Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Endocrinol Metab > Volume 39(1); 2024 > Article
-
Review ArticleDiabetes, obesity and metabolism Initial Combination Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes
 Keypoint
Keypoint
This review explores the rationale behind early combination therapy in type 2 diabetes and provides an overview of its clinical benefits and limitations. Evidence indicates that initial combination therapy has multiple advantages over monotherapy, including long-term durable glycemic control, fewer complications in type 2 diabetes, less frequent treatment failure, and improvement in beta cell function. However, cost-effectiveness and adverse events with combination therapy are issues that should be considered. -
Ji Yoon Kim1
 , Nam Hoon Kim2
, Nam Hoon Kim2
-
Endocrinology and Metabolism 2023;39(1):23-32.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1816
Published online: November 30, 2023
1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding author: Nam Hoon Kim. Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, 73 Goryeodae-ro, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul 02841, Korea Tel: +82-2-920-5421, Fax: +82-2-953-9355, E-mail: pourlife@korea.ac.kr
Copyright © 2024 Korean Endocrine Society
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 2,083 Views
- 250 Download
- ABSTRACT
- INTRODUCTION
- LESSONS FROM LANDMARK TRIALS OF GLYCEMIC CONTROL IN THE EARLY STAGE OF TYPE 2 DIABETES
- INITIAL DUAL COMBINATION THERAPY
- INITIAL TRIPLE COMBINATION THERAPY
- INITIAL COMBINATION THERAPY AND BETA CELL FUNCTION
- INITIAL COMBINATION THERAPY AND COMPLICATIONS
- APPLYING INITIAL COMBINATION THERAPY: SUMMARY AND RECOMMENDATIONS
- CONCLUSIONS
- Article information
- References
ABSTRACT
- Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a progressive disease in which it is challenging to achieve long-term durable glycemic control. However, intensive glycemic control is crucial for preventing diabetes-related complications. Previous studies showed that monotherapy with a stepwise add-on approach was seldom effective for long-term durable glycemic control. Combination therapy, which refers to the use of two or more drugs to control hyperglycemia, has multiple benefits, including the ability to target a variety of pathophysiological processes underlying hyperglycemia. In clinical trials, initial combination therapy showed better glycemic control than monotherapy or a stepwise approach. Emerging evidence indicates that initial combination therapy is associated with preserved β-cell function and fewer complications in T2D. However, cost-effectiveness and adverse events with combination therapy are issues that should be considered. Therefore, initial combination therapy is an important option for patients with T2D that clinicians should consider with a view toward balancing benefits and potential harms. In this review, we summarize the literature addressing initial combination therapy in T2D, and we suggest optimal strategies based on clinical situations and patient characteristics.
- Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is a metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and progressive deterioration of β-cell function [1]. Glycemic control is a crucial component of diabetes management, as hyperglycemia is a significant risk factor for disease progression and vascular complications [2,3]. Although multiple clinical trials have demonstrated that intensive glycemic control reduces the risk of complications [4-6], it remains challenging to achieve long-term durable glycemic control in clinical practice [7,8]. This challenge stems from both the lack of fundamental therapies addressing progressive β-cell dysfunction and therapeutic inertia experienced by healthcare providers and patients [9]. Therapeutic inertia commonly occurs in the traditional stepwise treatment approach, and is observed during treatment intensification or the addition of medications [10,11]. Early combination therapy has been proposed as an approach to rapidly lower blood glucose levels and overcome therapeutic inertia. In this review, we explore the rationale behind early combination therapy in patients with T2D and provide an overview of its clinical benefits and limitations.
INTRODUCTION
- The United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) was a randomized controlled trial comparing intensive glycemic control to conventional glycemic control for microvascular and macrovascular complications in patients who were newly diagnosed with T2D. Intensive glycemic control exhibited a 25% reduction in microvascular endpoints compared to conventional treatment [4]. Long-term follow-up of the UKPDS indicated additional reductions in macrovascular endpoints (a 15% decrease in myocardial infarction) and mortality (a 13% decrease in death from any cause) in the intensive control arm compared to the conventional treatment arm [12]. Although this study provided clear evidence of the benefits of intensive glycemic control in reducing the risk of complications and mortality in newly diagnosed patients with T2D, some limitations need to be considered. First, the study targeted fasting plasma glucose levels rather than glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels (fasting plasma glucose target <6 mmol/L [108 mg/dL] in the intensive control group). Second, the blood glucose-lowering agents used were limited to insulin, sulfonylureas, and metformin. Third, over 10 years, the median HbA1c level was 7.0% in the intensive control group and 7.9% in the conventional control group; however, in the last 3 years, the median HbA1c level increased to 8.1% and 8.7%, respectively. These values indicate high blood glucose levels and cannot be considered to reflect intensive blood glucose control. Post-analysis of the UKPDS revealed high monotherapy failure rates with any medication, including insulin [7]. An increase in HbA1c levels to 7.0% or higher was experienced by approximately 50% of patients within 3 years and 75% within 9 years. This suggested that single-agent therapy was unlikely to ensure long-term durable glycemic control. Therefore, while intensive glycemic control in the early stages of diabetes is an important strategy for preventing complications, there remains a need for alternative strategies beyond monotherapy to achieve sustained glycemic control.
- A Diabetes Outcome Progression Trial (ADOPT) was a randomized controlled trial that compared the effects of three oral antidiabetic agents (metformin, glyburide, and rosiglitazone) on durable glycemic control in recently diagnosed T2D patients [13]. Rosiglitazone demonstrated superior long-term durable glycemic control effects compared to other agents. However, even the rosiglitazone treatment arm approached a mean HbA1c of 7.0% by the 5th year, suggesting primary treatment failure, in a substantial number of patients. Using the HbA1c target of 6.5% recommended by the Korean Diabetes Association [14], more patients could be deemed treatment failures.
- The Glycemia Reduction Approaches in Diabetes: A Comparative Effectiveness Study (GRADE) compared the sustained glycemic-lowering effects of four agents (glimepiride, sitagliptin, liraglutide, insulin glargine) added to metformin therapy in patients with T2D with a disease duration of 10 years or less [15]. The study found that insulin glargine and liraglutide were more effective than other medications in maintaining target HbA1c levels. Despite some differences between agents, a relatively short time (1.9 to 2.4 years) elapsed before HbA1c rose above the target of 7.0% after the addition of the study drugs to metformin.
- These studies primarily involved patients with T2D of relatively short duration. Current diabetes management guidelines suggest lower HbA1c targets (less than 7.0%), especially for patients with a shorter duration of diabetes and those who are younger [16]. However, considering the results of the previously mentioned studies, treatment with a single medication with a stepwise add-on approach is not effective for long-term durable glycemic control.
LESSONS FROM LANDMARK TRIALS OF GLYCEMIC CONTROL IN THE EARLY STAGE OF TYPE 2 DIABETES
- Clinical trials of initial combination therapy have been conducted since the early 2000s (Table 1) [17-36]. Most studies compared the glycemic effects of a dual therapy in combination with metformin to monotherapy with each agent. A study involving metformin and nateglinide as an initial combination therapy showed a significant reduction of HbA1c levels compared to metformin or nateglinide monotherapy at 24 weeks (combination therapy: −1.4%, metformin: −0.8%, nateglinide: −0.5%) [17]. The baseline mean HbA1c of the study patients was 8.3%, and only combination therapy achieved a mean HbA1c level below 7.0%. Similar results were found in a study involving Korean patients with metformin and gemigliptin as the initial dual combination therapy, where the combination therapy showed superiority in HbA1c reduction over monotherapy (combination therapy: −2.1%, metformin: −1.5%, gemigliptin: −1.2%) [18]. Only combination therapy reduced the mean HbA1c level to less than 7.0% after 24 weeks, from a baseline of 8.7%.
- In most clinical trials, initial dual combination therapy showed a greater reduction of HbA1c and a higher probability of achieving the target HbA1c level compared to monotherapy. The reduction of HbA1c levels by initial dual combination therapy was approximately 1.0% to 2.0% depending on the type of medication and baseline HbA1c of the study subjects. In most studies, the basal mean HbA1c level was 8.0% or higher, and the HbA1c target of less than 7.0% could not be achieved with monotherapy. Therefore, combination therapy could be an optimal strategy in patients with diabetes who are first diagnosed with an HbA1c level higher than 8.0%. Nonetheless, most of these clinical studies were conducted over a short period of 6 months to 1 year, meaning that their results do not demonstrate that long-term durable glycemic control can be achieved with initial dual combination therapy.
- The Vildagliptin Efficacy in combination with metfoRmIn For earlY treatment of type 2 diabetes (VERIFY) study is one of the few large-scale studies that demonstrated the long-term (5 years) effect of initial dual combination therapy [19]. This study, which included 2001 newly diagnosed patients with T2D who had initial HbA1c level of 6.5% to 7.5%, compared the time to treatment failure (HbA1c ≥7.0%) between one group starting with metformin and adding vildagliptin and another starting with the combination of metformin and vildagliptin. The median time to initial treatment failure was significantly longer in the initial combination therapy group than in the initial metformin monotherapy group (61.9 months vs. 36.1 months; hazard ratio [HR], 0.51; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.45 to 0.58). Moreover, the relative risk for time to second treatment failure (i.e., when combination therapy failed in both groups), was significantly lower in the initial combination therapy group (HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.63 to 0.86). This demonstrated the advantage of initial combination therapy over stepwise therapy in terms of durable glycemic control. However, this study also has some limitations. First, since the subjects’ initial HbA1c was limited to 6.5% to 7.5% at baseline, it would be inappropriate to apply the findings to patients whose HbA1c is 7.5% or higher. Second, the study used metformin and vildagliptin, making it challenging to generalize the results to other antidiabetic agents. Third, at the end of the study, even in the initial combination therapy group, fewer than 70% achieved HbA1c levels below 7.0% and fewer than half reached levels below 6.5%. Considering that study patients had initial HbA1c levels below 7.5%, this underscores the challenge of long-term glycemic control.
INITIAL DUAL COMBINATION THERAPY
- The Efficacy and Durability of Initial Combination Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes (EDICT) study validated the effects of initial triple combination therapy on durable glycemic control in patients with T2D [20,36]. This study compared the glucose-lowering effects of initial triple combination therapy (metformin, pioglitazone, and exenatide) and a stepwise treatment strategy initiated with metformin, followed by the addition of sulfonylurea and insulin glargine, for a 3-year period in drug-naïve, recently diagnosed patients with T2D. After 2 years of treatment, the initial triple combination therapy group showed significantly greater HbA1c reductions (achieved HbA1c, 6.0% vs. 6.5% from a baseline HbA1c of 8.6%; P<0.001) than the stepwise therapy group. In the second year, 83% of patients in the initial triple therapy group achieved HbA1c levels below 6.5%, significantly exceeding the proportion of 56% in the stepwise therapy group. Furthermore, the initial triple therapy group exhibited significant weight loss (−1.2 kg vs. 4.1 kg) and fewer occurrences of hypoglycemia (14% vs. 46%) compared to the stepwise therapy group. Even after 3 years of follow-up, the initial triple therapy group maintained an average HbA1c level of 6.4%, significantly lower than the 6.9% in the stepwise therapy group (baseline HbA1c, 8.9%) [36]. This study was the first to verify the efficacy of triple-drug combination therapy in patients with T2D, demonstrating the superiority of triple combination therapy over stepwise therapy in terms of long-term durable glycemic control. In particular, patients with a baseline HbA1c of 8.5% or higher experienced a significant reduction of 4.1% in HbA1c over 2 years; this potent glycemic-lowering effect surpassed that of any previous treatment regimens. However, this study had limitations, as it was a relatively small-scale study conducted at a single institution, and the patient retention rate was low (58%) in the initial triple therapy group in the 2nd year.
- Another study involving initial triple combination therapy is the Efficacy and tolerability of initial triple combination therapy with metformin, dapagliflozin, and saxagliptin compared with stepwise add-on therapy in drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes (TRIPLE-AXEL) study [37]. In that study, patients newly diagnosed with T2D having a baseline HbA1c of 8.0% or higher were allocated to receive triple combination therapy (metformin, dapagliflozin, and saxagliptin) or a stepwise therapy initiated with metformin, followed by addition of glimepiride and sitagliptin for 2 years. The primary outcome was the proportion of patients who achieved HbA1c less than 6.5% at 104 weeks without hypoglycemia, weight gain greater than 5%, or drug discontinuation due to side effects. Unlike the EDICT study, the triple combination regimen involved only oral antidiabetic drugs and included sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. The study was completed at the end of 2022 and is awaiting publication, with particular attention given to the findings of a novel initial triple combination therapy.
INITIAL TRIPLE COMBINATION THERAPY
- T2D is characterized by progressive deterioration of β-cell function, with an annual decline ranging from 1.8% to 9.5% [38,39]. β-cell dysfunction progresses rapidly after the onset of T2D, and glucotoxicity is one of the major factors involved [40-42]. Therefore, early intensive glycemic control in T2D is a promising strategy for preserving β-cell function. This has been supported by several clinical trials involving initial dual and triple combination therapy discussed earlier.
- A 24-week clinical trial comparing the combination of sitagliptin and metformin to each treatment alone measured β-cell responsivity to a mixed meal tolerance test using a C-peptide minimal model [43]. After 24 weeks of treatment, the sitagliptin and metformin combination therapy showed better β-cell function than the monotherapy groups. Changes in β-cell function were significantly correlated with changes in HbA1c levels, implying that glucose reduction significantly impacted β-cell function. A study comparing the glycemic effects of placebo, alogliptin, and an alogliptin/pioglitazone combination over 16 weeks in patients with recent-onset T2D measured β-cell function changes using a standardized meal test [44]. The alogliptin/pioglitazone combination showed a significant increase in the insulin secretion rate compared to placebo, while alogliptin alone did not. The EDICT study also measured β-cell function changes based on a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test over 3 years [36]. Compared to conventional therapy, the triple combination therapy group demonstrated significant improvements in insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion. While insulin sensitivity (Matsuda index) remained unchanged in the conventional therapy group, it increased by over 3-fold in the triple combination therapy group. β-cell function (quantified using the disposition index) increased 1.5-fold in the conventional therapy group, whereas it increased by over 30-fold in the triple combination therapy group. The most likely explanation for these results is that pioglitazone and exenatide improved insulin sensitivity and β-cell function, along with glucose reduction with the triple combination therapy.
- These studies indicate that early combination therapy is more effective in improving or preserving β-cell function than monotherapy. However, it remains unclear to what extent the effects are due to HbA1c reduction or the medications themselves. Except for the EDICT study, the other studies involved short-term follow-up (24 weeks or less), indicating a need for more long-term studies to explore which drug combinations are effective both for glycemic reduction and for β-cell function improvement.
INITIAL COMBINATION THERAPY AND BETA CELL FUNCTION
- Little is known about the cardiovascular or renal effects of initial combination therapy. Previous studies mainly targeted patients newly diagnosed with T2D who were not at high cardiovascular risk. Additionally, most of the studies had relatively short durations (within 1 year). For these reasons, there was a low occurrence of cardiovascular or renal events. The VERIFY study, the study with the longest follow-up in this context, observed adverse cardiovascular events (cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction or stroke, and hospitalization for heart failure) [19]. However, there were few events, with 24 in the early combination therapy group and 33 in the monotherapy group. Nonetheless, the early combination therapy group exhibited a numerically lower risk of macrovascular events (2.4% vs. 3.3%; HR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.42 to 1.19). There is also a paucity of studies measuring the occurrence of microvascular complications. The UKPDS study, which spanned over 10 years, reported an 8.9% (346/3,867) occurrence rate of microvascular events [4]. Therefore, larger and longer-term studies are necessary to clarify whether early combination therapy reduces complications. Some cohort studies suggest that the extent of glucose reduction immediately after diabetes onset is associated both with the durability of glycemic control and a decreased risk of microvascular complications [45-47].
INITIAL COMBINATION THERAPY AND COMPLICATIONS
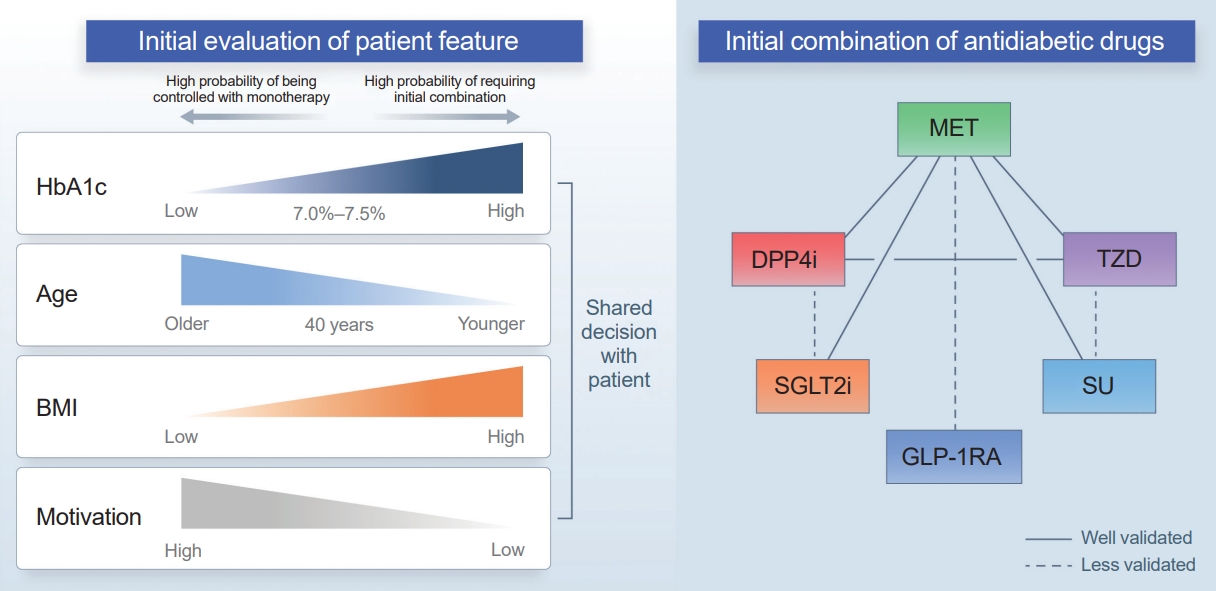
- Most guidelines for the management of T2D now consider initial combination therapy as an important option. The American Diabetes Association guidelines state that patients with initial HbA1c levels 1.5% to 2.0% above target are primary candidates for early combination therapy [48]. The American Association of Clinical Endocrinology guidelines also recommend initial combination therapy for patients with initial HbA1c levels above 7.5% [49]. In addition, if the HbA1c level is above 9.0% or exceeds the target by 1.5%, triple combination therapy could be considered. The Korean Diabetes Association guidelines strongly recommend early combination therapy to reduce the risk of treatment failure, especially for patients with HbA1c levels above 7.5% or exceeding the target by 1.5% [14]. Accordingly, the initial HbA1c level would be the most important consideration for choosing whether to administer initial combination therapy to patients with T2D.
- In our opinion, initial combination therapy should be considered as the basic approach except for patients who are expected to be well-controlled with monotherapy, rather than considering initial monotherapy as the basic approach. Initial combination therapy is needed for all patients who are expected to have difficulty achieving the target HbA1c level with initial monotherapy. Most dual combination therapy studies have demonstrated that achieving an HbA1c less than 7.0% with monotherapy alone is challenging within 6 months. In particular, early combination therapy should be considered for all patients with HbA1c levels of 7.5% or higher, considering that the inclusion criteria in most studies were an HbA1c level ≥7.0% to 7.5%, and that the baseline mean HbA1c level was ≥8.0%. The type of drugs to be combined, the glucose-lowering effect of the drugs, and the durability of glycemic control should all be considered.
- Another consideration is the patient’s age at diagnosis. A subanalysis of the VERIFY study showed that patients aged ≤40 years had a higher second treatment failure rate than those older than 40 years. Younger patients in the early combination group showed a higher treatment failure rate than both older patients in the early combination group and older patients in the monotherapy group [50]. In several clinical trials, patients with youthonset T2D often showed less effective glucose-lowering effects than adult patients [38,51-54]. This might be due to unique pathophysiology in younger patients, such as strong associations with obesity and aggravated β-cell dysfunction; alternatively, it could be attributed to lower compliance, which is observed more frequently in young patients [55].
- Determining the best drug combination is challenging (Fig. 1). Considering only glycemic control, combining drugs with strong glucose-lowering effects would be beneficial for patients with higher initial HbA1c levels. However, hypoglycemia, weight gain, and the side effects of drugs are essential considerations regarding early intensive therapy. Most clinical trials have focused on metformin-based combination therapy. Metformin has strong glucose-lowering effects, no risk of weight gain, and is cost-effective. One aspect warranting attention is the gastrointestinal side effects that commonly occur when a high dose of metformin is used initially. If atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, heart failure, or chronic kidney disease is present, a treatment regimen including an SGLT2 inhibitor or glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) should be considered [14,48,56]. Although few patients experience these complications at the time of diabetes diagnosis, SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1RAs could also be considered for obese patients or those with several cardiovascular risk factors. Thiazolidinedione is the most effective drug for improving insulin resistance and has a durable glucose-lowering effect. Therefore, it can be considered first in patients with insulin resistance or metabolic syndrome; however, due to its side effects (such as weight gain or edema), combination therapy with drugs that have a weight-reducing effect can be helpful. Sulfonylureas have powerful glucose-lowering effects; however, caution related to hypoglycemia is needed. Thus, starting with a low dose and then escalating the dose would be necessary.
APPLYING INITIAL COMBINATION THERAPY: SUMMARY AND RECOMMENDATIONS
- Current guidelines for the management of T2D recommend initial combination therapy to reduce the treatment failure rate, especially for those with marked hyperglycemia. Evidence indicates that initial combination therapy has multiple advantages over monotherapy, including long-term durable glycemic control, less frequent treatment failure, and improvement in β-cell function. Some trials have shown the benefit of initial triple combination therapy over sequential therapy. The cardiovascular or renal benefits of initial combination therapy have not been validated and require more evidence.
CONCLUSIONS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Article information
-
Acknowledgements
- This work was supported by the Korean Endocrine Society New Faculty Research Award 2018.
| Study | Drugs for combination therapy | Duration of study | Inclusion criterion for HbA1c, % | Mean HbA1c level at baseline, % | Changes in mean HbA1c level from baseline, %a | Estimated mean achieved HbA1c level, %a,b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual combination therapy | |||||||||
| SU/Glinide+MET | |||||||||
| Horton et al. (2000) [17] | Nateglinide+metformin | 24 wk | 6.8–11.0 | 8.3 | Combination therapy: −1.4 | Combination therapy: 6.9 | |||
| Nateglinide monotherapy: −0.5 | Nateglinide monotherapy: 7.8 | ||||||||
| Metformin monotherapy: −0.8 | Metformin monotherapy: 7.5 | ||||||||
| Garber et al. (2002) [21] | Glyburide+metformin | 20 wk | 7.0–11.0 | 8.2 | Combination therapy: −1.5 | Combination therapy: 6.7 | |||
| Glyburide monotherapy: −1.2 | Glyburide monotherapy: 7.0 | ||||||||
| Metformin monotherapy: −1.0 | Metformin monotherapy: 7.2 | ||||||||
| DPP4i+MET | |||||||||
| Goldstein et al. (2007) [22] | Sitagliptin+metformin | 24 wk | 7.5–11.0 | 8.8 | Combination therapy: −1.9 | Combination therapy: 6.9 | |||
| Sitagliptin monotherapy: −0.7 | Sitagliptin monotherapy: 8.1 | ||||||||
| Metformin monotherapy: −1.1 | Metformin monotherapy: 7.7 | ||||||||
| Bosi et al. (2009) [23] | Vildagliptin+metformin | 24 wk | 7.5–11.0 | 8.7 | Combination therapy: −1.8 | Combination therapy: 6.9 | |||
| Vildagliptin monotherapy: −1.1 | Vildagliptin monotherapy: 7.6 | ||||||||
| Metformin monotherapy: −1.4 | Metformin monotherapy: 7.3 | ||||||||
| Williams-Herman et al. (2009) [24] | Sitagliptin+metformin | 54 wk | 7.5–11.0 | 8.7 | Combination therapy: −1.8 | Combination therapy: 6.9 | |||
| Sitagliptin monotherapy: −0.8 | Sitagliptin monotherapy: 7.9 | ||||||||
| Metformin monotherapy: −1.3 | Metformin monotherapy: 7.4 | ||||||||
| Jadzinsky et al. (2009) [25] | Saxagliptin+metformin | 24 wk | 8.0–12.0 | 9.5 | Combination therapy: −2.5 | Combination therapy: 7.0 | |||
| Saxagliptin monotherapy: −1.7 | Saxagliptin monotherapy: 7.8 | ||||||||
| Metformin monotherapy: −2.0 | Metformin monotherapy: 7.5 | ||||||||
| Haak et al. (2012) [26] | Linagliptin+metformin | 24 wk | 7.0–11.0 | 8.7 | Combination therapy: −1.6 | Combination therapy: 7.1 | |||
| Linagliptin monotherapy: −0.5 | Linagliptin monotherapy: 8.2 | ||||||||
| Metformin monotherapy: −1.1 | Metformin monotherapy: 7.6 | ||||||||
| Lim et al. (2017) [18] | Gemigliptin+metformin | 24 wk | 7.5–11.0 | 8.7 | Combination therapy: −2.1 | Combination therapy: 6.6 | |||
| Gemigliptin monotherapy: −1.2 | Gemigliptin monotherapy: 7.5 | ||||||||
| Metformin monotherapy: −1.5 | Metformin monotherapy: 7.2 | ||||||||
| Matthews et al. (2019) [19]c | Vildagliptin+metformin | 5 yr | 6.5–7.5 | 6.7 | Combination therapy: | ||||
| 63% of the participants achieved HbA1c <7.0 | |||||||||
| 39% of the participants achieved HbA1c <6.5 | |||||||||
| Sequential therapy: | |||||||||
| 57% of the participants achieved HbA1c <7.0 | |||||||||
| 27% of the participants achieved HbA1c <6.5 | |||||||||
| TZD+MET | |||||||||
| Rosenstock et al. (2006) [27] | Rosiglitazone+metformin | 32 wk | 7.5–11.0 | 8.8 | Combination therapy: −2.3 | Combination therapy: 6.5 | |||
| Rosiglitazone monotherapy: −1.8 | Rosiglitazone monotherapy: 7.0 | ||||||||
| Metformin monotherapy: −1.6 | Metformin monotherapy: 7.2 | ||||||||
| Perez et al. (2009) [28] | Pioglitazone+metformin | 24 wk | 7.5–10.0 | 8.7 | Combination therapy: −1.8 | Combination therapy: 6.9 | |||
| Pioglitazone monotherapy: −1.0 | Pioglitazone monotherapy: 7.7 | ||||||||
| Metformin monotherapy: −1.0 | Metformin monotherapy: 7.7 | ||||||||
| SGLT2i+MET | |||||||||
| Henry et al. (2012) [29] | Dapagliflozin+metformin | 24 wk | 7.5–12.0 | 9.1 | Combination therapy: −2.0 | Combination therapy: 7.1 | |||
| Dapagliflozin monotherapy: −1.5 | Dapagliflozin monotherapy: 7.6 | ||||||||
| Metformin monotherapy: −1.4 | Metformin monotherapy: 7.7 | ||||||||
| Hadjadj et al. (2016) [30] | Empagliflozin+metformin | 24 wk | 7.5–12.0 | 8.7 | Combination therapy: −2.1 | Combination therapy: 6.6 | |||
| Empagliflozin monotherapy: −1.4 | Empagliflozin monotherapy: 7.3 | ||||||||
| Metformin monotherapy: −1.8 | Metformin monotherapy: 6.9 | ||||||||
| Rosenstock et al. (2016) [31] | Canagliflozin+metformin | 26 wk | 7.5–12.0 | 8.8 | Combination therapy: −1.8 | Combination therapy: 7.0 | |||
| Canagliflozin monotherapy: −1.4 | Canagliflozin monotherapy: 7.4 | ||||||||
| Metformin monotherapy: −1.3 | Metformin monotherapy: 7.5 | ||||||||
| DPP4i+TZD | |||||||||
| Rosenstock et al. (2007) [32] | Vildagliptin+pioglitazone | 24 wk | 7.5–11.0 | 8.7 | Combination therapy: −1.9 | Combination therapy: 6.8 | |||
| Vildagliptin monotherapy: −1.1 | Vildagliptin monotherapy: 7.6 | ||||||||
| Pioglitazone monotherapy: −1.4 | Pioglitazone monotherapy: 7.3 | ||||||||
| Rosenstock et al. (2010) [33] | Alogliptin+pioglitazone | 26 wk | 7.5–11.0 | 8.8 | Combination therapy: −1.7 | Combination therapy: 7.1 | |||
| Alogliptin monotherapy: −1.0 | Alogliptin monotherapy: 7.8 | ||||||||
| Pioglitazone monotherapy: −1.2 | Pioglitazone monotherapy: 7.6 | ||||||||
| Henry et al. (2014) [34]d | Sitagliptin+pioglitazone | 24 wk | 7.5–11.0 | 8.8 | Combination therapy: −1.8 | Combination therapy: 7.0 | |||
| Sitagliptin monotherapy: −1.1 | Sitagliptin monotherapy: 7.7 | ||||||||
| Pioglitazone monotherapy: −1.2 | Pioglitazone monotherapy: 7.6 | ||||||||
| DPP4i+SGLT2i | |||||||||
| Lewin et al. (2015) [35]e | Linagliptin+empagliflozin | 24 wk | 7.0–10.5 | 8.0 | Combination therapy: −1.1 | Combination therapy: 6.9 | |||
| Linagliptin monotherapy: −0.7 | Linagliptin monotherapy: 7.3 | ||||||||
| Empagliflozin monotherapy: −1.0 | Empagliflozin monotherapy: 7.0 | ||||||||
| Triple combination therapy | |||||||||
| Abdul-Ghani et al. (2021) [36]f | Metformin+pioglitazone+exenatide | 3 yr | No limit (the range of initial HbA1c, 6.5–14.0) | 8.9 | Triple combination therapy: −2.6 | Triple combination therapy: 6.4 | |||
| Sequential therapy (sequential addition of metformin followed by glipizide and insulin): −2.0 | Sequential therapy (sequential addition of metformin followed by glipizide and insulin): 6.9 | ||||||||
HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; SU, sulfonylurea; MET, metformin; DPP4i, dipeptidylpeptidase-4 inhibitor; TZD, thiazolidinedione; SGLT2i, sodiumglucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor.
a The results of RCTs that tested multiple doses are presented based on the highest doses used;
b This value is calculated as mean HbA1c level at baseline minus changes in mean HbA1c level from baseline. Please note that this calculated value may not be exactly the same as the actual mean value;
c Changes in mean HbA1c levels were not reported. Instead, the percentages of participants achieving HbA1c levels <7.0% and <6.5% were presented;
d,e These studies were conducted for 54 weeksd and 52 weekse, respectively, however, week 24 was the primary time point for efficacy analyses. The results presented here are those from week 24;
f Changes in mean HbA1c level from baseline are calculated as mean achieved HbA1c level minus mean HbA1c level at baseline. Please note that this calculated value may differ from the actual value.
- 1. Kahn SE. The relative contributions of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction to the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2003;46:3–19.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. Marcovecchio ML, Lucantoni M, Chiarelli F. Role of chronic and acute hyperglycemia in the development of diabetes complications. Diabetes Technol Ther 2011;13:389–94.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Poitout V, Robertson RP. Minireview: secondary beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes: a convergence of glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity. Endocrinology 2002;143:339–42.ArticlePubMed
- 4. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998;352:837–53.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Nathan DM, Cleary PA, Backlund JY, Genuth SM, Lachin JM, Orchard TJ, et al. Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2005;353:2643–53.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Hayward RA, Reaven PD, Wiitala WL, Bahn GD, Reda DJ, Ge L, et al. Follow-up of glycemic control and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2015;372:2197–206.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Turner RC, Cull CA, Frighi V, Holman RR. Glycemic control with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: progressive requirement for multiple therapies (UKPDS 49). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. JAMA 1999;281:2005–12.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Ko JH, Kim TN. Type 2 diabetes remission with significant weight loss: definition and evidence-based interventions. J Obes Metab Syndr 2022;31:123–33.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Reach G, Pechtner V, Gentilella R, Corcos A, Ceriello A. Clinical inertia and its impact on treatment intensification in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab 2017;43:501–11.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Russell-Jones D, Pouwer F, Khunti K. Identification of barriers to insulin therapy and approaches to overcoming them. Diabetes Obes Metab 2018;20:488–96.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 11. Pantalone KM, Wells BJ, Chagin KM, Ejzykowicz F, Yu C, Milinovich A, et al. Intensification of diabetes therapy and time until A1C goal attainment among patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes who fail metformin monotherapy within a large integrated health system. Diabetes Care 2016;39:1527–34.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR, Neil HA. 10-Year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;359:1577–89.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Kahn SE, Haffner SM, Heise MA, Herman WH, Holman RR, Jones NP, et al. Glycemic durability of rosiglitazone, metformin, or glyburide monotherapy. N Engl J Med 2006;355:2427–43.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Hur KY, Moon MK, Park JS, Kim SK, Lee SH, Yun JS, et al. 2021 Clinical practice guidelines for diabetes mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:461–81.PubMedPMC
- 15. GRADE Study Research Group, Nathan DM, Lachin JM, Balasubramanyam A, Burch HB, Buse JB, et al. Glycemia reduction in type 2 diabetes: glycemic outcomes. N Engl J Med 2022;387:1063–74.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, Bannuru RR, Brown FM, Bruemmer D, et al. 6. Glycemic targets: standards of care in diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care 2023;46(Suppl 1):S97–110.
- 17. Horton ES, Clinkingbeard C, Gatlin M, Foley J, Mallows S, Shen S. Nateglinide alone and in combination with metformin improves glycemic control by reducing mealtime glucose levels in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000;23:1660–5.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 18. Lim S, Han KA, Yu J, Chamnan P, Kim ES, Yoon KH, et al. Efficacy and safety of initial combination therapy with gemigliptin and metformin compared with monotherapy with either drug in patients with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind randomized controlled trial (INICOM study). Diabetes Obes Metab 2017;19:87–97.PubMed
- 19. Matthews DR, Paldanius PM, Proot P, Chiang Y, Stumvoll M, Del Prato S, et al. Glycaemic durability of an early combination therapy with vildagliptin and metformin versus sequential metformin monotherapy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes (VERIFY): a 5-year, multicentre, randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet 2019;394:1519–29.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Abdul-Ghani MA, Puckett C, Triplitt C, Maggs D, Adams J, Cersosimo E, et al. Initial combination therapy with metformin, pioglitazone and exenatide is more effective than sequential add-on therapy in subjects with new-onset diabetes: results from the Efficacy and Durability of Initial Combination Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes (EDICT): a randomized trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 2015;17:268–75.PubMedPMC
- 21. Garber AJ, Larsen J, Schneider SH, Piper BA, Henry D; Glyburide/Metformin Initial Therapy Study Group. Simultaneous glyburide/metformin therapy is superior to component monotherapy as an initial pharmacological treatment for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 2002;4:201–8.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Goldstein BJ, Feinglos MN, Lunceford JK, Johnson J, Williams-Herman DE; Sitagliptin 036 Study Group. Effect of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, and metformin on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007;30:1979–87.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 23. Bosi E, Dotta F, Jia Y, Goodman M. Vildagliptin plus metformin combination therapy provides superior glycaemic control to individual monotherapy in treatment-naive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab 2009;11:506–15.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Williams-Herman D, Johnson J, Teng R, Luo E, Davies MJ, Kaufman KD, et al. Efficacy and safety of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin and metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 54-week study. Curr Med Res Opin 2009;25:569–83.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Jadzinsky M, Pfutzner A, Paz-Pacheco E, Xu Z, Allen E, Chen R, et al. Saxagliptin given in combination with metformin as initial therapy improves glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes compared with either monotherapy: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 2009;11:611–22.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Haak T, Meinicke T, Jones R, Weber S, von Eynatten M, Woerle HJ. Initial combination of linagliptin and metformin improves glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Obes Metab 2012;14:565–74.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Rosenstock J, Rood J, Cobitz A, Biswas N, Chou H, Garber A. Initial treatment with rosiglitazone/metformin fixed-dose combination therapy compared with monotherapy with either rosiglitazone or metformin in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 2006;8:650–60.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Perez A, Zhao Z, Jacks R, Spanheimer R. Efficacy and safety of pioglitazone/metformin fixed-dose combination therapy compared with pioglitazone and metformin monotherapy in treating patients with T2DM. Curr Med Res Opin 2009;25:2915–23.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Henry RR, Murray AV, Marmolejo MH, Hennicken D, Ptaszynska A, List JF. Dapagliflozin, metformin XR, or both: initial pharmacotherapy for type 2 diabetes, a randomised controlled trial. Int J Clin Pract 2012;66:446–56.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Hadjadj S, Rosenstock J, Meinicke T, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC. Initial combination of empagliflozin and metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016;39:1718–28.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 31. Rosenstock J, Chuck L, Gonzalez-Ortiz M, Merton K, Craig J, Capuano G, et al. Initial combination therapy with canagliflozin plus metformin versus each component as monotherapy for drug-naïve type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016;39:353–62.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 32. Rosenstock J, Kim SW, Baron MA, Camisasca RP, Cressier F, Couturier A, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of initial combination therapy with vildagliptin and pioglitazone compared with component monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 2007;9:175–85.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Rosenstock J, Inzucchi SE, Seufert J, Fleck PR, Wilson CA, Mekki Q. Initial combination therapy with alogliptin and pioglitazone in drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2010;33:2406–8.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 34. Henry RR, Staels B, Fonseca VA, Chou MZ, Teng R, Golm GT, et al. Efficacy and safety of initial combination treatment with sitagliptin and pioglitazone: a factorial study. Diabetes Obes Metab 2014;16:223–30.ArticlePubMed
- 35. Lewin A, DeFronzo RA, Patel S, Liu D, Kaste R, Woerle HJ, et al. Initial combination of empagliflozin and linagliptin in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015;38:394–402.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 36. Abdul-Ghani M, Puckett C, Adams J, Khattab A, Baskoy G, Cersosimo E, et al. Durability of triple combination therapy versus stepwise addition therapy in patients with new-onset T2DM: 3-year follow-up of EDICT. Diabetes Care 2021;44:433–9.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 37. Kim NH, Lim S, Kwak SH, Moon MK, Moon JS, Lee YH, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of novel triple combination therapy in drug-naïve patients with type 2 diabetes from the TRIPLE-AXEL trial: protocol for an open-label randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2018;8:e022448.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 38. Nadeau KJ, Anderson BJ, Berg EG, Chiang JL, Chou H, Copeland KC, et al. Youth-onset type 2 diabetes consensus report: current status, challenges, and priorities. Diabetes Care 2016;39:1635–42.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 39. Gao Z, Yan W, Fang Z, Zhang Z, Yuan L, Wang X, et al. Annual decline in β-cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes in China. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2021;37:e3364.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 40. Bagust A, Beale S. Deteriorating beta-cell function in type 2 diabetes: a long-term model. QJM 2003;96:281–8.ArticlePubMed
- 41. Kahn SE. Clinical review 135: the importance of beta-cell failure in the development and progression of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001;86:4047–58.PubMed
- 42. Ahn CH, Oh TJ, Min SH, Cho YM. Incretin and pancreatic β-cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 2023;38:1–9.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 43. Williams-Herman D, Xu L, Teng R, Golm GT, Johnson J, Davies MJ, et al. Effect of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin and metformin on β-cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 2012;14:67–76.ArticlePubMed
- 44. Van Raalte DH, van Genugten RE, Eliasson B, Moller-Goede DL, Mari A, Tura A, et al. The effect of alogliptin and pioglitazone combination therapy on various aspects of β-cell function in patients with recent-onset type 2 diabetes. Eur J Endocrinol 2014;170:565–74.ArticlePubMed
- 45. Kim KJ, Choi JH, Kim KJ, An JH, Kim HY, Kim SG, et al. Determinants of long-term durable glycemic control in new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:284–95.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 46. Kim KJ, Choi J, Bae JH, Kim KJ, Yoo HJ, Seo JA, et al. Time to reach target glycosylated hemoglobin is associated with long-term durable glycemic control and risk of diabetic complications in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 6-year observational study. Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368–78.PubMed
- 47. Laiteerapong N, Ham SA, Gao Y, Moffet HH, Liu JY, Huang ES, et al. The legacy effect in type 2 diabetes: impact of early glycemic control on future complications (the diabetes & aging study). Diabetes Care 2019;42:416–26.PubMed
- 48. ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, Bannuru RR, Brown FM, Bruemmer D, et al. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of care in diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care 2023;46(Suppl 1):S140–57.
- 49. Samson SL, Vellanki P, Blonde L, Christofides EA, Galindo RJ, Hirsch IB, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinology consensus statement: comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm-2023 update. Endocr Pract 2023;29:305–40.ArticlePubMed
- 50. Chan JC, Paldanius PM, Mathieu C, Stumvoll M, Matthews DR, Del Prato S. Early combination therapy delayed treatment escalation in newly diagnosed young-onset type 2 diabetes: a subanalysis of the VERIFY study. Diabetes Obes Metab 2021;23:245–51.PubMed
- 51. Tamborlane WV, Bishai R, Geller D, Shehadeh N, Al-Abdulrazzaq D, Vazquez EM, et al. Once-weekly exenatide in youth with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2022;45:1833–40.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 52. Arslanian SA, Hannon T, Zeitler P, Chao LC, Boucher-Berry C, Barrientos-Perez M, et al. Once-weekly dulaglutide for the treatment of youths with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2022;387:433–43.ArticlePubMed
- 53. Tamborlane WV, Laffel LM, Shehadeh N, Isganaitis E, Van Name M, Ratnayake J, et al. Efficacy and safety of dapagliflozin in children and young adults with type 2 diabetes: a prospective, multicentre, randomised, parallel group, phase 3 study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2022;10:341–50.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 54. Laffel LM, Danne T, Klingensmith GJ, Tamborlane WV, Willi S, Zeitler P, et al. Efficacy and safety of the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin versus placebo and the DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin versus placebo in young people with type 2 diabetes (DINAMO): a multicentre, randomised, doubleblind, parallel group, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2023;11:169–81.PubMedPMC
- 55. Yang YS, Han K, Sohn TS, Kim NH. Young-onset type 2 diabetes in South Korea: a review of the current status and unmet need. Korean J Intern Med 2021;36:1049–58.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 56. Saucedo-Orozco H, Voorrips SN, Yurista SR, de Boer RA, Westenbrink BD. SGLT2 inhibitors and ketone metabolism in heart failure. J Lipid Atheroscler 2022;11:1–19.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations


 KES
KES
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite