Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Thyroid
- Exploring the Association between Thyroid Function and Frailty: Insights from Representative Korean Data
- Youn-Ju Lee, Min-Hee Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Jung-Min Lee, Sang Ah Chang, Jeongmin Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):729-738. Published online November 2, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1769
- 1,124 View
- 73 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigates the association between thyroid function and frailty in the old patients using representative data.
Methods
The study was conducted using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey conducted from 2013 to 2015. The study population included 2,416 participants aged 50 years and older with available thyroid function test data. Frailty assessment was performed using the Fried frailty phenotype. The prevalence of frailty was analyzed across different thyroid diseases and thyroid function parameters.
Results
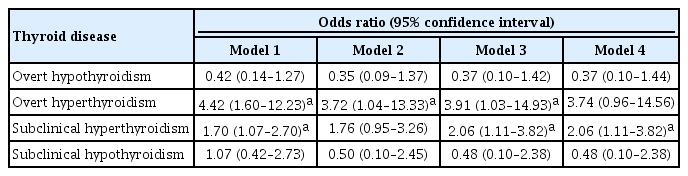
The significant association between thyroid dysfunction and frailty was observed in overt hyperthyroidism and subclinical hyperthyroidism. After adjusting for various factors, the association between thyroid dysfunction and frailty remained significant. On the other hand, overt hypothyroidism did not show a significant association with frailty in the adjusted analysis. For individuals with overt hyperthyroidism and subclinical hyperthyroidism, higher levels of free thyroxine (FT4) were significantly associated with an increased risk of frailty (aOR >999; 95% CI, >999 to 999). Among individuals with overt hypothyroidism, lower level of FT4 levels and high thyrotropin (TSH) levels showed a significant association with frailty risk (FT4: aOR, <0.01; TSH: aOR, 999). In participants with subclinical hypothyroidism, there were no significant associations between parameters for thyroid and frailty risk.
Conclusion
These findings suggest that thyroid dysfunction, particularly overt hyperthyroidism and subclinical hyperthyroidism, may be associated with an increased risk of frailty in the old patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations of thyroid feedback quantile-based index with diabetes in euthyroid adults in the United States and China
Heng Wan, Genfeng Yu, Yajun He, Siyang Liu, Xingying Chen, Yuqi Jiang, Hualin Duan, Xu Lin, Lan Liu, Jie Shen
Annals of Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Associations of thyroid feedback quantile-based index with diabetes in euthyroid adults in the United States and China

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee, Committee of Big Data, Korean Endocrine Society
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):525-537. Published online September 7, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1765
- 1,593 View
- 91 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigated the risk of cause-specific mortality according to glucose tolerance status in elderly South Koreans.
Methods
A total of 1,292,264 individuals aged ≥65 years who received health examinations in 2009 were identified from the National Health Information Database. Participants were classified as normal glucose tolerance, impaired fasting glucose, newly-diagnosed diabetes, early diabetes (oral hypoglycemic agents ≤2), or advanced diabetes (oral hypoglycemic agents ≥3 or insulin). The risk of system-specific and disease-specific deaths was estimated using multivariate Cox proportional hazards analysis.
Results
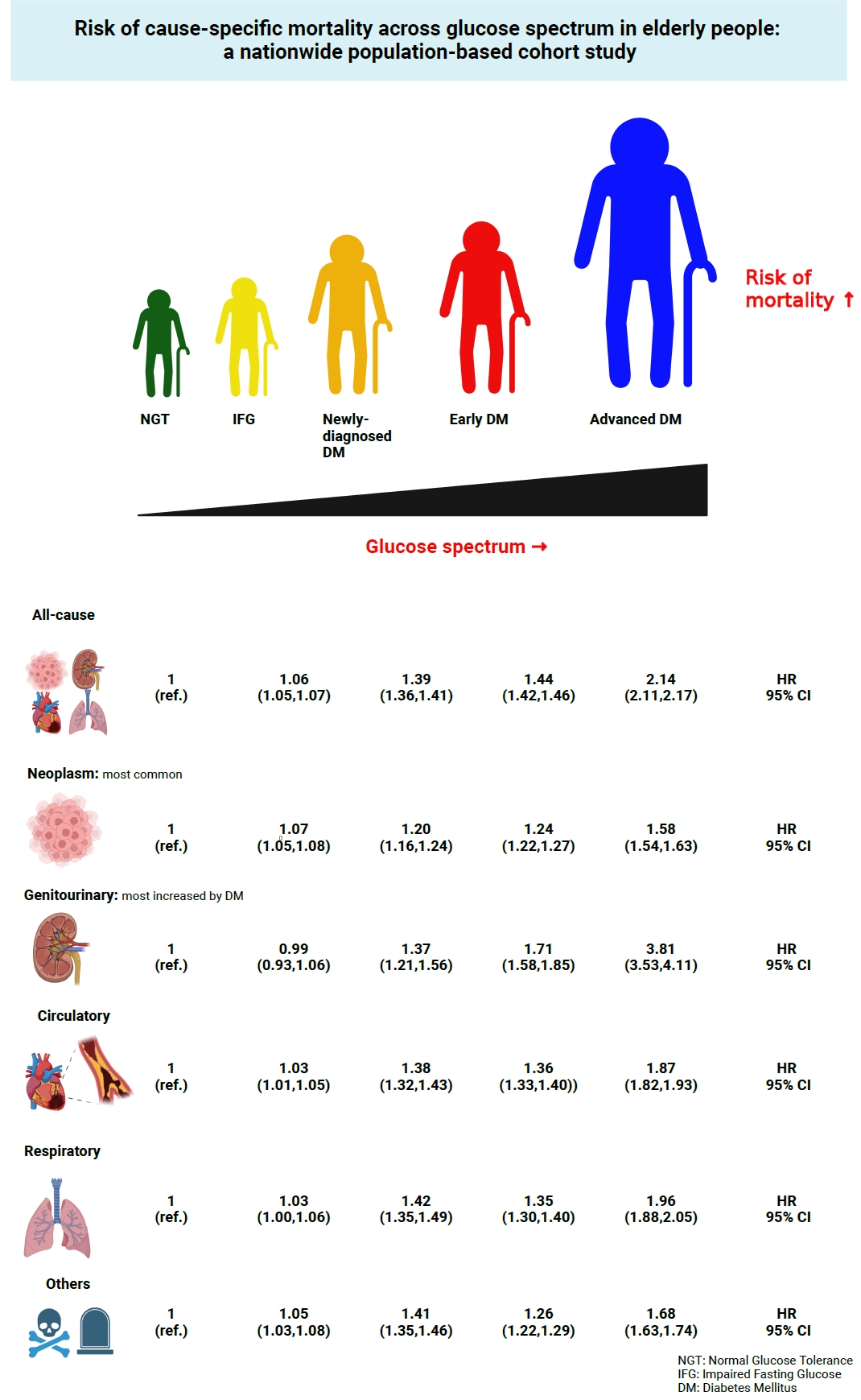
During a median follow-up of 8.41 years, 257,356 deaths were recorded. Diabetes was associated with significantly higher risk of all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 1.58; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.57 to 1.60); death due to circulatory (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.46 to 1.52), respiratory (HR, 1.51; 95% CI, 1.47 to 1.55), and genitourinary systems (HR, 2.22; 95% CI, 2.10 to 2.35); and neoplasms (HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.28 to 1.32). Diabetes was also associated with a significantly higher risk of death due to ischemic heart disease (HR, 1.70; 95% CI, 1.63 to 1.76), cerebrovascular disease (HR, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.41 to 1.50), pneumonia (HR, 1.69; 95% CI, 1.63 to 1.76), and acute or chronic kidney disease (HR, 2.23; 95% CI, 2.09 to 2.38). There was a stepwise increase in the risk of death across the glucose spectrum (P for trend <0.0001). Stroke, heart failure, or chronic kidney disease increased the risk of all-cause mortality at every stage of glucose intolerance.
Conclusion
A dose-dependent association between the risk of mortality from various causes and severity of glucose tolerance was noted in the elderly population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Characteristics and Risk of Mortality in the Elderly Korean Population
Sunghwan Suh
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 522. CrossRef
- The Characteristics and Risk of Mortality in the Elderly Korean Population

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
- Han-sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Jin Yu, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Jeonghoon Ha, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Dong-Jun Lim, Hun-Sung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(4):641-651. Published online August 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1501
- 6,198 View
- 166 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The prevalence of young-onset diabetes (YOD) has been increasing worldwide. As the incidence of YOD increases, it is necessary to determine the characteristics of YOD and the factors that influence its development and associated complications.
Methods
In this retrospective study, we recruited patients who were diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus between June 2001 and December 2021 at a tertiary hospital. The study population was categorized according to age: YOD (age <40 years), middle-age-onset diabetes (MOD, 40≤ age <65 years), and late-onset diabetes (LOD, age ≥65 years). We examined trends in glycemic control by analyzing fasting glucose levels during the first year in each age group. A Cox proportional-hazards model was used to determine the relative risk of developing complications according to glycemic control trends.
Results
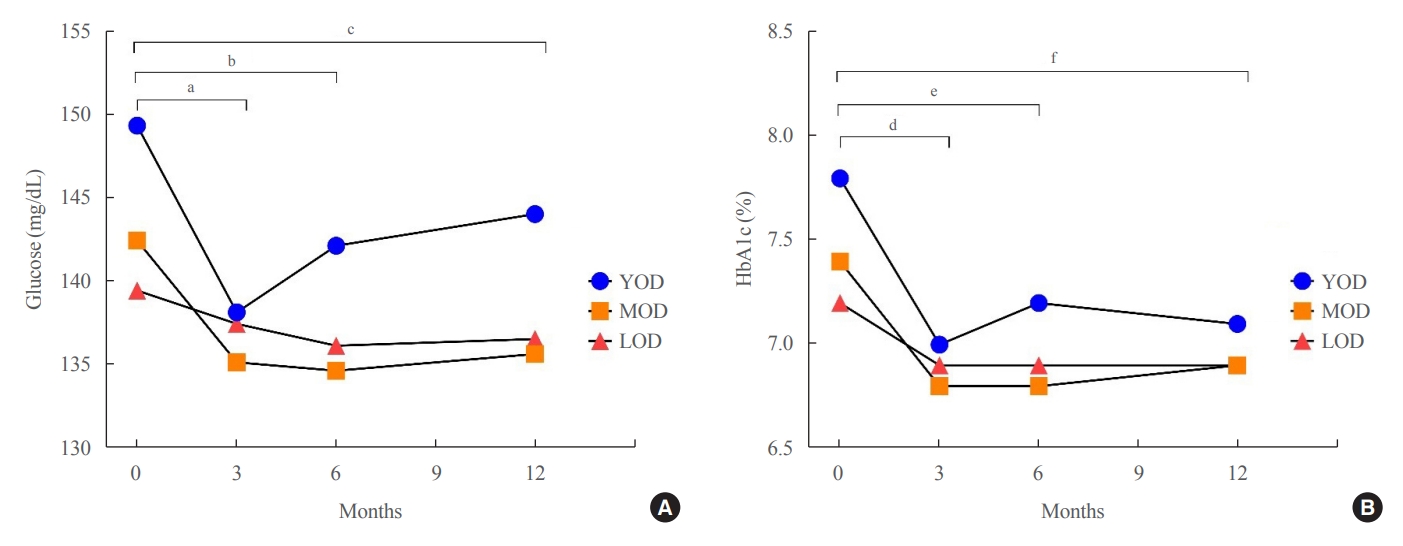
The fasting glucose level at the time of diagnosis was highest in the YOD group (YOD 149±65 mg/dL; MOD 143±54 mg/dL; and LOD 140±55 mg/dL; p=0.009). In the YOD group, glucose levels decreased at 3 months, but increased by 12 months. YOD patients and those with poor glycemic control in the first year were at a higher risk of developing complications, whereas the risk in patients with LOD was not statistically significant.
Conclusion
YOD patients had higher glucose levels at diagnosis, and their glycemic control was poorly maintained. As poor glycemic control can influence the development of complications, especially in young patients, intensive treatment is necessary for patients with YOD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Increased risk of incident mental disorders in adults with new-onset type 1 diabetes diagnosed after the age of 19: A nationwide cohort study
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, So Hyun Cho, Rosa Oh, Ji Yoon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism.2024; 50(1): 101505. CrossRef - Association between age at diagnosis of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality risks: A nationwide population-based study
Da Hea Seo, Mina Kim, Young Ju Suh, Yongin Cho, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, So Hun Kim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 208: 111098. CrossRef - Impact of diabetes distress on glycemic control and diabetic complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hye-Sun Park, Yongin Cho, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, Young Ju Suh, Suk Chon, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Kwan Woo Lee, So Hun Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Early onset type 2 diabetes mellitus: an update
Myrsini Strati, Melpomeni Moustaki, Theodora Psaltopoulou, Andromachi Vryonidou, Stavroula A. Paschou
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Complications and Treatment of Early-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Fahimeh Soheilipour, Naghmeh Abbasi Kasbi, Mahshid Imankhan, Delaram Eskandari
International Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2022;37:641-51, Han-sang Baek et al.)
Han-sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Jin Yu, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Jeonghoon Ha, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Dong-Jun Lim, Hun-Sung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 945. CrossRef -
ISPAD
Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2022: Management of the child, adolescent, and young adult with diabetes in limited resource settings
Anju Virmani, Stuart J. Brink, Angela Middlehurst, Fauzia Mohsin, Franco Giraudo, Archana Sarda, Sana Ajmal, Julia E. von Oettingen, Kuben Pillay, Supawadee Likitmaskul, Luis Eduardo Calliari, Maria E. Craig
Pediatric Diabetes.2022; 23(8): 1529. CrossRef - Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2022;37:641-51, Han-sang Baek et al.)
May Thu Hla Aye, Sajid Adhi Raja, Vui Heng Chong
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 943. CrossRef
- Increased risk of incident mental disorders in adults with new-onset type 1 diabetes diagnosed after the age of 19: A nationwide cohort study

- Thyroid
- Clinical Outcomes of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients with Local Recurrence or Distant Metastasis Detected in Old Age
- Ji Min Han, Ji Cheol Bae, Hye In Kim, Sam Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(4):459-465. Published online November 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.4.459
- 4,772 View
- 54 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) shows a very good prognosis, but older patients have a higher recurrence rate and those show poor prognosis than younger patients. The aim of this study was to determine the clinical outcomes of thyroid cancer patients who experienced recurrence in old age according to the treatment strategy used.
Methods This retrospective observational cohort study was conducted at Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. Among DTC patients with no evidence of disease after initial treatment, we enrolled 86 patients who experienced recurrence at an age >65 years from 1994 to 2012. Sixty-nine patients had local recurrence and 17 patients showed distant metastasis.
Results The mean age of patients at recurrence was 72 years. Patients were followed up for a median of 4.1 years after recurrence. Sixty-three of the 69 patients with local recurrence received additional treatment, while the other six received conservative care. The cancer-specific mortality rate was 15.5% in the local recurrence group. Airway problems were the main cause of death in patients who did not receive further treatment for local recurrence. Among the 17 patients with distant metastasis, 10 underwent specific treatment for metastasis and seven received only supportive management. Seven of those 17 patients died, and the cancer-specific mortality rate was 35% in the distant metastasis group.
Conclusion The overall cancer-specific mortality rate was 20% in DTC patients in whom recurrence was first detected at an age >65 years. Mortality due to uncontrolled local disease occurred frequently in patients who did not receive definitive management for recurrence.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Identification of Circulating Tumor Cell Phenotype in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma
Huiling Wang, Mian Lv, Yonghong Huang, Xiaoming Pan, Changyuan Wei
Journal of Biomaterials and Tissue Engineering.2022; 12(4): 813. CrossRef - Long-Term Outcomes and Prognoses of Elderly Patients (≥65-Years-Old) With Distant Metastases From Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer During Radioiodine Therapy and Follow-Up
Zhong-Ling Qiu, Chen-Tian Shen, Zhen-Kui Sun, Hong-Jun Song, Chuang Xi, Guo-Qiang Zhang, Yang Wang, Quan-Yong Luo
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Head-to-Head Comparison of Neck 18F-FDG PET/MR and PET/CT in the Diagnosis of Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma Patients after Comprehensive Treatment
Yangmeihui Song, Fang Liu, Weiwei Ruan, Fan Hu, Muhsin H. Younis, Zairong Gao, Jie Ming, Tao Huang, Weibo Cai, Xiaoli Lan
Cancers.2021; 13(14): 3436. CrossRef - Highly sensitive electrochemical immunosensor using a protein-polyvinylidene fluoride nanocomposite for human thyroglobulin
Maria Oneide Silva de Moraes, João de Deus Pereira de Moraes Segundo, Marcos Marques da Silva Paula, Maria Goreti Ferreira Sales, Walter Ricardo Brito
Bioelectrochemistry.2021; 142: 107888. CrossRef
- Identification of Circulating Tumor Cell Phenotype in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma

- Intermuscular Adipose Tissue Content and Intramyocellular Lipid Fatty Acid Saturation Are Associated with Glucose Homeostasis in Middle-Aged and Older Adults
- Jung Eun Kim, Keagan Dunville, Junjie Li, Ji Xin Cheng, Travis B. Conley, Cortni S. Couture, Wayne W. Campbell
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(2):257-264. Published online May 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.2.257
- 4,968 View
- 59 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Insulin resistance is associated with the higher content of intermuscular adipose tissue (IMAT) and the saturation of intramyocellular lipid (IMCL), but a paucity of data exist in humans. This study examined associations among IMAT content, IMCL saturation, and fasting glucose concentration in middle-aged and older adults with overweight or obesity.
Methods Seventy-five subjects (26 males, 49 females) were recruited and thigh muscle and IMAT were assessed using magnetic resonance imaging.
Vastus lateralis tissue was acquired from a subset of nine subjects and IMCL content and saturation were assessed using nonlinear dual complex microscopy.Results The characteristics of the 75 subjects were as follows: age 59±11 years, body mass index 30±5 kg/m2, fasting glucose concentration 5.2±0.5 mmol/L, fasting insulin concentration 12.2±7.3 µU/mL, fasting homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) 2.9±2.0 (mean±SD). IMAT to muscle tissue (MT) volume ratio was positively associated with the saturated fatty acid to unsaturated fatty acid ratio in IMCL. IMAT:MT was positively associated with fasting glucose concentration and HOMA-IR. IMCL saturation was positively associated with fasting glucose concentration while muscle cell area, IMCL area, and % IMCL in muscle cell were not associated with fasting glucose concentration.
Conclusion These results indicate that higher intermuscular fat content and IMCL saturation may impact fasting glucose concentration in middle-aged and older adults with overweight or obesity. The centralization of adipose tissue in the appendicular region of the body may promote insulin resistance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Reliability of ultrasound measurements of muscle thickness and echointensity in older adults with type 2 diabetes
Kirsten E. Bell, Michael T. Paris, Maryia Samuel, Marina Mourtzakis
WFUMB Ultrasound Open.2024; 2(1): 100032. CrossRef - Precision MRI phenotyping of muscle volume and quality at a population scale
Marjola Thanaj, Nicolas Basty, Brandon Whitcher, Elena P. Sorokin, Yi Liu, Ramprakash Srinivasan, Madeleine Cule, E. Louise Thomas, Jimmy D. Bell
Frontiers in Physiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impaired skeletal muscle regeneration in diabetes: From cellular and molecular mechanisms to novel treatments
Ever Espino-Gonzalez, Emilie Dalbram, Rémi Mounier, Julien Gondin, Jean Farup, Niels Jessen, Jonas T. Treebak
Cell Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of daily carbohydrate intake with intermuscular adipose tissue in Korean individuals with obesity: a cross-sectional study
Ha-Neul Choi, Young-Seol Kim, Jung-Eun Yim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(1): 78. CrossRef - Intermuscular adipose tissue in metabolic disease
Bret H. Goodpaster, Bryan C. Bergman, Andrea M. Brennan, Lauren M. Sparks
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2023; 19(5): 285. CrossRef - Muscle function and architecture in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Pierre Bourdier, Anthony Birat, Emmanuelle Rochette, Éric Doré, Daniel Courteix, Frédéric Dutheil, Bruno Pereira, Sébastien Ratel, Etienne Merlin, Pascale Duché
Acta Paediatrica.2021; 110(1): 280. CrossRef - NLRP3 Inflammasome: Potential Role in Obesity Related Low-Grade Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle
Gonzalo Jorquera, Javier Russell, Matías Monsalves-Álvarez, Gonzalo Cruz, Denisse Valladares-Ide, Carla Basualto-Alarcón, Genaro Barrientos, Manuel Estrada, Paola Llanos
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(6): 3254. CrossRef - Intermuscular Fat Content in Young Chinese Men With Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes: Based on MR mDIXON-Quant Quantitative Technique
Fuyao Yu, Bing He, Li Chen, Fengzhe Wang, Haidong Zhu, Yanbin Dong, Shinong Pan
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Valid and Precise Semiautomated Method for Quantifying Intermuscular Fat Intramuscular Fat in Lower Leg Magnetic Resonance Images
Andy K.O. Wong, Eva Szabo, Marta Erlandson, Marshall S. Sussman, Sravani Duggina, Anny Song, Shannon Reitsma, Hana Gillick, Jonathan D. Adachi, Angela M. Cheung
Journal of Clinical Densitometry.2020; 23(4): 611. CrossRef - Adipose Tissue Distribution, Inflammation and Its Metabolic Consequences, Including Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease
Alan Chait, Laura J. den Hartigh
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of weight loss during a very low carbohydrate diet on specific adipose tissue depots and insulin sensitivity in older adults with obesity: a randomized clinical trial
Amy M Goss, Barbara Gower, Taraneh Soleymani, Mariah Stewart, May Pendergrass, Mark Lockhart, Olivia Krantz, Shima Dowla, Nikki Bush, Valene Garr Barry, Kevin R. Fontaine
Nutrition & Metabolism.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Local In Vivo Measures of Muscle Lipid and Oxygen Consumption Change in Response to Combined Vitamin D Repletion and Aerobic Training in Older Adults
D. Thomas, David Schnell, Maja Redzic, Mingjun Zhao, Hideat Abraha, Danielle Jones, Howard Brim, Guoqiang Yu
Nutrients.2019; 11(4): 930. CrossRef - Impact of different ectopic fat depots on cardiovascular and metabolic diseases
Daniele Ferrara, Fabrizio Montecucco, Franco Dallegri, Federico Carbone
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2019; 234(12): 21630. CrossRef - Differential Relationship between Intermuscular Adipose Depots with Indices of Cardiometabolic Health
Robert E. Bergia, Jung Eun Kim, Wayne W. Campbell
International Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Association of sarcopenic obesity predicted by anthropometric measurements and 24-y all-cause mortality in elderly men: The Kuakini Honolulu Heart Program
Kiyoshi Sanada, Randi Chen, Bradley Willcox, Tomoyuki Ohara, Aida Wen, Cody Takenaka, Kamal Masaki
Nutrition.2018; 46: 97. CrossRef
- Reliability of ultrasound measurements of muscle thickness and echointensity in older adults with type 2 diabetes

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Plasma Adiponectin Levels in Elderly Patients with Prediabetes
- Si Eun Kong, Yea Eun Kang, Kyong Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(3):326-333. Published online August 4, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.3.326
- 3,239 View
- 36 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The significance of adiponectin levels in elderly individuals with prediabetes has yet to be determined. Thus, the present study was performed to evaluate the relationships between adiponectin levels and anthropometric variables, body composition parameters, insulin sensitivity, and lipid profiles in elderly prediabetic patients.
Methods The present study included 120 subjects with prediabetes who were >65 years of age and were selected from among 1,993 subjects enrolled in the Korea Rural Genomic Cohort Study. All subjects underwent a 75 g oral glucose tolerance test and tests for measurement of insulin sensitivity. All diagnoses of prediabetes satisfied the criteria of the American Diabetes Association.
Results Plasma adiponectin levels were lower in elderly prediabetic subjects than elderly subjects with normal glucose tolerance (
P <0.01) as well as in elderly prediabetic patients with metabolic syndrome (MetS) than in those without MetS (P <0.02). When the subjects were categorized into two groups according to plasma adiponectin levels, the waist-to-hip ratio and 2-hour insulin levels were significantly lower in individuals with high plasma adiponectin levels than in those with low plasma adiponectin levels. Additionally, the plasma adiponectin levels of elderly prediabetic subject were inversely correlated with body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), waist-to-hip ratio, visceral fat, visceral fat ratio, and 2-hour insulin levels.Conclusion The present findings demonstrated that the major factors correlated with adiponectin levels in elderly prediabetic subjects were BMI, WC, waist-to-hip ratio, visceral fat, visceral fat ratio, and 2-hour insulin levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differential Association of Selected Adipocytokines, Adiponectin, Leptin, Resistin, Visfatin and Chemerin, with the Pathogenesis and Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in the Asir Region of Saudi Arabia: A Case Control Study
Mohammad Muzaffar Mir, Rashid Mir, Mushabab Ayed Abdullah Alghamdi, Javed Iqbal Wani, Zia Ul Sabah, Mohammed Jeelani, Vijaya Marakala, Shahzada Khalid Sohail, Mohamed O’haj, Muffarah Hamid Alharthi, Mohannad Mohammad S. Alamri
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(5): 735. CrossRef - Postloading insulinemia is independently associated with arterial stiffness in young Japanese persons
Norimitsu Murai, Naoko Saito, Sayuri Nii, Yuto Nishikawa, Asami Suzuki, Eriko Kodama, Tatsuya Iida, Kentaro Mikura, Hideyuki Imai, Mai Hashizume, Yasuyoshi Kigawa, Rie Tadokoro, Chiho Sugisawa, Kei Endo, Toru Iizaka, Fumiko Otsuka, Shun Ishibashi, Shoichi
Hypertension Research.2021; 44(11): 1515. CrossRef - Association of Adiponectin and rs1501299 of the ADIPOQ Gene with Prediabetes in Jordan
Mahmoud Alfaqih, Faheem Al-Mughales, Othman Al-Shboul, Mohammad Al Qudah, Yousef Khader, Muhammad Al-Jarrah
Biomolecules.2018; 8(4): 117. CrossRef
- Differential Association of Selected Adipocytokines, Adiponectin, Leptin, Resistin, Visfatin and Chemerin, with the Pathogenesis and Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in the Asir Region of Saudi Arabia: A Case Control Study


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



