Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Adrenal Gland
- Recent Updates on the Management of Adrenal Incidentalomas
- Seung Shin Park, Jung Hee Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):373-380. Published online August 16, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1779
- 7,476 View
- 1,484 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
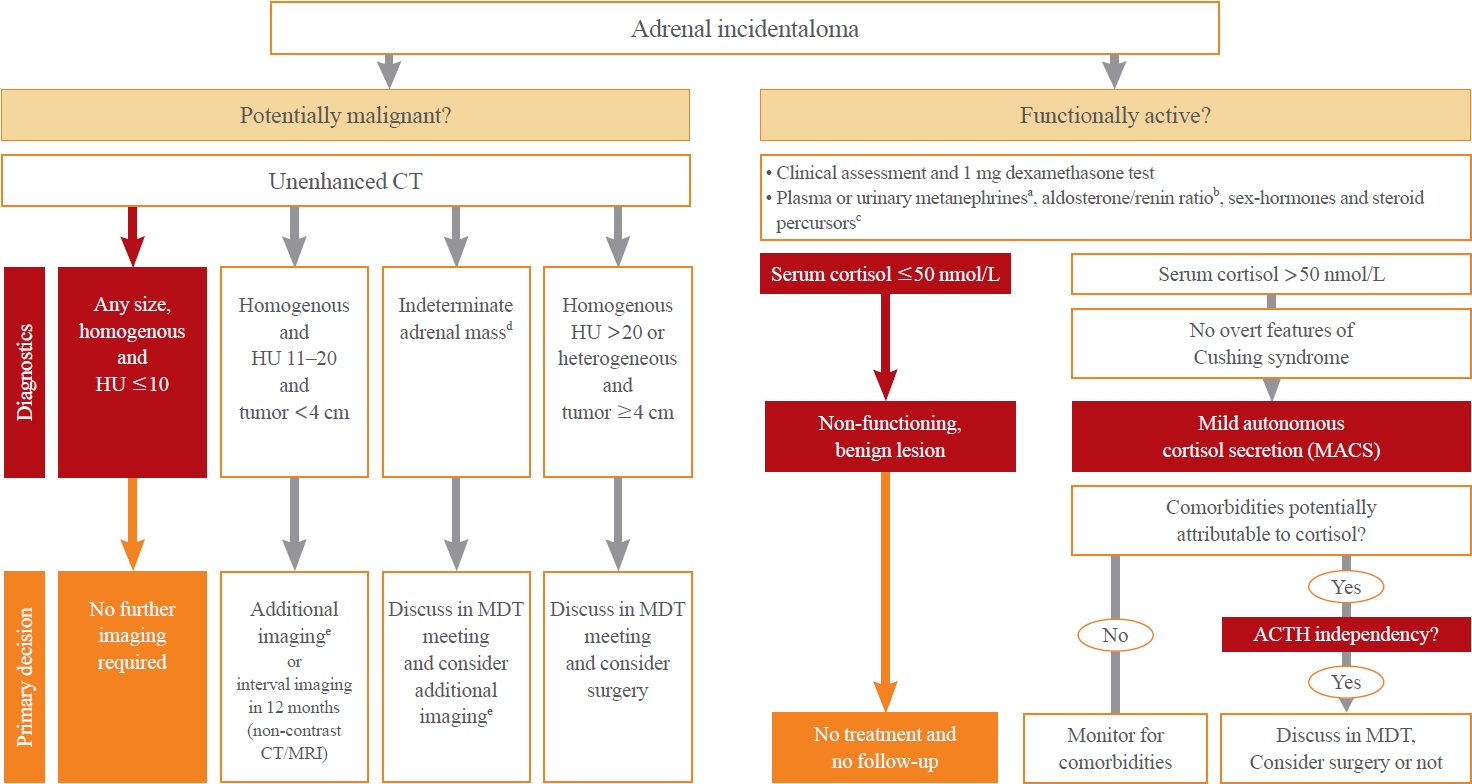
ePub - Adrenal incidentalomas represent an increasingly common clinical conundrum with significant implications for patients. The revised 2023 European Society of Endocrinology (ESE) guideline incorporates cutting-edge evidence for managing adrenal incidentalomas. This paper provides a concise review of the updated contents of the revised guideline. In the 2023 guideline, in patients without signs and symptoms of overt Cushing’s syndrome, a post-dexamethasone cortisol level above 50 nmol/L (>1.8 μg/dL) should be considered as mild autonomous cortisol secretion. Regarding the criteria of benign adrenal adenomas, a homogeneous adrenal mass with ≤10 Hounsfield units on non-contrast computed tomography requires no further follow-up, irrespective of its size. The updated guideline also discusses steroid metabolomics using tandem mass spectrometry to discriminate malignancy. It underscores the importance of high-volume surgeons performing adrenalectomy and emphasizes the pivotal role of a multidisciplinary team approach in deciding the treatment plan for indeterminate adrenal masses. The guideline advocates for more proactive surgical treatment for indeterminate adrenal masses in young patients (<40 years) and pregnant women. This review of the 2023 ESE guideline underscores the ongoing evolution of the adrenal incidentaloma management landscape, emphasizing the need for further research and adaptation of diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.

- Adrenal Gland
- Clinical and Technical Aspects in Free Cortisol Measurement
- Man Ho Choi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(4):599-607. Published online August 19, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1549
- 4,785 View
- 294 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
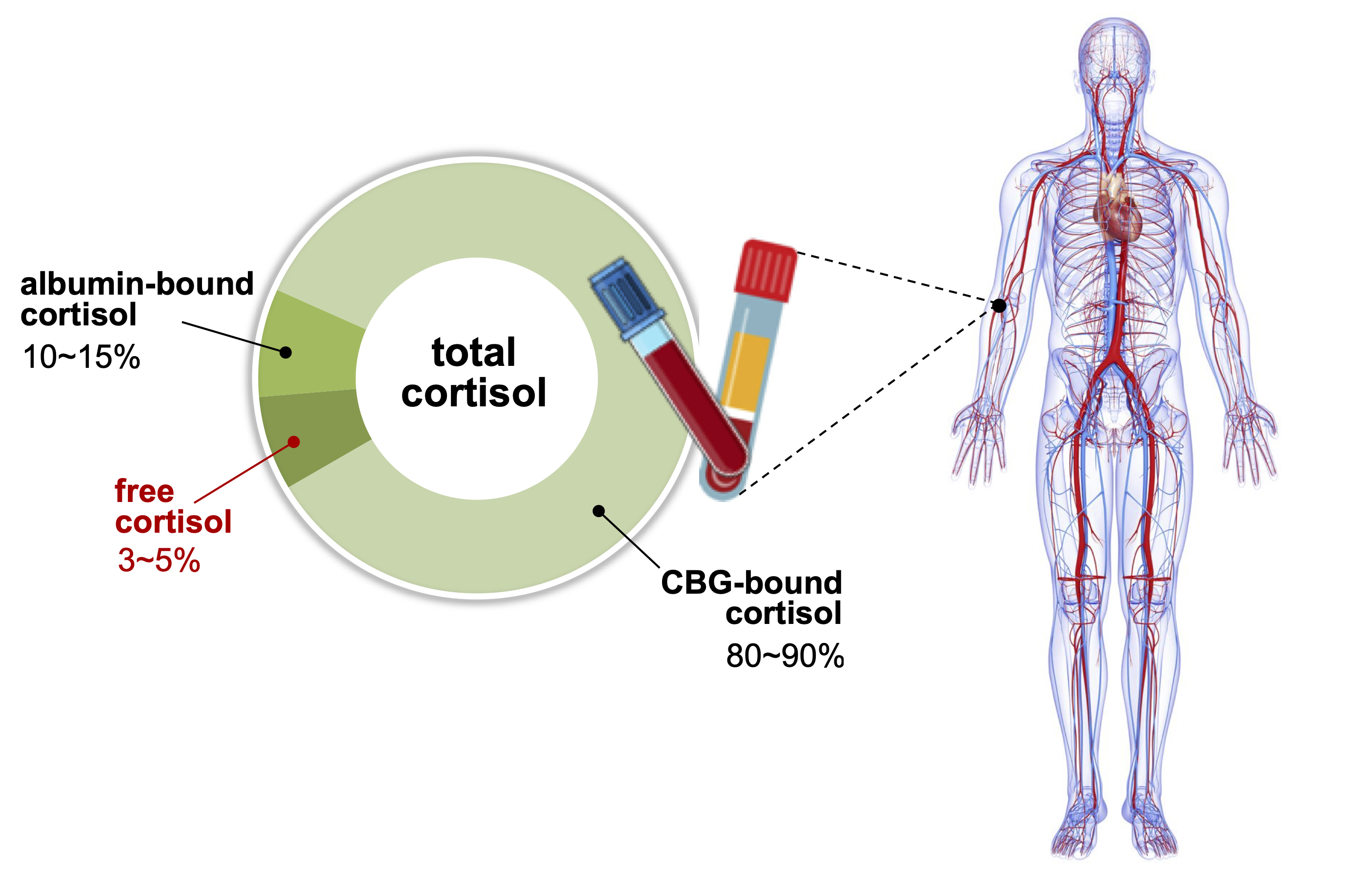
ePub - Accurate measurement of cortisol is critical in adrenal insufficiency as it reduces the risk associated with misdiagnosis and supports the optimization of stress dose. Comprehensive assays have been developed to determine the levels of bioactive free cortisol and their clinical and analytical efficacies have been extensively discussed because the level of total cortisol is affected by changes in the structure or circulating levels of corticoid-binding globulin and albumin, which are the main reservoirs of cortisol in the human body. Antibody-based immunoassays are routinely used in clinical laboratories; however, the lack of molecular specificity in cortisol assessment limits their applicability to characterize adrenocortical function. Improved specificity and sensitivity can be achieved by mass spectrometry coupled with chromatographic separation methods, which is a cutting-edge technology to measure individual as well as a panel of steroids in a single analytical run. The purpose of this review is to introduce recent advances in free cortisol measurement from the perspectives of clinical specimens and issues associated with prospective analytical technologies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Highly Responsive Bioassay for Quantification of Glucocorticoids
Mathias Flensted Poulsen, Martin Overgaard, Christian Brix Folsted Andersen, Andreas Lodberg
Analytical Chemistry.2024; 96(5): 2000. CrossRef - An LC-MS/MS Method for the Simultaneous Quantification of Insulin, Cortisol, Glucagon-like Peptide 1, Ghrelin, and Osteocalcin
Zhichao Zhang, Hareem Siddiqi, Yu-Ping Huang, Shannon McClorry, Peng Ji, Daniela Barile, Carolyn M. Slupsky
Separations.2024; 11(2): 41. CrossRef - Determination of cortisol cut-off limits and steroid dynamics in the ACTH stimulation test: a comparative analysis using Roche Elecsys Cortisol II immunoassay and LC-MS/MS
Sema Okutan, Nanna Thurmann Jørgensen, Lars Engers Pedersen, Stina Willemoes Borresen, Linda Hilsted, Lennart Friis Hansen, Ulla Feldt-Rasmussen, Marianne Klose
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Advancements in Cortisol Detection: From Conventional Methods to Next-Generation Technologies for Enhanced Hormone Monitoring
Visesh Vignesh, Bernardo Castro-Dominguez, Tony D. James, Julie M. Gamble-Turner, Stafford Lightman, Nuno M. Reis
ACS Sensors.2024; 9(4): 1666. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of salivary cortisol measurements using different assay methods in relation to serum-free cortisol measurement
Anna Lee, Sooah Jang, Sanghoo Lee, Hyun-Kyung Park, In-Young Kim, Ryunsup Ahn, Jeong-Ho Seok, Kyoung-Ryul Lee
Practical Laboratory Medicine.2024; 40: e00393. CrossRef - A dilute and shoot method for urinary free cortisol analysis by LC-MS/MS
Ying Shen, Xia Luo, Qing Guan, Liming Cheng
Journal of Chromatography B.2024; 1239: 124127. CrossRef - Osteopathic Manipulation as a Method of Cortisol Modification: A Systematic Review
Dylan Thibaut, Valentine Santarlas, Joseph Hoppes, Alejandra Vásquez-Castillo, Alexa Morrow, Eddie Oviedo, James Toldi
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pitfalls in the Diagnosis and Management of Hypercortisolism (Cushing Syndrome) in Humans; A Review of the Laboratory Medicine Perspective
Kade C. Flowers, Kate E. Shipman
Diagnostics.2023; 13(8): 1415. CrossRef - Electrochemical sensors for cortisol detection: Principles, designs, fabrication, and characterisation
Gopi Karuppaiah, Min-Ho Lee, Shekhar Bhansali, Pandiaraj Manickam
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2023; 239: 115600. CrossRef - The role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in depression across the female reproductive lifecycle: current knowledge and future directions
Liisa Hantsoo, Kathleen M. Jagodnik, Andrew M. Novick, Ritika Baweja, Teresa Lanza di Scalea, Aysegul Ozerdem, Erin C. McGlade, Diana I. Simeonova, Sharon Dekel, Sara L. Kornfield, Michelle Nazareth, Sandra J. Weiss
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - РІВЕНЬ СТРЕСУ В ДІТЕЙ ШКІЛЬНОГО ВІКУ З COVID-19
Г. А. Павлишин, О. І. Панченко
Здобутки клінічної і експериментальної медицини.2023; (4): 119. CrossRef - Corticotropin-stimulated steroid profiles to predict shock development and mortality in sepsis: From the HYPRESS study
Josef Briegel, Patrick Möhnle, Didier Keh, Johanna M. Lindner, Anna C. Vetter, Holger Bogatsch, Dorothea Lange, Sandra Frank, Ludwig C. Hinske, Djillali Annane, Michael Vogeser, Michael Bauer, Thorsten Brenner, Patrick Meybohm, Markus Weigand, Matthias Gr
Critical Care.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Highly Responsive Bioassay for Quantification of Glucocorticoids

- Adrenal gland
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone-Independent Cushing Syndrome with Bilateral Cortisol-Secreting Adenomas
- Eu Jeong Ku, A Ram Hong, Ye An Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Mee Soo Chang, Sang Wan Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(2):133-137. Published online June 18, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.2.133
- 3,999 View
- 44 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader A 48-year-old woman was incidentally found to have bilateral adrenal masses, 2.8 cm in diameter on the right, and 2.3 cm and 1.7 cm in diameter on the left, by abdominal computed tomography. The patient had a medical history of hypertension, which was not being controlled by carvedilol, at a dose of 25 mg daily. She presented with signs and symptoms that suggested Cushing Syndrome. We diagnosed adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)-independent Cushing Syndrome based on the results of basal and dynamic hormone tests. Adrenal vein sampling (AVS) was performed to localize a functioning adrenal cortical mass. AVS results were consistent with hypersecretion of cortisol from both adrenal glands, with a cortisol lateralization ratio of 1.1. Upon bilateral laparoscopic adrenalectomy, bilateral ACTH-independent adrenal adenomas were found. The patient's signs and symptoms of Cushing Syndrome improved after surgery just as the blood pressure was normalized. After surgery, the patient was started on glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid replacement therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Recent Advances in the Clinical Application of Adrenal Vein Sampling
Shan Zhong, Tianyue Zhang, Minzhi He, Hanxiao Yu, Zhenjie Liu, Zhongyi Li, Xiaoxiao Song, Xiaohong Xu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of adrenal venous sampling (AVS) in primary bilateral macronodular adrenocortical hyperplasia (PBMAH): a study of 16 patients
German Rubinstein, Andrea Osswald, Leah Theresa Braun, Frederick Vogel, Matthias Kroiss, Stefan Pilz, Sinan Deniz, Laura Aigner, Thomas Knösel, Jérôme Bertherat, Lucas Bouys, Roland Ladurner, Anna Riester, Martin Bidlingmaier, Felix Beuschlein, Martin Rei
Endocrine.2022; 76(2): 434. CrossRef - Concomitant coexistence of ACTH‐dependent and independent Cushing syndrome
Ach Taieb, Saad Ghada, Gorchène Asma, Ben Abdelkrim Asma, Kacem Maha, Ach Koussay
Clinical Case Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Value of Adrenal Androgens for Correcting Cortisol Lateralization in Adrenal Venous Sampling in Patients with Normal Cortisol Secretion
Wenjing Zhang, Keying Zhu, Hongyun Li, Yan Zhang, Dalong Zhu, Xuebin Zhang, Ping Li
International Journal of Endocrinology.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Adrenal venous sampling in patients with ACTH-independent hypercortisolism
Eleni Papakokkinou, Hugo Jakobsson, Augustinas Sakinis, Andreas Muth, Bo Wängberg, Olof Ehn, Gudmundur Johannsson, Oskar Ragnarsson
Endocrine.2019; 66(2): 338. CrossRef - ACTH-independent Cushing’s syndrome with bilateral cortisol-secreting adrenal adenomas: a case report and review of literatures
Jia Wei, Sheyu Li, Qilin Liu, Yuchun Zhu, Nianwei Wu, Ying Tang, Qianrui Li, Kaiyun Ren, Qianying Zhang, Yerong Yu, Zhenmei An, Jing Chen, Jianwei Li
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - A case of adrenal Cushing’s syndrome with bilateral adrenal masses
Ya-Wun Guo, Chii-Min Hwu, Justin Ging-Shing Won, Chia-Huei Chu, Liang-Yu Lin
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism Case Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Bilateral Adrenocortical Masses Producing Aldosterone and Cortisol Independently
Seung-Eun Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Hyeri Seok, In Seub Shin, Yeong Hee Eun, Jung-Han Kim, Young Lyun Oh
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(4): 607. CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef - A Case of Bilateral ACTH-independent Adrenal Adenomas with Cushing's Syndrome Treated by Ipsilateral Total and Contralateral Partial Laparoscopic Adrenalectomy
Seung Ah Park, Dong min Jung, Soon young Kim, Nan Young Choi, Tae-jun Kim, Yong kyun Kim, Seong kyun Na, Chul Sik Kim, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm, Jun Goo Kang
The Korean Journal of Obesity.2013; 22(4): 254. CrossRef
- Recent Advances in the Clinical Application of Adrenal Vein Sampling

- A Case of Primary Adrenal Insufficiency in a Patient with Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome.
- Jae Ho Choi, Suk Chon, Yu Chul Hwang, Jun Seong Son, Seung Joon Oh, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Jeong Taek Woo, Sung Woon Kim, Jin Woo Kim, Young Seol Kim, In Kyung Jeong
- Endocrinol Metab. 2011;26(3):253-257. Published online September 1, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2011.26.3.253
- 2,138 View
- 24 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The adrenal gland is the most commonly involved endocrine organ in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Adrenal function abnormality is more common in HIV patients than in the general population. It is important to recognize the condition of adrenal insufficiency, as this adrenal disorder may prove fatal if left untreated. Herein, we report a case of primary adrenal insufficiency in a 37-year-old male patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. The patient complained of fever, general weakness, and fatigue. Impaired adrenal function was noted in the rapid ACTH stimulation test. After steroid supplementation, the patient's symptoms were improved. Therefore, HIV care physicians should ascertain adrenal dysfunction in HIV patients when they complain of fever and general weakness.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Case Report of Adrenal Insufficiency Treated with Korean Medicine
Young-ji Kim, Jung-yeon Kwon, Ho-yeon Go, Kyung-hwan Kong
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine.2017; 38(5): 583. CrossRef
- A Case Report of Adrenal Insufficiency Treated with Korean Medicine

- A Case of Adrenocortical Carcinoma Secreting Cortisol, Androgen and Aldosterone.
- Jae Ho Choi, Ye Ri So, Yu Chul Hwang, In Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Seung Ae Yang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2011;26(3):239-242. Published online September 1, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2011.26.3.239
- 2,086 View
- 30 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary adrenocortical carcinoma is a rare tumor, and is characterized by a peri-tumor mass effect and hormone excess signs. Adrenocortical carcinoma most commonly secretes cortisol, but tumors that secrete other adrenal hormones (aldosterone, androgen) are rare. Herein, we report the case of a 70-year-old woman with cortisol, androgen, and aldosterone-secreting adrenal carcinoma. The patient complained of generalized weakness, moon face, and central obesity. On laboratory examination, hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis was detected. On the hormone test, cortisol, DHEA-S, and aldosterone were all increased. Abdominal CT showed a large right adrenal mass. She underwent right adrenalectomy and the histology revealed the presence of an adrenocortical carcinoma. After adrenalectomy, the patient was treated with hydrocortisone and mitotane.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Case of Adrenocortical Carcinoma Secreting Cortisol and Aldosterone
Jiyoon Ha, Min Kyung Kim, Yoon Jin Cha, Seung Kyu Kim, Gi Young Yun, Kwangwon Rhee, Joon Seong Park, Eun-Suk Cho, Chul Woo Ahn, Jong Suk Park
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine.2012; 29(2): 132. CrossRef
- A Case of Adrenocortical Carcinoma Secreting Cortisol and Aldosterone

- No Significance of the Free Cortisol Index Compared to Total Cortisol in Critically Ill Patients.
- Kyung Won Kim, Sang Wan Kim, Hee Joung Kim, Chan Soo Shin, Sung Jae Park, Gil Joon Suh, Seong Yeon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2011;26(2):120-125. Published online June 1, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2011.26.2.120
- 1,895 View
- 21 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Some patients exhibit an inadequate response of cortisol to stressful conditions; this state is known as critical illness-related corticosteroid insufficiency. These patients have low serum binding protein concentrations, thereby suggesting that total serum cortisol may not be reflective of circulating cortisol activity. As the free cortisol index (FCI = total cortisol/corticosteroid-binding globulin) has been correlated with serum free cortisol, we measured FCI in Korean patients for the first time. In this study, we attempted to determine whether FCI was superior to total cortisol in predicting 30-day mortality. METHODS: We recruited 65 critically ill patients with relatively high Acute Physiology, Age and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE III) scores. Fourteen patients with pituitary disease but normal pituitary function were recruited from outpatient clinics. Total cortisol and corticosteroid-binding globulin were measured in patients and controls during the short Synacthen test. RESULTS: The basal cortisol level and basal FCI level were higher in patients (n = 65) than in healthy controls (P < 0.001, respectively). We found that total cortisol was strongly correlated with FCI (P < 0.001) in critically ill patients; however, neither total cortisol nor FCI were associated with 30-day mortality among patients. Only severe clinical criteria (such as APACHE-III scores and low albumin) were associated with 30-day mortality. CONCLUSION: Our results do not suggest that FCI is more accurate than total cortisol in predicting clinical outcomes in critically ill patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- No Significance of the Free Cortisol Index Compared to Total Cortisol in Critically Ill Patients
Doo-Man Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2011; 26(2): 118. CrossRef
- No Significance of the Free Cortisol Index Compared to Total Cortisol in Critically Ill Patients

- A Case of Aortic Dissection Associated with Cushing's Syndrome.
- Soo Heon Kwak, Eun Jung Lee, Sun Wook Cho, Hyung Jin Choi, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Min Cho, Seong Yeon Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(6):556-559. Published online December 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.6.556
- 1,740 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Herein is reported the case of a 43-year-old woman, who experienced an acute aortic dissection associated with underlying Cushing's syndrome. The patient had central obesity and a moon face of ten years duration, but had never sought medical consultation. On the day of her presentation, she experienced a severe chest pain radiating to her back. Computed tomography revealed a Stanford type B acute aortic dissection and a left adrenal mass. From her hormonal study results, clinical symptoms and signs, she was diagnosed with Cushing's syndrome, which was due to a left adrenal adenoma. After medical treatment to stabilize the aortic dissection, she underwent left adrenalectomy. The aortic lesion of the present patient suggests that hypercortisolemia arising from Cushing's syndrome might be related to the development of acute aortic dissection.

- A Case of Adrenocortical Carcinoma showing Variable Cortisol Production during the Clinical Course.
- Yun Hyi Ku, Hyung Jin Choi, Jin Taek Kim, Ji Won Yoon, Eun Kyung Lee, Hwa Young Cho, Mi Yeon Kang, Jie Seon Lee, Young Min Cho, Seong Yeon Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(5):419-423. Published online October 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.5.419
- 1,516 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Patients with adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC) present with evidence of excessive adrenal steroid hormone in approximately 60% of cases, in which rapidly progressing Cushing's syndrome with or without virilization is the most frequent presentation. Some patients experience an increase or a decline in cortisol production through the progression of their ACC. We report on an unusual case of a cortisol-producing ACC, and the patient presented with a decline in cortisol production, followed by an increase in cortisol production, through the progression of the tumor. A 65-year-old woman who manifested with facial edema and weight gain was diagnosed with Cushing's syndrome, caused by cortisol producing ACC. The patient was treated with adrenalectomy. However, 8 months later, a metastatic hepatic tumor of recurred ACC was detected. At that time, the hormonal evaluation revealed that the liver mass did not produce any hormones. The patient was treated with metastatectomy. Four months later, a relapsed tumor was detected. Increased cortisol production was observed at that time. We speculate there was a change in the clonal dominance within the ACC and this change might cause such a difference. This is the first case report of ACC that showed variable hormone production during progression.

- Reversible Pituitary Dysfunction in a Patient with Cushing's Syndrome due to Adrenal Adenoma.
- Jee Hyun Kong, Kyung Wook Kim, Hei Jin Kim, Ji Sun Nam, Jin A Park, Jong Sook Park, Chul Sik Kim, Byung Soo Moon, Soon Won Hong, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Rae Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(2):146-152. Published online April 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.2.146
- 1,634 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 45-year-old woman who complained of weight gain and irregular menstruation was diagnosed as having Cushing's syndrome due to a 3 cm sized left adrenal adenoma. She underwent left adrenalectomy, and she also underwent combined anterior pituitary tests before and 9 months after the surgery. The growth hormone and adrenocorticotropic hormone levels failed to respond to hypoglycemia before the surgery, but their responses recovered after the surgery. Cortisol and thyroid stimulating hormone failed to respond to hypoglycemia and thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) before the surgery, respectively, but these were improved after the surgery. Luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone, and prolactin adequately responded to gonadotropin-releasing hormone and TRH, respectively, before and after the surgery. However, the basal levels of these hormones were higher after adrenalectomy, suggesting that hypercortisolemia had a significant influence on all the pituitary hormones.

- A Case of Protein-losing Enteropathy with an Abnormal Cortisol Response to ACTH Stimulation.
- Hong Il Kim, Bo Kyeong Koo, You Jin Lee, Eun Jung Lee, Soo Heon Kwak, Sun Wook Cho, Hyung Jin Choi, Young Min Cho, Seong Yeon Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2005;20(1):90-95. Published online February 1, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2005.20.1.90
- 1,674 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - We hereby report a case of a 62-year-old male patient who was misdiagnosed with adrenal insufficiency during the course of protein-losing enteropathy caused by superior mesenteric arterial thrombosis. The patient was suspected to have adrenal insufficiency due to hyponatremia and severe weakness. The cortisol responses to the initial challenge of 250microgram ACTH were inadequate (maximum serum cortisol level after ACTH challenge was 10.9microgram/dL), while the serum albumin concentration was 1.9g/dL. Subsequently, intravenous steroid therapy was given to the patient. However, after bowel resection, the serum albumin level increased to 3.4g/dL and the cortisol response to the follow-up rapid ACTH stimulation was completely normal. Accordingly, we discontinued steroid replacement and discharged the patient without any problem. In conclusion, measuring total serum cortisol in a patient with hypo-pro-teinemia may lead to misdiagnosis of adrenal insufficiency. In such cases, caution should be exercised in interpreting the results in terms of total serum cortisol level or measurement of serum free cortisol levels should be considered.

- A Case of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia due to 11beta-Hydroxylase Deficiency.
- Ohk Hyun Ryu, Hye Jin Yoo, Soo Yeon Park, Soon Beom Kwon, Sang Soo Park, Hee Young Kim, Kye Won Lee, Ji A Seo, Jeong Heon Oh, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Dong Seop Choi
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2004;19(1):58-63. Published online February 1, 2004
- 1,223 View
- 35 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Congenital adrenal hyperplasia refers to a group of autosomal recessive disorders that is defective in the synthesis of cortisol. The enzymes most often affected are 21-hydroxylase and 11beta hydroxylase. The low levels of cortisol stimulate the pituitary gland to release ACTH. Chronic elevation of the ACTH level causes bilateral adrenal hyperplasia and a secondary increase in androgen formation. We examined a 19 year-old woman presented with clitoral hypertrophy and vaginal spotting. The subjects basal level of serum cortisol was low, but the serum levels of ACTH, 17a-hydroxyprogesterone, deoxy-corticosterone were elevated. The urinary excretions of 17-ketosteroids and 17-hydroxycorticosteroids were also increased. The karyotyping study and transrectal ultrasonography showed normal findings. The patient underwent clitoris reduction surgery and received hydrocortisone. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of 11beta-Hydroxylase deficiency in Korea.

- Usefullness of Urinary Free Cortisol Measurement in Diagnosis of Iatrogenic Cushing Syndrome.
- Yong Hyun Kim, Sang Jin Kim, Dong Seop Choi
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2000;15(2):162-169. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,059 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Although insulin induced hypoglycemia test is a standard diagnostic method in assessment of hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis, rapid ACTH stimulation test using 250microgram has been used as a first line diagnostic test especially in secondary adrenal insufficiency due to iatrogenic Cushing syndrome because it is easy and safe. However, it was suggested that a maximal cortisol response can be achieved with a much lower ACTH dose and 1microgram ACTH enhances the sensitivity without decreasing specificity of test. Also recently, there was a report that midnight to morning urine cortisol increment is more accurate, noninvasive method can be used for measurement of hypothalmo-pituitary-adrenal axis. In this study, we compared the 1microgram ACTH stimulation test with midnight to morning urinary free cortisol increment in secondary adrenal insufficiency due to iatrogenic Cushing syndrome to study the agreement of two test and accuracy of increment of urinary free cortisol in diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency. METHODS: Double voided urine sample were collected at midnight and 8 A.M. in 12 patients who have Cushing-like feature and history of taking glucocorticoids and in 12 normal controls. Urinary free cortisol was measured and cortisol increment was defined as the morning urine free cortisol minus the midnight urine free cortisol. The 1microgram ACTH stimulation test was performed in 12 iatrogenic Cushing syndrome patients at the same day and compard with the result of cortisol increment. RESULTS: Using the results of 12 controls, normal urine free cortisol increment was defined as greater than 165.5nmol/L(6.0microgram/dL). Subnormal cortisol response in 1microgram ACTH stimulation test was noted in 8 out of 12 patients group and urinary free cortisol increment was not observed in 7 out of 8 subnormal response group. Normal cortisol response in 1microgram ACTH stimulation test was noted in 4 out of 12 patients group and urinary free cortisol increment was observed in 3 out of 4 normal response group. So 83% of concordance rate between 1microgram ACTH stimulation test and urine free cortisol increment was recorded. CONCLUSION: Urinary free cortisol increment has high concordance rate with 1microgram ACTH stimulation test and simple, easy test in diagnosing secondary adrenal insufficiency due to iatrogenic Cushing syndrome. Further study including more patients will be helpful to know the adequacy and reliability of test in evaluation of hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis.

- Changes in Plasma Dehydroepiandrosterone-Sulfate ( DHEA-S ) Level & DHEA-S / cortisol Ratio by Age in Healthy Korean.
- Jae Myung Yu, Cheol Soo Park, Hyung Joon Yoo, Kwon Yeop Lee, Kyu Yong Park, Cheol Hong Kim, Min Sook Park, Hyun Gyu Kim, Du Man Kim, Sung Hee Ihm, Moon Gi Choi, Sung Woo Park
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1997;12(2):245-154. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,091 View
- 30 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
DHEA-S is the most abundant steroid hormone in circulation, and primarily secreted from the adrenal cortex, but its physiological role is little known. One of the characteristic features of DHEA-S is progressive decrement of plasma DHEA-S level with advancing age, in contrast, plasma levels of other adrenal hormones are not chaging or littie decreasing. To grasp the trends of plasma DHEA-S level and DHEA-S/cortisol ratio by age in healthy Korean, we measured the plasma DHEA-S levels and DHEA-S/cortisol ratios in healthy Korean. METHODS: Healthy Korean (men: 99, women: 102, age range: 15-97 year old)were studied. Subjects were not taking drugs (such as glucocorticoid or androgenic medication) or cigarettes known to modify the plasma level of DHEA-S and cortisol, and had no evidence of hepatic, renal disease or hyperlipidemia as determined by serum lipid, bilirubin, SGOT, SGPT, BUN, creatinine. Data were analyzed by 10-year age group for men and women: i.e, 10-19, 20-29, 30-39, 40-49, 50-59, 60-69, 70-79, 80-89 and 90 year or more. Plasma DHEA-S levels were measured by using a commercially available RIA kit with 125I labeled-DHEA-SO4 (Coat-A Count DHEA-SO4), and for the measurement of plasma cortisol levels, commercial Gamma Coat TM[125I] Cortisol Radioimmunassay Kit was used. RESULTS:. 1) In both men and women, plasma DHEA-S level showed high interindividual variation within the same age group. 2) There were individual sex differences in plasma levels of DHEA-S, in all age groups, plasma DHEA-S levels were significantly higher values for men than for women. 3) Maximum plasma DHEA-S levels (men; 237+-3.35 ug/dL, women; 108+-17.5 ug/dL) were at third decade in both men and women. 4) Both men and women showed the continuous decline in plasma DHEA-S level with age. These age-related decline was more prominent in men than in women (men; y=-3.152 * +292.6, r2= 0.8459, P<0.05, women; y= -1.417 * +143.3, r2 = 0.7278, P< 0.05). 5) As an index of aging, there was no stastical difference between DHEA-S and DHEA-S/cortisol ratio. CONCLUSION: In healthy Korean, there were high interindividual variation of plasrna DHEA-S levels. In both men and women plasma DHEA-S level was peak at third decade, and from when it declined progressively with age. These results suggest that although the reliability of single plasma DHEA-S measurement are limited, the decline of DHEA-S with advancing age might be a specific marker of endocrinologic hormonal milieu (aging index). Also, concerning to individual adrenal secreting capacity, we measured DHEA-S/cortisol ratio. But we did not found that plasma DHEA-S/cortisol ratio is superior to the plasma DHEA-S level as an aging index.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



