Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Endocrinol Metab > Volume 38(4); 2023 > Article
-
Review ArticleThyroid Management of Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Focus on Proven Health Effects in the 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines
 Keypoint
Keypoint
The 2023 Korean Thyroid Association guidelines offer an updated approach to subclinical hypothyroidism management. They present new diagnostic criteria, region-specific thyroid-stimulating hormone reference ranges, and classify subclinical hypothyroidism severity based on age. The guidelines also recommend levothyroxine treatment considerations, factoring in subclinical hypothyroidism severity, patient age, and proven health impacts. This aligns with global evidence-based guidelines, emphasizing tailored management. -
Eu Jeong Ku1*
 , Won Sang Yoo2*
, Won Sang Yoo2* , Hyun Kyung Chung2
, Hyun Kyung Chung2
-
Endocrinology and Metabolism 2023;38(4):381-391.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1778
Published online: August 8, 2023
1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital Healthcare System Gangnam Center, Seoul, Korea
2Department of Internal Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea
- Corresponding author: Hyun Kyung Chung Department of Internal Medicine, Dankook University College of Medicine, 119 Dandae-ro, Dongnam-gu, Cheonan 31116, Korea Tel: +82-41-550-3057, Fax: +82-41-556-3256, E-mail: chkendo@dankook.ac.kr
- *These authors contributed equally to this work.
This guideline has been originally written in Korean and published in the International Journal of Thyroidology 2023;16:32-50.
Copyright © 2023 Korean Endocrine Society
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- ABSTRACT
- INTRODUCTION
- SUMMARY OF KEY CONTENTS OF THE 2023 KTA GUIDELINES FOR SCH MANAGEMENT
- THE RATIONALE FOR SETTING THE UPPER LIMIT OF NORMAL TSH AT 6.8 mIU/L
- SCH IN DIFFERENT AGE GROUPS: STUDIES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS
- CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE, HEART FAILURE, AND DYSLIPIDEMIA: IMPACT ON SCH MANAGEMENT
- LT4 TREATMENT: WHEN IS IT NECESSARY?
- UNMET NEEDS IN THE 2023 KTA GUIDELINES FOR SCH MANAGEMENT
- CONCLUSIONS
- Article information
- References
ABSTRACT
- Subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) is characterized by elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and normal free thyroxine levels. The Korean Thyroid Association recently issued a guideline for managing SCH, which emphasizes Korean-specific TSH diagnostic criteria and highlights the health benefits of levothyroxine (LT4) treatment. A serum TSH level of 6.8 mIU/L is presented as the reference value for diagnosing SCH. SCH can be classified as mild (TSH 6.8 to 10.0 mIU/L) or severe (TSH >10.0 mIU/L), and patients can be categorized as adults (age <70 years) or elderly (age ≥70 years), depending on the health effects of LT4 treatment. An initial increase in serum TSH levels should be reassessed with a subsequent measurement, including a thyroid peroxidase antibody test, preferably 2 to 3 months after the initial assessment. While LT4 treatment is not generally recommended for mild SCH in adults, it is necessary for severe SCH in patients with underlying coronary artery disease or heart failure and it may be considered for those with concurrent dyslipidemia. Conversely, LT4 treatment is generally not recommended for elderly patients, regardless of SCH severity. For those SCH patients who are prescribed LT4 treatment, the dosage should be personalized, and serum TSH levels should be regularly monitored to maintain the optimal LT4 regimen.
- Subclinical hypothyroidism (SCH) is a condition characterized by normal levels of serum free thyroxine (T4) despite elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels. SCH has often sparked considerable debate, primarily because it is frequently detected during health screenings and can manifest in individuals without any noticeable symptoms—hence the term “subclinical.” The prevalence of SCH varies based on different criteria for the normal TSH range, race, iodine intake, and age, but it is generally estimated to be between 5% and 15% [1]. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III study in the United States reported an overall prevalence of 4.3% in the general population, a figure that rose to 12.7% among individuals over the age of 65 [2]. A cohort study in Korea found the prevalence to be 6.5% in men and 16.4% in women [3]. Most previously reported prevalence rates have been based on an upper normal limit of TSH at 4.0 mIU/L [4,5]. However, TSH levels can vary depending on geographical location, race, age, and sex. As a result, there have been a continuous effort to establish appropriate TSH reference ranges for each region [4,5]. Recently, 2023 Korean Thyroid Association (KTA) Management Guidelines for Patients with Subclinical Hypothyroidism [6] introduced new diagnostic criteria for SCH, emphasizing a regionspecific TSH reference range of 6.8 mIU/L based on the sixth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) [7]. This innovative approach also recognizes the heterogeneity of SCH and categorizes the condition into mild and severe types, taking into account the patient’s age and the distinctive implications of levothyroxine (LT4) treatment in adults (under 70 years) and the elderly (70 years and older). These recent KTA guidelines provide comprehensive recommendations on LT4 treatment selection, stratified by the severity of SCH and the patient’s age. The guidelines also consider key factors such as underlying coronary artery disease, heart failure, and dyslipidemia, offering a more personalized approach to treatment. This aligns with evidence-based clinical guidelines developed by relevant medical societies worldwide, which have been established based on research findings from the past decade (Table 1) [4-6,8-10].
- This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the 2023 KTA guidelines for SCH management, highlighting their significance in improving the understanding and management of this highly prevalent but frequently under-recognized condition. Through this review, we hope to bridge the gap between these practice guidelines and their application in clinical practice, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
INTRODUCTION
- Newly proposed diagnostic criteria for SCH
- 1. The TSH reference range for diagnosing SCH is based on the values obtained from population studies in different regions and age groups without thyroid disease (Strong, Moderate).
- 2. The TSH reference range in Korea is 0.6 to 6.8 mIU/L, based on the Sixth KNHANES conducted from 2013 to 2015 (Strong, Moderate). However, differences in measurements among TSH measurement kits must be considered when applying the results.
- 3. SCH is classified as mild (TSH 6.8 to 10 mIU/L) or severe (TSH >10 mIU/L). Given the distinct health effects of LT4 treatment with age, patients are divided into adults and elderly, using 70 years as the cutoff (Strong, Moderate).
- LT4 treatment selection for SCH
- 1. LT4 treatment is generally not recommended for mild SCH in adults (<70 years) (Weak, Moderate).
- 2. For severe SCH in adults (<70 years):
- 1) LT4 treatment is necessary if SCH is accompanied by underlying coronary artery disease or heart failure (Strong, Moderate).
- 2) LT4 treatment can be considered for improving concomitant dyslipidemia (Weak, Moderate).
- 3. LT4 treatment is not indicated for mild SCH in the elderly (≥70 years) (Strong, High).
- 4. LT4 treatment is generally not recommended for severe SCH in the elderly (≥70 years) (Weak, Moderate).
- Clinical considerations in the diagnosis and treatment of SCH
- 1. Following the initial detection of SCH, TSH levels, and thyroid peroxidase (TPO) antibodies should be measured, preferably after 2 to 3 months, to guide LT4 treatment decisions and predict the prognosis (Strong, Moderate).
- 2. High TSH and low free T4 levels at diagnosis, positive TPO antibodies, TSH doubling upon follow-up, female sex, and thyroiditis are risk factors for progression to overt hypothyroidism. Therefore, follow-up testing and treatment should consider these factors (Weak, Moderate).
- 3. The required dosage of LT4 varies depending on weight and sex, and for elderly patients or those at risk of cardiovascular disease, treatment should begin with a dose of 12.5 to 25 μg/day. Thyroid function tests should be monitored at intervals of 1 to 2 months, and the dosage adjusted with the aim of normalizing serum TSH levels (Strong, Moderate).
- 4. SCH that is not treated with LT4 should be periodically monitored, with the follow-up intervals determined based on the severity (Weak, Moderate).
SUMMARY OF KEY CONTENTS OF THE 2023 KTA GUIDELINES FOR SCH MANAGEMENT
- The upper limit for the TSH reference range is typically established by referring to the manufacturer’s manual for the specific assay kit utilized in the laboratory. It’s important to note that the upper normal limit for TSH can vary based on geographical location, necessitating data analysis through cohort studies to establish reference values. For instance, the NHANES in the United States, which analyzed 17,353 disease-free individuals, reported a TSH upper limit of 4.5 mIU/L [2]. Similarly, the Hanford Thyroid Disease Study, which monitored individuals from 1950 to 2000 who showed no evidence of thyroid disease, had negative anti-thyroid antibodies, were not on thyroid medications, and had normal ultrasound results, reported a TSH upper limit of 4.1 mIU/L [11]. Based on these studies, the 2012 American Thyroid Association Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hypothyroidism recommended that for third-generation TSH assays, each laboratory’s reference range should determine the upper limit of normal. A normal TSH reference range should consider the upper limit of 4.12 mIU/L in iodine-sufficient regions [4]. In Europe, the Busselton Health Survey observed 1,100 individuals from 1981 to 1994 and proposed a normal upper limit of 4.10 mIU/L for all age groups [12]. Based on this study, the European Thyroid Association (ETA) published the 2013 ETA Guideline: Management of Subclinical Hypothyroidism, which set the TSH threshold at 4.0 mIU/L and classified TSH levels between 4.0 and 10.0 mIU/L as mildly increased and levels above 10 as severely increased [5].
- TSH levels can fluctuate depending on iodine intake. Meta-analyses have revealed that TSH levels tend to be higher in iodine-sufficient regions, and as a result, they were generally higher in Asian and North American countries than in most European countries [13]. In Korea, which is characterized by excessive iodine intake due to geographical and cultural factors related to seaweed consumption, the average urinary iodine concentration (UIC) measured in the KNHANES exceeded the World Health Organization’s proposed adequate iodine intake level (adequate level, 100 to 199 μg/L). Specifically, 66.3% of the population had UIC levels above this range, and the average iodine intake level was 299.3 μg/L (interquartile range, 158.8 to 699.8), indicating a high level of iodine intake [14]. Therefore, it can be expected that TSH levels in Korea would be higher than in other countries.
- The Sixth KNHANES, conducted from 2013 to 2015, analyzed the TSH levels of 6,546 individuals without thyroid disorders. The average TSH concentration was found to be 2.16 mIU/L. The reference range, which corresponds to the TSH concentrations of 2.5% to 97.5% of the study population, was between 0.62 and 6.86 mIU/L (Table 2) [7,15]. Another retrospective analysis of health examination data from approximately 20,000 individuals reported an average TSH concentration of 2.38 mIU/L, with a reference range of 0.73 to 7.06 mIU/L (Table 3) [16]. TSH levels within the true reference range should not adversely affect health. Therefore, cohort studies that analyze the health effects of various TSH levels are necessary. These studies can provide insights into the potential health impacts of different TSH levels and assist in establishing reference ranges that accurately reflect health status. A prospective cohort study conducted in Ansung, South Korea, observed 3,021 individuals over a 12-year period. This study reported an increase in the prevalence and mortality of cardiovascular diseases only in cases where TSH levels exceeded 6.57 mIU/L from the 8th year of observation [3]. Interestingly, patients with TSH levels between 4.0 and 6.5 mIU/L did not exhibit any adverse health effects during the 12-year observation period. This suggests that a higher upper normal limit of TSH (above 6.5 mIU/L) would not have detrimental health effects. In light of these findings, the clinical practice guidelines for SCH presented by the KTA in 2023 established the upper normal limit at 6.8 mIU/L.
THE RATIONALE FOR SETTING THE UPPER LIMIT OF NORMAL TSH AT 6.8 mIU/L
- Large-scale studies on the effectiveness of LT4 treatment in elderly SCH patients have recently been published [17-20]. One such study utilized data from four prospective cohorts within the Towards Understanding Longitudinal International older People Studies (TULIPS) consortium to examine the relationship between SCH and functional outcomes in individuals aged 80 years and older [20]. The findings suggested that thyroid dysfunction was not linked to disability in daily living, cognitive function, depressive symptoms, physical function, or mortality in this demographic, indicating limited clinical significance for this age group. The Thyroid Hormone replacement for Untreated Older Adults with Subclinical Hypothyroidism (TRUST) study was designed to explore the potential improvement of clinical symptoms in older adults (≥65 years) with SCH (mean baseline TSH, 6.4 mIU/L) who were administered LT4 (median dose, 50 μg/day) or a placebo [18]. After 1 year of treatment, changes in thyroid-related quality of life, hypothyroid symptoms, tiredness score, hand-grip strength, cognitive function, blood pressure, weight, body-mass index, and waist circumference were observed. However, no significant differences were found when compared to the placebo group. In 2019, another randomized controlled trial (RCT) was conducted with elderly patients (≥80 years), which found that LT4 treatment for SCH had no impact on thyroid-related symptoms, cognitive function, gait speed improvement, or reduction in cardiovascular disease and overall mortality [19]. The Birmingham Elderly Thyroid study, published in 2010, assessed mental states such as learning, memory, attention, and language skills in older adults (≥65 years) with SCH after 12 months of LT4 treatment compared to a placebo group [17]. The results showed no significant improvement. Therefore, LT4 treatment in elderly patients does not appear to be effective in preventing cardiovascular diseases, improving cognitive function, or alleviating thyroid-related symptoms. Particularly in cases of mild SCH with TSH <10 mIU/L, the KTA guidelines strongly recommend against treatment due to clear evidence. For cases with TSH >10 mIU/L, research is limited and sufficient evidence is still lacking. However, unless clear progression to overt hypothyroidism occurs, it is generally recommended to proceed with caution rather than considering LT4 treatment as the first line of therapy.
SCH IN DIFFERENT AGE GROUPS: STUDIES IN ELDERLY PATIENTS
- SCH is associated not only with left ventricular diastolic dysfunction, but also with a reduction in left ventricular systolic function during both rest and exercise, heightened vascular resistance, arterial stiffness, endothelial dysfunction, and a higher risk of atherosclerosis [21-25]. Moreover, numerous intervention studies, inclusive of RCTs, have demonstrated that LT4 treatment for SCH enhances cardiac structure and functional markers [26,27]. This suggests that alterations in myocardial function, metabolic indicators, and vascular function caused by SCH heighten the risk of major cardiovascular diseases, and that these risks can be mitigated through LT4 treatment.
- Recent meta-analyses that included large-scale cohort studies have reported associations between specific cardiovascular conditions and SCH. Although these meta-analyses did not conclusively establish an association between SCH and cardiovascular diseases in general, they did reveal significantly increased risks of congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, and mortality related to coronary artery disease in patients with severe SCH (TSH >10 mIU/L) when compared to the euthyroid population [28-30]. Furthermore, a meta-analysis that incorporated 35 retrospective cohort studies reported a 1.33-fold increased risk of cardiovascular disease in SCH. This trend was more pronounced in the high-risk group for cardiovascular disease, but it did not significantly increase in individuals aged 65 or older [31].
- Large-scale epidemiological studies have identified a linear correlation between TSH levels and dyslipidemia. SCH is a condition that falls between overt hypothyroidism and normal thyroid function, and it is characterized by elevated levels of total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) [32]. The European Prospective Investigation into Cancer (EPIC)-Norfolk study specifically found that only women with SCH showed increases in total cholesterol, LDL-C, and triglycerides, suggesting there may be gender-specific variations in how SCH affects serum lipid profiles [33]. Recent meta-analyses have further corroborated these findings, showing higher levels of total cholesterol, LDL-C, and triglycerides in patients with SCH compared to those with normal thyroid function [34]. However, no significant association was found between SCH and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels.
- In a small-scale RCT, LT4 treatment in patients with SCH reduced total cholesterol and LDL-C levels, particularly in adults with severe SCH (TSH >12 mIU/L) [24,35-37]. Recent meta-analyses and systematic reviews have further substantiated that LT4 therapy significantly decreases total cholesterol by 11.2 mg/dL and LDL-C by 8.5 mg/dL [38,39]. These findings suggest that LT4 treatment could be a viable option for improving dyslipidemia in adults with severe SCH. However, the effectiveness of LT4 treatment for dyslipidemia in patients with mild SCH has produced inconsistent results [39].
- Meanwhile, consistent benefits of LT4 treatment have not been proven in studies targeting patients with SCH and concomitant depression, cognitive impairment, and dementia [18,40]. Therefore, the 2023 KTA guidelines for SCH management do not recommend LT4 treatment for the purpose of improving depression and cognitive function.
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE, HEART FAILURE, AND DYSLIPIDEMIA: IMPACT ON SCH MANAGEMENT
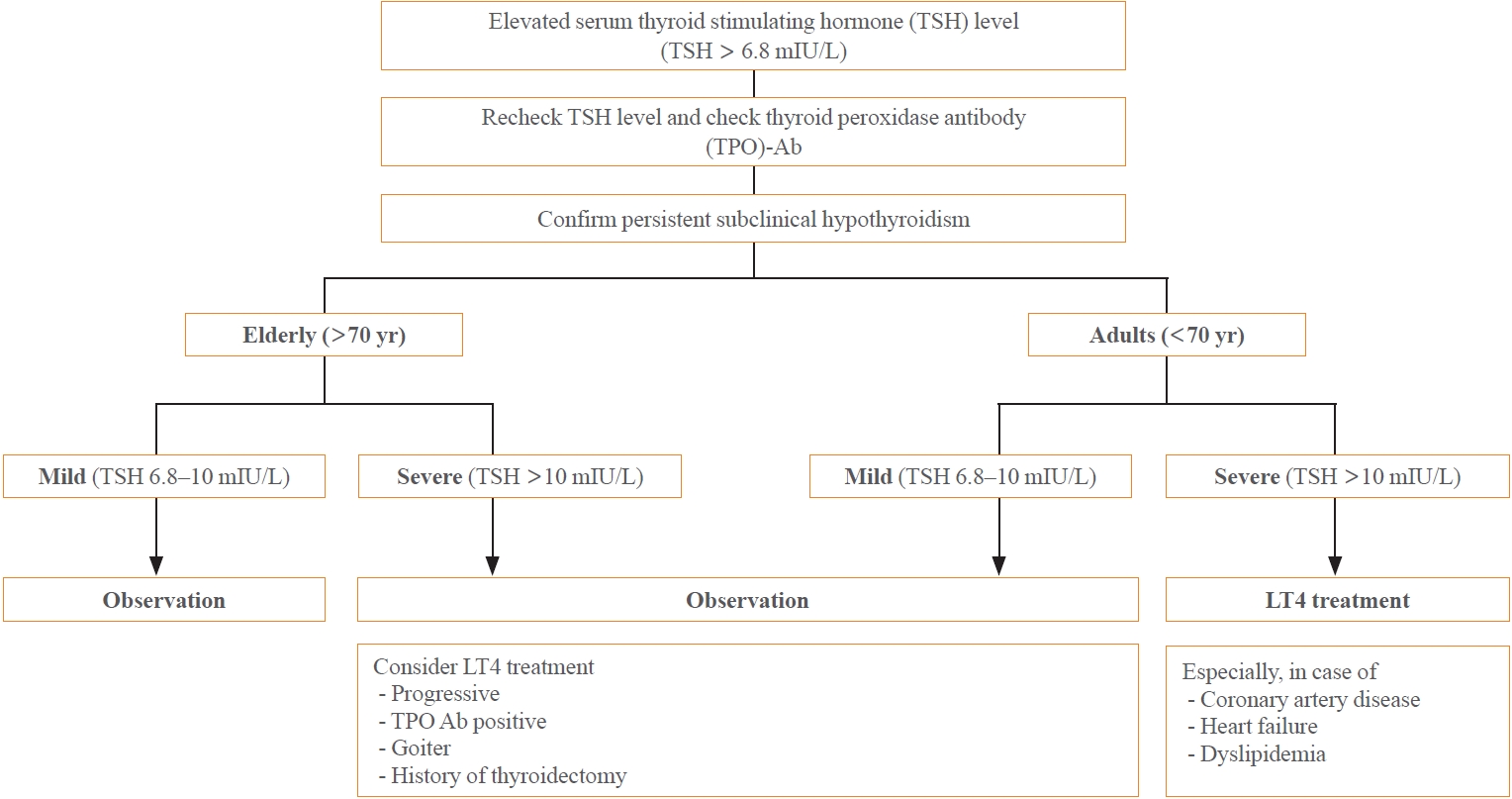
- SCH may occur transiently or due to external factors such as environmental conditions or the use of certain medications. Consequently, it is crucial to conduct repeated thyroid function tests to verify the persistence of SCH. The frequency of these tests may differ based on the patient’s age and the severity of the condition. During follow-up, it is advisable to measure TPO antibodies to evaluate the existence of autoimmune thyroiditis (Fig. 1).
- Once a diagnosis of persistent SCH is confirmed, the treatment strategy should consider the patient’s age and any existing health conditions. For elderly patients (those aged 70 or older), it is generally preferable to monitor the condition without treatment, especially in mild cases (TSH levels between 6.8 and 10 mIU/L). This is because the benefits of LT4 therapy are not substantiated for this group. Conversely, for adults under 70, LT4 treatment is recommended, particularly for severe cases (TSH levels above 10 mIU/L). This approach aims to lower the risk of cardiovascular diseases through proactive medication. Furthermore, LT4 treatment should be contemplated if TSH levels continue to escalate, or if the patient has concurrent chronic thyroiditis, thyroid nodules, or a history of thyroidectomy. A careful evaluation of these factors will assist in determining the most suitable treatment plan for individuals with SCH, taking into account their unique circumstances and potential risks.
- A notable change from previous guidelines is that the presence of hypothyroidism-related symptoms is no longer the sole criterion for initiating LT4 treatment. Symptoms often associated with hypothyroidism, such as fatigue, muscle discomfort, cold intolerance, dry skin, voice changes, and constipation, are largely nonspecific. Despite this, earlier guidelines suggested considering treatment for SCH based on symptom presence [4,5]. It is important to note; however, that the studies used as evidence for these guidelines were primarily small-scale observational studies. There is often uncertainty in classifying the severity of the condition, which limits interpretation. Approximately 30% of individuals with SCH did not exhibit symptoms, while conversely, 20% to 25% of euthyroid individuals reported experiencing related symptoms [32]. Therefore, the relationship between symptoms and biochemical TSH levels remains unclear. Recent RCTs on SCH have prompted a shift in the perceived need for symptom-based treatment. In a United Kingdom-based RCT involving 100 patients with SCH, the group treated with LT4 showed lower levels of fatigue than the placebo group. However, there were no significant differences in most other symptoms or quality of life scores [41]. Meta-analyses have also demonstrated that LT4 treatment does not significantly improve quality of life or symptom resolution [40]. In the TRUST study involving elderly patients with SCH, those who received LT4 treatment did not show significant differences from the placebo group in symptom improvement or fatigue reduction [18].
- Based on these findings, the KTA treatment guidelines do not recommend LT4 treatment solely for the improvement of comorbid symptoms. The KTA guideline also does not advocate for routine LT4 treatment. The link between SCH and conditions such as depression, cognitive dysfunction, and dementia lacks consistent and conclusive evidence, leading to their exclusion from treatment consideration. Treatment is only recommended when there is clear evidence of effectiveness, such as in cases with a high likelihood of progressing to overt hypothyroidism, individuals at high-risk of cardiovascular disease, or for the purpose of improving dyslipidemia. The 2019 publication by Bekkering et al. [8], entitled “Thyroid hormones treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism: a clinical practice guideline,” takes a similar position. The guideline strongly emphasizes that general LT4 treatment in SCH is not beneficial. However, exceptions are made for women preparing for pregnancy, individuals with TSH levels exceeding 20 mIU/L, those experiencing severe symptoms, and individuals under 30 years of age [8].
LT4 TREATMENT: WHEN IS IT NECESSARY?
- Several issues have not been fully addressed in the 2023 KTA guidelines for SCH management. First, the TSH fluctuations did not account for the variations among different kits used in clinical settings. Table 4 summarizes the TSH measurement kits used in each of the studies that provided the reference ranges for TSH [1,3,7,11,12,15,16,42]. The reference range provided by the KNHANES, which serves as the basis for the guidelines, is based on TSH results obtained through a single assay method (electrochemiluminescence immunoassay, Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). However, different hospitals and institutions currently utilize reference ranges provided by various kit manufacturers. This can lead to discrepancies in the interpretation of normal versus abnormal results for the same TSH elevation, causing confusion for patients. Therefore, it is essential to clearly communicate and promote the intentions and recommendations of the guidelines, while also considering potential variations in results when different kits are used in healthcare facilities. Further research in this area is anticipated in the near future.
- Second, while increasing the TSH threshold may reduce overdiagnosis, it could potentially lead to an increase in undiagnosed conditions that necessitate active treatment. This is especially crucial for women planning to become pregnant or for children in their growth phases. It’s important to remember that during the development of these recent KTA guidelines, children, adolescents, pregnant women, and women attempting to conceive were not included in the target group. According to the recently updated “Diagnosis and management of thyroid disease during pregnancy and postpartum” by the KTA, it is recommended that women planning to conceive maintain a TSH level below 4.0 mIU/L, and active treatment for SCH is strongly recommended [43,44].
- Lastly, there are certain ambiguities in some treatment guidelines. Although there is a clear stance against treatment in elderly patients, guidelines are not explicit about when treatment should commence. They suggest that treatment should be considered when there is a progression in TSH elevation or when it nears overt hypothyroidism. However, given the wide range of clinical situations, it is challenging to apply a one-size-fits-all approach. The ETA, the Latin American Thyroid Society, and the Society for Endocrinology, Metabolism and Diabetes of South Africa have also recommended against LT4 treatment for elderly patients with mild SCH, where the health benefits have not been proven [5,45,46]. Yet, the reality is that most clinicians, despite being aware of the updated SCH management guidelines, continue to administer LT4 treatment to a significant number of elderly patients with mild SCH [47]. More efforts are needed to widely disseminate the guidelines and understand the obstacles to adherence in order to encourage appropriate management of SCH in older individuals. Additionally, to establish more comprehensive and clear treatment plans, adequate research is needed on the effects of LT4 treatment in younger age groups, appropriate intervals and durations for follow-up observations, and attempts to discontinue LT4 treatment.
UNMET NEEDS IN THE 2023 KTA GUIDELINES FOR SCH MANAGEMENT
- The 2023 KTA guidelines for SCH management introduce new diagnostic criteria, region-specific TSH reference ranges, and a classification of SCH into mild and severe types based on age. These guidelines also provide comprehensive recommendations for selecting LT4 treatment, considering the severity of SCH, the patient’s age, and specific proven health effects. These guidelines are in line with evidence-based clinical guidelines from other global medical societies, underscoring the importance of personalized management. However, there are still some unresolved issues, such as the variation in TSH reference ranges among different kits, the effect of increased TSH thresholds on missed diagnoses, the adjustment of treatment goals for patients with overt hypothyroidism, and the need for more explicit guidelines on when to initiate treatment, particularly in elderly patients. Bridging this gap between guidelines and clinical practice will result in improved outcomes for patients with this common but often overlooked condition.
CONCLUSIONS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Article information
-
Acknowledgements
- This research was supported by a grant from the Patient Centered Clinical Research Coordinating Center funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number: HC19C0103040020). The funding source had no role in the collection of the data or in the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. The funding sources did not have a role in the design, data collection, analysis, interpretation of data, or writing of the manuscript of this study. We thank all members of the task force team (Yea Eun Kang, Kyeong Jin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Tae-Yong Kim, Chang Ho Ahn, Jee Hee Yoon, Jong Min Lee, Eui Dal Jung, Jae Hoon Chung, Yun Jae Chung, Won Bae Kim, Ka Hee Yi, Ho-Cheol Kang, and Do Joon Park) who participated in the work of the 2023 Korean Thyroid Association (KTA) Management Guidelines for Patients with Subclinical Hypothyroidism and we also thank Young Joo Park and Eun Kyung Lee, the director and secretary of the Practice Guideline Committee of KTA.
| Guidelines | Consideration of LT4 treatment | Observation without LT4 treatment |
|---|---|---|
| ATA (2012) [4] | TSH >10 mIU/L, age <70 years | TSH <10 mIU/L, age >70 years |
| TSH 4–10 mIU/L, age <65 years, symptoms (+) | TSH 4–10 mIU/L, age >65 years | |
| ETA (2013) [5] | TSH >10 mIU/L, age <70 years | TSH <10 mIU/L symptoms (–), age <70 years |
| TSH <10 mIU/L, age <70 years, symptoms (+) | TSH <10 mIU/L, age >70 years | |
| TSH <10 mIU/L, age >70 years, symptoms (+) or high cardiovascular (CV) risk | ||
| Clinical practice guideline (2017) [10] | TSH >10 mIU/L, age <70 years | TSH >10 mIU/L, age >70 years |
| Especially, symptoms (+) or CV risk factors | ||
| 6 months of LT4 treatment in the cases of TSH >4.5 and <7 mIU/L with symptoms or TSH >7 and <10 mIU/L, age <70 years symptoms (+) regardless of age, CV risk factors, TPOAb | ||
| NICE guideline (2018) [9] | TSH >10 mIU/L, age <70 years | TSH >10 mIU/L, age >70 years |
| TSH 4–10 mIU/L, age <65 years, symptoms (+) | TSH 4–10 mIU/L, age >65 years | |
| Clinical practice guideline (2019) [8] | Only women who are or trying to become pregnant or patients with TSH >20 mIU/L | Almost all adults |
| KTA (2023) [6] | TSH >10 mIU/L, age <70 years | TSH 6.8–10 mIU/L, age <70 years |
| All elderly patients | ||
| Study | Age, yr |
All |
Men |
Women |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean |
Percentile |
Mean |
Percentile |
Mean |
Percentile |
||||||||
| 2.5 | Median | 97.5 | 2.5 | Median | 97.5 | 2.5 | Median | 97.5 | |||||
| Kim et al. (2017) [7]a | Total | NA | 0.62 | 2.23 | 6.86 | NA | 0.63 | 2.15 | 6.44 | NA | 0.60 | 2.31 | 7.21 |
| Park et al. (2018) [15]b | 10–19 | 2.33 | 0.63 | 2.45 | 7.37 | 2.44 | 0.75 | 2.47 | 6.92 | 2.31 | 0.57 | 2.39 | 7.47 |
| 20–29 | 2.15 | 0.67 | 2.25 | 6.05 | 2.13 | 0.66 | 2.22 | 6.09 | 2.22 | 0.67 | 2.26 | 6.00 | |
| 30–39 | 2.05 | 0.61 | 2.07 | 6.42 | 2.00 | 0.68 | 2.04 | 6.05 | 2.12 | 0.50 | 2.17 | 6.54 | |
| 40–49 | 2.04 | 0.58 | 2.09 | 6.20 | 1.94 | 0.59 | 1.97 | 5.96 | 2.16 | 0.55 | 2.20 | 7.20 | |
| 50–59 | 2.20 | 0.49 | 2.30 | 8.11 | 2.06 | 0.53 | 2.08 | 7.02 | 2.38 | 0.42 | 2.56 | 9.19 | |
| 60–69 | 2.17 | 0.56 | 2.21 | 7.77 | 2.07 | 0.53 | 2.13 | 7.35 | 2.26 | 0.56 | 2.28 | 7.87 | |
| >70 | 2.32 | 0.42 | 2.28 | 6.68 | 2.18 | 0.28 | 2.04 | 6.53 | 2.48 | 0.44 | 2.42 | 6.80 | |
| Total | 2.16 | 0.59 | 2.23 | 7.03 | 2.09 | 0.62 | 2.14 | 6.57 | 2.24 | 0.56 | 2.31 | 7.43 | |
This table was adapted and modified from Kim et al. (2017) [7] and Park et al. (2018) [15].
NA, not available.
a The reference population was defined as subjects with no prior history of thyroid disease, no history of taking medications that could influence thyroid function, no family history of thyroid disease, negative anti-thyroid peroxidase antibody results, and serum free thyroxine levels in the reference range (0.89 to 1.76 ng/dL);
b The reference population was defined as individuals without known thyroid disease, family history of thyroid dysfunction and positive thyroid peroxidase antibody, and current pregnancy.
| The 6th KNHANES | Data from health check-ups (Asan Medical Center) | Ansung cohorta KLoSHAb | Data from health check-ups (Yeungnam University Medical Center) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Published year | 2017 | 2014 | 2010 | 2008 |
| Number | 6,564 | 5,778 | 3,399a and 940b | 1,591 |
| TSH, mIU/L | 2.23 (IQR, 1.55–3.18) | 2.38 (95% CI, 0.72–7.79) | 2.53±3.31a 3.49±7.12b | 1.37±1.95 |
| Reference rangec | 0.62–6.86 | 0.73–7.06 | NA | 0.38–4.35 for men |
| 0.35–6.42 for women |
Values are expressed as mean±standard deviation.
TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone; KNHANES, Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; KLoSHA, the Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging; IQR, interquartile range; CI, confidence interval; NA, not available.
a Ansung cohort;
b KLoSHA;
c 2.5–97.5 percentile.
| Study | Nation | Study | Method | Kit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biondi et al. (2019) [1] | USA | NHANES III | Chemiluminescence immunometric assay | Nichols Institute Diagnostics, San Juan Capistrano, CA, USA |
| Choi et al. (2010) [3] | South Korea | Ansung cohort and KLoSHA | Immunoradiometric assay | CIS Bio International, IBA, Gif-sur-Yvette, France |
| Kim et al. (2017) [7] | South Korea | The 6th KNHANES | Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay | Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany |
| Hamilton et al. (2008) [11] | USA | The Hanford Thyroid Disease Study | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay | Abbott IMX, Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, IL, USA |
| Bremner et al. (2012) [12] | Western Australia | The Busselton Health Study | Chemiluminescence immunoassay | Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics Products, Deerfield, IL, USA |
| Park et al. (2017) [15] | South Korea | The 6th KNHANES | Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay | Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany |
| Kim et al. (2015) [16] | South Korea | Data from health check-ups of Asan Medical Center | Immunoradiometric assay | TSH-CTK-3 kit, DiaSorin S.p.A., Saluggia, Italy |
| Jang et al. (2008) [42] | South Korea | Data from health check-ups of Yeungnam University Medical Center | Enzyme-amplified chemilumnescence | Immulite 2000, third generation TSH, Los Angeles, CA, USA |
- 1. Biondi B, Cappola AR, Cooper DS. Subclinical hypothyroidism: a review. JAMA 2019;322:153–60.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Hollowell JG, Staehling NW, Flanders WD, Hannon WH, Gunter EW, Spencer CA, et al. Serum TSH, T(4), and thyroid antibodies in the United States population (1988 to 1994): National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002;87:489–99.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Choi HS, Park YJ, Kim HK, Choi SH, Lim S, Park DJ, et al. Prevalence of subclinical hypothyroidism in two population based-cohort: Ansung and KLoSHA cohort in Korea. J Korean Thyroid Assoc 2010;3:32–40.
- 4. Garber JR, Cobin RH, Gharib H, Hennessey JV, Klein I, Mechanick JI, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for hypothyroidism in adults: cosponsored by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American Thyroid Association. Thyroid 2012;22:1200–35.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Pearce SH, Brabant G, Duntas LH, Monzani F, Peeters RP, Razvi S, et al. 2013 ETA guideline: management of subclinical hypothyroidism. Eur Thyroid J 2013;2:215–28.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Chung HK, Ku EJ, Yoo WS, Kang YE, Kim KJ, Kim BH, et al. 2023 Korean Thyroid Association management guidelines for patients with subclinical hypothyroidism. Int J Thyroidol 2023;16:32–50.Article
- 7. Kim WG, Kim WB, Woo G, Kim H, Cho Y, Kim TY, et al. Thyroid stimulating hormone reference range and prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in the Korean population: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013 to 2015. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 2017;32:106–14.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 8. Bekkering GE, Agoritsas T, Lytvyn L, Heen AF, Feller M, Moutzouri E, et al. Thyroid hormones treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism: a clinical practice guideline. BMJ 2019;365:l2006.ArticlePubMed
- 9. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. CKS is only available in the UK [Internet]. London: NICE; 2018 [cited 2023 Jul 20]. Available from: https://cks.nice.org.uk/hypothyroidism#!scenario:1.
- 10. Peeters RP. Subclinical hypothyroidism. N Engl J Med 2017;376:2556–65.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Hamilton TE, Davis S, Onstad L, Kopecky KJ. Thyrotropin levels in a population with no clinical, autoantibody, or ultrasonographic evidence of thyroid disease: implications for the diagnosis of subclinical hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;93:1224–30.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Bremner AP, Feddema P, Leedman PJ, Brown SJ, Beilby JP, Lim EM, et al. Age-related changes in thyroid function: a longitudinal study of a community-based cohort. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012;97:1554–62.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Xing D, Liu D, Li R, Zhou Q, Xu J. Factors influencing the reference interval of thyroid-stimulating hormone in healthy adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2021;95:378–89.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 14. Joung JY, Cho YY, Park SM, Kim TH, Kim NK, Sohn SY, et al. Effect of iodine restriction on thyroid function in subclinical hypothyroid patients in an iodine-replete area: a long period observation in a large-scale cohort. Thyroid 2014;24:1361–8.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Park SY, Kim HI, Oh HK, Kim TH, Jang HW, Chung JH, et al. Age- and gender-specific reference intervals of TSH and free T4 in an iodine-replete area: data from Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey IV (2013-2015). PLoS One 2018;13:e0190738.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Kim M, Kim TY, Kim SH, Lee Y, Park SY, Kim HD, et al. Reference interval for thyrotropin in a ultrasonography screened Korean population. Korean J Intern Med 2015;30:335–44.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 17. Parle J, Roberts L, Wilson S, Pattison H, Roalfe A, Haque MS, et al. A randomized controlled trial of the effect of thyroxine replacement on cognitive function in community-living elderly subjects with subclinical hypothyroidism: the Birmingham Elderly Thyroid study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010;95:3623–32.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Stott DJ, Rodondi N, Kearney PM, Ford I, Westendorp RG, Mooijaart SP, et al. Thyroid hormone therapy for older adults with subclinical hypothyroidism. N Engl J Med 2017;376:2534–44.PubMed
- 19. Mooijaart SP, Du Puy RS, Stott DJ, Kearney PM, Rodondi N, Westendorp RG, et al. Association between levothyroxine treatment and thyroid-related symptoms among adults aged 80 years and older with subclinical hypothyroidism. JAMA 2019;322:1977–86.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. Du Puy RS, Poortvliet RK, Mooijaart SP, den Elzen WP, Jagger C, Pearce SH, et al. Outcomes of thyroid dysfunction in people aged eighty years and older: an individual patient data meta-analysis of four prospective studies (towards understanding longitudinal international older people studies consortium). Thyroid 2021;31:552–62.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Yazici M, Gorgulu S, Sertbas Y, Erbilen E, Albayrak S, Yildiz O, et al. Effects of thyroxin therapy on cardiac function in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism: index of myocardial performance in the evaluation of left ventricular function. Int J Cardiol 2004;95:135–43.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Taddei S, Caraccio N, Virdis A, Dardano A, Versari D, Ghiadoni L, et al. Impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in subclinical hypothyroidism: beneficial effect of levothyroxine therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003;88:3731–7.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 23. Monzani F, Di Bello V, Caraccio N, Bertini A, Giorgi D, Giusti C, et al. Effect of levothyroxine on cardiac function and structure in subclinical hypothyroidism: a double blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001;86:1110–5.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Monzani F, Caraccio N, Kozakowa M, Dardano A, Vittone F, Virdis A, et al. Effect of levothyroxine replacement on lipid profile and intima-media thickness in subclinical hypothyroidism: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004;89:2099–106.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Hak AE, Pols HA, Visser TJ, Drexhage HA, Hofman A, Witteman JC. Subclinical hypothyroidism is an independent risk factor for atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction in elderly women: the Rotterdam Study. Ann Intern Med 2000;132:270–8.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Shakoor SK, Aldibbiat A, Ingoe LE, Campbell SC, Sibal L, Shaw J, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells in subclinical hypothyroidism: the effect of thyroid hormone replacement therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010;95:319–22.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Cabral MD, Teixeira PF, Silva NA, Morais FF, Soares DV, Salles E, et al. Normal flow-mediated vasodilatation of the brachial artery and carotid artery intima-media thickness in subclinical hypothyroidism. Braz J Med Biol Res 2009;42:426–32.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Rodondi N, den Elzen WP, Bauer DC, Cappola AR, Razvi S, Walsh JP, et al. Subclinical hypothyroidism and the risk of coronary heart disease and mortality. JAMA 2010;304:1365–74.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Gencer B, Collet TH, Virgini V, Bauer DC, Gussekloo J, Cappola AR, et al. Subclinical thyroid dysfunction and the risk of heart failure events: an individual participant data analysis from 6 prospective cohorts. Circulation 2012;126:1040–9.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Chaker L, Baumgartner C, den Elzen WP, Ikram MA, Blum MR, Collet TH, et al. Subclinical hypothyroidism and the risk of stroke events and fatal stroke: an individual participant data analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015;100:2181–91.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 31. Moon S, Kim MJ, Yu JM, Yoo HJ, Park YJ. Subclinical hypothyroidism and the risk of cardiovascular disease and allcause mortality: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Thyroid 2018;28:1101–10.ArticlePubMed
- 32. Canaris GJ, Manowitz NR, Mayor G, Ridgway EC. The Colorado thyroid disease prevalence study. Arch Intern Med 2000;160:526–34.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Boekholdt SM, Titan SM, Wiersinga WM, Chatterjee K, Basart DC, Luben R, et al. Initial thyroid status and cardiovascular risk factors: the EPIC-Norfolk prospective population study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2010;72:404–10.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Liu XL, He S, Zhang SF, Wang J, Sun XF, Gong CM, et al. Alteration of lipid profile in subclinical hypothyroidism: a meta-analysis. Med Sci Monit 2014;20:1432–41.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Caraccio N, Ferrannini E, Monzani F. Lipoprotein profile in subclinical hypothyroidism: response to levothyroxine replacement, a randomized placebo-controlled study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002;87:1533–8.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Meier C, Staub JJ, Roth CB, Guglielmetti M, Kunz M, Miserez AR, et al. TSH-controlled L-thyroxine therapy reduces cholesterol levels and clinical symptoms in subclinical hypothyroidism: a double blind, placebo-controlled trial (Basel Thyroid Study). J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001;86:4860–6.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Teixeira PF, Reuters VS, Ferreira MM, Almeida CP, Reis FA, Melo BA, et al. Treatment of subclinical hypothyroidism reduces atherogenic lipid levels in a placebo-controlled double-blind clinical trial. Horm Metab Res 2008;40:50–5.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Abreu IM, Lau E, de Sousa Pinto B, Carvalho D. Subclinical hypothyroidism: to treat or not to treat, that is the question!: a systematic review with meta-analysis on lipid profile. Endocr Connect 2017;6:188–99.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 39. Li X, Wang Y, Guan Q, Zhao J, Gao L. The lipid-lowering effect of levothyroxine in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2017;87:1–9.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 40. Feller M, Snel M, Moutzouri E, Bauer DC, de Montmollin M, Aujesky D, et al. Association of thyroid hormone therapy with quality of life and thyroid-related symptoms in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2018;320:1349–59.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 41. Razvi S, Ingoe L, Keeka G, Oates C, McMillan C, Weaver JU. The beneficial effect of L-thyroxine on cardiovascular risk factors, endothelial function, and quality of life in subclinical hypothyroidism: randomized, crossover trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007;92:1715–23.PubMed
- 42. Jang YY, Kim CY, Hwang TY, Kim KD, Lee CH. Reference interval of serum thyroid hormones in healthy Korean adults. J Prev Med Public Health 2008;41:128–34.ArticlePubMed
- 43. Ahn HY, Yi KH. Diagnosis and management of thyroid disease during pregnancy and postpartum: 2023 revised Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 2023;38:289–94.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 44. Yi KH, Ahn HY, Kim JH, Park SY, Yoo WS, Jung KY, et al. 2023 Revised Korean Thyroid Association guidelines for the diagnosis and management of thyroid disease during pregnancy and postpartum. Int J Thyroidol 2023;16:51–88.Article
- 45. Brenta G, Vaisman M, Sgarbi JA, Bergoglio LM, Andrada NC, Bravo PP, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of hypothyroidism. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 2013;57:265–91.ArticlePubMed
- 46. Dave JA, Klisiewicz A, Bayat Z, Mohamed NA, Stevens Z, Mollentze WF, et al. SEMDSA/ACE-SA guideline for the management of hypothyroidism in adults. J Endocrinol Metab Diabetes S Afr 2015;20:18–26.ArticlePDF
- 47. Razvi S, Arnott B, Teare D, Hiu S, O’Brien N, Pearce SH. Multinational survey of treatment practices of clinicians managing subclinical hypothyroidism in older people in 2019. Eur Thyroid J 2021;10:330–8.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Clinical Implications of Different Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Reference Intervals between TSH Kits for the Management of Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Won Sang Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 188. CrossRef

 KES
KES
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite


