Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Based Therapies: A New Horizon in Obesity Management
- Jang Won Son, Soo Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(2):206-221. Published online April 16, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2024.1940
- 1,318 View
- 101 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
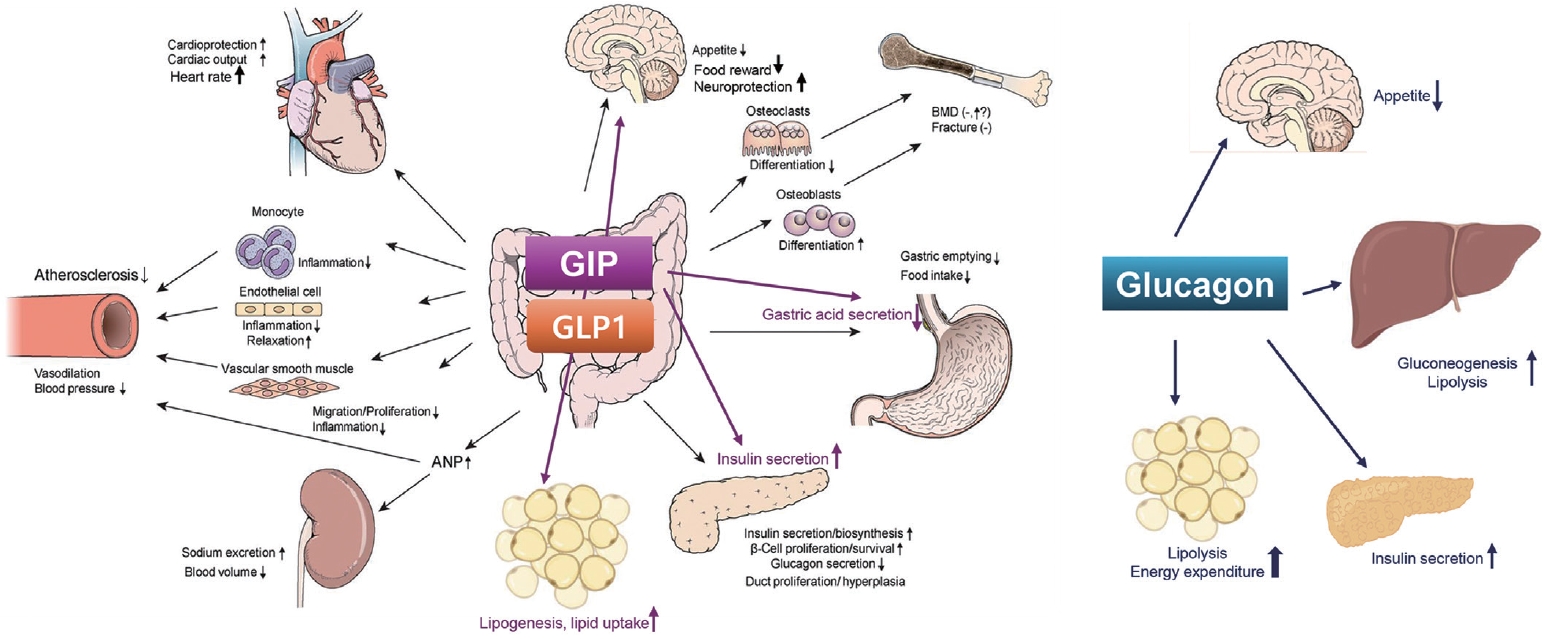
ePub - Obesity is a significant risk factor for health issues like type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. It often proves resistant to traditional lifestyle interventions, prompting a need for more precise therapeutic strategies. This has led to a focus on signaling pathways and neuroendocrine mechanisms to develop targeted obesity treatments. Recent developments in obesity management have been revolutionized by introducing novel glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) based drugs, such as semaglutide and tirzepatide. These drugs are part of an emerging class of nutrient-stimulated hormone-based therapeutics, acting as incretin mimetics to target G-protein–coupled receptors like GLP-1, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), and glucagon. These receptors are vital in regulating body fat and energy balance. The development of multiagonists, including GLP-1–glucagon and GIP–GLP-1–glucagon receptor agonists, especially with the potential for glucagon receptor activation, marks a significant advancement in the field. This review covers the development and clinical efficacy of various GLP-1-based therapeutics, exploring the challenges and future directions in obesity management.

Original Article
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Docosahexanoic Acid Attenuates Palmitate-Induced Apoptosis by Autophagy Upregulation via GPR120/mTOR Axis in Insulin-Secreting Cells
- Seok-Woo Hong, Jinmi Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(2):353-363. Published online January 23, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1809
- 1,511 View
- 43 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) reportedly have protective effects on pancreatic β-cells; however, the underlying mechanisms are unknown.
Methods
To investigate the cellular mechanism of PUFA-induced cell protection, mouse insulinoma 6 (MIN6) cells were cultured with palmitic acid (PA) and/or docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and alterations in cellular signaling and apoptosis were examined.
Results
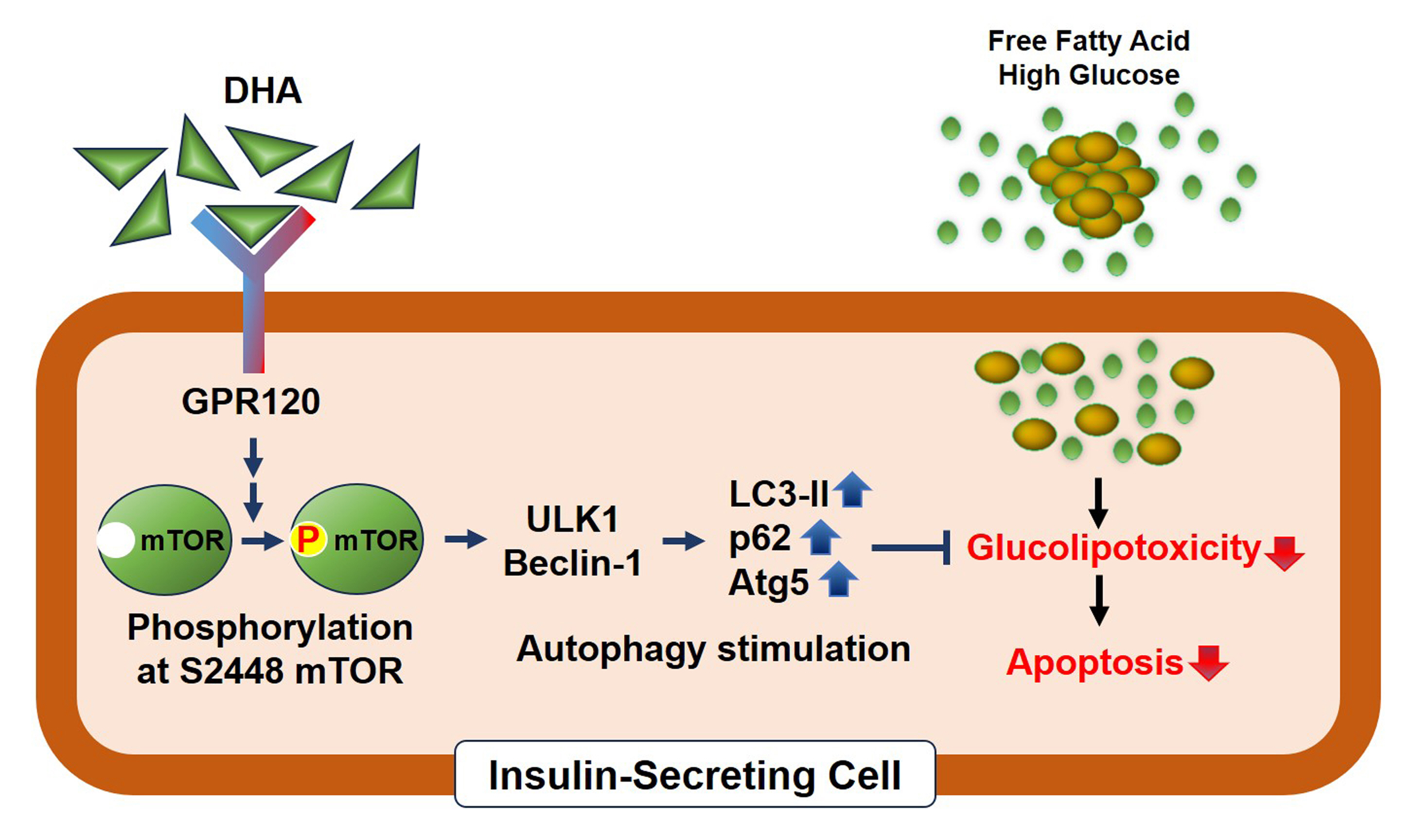
DHA treatment remarkably repressed caspase-3 cleavage and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated UTP nick end labeling (TUNEL)-positive red dot signals in PA-treated MIN6 cells, with upregulation of autophagy, an increase in microtubule- associated protein 1-light chain 3 (LC3)-II, autophagy-related 5 (Atg5), and decreased p62. Upstream factors involved in autophagy regulation (Beclin-1, unc51 like autophagy activating kinase 1 [ULK1], phosphorylated mammalian target of rapamycin [mTOR], and protein kinase B) were also altered by DHA treatment. DHA specifically induced phosphorylation on S2448 in mTOR; however, phosphorylation on S2481 decreased. The role of G protein-coupled receptor 120 (GPR120) in the effect of DHA was demonstrated using a GPR120 agonist and antagonist. Additional treatment with AH7614, a GPR120 antagonist, significantly attenuated DHA-induced autophagy and protection. Taken together, DHA-induced autophagy activation with protection against PA-induced apoptosis mediated by the GPR120/mTOR axis.
Conclusion
These findings indicate that DHA has therapeutic effects on PA-induced pancreatic β-cells, and that the cellular mechanism of β-cell protection by DHA may be a new research target with potential pharmacotherapeutic implications in β-cell protection.

Review Articles
- Calcium & bone metabolism
- Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Regulation of Osteoclastogenesis and Osteoblastogenesis
- Brendan F. Boyce, Jinbo Li, Zhenqiang Yao, Lianping Xing
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):504-521. Published online September 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.501
- 2,211 View
- 101 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
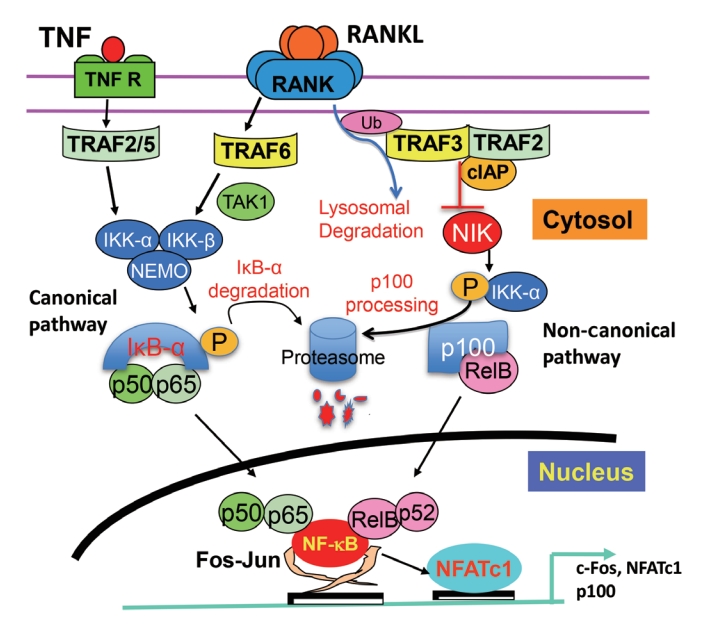
ePub - Maintenance of skeletal integrity requires the coordinated activity of multinucleated bone-resorbing osteoclasts and bone-forming osteoblasts. Osteoclasts form resorption lacunae on bone surfaces in response to cytokines by fusion of precursor cells. Osteoblasts are derived from mesenchymal precursors and lay down new bone in resorption lacunae during bone remodeling. Nuclear factorkappa B (NF-κB) signaling regulates osteoclast and osteoblast formation and is activated in osteoclast precursors in response to the essential osteoclastogenic cytokine, receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL), which can also control osteoblast formation through RANK-RANKL reverse signaling in osteoblast precursors. RANKL and some pro-inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF), activate NF-κB signaling to positively regulate osteoclast formation and functions. However, these cytokines also limit osteoclast and osteoblast formation through NF-κB signaling molecules, including TNF receptor-associated factors (TRAFs). TRAF6 mediates RANKL-induced osteoclast formation through canonical NF-κB signaling. In contrast, TRAF3 limits RANKL- and TNF-induced osteoclast formation, and it restricts transforming growth factor β (TGFβ)-induced inhibition of osteoblast formation in young and adult mice. During aging, neutrophils expressing TGFβ and C-C chemokine receptor type 5 (CCR5) increase in bone marrow of mice in response to increased NF-κB-induced CC motif chemokine ligand 5 (CCL5) expression by mesenchymal progenitor cells and injection of these neutrophils into young mice decreased bone mass. TGFβ causes degradation of TRAF3, resulting in decreased glycogen synthase kinase-3β/β-catenin-mediated osteoblast formation and age-related osteoporosis in mice. The CCR5 inhibitor, maraviroc, prevented accumulation of TGFβ+/CCR5+ neutrophils in bone marrow and increased bone mass by inhibiting bone resorption and increasing bone formation in aged mice. This paper updates current understanding of how NF-κB signaling is involved in the positive and negative regulation of cytokine-mediated osteoclast and osteoblast formation and activation with a focus on the role of TRAF3 signaling, which can be targeted therapeutically to enhance bone mass.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Rosavin in the Pathophysiology of Bone Metabolism
Piotr Wojdasiewicz, Paweł Turczyn, Anna Lach-Gruba, Łukasz A. Poniatowski, Daryush Purrahman, Mohammad-Reza Mahmoudian-Sani, Dariusz Szukiewicz
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(4): 2117. CrossRef - The role of monocyte/macrophage chemokines in pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: A review
Hao Luo, Linfeng Li, Song Han, Tao Liu
International Journal of Immunogenetics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of low-level laser therapy on osteoclast differentiation: Clinical implications for tooth movement and bone density
Chun-Yi Huang, Huynh Hoai Thuong Le, Hsiao-Chi Tsai, Chih-Hsin Tang, Jian-Hong Yu
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Genetic Deficiency of the Long Pentraxin 3 Affects Osteogenesis and Osteoclastogenesis in Homeostatic and Inflammatory Conditions
Valentina Granata, Dario Strina, Maria Lucia Schiavone, Barbara Bottazzi, Alberto Mantovani, Antonio Inforzato, Cristina Sobacchi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(23): 16648. CrossRef
- The Role of Rosavin in the Pathophysiology of Bone Metabolism

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Renal Protection of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist, Finerenone, in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Dong-Lim Kim, Seung-Eun Lee, Nan Hee Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):43-55. Published online February 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1629
- 5,721 View
- 774 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
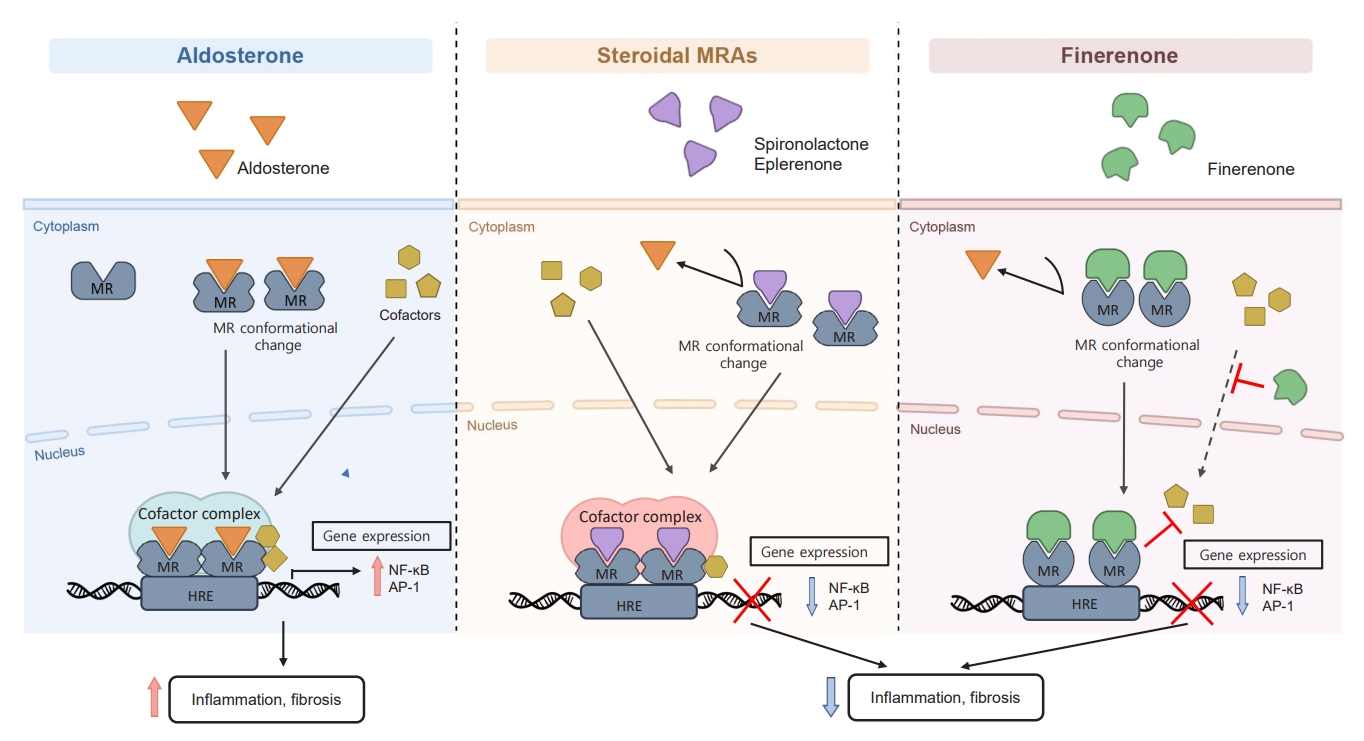
ePub - Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the most common cause of end-stage renal disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). CKD increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases; therefore, its prevention and treatment are important. The prevention of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) can be achieved through intensive glycemic control and blood pressure management. Additionally, DKD treatment aims to reduce albuminuria and improve kidney function. In patients with T2DM, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors, sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists can delay the progression of DKD. Hence, there is a need for novel treatments that can effectively suppress DKD progression. Finerenone is a first-in-class nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist with clinically proven efficacy in improving albuminuria, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and risk of cardiovascular events in early and advanced DKD. Therefore, finerenone is a promising treatment option to delay DKD progression. This article reviews the mechanism of renal effects and major clinical outcomes of finerenone in DKD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Neue Antihypertensiva im Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosteron-System
Markus van der Giet
CardioVasc.2024; 24(1): 33. CrossRef -
Chicoric acid
advanced PAQR3 ubiquitination to ameliorate ferroptosis in diabetes nephropathy through the relieving of the interaction between PAQR3 and P110α pathway
Weiwei Zhang, Yong Liu, Jiajun Zhou, Teng Qiu, Haitang Xie, Zhichen Pu
Clinical and Experimental Hypertension.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endothelial CXCR2 deficiency attenuates renal inflammation and glycocalyx shedding through NF-κB signaling in diabetic kidney disease
Siyuan Cui, Xin Chen, Jiayu Li, Wei Wang, Deqi Meng, Shenglong Zhu, Shiwei Shen
Cell Communication and Signaling.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular Targets of Novel Therapeutics for Diabetic Kidney Disease: A New Era of Nephroprotection
Alessio Mazzieri, Francesca Porcellati, Francesca Timio, Gianpaolo Reboldi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3969. CrossRef - Epigenetic modification in diabetic kidney disease
Zhe Liu, Jiahui Liu, Wanning Wang, Xingna An, Ling Luo, Dehai Yu, Weixia Sun
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel Approaches in Chronic Renal Failure without Renal Replacement Therapy: A Review
Sandra Martínez-Hernández, Martín Muñoz-Ortega, Manuel Ávila-Blanco, Mariana Medina-Pizaño, Javier Ventura-Juárez
Biomedicines.2023; 11(10): 2828. CrossRef - Finerenone and other future therapeutic options for Alport syndrome
Helen Pearce, Holly Mabillard
Journal of Rare Diseases.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Neue Antihypertensiva im Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosteron-System

Original Articles
- Thyroid
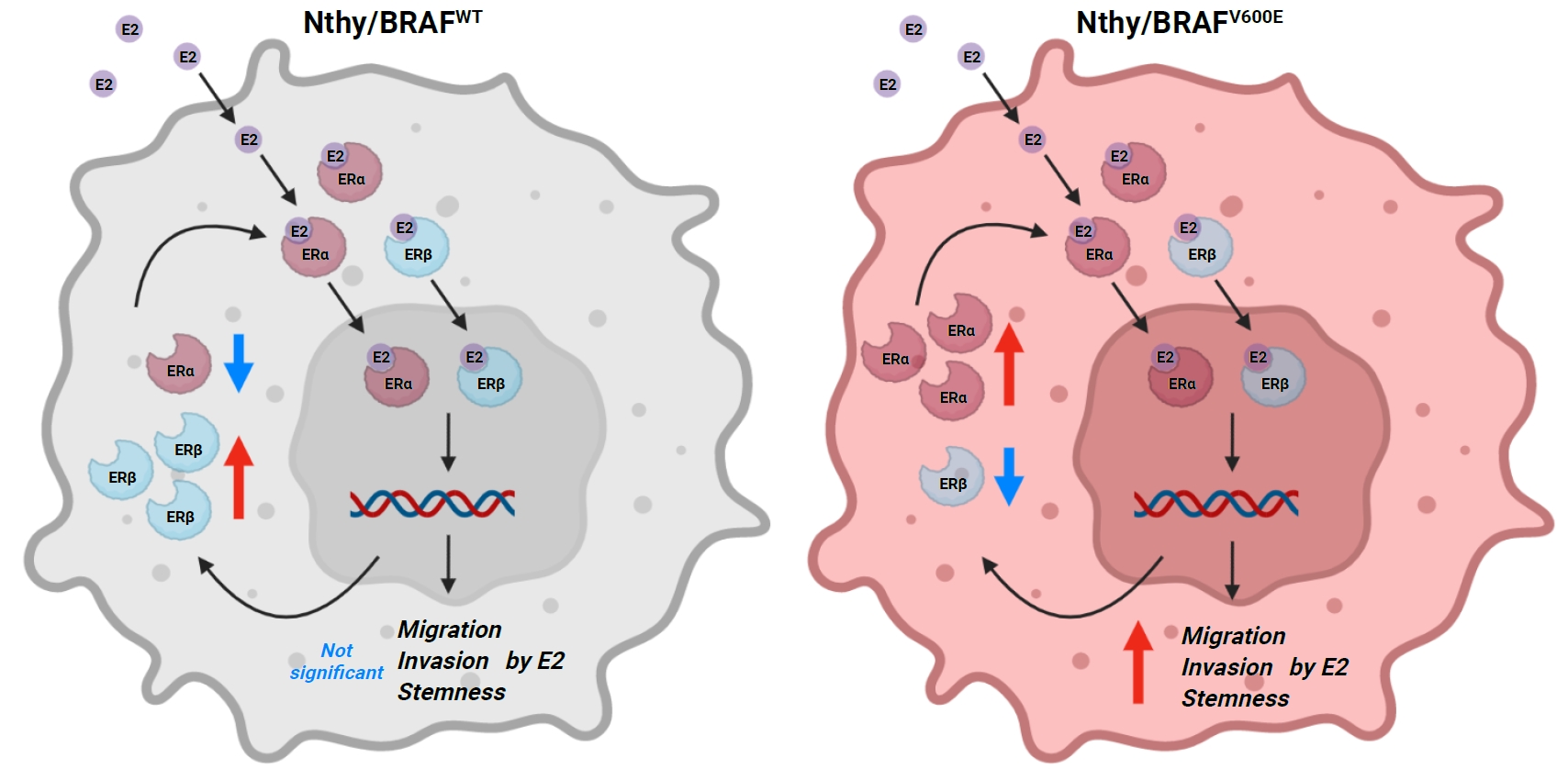
- BRAFV600E Mutation Enhances Estrogen-Induced Metastatic Potential of Thyroid Cancer by Regulating the Expression of Estrogen Receptors
- Minjun Kim, Su-jin Kim, Seong Yun Ha, Zhen Xu, Youngjin Han, Hyeon-Gun Jee, Sun Wook Cho, Young Joo Park, Kyu Eun Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):879-890. Published online December 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1563
- 2,846 View
- 216 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Cross-talk between mitogen-activated protein kinase and estrogen has been reported; however, the role of BRAFV600E in the estrogen responsiveness of thyroid cancer is unknown. We elucidated the effect of BRAFV600E on the estrogen-induced increase in metastatic potential in thyroid cancer.
Methods
Using a pair of cell lines, human thyroid cell lines which harbor wild type BRAF gene (Nthy/WT) and Nthy/BRAFV600E (Nthy/V600E), the expression of estrogen receptors (ERs) and estrogen-induced metastatic phenotypes were evaluated. Susceptibility to ERα- and ERβ-selective agents was evaluated to confirm differential ER expression. ESR expression was analyzed according to BRAFV600E status and age (≤50 years vs. >50 years) using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data.
Results
Estradiol increased the ERα/ERβ expression ratio in Nthy/V600E, whereas the decreased ERα/ERβ expression ratio was found in Nthy/WT. BRAFV600E-mutated cell lines showed a higher E2-induced increase in metastatic potential, including migration, invasion, and anchorage-independent growth compared with Nthy/WT. An ERα antagonist significantly inhibited migration in Nthy/V600E cells, whereas an ERβ agonist was more effective in Nthy/WT. In the BRAFV600E group, ESR1/ESR2 ratio was significantly higher in younger age group (≤50 years) compared with older age group (>50 years) by TCGA data analysis.
Conclusion
Our data show that BRAFV600E mutation plays a crucial role in the estrogen responsiveness of thyroid cancer by regulating ER expression. Therefore, BRAFV600E might be used as a biomarker when deciding future hormone therapies based on estrogen signaling in thyroid cancer patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The importance of protein domain mutations in cancer therapy
Kiran Kumar Chitluri, Isaac Arnold Emerson
Heliyon.2024; 10(6): e27655. CrossRef - Three cases of thyroid cancer in transgender female veterans receiving gender-affirming estrogen treatment
John D. Christensen, Hiba T. Basheer
Endocrine and Metabolic Science.2024; 15: 100177. CrossRef - Thyroid Cancer Prevalence, Risk Exposure, and Clinical Features Among Transgender Female Veterans
John David Christensen, Hiba T Basheer, Jose Joaquin Lado Abeal
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of DNA Promoter Methylation and BRAF Mutation in Thyroid Cancer
Farzana Jasmine, Briseis Aschebrook-Kilfoy, Mohammad M. Rahman, Garrett Zaagman, Raymon H. Grogan, Mohammed Kamal, Habibul Ahsan, Muhammad G. Kibriya
Current Oncology.2023; 30(3): 2978. CrossRef - Editorial: Recent advances in papillary thyroid carcinoma: Progression, treatment and survival predictors
Erivelto Martinho Volpi, Margarita Carmen Ramirez-Ortega, Jose Federico Carrillo
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The importance of protein domain mutations in cancer therapy

- Miscellaneous
- DN200434 Inhibits Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Prevents Neointima Formation in Mice after Carotid Artery Ligation
- Sudeep Kumar, Jonghwa Jin, Hyeon Young Park, Mi-Jin Kim, Jungwook Chin, Sungwoo Lee, Jina Kim, Jung-Guk Kim, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Keun-Gyu Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(5):800-809. Published online September 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1462

- 3,077 View
- 201 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Excessive proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), which contributes to the development of occlusive vascular diseases, requires elevated mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation to meet the increased requirements for energy and anabolic precursors. Therefore, therapeutic strategies based on blockade of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation are considered promising for treatment of occlusive vascular diseases. Here, we investigated whether DN200434, an orally available estrogen receptor-related gamma inverse agonist, inhibits proliferation and migration of VSMCs and neointima formation by suppressing mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation.
Methods
VSMCs were isolated from the thoracic aortas of 4-week-old Sprague-Dawley rats. Oxidative phosphorylation and the cell cycle were analyzed in fetal bovine serum (FBS)- or platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-stimulated VSMCs using a Seahorse XF-24 analyzer and flow cytometry, respectively. A model of neointimal hyperplasia was generated by ligating the left common carotid artery in male C57BL/6J mice.
Results
DN200434 inhibited mitochondrial respiration and mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 activity and consequently suppressed FBS- or PDGF-stimulated proliferation and migration of VSMCs and cell cycle progression. Furthermore, DN200434 reduced carotid artery ligation-induced neointima formation in mice.
Conclusion
Our data suggest that DN200434 is a therapeutic option to prevent the progression of atherosclerosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Jatrorrhizine inhibits Piezo1 activation and reduces vascular inflammation in endothelial cells
Tianying Hong, Xianmei Pan, Han Xu, Zhijuan Zheng, Lizhen Wen, Jing Li, Mingfeng Xia
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 163: 114755. CrossRef
- Jatrorrhizine inhibits Piezo1 activation and reduces vascular inflammation in endothelial cells

Brief Report
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
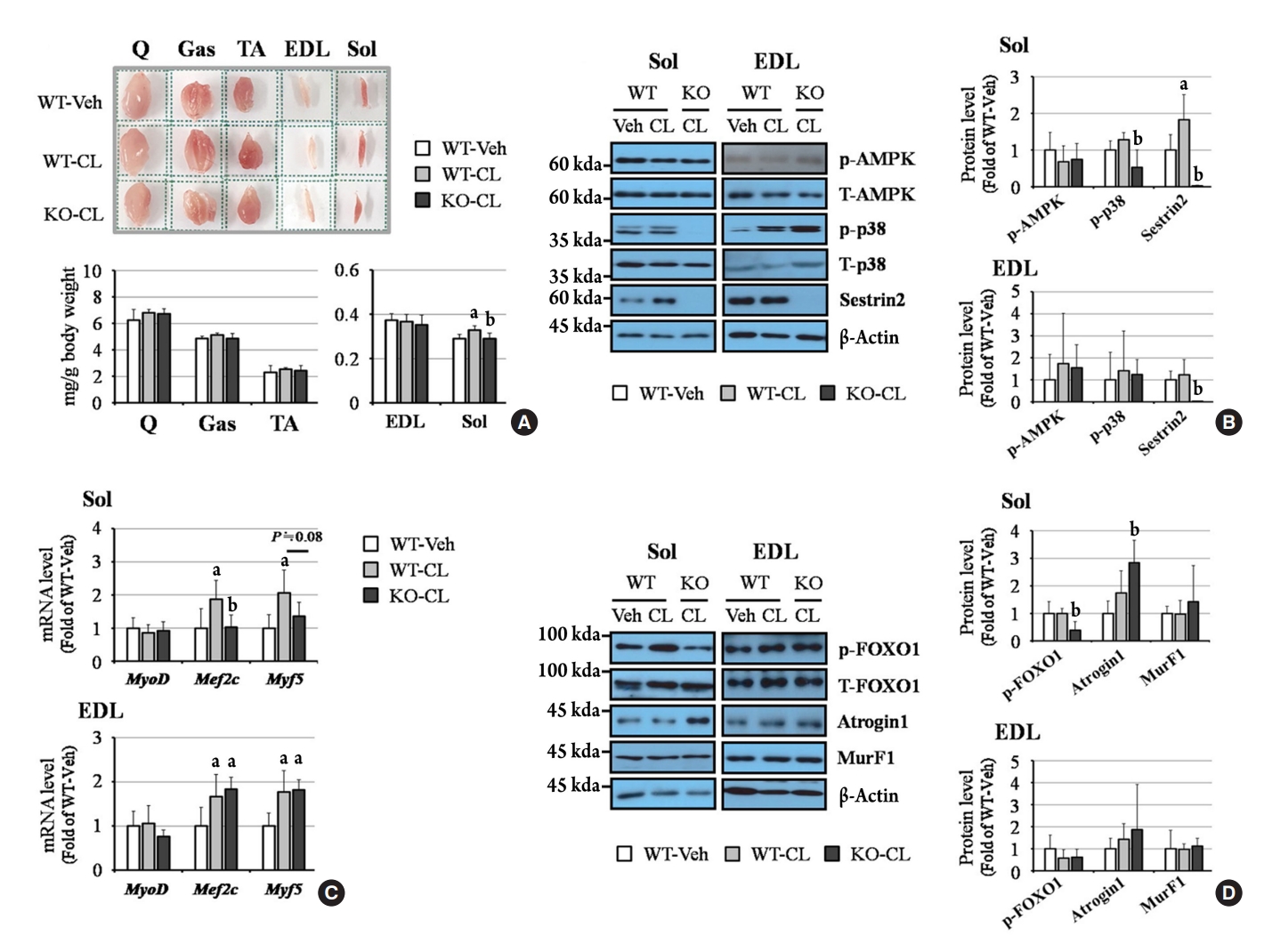
- Sestrin2 Regulates Beneficial β3-Adrenergic Receptor-Mediated Effects Observed in Inguinal White Adipose Tissue and Soleus Muscle
- Min Jeong Park, Joo Won Kim, Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hwan-Jin Hwang, Hye Jin Yoo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):552-557. Published online June 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1421
- 2,667 View
- 108 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Sestrin2, a well-known adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) regulator, plays a protective role against metabolic stress. The β3-adrenergic receptor (β3AR) induces fat browning and inhibits muscle atrophy in an AMPK-dependent manner. However, no prior research has examined the relationship of sestrin2 with β3AR in body composition changes. In this study, CL 316,243 (CL), a β3AR agonist, was administered to wild-type and sestrin2-knockout (KO) mice for 2 weeks, and fat and muscle tissues were harvested. CL induced AMPK phosphorylation, expression of brown-fat markers, and mitochondrial biogenesis, which resulted in the reduction of lipid droplet size in inguinal white adipose tissue (iWAT). These effects were not observed in sestrin2-KO mice. In CL-treated soleus muscle, sestrin2-KO was related to decreased myogenic gene expression and increased levels of muscle atrophy-related molecules. Our results suggest that sestrin2 is associated with beneficial β3AR-mediated changes in body composition, especially in iWAT and in the soleus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sestrin2 levels in patients with anxiety and depression myocardial infarction was up-regulated and suppressed inflammation and ferroptosis by LKB1-mediated AMPK activation
Yufeng Qian, Lian Chen, Beibei Gao, Xianhua Ye
Clinical and Experimental Hypertension.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sestrin2 in diabetes and diabetic complications
Xiaodan Zhang, Zirui Luo, Jiahong Li, Yaxuan Lin, Yu Li, Wangen Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Sestrin2 levels in patients with anxiety and depression myocardial infarction was up-regulated and suppressed inflammation and ferroptosis by LKB1-mediated AMPK activation

Original Articles
- Thyroid
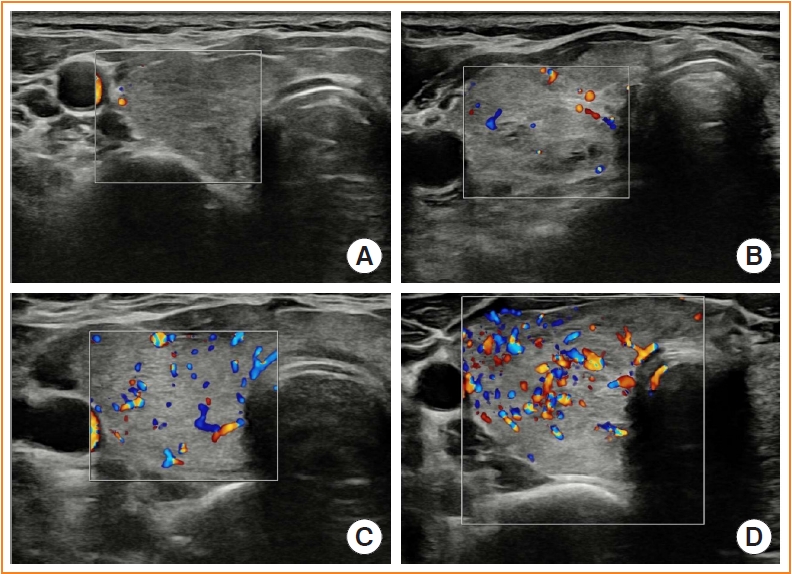
- Usefulness of Real-Time Quantitative Microvascular Ultrasonography for Differentiation of Graves’ Disease from Destructive Thyroiditis in Thyrotoxic Patients
- Han-Sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Chai-Ho Jeong, Jeonghoon Ha, Moo Il Kang, Dong-Jun Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):323-332. Published online April 13, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1413
- 3,723 View
- 144 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Microvascular ultrasonography (MVUS) is a third-generation Doppler technique that was developed to increase sensitivity compared to conventional Doppler. The purpose of this study was to compare MVUS with conventional color Doppler (CD) and power Doppler (PD) imaging to distinguish Graves’ disease (GD) from destructive thyroiditis (DT).
Methods
This prospective study included 101 subjects (46 GDs, 47 DTs, and eight normal controls) from October 2020 to November 2021. All ultrasonography examinations were performed using microvascular flow technology (MV-Flow). The CD, PD, and MVUS images were semi-quantitatively graded according to blood flow patterns. On the MVUS images, vascularity indices (VIs), which were the ratio (%) of color pixels in the total grayscale pixels in a defined region of interest, were obtained automatically. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was performed to verify the diagnostic performance of MVUS. The interclass correlation coefficient and Cohen’s kappa analysis were used to analyze the reliability of MVUS (ClinicalTrials.gov:NCT04879173).
Results
The area under the curve (AUC) for CD, PD, MVUS, and MVUS-VI was 0.822, 0.844, 0.808, and 0.852 respectively. The optimal cutoff value of the MVUS-VI was 24.95% for distinguishing GD and DT with 87% sensitivity and 80.9% specificity. We found a significant positive correlation of MVUS-VI with thyrotropin receptor antibody (r=0.554) and with thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin bioassay (r=0.841). MVUS showed high intra- and inter-observer reliability from various statistical method.
Conclusion
In a real time and quantitative manner, MVUS-VI could be helpful to differentiate GD from thyroiditis in thyrotoxic patients, with less inter-observer variability. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of autoimmune thyroid disease with type 1 diabetes mellitus and its ultrasonic diagnosis and management
Jin Wang, Ke Wan, Xin Chang, Rui-Feng Mao
World Journal of Diabetes.2024; 15(3): 348. CrossRef - The Early Changes in Thyroid-Stimulating Immunoglobulin Bioassay over Anti-Thyroid Drug Treatment Could Predict Prognosis of Graves’ Disease
Jin Yu, Han-Sang Baek, Chaiho Jeong, Kwanhoon Jo, Jeongmin Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Min Hee Kim, Jungmin Lee, Dong-Jun Lim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(3): 338. CrossRef - Duplex Hemodynamic Parameters of Both Superior and Inferior Thyroid Arteries in Evaluation of Thyroid Hyperfunction Disorders
Maha Assem Hussein, Alaa Abdel Hamid, Rasha M Abdel Samie, Elshaymaa Hussein, Shereen Sadik Elsawy
International Journal of General Medicine.2022; Volume 15: 7131. CrossRef - Case 5: A 41-Year-Old Woman With Palpitation
Jiwon Yang, Kabsoo Shin, Jeongmin Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Dong-Jun Lim, Han-Sang Baek
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Microvascular assessment of fascio-cutaneous flaps by ultrasound: A large animal study
Guillaume Goudot, Yanis Berkane, Eloi de Clermont-Tonnerre, Claire Guinier, Irina Filz von Reiterdank, Antonia van Kampen, Korkut Uygun, Curtis L. Cetrulo, Basak E. Uygun, Anahita Dua, Alexandre G. Lellouch
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association of autoimmune thyroid disease with type 1 diabetes mellitus and its ultrasonic diagnosis and management

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
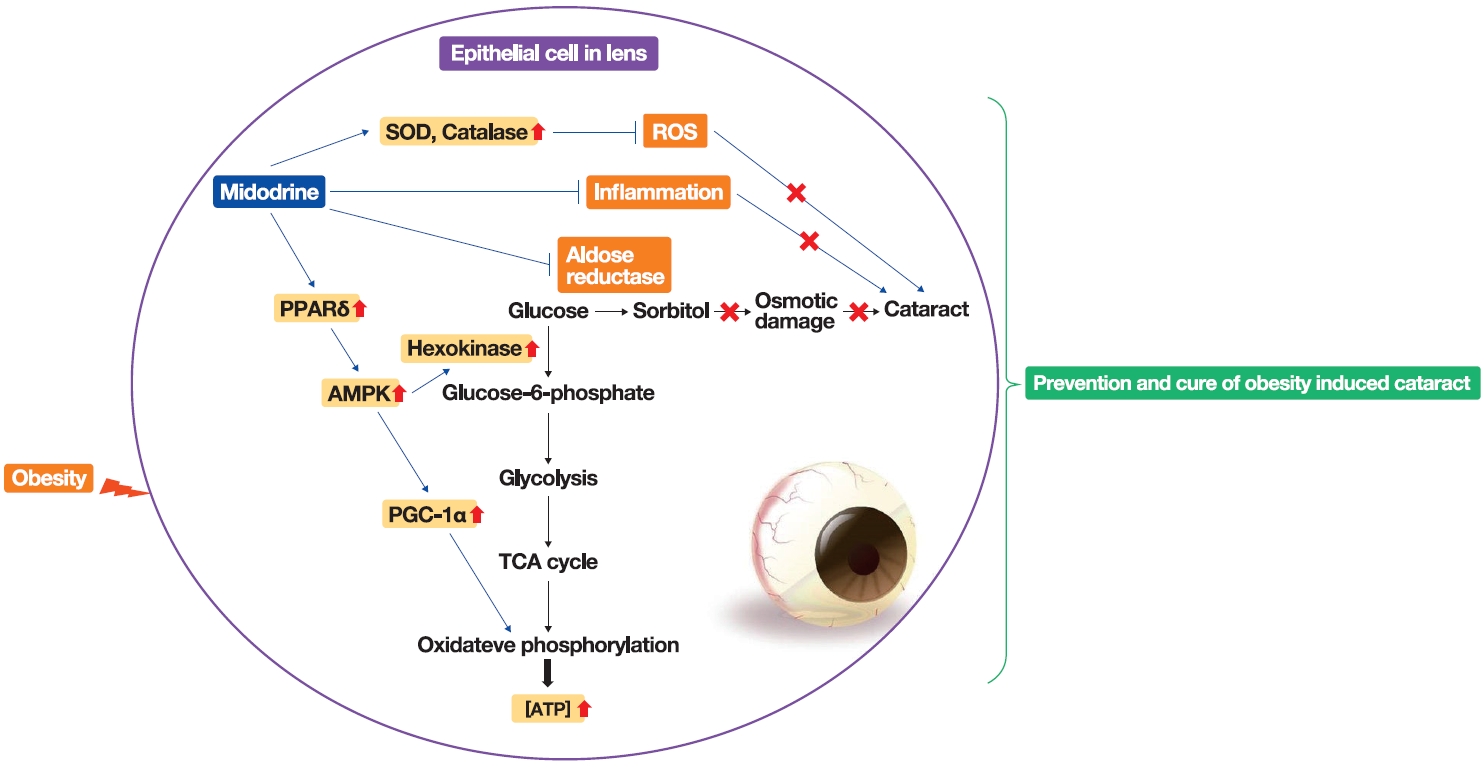
- Stimulation of Alpha-1-Adrenergic Receptor Ameliorates Obesity-Induced Cataracts by Activating Glycolysis and Inhibiting Cataract-Inducing Factors
- Yong-Jik Lee, Yoo-Na Jang, Hyun-Min Kim, Yoon-Mi Han, Hong Seog Seo, Youngsub Eom, Jong-suk Song, Ji Hoon Jeong, Tae Woo Jung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):221-232. Published online March 23, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1237
- 3,663 View
- 137 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Obesity, the prevalence of which is increasing due to the lack of exercise and increased consumption of Westernized diets, induces various complications, including ophthalmic diseases. For example, obesity is involved in the onset of cataracts.
Methods
To clarify the effects and mechanisms of midodrine, an α1-adrenergic receptor agonist, in cataracts induced by obesity, we conducted various analytic experiments in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats, a rat model of obesity.
Results
Midodrine prevented cataract occurrence and improved lens clearance in OLETF rats. In the lenses of OLETF rats treated with midodrine, we observed lower levels of aldose reductase, tumor necrosis factor-α, and sorbitol, but higher levels of hexokinase, 5’-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase-alpha, adenosine 5´-triphosphate, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptordelta, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha, superoxide dismutase, and catalase.
Conclusion
The ameliorating effects of midodrine on cataracts in the OLETF obesity rat model are exerted via the following three mechanisms: direct inhibition of the biosynthesis of sorbitol, which causes cataracts; reduction of reactive oxygen species and inflammation; and (3) stimulation of normal aerobic glycolysis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- α1-Adrenergic Receptors: Insights into Potential Therapeutic Opportunities for COVID-19, Heart Failure, and Alzheimer’s Disease
Dianne M. Perez
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 4188. CrossRef - A new use for old drugs: identifying compounds with an anti-obesity effect using a high through-put semi-automated Caenorhabditis elegans screening platform
Freek Haerkens, Charlotte Kikken, Laurens Kirkels, Monique van Amstel, Willemijn Wouters, Els van Doornmalen, Christof Francke, Samantha Hughes
Heliyon.2022; 8(8): e10108. CrossRef
- α1-Adrenergic Receptors: Insights into Potential Therapeutic Opportunities for COVID-19, Heart Failure, and Alzheimer’s Disease

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- EW-7197 Attenuates the Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy in db/db Mice through Suppression of Fibrogenesis and Inflammation
- Kyung Bong Ha, Weerapon Sangartit, Ah Reum Jeong, Eun Soo Lee, Hong Min Kim, Soyeon Shim, Upa Kukongviriyapan, Dae-Kee Kim, Eun Young Lee, Choon Hee Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):96-111. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1305
- 4,027 View
- 182 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
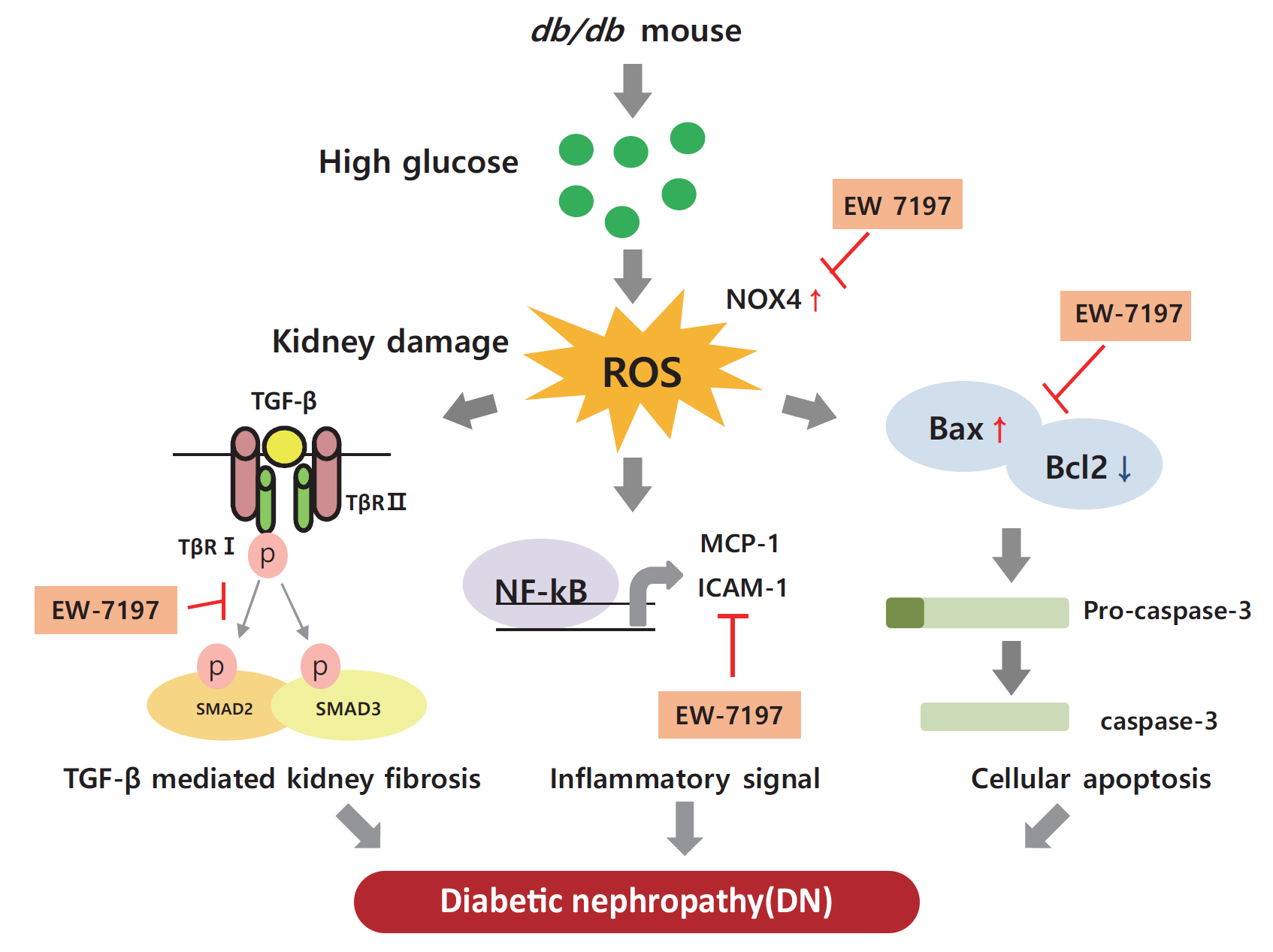
ePub - Background
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is characterized by albuminuria and accumulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) in kidney. Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) plays a central role in promoting ECM accumulation. We aimed to examine the effects of EW-7197, an inhibitor of TGF-β type 1 receptor kinase (ALK5), in retarding the progression of DN, both in vivo, using a diabetic mouse model (db/db mice), and in vitro, in podocytes and mesangial cells.
Methods
In vivo study: 8-week-old db/db mice were orally administered EW-7197 at a dose of 5 or 20 mg/kg/day for 10 weeks. Metabolic parameters and renal function were monitored. Glomerular histomorphology and renal protein expression were evaluated by histochemical staining and Western blot analyses, respectively. In vitro study: DN was induced by high glucose (30 mM) in podocytes and TGF-β (2 ng/mL) in mesangial cells. Cells were treated with EW-7197 (500 nM) for 24 hours and the mechanism associated with the attenuation of DN was investigated.
Results
Enhanced albuminuria and glomerular morphohistological changes were observed in db/db compared to that of the nondiabetic (db/m) mice. These alterations were associated with the activation of the TGF-β signaling pathway. Treatment with EW-7197 significantly inhibited TGF-β signaling, inflammation, apoptosis, reactive oxygen species, and endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetic mice and renal cells.
Conclusion
EW-7197 exhibits renoprotective effect in DN. EW-7197 alleviates renal fibrosis and inflammation in diabetes by inhibiting downstream TGF-β signaling, thereby retarding the progression of DN. Our study supports EW-7197 as a therapeutically beneficial compound to treat DN. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- TGF-β signaling in health, disease, and therapeutics
Ziqin Deng, Tao Fan, Chu Xiao, He Tian, Yujia Zheng, Chunxiang Li, Jie He
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic nephropathy: role of polyphenols
Qi Jin, Tongtong Liu, Yuan Qiao, Donghai Liu, Liping Yang, Huimin Mao, Fang Ma, Yuyang Wang, Liang Peng, Yongli Zhan
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Beneficial Effects of a Curcumin Derivative and Transforming Growth Factor-β Receptor I Inhibitor Combination on Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
Kyung Bong Ha, Eun Soo Lee, Na Won Park, Su Ho Jo, Soyeon Shim, Dae-Kee Kim, Chan Mug Ahn, Choon Hee Chung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(4): 500. CrossRef
- TGF-β signaling in health, disease, and therapeutics

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Dulaglutide Ameliorates Palmitic Acid-Induced Hepatic Steatosis by Activating FAM3A Signaling Pathway
- Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Min-Jeong Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):74-83. Published online February 9, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1293
- 4,941 View
- 235 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
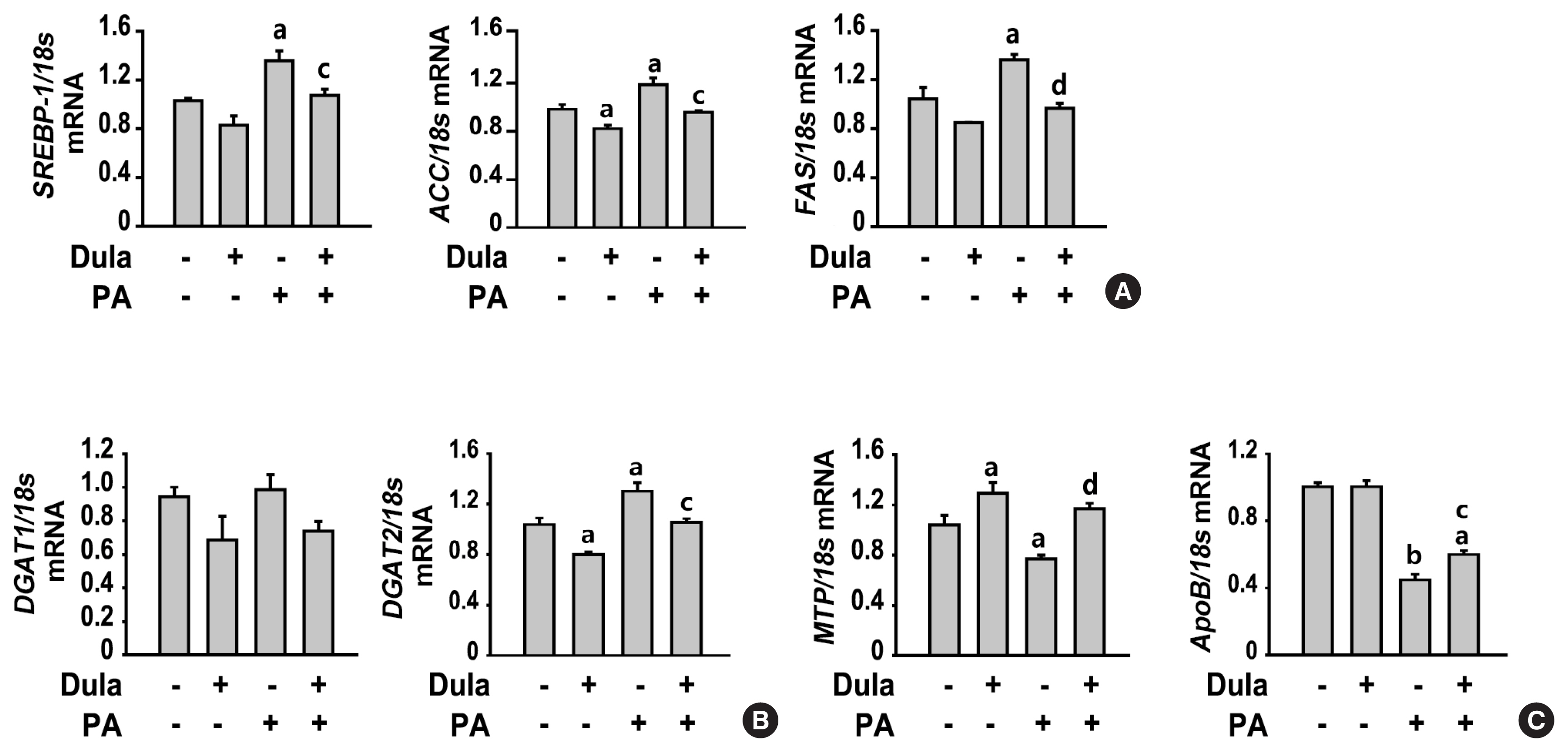
ePub - Background
Dulaglutide, a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA), has been shown to reduce body weight and liver fat content in patients with type 2 diabetes. Family with sequence similarity 3 member A (FAM3A) plays a vital role in regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. The aim of this study was to determine the mechanisms by which dulaglutide protects against hepatic steatosis in HepG2 cells treated with palmitic acid (PA).
Methods
HepG2 cells were pretreated with 400 μM PA for 24 hours, followed by treatment with or without 100 nM dulaglutide for 24 hours. Hepatic lipid accumulation was determined using Oil red O staining and triglyceride (TG) assay, and the expression of lipid metabolism-associated factor was analyzed using quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting.
Results
Dulaglutide significantly decreased hepatic lipid accumulation and reduced the expression of genes associated with lipid droplet binding proteins, de novo lipogenesis, and TG synthesis in PA-treated HepG2 cells. Dulaglutide also increased the expression of proteins associated with lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation and FAM3A in PA-treated cells. However, exendin-(9-39), a GLP-1R antagonist, reversed the expression of FAM3A, and fatty acid oxidation-associated factors increased due to dulaglutide. In addition, inhibition of FAM3A by siRNA attenuated the reducing effect of dulaglutide on TG content and its increasing effect on regulation of fatty acid oxidation.
Conclusion
These results suggest that dulaglutide could be used therapeutically for improving nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and its effect could be mediated in part via upregulation of FAM3A expression through a GLP-1R-dependent pathway. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- GLP-1/GLP-1RAs: New Options for the Drug Treatment of NAFLD
Haoran Jiang, Linquan Zang
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2024; 30(2): 100. CrossRef - GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives
Riccardo Nevola, Raffaella Epifani, Simona Imbriani, Giovanni Tortorella, Concetta Aprea, Raffaele Galiero, Luca Rinaldi, Raffaele Marfella, Ferdinando Carlo Sasso
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(2): 1703. CrossRef - FAM3A mediates the phenotypic switch of human aortic smooth muscle cells stimulated with oxidised low-density lipoprotein by influencing the PI3K-AKT pathway
Lei Yang, Baoshun Du, Shitao Zhang, Maode Wang
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal.2023; 59(6): 431. CrossRef - ATP Secretion and Metabolism in Regulating Pancreatic Beta Cell Functions and Hepatic Glycolipid Metabolism
Jing Li, Han Yan, Rui Xiang, Weili Yang, Jingjing Ye, Ruili Yin, Jichun Yang, Yujing Chi
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeted therapeutics and novel signaling pathways in non-alcohol-associated fatty liver/steatohepatitis (NAFL/NASH)
Xiaohan Xu, Kyle L. Poulsen, Lijuan Wu, Shan Liu, Tatsunori Miyata, Qiaoling Song, Qingda Wei, Chenyang Zhao, Chunhua Lin, Jinbo Yang
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- GLP-1/GLP-1RAs: New Options for the Drug Treatment of NAFLD

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- The Effects of PPAR Agonists on Atherosclerosis and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in ApoE−/−FXR−/− Mice
- Yenna Lee, Bo-Rahm Kim, Geun-Hyung Kang, Gwan Jae Lee, Young Joo Park, Haeryoung Kim, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1243-1253. Published online December 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1100
- 5,663 View
- 159 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
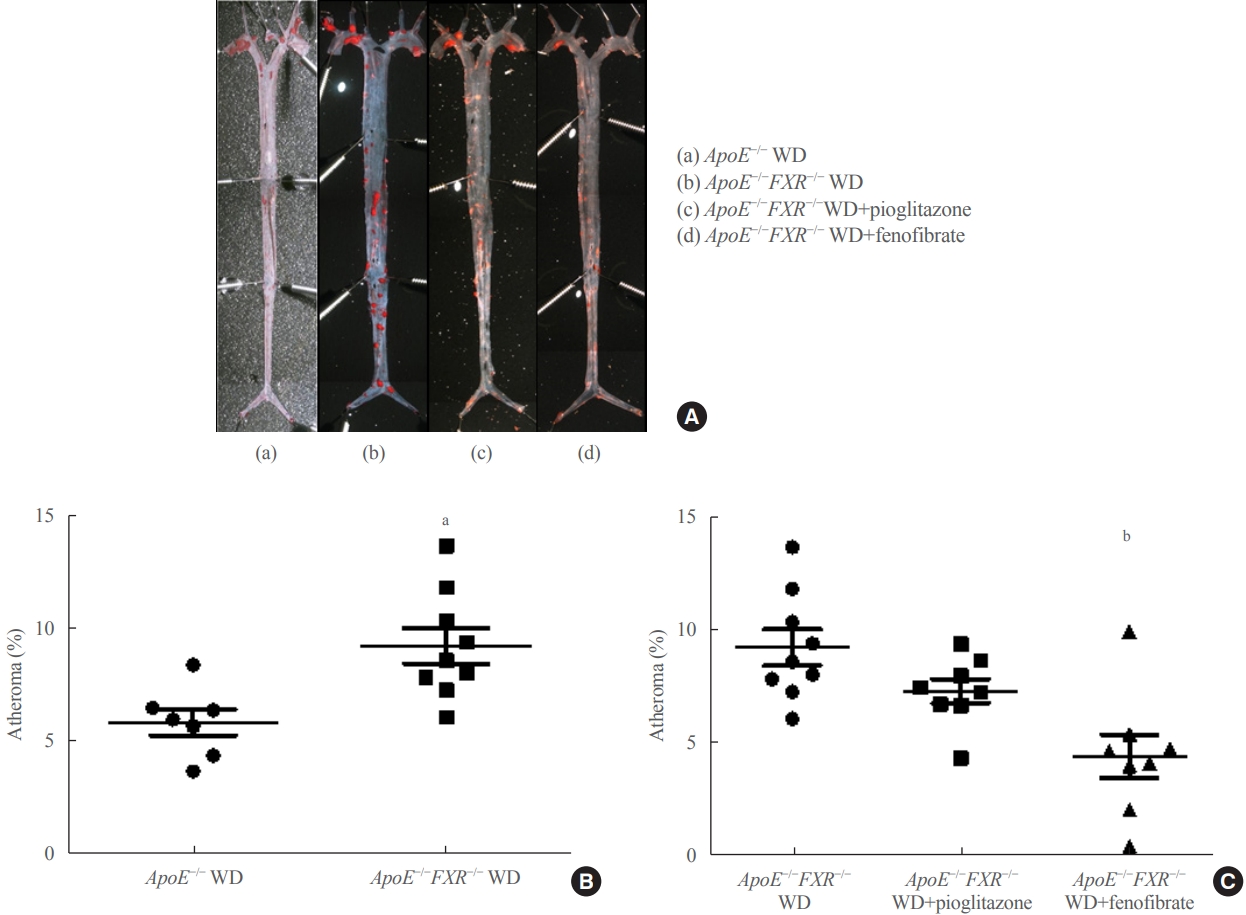
ePub - Background
Farnesoid X receptor (FXR), a bile acid–activated nuclear receptor, is a potent regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism as well as of bile acid metabolism. Previous studies have demonstrated that FXR deficiency is associated with metabolic derangements, including atherosclerosis and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), but its mechanism remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the role of FXR in atherosclerosis and NAFLD and the effect of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) agonists in mouse models with FXR deficiency.
Methods
En face lipid accumulation analysis, liver histology, serum levels of glucose and lipids, and mRNA expression of genes related to lipid metabolism were compared between apolipoprotein E (ApoE)−/− and ApoE−/−FXR−/− mice. The effects of PPARα and PPARγ agonists were also compared in both groups of mice.
Results
Compared with ApoE−/− mice, ApoE−/−FXR−/− mice showed more severe atherosclerosis, hepatic steatosis, and higher levels of serum cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and triglycerides, accompanied by increased mRNA expression of FAS, ApoC2, TNFα, IL-6 (liver), ATGL, TGH, HSL, and MGL (adipocytes), and decreased mRNA expressions of CPT2 (liver) and Tfam (skeletal muscle). Treatment with a PPARα agonist, but not with a PPARγ agonist, partly reversed atherosclerosis and hepatic steatosis, and decreased plasma triglyceride levels in the ApoE−/−FXR−/− mice, in association with increased mRNA expression of CD36 and FATP and decreased expression of ApoC2 and ApoC3 (liver).
Conclusion
Loss of FXR is associated with aggravation of atherosclerosis and hepatic steatosis in ApoE-deficient mice, which could be reversed by a PPARα agonist through induction of fatty acid uptake, β-oxidation, and triglyceride hydrolysis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the hepatotoxicity of Psoralea corylifolia L. based on a zebrafish model
Shu-Yan Gao, Jing-Cheng Zhao, Qing Xia, Chen Sun, Maimaiti Aili, Ainiwaer Talifu, Shi-Xia Huo, Yun Zhang, Zhi-Jian Li
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: from mechanisms to therapeutics
Yuxiao Jiang, Lili Wu, Xiaopeng Zhu, Hua Bian, Xin Gao, Mingfeng Xia
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mitochondrial carnitine palmitoyltransferase-II dysfunction: A possible novel mechanism for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in hepatocarcinogenesis
Min Yao, Ping Zhou, Yan-Yan Qin, Li Wang, Deng-Fu Yao
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 29(12): 1765. CrossRef - Emerging Roles of Gut Microbial Modulation of Bile Acid Composition in the Etiology of Cardiovascular Diseases
Tess Yntema, Debby P. Y. Koonen, Folkert Kuipers
Nutrients.2023; 15(8): 1850. CrossRef - The interplay between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Alexandra C. Finney, Sandeep Das, Dhananjay Kumar, M. Peyton McKinney, Bishuang Cai, Arif Yurdagul, Oren Rom
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting PPARs for therapy of atherosclerosis: A review
Miao Miao, Xue Wang, Tian Liu, Yan-Jie Li, Wen-Qian Yu, Tong-Mei Yang, Shou-Dong Guo
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2023; 242: 125008. CrossRef - Cabernet sauvignon dry red wine ameliorates atherosclerosis in mice by regulating inflammation and endothelial function, activating AMPK phosphorylation, and modulating gut microbiota
Xinlong Cheng, Xue Han, Liangfu Zhou, Yasai Sun, Qian Zhou, Xuan Lin, Zhe Gao, Jie Wang, Wen Zhao
Food Research International.2023; 169: 112942. CrossRef - Impacts of dietary lipids derived from animal or vegetable sources on healthy rats
Mostafa M Dalal, Gamal M Edrees, Hanaa A Hassan, Mamdouh Abdel-Mogib, Mai Alaa El-Dein
Egyptian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences.2023; 10(1): 618. CrossRef - Whey protein hydrolysate alleviated atherosclerosis and hepatic steatosis by regulating lipid metabolism in apoE-/- mice fed a Western diet
Kai Wang, Zixin Fu, Xiaoyi Li, Hui Hong, Xin Zhan, Xiaohong Guo, Yongkang Luo, Yuqing Tan
Food Research International.2022; 157: 111419. CrossRef - Melatonin alleviates PM2.5‐induced glucose metabolism disorder and lipidome alteration by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress
Zhou Du, Junjie Hu, Lisen Lin, Qingqing Liang, Mengqi Sun, Zhiwei Sun, Junchao Duan
Journal of Pineal Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipoprotein Lipase: Is It a Magic Target for the Treatment of Hypertriglyceridemia
Joon Ho Moon, Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 575. CrossRef - The role of the gut microbiota in health and cardiovascular diseases
Lu Wang, Shiqi Wang, Qing Zhang, Chengqi He, Chenying Fu, Quan Wei
Molecular Biomedicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of the hepatotoxicity of Psoralea corylifolia L. based on a zebrafish model

- Miscellaneous
- Clinical Value of Serum Mitochondria-Inhibiting Substances in Assessing Renal Hazards: A Community-Based Prospective Study in Korea
- Hoon Sung Choi, Jin Taek Kim, Hong Kyu Lee, Wook Ha Park, Youngmi Kim Pak, Sung Woo Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1298-1306. Published online November 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1226
- 3,328 View
- 95 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
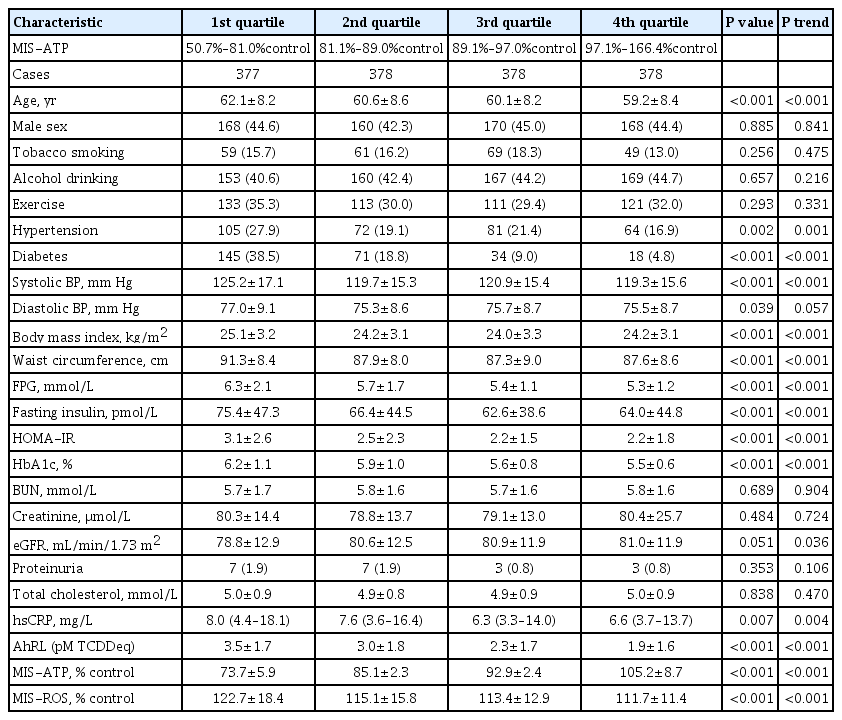
ePub - Background
Mitochondrial dysfunction is strongly associated with several kidney diseases. However, no studies have evaluated the potential renal hazards of serum mitochondria-inhibiting substance (MIS) and aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand (AhRL) levels.
Methods
We used serum level of MIS and AhRL and clinical renal outcomes from 1,511 participants of a prospective community-based cohort in Ansung. MIS was evaluated based on intracellular adenosine triphosphate (MIS-ATP) or reactive oxygen species (MIS-ROS) generation measured using cell-based assays.
Results
During a mean 6.9-year follow-up, 84 participants (5.6%) developed a rapid decline in kidney function. In the lowest quartile group of MIS-ATP, patients were older and had metabolically deleterious parameters. In multivariate logistic regression analysis, higher MIS-ATP was associated with decreased odds for rapid decline: the odds ratio (OR) of 1% increase was 0.977 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.957 to 0.998; P=0.031), while higher MIS-ROS was marginally associated with increased odds for rapid decline (OR, 1.014; 95% CI, 0.999 to 1.028; P=0.055). However, serum AhRL was not associated with the rapid decline in kidney function. In subgroup analysis, the renal hazard of MIS was particularly evident in people with hypertension and low baseline kidney function.
Conclusion
Serum MIS was independently associated with a rapid decline in kidney function, while serum AhRL was not. The clinical implication of renal hazard on serum MIS requires further evaluation in future studies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Interactive Online App for Predicting Diabetes via Machine Learning from Environment-Polluting Chemical Exposure Data
Rosy Oh, Hong Kyu Lee, Youngmi Kim Pak, Man-Suk Oh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(10): 5800. CrossRef
- An Interactive Online App for Predicting Diabetes via Machine Learning from Environment-Polluting Chemical Exposure Data

Review Article
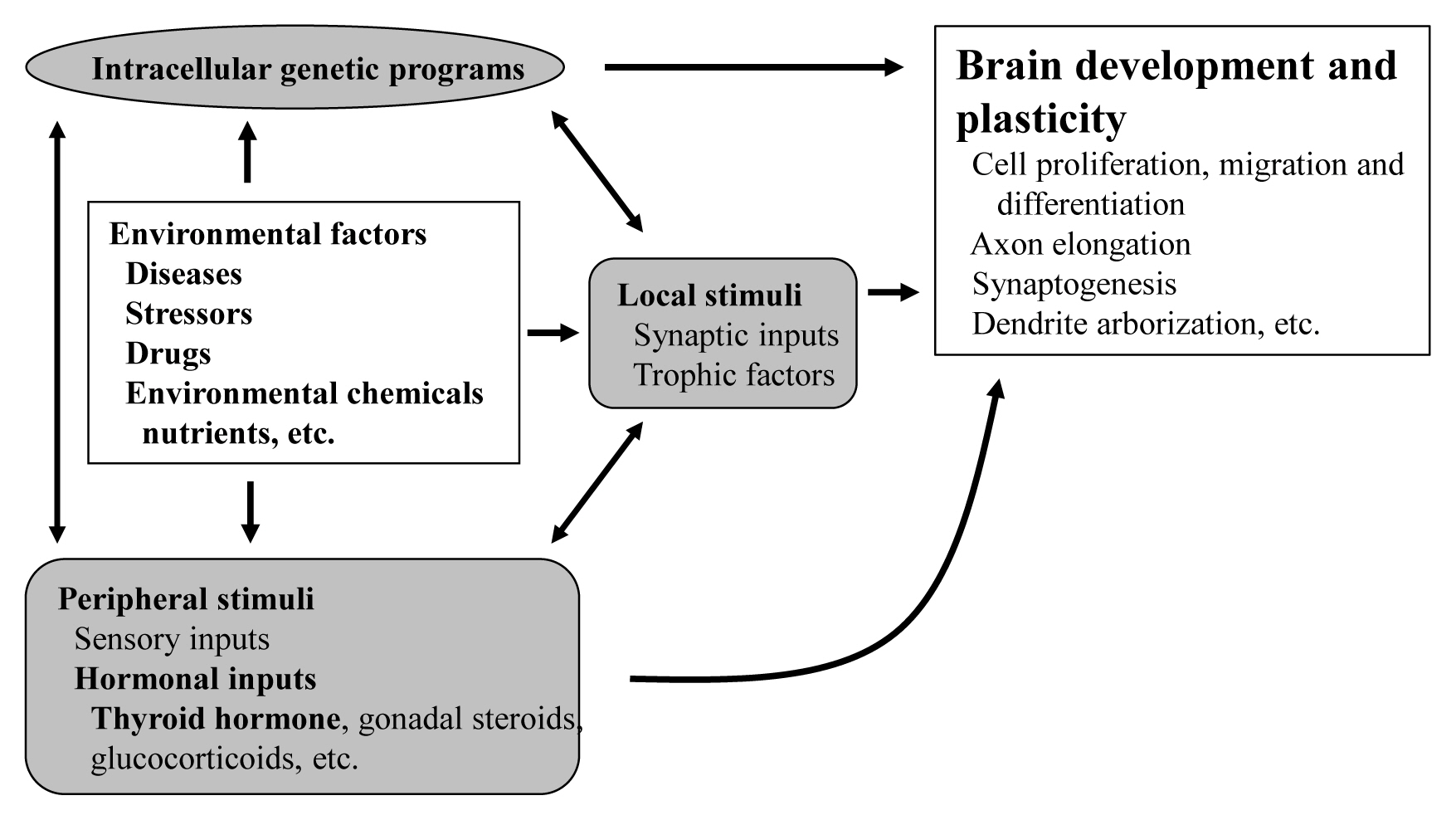
- Thyroid
- The Role of Thyroid Hormone in the Regulation of Cerebellar Development
- Sumiyasu Ishii, Izuki Amano, Noriyuki Koibuchi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):703-716. Published online August 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1150
- 4,538 View
- 170 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The proper organized expression of specific genes in time and space is responsible for the organogenesis of the central nervous system including the cerebellum. The epigenetic regulation of gene expression is tightly regulated by an intrinsic intracellular genetic program, local stimuli such as synaptic inputs and trophic factors, and peripheral stimuli from outside of the brain including hormones. Some hormone receptors are expressed in the cerebellum. Thyroid hormones (THs), among numerous circulating hormones, are well-known major regulators of cerebellar development. In both rodents and human, hypothyroidism during the postnatal developmental period results in abnormal morphogenesis or altered function. THs bind to the thyroid hormone receptors (TRs) in the nuclei and with the help of transcriptional cofactors regulate the transcription of target genes. Gene regulation by TR induces cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation, which are necessary for brain development and plasticity. Thus, the lack of TH action mediators may directly cause aberrant cerebellar development. Various kinds of animal models have been established in a bid to study the mechanism of TH action in the cerebellum. Interestingly, the phenotypes differ greatly depending on the models. Herein we summarize the actions of TH and TR particularly in the developing cerebellum.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Neuropeptides and Their Roles in the Cerebellum
Zi-Hao Li, Bin Li, Xiao-Yang Zhang, Jing-Ning Zhu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(4): 2332. CrossRef - Exploring the underlying molecular mechanism of tri(1,3-dichloropropyl) phosphate-induced neurodevelopmental toxicity via thyroid hormone disruption in zebrafish by multi-omics analysis
Ying Xu, Lei Yang, Yanguo Teng, Jian Li, Na Li
Aquatic Toxicology.2023; 258: 106510. CrossRef - Association of Maternal TSH, FT4 With Children's BMI Trajectories, and Obesity: A Birth Cohort Study
Mengting Yang, Shanshan Zhang, Yuzhu Teng, Xue Ru, Linlin Zhu, Yan Han, Xingyong Tao, Hui Cao, Shuangqin Yan, Fangbiao Tao, Kun Huang
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 109(1): e190. CrossRef - Thyroid hormone receptor beta: Relevance in human health and diseases
Ghausiya Rehman, Neha Kumari, Farhad Bano, Rakesh K. Tyagi
Endocrine and Metabolic Science.2023; 13: 100144. CrossRef - Targeting Thyroid Hormone/Thyroid Hormone Receptor Axis: An Attractive Therapy Strategy in Liver Diseases
Qianyu Tang, Min Zeng, Linxi Chen, Nian Fu
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Histone Deacetylase 3 Inhibitor Alleviates Cerebellar Defects in Perinatal Hypothyroid Mice by Stimulating Histone Acetylation and Transcription at Thyroid Hormone-Responsive Gene Loci
Alvin Susetyo, Sumiyasu Ishii, Yuki Fujiwara, Izuki Amano, Noriyuki Koibuchi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(14): 7869. CrossRef - Selection-driven adaptation to the extreme Antarctic environment in the Emperor penguin
Federica Pirri, Lino Ometto, Silvia Fuselli, Flávia A. N. Fernandes, Lorena Ancona, Nunzio Perta, Daniele Di Marino, Céline Le Bohec, Lorenzo Zane, Emiliano Trucchi
Heredity.2022; 129(6): 317. CrossRef - Long-term depression–inductive stimulation causes long-term potentiation in mouse Purkinje cells with a mutant thyroid hormone receptor
Ayane Ninomiya, Izuki Amano, Michifumi Kokubo, Yusuke Takatsuru, Sumiyasu Ishii, Hirokazu Hirai, Nobutake Hosoi, Noriyuki Koibuchi
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Neuropeptides and Their Roles in the Cerebellum

Original Article
- Adrenal Gland
- Aldosterone Inhibits In Vitro Myogenesis by Increasing Intracellular Oxidative Stress via Mineralocorticoid Receptor
- Jin Young Lee, Da Ae Kim, Eunah Choi, Yun Sun Lee, So Jeong Park, Beom-Jun Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):865-874. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1108

- 4,309 View
- 112 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Despite clinical evidence indicating poor muscle health in subjects with primary aldosteronism (PA), it is still unclear whether the role of aldosterone in muscle metabolism is direct or mediated indirectly via factors, such as electrolyte imbalance or impaired glucose uptake. As one approach to clarify this issue, we investigated the effect of aldosterone on in vitro myogenesis and the potential mechanism explaining it.
Methods
Myogenesis was induced in mouse C2C12 myoblasts with 2% horse serum. Immunofluorescence, quantitative reversetranscription polymerase chain reaction, Western blot, viability, and migration analyses were performed for experimental research.
Results
Recombinant aldosterone treatment suppressed muscle differentiation from mouse C2C12 myoblasts in a dose-dependent manner, and consistently reduced the expression of myogenic differentiation markers. Furthermore, aldosterone significantly increased intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in myotubes, and treatment with N-acetyl cysteine, a potent biological thiol antioxidant, reversed the decrease of myotube area, myotube area per myotube, nucleus number per myotube, and fusion index due to aldosterone through decreasing oxidative stress. A binding enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay confirmed that mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) interacted with aldosterone in C2C12 myoblasts, while eplerenone, an MR inhibitor, blocked aldosterone-stimulated intracellular ROS generation during myogenesis and markedly attenuated the suppression of in vitro myogenesis by aldosterone.
Conclusion
These findings support the hypothesis that hypersecretion of aldosterone, like PA, directly contributes to muscular deterioration and suggest that antioxidants and/or MR antagonists could be effective therapeutic options to reduce the risk of sarcopenia in these patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Molecular mechanisms underlying sarcopenia in heart failure
Cody A. Rutledge
The Journal of Cardiovascular Aging.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) skeletal muscle: A transcriptomic perspective of cortisol action
Jorge E. Aedo, Rodrigo Zuloaga, Daniela Aravena-Canales, Alfredo Molina, Juan Antonio Valdés
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of 11-Deoxycorticosterone in the Transcriptomic Response to Stress in Rainbow Trout Skeletal Muscle
Rodrigo Zuloaga, Daniela Aravena-Canales, Jorge Eduardo Aedo, Cesar Osorio-Fuentealba, Alfredo Molina, Juan Antonio Valdés
Genes.2023; 14(2): 512. CrossRef - Heart Failure Medication and Muscle Wasting
Yasuhiro Izumiya
Circulation Journal.2023; 88(1): 20. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Endocrine Society Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Primary Aldosteronism
Jeonghoon Ha, Jung Hwan Park, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Kyong Yeun Jung, Jeongmin Lee, Jong Han Choi, Seung Hun Lee, Namki Hong, Jung Soo Lim, Byung Kwan Park, Jung-Han Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Jooyoung Cho, Mi-kyung Kim, Choon Hee Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 597. CrossRef - Higher Plasma Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1 Is Associated with Lower Risk for Sarcopenia in Older Asian Adults
Sunghwan Ji, Kyunggon Kim, So Jeong Park, Jin Young Lee, Hee-Won Jung, Hyun Ju Yoo, Il-Young Jang, Eunju Lee, Ji Yeon Baek, Beom-Jun Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 701. CrossRef - The Role of Aldosterone in OSA and OSA-Related Hypertension
Yi Wang, Chuan Xiang Li, Ying Ni Lin, Li Yue Zhang, Shi Qi Li, Liu Zhang, Ya Ru Yan, Fang Ying Lu, Ning Li, Qing Yun Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Daiji Kawanami, Yuichi Takashi, Yoshimi Muta, Naoki Oda, Dai Nagata, Hiroyuki Takahashi, Makito Tanabe
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Molecular mechanisms underlying sarcopenia in heart failure


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



