Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Adrenal gland
- A Contemporary Approach to the Diagnosis and Management of Adrenal Insufficiency
- Suranut Charoensri, Richard J. Auchus
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):73-82. Published online January 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2024.1894
- 2,505 View
- 246 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
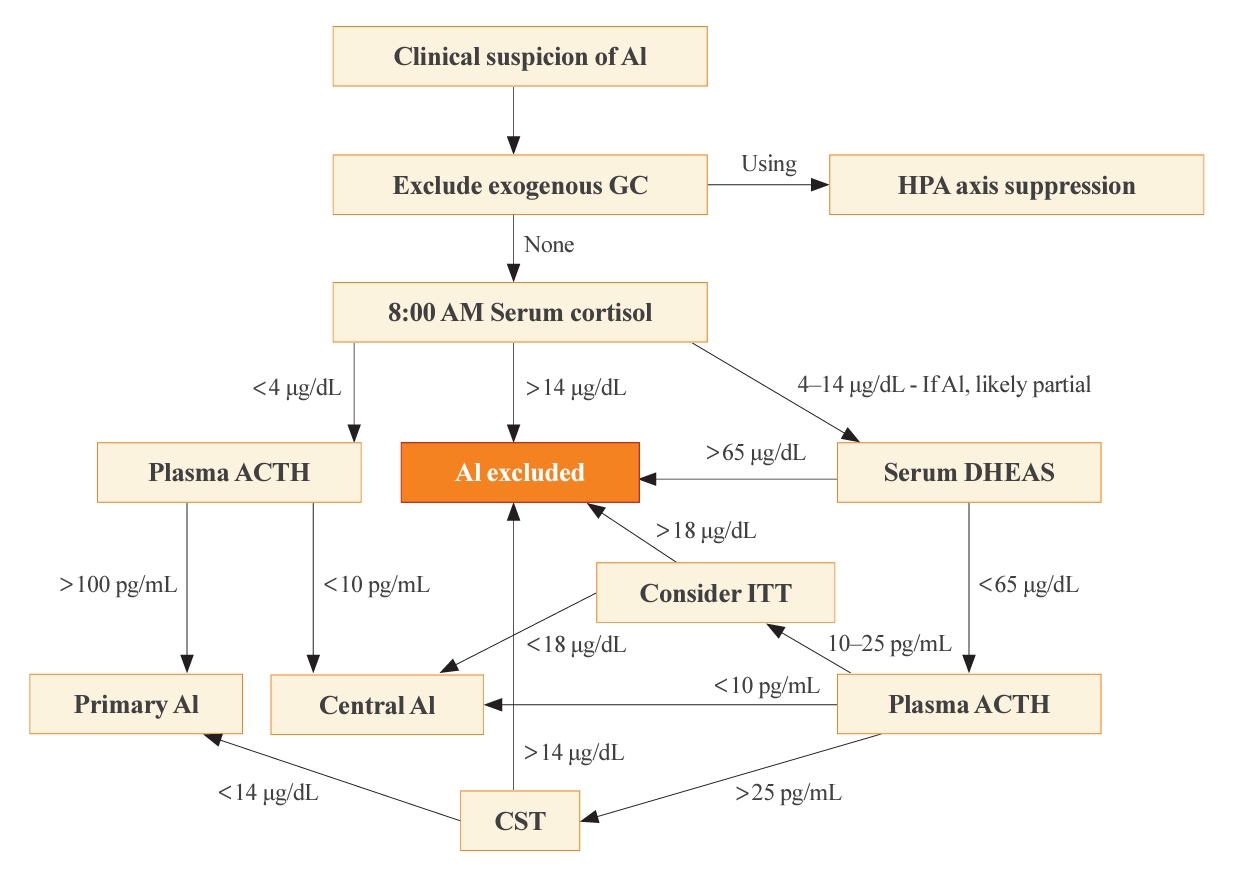
ePub - Adrenal insufficiency (AI) can be classified into three distinct categories based on its underlying causes: primary adrenal disorders, secondary deficiencies in adrenocorticotropin, or hypothalamic suppression from external factors, most commonly glucocorticoid medications used for anti-inflammatory therapy. The hallmark clinical features of AI include fatigue, appetite loss, unintentional weight loss, low blood pressure, and hyponatremia. Individuals with primary AI additionally manifest skin hyperpigmentation, hyperkalemia, and salt craving. The diagnosis of AI is frequently delayed due to the non-specific symptoms and signs early in the disease course, which poses a significant challenge to its early detection prior to an adrenal crisis. Despite the widespread availability of lifesaving glucocorticoid medications for decades, notable challenges persist, particularly in the domains of timely diagnosis while simultaneously avoiding misdiagnosis, patient education for averting adrenal crises, and the determination of optimal replacement therapies. This article reviews recent advancements in the contemporary diagnostic strategy and approaches to optimal treatment for AI.

- Miscellaneous
- Incidence of Endocrine-Related Dysfunction in Patients Treated with New Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Meta-Analysis and Comprehensive Review
- Won Sang Yoo, Eu Jeong Ku, Eun Kyung Lee, Hwa Young Ahn
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):750-759. Published online November 13, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1785
- 1,446 View
- 122 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigated the incidence of endocrine immune-related adverse events (irAEs) for recently developed immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) drugs.
Methods
We collected studies on newly developed ICI drugs using PubMed/Medline, Embase, and Cochrane Library from inception through January 31, 2023. Among ICI drugs, nivolumab, pembrolizumab, and ipilimumab were excluded from the new ICI drugs because many papers on endocrine-related side effects have already been published.
Results
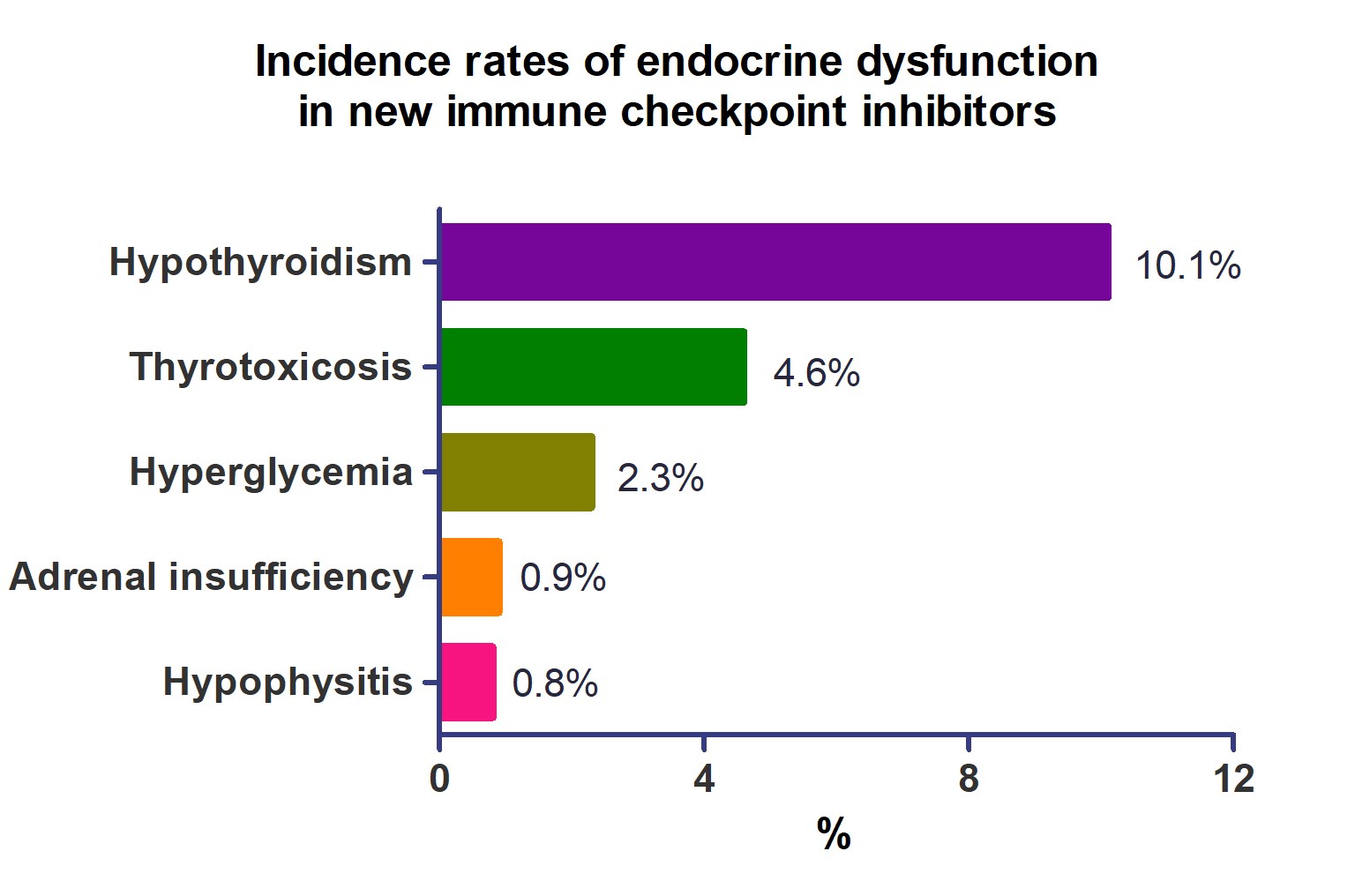
A total of 44,595 patients from 177 studies were included in this analysis. The incidence of hypothyroidism was 10.1% (95% confidence interval [CI], 8.9% to 11.4%), thyrotoxicosis was 4.6% (95% CI, 3.8% to 5.7%), hypophysitis was 0.8% (95% CI, 0.5% to 1.1%), adrenal insufficiency was 0.9% (95% CI, 0.7% to 1.1%), and hyperglycemia was 2.3% (95% CI, 1.6% to 3.4%). Hypothyroidism and thyrotoxicosis occurred most frequently with programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) inhibitors (13.7% and 7.5%, respectively). The rate of endocrine side effects for the combination of a programmed death-ligand 1 inhibitor (durvalumab) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 inhibitor (tremelimumab) was higher than that of monotherapy. In a meta-analysis, the combination of tremelimumab and durvalumab had a 9- to 10-fold higher risk of pituitary and adrenal-related side effects than durvalumab alone.
Conclusion
Newly developed PD-1 inhibitors had a high incidence of thyroid-related irAEs, and combined treatment with durvalumab and tremelimumab increased the risk of pituitary- and adrenal-related irAEs. Based on these facts, it is necessary to predict the endocrine side effects corresponding to each ICI drug, diagnose and treat them appropriately, and try to reduce the morbidity and mortality of patients.

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Renal Protection of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist, Finerenone, in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Dong-Lim Kim, Seung-Eun Lee, Nan Hee Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):43-55. Published online February 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1629
- 5,642 View
- 766 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
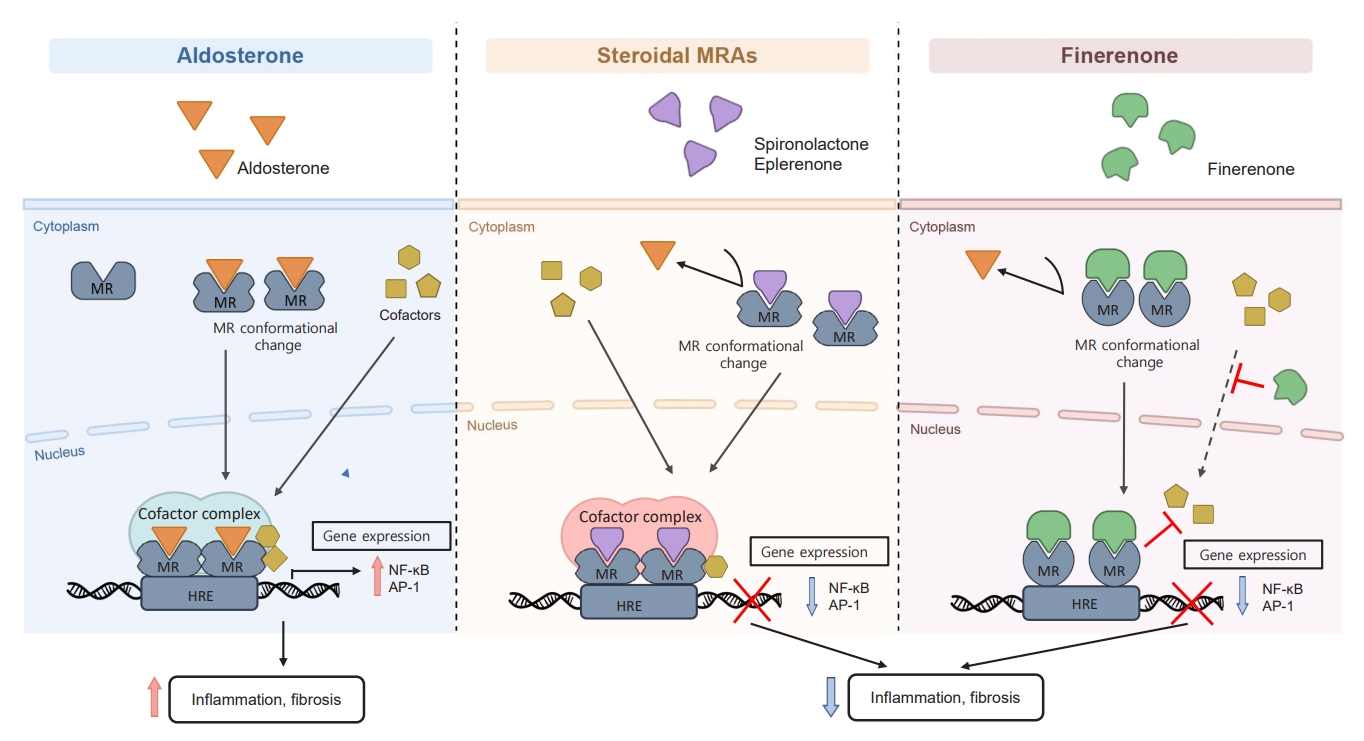
ePub - Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the most common cause of end-stage renal disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). CKD increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases; therefore, its prevention and treatment are important. The prevention of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) can be achieved through intensive glycemic control and blood pressure management. Additionally, DKD treatment aims to reduce albuminuria and improve kidney function. In patients with T2DM, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors, sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists can delay the progression of DKD. Hence, there is a need for novel treatments that can effectively suppress DKD progression. Finerenone is a first-in-class nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist with clinically proven efficacy in improving albuminuria, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and risk of cardiovascular events in early and advanced DKD. Therefore, finerenone is a promising treatment option to delay DKD progression. This article reviews the mechanism of renal effects and major clinical outcomes of finerenone in DKD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Neue Antihypertensiva im Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosteron-System
Markus van der Giet
CardioVasc.2024; 24(1): 33. CrossRef -
Chicoric acid
advanced PAQR3 ubiquitination to ameliorate ferroptosis in diabetes nephropathy through the relieving of the interaction between PAQR3 and P110α pathway
Weiwei Zhang, Yong Liu, Jiajun Zhou, Teng Qiu, Haitang Xie, Zhichen Pu
Clinical and Experimental Hypertension.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endothelial CXCR2 deficiency attenuates renal inflammation and glycocalyx shedding through NF-κB signaling in diabetic kidney disease
Siyuan Cui, Xin Chen, Jiayu Li, Wei Wang, Deqi Meng, Shenglong Zhu, Shiwei Shen
Cell Communication and Signaling.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular Targets of Novel Therapeutics for Diabetic Kidney Disease: A New Era of Nephroprotection
Alessio Mazzieri, Francesca Porcellati, Francesca Timio, Gianpaolo Reboldi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3969. CrossRef - Epigenetic modification in diabetic kidney disease
Zhe Liu, Jiahui Liu, Wanning Wang, Xingna An, Ling Luo, Dehai Yu, Weixia Sun
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel Approaches in Chronic Renal Failure without Renal Replacement Therapy: A Review
Sandra Martínez-Hernández, Martín Muñoz-Ortega, Manuel Ávila-Blanco, Mariana Medina-Pizaño, Javier Ventura-Juárez
Biomedicines.2023; 11(10): 2828. CrossRef - Finerenone and other future therapeutic options for Alport syndrome
Helen Pearce, Holly Mabillard
Journal of Rare Diseases.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Neue Antihypertensiva im Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosteron-System

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Therapy: From Discovery to Type 2 Diabetes and Beyond
- Adie Viljoen, Stephen C. Bain
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):25-33. Published online February 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1642
- 2,787 View
- 307 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The therapeutic benefits of the incretin hormone, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP1), for people with type 2 diabetes and/or obesity, are now firmly established. The evidence-base arising from head-to-head comparative effectiveness studies in people with type 2 diabetes, as well as the recommendations by professional guidelines suggest that GLP1 receptor agonists should replace more traditional treatment options such as sulfonylureas and dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitors. Furthermore, their benefits in reducing cardiovascular events in people with type 2 diabetes beyond improvements in glycaemic control has led to numerous clinical trials seeking to translate this benefit beyond type 2 diabetes. Following early trial results their therapeutic benefit is currently being tested in other conditions including fatty liver disease, kidney disease, and Alzheimer’s disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Road towards Triple Agonists: Glucagon-Like Peptide 1, Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide and Glucagon Receptor - An Update
Agnieszka Jakubowska, Carel W. le Roux, Adie Viljoen
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 12. CrossRef - Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: cardiovascular benefits and mechanisms of action
John R. Ussher, Daniel J. Drucker
Nature Reviews Cardiology.2023; 20(7): 463. CrossRef - A new class of glucose-lowering therapy for type 2 diabetes: the latest development in the incretin arena
Stephen C Bain, Thinzar Min
The Lancet.2023; 402(10401): 504. CrossRef - Flattening the biological age curve by improving metabolic health: to taurine or not to taurine, that’ s the question
Kwok M. Ho, Anna Lee, William Wu, Matthew T.V. Chan, Lowell Ling, Jeffrey Lipman, Jason Roberts, Edward Litton, Gavin M. Joynt, Martin Wong
Journal of Geriatric Cardiology.2023; 20(11): 813. CrossRef
- The Road towards Triple Agonists: Glucagon-Like Peptide 1, Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide and Glucagon Receptor - An Update

- Adrenal Gland
- Clinical and Technical Aspects in Free Cortisol Measurement
- Man Ho Choi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(4):599-607. Published online August 19, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1549
- 4,699 View
- 290 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
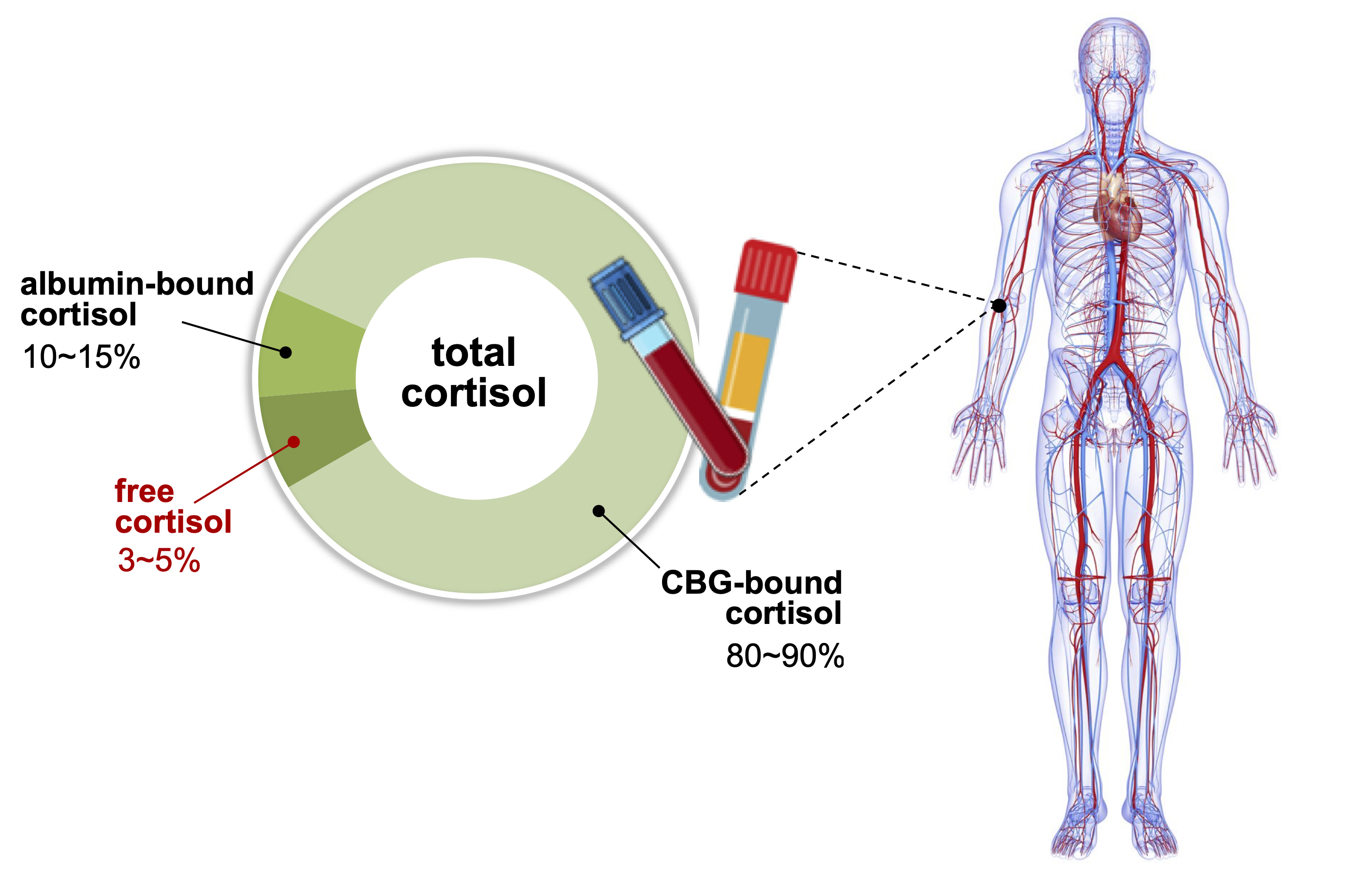
ePub - Accurate measurement of cortisol is critical in adrenal insufficiency as it reduces the risk associated with misdiagnosis and supports the optimization of stress dose. Comprehensive assays have been developed to determine the levels of bioactive free cortisol and their clinical and analytical efficacies have been extensively discussed because the level of total cortisol is affected by changes in the structure or circulating levels of corticoid-binding globulin and albumin, which are the main reservoirs of cortisol in the human body. Antibody-based immunoassays are routinely used in clinical laboratories; however, the lack of molecular specificity in cortisol assessment limits their applicability to characterize adrenocortical function. Improved specificity and sensitivity can be achieved by mass spectrometry coupled with chromatographic separation methods, which is a cutting-edge technology to measure individual as well as a panel of steroids in a single analytical run. The purpose of this review is to introduce recent advances in free cortisol measurement from the perspectives of clinical specimens and issues associated with prospective analytical technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Highly Responsive Bioassay for Quantification of Glucocorticoids
Mathias Flensted Poulsen, Martin Overgaard, Christian Brix Folsted Andersen, Andreas Lodberg
Analytical Chemistry.2024; 96(5): 2000. CrossRef - An LC-MS/MS Method for the Simultaneous Quantification of Insulin, Cortisol, Glucagon-like Peptide 1, Ghrelin, and Osteocalcin
Zhichao Zhang, Hareem Siddiqi, Yu-Ping Huang, Shannon McClorry, Peng Ji, Daniela Barile, Carolyn M. Slupsky
Separations.2024; 11(2): 41. CrossRef - Determination of cortisol cut-off limits and steroid dynamics in the ACTH stimulation test: a comparative analysis using Roche Elecsys Cortisol II immunoassay and LC-MS/MS
Sema Okutan, Nanna Thurmann Jørgensen, Lars Engers Pedersen, Stina Willemoes Borresen, Linda Hilsted, Lennart Friis Hansen, Ulla Feldt-Rasmussen, Marianne Klose
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancements in Cortisol Detection: From Conventional Methods to Next-Generation Technologies for Enhanced Hormone Monitoring
Visesh Vignesh, Bernardo Castro-Dominguez, Tony D. James, Julie M. Gamble-Turner, Stafford Lightman, Nuno M. Reis
ACS Sensors.2024; 9(4): 1666. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of salivary cortisol measurements using different assay methods in relation to serum-free cortisol measurement
Anna Lee, Sooah Jang, Sanghoo Lee, Hyun-Kyung Park, In-Young Kim, Ryunsup Ahn, Jeong-Ho Seok, Kyoung-Ryul Lee
Practical Laboratory Medicine.2024; 40: e00393. CrossRef - A dilute and shoot method for urinary free cortisol analysis by LC-MS/MS
Ying Shen, Xia Luo, Qing Guan, Liming Cheng
Journal of Chromatography B.2024; 1239: 124127. CrossRef - Osteopathic Manipulation as a Method of Cortisol Modification: A Systematic Review
Dylan Thibaut, Valentine Santarlas, Joseph Hoppes, Alejandra Vásquez-Castillo, Alexa Morrow, Eddie Oviedo, James Toldi
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pitfalls in the Diagnosis and Management of Hypercortisolism (Cushing Syndrome) in Humans; A Review of the Laboratory Medicine Perspective
Kade C. Flowers, Kate E. Shipman
Diagnostics.2023; 13(8): 1415. CrossRef - Electrochemical sensors for cortisol detection: Principles, designs, fabrication, and characterisation
Gopi Karuppaiah, Min-Ho Lee, Shekhar Bhansali, Pandiaraj Manickam
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2023; 239: 115600. CrossRef - The role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in depression across the female reproductive lifecycle: current knowledge and future directions
Liisa Hantsoo, Kathleen M. Jagodnik, Andrew M. Novick, Ritika Baweja, Teresa Lanza di Scalea, Aysegul Ozerdem, Erin C. McGlade, Diana I. Simeonova, Sharon Dekel, Sara L. Kornfield, Michelle Nazareth, Sandra J. Weiss
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - РІВЕНЬ СТРЕСУ В ДІТЕЙ ШКІЛЬНОГО ВІКУ З COVID-19
Г. А. Павлишин, О. І. Панченко
Здобутки клінічної і експериментальної медицини.2023; (4): 119. CrossRef - Corticotropin-stimulated steroid profiles to predict shock development and mortality in sepsis: From the HYPRESS study
Josef Briegel, Patrick Möhnle, Didier Keh, Johanna M. Lindner, Anna C. Vetter, Holger Bogatsch, Dorothea Lange, Sandra Frank, Ludwig C. Hinske, Djillali Annane, Michael Vogeser, Michael Bauer, Thorsten Brenner, Patrick Meybohm, Markus Weigand, Matthias Gr
Critical Care.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Highly Responsive Bioassay for Quantification of Glucocorticoids

- Miscellaneous
- Clinical Value of Serum Mitochondria-Inhibiting Substances in Assessing Renal Hazards: A Community-Based Prospective Study in Korea
- Hoon Sung Choi, Jin Taek Kim, Hong Kyu Lee, Wook Ha Park, Youngmi Kim Pak, Sung Woo Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1298-1306. Published online November 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1226
- 3,279 View
- 95 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
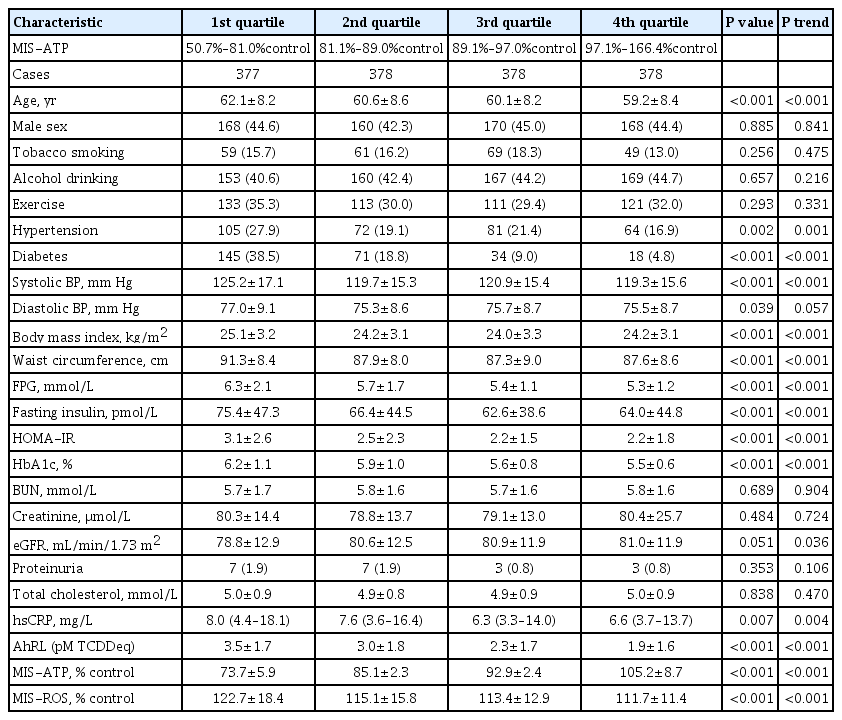
Mitochondrial dysfunction is strongly associated with several kidney diseases. However, no studies have evaluated the potential renal hazards of serum mitochondria-inhibiting substance (MIS) and aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand (AhRL) levels.
Methods
We used serum level of MIS and AhRL and clinical renal outcomes from 1,511 participants of a prospective community-based cohort in Ansung. MIS was evaluated based on intracellular adenosine triphosphate (MIS-ATP) or reactive oxygen species (MIS-ROS) generation measured using cell-based assays.
Results
During a mean 6.9-year follow-up, 84 participants (5.6%) developed a rapid decline in kidney function. In the lowest quartile group of MIS-ATP, patients were older and had metabolically deleterious parameters. In multivariate logistic regression analysis, higher MIS-ATP was associated with decreased odds for rapid decline: the odds ratio (OR) of 1% increase was 0.977 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.957 to 0.998; P=0.031), while higher MIS-ROS was marginally associated with increased odds for rapid decline (OR, 1.014; 95% CI, 0.999 to 1.028; P=0.055). However, serum AhRL was not associated with the rapid decline in kidney function. In subgroup analysis, the renal hazard of MIS was particularly evident in people with hypertension and low baseline kidney function.
Conclusion
Serum MIS was independently associated with a rapid decline in kidney function, while serum AhRL was not. The clinical implication of renal hazard on serum MIS requires further evaluation in future studies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Interactive Online App for Predicting Diabetes via Machine Learning from Environment-Polluting Chemical Exposure Data
Rosy Oh, Hong Kyu Lee, Youngmi Kim Pak, Man-Suk Oh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(10): 5800. CrossRef
- An Interactive Online App for Predicting Diabetes via Machine Learning from Environment-Polluting Chemical Exposure Data

- Miscellaneous
- COVID-19 Vaccination for Endocrine Patients: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
- Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Chang Ho Ahn, Jun Sung Moon, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Hee Kyung Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Eun Roh, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim, the Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline of the Korean Endocrine Society
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):757-765. Published online August 17, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.404
- 10,369 View
- 419 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 21 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Since the first outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), ongoing efforts have been made to discover an efficacious vaccine against COVID-19 to combat the pandemic. In most countries, both mRNA and DNA vaccines have been administered, and their side effects have also been reported. The clinical course of COVID-19 and the effects of vaccination against COVID-19 are both influenced by patients’ health status and involve a systemic physiological response. In view of the systemic function of endocrine hormones, endocrine disorders themselves and the therapeutics used to treat them can influence the outcomes of vaccination for COVID-19. However, there are very limited data to support the development of clinical guidelines for patients with specific medical backgrounds based on large clinical trials. In the current severe circumstances of the COVID-19 pandemic, position statements made by clinical specialists are essential to provide appropriate recommendations based on both medical evidence and clinical experiences. As endocrinologists, we would like to present the medical background of COVID-19 vaccination, as well as precautions to prevent the side effects of COVID-19 vaccination in patients with specific endocrine disorders, including adrenal insufficiency, diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, autoimmune thyroid disease, hypogonadism, and pituitary disorders.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- COVID-19 mRNA vaccine may trigger subacute thyroiditis
Mehmet Sözen, Ömercan Topaloğlu, Berrin Çetinarslan, Alev Selek, Zeynep Cantürk, Emre Gezer, Damla Köksalan, Taner Bayraktaroğlu
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2024; 17(12): 5120. CrossRef - The role of co-morbidities in the development of an AEFI after COVID-19 vaccination in a large prospective cohort with patient-reported outcomes in the Netherlands
C. Ouaddouh, J.W. Duijster, T. Lieber, F.P.A.M. van Hunsel
Expert Opinion on Drug Safety.2024; 23(3): 323. CrossRef - Thyroid dysfunction in COVID-19
David Tak Wai Lui, Chi Ho Lee, Yu Cho Woo, Ivan Fan Ngai Hung, Karen Siu Ling Lam
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Adult-Onset Type 1 Diabetes Development Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination
Hyeyeon Moon, Sunghwan Suh, Mi Kyoung Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prior immunization status of COVID-19 patients and disease severity: A multicenter retrospective cohort study assessing the different types of immunity
Javaria Aslam, Faisal Shahzad Khan, Muhammad Talha Haris, Hewad Hewadmal, Maryam Khalid, Mohammad Y. Alshahrani, Qurrat-ul-ain Aslam, Irrum Aneela, Urooj Zafar
Vaccine.2023; 41(2): 598. CrossRef - Mortality and Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Patients with Long-Term Glucocorticoid Therapy: A Korean Nationwide Cohort Study
Eu Jeong Ku, Keeho Song, Kyoung Min Kim, Gi Hyeon Seo, Soon Jib Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 253. CrossRef - Pituitary Diseases and COVID-19 Outcomes in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Jeonghoon Ha, Kyoung Min Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(14): 4799. CrossRef - Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccination does not disturb the clinical course of Graves’ disease: An observational cohort study
Shichen Xu, Huixin Yu, Xian Cheng, Jing Wu, Jiandong Bao, Li Zhang
Vaccine.2023; 41(38): 5648. CrossRef - Adrenal Crisis Associated With COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients With Adrenal Insufficiency
Yukako Kurematsu, Takako Mohri, Sadanori Okada, Yutaka Takahashi
JCEM Case Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adverse Events Associated with COVID-19 Vaccination in Adolescents with Endocrinological Disorders: A Cross-Sectional Study
İbrahim Mert Erbaş, İrem Ceren Erbaş, Gözde Akın Kağızmanlı, Kübra Yüksek Acinikli, Özge Besci, Korcan Demir, Ece Böber, Nurşen Belet, Ayhan Abacı
Journal of Clinical Research in Pediatric Endocrinology.2023; 15(3): 248. CrossRef - Neue Aspekte der Glukokortikoidsubstitution bei Nebennierenrindeninsuffizienz
Tina Kienitz, Gesine Meyer
Der Internist.2022; 63(1): 12. CrossRef - Endocrine Follow-up During Post-Acute COVID-19: Practical Recommendations Based on Available Clinical Evidence
Rimesh Pal, Ameya Joshi, Sanjay K. Bhadada, Mainak Banerjee, Suresh Vaikkakara, Satinath Mukhopadhyay
Endocrine Practice.2022; 28(4): 425. CrossRef - Safety of Inactivated and mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination Among Patients Treated for Hypothyroidism: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Xi Xiong, Carlos King Ho Wong, Ivan Chi Ho Au, Francisco Tsz Tsun Lai, Xue Li, Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Celine Sze Ling Chui, Esther Wai Yin Chan, Franco Wing Tak Cheng, Kristy Tsz Kwan Lau, Chi Ho Lee, Yu Cho Woo, David Tak Wai Lui, Ian Chi Kei Wong
Thyroid.2022; 32(5): 505. CrossRef - The New Entity of Subacute Thyroiditis amid the COVID-19 Pandemic: From Infection to Vaccine
Mihaela Popescu, Adina Ghemigian, Corina Maria Vasile, Andrei Costache, Mara Carsote, Alice Elena Ghenea
Diagnostics.2022; 12(4): 960. CrossRef - Adrenal Crisis Secondary to COVID-19 Vaccination in a Patient With Hypopituitarism
Nikolina Markovic, Anila Faizan, Chirag Boradia, Sridhar Nambi
AACE Clinical Case Reports.2022; 8(4): 171. CrossRef - The Effect of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines on TRAB in Graves’ Disease
LingHong Huang, ZhengRong Jiang, JingXiong Zhou, YuPing Chen, HuiBin Huang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Osteoporosis in Patients With Respiratory Diseases
Yue Ma, Shui Qiu, Renyi Zhou
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Pilot Findings on SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine-Induced Pituitary Diseases: A Mini Review from Diagnosis to Pathophysiology
Ach Taieb, El Euch Mounira
Vaccines.2022; 10(12): 2004. CrossRef - Forty Years Together, New Leap Forward! The 40th Anniversary of the Korean Endocrine Society
Jong Chul Won, Ki-Hyun Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 851. CrossRef - No need of glucocorticoid dose adjustment in patients with adrenal insufficiency before COVID-19 vaccine
Tania Pilli, Cristina Dalmiglio, Gilda Dalmazio, Alfonso Sagnella, Raffaella Forleo, Lucia Brilli, Fabio Maino, Cristina Ciuoli, Maria Grazia Castagna
European Journal of Endocrinology.2022; 187(1): K7. CrossRef - Diabetes and COVID-19 Vaccination
Hae Dong Choi, Jun Sung Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(4): 221. CrossRef
- COVID-19 mRNA vaccine may trigger subacute thyroiditis

- Miscellaneous
- Clinical Characteristics, Management, and Potential Biomarkers of Endocrine Dysfunction Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
- Shintaro Iwama, Tomoko Kobayashi, Hiroshi Arima
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(2):312-321. Published online April 27, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1007
- 5,492 View
- 267 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
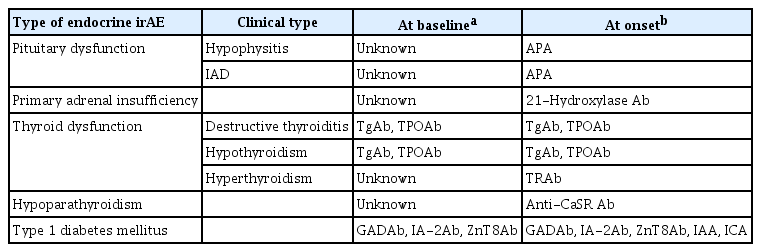
ePub - Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) affecting the endocrine glands are among the most frequent irAEs induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and include hypopituitarism, primary adrenal insufficiency, thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism, hypoparathyroidism, and type 1 diabetes mellitus. Since the incidence and clinical features of endocrine irAEs vary according to the ICI used, it is important to understand the characteristics of these irAEs and to manage each one appropriately. Since some endocrine irAEs, including adrenal crisis and diabetic ketoacidosis, are potentially life-threatening, predicting the risk of endocrine irAEs before their onset is critical. Several autoantibodies have been detected in patients who develop endocrine irAEs, among which anti-thyroid antibodies may be predictive biomarkers of thyroid dysfunction. In this review, we describe the clinical features of each endocrine irAE induced by ICIs and discuss their potential biomarkers, including autoantibodies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical characteristics and potential biomarkers of thyroid and pituitary immune-related adverse events
Tomoko Kobayashi, Shintaro Iwama, Hiroshi Arima
Endocrine Journal.2024; 71(1): 23. CrossRef - A case of rapidly progressive insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus without islet autoantibodies developed over two years after the first dose of nivolumab
Kota Nishihama, Yuko Okano, Chisa Inoue, Kanako Maki, Kazuhito Eguchi, Soichiro Tanaka, Atsuro Takeshita, Mei Uemura, Taro Yasuma, Toshinari Suzuki, Esteban C. Gabazza, Yutaka Yano
Diabetology International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endocrinopathies Associated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Use
Anupam Kotwal, Randol Kennedy, Nupur Kikani, Sonali Thosani, Whitney Goldner, Afreen Shariff
Endocrine Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recovery from insulin dependence in immune checkpoint inhibitor‐associated diabetes mellitus: A case report
Marie Okubo, Yuji Hataya, Kanta Fujimoto, Toshio Iwakura, Naoki Matsuoka
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(1): 147. CrossRef - Case Report: A Rising Cause of New-Onset Endocrinopathies After Immunotherapy
Charity Tan, Sarah Hendricks, Kristina Hernandez, Martha Benavides, Rupinderjit Samra
The Journal for Nurse Practitioners.2023; 19(5): 104582. CrossRef - Risk of Thyroid Dysfunction in PD-1 Blockade Is Stratified by the Pattern of TgAb and TPOAb Positivity at Baseline
Xin Zhou, Shintaro Iwama, Tomoko Kobayashi, Masahiko Ando, Hiroshi Arima
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(10): e1056. CrossRef - Severe thyrotoxicosis induced by tislelizumab: a case report and literature review
Liman Huo, Chao Wang, Haixia Ding, Xuelian Shi, Bin Shan, Ruoying Zhou, Ping Liang, Juan Hou
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Life-Threatening Endocrinological Immune-Related Adverse Events of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy
Aleksandra Basek, Grzegorz K. Jakubiak, Grzegorz Cieślar, Agata Stanek
Cancers.2023; 15(24): 5786. CrossRef - Increased Risk of Thyroid Dysfunction by PD-1 and CTLA-4 Blockade in Patients Without Thyroid Autoantibodies at Baseline
Shintaro Iwama, Tomoko Kobayashi, Yoshinori Yasuda, Takayuki Okuji, Masaaki Ito, Masahiko Ando, Xin Zhou, Ayana Yamagami, Takeshi Onoue, Yohei Kawaguchi, Takashi Miyata, Mariko Sugiyama, Hiroshi Takagi, Daisuke Hagiwara, Hidetaka Suga, Ryoichi Banno, Tets
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(4): e1620. CrossRef - Biomarkers and risk factors for the early prediction of immune-related adverse events: a review
Ying Zhang, Xiaoling Zhang, Weiling Li, Yunyi Du, Wenqing Hu, Jun Zhao
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors as a Threat to the Hypothalamus–Pituitary Axis: A Completed Puzzle
Agnese Barnabei, Andrea Corsello, Rosa Maria Paragliola, Giovanni Maria Iannantuono, Luca Falzone, Salvatore Maria Corsello, Francesco Torino
Cancers.2022; 14(4): 1057. CrossRef - Elevated TSH Level, TgAb, and Prior Use of Ramucirumab or TKIs as Risk Factors for Thyroid Dysfunction in PD-L1 Blockade
Tomoko Kobayashi, Shintaro Iwama, Ayana Yamagami, Yoshinori Yasuda, Takayuki Okuji, Masaaki Ito, Xin Zhou, Masahiko Ando, Takeshi Onoue, Takashi Miyata, Mariko Sugiyama, Daisuke Hagiwara, Hidetaka Suga, Ryoichi Banno, Tetsunari Hase, Masahiro Morise, Taka
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(10): e4115. CrossRef - Preconditioning of the immune system modulates the response of papillary thyroid cancer to immune checkpoint inhibitors
Fabiana Pani, Yoshinori Yasuda, Sylvie T Rousseau, Kevin C Bermea, Solmaz Roshanmehr, Rulin Wang, Srinivasan Yegnasubramanian, Patrizio Caturegli, Luigi Adamo
Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer.2022; 10(12): e005538. CrossRef - Survival benefit of endocrine dysfunction following immune checkpoint inhibitors for nonthyroidal cancers
Anupam Kotwal, Mabel Ryder
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2021; 28(5): 517. CrossRef
- Clinical characteristics and potential biomarkers of thyroid and pituitary immune-related adverse events

- Diabetes
- Cardiorenal Protection in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Jason F. Lee, Ecaterina Berzan, Vikas S. Sridhar, Ayodele Odutayo, David Z.I. Cherney
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(2):256-269. Published online April 19, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.987
- 5,734 View
- 300 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
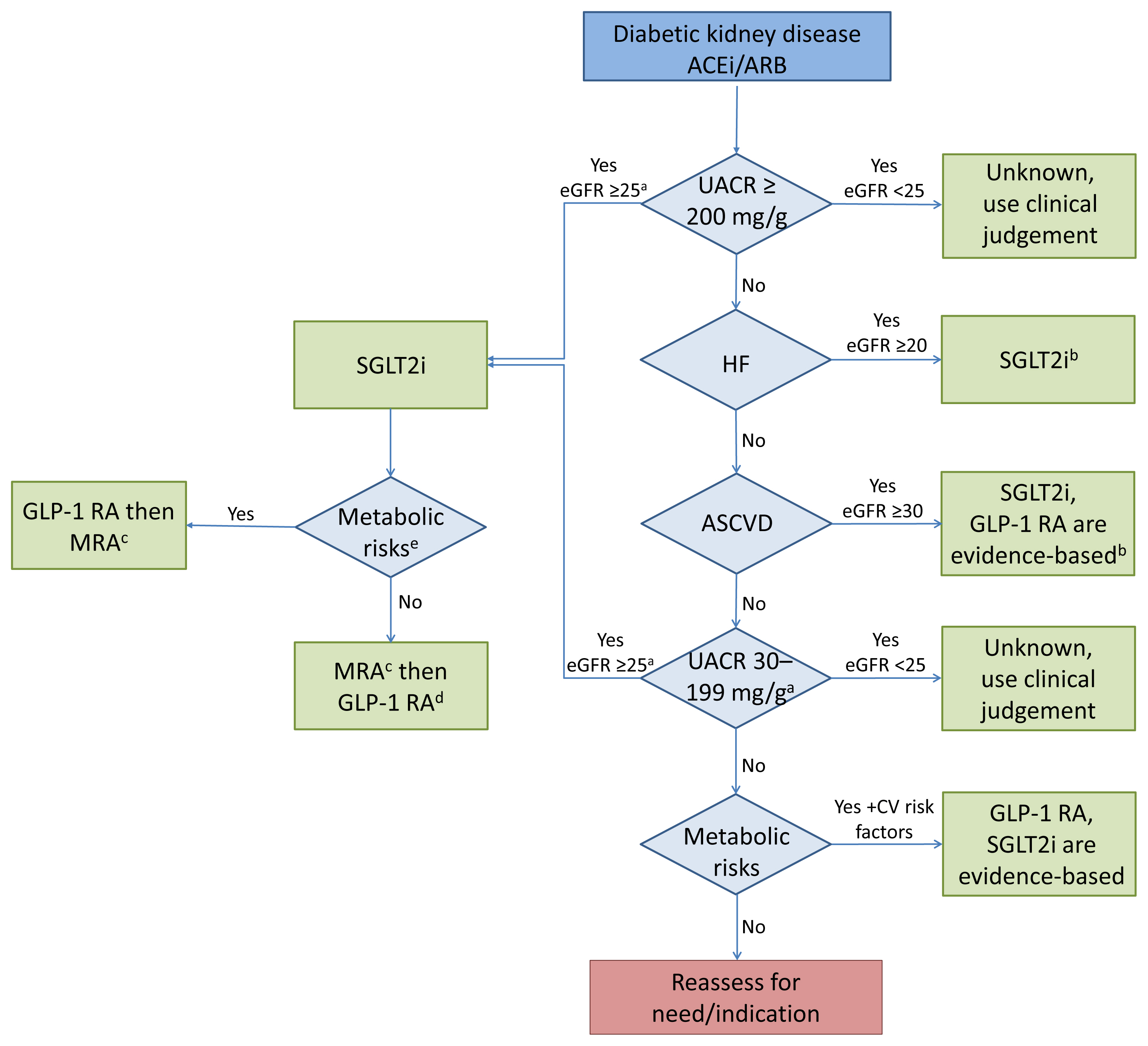
ePub - Over the last 5 years there have been many new developments in the management of diabetic kidney disease. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors were initially used for glycemic control, but more recent studies have now shown that their benefits extend to cardiovascular and kidney outcomes. The recent addition of data on the novel mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) gives us another approach to further decrease the residual risk of diabetic kidney disease progression. In this review we describe the mechanism of action, key studies, and possible adverse effects related to these three classes of medications. The management of type 2 diabetes now includes an increasing number of medications for the management of comorbidities in a patient population at significant risk of cardiovascular disease and progression of chronic kidney disease. It is from this perspective that we seek to outline the rationale for the sequential and/or combined use of SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 RA and MRAs in patients with type 2 diabetes for heart and kidney protection.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relative and Absolute Risks of Adverse Events with Real-World Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in CKD
Ayodele Odutayo, Adeera Levin
Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.2023; 18(5): 557. CrossRef - Renal Protection of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist, Finerenone, in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Dong-Lim Kim, Seung-Eun Lee, Nan Hee Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 43. CrossRef - Intrarenal Mechanisms of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors on Tubuloglomerular Feedback and Natriuresis
Eun Sil Koh, Gheun-Ho Kim, Sungjin Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 359. CrossRef - SGLT2 and DPP4 inhibitors improve Alzheimer’s disease–like pathology and cognitive function through distinct mechanisms in a T2D–AD mouse model
A Young Sim, Da Hyun Choi, Jong Youl Kim, Eun Ran Kim, A-ra Goh, Yong-ho Lee, Jong Eun Lee
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 168: 115755. CrossRef - Narrative review investigating the nephroprotective mechanisms of sodium glucose cotransporter type 2 inhibitors in diabetic and nondiabetic patients with chronic kidney disease
Emma S. Speedtsberg, Martin Tepel
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of CKD
Nimrit Goraya, Jennifer D. Moran
Nephrology Self-Assessment Program.2022; 21(2): 146. CrossRef - Nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonism for cardiovascular and renal disorders − New perspectives for combination therapy
Peter Kolkhof, Amer Joseph, Ulrich Kintscher
Pharmacological Research.2021; 172: 105859. CrossRef - Sodium‐Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors, All‐Cause Mortality, and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Bayesian Meta‐Analysis and Meta‐Regression
Ayodele Odutayo, Bruno R. da Costa, Tiago V. Pereira, Vinay Garg, Samir Iskander, Fatimah Roble, Rahim Lalji, Cesar A. Hincapié, Aquila Akingbade, Myanca Rodrigues, Arnav Agarwal, Bishoy Lawendy, Pakeezah Saadat, Jacob A. Udell, Francesco Cosentino, Peter
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Finerenone: A Potential Treatment for Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Luis D’Marco, María Jesús Puchades, Lorena Gandía, Claudia Forquet, Elena Giménez-Civera, Nayara Panizo, Javier Reque, Isabel Juan-García, Valmore Bermúdez, José Luis Gorriz
touchREVIEWS in Endocrinology.2021; 17(2): 84. CrossRef - Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Mechanisms of Action: A Review
Jorge I. Fonseca-Correa, Ricardo Correa-Rotter
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Relative and Absolute Risks of Adverse Events with Real-World Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in CKD

- Clinical Study
- Stimulated Salivary Cortisol as a Noninvasive Diagnostic Tool for Adrenal Insufficiency
- Yoon Ji Kim, Jung Hee Kim, A Ram Hong, Kyeong Seon Park, Sang Wan Kim, Chan Soo Shin, Seong Yeon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):628-635. Published online September 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.707
- 5,834 View
- 201 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Salivary cortisol is routinely used as a diagnostic test for Cushing syndrome. The diagnostic use of salivary cortisol for adrenal insufficiency (AI), however, is less established. We aimed to investigate the utility of morning basal and adrenocorticotropic hormone-stimulated salivary cortisol in diagnosing AI in Korean adults.
Methods
We prospectively included 120 subjects (female, n=70) from Seoul National University Hospital. AI was defined as a stimulated serum cortisol level of <496.8 nmol/L during the short Synacthen test (SST). Serum and saliva samples were drawn between 8:00 AM and 10:00 AM. Salivary cortisol levels were measured using an enzyme immunoassay kit.
Results
Thirty-four patients were diagnosed with AI according to the SST results. Age, sex, body mass index, serum albumin levels, and serum creatinine levels did not significantly differ between the normal and AI groups. Basal and stimulated salivary cortisol levels were positively correlated with basal (r=0.538) and stimulated serum cortisol levels (r=0.750), respectively (all P<0.001). Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis yielded a cutoff level of morning basal salivary cortisol of 3.2 nmol/L (sensitivity, 84.9%; specificity, 73.5%; area under the curve [AUC]=0.822). The optimal cutoff value of stimulated salivary cortisol was 13.2 nmol/L (sensitivity, 90.7%; specificity, 94.1%; AUC=0.959). Subjects with a stimulated salivary cortisol level above 13.2 nmol/L but a stimulated serum cortisol level below 496.8 nmol/L (n=2) had lower serum albumin levels than those showing a concordant response.
Conclusion
The diagnostic performance of stimulated salivary cortisol measurements after the SST was comparable to serum cortisol measurements for diagnosing AI. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extensive expertise in endocrinology: adrenal crisis in assisted reproduction and pregnancy
Ulla Feldt-Rasmussen
European Journal of Endocrinology.2024; 190(1): R10. CrossRef - Turning Antibodies into Ratiometric Bioluminescent Sensors for Competition-Based Homogeneous Immunoassays
Eva A. van Aalen, Joep J. J. Lurvink, Leandra Vermeulen, Benice van Gerven, Yan Ni, Remco Arts, Maarten Merkx
ACS Sensors.2024; 9(3): 1401. CrossRef - A Contemporary Approach to the Diagnosis and Management of Adrenal Insufficiency
Suranut Charoensri, Richard J. Auchus
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 73. CrossRef - Diagnostic strategies in adrenal insufficiency
Vasiliki Siampanopoulou, Elisavet Tasouli, Anna Angelousi
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2023; 30(3): 141. CrossRef - The association between neuropeptide oxytocin and neuropsychiatric disorders after orthopedic surgery stress in older patients
Wanru Dong, Zengbo Ding, Xiao Wu, Ran Wan, Ying Liu, Liubao Pei, Weili Zhu
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Reliability of Salivary Cortisol Compared to Serum Cortisol for Diagnosing Adrenal Insufficiency with the Gold Standard ACTH Stimulation Test in Children
Silvia Ciancia, Sjoerd A. A. van den Berg, Erica L. T. van den Akker
Children.2023; 10(9): 1569. CrossRef - РІВЕНЬ СТРЕСУ В ДІТЕЙ ШКІЛЬНОГО ВІКУ З COVID-19
Г. А. Павлишин, О. І. Панченко
Здобутки клінічної і експериментальної медицини.2023; (4): 119. CrossRef - Secondary adrenal suppression related to high doses of inhaled corticosteroids in patients with severe asthma
Mariana Lobato, João Gaspar-Marques, Pedro Carreiro-Martins, Paula Leiria-Pinto
Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology.2022; 128(4): 464. CrossRef - Clinical and Technical Aspects in Free Cortisol Measurement
Man Ho Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 599. CrossRef - Continuous biomarker monitoring with single molecule resolution by measuring free particle motion
Alissa D. Buskermolen, Yu-Ting Lin, Laura van Smeden, Rik B. van Haaften, Junhong Yan, Khulan Sergelen, Arthur M. de Jong, Menno W. J. Prins
Nature Communications.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Reversible Immunosensor for the Continuous Monitoring of Cortisol in Blood Plasma Sampled with Microdialysis
Laura van Smeden, Annet Saris, Khulan Sergelen, Arthur M. de Jong, Junhong Yan, Menno W. J. Prins
ACS Sensors.2022; 7(10): 3041. CrossRef - Adrenal insufficiency in HIV/AIDS: a review
Simon Mifsud, Zachary Gauci, Mark Gruppetta, Charles Mallia Azzopardi, Stephen Fava
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 16(6): 351. CrossRef
- Extensive expertise in endocrinology: adrenal crisis in assisted reproduction and pregnancy

- Miscellaneous
- Encountering COVID-19 as Endocrinologists
- Eun-Jung Rhee, Jung Hee Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):197-205. Published online June 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.197
- 13,302 View
- 277 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The world is entering an era of disaster and chaos due to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Since its first emergence in December 2019 in Wuhan, China, COVID-19 has swept through Asia and propagated throughout the world to Europe and North America. As of April 13, 1,773,084 people were infected and 111,652 people had died from COVID-19 globally, and new record levels of infection are being reported every day. Based on the data that have been amassed so far, the primary risk factors for a severe disease course or even mortality from COVID-19 are underlying diseases such as diabetes and hypertension. As the global prevalence of diabetes continues to increase, patients with endocrine diseases such as diabetes mellitus and those who are on long-term corticosteroid therapy due to adrenal insufficiency or hypopituitarism are at risk for a poor prognosis of COVID-19. As endocrinologists, we would like to briefly review the current knowledge about the relationship between COVID-19 and endocrine diseases and to discuss what we can do for the safety and health of our patients with endocrine diseases in this globally threatening situation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adverse Events Associated with COVID-19 Vaccination in Adolescents with Endocrinological Disorders: A Cross-Sectional Study
İbrahim Mert Erbaş, İrem Ceren Erbaş, Gözde Akın Kağızmanlı, Kübra Yüksek Acinikli, Özge Besci, Korcan Demir, Ece Böber, Nurşen Belet, Ayhan Abacı
Journal of Clinical Research in Pediatric Endocrinology.2023; 15(3): 248. CrossRef - Pituitary Diseases and COVID-19 Outcomes in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Jeonghoon Ha, Kyoung Min Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(14): 4799. CrossRef - New-onset and relapsed Graves’ disease following COVID-19 vaccination: a comprehensive review of reported cases
Kan Chen, Yiyang Gao, Jing Li
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Neuroendocrine Changes and Hypothalamo-Pituitary
Autoimmunity in Patients with COVID-19
Mustafa Sait Gonen, Annamaria De Bellis, Emre Durcan, Giuseppe Bellastella, Paolo Cirillo, Lorenzo Scappaticcio, Miriam Longo, Basak Ecem Bircan, Serdar Sahin, Cem Sulu, Hande Mefkure Ozkaya, Dildar Konukoglu, Fatma Ferda Kartufan, Fahrettin Kelestimur
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2022; 54(03): 153. CrossRef - COVID-19 and diabetes: Association intensify risk factors for morbidity and mortality
Prateek Sharma, Tapan Behl, Neelam Sharma, Sukhbir Singh, Ajmer Singh Grewal, Ali Albarrati, Mohammed Albratty, Abdulkarim M. Meraya, Simona Bungau
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 151: 113089. CrossRef - The Relationship between COVID-19 and Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis: A Large Spectrum from Glucocorticoid Insufficiency to Excess—The CAPISCO International Expert Panel
Mojca Jensterle, Rok Herman, Andrej Janež, Wael Al Mahmeed, Khalid Al-Rasadi, Kamila Al-Alawi, Maciej Banach, Yajnavalka Banerjee, Antonio Ceriello, Mustafa Cesur, Francesco Cosentino, Massimo Galia, Su-Yen Goh, Sanjay Kalra, Peter Kempler, Nader Lessan,
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(13): 7326. CrossRef - WhatsApp-Based virtual consultation in clinical practice during COVID times: A prospective institutional study
RamakanthBhargav Panchangam, Pradeep Puthenveetil, SunilKumar Kota, Sabaretnam Mayilvaganan
Annals of African Medicine.2022; 21(2): 132. CrossRef - Thyroid and COVID-19: a review on pathophysiological, clinical and organizational aspects
G. Lisco, A. De Tullio, E. Jirillo, V. A. Giagulli, G. De Pergola, E. Guastamacchia, V. Triggiani
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2021; 44(9): 1801. CrossRef - Effects of a DPP-4 Inhibitor and RAS Blockade on Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Diabetes and COVID-19
Sang Youl Rhee, Jeongwoo Lee, Hyewon Nam, Dae-Sung Kyoung, Dong Wook Shin, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 251. CrossRef - COVID-19 Vaccination for Endocrine Patients: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Chang Ho Ahn, Jun Sung Moon, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Hee Kyung Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Eun Roh, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 757. CrossRef - Collateral Damage of the COVID‐19 Pandemic on Nutritional Quality and Physical Activity: Perspective from South Korea
Soo Lim, Hyunjung Lim, Jean‐Pierre Després
Obesity.2020; 28(10): 1788. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus and COVID-19 in the post-acute phase patients - possible links with physical and rehabilitation medicine and balneotherapy
Constantin Munteanu, Diana-Loreta PĂUN, Alina-Maria ȘUȚĂ, Simin Aysel FLORESCU, Gelu ONOSE, Mihail Hoteteu
Balneo Research Journal.2020; 11(Vol.11, no): 350. CrossRef - Managing Diabetes During the COVID-19 Pandemic
John Doupis, Konstantinos Avramidis
European Endocrinology.2020; 16(2): 85. CrossRef - Independent Impact of Diabetes on the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in 5,307 Patients in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Sun Joon Moon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Sung-Rae Kim, Won-Young Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 737. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) and the Endocrine System
Michelle D Lundholm, Caroline Poku, Nicholas Emanuele, Mary Ann Emanuele, Norma Lopez
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Adverse Events Associated with COVID-19 Vaccination in Adolescents with Endocrinological Disorders: A Cross-Sectional Study

- Comparison between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin in Renal Function Decline among Patients with Diabetes
- Eugene Han, Gyuri Kim, Ji-Yeon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Beom Seok Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(2):274-280. Published online June 23, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.2.274
- 5,247 View
- 175 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Although the beneficial effects of statin treatment in dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis have been well studied, there is limited information regarding the renal effects of statins in diabetic nephropathy. We aimed to investigate whether, and which, statins affected renal function in Asian patients with diabetes.
Methods We enrolled 484 patients with diabetes who received statin treatment for more than 12 months. We included patients treated with moderate-intensity dose statin treatment (atorvastatin 10 to 20 mg/day or rosuvastatin 5 to 10 mg/day). The primary outcome was a change in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) during the 12-month statin treatment, and rapid renal decline was defined as a >3% reduction in eGFR in a 1-year period.
Results In both statin treatment groups, patients showed improved serum lipid levels and significantly reduced eGFRs (from 80.3 to 78.8 mL/min/1.73 m2 for atorvastatin [
P =0.012], from 79.1 to 76.1 mL/min/1.73 m2 for rosuvastatin [P =0.001]). A more rapid eGFR decline was observed in the rosuvastatin group than in the atorvastatin group (48.7% vs. 38.6%,P =0.029). Multiple logistic regression analyses demonstrated more rapid renal function loss in the rosuvastatin group than in the atorvastatin group after adjustment for other confounding factors (odds ratio, 1.60; 95% confidence interval, 1.06 to 2.42).Conclusion These results suggest that a moderate-intensity dose of atorvastatin has fewer detrimental effects on renal function than that of rosuvastatin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with telmisartan, rosuvastatin, and ezetimibe in patients with dyslipidemia and hypertension: A randomized, double‐blind, multicenter, therapeutic confirmatory, phase III clinical trial
Chan Joo Lee, Woong Chol Kang, Sang Hyun Ihm, Il Suk Sohn, Jong Shin Woo, Jin Won Kim, Soon Jun Hong, Jung Hyun Choi, Jung‐Won Suh, Jae‐Bin Seo, Joon‐Hyung Doh, Jung‐Woo Son, Jae‐Hyeong Park, Ju‐Hee Lee, Young Joon Hong, Jung Ho Heo, Jinho Shin, Seok‐Min
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2024; 26(3): 262. CrossRef - Anti-hyperglycemic, anti-hyperlipidemic, and anti-inflammatory effect of the drug Guggulutiktaka ghrita on high-fat diet-induced obese rats
Samreen M. Sheik, Pugazhandhi Bakthavatchalam, Revathi P. Shenoy, Basavaraj S. Hadapad, Deepak Nayak M, Monalisa Biswas, Varashree Bolar Suryakanth
Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine.2022; 13(3): 100583. CrossRef - The challenge of reducing residual cardiovascular risk in patients with chronic kidney disease
Stefan Mark Nidorf
European Heart Journal.2022; 43(46): 4845. CrossRef - Diabetic Kidney Disease in Older People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Improving Prevention and Treatment Options
Ahmed H. Abdelhafiz
Drugs & Aging.2020; 37(8): 567. CrossRef - Intracellular Mechanism of Rosuvastatin-Induced Decrease in Mature hERG Protein Expression on Membrane
Pan-Feng Feng, Bo Zhang, Lei Zhao, Qing Fang, Yan Liu, Jun-Nan Wang, Xue-Qi Xu, Hui Xue, Yang Li, Cai-Chuan Yan, Xin Zhao, Bao-Xin Li
Molecular Pharmaceutics.2019; 16(4): 1477. CrossRef - The problem of safety of lipid-lowering therapy
M V. Zykov
Kardiologiia.2019; 59(5S): 13. CrossRef - Regional evidence and international recommendations to guide lipid management in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes with special reference to renal dysfunction
Titus WL Lau, Kevin E.K. Tan, Jason C.J. Choo, Tsun‐Gun Ng, Subramaniam Tavintharan, Juliana C.N. Chan
Journal of Diabetes.2018; 10(3): 200. CrossRef - Lipids: a personal view of the past decade
Niki Katsiki, Dimitri P Mikhailidis
Hormones.2018; 17(4): 461. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with telmisartan, rosuvastatin, and ezetimibe in patients with dyslipidemia and hypertension: A randomized, double‐blind, multicenter, therapeutic confirmatory, phase III clinical trial

- Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Adrenal Insufficiency in a General Hospital
- Ye Yeon Lee, Nan Hee Cho, Jong Won Lee, Nam Kyung Kim, Hye Soon Kim, Mi-Kyung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(1):83-89. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.1.83
- 4,458 View
- 60 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Adrenal insufficiency (AI) is a life-threatening disorder caused by the deficiency of adrenal steroid hormones. This retrospective cross-sectional study investigated the characteristics of patients with AI in Korea.
Methods All consecutive patients with suspected AI who received care at a tertiary referral center in Korea in 2014 and underwent adrenocorticotropic hormone stimulation or insulin-tolerance testing were identified through a review of medical charts. Patients diagnosed with AI were enrolled. Their demographic, clinical, and treatment details were extracted.
Results Of 771 patients with suspected AI, 183 (23.7%) received a definitive diagnosis. The most common reason for testing was the presence of suspicious AI-related symptoms (30.0%), followed by a history of steroid medications (23.5%). Their mean age was 66.7 years, and females predominated (67.8%). The most common symptoms were general weakness, anorexia, arthralgia, and fever. Approximately half (53.6%) had a history of steroid use. Hydrocortisone was the most common treatment (71.6%), with most patients taking a 30 mg dose (44.2%). The most common dose frequency was twice a day (78.6%). Fourteen patients were treated for adrenal crisis (
n =10, 5.5%) or an intercurrent illness (n =4, 2.2%).Conclusion AI may have been caused by steroid medication use in many of the patients included in this study. The detection of AI can be improved by careful history-taking and being alert to the possibility that a patient has used steroids.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of Mental Illnesses in Patients With Hypopituitarism: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
I-Hua Wei, Chih-Chia Huang
Psychiatry Investigation.2022; 19(6): 418. CrossRef - The Role of the Pharmacist in Optimizing Cancer Immunotherapy: A Retrospective Study of Nivolumab Adverse Events
Bradley D. Menz, Jacinta L. Johnson, Davina F. Gillard, William Chong, Michael B. Ward
Journal of Pharmacy Practice.2021; 34(3): 386. CrossRef - Clinical and biochemical factors to predict biochemical adrenal insufficiency in hospitalized patients with indeterminate cortisol levels: a retrospective study
Worapaka Manosroi, Natapong Kosachunhanan, Pichitchai Atthakomol
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Possible adrenal insufficiency among fatigue patients in a psychosomatic medical clinic
Sunao Matsubayashi, Nobuhiro Nakatake, Takeshi Hara
Endocrine Journal.2020; 67(1): 53. CrossRef - Encountering COVID-19 as Endocrinologists
Eun-Jung Rhee, Jung Hee Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 197. CrossRef - Glucocorticoid management of adrenal insufficiency in the United Kingdom: assessment using real-world data
Kamran Iqbal, Kate Halsby, Robert D Murray, Paul V Carroll, Robert Petermann
Endocrine Connections.2019; 8(1): 20. CrossRef
- Risk of Mental Illnesses in Patients With Hypopituitarism: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study

- Clinical Study
- Prevalent Rate of Nonalbuminuric Renal Insufficiency and Its Association with Cardiovascular Disease Event in Korean Type 2 Diabetes
- Hye Won Lee, A Ra Jo, Dong Won Yi, Yang Ho Kang, Seok Man Son
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(4):577-585. Published online December 20, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.4.577
- 3,874 View
- 44 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Nonalbuminuric renal insufficiency is a unique category of diabetic kidney diseases. The objectives of the study were to evaluate prevalent rate of nonalbuminuric renal insufficiency and to investigate its relationship with previous cardiovascular disease (CVD) event in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods Laboratory and clinical data of 1,067 subjects with T2DM were obtained and reviewed. Study subjects were allocated into four subgroups according to the CKD classification. Major CVD events were included with coronary, cerebrovascular, and peripheral vascular events.
Results Nonalbuminuric stage ≥3 CKD group, when compared with albuminuric stage ≥3 CKD group, had shorter diabetic duration, lower concentrations of glycated hemoglobin, high density lipoprotein cholesterol, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, lower prevalent rates of retinopathy and previous CVD, and higher rate of treatment with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin II receptor blockers. Nonalbuminuric stage ≥3 CKD group showed a greater association with prior CVD events than no CKD group; however, albuminuric stage ≥3 CKD group made addition to increase prevalence of prior CVD events significantly when CKD categories were applied as covariates. Association of prior CVD events, when compared with normal estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and nonalbuminuria categories, became significant for declined eGFR, which was higher for eGFR of <30 mL/min/1.73 m2, and albuminuria.
Conclusion The results show that subjects with nonalbuminuric stage ≥3 CKD is significantly interrelated with occurrence of prior CVD events than those with normal eGFR with or without albuminuria. Comparing with normal eGFR and nonalbuminuria categories, the combination of increased degree of albuminuria and declined eGFR is becoming significant for the association of prior CVD events.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Update on pathogenesis and diagnosis flow of normoalbuminuric diabetes with renal insufficiency
Le Deng, Wenjie Li, Gaosi Xu
European Journal of Medical Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetic kidney disease: new clinical and therapeutic issues. Joint position statement of the Italian Diabetes Society and the Italian Society of Nephrology on “The natural history of diabetic kidney disease and treatment of hyperglycemia in patients with
Giuseppe Pugliese, Giuseppe Penno, Andrea Natali, Federica Barutta, Salvatore Di Paolo, Gianpaolo Reboldi, Loreto Gesualdo, Luca De Nicola
Journal of Nephrology.2020; 33(1): 9. CrossRef - Diabetic kidney disease: New clinical and therapeutic issues. Joint position statement of the Italian Diabetes Society and the Italian Society of Nephrology on “The natural history of diabetic kidney disease and treatment of hyperglycemia in patients with
Giuseppe Pugliese, Giuseppe Penno, Andrea Natali, Federica Barutta, Salvatore Di Paolo, Gianpaolo Reboldi, Loreto Gesualdo, Luca De Nicola
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2019; 29(11): 1127. CrossRef - Soluble Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Levels Are Associated with Decreased Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eun-Hee Cho, Sang-Wook Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(1): 97. CrossRef - STORIA NATURALE DELLA MALATTIA RENALE NEL DIABETE E TRATTAMENTO DELL’IPERGLICEMIA NEI PAZIENTI CON DIABETE DI TIPO 2 E RIDOTTA FUNZIONE RENALE
il Diabete.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Nonalbuminuric Renal Insufficiency: Can It Be a Novel Category of Diabetic Nephropathy?
Masami Tanaka, Hiroshi Itoh
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(4): 533. CrossRef
- Update on pathogenesis and diagnosis flow of normoalbuminuric diabetes with renal insufficiency

- Clinical Study
- Eligibility for Statin Treatment in Korean Subjects with Reduced Renal Function: An Observational Study
- Byung Sub Moon, Jongho Kim, Ji Hyun Kim, Young Youl Hyun, Se Eun Park, Hyung-Geun Oh, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Kyu-Beck Lee, Hyang Kim, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(3):402-409. Published online August 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.3.402
- 3,934 View
- 33 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between statin eligibility and the degree of renal dysfunction using the Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III and the American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines in Korean adults.
Methods Renal function was assessed in 18,746 participants of the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study from January 2011 to December 2012. Subjects were divided into three groups according to estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR): stage 1, eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m2; stage 2, eGFR 60 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m2; and stages 3 to 5, eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2. Statin eligibility in these groups was determined using the ATP III and ACC/AHA guidelines, and the risk for 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) was calculated using the Framingham Risk Score (FRS) and Pooled Cohort Equation (PCE).
Results There were 3,546 (18.9%) and 4,048 (21.5%) statin-eligible subjects according to ATP III and ACC/AHA guidelines, respectively. The proportion of statin-eligible subjects increased as renal function deteriorated. Statin eligibility by the ACC/AHA guidelines showed better agreement with the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) recommendations compared to the ATP III guidelines in subjects with stage 3 to 5 chronic kidney disease (CKD) (κ value, 0.689 vs. 0.531). When the 10-year ASCVD risk was assessed using the FRS and PCE, the mean risk calculated by both equations significantly increased as renal function declined.
Conclusions The proportion of statin-eligible subjects significantly increased according to worsening renal function in this Korean cohort. ACC/AHA guideline showed better agreement for statin eligibility with that recommended by KDIGO guideline compared to ATP III in subjects with CKD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases risk and renal outcome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Honghong Ren, Lijun Zhao, Yutong Zou, Yiting Wang, Junlin Zhang, Yucheng Wu, Rui Zhang, Tingli Wang, Jiali Wang, Yitao Zhu, Ruikun Guo, Huan Xu, Lin Li, Mark E. Cooper, Fang Liu
Renal Failure.2021; 43(1): 477. CrossRef - Long-term effects of various types of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors on changes in glomerular filtration rate in Korea
Seo Yeon Baik, Hyunah Kim, So Jung Yang, Tong Min Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Hun-Sung Kim
Frontiers of Medicine.2019; 13(6): 713. CrossRef - Analysis and comparison of the cost-effectiveness of statins according to the baseline low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level in Korea
Y. J. Jeong, H. Kim, S. J. Baik, T. M. Kim, S. J. Yang, S.-H. Lee, J.-H. Cho, H. Lee, H. W. Yim, I. Y. Choi, K.-H. Yoon, H.-S. Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2017; 42(3): 292. CrossRef - Comparison between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin in Renal Function Decline among Patients with Diabetes
Eugene Han, Gyuri Kim, Ji-Yeon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Beom Seok Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(2): 274. CrossRef
- Association between atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases risk and renal outcome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



