Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Articles
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Scaling Insulin-Producing Cells by Multiple Strategies
- Jinhyuk Choi, Fritz Cayabyab, Harvey Perez, Eiji Yoshihara
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(2):191-205. Published online April 4, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1910
- 443 View
- 52 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
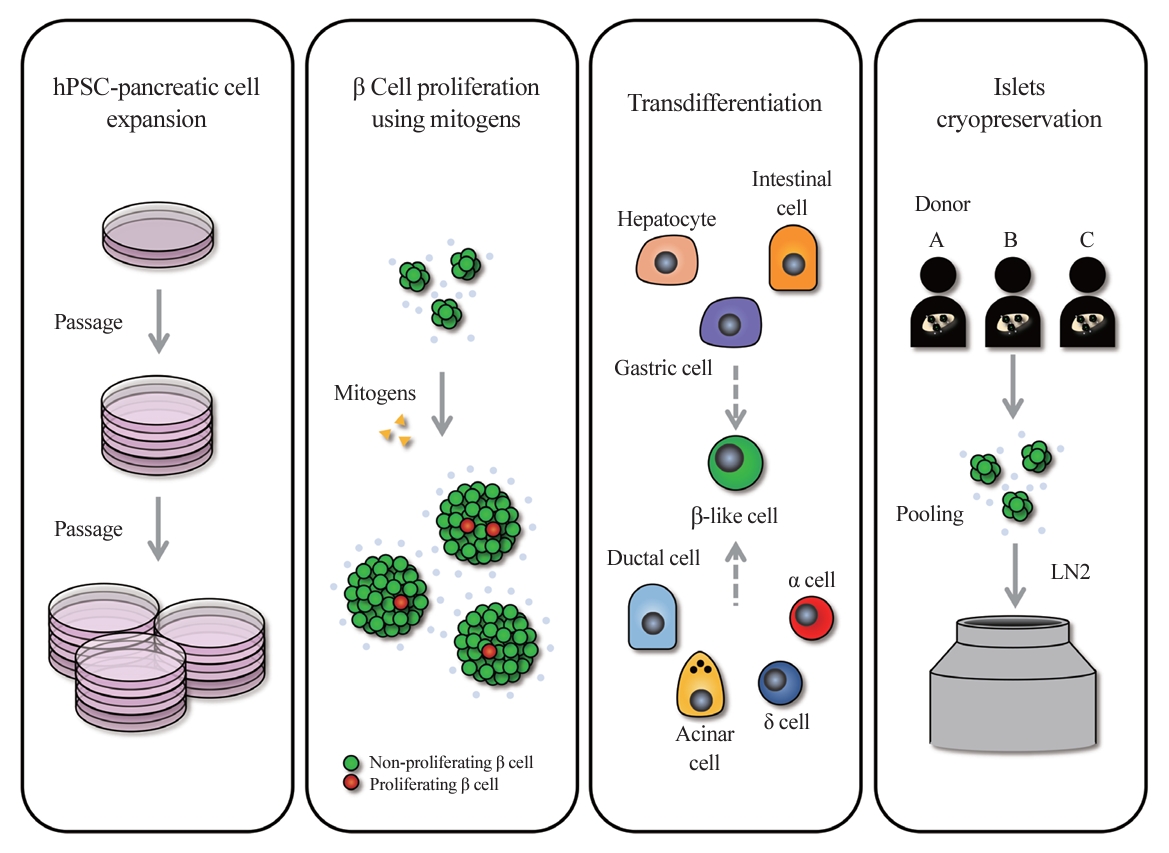
ePub - In the quest to combat insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM), allogenic pancreatic islet cell therapy sourced from deceased donors represents a significant therapeutic advance. However, the applicability of this approach is hampered by donor scarcity and the demand for sustained immunosuppression. Human induced pluripotent stem cells are a game-changing resource for generating synthetic functional insulin-producing β cells. In addition, novel methodologies allow the direct expansion of pancreatic progenitors and mature β cells, thereby circumventing prolonged differentiation. Nevertheless, achieving practical reproducibility and scalability presents a substantial challenge for this technology. As these innovative approaches become more prominent, it is crucial to thoroughly evaluate existing expansion techniques with an emphasis on their optimization and scalability. This manuscript delineates these cutting-edge advancements, offers a critical analysis of the prevailing strategies, and underscores pivotal challenges, including cost-efficiency and logistical issues. Our insights provide a roadmap, elucidating both the promises and the imperatives in harnessing the potential of these cellular therapies for IDDM.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Glucocorticoid-Induced Hyperglycemia: A Neglected Problem
- Jung-Hwan Cho, Sunghwan Suh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(2):222-238. Published online March 27, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2024.1951
- 329 View
- 44 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
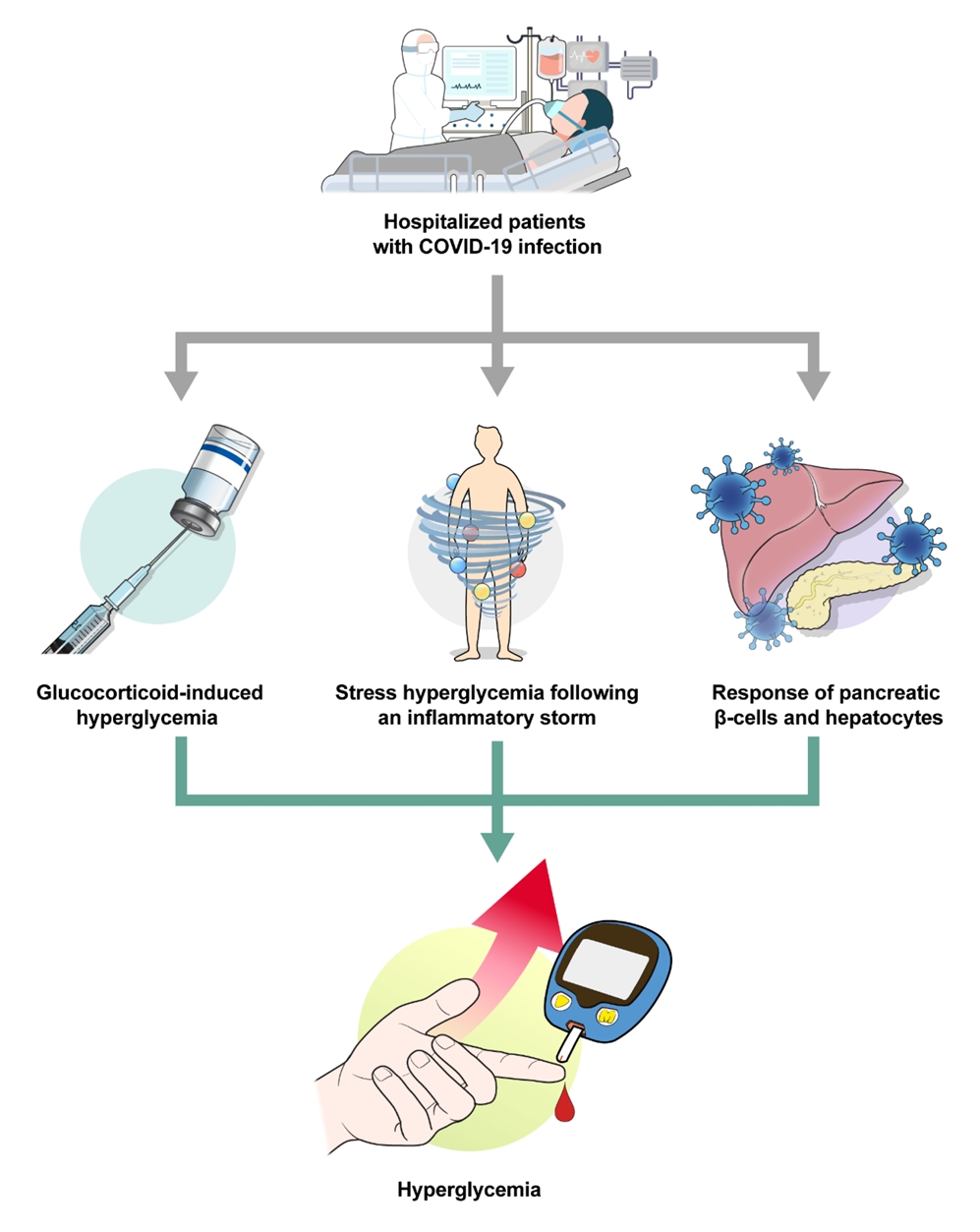
ePub - Glucocorticoids provide a potent therapeutic response and are widely used to treat a variety of diseases, including coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection. However, the issue of glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycemia (GIH), which is observed in over one-third of patients treated with glucocorticoids, is often neglected. To improve the clinical course and prognosis of diseases that necessitate glucocorticoid therapy, proper management of GIH is essential. The key pathophysiology of GIH includes systemic insulin resistance, which exacerbates hepatic steatosis and visceral obesity, as well as proteolysis and lipolysis of muscle and adipose tissue, coupled with β-cell dysfunction. For patients on glucocorticoid therapy, risk stratification should be conducted through a detailed baseline evaluation, and frequent glucose monitoring is recommended to detect the onset of GIH, particularly in high-risk individuals. Patients with confirmed GIH who require treatment should follow an insulin-centered regimen that varies depending on whether they are inpatients or outpatients, as well as the type and dosage of glucocorticoid used. The ideal strategy to maintain normoglycemia while preventing hypoglycemia is to combine basal-bolus insulin and correction doses with a continuous glucose monitoring system. This review focuses on the current understanding and latest evidence concerning GIH, incorporating insights gained from the COVID-19 pandemic.

Original Article
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Efficacy and Safety of Omarigliptin, a Novel Once-Weekly Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor, in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- A.B.M. Kamrul-Hasan, Muhammad Shah Alam, Samir Kumar Talukder, Deep Dutta, Shahjada Selim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):109-126. Published online January 23, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1839

- 1,161 View
- 39 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
No recent meta-analysis has holistically analyzed and summarized the efficacy and safety of omarigliptin in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We conducted a meta-analysis to address this knowledge gap.
Methods
Electronic databases were searched to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that included patients with T2DM who received omarigliptin in the intervention arm. The control arm consisted of either a placebo (passive control group [PCG]) or an active comparator (active control group [ACG]). The primary outcome assessed was changes in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), while secondary outcomes included variations in glucose levels, achievement of glycemic targets, adverse events (AEs), and hypoglycemic events.
Results
From 332 initially screened articles, data from 16 RCTs involving 8,804 subjects were analyzed. Omarigliptin demonstrated superiority over placebo in reducing HbA1c levels (mean difference, –0.58%; 95% confidence interval, –0.75 to –0.40; P<0.00001; I2=91%). Additionally, omarigliptin outperformed placebo in lowering fasting plasma glucose, 2-hour postprandial glucose, and in the percentage of participants achieving HbA1c levels below 7.0% and 6.5%. The glycemic efficacy of omarigliptin was similar to that of the ACG across all measures. Although the omarigliptin group experienced a higher incidence of hypoglycemic events compared to the PCG, the overall AEs, serious AEs, hypoglycemia, and severe hypoglycemia were comparable between the omarigliptin and control groups (PCG and ACG).
Conclusion
Omarigliptin has a favorable glycemic efficacy and safety profile for managing T2DM.

Review Article
- Adrenal gland
- The Fascinating Interplay between Growth Hormone, Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1, and Insulin
- Eline C. Nijenhuis-Noort, Kirsten A. Berk, Sebastian J. C. M. M. Neggers, Aart J. van der Lely
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):83-89. Published online January 9, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2024.101
- 1,634 View
- 119 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
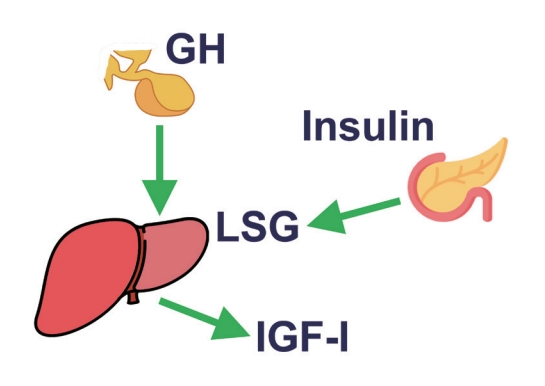
ePub - This review intends to provide the reader with a practical overview of several (patho)physiological conditions in which knowledge of the interplay between growth hormone (GH), insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), and insulin is important. This might help treating physicians in making the right decisions on how to intervene and improve metabolism for the benefit of patients, and to understand why and how metabolism responds in their specific cases. We will specifically address the interplay between GH, IGF-1, and insulin in type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus, liver cirrhosis, and acromegaly as examples in which this knowledge is truly necessary.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- IGF-1 and IGF-2 as Molecules Linked to Causes and Consequences of Obesity from Fetal Life to Adulthood: A Systematic Review
Justyna Szydlowska-Gladysz, Adrianna Edyta Gorecka, Julia Stepien, Izabela Rysz, Iwona Ben-Skowronek
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3966. CrossRef
- IGF-1 and IGF-2 as Molecules Linked to Causes and Consequences of Obesity from Fetal Life to Adulthood: A Systematic Review

Original Articles
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Effectiveness of a Social Networking Site Based Automatic Mobile Message Providing System on Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Kyuho Kim, Jae-Seung Yun, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Minhan Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn, Jae Hyoung Cho, Seung-Hyun Ko
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(2):344-352. Published online December 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1871
- 513 View
- 33 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigated the effectiveness of a social networking site (SNS)-based automatic mobile message providing system on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
A 3-month, randomized, open-label, controlled, parallel-group trial was conducted. One hundred and ten participants with T2DM were randomized to a mobile message system (MMS) (n=55) or control group (n=55). The MMS group received protocolbased automated messages two times per day for 10 weeks regarding diabetes self-management through KakaoTalk SNS messenger. The primary outcome was the difference in the change in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels (%) from baseline to week 12.
Results
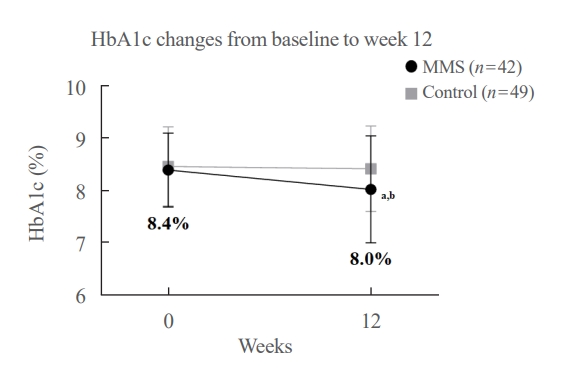
HbA1c levels were more markedly decreased in the MMS group (8.4%±0.7% to 8.0%±1.1%) than in the control group (8.5%±0.8% to 8.4%±0.8%), resulting in a significant between-group difference (P=0.027). No differences were observed in changes in fasting glucose levels, lipid profiles, and the number of participants who experienced hypoglycemia, or in changes in lifestyle behavior between groups. However, the self-monitoring of blood glucose frequency was significantly increased in the MMS group compared to the control group (P=0.003). In addition, sleep duration was increased in the MMS group, but was not changed in the control group.
Conclusion
An SNS-based automatic mobile message providing system was effective in improving glycemic control in patients in T2DM. Studies which based on a more individualized protocol, and investigate longer beneficial effect and sustainability will be required in the future.

- Calcium & bone metabolism
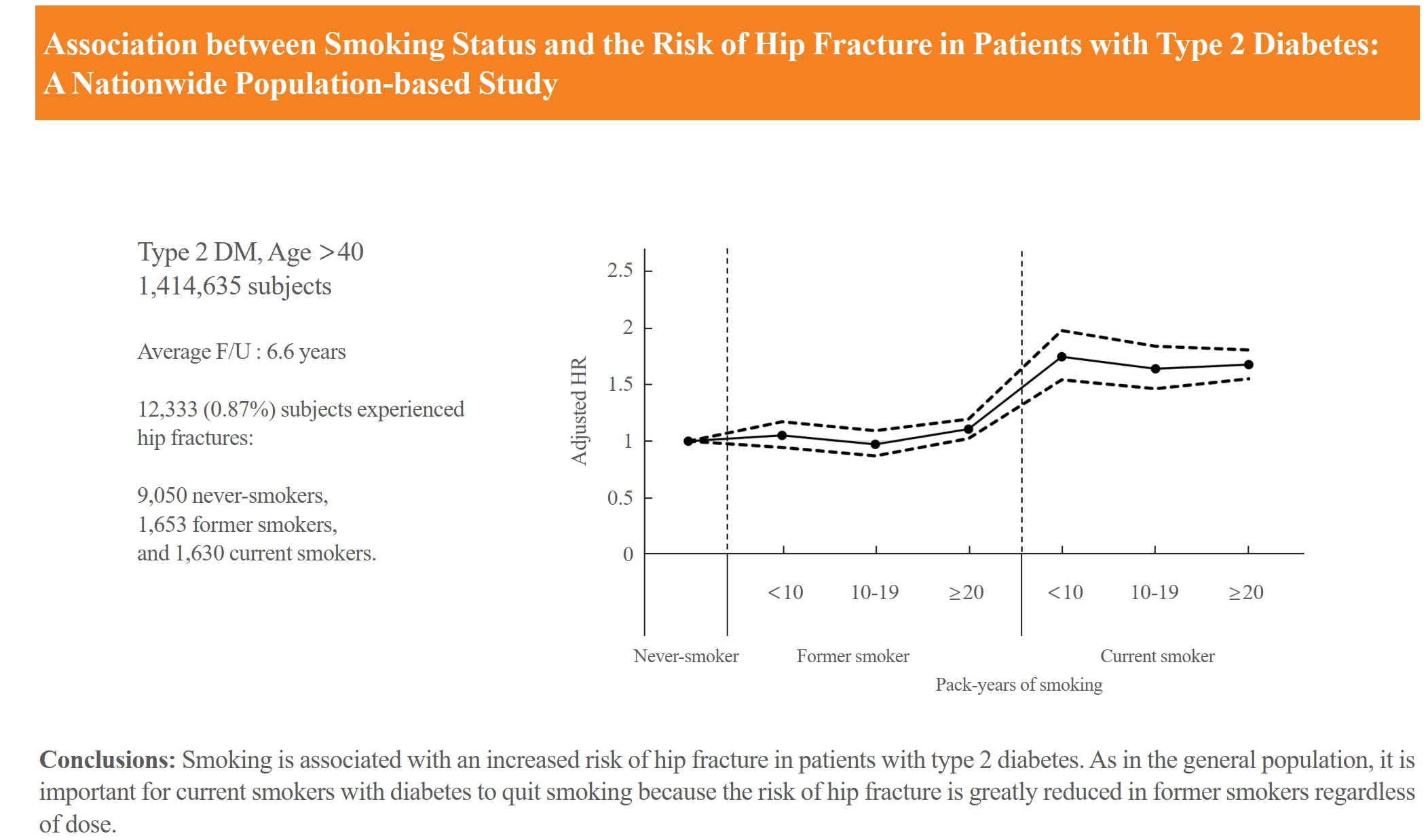
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Association between Smoking Status and the Risk of Hip Fracture in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
- Se-Won Lee, Jun-Young Heu, Ju-Yeong Kim, Jinyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):679-689. Published online December 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1760
- 1,176 View
- 66 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Limited longitudinal evidence exists regarding the potential association between smoking status and hip fracture among individuals with type 2 diabetes. We investigated this association using large-scale, nationwide cohort data for the Korean population.
Methods
This nationwide cohort study included 1,414,635 adults aged 40 and older who received Korean National Health Insurance Service health examinations between 2009 and 2012. Subjects with type 2 diabetes were categorized according to their smoking status, amount smoked (pack-years), number of cigarettes smoked per day, and duration of smoking. The results are presented as hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the associations between smoking status parameters and risk of hip fracture in multivariable Cox proportional hazard regression analysis.
Results
Compared with never-smokers, an increased adjusted HR (aHR) for hip fracture was observed in current smokers (1.681; 95% CI, 1.578 to 1.791), and a comparable aHR for hip fracture was found in former smokers (1.065; 95% CI, 0.999 to 1.136). For former smokers who had smoked 20 pack-years or more, the risk was slightly higher than that for never-smokers (aHR, 1.107; 95% CI, 1.024 to 1.196). The hip fracture risk of female former smokers was similar to that of female current smokers, but the hip fracture risk in male former smokers was similar to that of male never-smokers.
Conclusion
Smoking is associated with an increased risk of hip fracture in patients with type 2 diabetes. Current smokers with diabetes should be encouraged to quit smoking because the risk of hip fracture is greatly reduced in former smokers.

Review Articles
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
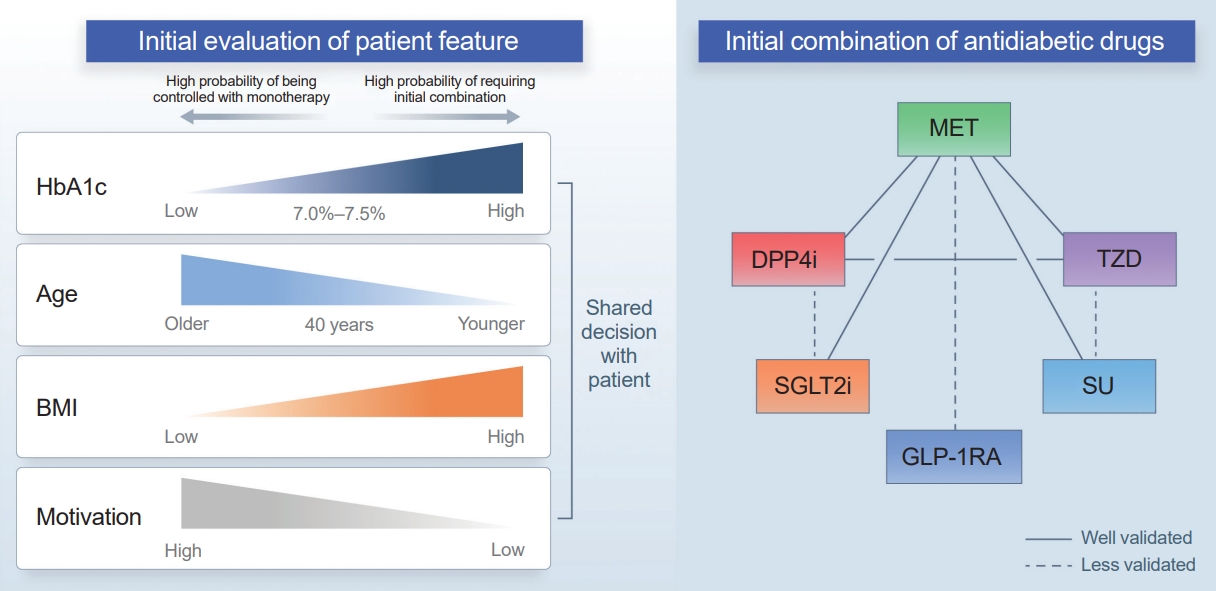
- Initial Combination Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes
- Ji Yoon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):23-32. Published online November 30, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1816
- 2,043 View
- 246 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a progressive disease in which it is challenging to achieve long-term durable glycemic control. However, intensive glycemic control is crucial for preventing diabetes-related complications. Previous studies showed that monotherapy with a stepwise add-on approach was seldom effective for long-term durable glycemic control. Combination therapy, which refers to the use of two or more drugs to control hyperglycemia, has multiple benefits, including the ability to target a variety of pathophysiological processes underlying hyperglycemia. In clinical trials, initial combination therapy showed better glycemic control than monotherapy or a stepwise approach. Emerging evidence indicates that initial combination therapy is associated with preserved β-cell function and fewer complications in T2D. However, cost-effectiveness and adverse events with combination therapy are issues that should be considered. Therefore, initial combination therapy is an important option for patients with T2D that clinicians should consider with a view toward balancing benefits and potential harms. In this review, we summarize the literature addressing initial combination therapy in T2D, and we suggest optimal strategies based on clinical situations and patient characteristics.

- Miscellaneous
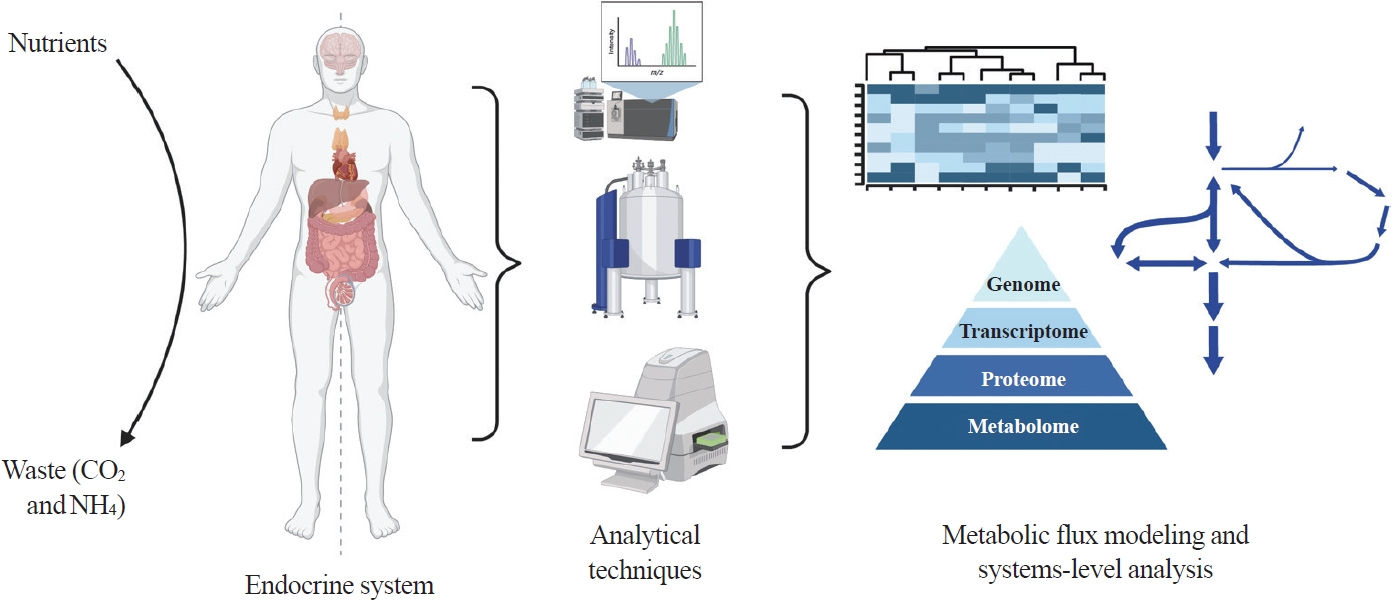
- Toward Systems-Level Metabolic Analysis in Endocrine Disorders and Cancer
- Aliya Lakhani, Da Hyun Kang, Yea Eun Kang, Junyoung O. Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):619-630. Published online November 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1814
- 2,451 View
- 111 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Metabolism is a dynamic network of biochemical reactions that support systemic homeostasis amidst changing nutritional, environmental, and physical activity factors. The circulatory system facilitates metabolite exchange among organs, while the endocrine system finely tunes metabolism through hormone release. Endocrine disorders like obesity, diabetes, and Cushing’s syndrome disrupt this balance, contributing to systemic inflammation and global health burdens. They accompany metabolic changes on multiple levels from molecular interactions to individual organs to the whole body. Understanding how metabolic fluxes relate to endocrine disorders illuminates the underlying dysregulation. Cancer is increasingly considered a systemic disorder because it not only affects cells in localized tumors but also the whole body, especially in metastasis. In tumorigenesis, cancer-specific mutations and nutrient availability in the tumor microenvironment reprogram cellular metabolism to meet increased energy and biosynthesis needs. Cancer cachexia results in metabolic changes to other organs like muscle, adipose tissue, and liver. This review explores the interplay between the endocrine system and systems-level metabolism in health and disease. We highlight metabolic fluxes in conditions like obesity, diabetes, Cushing’s syndrome, and cancers. Recent advances in metabolomics, fluxomics, and systems biology promise new insights into dynamic metabolism, offering potential biomarkers, therapeutic targets, and personalized medicine.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial: Tumor metabolism and programmed cell death
Dan-Lan Pu, Qi-Nan Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Editorial: Tumor metabolism and programmed cell death

Original Article
- Miscellaneous
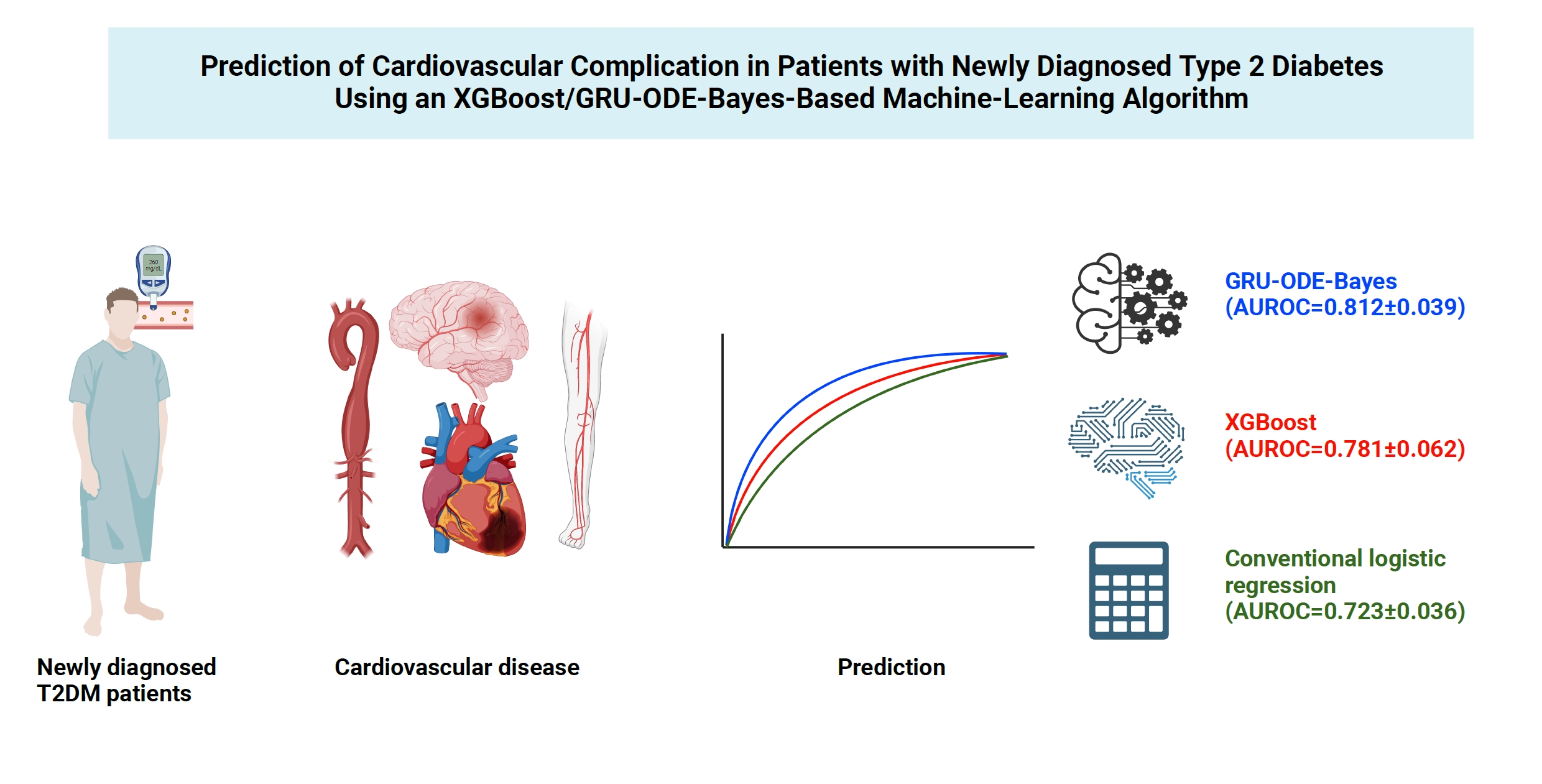
- Prediction of Cardiovascular Complication in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Using an XGBoost/GRU-ODE-Bayes-Based Machine-Learning Algorithm
- Joonyub Lee, Yera Choi, Taehoon Ko, Kanghyuck Lee, Juyoung Shin, Hun-Sung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):176-185. Published online November 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1739
- 1,197 View
- 60 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Cardiovascular disease is life-threatening yet preventable for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Because each patient with T2DM has a different risk of developing cardiovascular complications, the accurate stratification of cardiovascular risk is critical. In this study, we proposed cardiovascular risk engines based on machine-learning algorithms for newly diagnosed T2DM patients in Korea.
Methods
To develop the machine-learning-based cardiovascular disease engines, we retrospectively analyzed 26,166 newly diagnosed T2DM patients who visited Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital between July 2009 and April 2019. To accurately measure diabetes-related cardiovascular events, we designed a buffer (1 year), an observation (1 year), and an outcome period (5 years). The entire dataset was split into training and testing sets in an 8:2 ratio, and this procedure was repeated 100 times. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) was calculated by 10-fold cross-validation on the training dataset.
Results
The machine-learning-based risk engines (AUROC XGBoost=0.781±0.014 and AUROC gated recurrent unit [GRU]-ordinary differential equation [ODE]-Bayes=0.812±0.016) outperformed the conventional regression-based model (AUROC=0.723± 0.036).
Conclusion
GRU-ODE-Bayes-based cardiovascular risk engine is highly accurate, easily applicable, and can provide valuable information for the individualized treatment of Korean patients with newly diagnosed T2DM.

Review Article
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- The Benefits Of Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Pregnancy
- Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):472-481. Published online October 11, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1805

- 2,593 View
- 220 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Previous studies have consistently demonstrated the positive effects of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) on glycemic outcomes and complications of diabetes in people with type 1 diabetes. Guidelines now consider CGM to be an essential and cost-effective device for managing type 1 diabetes. As a result, insurance coverage for it is available. Evidence supporting CGM continues to grow and expand to broader populations, such as pregnant people with type 1 diabetes, people with type 2 diabetes treated only with basal insulin therapy, and even type 2 diabetes that does not require insulin treatment. However, despite the significant risk of hyperglycemia in pregnancy, which leads to complications in more than half of affected newborns, CGM indications and insurance coverage for those patients are unresolved. In this review article, we discuss the latest evidence for using CGM to offer glycemic control and reduce perinatal complications, along with its cost-effectiveness in pregestational type 1 and type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes mellitus. In addition, we discuss future prospects for CGM coverage and indications based on this evidence.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Wearable devices for glucose monitoring: A review of state-of-the-art technologies and emerging trends
Mohammad Mansour, M. Saeed Darweesh, Ahmed Soltan
Alexandria Engineering Journal.2024; 89: 224. CrossRef
- Wearable devices for glucose monitoring: A review of state-of-the-art technologies and emerging trends

Original Articles
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Coronary Artery Calcium Score as a Sensitive Indicator of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Long-Term Cohort Study
- Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Sang Min Lee, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Rae Cho, Young-Hoon Jeong, Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):568-577. Published online October 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1770

- 1,538 View
- 113 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Coronary artery calcium score (CACS) has become an important tool for evaluating cardiovascular disease (CVD). This study evaluated the significance of CACS for future CVD through more than 10 years of follow-up in asymptomatic Korean populations with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) known to have a relatively low CACS burden.
Methods
We enrolled 981 asymptomatic T2DM patients without CVD at baseline who underwent CACS evaluation using multidetector computed tomography between January 2008 and December 2014. They were grouped into five predefined CACS categories based on Agatston scores and followed up by August 2020. The primary endpoint was incident CVD events, including coronary, cerebrovascular, and peripheral arterial disease.
Results
The relative risk of CVD was significantly higher in patients with CACS ≥10, and the significance persisted after adjustment for known confounders. A higher CACS category indicated a higher incidence of future CVD: hazard ratio (95% confidence interval) 4.09 (1.79 to 9.36), 12.00 (5.61 to 25.69), and 38.79 (16.43 to 91.59) for 10≤ CACS <100, 100≤ CACS <400, and CACS ≥400, respectively. During the 12-year follow-up period, the difference in event-free survival more than doubled as the category increased. Patients with CACS below 10 had very low CVD incidence throughout the follow-up. The receiver operating characteristic analysis showed better area under curve when the CACS cutoff was 10 than 100.
Conclusion
CACS can be a sensitive marker of CVD risk. Specifically, CACS above 10 is an indicator of CVD high-risk requiring more intensive medical treatment in Koreans with T2DM.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
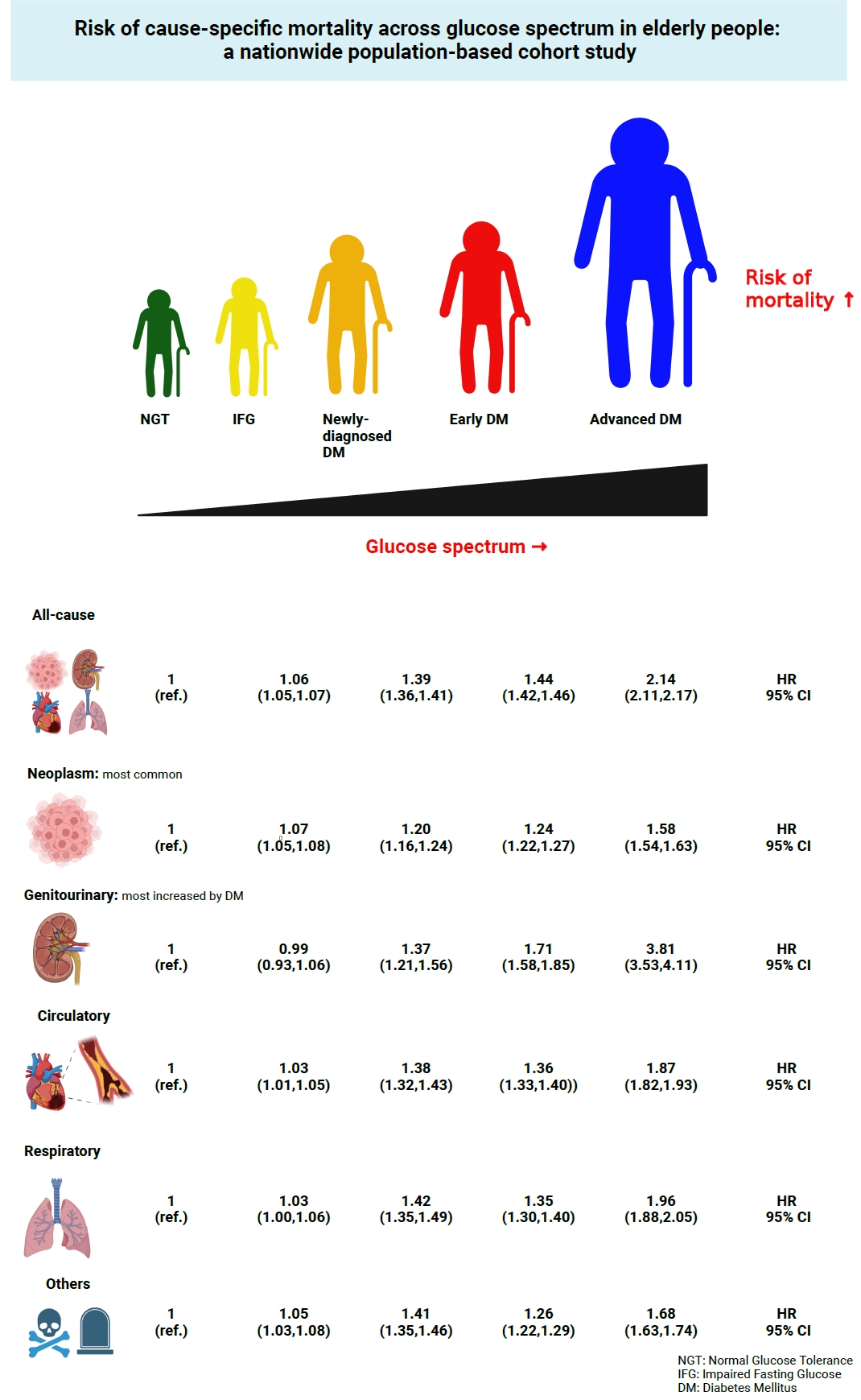
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee, Committee of Big Data, Korean Endocrine Society
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):525-537. Published online September 7, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1765
- 1,565 View
- 91 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigated the risk of cause-specific mortality according to glucose tolerance status in elderly South Koreans.
Methods
A total of 1,292,264 individuals aged ≥65 years who received health examinations in 2009 were identified from the National Health Information Database. Participants were classified as normal glucose tolerance, impaired fasting glucose, newly-diagnosed diabetes, early diabetes (oral hypoglycemic agents ≤2), or advanced diabetes (oral hypoglycemic agents ≥3 or insulin). The risk of system-specific and disease-specific deaths was estimated using multivariate Cox proportional hazards analysis.
Results
During a median follow-up of 8.41 years, 257,356 deaths were recorded. Diabetes was associated with significantly higher risk of all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 1.58; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.57 to 1.60); death due to circulatory (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.46 to 1.52), respiratory (HR, 1.51; 95% CI, 1.47 to 1.55), and genitourinary systems (HR, 2.22; 95% CI, 2.10 to 2.35); and neoplasms (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.28 to 1.32). Diabetes was also associated with a significantly higher risk of death due to ischemic heart disease (HR, 1.70; 95% CI, 1.63 to 1.76), cerebrovascular disease (HR, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.41 to 1.50), pneumonia (HR, 1.69; 95% CI, 1.63 to 1.76), and acute or chronic kidney disease (HR, 2.23; 95% CI, 2.09 to 2.38). There was a stepwise increase in the risk of death across the glucose spectrum (P for trend <0.0001). Stroke, heart failure, or chronic kidney disease increased the risk of all-cause mortality at every stage of glucose intolerance.
Conclusion
A dose-dependent association between the risk of mortality from various causes and severity of glucose tolerance was noted in the elderly population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Characteristics and Risk of Mortality in the Elderly Korean Population
Sunghwan Suh
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 522. CrossRef
- The Characteristics and Risk of Mortality in the Elderly Korean Population

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
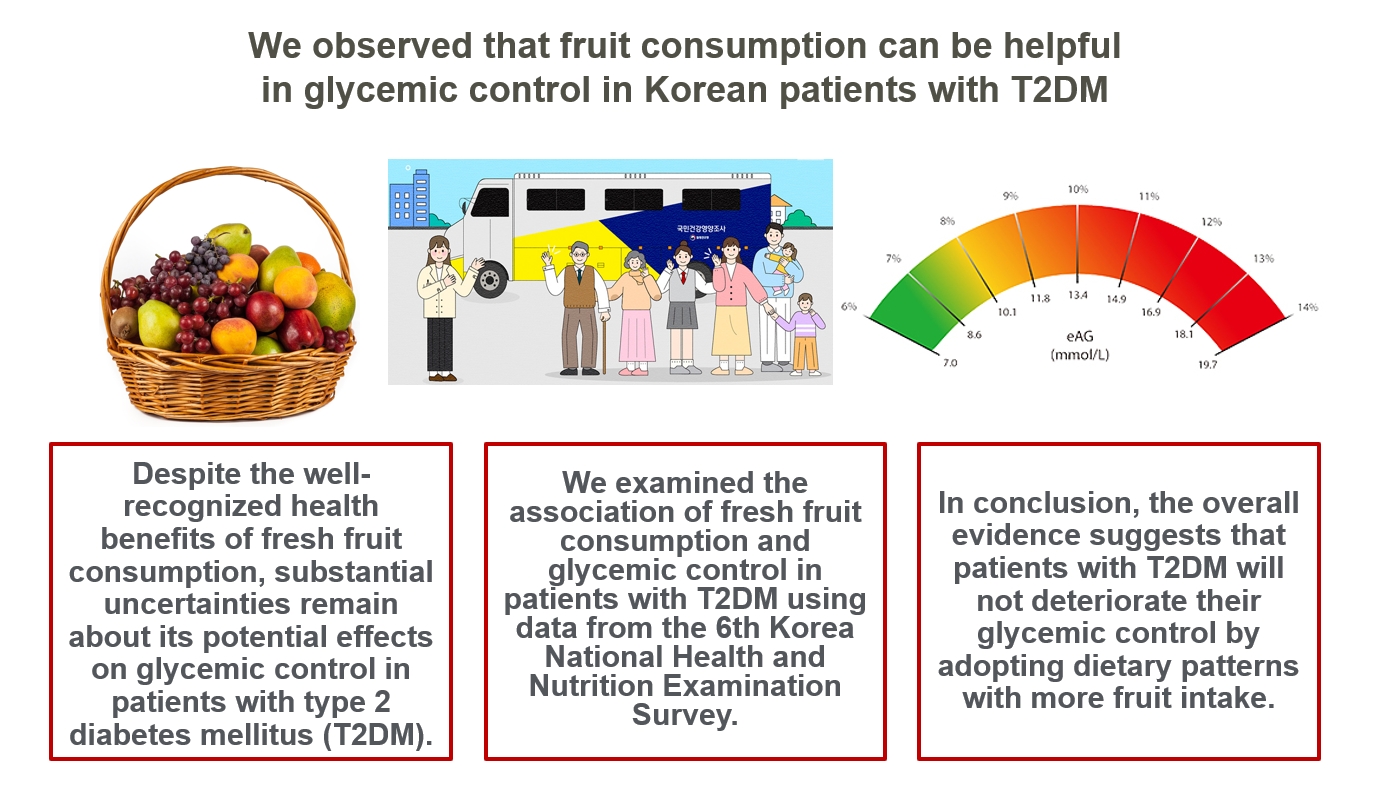
- Intake of Fruit and Glycemic Control in Korean Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Eunju Yoon, Ji Cheol Bae, Sunghwan Suh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):538-544. Published online August 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1730
- 1,922 View
- 110 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Despite the well-recognized health benefits of fresh fruit consumption, there is still substantial uncertainty about its potential effects on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
We examined the association of fresh fruit consumption and glycemic control in patients with T2DM using data from the 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. The study sample was divided into three groups based on weekly fruit consumption frequency for the analysis.
Results
Patients with the highest fruit intake were older than those in the other two groups, and women were more likely to consume fruits in general. Being a current smoker and weekly alcohol intake also showed negative correlations according to the fruit intake tertiles. Fruit consumption was positively correlated with better hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels. Moreover, patients in the highest tertile of fruit intake were 3.48 times more likely to be in good glycemic control defined as HbA1c <7%.
Conclusion
We observed that fruit consumption can be helpful in glycemic control in Korean patients with T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Relationship between Alcohol Consumption and Diabetes in Korean Adults
Gi Tae Kim, Jae Woong Sull
Biomedical Science Letters.2023; 29(3): 159. CrossRef
- The Relationship between Alcohol Consumption and Diabetes in Korean Adults

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Risk of Pancreatic Cancer and Use of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Propensity Score-Matching Analysis
- Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Soon Jib Yoo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):426-435. Published online July 20, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1737

- 2,089 View
- 135 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The effects of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors over the course of long-term treatment remain unclear, and concerns have been raised regarding the role of DPP-4 inhibitors in carcinogenesis in the pancreas. Earlier studies of pancreatic adverse events have reported conflicting results.
Methods
This study analyzed Korean National Health Insurance Service data from January 2009 to December 2012. Patients who had type 2 diabetes mellitus and took two or more oral glucose-lowering drugs (GLDs) were included. Patients prescribed DPP-4 inhibitors (n=51,482) or other GLDs (n=51,482) were matched at a 1:1 ratio using propensity score matching. The risk of pancreatic cancer was calculated using Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox proportional-hazards regression analysis.
Results
During a median follow-up period of 7.95 years, 1,051 new cases of pancreatic cancer were identified. The adjusted hazard ratio (HR) for DPP-4 inhibitor use was 0.99 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.88 to 1.12) compared with the other GLD group. In an analysis limited to cases diagnosed with pancreatic cancer during hospitalization, the adjusted HR for the use of DPP-4 inhibitors was 1.00 (95% CI, 0.86 to 1.17) compared with patients who took other GLDs. Using the other GLD group as the reference group, no trend was observed for elevated pancreatic cancer risk with increased DPP-4 inhibitor exposure.
Conclusion
In this population-based cohort study, DPP-4 inhibitor use over the course of relatively long-term follow-up showed no significant association with an elevated risk of pancreatic cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetes Duration, Cholesterol Levels, and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyu Na Lee, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Diabetes Duration, Cholesterol Levels, and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
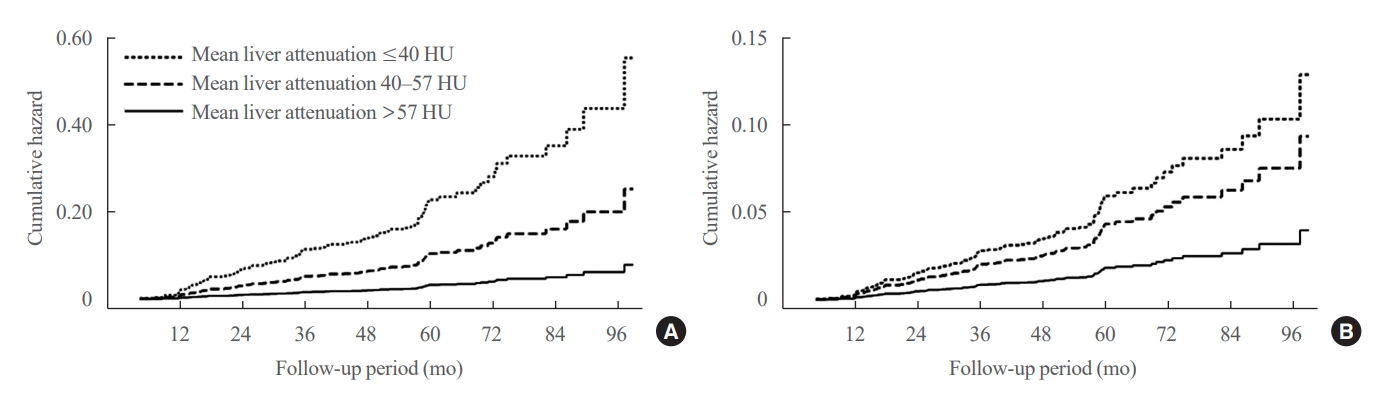
- Greater Severity of Steatosis Is Associated with a Higher Risk of Incident Diabetes: A Retrospective Longitudinal Study
- Ji Min Han, Jung Hwan Cho, Hye In Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Yu-Ji Lee, Jung Won Lee, Kwang Min Kim, Ji Cheol Bae
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):418-425. Published online July 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1729
- 1,049 View
- 77 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Fatty liver is associated with increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. We aimed to evaluate whether the severity of hepatic steatosis is associated with incident diabetes.
Methods
We conducted a longitudinal analysis using data from 1,798 participants who underwent a comprehensive health checkup and abdominal computed tomography (CT). We assessed the association between baseline liver attenuation value on non-contrast CT images and risk of incident diabetes. All the participants were categorized into three groups based on the baseline liver attenuation value on non-contrast CT images: without hepatic steatosis (>57 Hounsfield unit [HU]), mild hepatic steatosis (41–57 HU), and moderate to severe hepatic steatosis (≤40 HU).
Results
During a median follow-up period of 5 years, 6.0% of the study participants progressed to diabetes. The incidence of diabetes was 17.3% in the moderate to severe hepatic steatosis group, 9.0% in the mild steatosis group, and 2.9% in those without hepatic steatosis. In a multivariate adjustment model, as compared with participants without hepatic steatosis, those with moderate to severe steatosis had a hazard ratio (HR) of 3.24 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.64 to 4.2) for the development of diabetes, and those in the mild steatosis group had a HR of 2.33 (95% CI, 1.42 to 3.80). One standard deviation decrease in mean CT attenuation values of the liver was associated with a 40% increase in the development of diabetes (multivariate adjusted HR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.2 to 1.63).
Conclusion
We found a positive association between severity of hepatic steatosis and risk of incident diabetes. Greater severity of steatosis was associated with a higher risk of incident diabetes.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



