those SCH patients who are prescribed LT4 treatment, the dosage should be personalized, and serum TSH levels should be regularly monitored to maintain the optimal LT4 regimen.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Implications of Different Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Reference Intervals between TSH Kits for the Management of Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Won Sang Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 188. CrossRef
- Clinical Implications of Different Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Reference Intervals between TSH Kits for the Management of Subclinical Hypothyroidism

- Thyroid
- Identification of Mutations in the Thyroxine-Binding Globulin (TBG) Gene in Patients with TBG Deficiency in Korea
- Jung Heo, Sang-Mi Kim, Hyun Jin Ryu, Hyunju Park, Tae Hyuk Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Hyung-Doo Park, Sun Wook Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):870-878. Published online December 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1591
- 1,776 View
- 198 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
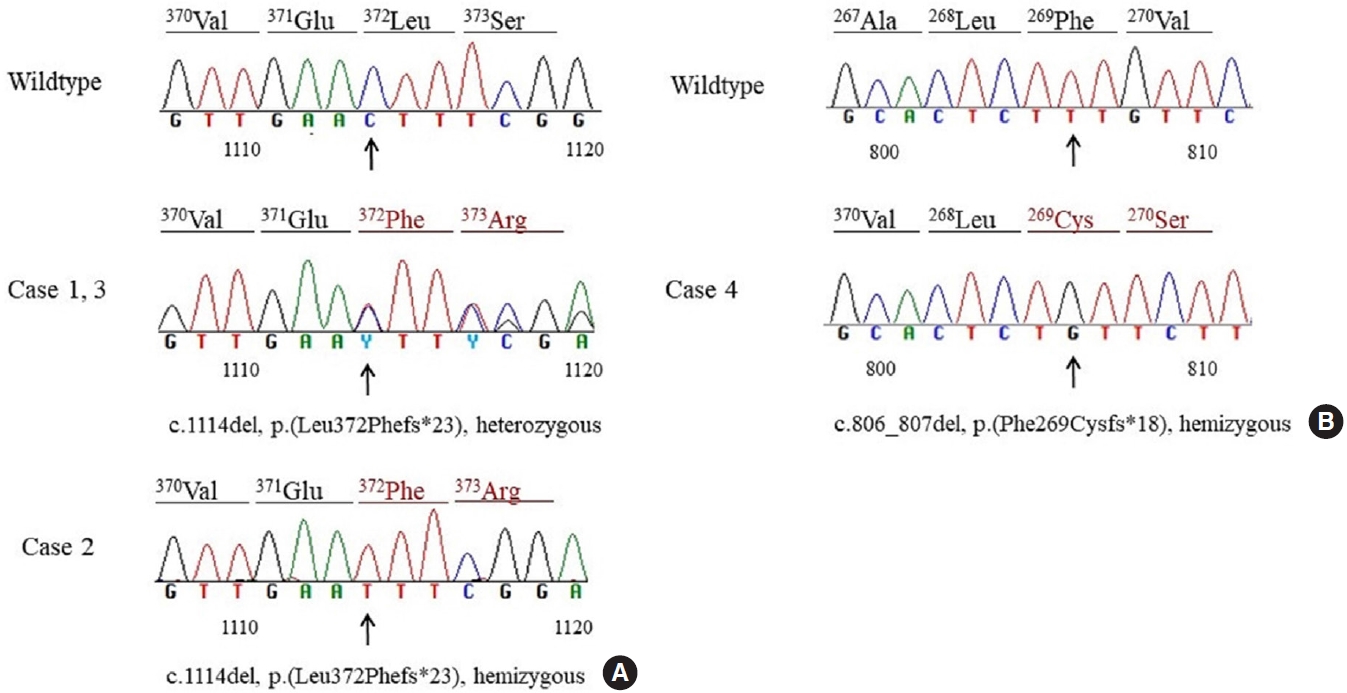
Thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG) is a major transporter protein for thyroid hormones. The serpin family A member 7 (SERPINA7) gene codes for TBG, and mutations of the SERPINA7 gene result in TBG deficiency. Although more than 40 mutations have been reported in several countries, only a few studies of TBG deficiency and SERPINA7 gene mutation have been performed in Korea. The aim of this study is to review the clinical presentations and laboratory findings of patients with TBG deficiency and to investigate the types of SERPINA7 gene mutation.
Methods
Five unrelated Korean adults with TBG deficiency attending endocrinology clinic underwent SERPINA7 gene sequencing. Four patients harbored a SERPINA7 gene mutation. Serum thyroid hormones, anti-microsomal antibodies, and TBG were measured. Genomic DNA was extracted from whole blood. All exons and intron-exon boundaries of the TBG gene were amplified and sequencing was performed.
Results
Two patients were heterozygous females, and the other two were hemizygous males. One heterozygous female had coexisting hypothyroidism. The other heterozygous female was erroneously prescribed levothyroxine at a local clinic. One hemizygous male harbored a novel mutation, p.Phe269Cysfs*18, which caused TBG partial deficiency. Three patients had the p.Leu372Phefs*23 mutation, which is known as TBG-complete deficiency Japan (TBG-CDJ) and was also presented in previous mutation analyses in Korea.
Conclusion
This study presents four patients diagnosed with TBG deficiency and provides the results of SERPINA7 gene sequencing. One novel mutation, p.Phe269Cysfs*18, causing TBD-partial deficiency and three cases of TBG-CDJ were demonstrated. It is necessary to identify TBG deficiency to prevent improper treatment. Also, sequencing of the SERPINA7 gene would provide valuable information about the TBG variants in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development and basic performance verification of a rapid homogeneous bioassay for agonistic antibodies against the thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor
Motoki Hoshina, Shiomi Ojima, Atsushi Kawasaki, Kosuke Doi, Satoshi Ohta, Asuka Inoue, Hiroshi Murayama
Journal of Immunological Methods.2024; 528: 113655. CrossRef
- Development and basic performance verification of a rapid homogeneous bioassay for agonistic antibodies against the thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor

- Thyroid
- A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Trial for Assessing the Usefulness of Suppressing Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Target Levels after Thyroid Lobectomy in Low to Intermediate Risk Thyroid Cancer Patients (MASTER): A Study Protocol
- Eun Kyung Lee, Yea Eun Kang, Young Joo Park, Bon Seok Koo, Ki-Wook Chung, Eu Jeong Ku, Ho-Ryun Won, Won Sang Yoo, Eonju Jeon, Se Hyun Paek, Yong Sang Lee, Dong Mee Lim, Yong Joon Suh, Ha Kyoung Park, Hyo-Jeong Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Mijin Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Ka Hee Yi, Sue K. Park, Eun-Jae Jung, June Young Choi, Ja Seong Bae, Joon Hwa Hong, Kee-Hyun Nam, Young Ki Lee, Hyeong Won Yu, Sujeong Go, Young Mi Kang, MASTER study group
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):574-581. Published online May 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.943
- 6,333 View
- 268 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
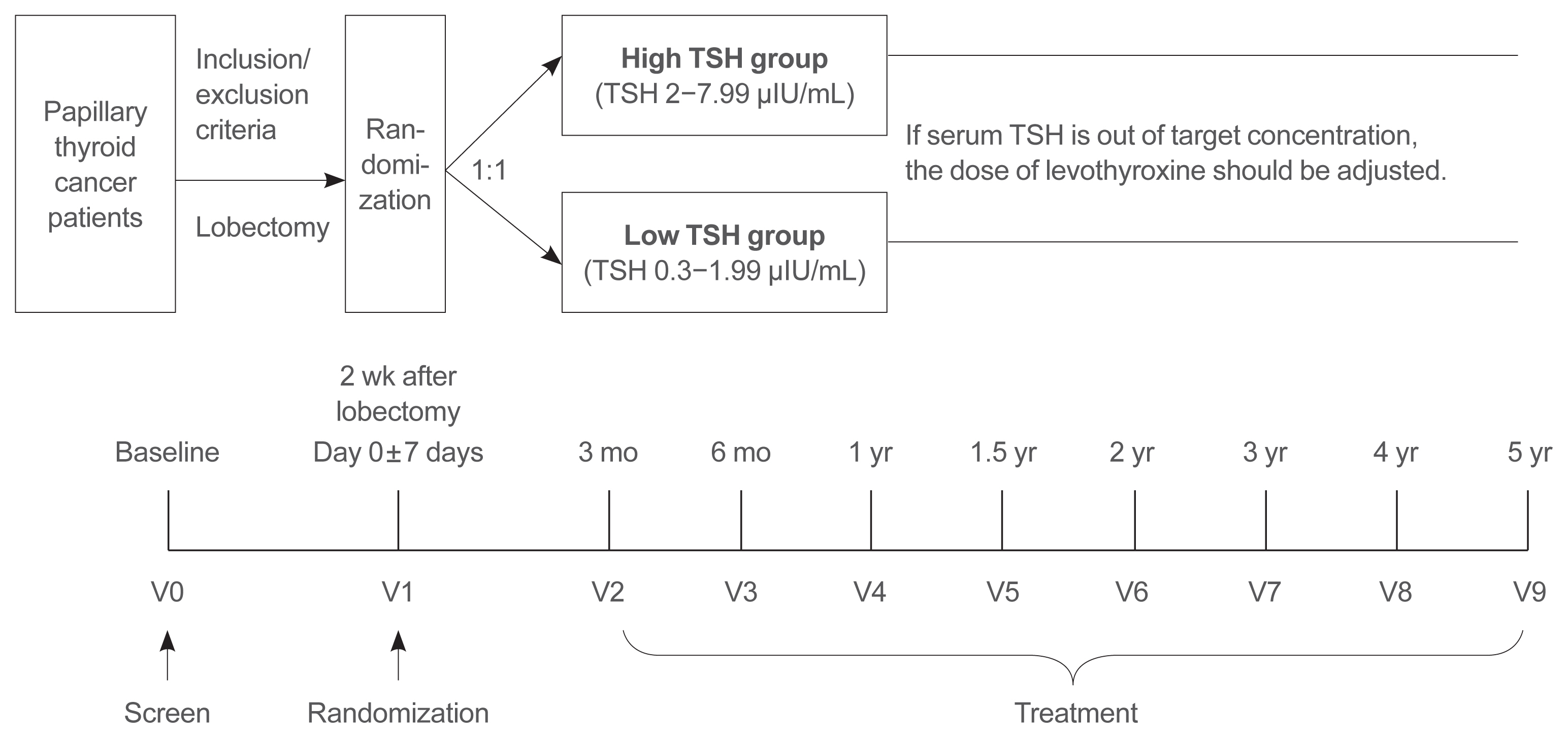
Postoperative thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) suppression therapy is recommended for patients with intermediate- and high-risk differentiated thyroid cancer to prevent the recurrence of thyroid cancer. With the recent increase in small thyroid cancer cases, the extent of resection during surgery has generally decreased. Therefore, questions have been raised about the efficacy and long-term side effects of TSH suppression therapy in patients who have undergone a lobectomy.
Methods
This is a multicenter, prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial in which 2,986 patients with papillary thyroid cancer are randomized into a high-TSH group (intervention) and a low-TSH group (control) after having undergone a lobectomy. The principle of treatment includes a TSH-lowering regimen aimed at TSH levels between 0.3 and 1.99 μIU/mL in the low-TSH group. The high-TSH group targets TSH levels between 2.0 and 7.99 μIU/mL. The dose of levothyroxine will be adjusted at each visit to maintain the target TSH level. The primary outcome is recurrence-free survival, as assessed by neck ultrasound every 6 to 12 months. Secondary endpoints include disease-free survival, overall survival, success rate in reaching the TSH target range, the proportion of patients with major cardiovascular diseases or bone metabolic disease, the quality of life, and medical costs. The follow-up period is 5 years.
Conclusion
The results of this trial will contribute to establishing the optimal indication for TSH suppression therapy in low-risk papillary thyroid cancer patients by evaluating the benefit and harm of lowering TSH levels in terms of recurrence, metabolic complications, costs, and quality of life. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of thyroid-stimulating hormone suppression on quality of life in thyroid lobectomy patients: interim analysis of a multicenter, randomized controlled trial in low- to intermediate-risk thyroid cancer patients (MASTER study)
Ja Kyung Lee, Eu Jeong Ku, Su-jin Kim, Woochul Kim, Jae Won Cho, Kyong Yeun Jung, Hyeong Won Yu, Yea Eun Kang, Mijin Kim, Hee Kyung Kim, Junsun Ryu, June Young Choi
Annals of Surgical Treatment and Research.2024; 106(1): 19. CrossRef - Clinical impact of coexistent chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis on central lymph node metastasis in low- to intermediate-risk papillary thyroid carcinoma: The MASTER study
Da Beom Heo, Ho-Ryun Won, Kyung Tae, Yea Eun Kang, Eonju Jeon, Yong Bae Ji, Jae Won Chang, June Young Choi, Hyeong Won Yu, Eu Jeong Ku, Eun Kyung Lee, Mijin Kim, Jun-Ho Choe, Bon Seok Koo
Surgery.2024; 175(4): 1049. CrossRef - Dynamic Changes in Treatment Response af-ter 131I in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer and Their Relationship with Recurrence Risk Stratification and TNM Staging
璐 狄
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(03): 1083. CrossRef - ASO Author Reflections: Active Surveillance may be Possible in Patients with T1b Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Over 55 Years of Age Without High-Risk Features on Preoperative Examinations
Ho-Ryun Won, Eonju Jeon, Da Beom Heo, Jae Won Chang, Minho Shong, Je Ryong Kim, Hyemi Ko, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Ju Hee Lee, Kyong Hye Joung, Ji Min Kim, Younju Lee, Sung-Woo Kim, Young Ju Jeong, Yong Bae Ji, Kyung Tae, Bon Seok Koo
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2023; 30(4): 2254. CrossRef - Outcomes and Trends of Treatments in High‐Risk Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Arash Abiri, Khodayar Goshtasbi, Sina J. Torabi, Edward C. Kuan, William B. Armstrong, Tjoson Tjoa, Yarah M. Haidar
Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery.2023; 168(4): 745. CrossRef - Current Controversies in Low-Risk Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Reducing Overtreatment in an Era of Overdiagnosis
Timothy M Ullmann, Maria Papaleontiou, Julie Ann Sosa
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(2): 271. CrossRef - Age-Dependent Clinicopathological Characteristics of Patients with T1b Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Implications for the Possibility of Active Surveillance
Ho-Ryun Won, Eonju Jeon, Da Beom Heo, Jae Won Chang, Minho Shong, Je Ryong Kim, Hyemi Ko, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Ju Hee Lee, Kyong Hye Joung, Ji Min Kim, Younju Lee, Sung-Woo Kim, Young Ju Jeong, Yong Bae Ji, Kyung Tae, Bon Seok Koo
Annals of Surgical Oncology.2023; 30(4): 2246. CrossRef - Potential impact of obesity on the aggressiveness of low- to intermediate-risk papillary thyroid carcinoma: results from a MASTER cohort study
Mijin Kim, Yae Eun Kang, Young Joo Park, Bon Seok Koo, Eu Jeong Ku, June Young Choi, Eun Kyung Lee, Bo Hyun Kim
Endocrine.2023; 82(1): 134. CrossRef - Differentiated thyroid cancer: a focus on post-operative thyroid hormone replacement and thyrotropin suppression therapy
Benjamin J. Gigliotti, Sina Jasim
Endocrine.2023; 83(2): 251. CrossRef - Thyroid stimulating hormone suppression and recurrence after thyroid lobectomy for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Mi Rye Bae, Sung Hoon Nam, Jong-Lyel Roh, Seung-Ho Choi, Soon Yuhl Nam, Sang Yoon Kim
Endocrine.2022; 75(2): 487. CrossRef - The Concept of Economic Evaluation and Its Application in Thyroid Cancer Research
Kyungsik Kim, Mijin Kim, Woojin Lim, Bo Hyun Kim, Sue K. Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 725. CrossRef
- Effect of thyroid-stimulating hormone suppression on quality of life in thyroid lobectomy patients: interim analysis of a multicenter, randomized controlled trial in low- to intermediate-risk thyroid cancer patients (MASTER study)

- Thyroid
- Update on Thyroid Hormone Levels and Thyroid Dysfunction in the Korean Population Based on Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI (2013 to 2015)
- Jae Hoon Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):7-13. Published online March 19, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.7
- 6,981 View
- 150 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
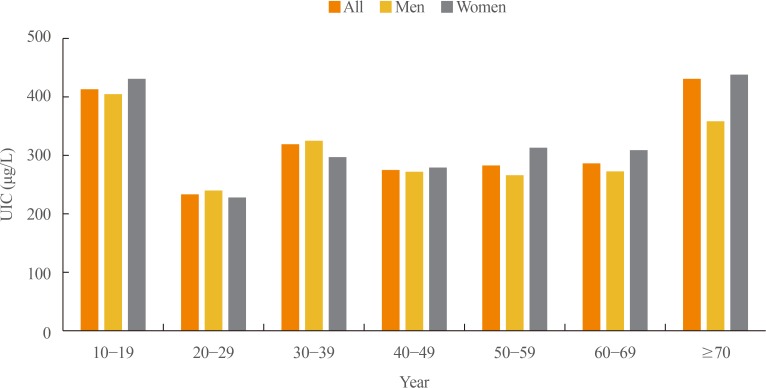
ePub In 2017, the first Korean nationwide data on serum thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) levels, serum free thyroxine (fT4) levels, and urinary iodine concentration (UIC) were published based on a population of 7,061 Koreans who participated in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI. The mean TSH level was 2.16 mIU/L, with a reference interval of 0.59 to 7.03 mIU/L (men 2.09 mIU/L, women 2.24 mIU/L,
P <0.001). A U-shaped association was found between serum TSH levels and age. The mean fT4 level was 1.25 ng/dL, and its reference interval was 0.92 to 1.60 ng/dL (men 1.29 ng/dL, women 1.20 ng/dL,P <0.0001). Serum fT4 levels decreased with age (P for trend <0.0001). Serum thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPOAb) was detected in 7.30% of participants (men 4.33%, women 10.62%). TPOAb titers tended to increase with age, and were higher in women than in men. The median UIC was 294 µg/L, and UIC showed a U-shaped relationship with age. According to the World Health Organization recommendations, only 23% of participants were in the adequate range of iodine intake, while 65% were in the above requirements or excessive, and 12% in insufficient. The prevalence of overt hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism in Koreans was 0.34% to 0.54% and 0.73% to 1.43%, respectively.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Thyroid Function and Insulin Resistance Indices in Korean Adolescents: Findings from the 2014–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eunji Mun, Hye Ah Lee, Jung Eun Choi, Rosie Lee, Kyung Hee Kim, Hyesook Park, Hae Soon Kim
Children.2024; 11(3): 370. CrossRef - Diagnostic Value of Carotid Plaque Assessment with AIS Based on Quantitative Parameters of Dual-Layer Detector Spectral CT
Xiaoying Meng, Fei Li, Wenpei Wu, Juncang Wu
International Journal of General Medicine.2024; Volume 17: 1263. CrossRef - Hyperthyroidism
Sun Y. Lee, Elizabeth N. Pearce
JAMA.2023; 330(15): 1472. CrossRef - Exploring the Association between Thyroid Function and Frailty: Insights from Representative Korean Data
Youn-Ju Lee, Min-Hee Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Jung-Min Lee, Sang Ah Chang, Jeongmin Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 729. CrossRef - Subclinical Hypothyroidism: Prevalence, Health Impact, and Treatment Landscape
Won Sang Yoo, Hyun Kyung Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 500. CrossRef - Association between Iodine Intake, Thyroid Function, and Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Case-Control Study
Kyungsik Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Young Joo Park, Kyu Eun Lee, Dong-Wook Lee, Sue K. Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 790. CrossRef
- Association between Thyroid Function and Insulin Resistance Indices in Korean Adolescents: Findings from the 2014–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey

- Clinical Study
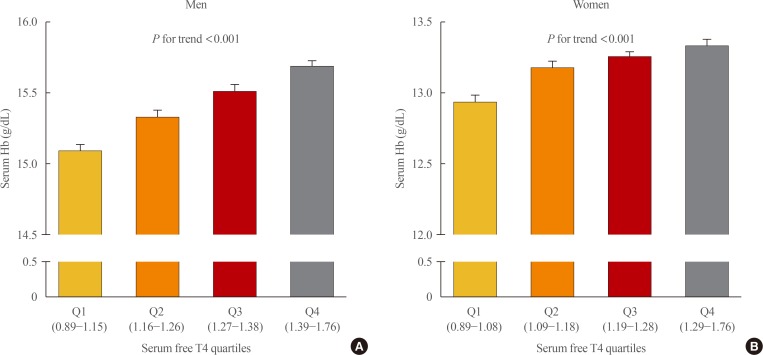
- Association between Serum Free Thyroxine and Anemia in Euthyroid Adults: A Nationwide Study
- Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Hyungi Lee, Min Hee Jang, Jeong Mi Kim, Eun Heui Kim, Yun Kyung Jeon, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):106-114. Published online March 19, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.106
- 6,149 View
- 121 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Studies on the relationship between thyroid function and anemia in the euthyroid range are scarce. We aimed to evaluate the association between anemia and serum free thyroxine (fT4) and thyrotropin (TSH) in euthyroid adults.
Methods Data on 5,352 participants aged ≥19 years were obtained from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI (2013 to 2015). Anemia was defined as hemoglobin (Hb) <13 and <12 g/dL for men and women, respectively.
Results Overall, 6.1% of participants had anemia, and more women (9.9%) had anemia than men (2.8%,
P <0.001). In multivariate analysis, serum fT4 levels, but not TSH, were positively associated with serum Hb levels in both sexes (P <0.001, each). Serum Hb levels linearly reduced across decreasing serum fT4 quartile groups in both sexes (P <0.001, each). After adjusting for potential confounding factors, participants with low-normal fT4 had 4.4 (P =0.003) and 2.8 times (P <0.001) higher risk for anemia than those with high-normal fT4 among men and women, respectively. When participants were divided into two groups at 50 years of age, in younger participants, men and women with the first quartile were at higher risk of anemia than men with the second quartile (odds ratio [OR], 3.3;P =0.029) and women with the forth quartile (OR, 3.2;P <0.001), respectively. This association was not observed in older participants.Conclusion These results suggest that a low-normal level of serum fT4 was associated with a lower serum Hb level and a higher risk of anemia in euthyroid adults, especially in younger participants.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Thyroid Function and Risk of Anemia: A Multivariable-Adjusted and Mendelian Randomization Analysis in the UK Biobank
Nicolien A van Vliet, Annelies E P Kamphuis, Wendy P J den Elzen, Gerard J Blauw, Jacobijn Gussekloo, Raymond Noordam, Diana van Heemst
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(2): e643. CrossRef - Thyroid function, pernicious anemia and erythropoiesis: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study
Alisa D Kjaergaard, Alexander Teumer, Eirini Marouli, Panos Deloukas, Aleksander Kuś, Rosalie Sterenborg, Bjørn O Åsvold, Marco Medici, Christina Ellervik
Human Molecular Genetics.2022; 31(15): 2548. CrossRef - Changes of hematological indices in patients with diffuse toxic goiter
F. H. Saidova, L. M. Ahmedova, Zh. B. Aslanova, N. A. Najafov
Klinicheskaia khirurgiia.2021; 88(3-4): 76. CrossRef - Association between Serum Free Thyroxine and Anemia in Euthyroid Adults: A Nationwide Study (Endocrinol Metab 2020;35:106-14, Mijin Kim et al.)
Zheng Feei Ma
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 484. CrossRef - Association between Serum Free Thyroxine and Anemia in Euthyroid Adults: A Nationwide Study (Endocrinol Metab 2020;35:106-14, Mijin Kim et al.)
Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(3): 669. CrossRef
- Thyroid Function and Risk of Anemia: A Multivariable-Adjusted and Mendelian Randomization Analysis in the UK Biobank

- Changes in Serum Lipids and Apolipoproteins Levels According to the Thyroxine Treatment in The Patients with Subclinical Hypothyroidism.
- Hye Young Park, Bo Youn Cho, Won Bae Kim, Hong Gyu Lee, Chang Soon Koh, Geon Sang Park, Hyung Kyu Park, Sook Kyung Kim, Chan Soo Shin, Seong Yeon Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(1):41-51. Published online November 7, 2019
- 1,224 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Subclinical hypothyroidism(SCH) is a common biochemical abnormality which can be found in routine screening tests of thyroid function. We are increasingly faced with the question of whether its an indication for thyroxine replacement therapy. The effect of thyroxine replacement on lipid profile in SCH has aroused a great interest because of an association of overt hypothyroidism(OVH) with hyperlipidemia and increased risk of coronary artery disease. Method: We prospectively evaluated the changes in lipids and apoproteins before and after thyroxine replacement therapy in 23 patients with SCH and in 37 patients with OVH. We measured serum total cholesterol and triglyceride using autoanalyzer, high density lipoprotein(HDL) chole-sterol by dextran sulfate method, Apo A1 and Apo B by immunonephelometric assay. Results: Thyroxine replacement therapy significantly decreased total cholesterol, low density lipoprotein(LDL) cholesterol and apo B levels, but did not affect the level of triglyceride, HDL cholesterol or apo AI in patients with OVH. In SCH, thyroxine replacement therapy with the doses to normalize serum TSH concentrations also decreased significantly the level of cholesterol and LDL cholesterol albeit apo B levels did not change. Moreover, in most of patients with OVH (11 of 12) and in all of patients with SCH(5 of 5) who had had hyperchlesterolemia before treatment, thyroxine replament normalized their cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels. Conclusion: In regard to the beneficial changes in blood lipid levels, patients with SCH should be treated, especially in cases who have other risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis. If thyroxine replacement only will reduce the incidence of coronary artery disease in SCH remains to be elucidated by long-term prospective studies.

- Changes of Thyroid Function According to the Stages of Normal Pregnancy.
- W B Kim, B H Yoon, J H Chung, S I Lee, M S Kim, T G Oh, B Y Cho, H K Lee, C S Koh
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(3):183-189. Published online November 6, 2019
- 1,110 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - It is well known that normal pregnancy is accompanied by a rise in serum concentrations of thyroxine-binding globulin(TBG) and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). Alterations of biochemical parameters of thyroid function are recognized during gestation and sensitive tests to evaluate the alterations easily are required. Therefore, a cross-sectional study was undertaken in 140 healthy pregnant women to evaluate the efficacy of free T_4 measured by 2-step RIA compared to other thyroid function tests and to confirm the changes of thyroid function according to the stages of normal pregnancy.The sensitivities of free T_4 index, free T_4(by 2-step RIA), T_3 and TSH were realtively high(99.3%, 93.6%, 92.9%, 83.6%, respectively) compared to those of T_4 and T_3 bead upgake(49.3%, 21.4%) during all stages of pregnancy. There were positive correlations between free T_4 index and free T_4 or total T_4(r=0.68, r=0.72; p<0.001). The values of free T_4 index sharply decreased from 3.22+-0.10(meam +-SEM) during 6th-12th week to an plateau after 16th-20th week of gestation(p<0.01). The serum concentrations free T_4 and T_3 bead uptake also significantly decreased from 1.65+-0.05 ng/dl, 24.7+- 0.7% during 6th-12th week to an plateau after 16th-20th week of gestation, respectively(p<0.001), No differences were found in the changes of serum concentrations of T_3, T_4 and TSH according to the stages of pregnancy.In conclusion, it is adequate to measure some tests including free T_4 index and free T_4 to evaluate thyroid function during pregnancy. The thyroid physiology and changes of thyroid function according to the stages of pregnancy should be considered in the interpretation of thyroid function status during pregnancy.

- Evaluation of the Usefulness of Free T4 Measured by 2 - Step Iimmunoextraction in the Patients with Thyroid and Non - Thyroid Diseases.
- Bo Youn Cho, Hong Kyu Lee, Jae Hoon Chung, Seok In Lee, Won Bae Kim, Chang Soon Koh
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;10(2):98-104. Published online November 6, 2019
- 1,180 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Many methods and commercial kits have become available for directly measuring free thyroxine(free T_4). However, most of them are inadequate for routine laboratory use because of their complexity and inaccuracy. Recently, 2-step RIA methods by immunoextraction(2-step immunoextraction) for free T_4 have been developed to improve its accuracy and convenience. We evaluated the usefulness of free T_4 measured by 2-step immunoextraction compared to free T_4 index(FT_4I), free T_4 measured by 1-step RIA, and TSH in 204 patients with thyroid and non-thyroid disease. There were no differences in sensitivities and specificities of free T_4(1-step, 2-step), FT_4I and TSH in the patients with hyperthyroidism and euthyroid nodule. However, the sensitivity of TSH in hypothyroidism was remarkablely higher than the others(100.0% vs. 61.5-81.5%). The sensitivity of free T_4(2-step) was also higher than those of free T_4(1-step), FT_4I and TSH in the patients with non-thyroid disease(94.3% vs. 74.3-83.8%). The values of free T_4 measured by 1-step RIA were significantly lower than those by 2-step immunoextraction, especially in the patients with non-thyroid disease(1.10+-0.04 vs. 1.55+-0.03ng/dL, p<0.05).In conclusion, no significant differences were found in sensitivity and specificity of free T_4(1-step, 2-step), FT_4I, and TSH in the patients with thyroid diseases except in hypothyroidism. However, the sensitivity of free T_4 measured by 2-step immunoextraction was significantly higher than the other tests, especially in the patients with non-thyroid disease. Therefore, free T_4 assay using 2-step immunoextraction is useful to differentiate the non-thyroid disease from thyroid diseases.

- Clinical Study
- Detection of Polyethylene Glycol Thyrotropin (TSH) Precipitable Percentage (Macro-TSH) in Patients with a History of Thyroid Cancer
- Massimo Giusti, Lucia Conte, Anna Maria Repetto, Stefano Gay, Paola Marroni, Miranda Mittica, Michele Mussap
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(4):460-465. Published online December 14, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.4.460
- 4,870 View
- 97 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Owing to its large molecular size, polyethylene glycol (PEG)-precipitable thyrotropin (TSH) can accumulate in the circulation, elevating TSH levels. PEG-precipitable TSH can be used to detect macro-TSH (mTSH) in serum. Our aim was to evaluate the prevalence of mTSH in patients who had undergone thyroidectomy for thyroid cancer.
Methods Seventy-three thyroid cancer patients and 24 control subjects on levothyroxine (LT4) TSH-suppressive or replacement therapy were evaluated. Screening for mTSH was performed by adding PEG to serum in order to precipitate γ-globulin. A percentage of PEG-precipitable TSH ≥80% was considered suggestive of mTSH.
Results No correlation between free-T4 (fT4) and TSH levels was found. PEG-precipitable TSH was 39.3%±1.9% in thyroid cancer patients and 44.1%±3.9% in controls. Macro-TSH was deemed to be present in one thyroid cancer patient and in two control subjects. Only in the thyroid cancer group was PEG-precipitable TSH found to be negatively correlated with fT4 concentration. No correlation was found between PEG-precipitable TSH and other clinical conditions in any patients.
Conclusion The presence of mTSH seems to be a rare phenomenon in thyroid cancer. In some patients with low PEG-precipitable TSH, a reduction in LT4 dosage could be suggested. LT4 dosage adjusted to body weight is the main factor in maintaining TSH in a semi-suppressed or normal range. Evaluation of mTSH could be necessary in patients in whom a balance is required between adequate TSH suppression and the avoidance of unnecessary exogenous hyperthyroxinemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence and Pathogenesis of Macro-Thyrotropin in Neonates: Analysis of Umbilical Cord Blood from 939 Neonates and Their Mothers
Naoki Hattori, Kohzo Aisaka, Ayato Yamada, Takeshi Matsuda, Akira Shimatsu
Thyroid.2023; 33(1): 45. CrossRef - Pars Distalis and Pars Tuberalis Thyroid-Stimulating Hormones and Their Roles in Macro-Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Formation
Eleonore Fröhlich, Richard Wahl
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(14): 11699. CrossRef - Falsely Elevated Thyroid Stimulating Hormone in Two Cases Requiring Special Follow-up
Serpil YANIK ÇOLAK, Eray ÖZGÜN, Burak ANDAÇ, Mine OKUR, Buket YILMAZ BÜLBÜL, Mehmet ÇELİK
Namık Kemal Tıp Dergisi.2023; 11(4): 395. CrossRef - A comparative cross-sectional study on sleep quality in patients with a history of differentiated thyroid carcinoma and its correlation with quality of life
Marsida Teliti, Eleonora Monti, Martina Comina, Lucia Conte, Lara Vera, Stefano Gay, Giorgia Saccomani, Diego Ferone, Massimo Giusti
Endocrine.2021; 73(2): 347. CrossRef - A rare cause of subclinical hypothyroidism: macro-thyroid-stimulating hormone
Cem Onur Kirac, Sedat Abusoglu, Esra Paydas Hataysal, Aysegul Kebapcilar, Suleyman Hilmi Ipekci, Ali Ünlü, Levent Kebapcilar
Diagnosis.2020; 7(1): 75. CrossRef - Neuroendocrine neoplasms – think about it and choose the most appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic steps
Christian A. Koch, S. Petersenn
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2018; 19(2): 107. CrossRef
- Prevalence and Pathogenesis of Macro-Thyrotropin in Neonates: Analysis of Umbilical Cord Blood from 939 Neonates and Their Mothers

- Free Thyroxine, Anti-Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Receptor Antibody Titers, and Absence of Goiter Were Associated with Responsiveness to Methimazole in Patients with New Onset Graves' Disease
- Hoon Sung Choi, Won Sang Yoo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(2):281-287. Published online June 23, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.2.281
- 3,745 View
- 39 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Anti-thyroid drug therapy is considered a treatment of choice for Graves' disease; however, treatment response varies among individuals. Although several studies have reported risk factors for relapse after initial treatment, few have assessed responsiveness during the early treatment period. Our study aimed to identify the clinical characteristics for responsiveness to methimazole.
Methods We included 99 patients diagnosed with Graves' disease for the first time. Drug responsiveness was defined as the correlation coefficients between decreasing rates of free thyroxine level per month and methimazole exposure dose. According to their responsiveness to treatment, the patients were classified into rapid or slow responder groups, and age, sex, free thyroxine level, and thyrotropin binding inhibiting immunoglobulin (TBII) titers were compared between groups.
Results The mean patient age was 44.0±13.5 years and 40 patients were male (40%). The mean TBII titer was 36.6±74.4 IU/L, and the mean free thyroxine concentration was 48.9±21.9 pmol/L. The rapid responder group showed higher TBII titer and free thyroxine level at diagnosis, while age, sex, smoking, and presence of goiter did not differ between the two groups. Logistic regression analyses revealed that high level of serum thyroxine, high titer of TBII, and absence of goiter were significantly associated with a rapid response, while age, sex, and smoking were not significant factors for the prediction of responsiveness.
Conclusion In patients with new onset Graves' disease, high level of free thyroxine, high titer of TBII, and absence of goiter were associated with rapid responsiveness to methimazole treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Enhanced predictive validity of integrative models for refractory hyperthyroidism considering baseline and early therapy characteristics: a prospective cohort study
Xinpan Wang, Tiantian Li, Yue Li, Qiuyi Wang, Yun Cai, Zhixiao Wang, Yun Shi, Tao Yang, Xuqin Zheng
Journal of Translational Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Related Factors in Refractory Graves’ Disease
鑫 王
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(08): 13439. CrossRef - Clinical efficacy of thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin detection for diagnosing Graves’ disease and predictors of responsiveness to methimazole
KunY Liu, Yu Fu, TianT Li, SunQ Liu, DouD Chen, ChengC Zhao, Yun Shi, Yun Cai, Tao Yang, XuQ Zheng
Clinical Biochemistry.2021; 97: 34. CrossRef - Changes in Thyroid Peroxidase and Thyroglobulin Antibodies Might Be Associated with Graves' Disease Relapse after Antithyroid Drug Therapy
Yun Mi Choi, Mi Kyung Kwak, Sang Mo Hong, Eun-Gyoung Hong
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(3): 268. CrossRef - When should antithyroid drug therapy to reduce the relapse rate of hyperthyroidism in Graves’ disease be discontinued?
Suyeon Park, Eyun Song, Hye-Seon Oh, Mijin Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Doo Man Kim, Won Bae Kim
Endocrine.2019; 65(2): 348. CrossRef
- Enhanced predictive validity of integrative models for refractory hyperthyroidism considering baseline and early therapy characteristics: a prospective cohort study

- Thyroid
- Clinical Update in Aspects of the Management of Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases
- Duncan J. Topliss
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(4):493-499. Published online December 20, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.4.493
- 5,306 View
- 70 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 21 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Aspects of autoimmune thyroid disease updated in this review include: immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-related thyroid disease (Riedel's thyroiditis, fibrosing variant of Hashimoto's thyroiditis, IgG4-related Hashimoto's thyroiditis, and Graves' disease with elevated IgG4 levels); recent epidemiological studies from China and Denmark indicating that excess iodine increases the incidence of Hashimoto's thyroiditis and hypothyroidism; immunomodulatory agents (ipilimumab, pembrolizumab, nivolumab) activate immune response by inhibiting T-cell surface receptors which down-regulate immune response, i.e., cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 and programmed cell death protein 1 pathways; alemtuzumab is a humanised monoclonal antibody to CD52 which causes immune depletion and thyroid autoimmune disease especially Graves' hyperthyroidism; small molecule ligand (SML) agonists which activate receptors, SML neutral antagonists, which inhibit receptor activation by agonists, and SML inverse agonists which inhibit receptor activation by agonists and inhibit constitutive agonist independent signaling have been identified. SML antagonism of thyroid-stimulating hormone-receptor stimulatory antibody could treat Graves' hyperthyroidism and Graves' ophthalmopathy; and thyroxine treatment of subclinical hypothyroidism can produce iatrogenic subclinical hyperthyroidism with the risk of atrial fibrillation and osteoporosis. The increased risk of harm from subclinical hyperthyroidism may be stronger than the potential benefit from treatment of subclinical hypothyroidism.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of autoimmune thyroid disease with type 1 diabetes mellitus and its ultrasonic diagnosis and management
Jin Wang, Ke Wan, Xin Chang, Rui-Feng Mao
World Journal of Diabetes.2024; 15(3): 348. CrossRef - The impact of gut microbiota on autoimmune thyroiditis and relationship with pregnancy outcomes: a review
Yu Song, Yu Bai, Cong Liu, Xiaodan Zhai, Le Zhang
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of vitamin D treatment on thyroid function and autoimmunity markers in patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis—A meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials
Hui Jiang, Xiaoluo Chen, Xiaoqin Qian, Shihe Shao
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2022; 47(6): 767. CrossRef - Immunoglobulin G4-Related Thyroid Disease: A Single-Center Experience and Literature Review
Meihua Jin, Bictdeun Kim, Ahreum Jang, Min Ji Jeon, Young Jun Choi, Yu-Mi Lee, Dong Eun Song, Won Gu Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 312. CrossRef - DNA Methylation in Autoimmune Thyroid Disease
Nicole Lafontaine, Scott G Wilson, John P Walsh
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of Components of Metabolic Syndrome Among Adults with the Presence of Autoimmune Thyroid Condition in an Iodine-Sufficient Region
Binyu Pan, Qin Zhang, Hang Zhou, Zheng Feei Ma
Biological Trace Element Research.2021; 199(8): 2837. CrossRef - Hashimoto's thyroiditis: An update on pathogenic mechanisms, diagnostic protocols, therapeutic strategies, and potential malignant transformation
Massimo Ralli, Diletta Angeletti, Marco Fiore, Vittorio D'Aguanno, Alessandro Lambiase, Marco Artico, Marco de Vincentiis, Antonio Greco
Autoimmunity Reviews.2020; 19(10): 102649. CrossRef - Myasthenia Gravis and its Association With Thyroid Diseases
Saba Amin, Myat Aung, Fenil R Gandhi, Julio A Pena Escobar, Azouba Gulraiz, Bilal Haider Malik
Cureus.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of large dosage of Prunella on Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Pei Chen, Chaomin Li, Siliang Zhao, Lizhen Wang, Lingyu Liu, Qiuhong Fan
Medicine.2020; 99(50): e23391. CrossRef - Establishment of clinical diagnosis model of Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
Zhaohui Cui, Zhixiao Wang, Xiaoyun Liu, Yun Cai, Xinyu Xu, Tao Yang
Journal of Translational Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The value of preoperative antithyroidperoxidase antibody as a novel predictor of recurrence in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Eyun Song, Hye‐Seon Oh, Min Ji Jeon, Ki Wook Chung, Suck Joon Hong, Jin Sook Ryu, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Won Gu Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Tae Yong Kim
International Journal of Cancer.2019; 144(6): 1414. CrossRef - Sonographic Characteristics of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma with Coexistent Hashimoto's Thyroiditis: Conventional Ultrasound, Acoustic Radiation Force Impulse Imaging and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound
Qinghai Peng, Chengcheng Niu, Meixiang Zhang, Qiang Peng, Sijie Chen
Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology.2019; 45(2): 471. CrossRef - The incidental thyroid nodule
Sarah B. Fisher, Nancy D. Perrier
CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.2018; 68(2): 97. CrossRef - Development of thyroid dysfunction is associated with clinical response to PD-1 blockade treatment in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
Hye In Kim, Mijin Kim, Se-Hoon Lee, So Young Park, Young Nam Kim, Hosu Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Won Bae Kim, Sang-We Kim, Dae Ho Lee, Keunchil Park, Myung-Ju Ahn, Jae Hoon Chung, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim, Tae Hyuk Kim
OncoImmunology.2018; 7(1): e1375642. CrossRef - A case report of a novel, integrative approach to Hashimoto’s thyroiditis with unexpected results
Nicole Avard, Suzanne J. Grant
Advances in Integrative Medicine.2018; 5(2): 75. CrossRef - Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases in Patients Treated with Alemtuzumab for Multiple Sclerosis: An Example of Selective Anti-TSH-Receptor Immune Response
Mario Rotondi, Martina Molteni, Paola Leporati, Valentina Capelli, Michele Marinò, Luca Chiovato
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Implications of Immunoglobulin G4 to Graves' Ophthalmopathy
Sung Hoon Yu, Jun Goo Kang, Chul Sik Kim, Sung-Hee Ihm, Moon Gi Choi, Hyung Joon Yoo, Seong Jin Lee
Thyroid.2017; 27(9): 1185. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Correlation of hormonal and cytokines regulation in case of autoimmune thyroiditis
Victoria V. Zdor
Clinical and experimental thyroidology.2017; 13(2): 45. CrossRef - Autoimmune Thyroiditis and Myasthenia Gravis
Angela Lopomo, Sonia Berrih-Aknin
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Age-specific reference interval of serum TSH levels is high in adolescence in an iodine excess area: Korea national health and nutrition examination survey data
Hyemi Kwon, Won Gu Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Minkyu Han, Mijin Kim, Suyeon Park, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Endocrine.2017; 57(3): 445. CrossRef
- Association of autoimmune thyroid disease with type 1 diabetes mellitus and its ultrasonic diagnosis and management

- A Case of Sheehan's Syndrome with Pancytopenia.
- Hyun Suk Lee, Byung Woon Kwon, Jin Hyung Han, Hee Jin Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2012;27(1):54-58. Published online March 1, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.1.54
- 2,571 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Sheehan's syndrome is characterized by varying degrees of anterior pituitary dysfunction due to postpartum ischemic necrosis of the pituitary gland after massive bleeding. The spectrum of clinical presentation of Sheehan's syndrome is broad, with changes from nonspecific complaints, such as weakness, fatigue, and anemia, to severe pituitary insufficiency resulting in coma and death. Normochromic anemia is commonly associated with Sheehan's syndrome, but pancytopenia is rarely observed in patients with Sheehan's syndrome. We describe a 57-year-old woman with Sheehan's syndrome who presented with pancytopenia that was treated by hormone replacement with levothyroxine and glucocorticoid.

- Factors Influencing Peripheral Conversion of Thyroxine to Tri-Iodothyronine in Athyreotic Individuals during Levothyroxine Replacement.
- Eui Young Kim, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Jong Ho Yoon, Suck Joon Hong, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2010;25(2):119-124. Published online June 1, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2010.25.2.119
- 1,953 View
- 30 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Tri-iodothyronine (T3) is the main active hormone, and 20% of this is derived from the thyroid gland and 80% is from the peripheral tissue according to 5'-monodeiodination of thyroxine (T4). In the previous studies, normal T3 levels were achieved with traditional levothyroxine (LT4) therapy alone in athyreotic patients, but there has been no data about the factors influencing peripheral conversion of LT4. The aim of this study was to determine the factor(s) influencing peripheral conversion of LT4 to T3 in athyreotic patients during LT4 replacement. METHODS: The patients who underwent total-thyroidectomy for any cause, and mostly for thyroid cancers, at Asan Medical Center between 2000 and 2008 were enrolled. The free T4, T3 and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) levels and age, gender, weight, height, body mass index (BMI) and the T4 dose were measured. Only patients with normal ranges of free T4 and TSH were included in the analysis. RESULTS: A total of 143 patients were enrolled. The mean T3, free T4 and TSH levels were 143.7 ng/dL, 1.4 ng/dL and 1.6 microU/mL, respectively. The mean weight and BMI were 62.9 kg and 24.6 kg/m2, respectively. We divided them into two groups according to the serum T3 level and we compared the characteristics of the groups. There were no differences in age, the gender distribution, the T4 dose/weight and the BMI between the low T3 group (T3 < or = 122 ng/dL, n = 14) and the normal T3 group (T3 > 122 ng/dL, n = 129). In the low T3 group, the mean body weight was significantly lower than that of the normal T3 group (59.0 +/- 6.0 vs. 63.4 +/- 9.9, respectively, P = 0.025). CONCLUSION: Lean body mass seems to be an important factor for determining the peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 in human. This suggest that a combination of T3/T4 is better than T4 only when we treat the patients with hypothyroidism and who have a negligible amount of functioning thyroid tissue, if they have a low lean body mass.

- The Efficacy of Thyroxine Suppression Therapy in Benign Thyroid Nodules.
- Seog Ki Yun, Chul Hee Kim, Young Sun Kim, Dong Won Byun, Kyo Il Suh, Myung Hi Yoo
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2000;15(4-5):532-541. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,162 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Benign pathologic findings are shown in 800% of thyroid nodules by fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) or needle biopsy. About half of these benign nodules are follicular lesions which are presented only as thyroid follicles or thyroid cell clumps. Differential diagnosis of follicular adenoma, follicular carcinoma and adenomatous goiter is impossible by FNAC or needle biopsy. Thyroxine suppression therapy has been performed traditionally in order to discriminate malignant nodules, but few studies are available which confirmed the efficacy of thyroxine suppression therapy in thyroid nodules of those the initial pathologic findings were follicular lesions. So we tried to evaluate the efficacy of thyroxine suppression therapy in benign thyroid nodules and also the incidence of thyroid cancer of the thyroid nosules which were not decreased on thyroxine suppression therapy after surgical resection. METHODS: Total 1027 patients with thyroid nodules were evaluated by FNAC or needle biopsy at Soonchunhyang university hospital from 1990 to 1996. Among 1027 patients, 507 patients showed follicular lesions in FNAC or needle biopsy and they received thyroxine suppression therapy. Thyroid nodule volume was measured before and after thyroxine suppression therapy using ultrasonography. We studied 184 patients who were followed up for more than 1 year. Serial changes of thyroid function tests, thyroid nodule volume, serum thyroglubulin (Tg) level before and after therapy were analyzed. RESULTS: l. In 80 (43.5%) of the 184 patients, nodule volumes decreased more than 50 percent after thyroxine suppression therapy. 2. There was no significant difference in serum T3, T4, TSH levels before and after thyroxine suppression therapy between group I (nodule volume decreased less than 50%) and group II (nodule volume decreased more than 50%). 3. In group II patients, thyroid nodule volumes were decreased continuously at 12 month, 18 month and 30 month after thyroxine suppression (p<0.05). 4. There was no significant difference between the group I and group II in the frequency of multiple thyroid nodules on ultrasonography. 5. Among 37 patients who underwent thyroidectomy, 19 cases (51.4%) were revealed as malignant thyroid nodules (papillary cancer 4 cases, follicular cancer 15 cases). Eighteen cases (48.6%) were revealed as benign thyroid nodules (follicular adenoma 10 cases, adenomatous goiter 8 cases). 6. There was no significant difference in the frequency of multiple nodules on ultrasonography between benign and malignant nodules. CONCLUSION: Our data suggested thyroxine suppression therapy was effective in discriminating malignant thyroid nodules from benign nodules, especially in selecting follicular carcinoma from follicular lesion by FNAC or biopsy.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



