Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Bone Metabolism
- Long-Term Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
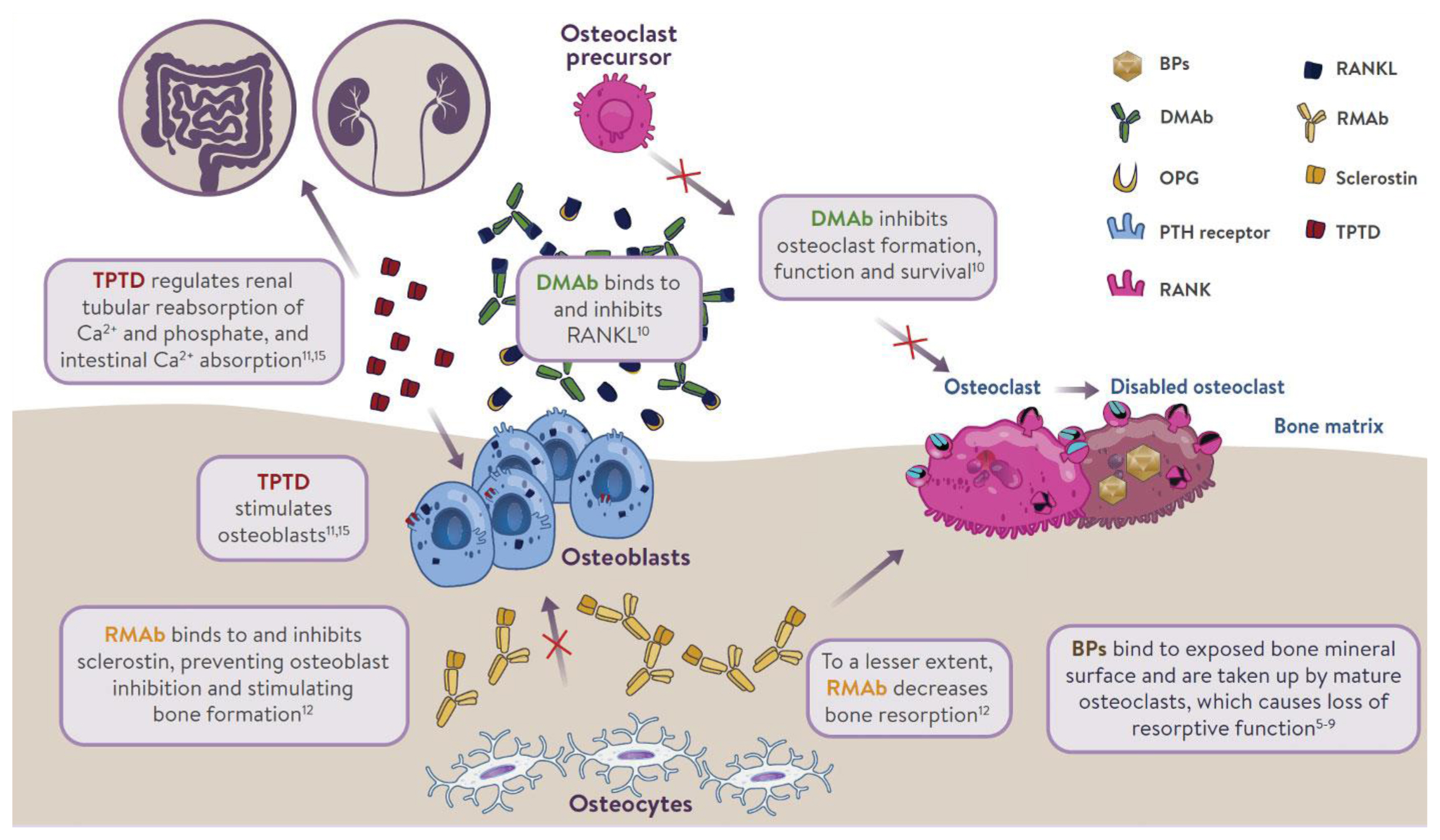
- Jacques P. Brown
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):544-552. Published online June 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.301
- 15,210 View
- 951 Download
- 39 Web of Science
- 37 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Osteoporosis is an incurable chronic condition, like heart disease, diabetes, or hypertension. A large gap currently exists in the primary prevention of fractures, and studies show that an estimated 80% to 90% of adults do not receive appropriate osteoporosis management even in the secondary prevention setting. Case finding strategies have been developed and effective pharmacological interventions are available. This publication addresses how best to use the pharmacological options available for postmenopausal osteoporosis to provide lifelong fracture protection in patients at high and very high risk of fracture. The benefit of osteoporosis therapies far outweighs the rare risks.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of stepwise administration of osteoprotegerin and parathyroid hormone-related peptide DNA vectors on bone formation in ovariectomized rat model
Ye Ji Eom, Jang-Woon Kim, Yeri Alice Rim, Jooyoung Lim, Se In Jung, Ji Hyeon Ju
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycolithocholic acid increases the frequency of circulating Tregs through constitutive androstane receptor to alleviate postmenopausal osteoporosis
Xiaoyu Cai, Zhi Li, Yao Yao, Yongquan Zheng, Meng Zhang, Yiqing Ye
Biochemical Pharmacology.2024; 219: 115951. CrossRef - Cucumber seed polypeptides regulate RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis through OPG/RANKL/RANK and NF-κB
Tao Yu, Xiao Liu, Meng Jiang, Yuanyue Li, Heng Su, Ben Niu
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal.2024; 60(1): 54. CrossRef - Eupatilin ameliorates postmenopausal osteoporosis via elevating microRNA‐211‐5p and repressing JAK2/STAT3 pathway
Liu Hong, Chao Yang
Environmental Toxicology.2024; 39(4): 2218. CrossRef - Strontium-Doped Mesoporous Bioactive Glass-Loading Bisphosphonates Inhibit Osteoclast Differentiation and Prevent Osteoporosis in Ovariectomized Mice
Zhi Zhou, Shicheng Huo, Zhanchun Li
Coatings.2024; 14(1): 97. CrossRef - A novel PDIA3/FTO/USP20 positive feedback regulatory loop induces osteogenic differentiation of preosteoblast in osteoporosis
Fei Zhang, Chen Liu, Zhiyong Chen, Chengyi Zhao
Cell Biology International.2024; 48(4): 541. CrossRef - Research Progress of Zoledronic Acid in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis
保成 刘
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(02): 2821. CrossRef - A novel mechanism of Vildagliptin in regulating bone metabolism and mitigating osteoporosis
Jinwen He, Dacheng Zhao, Bo Peng, Xingwen Wang, Shenghong Wang, Xiaobing Zhao, Peng Xu, Bin Geng, Yayi Xia
International Immunopharmacology.2024; 130: 111671. CrossRef - Positive benefit-risk ratio of Psoraleae Fructus: Comprehensive safety assessment and osteogenic effects in rats
Zhuo Shi, Jin-chao Pan, Yi Ru, Ning-ning Shen, Yu-fu Liu, Cheng Zhang, Xiang-jun Wu, Fang-yang Li, Jia-lu Cui, Chun-qi Yang, Jun-ling Yang, Mao-xing Li, Cheng-rong Xiao, Zeng-chun Ma, Chuan Li, Yu-guang Wang, Yue Gao
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2024; 326: 117967. CrossRef - Function-oriented mechanism discovery of coumarins from Psoralea corylifolia L. in the treatment of ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis based on multi-omics analysis
Qianyi Wei, Yongrong Zhou, Zhengtao Hu, Ye Shi, Qing Ning, Keyun Ren, Xinyu Guo, Ronglin Zhong, Zhi Xia, Yinghao Yin, Yongxin Hu, Yingjie Wei, Ziqi Shi
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2024; 329: 118130. CrossRef - Efficacy and Possible Mechanisms of Astragali Radix and its Ingredients
in Animal Models of Osteoporosis: A Preclinical Review and Metaanalysis
Ning Cao, Zhangxuan Shou, Yi Xiao, Puqing Liu
Current Drug Targets.2024; 25(2): 135. CrossRef - Enhanced oral bioavailability of levormeloxifene and raloxifene by nanoemulsion: simultaneous bioanalysis using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
Divya Chauhan, Debalina Maity, Pavan K Yadav, Sachin Vishwakarma, Arun Agarwal, Manish K Chourasia, Jiaur R Gayen
Nanomedicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Testing and Treatment Methods in Osteoporosis Care
Takashi Nagai, Koji Ishikawa, Koki Tsuchiya, Soji Tani, Yusuke Dodo, Yusuke Oshita, Keizo Sakamoto, Nobuyuki Kawate, Yoshifumi Kudo, Deepak Kumar Khajuria
Journal of Osteoporosis.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - CircRNA hsa_circ_0006859 inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs and aggravates osteoporosis by targeting miR-642b-5p/miR-483-3p and upregulating EFNA2/DOCK3
Peng Yin, Yuan Xue
International Immunopharmacology.2023; 116: 109844. CrossRef - Resveratrol induces proliferation and differentiation of mouse pre-osteoblast MC3T3-E1 by promoting autophagy
Weiye Cai, Bin Sun, Chao Song, Fei Liu, Zhengliang Wu, Zongchao Liu
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Oridonin Attenuates Thioacetamide-Induced Osteoclastogenesis Through MAPK/NF-κB Pathway and Thioacetamide-Inhibited Osteoblastogenesis Through BMP-2/RUNX2 Pathway
XiaoLi Jin, Jia Xu, Fanfan Yang, Jin Chen, Feng Luo, Bin Xu, Jian Xu
Calcified Tissue International.2023; 112(6): 704. CrossRef - Phytochemical Compounds Involved in the Bone Regeneration Process and Their Innovative Administration: A Systematic Review
Alina Hanga-Farcaș, Florina Miere (Groza), Gabriela Adriana Filip, Simona Clichici, Luminita Fritea, Laura Grațiela Vicaș, Eleonora Marian, Annamaria Pallag, Tunde Jurca, Sanda Monica Filip, Mariana Eugenia Muresan
Plants.2023; 12(10): 2055. CrossRef - Screening of superior anti‐osteoporotic flavonoids from Epimedii Folium with dual effects of reversing iron overload and promoting osteogenesis
Jun Jiang, Jinjin He, Shichang Xiao, Jiayi Shenyuan, Tong Chen, Dan Pei
Biomedical Chromatography.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on the Effect of Bushen Zhuanggu Tablet Combined with Conventional Regimen on Bone Mineral Density Improvement, Functional Recovery and Fracture Risk Prevention in Patients with Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
Tianliang Chen, Guilan Li, Yongtao Xu, Min Tang
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Circ_0001825 promotes osteogenic differentiation in human-derived mesenchymal stem cells via miR-1270/SMAD5 axis
Changjun Zheng, Lingzhi Ding, Ziming Xiang, Mingxuan Feng, Fujiang Zhao, Zhaoxin Zhou, Chang She
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of ROCK1 as a novel biomarker for postmenopausal osteoporosis and pan-cancer analysis
Bowen Lai, Heng Jiang, Yuan Gao, Xuhui Zhou
Aging.2023; 15(17): 8873. CrossRef - The Mechanotransduction Signaling Pathways in the Regulation of Osteogenesis
Zhaoshuo Liu, Qilin Wang, Junyou Zhang, Sihan Qi, Yingying Duan, Chunyan Li
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(18): 14326. CrossRef - Decoding the mechanism of Eleutheroside E in treating osteoporosis via network pharmacological analysis and molecular docking of osteoclast-related genes and gut microbiota
Tianyu Zhou, Yilin Zhou, Dongdong Ge, Youhong Xie, Jiangyan Wang, Lin Tang, Qunwei Dong, Ping Sun
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Epigallocatechin gallate alleviates osteoporosis by regulating the gut microbiota and serum metabolites in rats
Xuebing Han, Yifeng Fu, Keyu Wang, Siying Li, Chang Jiang, Shuangshuang Wang, Zheng Wang, Gang Liu, Siwang Hu
Food & Function.2023; 14(23): 10564. CrossRef - The Molecular Role of Polyamines in Age-Related Diseases: An Update
Guadalupe Elizabeth Jimenez Gutierrez, Fabiola V. Borbolla Jiménez, Luis G. Muñoz, Yessica Sarai Tapia Guerrero, Nadia Mireya Murillo Melo, José Melesio Cristóbal-Luna, Norberto Leyva Garcia, Joaquín Cordero-Martínez, Jonathan J. Magaña
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(22): 16469. CrossRef - Pueraria lobata-derived exosome-like nanovesicles alleviate osteoporosis by enhacning autophagy
Weiqiang Zhan, Mingzhu Deng, Xinqia Huang, Dong Xie, Xiang Gao, Jiaxian Chen, Zhen Shi, Jiaxu Lu, Hao Lin, Peng Li
Journal of Controlled Release.2023; 364: 644. CrossRef - Based on network pharmacology and molecular docking to explore the molecular mechanism of Ginseng and Astragalus decoction against postmenopausal osteoporosis
Wei Fan, Zong-Zhe Jiang, Sheng-Rong Wan
Medicine.2023; 102(46): e35887. CrossRef - Network pharmacology-based pharmacological mechanism prediction of Lycii Fructus against postmenopausal osteoporosis
Jianbo Wang, Yi Wang, Leyan Li, Shuiqi Cai, Dandan Mao, Hongkan Lou, Jian Zhao
Medicine.2023; 102(48): e36292. CrossRef - Benefits of lumican on human bone health: clinical evidence using bone marrow aspirates
Yun Sun Lee, So Jeong Park, Jin Young Lee, Eunah Choi, Beom-Jun Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2022; 37(4): 821. CrossRef - ED-71 inhibited osteoclastogenesis by enhancing EphrinB2–EphB4 signaling between osteoclasts and osteoblasts in osteoporosis
Yuan Zhang, Yuying Kou, Panpan Yang, Xing Rong, Rong Tang, Hongrui Liu, Minqi Li
Cellular Signalling.2022; 96: 110376. CrossRef - Effects of Muscles on Bone Metabolism—with a Focus on Myokines
Beom-Jun Kim
Annals of Geriatric Medicine and Research.2022; 26(2): 63. CrossRef - Evaluation of the tolerability of zoledronic acid preparations for parenteral administration
I. A. Shafieva, S. V. Bulgakova, A. V. Shafieva
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2022; (11): 96. CrossRef - Impact of Alendronate Sodium plus Elcatonin on Postoperative Bone Pain in Patients with Osteoporotic Fractures
Baohui Wang, Yindi Sun, Da Shi, Xiuwei Han, Na Liu, Bo Wang, Zhijun Liao
BioMed Research International.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Current use of bone turnover markers in the management of osteoporosis
Jacques P. Brown, Andrew Don-Wauchope, Pierre Douville, Caroline Albert, Samuel D. Vasikaran
Clinical Biochemistry.2022; 109-110: 1. CrossRef - Study on the influence of balloon dilation mode on the intravertebral cleft of osteoporotic fracture
Nanning Lv, Xiaoxiao Feng, Haojun Liu, Xuejun Jia, Shanqin Han, Mingming Liu
BMC Surgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - An Acid-Sensitive Bone Targeting Delivery System Carrying Acacetin Prevents Osteoporosis in Ovariectomized Mice
Xiaochen Sun, Chenyu Song, Chenxi Zhang, Chunlei Xing, Juan Lv, Huihui Bian, Nanning Lv, Dagui Chen, Xin Dong, Mingming Liu, Li Su
Pharmaceuticals.2022; 16(1): 2. CrossRef - Changes in Serum Dickkopf-1, RANK Ligand, Osteoprotegerin, and Bone Mineral Density after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Treatment
Eunhee Jang, Jeonghoon Ha, Ki-Hyun Baek, Moo Il Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(6): 1211. CrossRef
- Effects of stepwise administration of osteoprotegerin and parathyroid hormone-related peptide DNA vectors on bone formation in ovariectomized rat model

- Estrogen Receptor Gene Polymorphism, Urinary Estrogen Metabolites and Bone Mineral Density in Korean Postmenopausal Women.
- Ji Hyun Lee, Sung Kil Lim, Young Jun Won, Seok Ho Kwon, Bong Soo Cha, Young Duk Song, Hyun Chul Lee, Kap Bum Huh
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(4):468-478. Published online November 7, 2019
- 1,236 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Estrogen status is important for maintaining the homeostasis of bone. Estrogen has direct effects on bone cells, through binding to the high-affinity estrogen receptor. Several recent studies suggest that there might be genetically determined variations in biosynthesis and function of estrogen receptor in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Also the main cause of postmenopausal osteoporosis is decreased level of serum estrogen, whereas there had been some suggestion that the remaining estrogen have some effect on bone metabolism after menopause. We investigated the relationship between estrogen receptor gene PvulI polymorphism and bone mineral density(BMD), and the relationship between 18 urinary metabolites of estrogen and BMD in Korean postmeno- pausal osteoporosis. Methods: We examined the PvuII polymorphism of the estrogen receptor gene in 5' upstream region and the first intron by restrietion frapnent length polymorphism analysis in 62 postmeno- pausal wornen, BMD was measured by DEXA. The urinary estrogen metabolites were determined by GC/MS(Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry) at Korean Institute of Science and Techno- logy Doping Control Center. Results: BMD of the spine and the femoral neck correlated with body weight, height, body mass index as we expected. There was no polymorphism of PvuII restriction site on 5 upstream region of estrogen receptor gene. Whereas the prevalen~ee of the PP, Pp, pp genotype in the first intron of estrogen receptor was 12.9%, 45.2%, 41.9%, respectively. But, there was no correlation between PvuII genotype and the spinel and femoral neck BMD. 2(OH)E2 among 18 urinary metabolites of estrogen, showed a negative correlation with the spinal and femoral neck BMD(r =-0.2551, p<0.05, and r =-0.3341, p<0.01, respectively), and the ratio of 16a(OH)E2/2(OH)E1> revealed a positive correlation with the spinal BMD(r =0.3057, p<0.05). In stepwise multiple regression analysis, body weight, 2(OH)E2, 16a(OH)E1, 2(Meo)E1 were independent predictors of the spinal bone density, and body weight and 2(OH)E2 were independent predictors of the femoral neck bone density. Conclusion: These results suggested that restrietion fragment length polymorphism analysis of the estrogen receptor gene with PvuII restriction enzyme was not helpful for early detection of patients at risk of developing osteoporosis. However, the ratio of 16-hydroxylation to 2-hydroxylation of estrogen metabolism was reduced in postmenopausal women and high catecholestrogen formation might be a greater risk factor for osteoporosis.

- Bone Metabolism
- Association between Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Levels and Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women
- Hoon Sung Choi, Hyang Ah Lee, Sang-Wook Kim, Eun-Hee Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(2):273-277. Published online June 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.2.273
- 3,542 View
- 51 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Despite the beneficial effect of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) on metabolic disease, there are concerns about adverse effects on bone metabolism, supported by animal studies. However, a recent human study showed the positive association between serum FGF21 level and bone mineral density (BMD) in healthy premenopausal women. We undertook this study to examine the association between FGF21 level and BMD in healthy postmenopausal Korean women who are susceptible to osteoporosis.
Methods We used data of 115 participants from a cohort of healthy postmenopausal women (>50 years old) to examine the association between serum FGF21 level and BMD. The clinical characteristics were obtained from the participants, and blood testing and serum FGF21 testing were undertaken. BMD of the lumbar spine, femoral neck and total hip area, and bone markers were used in the analyses.
Results The mean age of the participants was 60.2±7.2 years. Serum FGF21 levels showed negative correlation with BMD and T-scores in all three areas, but there were no statistically significant differences. Multivariate analyses with adjustment for age and body mass index also did not show significant association between serum FGF21 level and BMD. In addition, serum FGF21 level also showed no correlation with osteocalcin and C-telopeptide levels.
Conclusion In our study, serum FGF21 level showed no significant correlation with BMD and T-scores.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fibroblast growth factor 21 and bone homeostasis
Yan Tang, Mei Zhang
Biomedical Journal.2023; 46(4): 100548. CrossRef - FGF21 negatively affects long-term female fertility in mice
Beat Moeckli, Thuy-Vy Pham, Florence Slits, Samuel Latrille, Andrea Peloso, Vaihere Delaune, Graziano Oldani, Stéphanie Lacotte, Christian Toso
Heliyon.2022; 8(11): e11490. CrossRef - Potential role of fibroblast growth factor 21 in the deterioration of bone quality in impaired glucose tolerance
D. T. W. Lui, C. H. Lee, V. W. K. Chau, C. H. Y. Fong, K. M. Y. Yeung, J. K. Y. Lam, A. C. H. Lee, W. S. Chow, K. C. B. Tan, Y. C. Woo, K. S. L. Lam
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2021; 44(3): 523. CrossRef - Skeletal Muscle and Bone – Emerging Targets of Fibroblast Growth Factor-21
Hui Sun, Matthew Sherrier, Hongshuai Li
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Age‐related bone loss is associated with FGF21 but not IGFBP1 in healthy adults
Shuen Yee Lee, Kai Deng Fam, Kar Ling Chia, Margaret M. C. Yap, Jorming Goh, Kwee Poo Yeo, Eric P. H. Yap, Sanjay H. Chotirmall, Chin Leong Lim
Experimental Physiology.2020; 105(4): 622. CrossRef - Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with Increased Plasma Levels of Fibroblast Growth Factors 19 and 21
Małgorzata Marchelek-Myśliwiec, Violetta Dziedziejko, Monika Nowosiad-Magda, Katarzyna Dołęgowska, Barbara Dołęgowska, Andrzej Pawlik, Krzysztof Safranow, Magda Wiśniewska, Joanna Stępniewska, Maciej Domański, Kazimierz Ciechanowski
Kidney and Blood Pressure Research.2019; 44(5): 1207. CrossRef
- Fibroblast growth factor 21 and bone homeostasis

- Bone Metabolism
- Association between Bone Mineral Density and Albuminuria: Cross-Sectional Analysis of Data from the 2011 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey V-2
- Tae Yang Yu, Ha-Young Kim, Jeong Mi Lee, Dae Ho Lee, Chung Gu Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(2):211-218. Published online May 4, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.2.211
- 4,096 View
- 45 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Albuminuria is known to be independently associated with progression of renal and cardiovascular disease. However, little is known regarding the exact relationship between albuminuria and bone mineral density (BMD). The aim of this population-based study conducted in Korea was to identify the association between albuminuria and BMD.
Methods We performed a cross-sectional analysis of data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES V-2) 2011. BMD was measured for total hip (TH), femur neck (FN), and lumbar spine (LS). Analysis of covariance was used to compare BMD levels between the groups at the TH, FN, and LS sites, after adjusting for age. Separate analyses were performed according to sex; women were divided into two groups according to menopausal status and each group was subdivided into three according to urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (level 1, <30 mg/g; level 2, 30 to 299 mg/g; level 3, ≥300 mg/g).
Results Data on a total of 1,831 adults (857 men and 974 women) were analyzed. In postmenopausal women, after adjusting for age, BMD of TH tended to decrease as levels of albuminuria increased (0.767±0.117, 0.757±0.129, 0.752±0.118, respectively;
P =0.040). However, there was no significant difference in BMD according to albuminuria level in premenopausal women and men.Conclusion Level of albuminuria was closely related with BMD of TH in postmenopausal women, after adjusting for age, but there was no significant relationship between albuminuria and BMD in premenopausal women and men.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between urinary albumin creatinine ratio and cardiovascular disease
Yoo Jin Kim, Sang Won Hwang, Taesic Lee, Jun Young Lee, Young Uh, Gulali Aktas
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(3): e0283083. CrossRef - Association between urine albumin to creatinine ratio and bone mineral density: a cross-sectional study
Kemal Sherefa Oumer, Yawen Liu, Tesfaye Getachew Charkos, Shuman Yang
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2022; 191(1): 427. CrossRef - Association between perfluoroalkyl substances concentration and bone mineral density in the US adolescents aged 12-19 years in NHANES 2005-2010
Xianmei Xiong, Baihang Chen, Zhongqing Wang, Liqiong Ma, Shijie Li, Yijia Gao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Mood and Metabolic Health Status of Elderly Osteoporotic Patients in Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study of a Nationally Representative Sample
Hyen Chul Jo, Gu-Hee Jung, Seong-Ho Ok, Ji Eun Park, Jong Chul Baek
Healthcare.2021; 9(1): 77. CrossRef
- Association between urinary albumin creatinine ratio and cardiovascular disease

- Serum Preadipocyte Factor 1 Levels Are Not Associated with Bone Mineral Density among Healthy Postmenopausal Korean Women
- Hoon Sung Choi, Sang-Wook Kim, Eun-Hee Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(1):124-128. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.1.124
- 3,397 View
- 34 Download
- 1 Web of Science
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells can differentiate into adipocytes or osteoblasts through closely regulated lineage-control processes. However, adipocyte precursor cells release preadipocyte factor 1 (Pref-1), which inhibits the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into mature adipocytes and osteoblasts. Previous studies have also reported an inverse association between Pref-1 levels and bone mineral density (BMD) among patients with anorexia nervosa.
Methods In this retrospective study, we examined the correlations between Pref-1 levels and BMD among 124 healthy postmenopausal women (>50 years old). The patients had provided information regarding their clinical characteristics, and underwent blood testing and serum Pref-1 testing.
Results The subjects' mean age was 59.9±7.1 years and the median time since menopause onset was 9.1 years. A history of osteoporotic fracture was identified in 23 subjects (19%). Serum Pref-1 levels were not significantly correlated with BMD values at the lumbar spine (
R 2=0.038,P =0.109), femur neck (R 2=0.017,P =0.869), and total hip (R 2=0.041,P =0.09), and multivariate analyses with adjustment for age and body mass index also did not detect any significant correlations. Subgroup analyses according to a history of fracture also did not detect significant associations between Pref-1 levels and BMD values.Conclusion In our study population, it does not appear that serum Pref-1 levels are significantly associated with BMD values and osteoporosis.

- A Case of Lymphocytic Hypophysitis in a Postmenopausal Woman.
- Sang Hyun Baik, Dong Sun Kim, Yoon Kyoung Sung, Jong Pyo Kim, Chang Beom Lee, Yong Soo Park, Woong Hwan Choi, You Hern Ahn, Tae Wha Kim, Yong Ko, Moon Hyang Park
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2002;17(5):713-719. Published online October 1, 2002
- 1,092 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 64-year-old Korean woman presented with a 3-week history of severe headache and ocular pain. Her brain MRI showed a cystic pituitary mass compressing the optic chiasm. A hormonal study revealed anterior pituitary insufficiency and a slightly increased prolactin level. We performed a transsphenoidal resection of the pituitary mass. A pathological examination revealed the presence of a heavy inflammatory infiltrate, composed of lymphocytes and plasma cells, and destruction of the adenohypophysial structures. Five months after surgery, her hormonal levels had nearly normalized, without hormone replacement therapy. A follow-up MRI showed no recurrence. We conclude that lymphocytic hypophysitis should be included in the differential diagnosis of pituitary mass at any age. We discuss the features that can help to make a preoperative differential diagnosis, and selection of the appropriate treatment.

- Serum Leptin Levels in Relation to Quantitative Ultrasound Values of Calcaneus in Korean Postmenopausal Women in Chung-Up District.
- Sang Wook Kim, Jung Min Koh, Ha Young Kim, Duk Jae Kim, Ghi Su Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2002;17(1):79-86. Published online February 1, 2002
- 1,005 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Obese postmenopausal women usually have a tend to have greater bone mineral density than lean women. This has been attributed to either the mechanical effects of their excessive weight on bone tissue or to their high body fat content. A recent study demonstrated that leptin, the hormone produced in adipocytes, acts on bone metabolism. These findings have prompted speculations on the possible role of leptin in the protective effect of obesity on bone. METHEODS: We studied the relationship between serum leptin levels and quantitative ultrasound (QUS) values of calcaneus in 94 postmenopausal Korean women who were randomly selected from the population of the Chung-Up osteoporosis prevalence study. QUS values, broadband ultrasound attenuation and speed of sound; were measured at the calcaneus. RESULTS: Leptin values were strongly correlated with body mass index (r = 0.478, p< 0.001), confirming a positive relationship between leptin levels and fat mass. In contrast, no significant correlations were observed between serum leptin levels and calcaneal QUS values. CONCLUSION: Our results suggest that circulating plasma leptin does not have a significant influence on QUS values of calcaneus in Korean postmenopausal women.

- Polymorphisms of the Interleukin - 6 Gene and Bone Mineral Density at Postmenopause in Korean Women.
- Soo Young Yoon, Sung Kil Lim, Song Zae Li, Young Duk Song, Hyun Chul Lee, Kyung Rae Kim, Kap Bum Huh
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1999;14(4):698-705. Published online January 1, 2001
- 969 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is one of the candidate cytokines to play an important role in bone loss followed by estrogen deficiency. Recently, the IL-6 VNTR (various number tandem repeats) genotype was reported to be associated with bone mineral density, raising the possibility that genotyping at this site might be of value in identifying women who are at risk for postmenopausal osteoporosis. To evaluate whether allelic variants in the gene encoding the polymorphism of VNTR located at the 3 flank of the IL-6 gene in Koreans were also the same as those of Caucasian, we analyzed the distribution pattern of the polymerase chain reaction product of the IL-6 gene. METHODS: The IL-6 VNTR were examined in 134 postmenopausal Korean women. Bone mineral densities were measured by DEXA (dual energy X-ray absorptiometry, Lunar Radiation, Madison, WI). RESULTS: The IL-6 VNTR polymorphism of Koreans was different from that of Caucasian, and four genotypes (KaKb, KbKb, KbKc and KbKd) were identified. The genotypes KaKb and KbKd were found only in one individual each and most Koreans had KbKb or KbKc genotypes. The overall prevalences of KbKb and KbKc genotypes were 76.9% Rlld 21.6%, respectively, and the distribution patterns of the genotypes were not different among normal, osteopenic and osteoporotic groups. The values of bone mineral density at the lumbar spine and femoral neck were not different between the frequent genotypes of KbKb and KbKc. Furthermore, the levels of alkaline phosphatase, osteocalcin and urinary deoxypyridinoline/creatinine were also not different between the two genotypes. CONCLUSION: There are ethnic differences in IL-6 VNTR polymorphism, and IL-6 VNTR polymorphism may not be associated with postmenopausal osteoporosis in Korean women. Our data suggest that the analysis of IL-6 VNTR polymorphism may not be helpful in detecting patients at risk of developing osteoporosis.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



