Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Endocrinol Metab > Volume 38(2); 2023 > Article
-
Review ArticleThyroid The Physiological Functions and Polymorphisms of Type II Deiodinase
 Keypoint
Keypoint
Type II deiodinase converts thyroxine to active triiodothyronine and plays important roles in tissue development, thermogenesis, and brain function. The Thr92Ala polymorphism in type II deiodinase is associated with clinical conditions such as diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and diseases like osteoarthritis and neurodegeneration. This review provides an overview of type II deiodinase's functions and its relevance to various disorders. -
Yan Deng1
 , Yi Han1, Sheng Gao2, Wei Dong2
, Yi Han1, Sheng Gao2, Wei Dong2 , Yang Yu1,2
, Yang Yu1,2
-
Endocrinology and Metabolism 2023;38(2):190-202.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1599
Published online: April 27, 2023
1Department of Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
2Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology of Ministry of Education and Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, China
- Corresponding authors: Yang Yu. Department of Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan 646000, China Tel: +86-13196247606, E-mail: yuyang80@swmu.edu.cn
- Wei Dong. Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology of Ministry of Education and Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan 646000, China Tel: +86-17760628008, E-mail: dongwei@swmu.edu.cn
Copyright © 2023 Korean Endocrine Society
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
- Type II deiodinase (DIO2) is thought to provide triiodothyronine (T3) to the nucleus to meet intracellular needs by deiodinating the prohormone thyroxine. DIO2 is expressed widely in many tissues and plays an important role in a variety of physiological processes, such as controlling T3 content in developing tissues (e.g., bone, muscles, and skin) and the adult brain, and regulating adaptive thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue (BAT). However, the identification and cloning of DIO2 have been challenging. In recent years, several clinical investigations have focused on the Thr92Ala polymorphism, which is closely correlated with clinical syndromes such as type 2 diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and osteoarthritis. Thr92Ala-DIO2 was also found to be related to bone and neurodegenerative diseases and tumors. However, relatively few reviews have synthesized research on individual deiodinases, especially DIO2, in the past 5 years. This review summarizes current knowledge regarding the physiological functions of DIO2 in thyroid hormone signaling and adaptive thermogenesis in BAT and the brain, as well as the associations between Thr92Ala-DIO2 and bone and neurodegenerative diseases and tumors. This discussion is expected to provide insights into the physiological functions of DIO2 and the clinical syndromes associated with Thr92Ala-DIO2.
- Iodothyronine deiodinases (DIOs) are essential for maintaining appropriate levels of triiodothyronine (T3) in the circulation and ensuring its intracellular availability; this role is important since T3 has been implicated in the control of a variety of biological events including growth, development, and metabolism in vertebrates. DIOs have three isoforms, (DIO1, DIO2, and DIO3), which differ in their catalytic properties, tissue distribution, and substrate specificity [1]. These isoforms are expressed in a tissue-specific manner in fetal and adult life and selectively catalyze the activation or inactivation of thyroid hormones (THs) [2]. Although both DIO1 and DIO2 activate THs, their functions are different; specifically, DIO1 is a scavenger enzyme that recycles iodine to replenish the thyroid’s iodine reservoirs, while DIO2 provides T3 to the nucleus to meet intracellular needs [3]. DIO3 is the major TH-inactivating enzyme, which converts the prohormone thyroxine (T4) to reverse-T3 or T3 to T2. Therefore, the balance between the enzyme activity of DIO2 and DIO3 might determine the local concentration of T3. DIO1 and DIO3 are integral plasma membrane proteins. The DIO1 gene is expressed in the liver, thyroid, and kidney [4], while the DIO3 gene is mainly expressed in fetal tissues and the placenta, and its expression declines dramatically in adulthood, persisting primarily in the skin and brain, as well as in the uterus during pregnancy [3,5,6]. DIO2 is an endoplasmic reticulum-resident protein that is localized along radial glial cells, in brain barriers, in Cajal-Retzius cells, in migrating fibers of the brainstem, and in some neurons and glial cells with particular and complex spatiotemporal patterns [7]. Moreover, the DIO2 gene is expressed in the telencephalon [8], pituitary gland and hypothalamus [9,10], cochlea [11], muscles [12], heart [13], bone [14], brown adipose tissue (BAT) [15], glia, and astrocytes [16,17]. The expression of DIO2 in humans is less restricted than in rats, and about 70% of circulating serum T3 is derived from the extrathyroidal conversion from T4 to T3 catalyzed by DIO1 and DIO2 [5]. In two opposite pathological conditions, DIO2 is upregulated in patients with hypothyroidism and downregulated in those with hyperthyroidism. Changes in DIO2 expression or enzyme activity contribute to the general effort to maintain T3 homeostasis, both in the circulation and in specific tissues [18].
- DIO2 expression or enzyme activity is essential for the maintenance of normal physiological function, including the central nervous system (CNS), BAT, and placenta. Its abnormal expression and enzyme activity are associated with various physiological and/or pathological processes, as listed in Table 1 [19-32]. A study showed that the overexpression of Dio2 could arrest trophoblast cell line proliferation at the G1 phase of the cell cycle by downregulating cyclin-D1 (Ccnd1) and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (Pcna), while promoting apoptosis via increased caspase-3 activity and inhibition of the Akt and extracellular signal‑regulated protein kinase (ERK1/2) signaling pathways [30]. These results indicate that DIO2 plays an indispensable role in many important physiological and/or pathological processes.
- In this review, we summarize the current knowledge on the physiological functions and polymorphisms of the DIO2 gene, thereby providing insights into the important roles of DIO2 in the pathogenesis of diseases.
INTRODUCTION
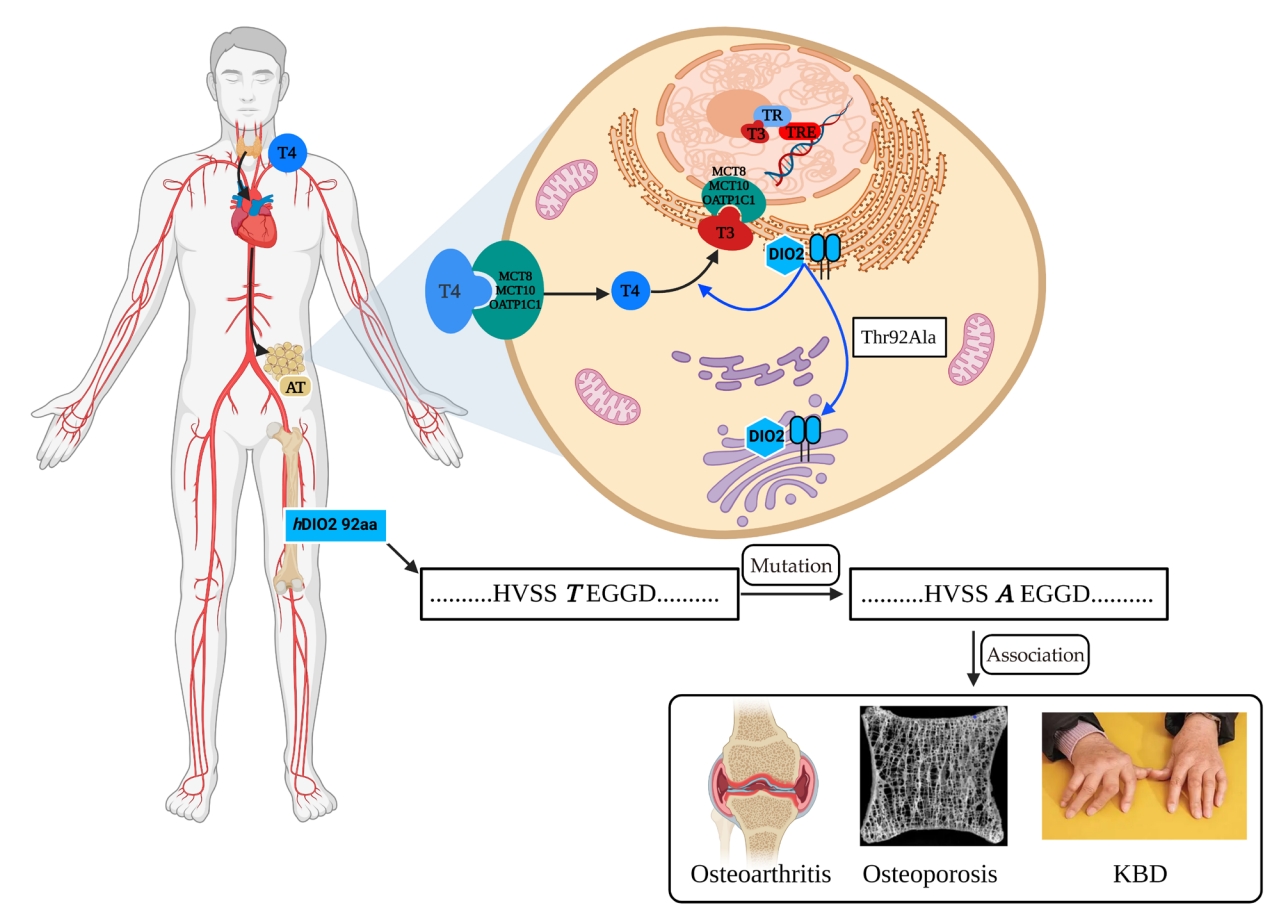
- The identification and cloning of the three deiodinases were remarkably difficult and proved to be extremely challenging, particularly DIO2. Utilizing the relatively short but highly conserved regions between the known Dio1 and Dio3 cDNAs, Davey et al. [33] used a reverse transcription/polymerase chain reaction strategy to clone a cDNA for Dio2 in the amphibian species Rana catesbeiana. Subsequently, Croteau et al. [34] used the amphibian Dio2 cDNA to obtain the sequences in rats and humans. Dio2 in rats contains an open reading frame of 798 nucleotides that includes two in-frame TGA codons; this 798-nucleotide open reading frame is predicted to code for a protein of 266 amino acids with a molecular weight of 29.8 kDa. In humans, DIO2 contains an open reading frame of 819 nucleotides that codes for a protein of 273 amino acids with a molecular weight of 30.0 kDa. Moreover, fluorescence in situ hybridization confirmed that human DIO2 is located in chromosome 14q24.2→q24.3 [35]. An analysis of protein structure showed that a critical residue (the active center Sec) confers high catalytic activity to deiodinases [36]. The three-dimensional modeling of the DIO2 protein based on hydrophobic cluster analyses [37] identified a unique 18-residue “instability” loop in the Dio2 molecule, which could be recognized by the WD-40 propeller of WD repeat and socs box-containing 1 (WSB-1), a part of an E3 ubiquitin ligase [38,39]. Ubiquitination of DIO2 is a switch mechanism that controls DIO2 activity and intracellular T3 production, whereby T4 binding and/or T4 catalysis triggers DIO2 inactivation by ubiquitination, which is mediated by the E3 ubiquitin ligases WSB-1 and/or the yeast Doa10 mammalian ortholog TEB4. Ubiquitinated DIO2 could be either targeted for proteasomal degradation or reactivated by deubiquitination, a process that is mediated by the deubiquitinases ubiquitin-specific proteases 20/30 (USP20/33) and is important in adaptive thermogenesis [40]. The subcellular localization of Dio2 is usually in the endoplasmic reticulum; it is also closely associated with the cell nucleus, but not with the Golgi apparatus (Fig. 1) [41-43]. The subcellular localization of Dio2 in the Golgi apparatus could constitute a disease mechanism associated with the Thr92Ala polymorphism in DIO2 (Fig. 1) [44].
MOLECULAR STRUCTURE OF DIO2
- As a deiodinase, the primary physiological function of DIO2 is to control the homeostasis of THs in the circulation and tissues, together with DIO1 and DIO3. It is also a key molecule for cold-adaptive thermogenesis in brown adipocytes, diet-induced thermogenic pathways, and it plays a metabolic role in humans [18]. The latest findings about DIO2 in TH signaling, adaptive thermogenesis in BAT, and the brain were summarized.
- Role of DIO2 in TH signaling
- Hypothyroidism is a state in which circulating TH levels are inadequate. It is commonly caused by autoimmune destruction or surgical removal of the thyroid gland (primary hypothyroidism). Therapy consisting of daily tablets of levothyroxine (LT4) to treat hypothyroidism is commonsensical and has become the standard of care for this disease [45,46]. Short-term LT4 treatment reduced the vestibular syndrome and significantly promoted vestibular compensation, and the observed presence of thyroid hormone receptors (TRs) and DIO2 in the vestibular nuclei supported the possibility that LT4 exerts local actions [47]. However, a small percentage of patients with hypothyroidism also experienced persistent symptoms despite LT4 therapy, with impaired cognition and tiredness [48]. These outcomes might be attributed to the lack of thyroid T3 secretion in LT4-treated hypothyroid patients. In patients with intrauterine adhesions, defective autophagy in the endometria has been shown to be associated with DIO2 downregulation, while overexpression of DIO2 or T3 treatment could restore autophagy and partly reverse the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in endometrial epithelial cells [28]. T3 is partially secreted by the thyroid gland, but mainly produced by DIO1 and DIO2 in various extrathyroidal tissues [49]. Therefore, several studies have investigated the efficiency of combined therapy with LT4+LT3. Shakir et al. [50] compared the treatment efficiency among LT4, LT4+LT3, and desiccated thyroid extract (DTE) and found similar outcomes among hypothyroid patients treated with LT4, LT4+LT3, and DTE; furthermore, the patients who were most symptomatic on LT4 preferred and responded positively to therapy with LT4+LT3 or DTE. A male patient with treatment-resistant depression and hypothyroidism responded to LT3/LT4 combination therapy, rather than LT4 alone, and he had a DIO2 polymorphism [51]. Wolff et al. [52] also addressed the problem of developing an optimal TH replacement strategy for hypothyroid patients and reported that LT3/LT4 combined therapy was slightly better than LT4 monotherapy for treating hypothyroidism. The European Thyroid Association guidelines state that LT4+LT3 combination therapy should be considered only as an experimental treatment modality in LT4-treated patients whose symptoms persist even though their serum thyroid-stimulating hormone levels are within the reference range [53]. The above results all indicate that the outcomes of combined therapy have shown progress in several fields, implying that DIO2 exerts an important effect in converting T4 to T3. However, debate continues regarding LT4+LT3 combination therapy in hypothyroidism patients. Drigo and Bianco [40] showed that DIO2 was associated with TH signaling in sensory organ development, skeletal development, regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis, adaptive thermogenesis, and metabolic control. The circulating TH levels remain fairly consistent during the entire adult life of healthy individuals. Therefore, deiodination carried out by deiodinases could control the important biological processes (growth, development, metabolism) regulated by THs despite no meaningful changes in plasma levels.
- Role of DIO2 in adaptive thermogenesis in BAT
- BAT is the main site of the sympathetic-mediated adaptive thermogenesis in human newborns and other small mammals, and the thermogenic pathway of BAT has been described in detail by Drigo et al. [54]. During cold exposure, DIO2 activity was found to show an acute approximately 50-fold increase in BAT, which accelerated the conversion from T4 to T3 [55]. Our understanding of the role of DIO2 in BAT physiology is based on the disruption of the Dio2 gene (Dio2−/−) in mice, which results in BAT-specific hypothyroidism in an otherwise euthyroid animal [56]. de Jesus et al. [15] demonstrated that the BAT of Dio2−/− mice had normal amounts of mitochondria and normal uncoupling protein 1 (UCP-1), which is a mitochondrial protein that shunts the energy derived from mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation from adenosine triphosphate formation to thermogenesis. In response to different adrenergic stimulants, Dio2−/− brown adipocytes exhibited a decreased cyclic adenosine monophosphate generation capacity, which might be the mechanism of impaired thermogenesis [15]. Another study also showed that cold exposure increased BAT sympathetic stimulation approximately 10-fold, with an increase in lipolysis as well as the mRNA levels of Ucp-1, guanosine monophosphate reductase (Gmpr), and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 (Pgc-1) in Dio2−/− mice [57]. Recent research found that T3 increased fatty acid oxidation and mitochondrial respiration as well as autophagic flux, mitophagy, and mitochondrial biogenesis; however, no significant induction of intracellular reactive oxygen species was found despite high mitochondrial respiration and Ucp-1 induction by T3, indicating that T3 exerted direct effects on mitochondrial autophagy, activity, and turnover in BAT that were essential for thermogenesis [58]. These results indicate that DIO2 is an essential component of the thyroid-sympathetic synergism required for thermal homeostasis in human newborns and small mammals.
- Role of DIO2 in the brain
- THs modulate the expression of a large number of genes in the CNS, and the expression of TH-targeted genes is regulated directly or indirectly through dynamic interactions of (non)ligand TRs with chromatin and DNA, in addition to epigenetic modifications. THs play a critical role in brain development, affecting neuronal migration, differentiation, and signal transduction, as well as myelin formation, neuronal cell proliferation, migration and maturation, synapse establishment and transmission [59]. In the brain, active T3 is either available directly from the circulation or is produced locally from T4 by Dio2, which is predominantly expressed in astrocytes [16,60]. Compared to hypothyroid mice, the T3 content in the brain of neonatal Dio2−/− mice was markedly reduced, while the mRNA levels of several T3-responsive genes were either unaffected or much less affected in the brain of the Dio2−/− mice, and the Dio2−/− mice exhibited a very mild neurological phenotype [59]. Notably, the Dio2−/− mice demonstrated no impairments in spatial learning and memory, but they displayed emotional alterations with increased anxiety-like behavior, as well as enhanced auditory-cued fear memory and spontaneous recovery of fear memory following extinction [61,62]. Another study indicated that Dio2 influenced working memory and verbal fluency in mice through neuropsychological testing [63]. Thus, the functions of Dio2 in learning and memory need further to be investigated. Studies have also shown that Dio2 expression is upregulated in a variety of neurological disorders. In mice that experienced 3 hours of status epilepticus (SE) caused by pilocarpine, the mRNA expression of Dio2 increased rapidly in the hippocampus, amygdala, and prefrontal cortex; however, the targeted disruption of Dio2 in astrocytes of mice had effects on highly induced genes in the hippocampus associated with inflammation, apoptosis, and cell death, suggesting that Dio2 induction caused by SE accelerated the production of T3 in different areas of the CNS and modified the hippocampal gene expression profile, affecting the balance between adaptive and maladaptive mechanisms [64]. Moreover, Dio2 mRNA expression significantly increased in the frontal cortex of two mandibular extension-treated rats compared with sham-operated rats, indicating the major involvement of Dio2 in an attempt to restore more physiological conditions and correct T3 levels, associated with normotensive status in the brain [65]. A recent result also showed that mice lacking both monocarboxylate transporter 8 (Mct8) and Dio2 presented peripheral and brain hypothyroidism; the severity of the brain hypothyroidism seemed permanent and varied across regions, with the striatum being a particularly affected area, and brain alterations were observed at the histological level compatible with TH deficiency and impaired motor skills [66]. Therefore, further investigations need to be carried out to understand the functional link between TH signaling and the role of Dio2 in different regions of the brain.
PHYSIOLOGICAL FUNCTIONS OF DIO2
- Polymorphisms of DIO2, including rs225014 (Thr92Ala), rs12885300, rs1352815, rs1388382, and rs955849187, have been shown to exert significant effects on physiological processes and diseases. Studies of polymorphisms of DIO2 in physiological and pathological processes or diseases are summarized in Table 2 [28,67-88]. Given its high prevalence in human populations (12% to 36%), the DIO2 rs225014 (Thr92Ala-DIO2) has been the most studied polymorphism in humans. It has also been researched in mouse and cell models [67], and has been found to be a potential risk factor for various diseases. Unfortunately, the clinical syndromes associated with DIO2 gene polymorphisms have not been reproduced in all population studies [67,89,90]. Maino et al. [53] summarized the clinical significance of the Thr92Ala-DIO2 polymorphism in patients with autoimmune or surgical hypothyroidism and in patients with physical/psychological disorders that could be associated with overt hypothyroidism, as well as severe type 2 diabetes mellitus or insulin resistance. Next, we focus on the latest findings on the role of Thr92Ala-DIO2 in bone diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, and other tumors.
- Thr92Ala alters the physical function of the DIO2 gene
- The subcellular localization of Thr92-Dio2 is usually in the endoplasmic reticulum, while Ala92-Dio2 accumulates in the Golgi apparatus, where its presence and/or ensuing oxidative stress disrupts basic cellular functions, including mitochondrial unbalancing and inflammation, and increases pre-apoptosis [43]. In patients with total thyroidectomy treated with LT4, heterozygous and rare homozygous patients carrying the Thr92Ala polymorphism in the DIO2 gene showed reduced free triiodothyronine (FT3) levels when data were analyzed assuming both dominant and recessive models, indicating that Thr92Ala-DIO2 might inhibit the conversion from T4 to T3 by DIO2 [91]. In Graves’ disease (GD) patients, the polymorphic inheritance (CC+CT genotype) of DIO2 rs225014 was associated with less body weight variation after GD treatment than in patients with the wild-type TT genotype, suggesting that DIO2 rs225014 genotyping might have an auxiliary role in predicting the posttreatment weight behavior of GD patients [92]. de Lima Beltrao et al. [93] investigated a possible association between the Thr92Ala-DIO2 polymorphism and in-hospital mortality from COVID-19 in adult patients admitted between June and August 2020, and the results showed lower lethality in people with the heterozygous genotype (Thr/Ala) than in those with homozygous genotypes (Thr/Thr and Ala/Ala), implying a protective role of Thr92Ala-DIO2 heterozygosity. An Ala92-Dio2 polymorphism-carrying mouse exhibited unfolded protein response and hypothyroidism in distinct brain areas, and the polymorphism-containing mice refrained from physical activity, slept more, and required additional time to memorize objects; however, LT3 treatment enhanced T3 signaling in the brain and improved cognition [94]. Compared with euthyroid noncarriers (Thr/Thr), euthyroid Ala92-DIO2 carriers showed higher body mass index values and fasting plasma glucose levels [95]. These results suggest that the Ala92-DIO2 might be deleterious for individuals with hypothyroidism and for euthyroid individuals.
- Thr92Ala is associated with bone diseases
- A study showed that the Tha92Ala-DIO2 polymorphism was associated with decreased femoral neck bone mineral density (BMD) and higher bone turnover independent of serum TH levels in patients with cured differentiated thyroid carcinoma, pointing to a potential functional role for Tha92Ala-DIO2 in bone metabolism [96]. In osteoporosis, female subjects carrying the Thr92Ala-DIO2 polymorphism had a significantly lower speed of sound and T-scores in the tibia than control participants, indicating a potential functional role of Thr92Ala-DIO2 in the maintenance of BMD [97]. However, the presence of the Thr92Ala-DIO2 polymorphism did not affect thyroid function tests in individuals who had a normal thyroid gland, but contradictory results were found in thyroidectomized patients kept on LT4 [90, 98,99]. In addition, the association between the Thr92Ala-DIO2 polymorphism and osteoarthritis was not reproduced by Kerkhof et al. [100] and a meta-analysis [101]. In contrast, Kerkhof et al. [100] showed that the T-allele of the rs12885300 single-nucleotide polymorphism in the DIO2 gene had a trend toward a protective effect for hip osteoarthritis. A recent study using CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing found that Dio2Thr92 mice had decreased cartilage volume and median thickness, with increased articular cartilage damage; in contrast, Dio2Ala92 mutants had no signs of osteoarthritis, indicating a protective role of the Ala92 polymorphism and providing the first functional evidence of a role for this candidate Dio2 polymorphism in vivo [102]. Notably, a meta-analysis found that the Thr92Ala-DIO2 polymorphism was also significantly associated with Kashin-Beck disease [103]. These results suggest that the Thr92Ala-DIO2 polymorphism might disrupt bone metabolism, and there might be an interaction between Thr92Ala-DIO2 and other polymorphisms of DIO2.
- Thr92Ala is associated with neurodegenerative diseases
- Previous research showed that both the Thr92Ala-DIO2 carriers and Ala92-Dio2-expressing HEK-293 cells exhibited a transcriptional fingerprint that included sets of genes involved in CNS diseases, ubiquitin, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, apoptosis, DNA repair, and growth factor signaling [43]. Subsequent studies pointed out that the Thr92Ala-DIO2 polymorphism in neurodegenerative diseases was related to racial differences. For instance, compared with European Americans, African Americans with Thr92Ala-DIO2 had greater odds of developing Alzheimer disease (AD), dementia, or cognitive impairment without dementia [104]. In older adults, the outcomes of a standard questionnaire and evaluations of thyroid function were similar regardless of genotyping results for the Thr92Ala-DIO2 polymorphism, suggesting that the Thr92Ala-DIO2 polymorphism may not be associated with relevant cognitive impairment in older adults [16]. In light of these inconsistent findings, the role of Thr92Ala-DIO2 in cognitive impairment in individuals from different populations remains to be elucidated. Moreover, neuropsychological testing revealed that homozygous Ala92-carriers showed both higher verbal fluency and higher accuracy in working memory [63], suggesting improved executive function in homozygous Ala92-carriers. In autistic spectrum disorder (ASD), the minor allele (Ala92) frequency was not significantly different in ASD children, but carriers of the Thr92Ala-DIO2 polymorphism exhibited higher adaptive behavior, such as daily living skills and communication [105]. Those results indicate the importance of Thr92Ala-DIO2 in neurodegenerative diseases, such as AD, dementia, and ASD. However, more evidence is needed in large populations to demonstrate whether Thr92Ala-DIO2 is a risk factor for neurodegenerative diseases, and it is not clear whether the localization of Ala92-DIO2 is associated with those diseases.
- Thr92Ala is associated with tumors
- Only one study has described the relationship between Thr92Ala and tumors; that study showed that there was a 1.99-fold higher risk of developing endometrial cancer in CC homozygotes, reflecting a DIO2 (rs225014) polymorphism, than in TT homozygotes, indicating that carriers of the DIO2 polymorphism might be predisposed to the development of endometrial cancer [106]. Because altered expression of DIO2 was correlated with thyroid, pituitary and brain tumors, we speculate that the Thr92Ala might also have a relationship with these tumors.
POLYMORPHISMS OF DIO2 LEAD TO MULTIPLE DISEASES
- Although the deiodinase family, which consists of DIO1, DIO2, and DIO3, is a dynamic system, DIO2 plays an essential role in TH signaling and adaptive thermogenesis in BAT and the brain by converting T4 to T3 in the target tissues. This review emphasizes the physiological functions and polymorphisms of the DIO2 gene, which is closely related to physiological/pathological processes and tumors; in particular, Thr92Ala-DIO2 has been shown to play deleterious or protective roles in different diseases (Table 3, Fig. 1). However, these results were based only on measurements of expression levels in several specific populations, and the reasons underlying these alterations in expression and associations with polymorphisms of the DIO2 gene have rarely been explored. Future studies need to be carried out to explore the pathogenic mechanisms by collectively analyzing subcellular localization, expression alterations, protein structure, and polymorphisms in the DIO2 gene. Considering the importance of the physiological functions of DIO2 and the clinical significance of polymorphisms of DIO2, it might be considered as a potential therapeutic target for metabolic diseases (bone metabolism), neurodegenerative diseases (AD, dementia, and ASD), and tumors (thyroid, pituitary, and brain tumors). The present review provides insights and orientations for future research on DIO2.
CONCLUSIONS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Article information
-
Acknowledgements
- This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31871031, 32170968), the Fund of the Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology in 2021 (KeyME-2021-01) and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2021M692700).

| Expression state of DIO2 | Species | Conditions | Processes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upregulation | Humans | In adipose tissue of overweight/obese subjects and in adipose tissue of pregnant subjects due to maternal exercise | Physiological | [19,20] |
| Mice | In intestinal polyps of a mouse model of familial adenomatous polyposis and early-stage sporadic colorectal cancer | Pathological | [21] | |
| Humans | In lungs from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis | Pathological | [22] | |
| Humans | Tumors including thyroid and pituitary, and brain gliomas | Pathological | [23-26] | |
| Downregulation | Humans | Associated with defective autophagy in endometria of patients with intrauterine adhesions | Pathological | [27] |
| Mice | Associated with acute lung injury in mice | Pathological | [28] | |
| Mice | Associated with impairment in muscle stem cell-endothelial cell crosstalk | Physiological | [29] | |
| Humans | Associated with papillary thyroid carcinoma | Pathological | [31] | |
| Humans | Associated with astrocytomas and glioblastomas | Pathological | [32] |
| Polymorphisms of DIO2 | Species | Processes or diseases | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| rs225014 | Humans | T2DM | [28,67-76] |
| Humans | Obesity | ||
| Humans | Arterial hypertension | ||
| Humans | Osteoarthritis | ||
| Mice | ALI and pulmonary fibrosis | ||
| Humans | Dementia | ||
| rs12885300 | Humans | Differentiated thyroid carcinoma | [75-83] |
| Humans | Mild cognitive impairment | ||
| Humans | Bipolar disorder | ||
| Humans | Depression | ||
| Humans | Advanced/symptomatic hip osteoarthritis in women | ||
| Humans | Increased mortality risk | ||
| Humans | A decreased rate of acute TSH-stimulated FT4 secretion | ||
| Humans | Stronger association between perfluorooctanoic acid, perfluorononanoic acid, and total T3 in the DIO2-CT genotype | ||
| Humans | Increased vulnerability of cartilage to nonoptimal bone shapes | ||
| rs1352815 | Humans | KBD | [84] |
| rs1388382 | Humans | KBD | [84] |
| rs955849187 | Humans | KBD | [85] |
| rs225011 | Humans | GD, early-onset T2DM, and hepatic glucose output | [69,86] |
| rs225017 | Humans | Greater IR in T2DM and interaction with Thr92Ala in the modulation of IR | [87] |
| rs225012/rs225010 | Humans | Intellectual disability | [88] |
| rs225015 | Humans | Early-onset T2DM and hepatic glucose output | [69] |
| rs6574549 | Humans | Hepatic glucose output, fasting insulin, insulin action, and energy expenditure | [69] |
- 1. Luongo C, Dentice M, Sal vatore D. Deiodinases and their intricate role in thyroid hormone homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2019;15:479–88.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. Dentice M, Marsili A, Zavacki A, Larsen PR, Salvatore D. The deiodinases and the control of intracellular thyroid hormone signaling during cellular differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013;1830:3937–45.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. St Germain DL, Galton VA. The deiodinase family of selenoproteins. Thyroid 1997;7:655–68.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Maia AL, Berry MJ, Sabbag R, Harney JW, Larsen PR. Structural and functional differences in the dio1 gene in mice with inherited type 1 deiodinase deficiency. Mol Endocrinol 1995;9:969–80.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Bianco AC, Salvatore D, Gereben B, Berry MJ, Larsen PR. Biochemistry, cellular and molecular biology, and physiological roles of the iodothyronine selenodeiodinases. Endocr Rev 2002;23:38–89.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Van der Geyten S, Segers I, Gereben B, Bartha T, Rudas P, Larsen PR, et al. Transcriptional regulation of iodothyronine deiodinases during embryonic development. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2001;183:1–9.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Lopez-Espindola D, Garcia-Aldea A, Gomez de la Riva I, Rodriguez-Garcia AM, Salvatore D, Visser TJ, et al. Thyroid hormone availability in the human fetal brain: novel entry pathways and role of radial glia. Brain Struct Funct 2019;224:2103–19.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Takemura Y, Yamaguchi S, Aoki N, Miura M, Homma KJ, Matsushima T. Gene expression of Dio2 (thyroid hormone converting enzyme) in telencephalon is linked with predisposed biological motion preference in domestic chicks. Behav Brain Res 2018;349:25–30.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Larsen PR. Thyroid-pituitary interaction: feedback regulation of thyrotropin secretion by thyroid hormones. N Engl J Med 1982;306:23–32.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Christoffolete MA, Ribeiro R, Singru P, Fekete C, da Silva WS, Gordon DF, et al. Atypical expression of type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase in thyrotrophs explains the thyroxinemediated pituitary thyrotropin feedback mechanism. Endocrinology 2006;147:1735–43.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 11. Campos-Barros A, Amma LL, Faris JS, Shailam R, Kelley MW, Forrest D. Type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase expression in the cochlea before the onset of hearing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2000;97:1287–92.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Marsili A, Tang D, Harney JW, Singh P, Zavacki AM, Dentice M, et al. Type II iodothyronine deiodinase provides intracellular 3,5,3’-triiodothyronine to normal and regenerating mouse skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2011;301:E818–24.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Bomer N, Pavez-Giani MG, Deiman FE, Linders AN, Hoes MF, Baierl CL, et al. Selenoprotein DIO2 is a regulator of mitochondrial function, morphology and UPRmt in human cardiomyocytes. Int J Mol Sci 2021;22:11906.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Bassett JH, Boyde A, Howell PG, Bassett RH, Galliford TM, Archanco M, et al. Optimal bone strength and mineralization requires the type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase in osteoblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010;107:7604–9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. de Jesus LA, Carvalho SD, Ribeiro MO, Schneider M, Kim SW, Harney JW, et al. The type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase is essential for adaptive thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 2001;108:1379–85.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Diez D, Morte B, Bernal J. Single-cell transcriptome profiling of thyroid hormone effectors in the human fetal neocortex: expression of SLCO1C1, DIO2, and THRB in specific cell types. Thyroid 2021;31:1577–88.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Freitas BC, Gereben B, Castillo M, Kallo I, Zeold A, Egri P, et al. Paracrine signaling by glial cell-derived triiodothyronine activates neuronal gene expression in the rodent brain and human cells. J Clin Invest 2010;120:2206–17.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 18. Gereben B, Zavacki AM, Ribich S, Kim BW, Huang SA, Simonides WS, et al. Cellular and molecular basis of deiodinase-regulated thyroid hormone signaling. Endocr Rev 2008;29:898–938.PubMedPMC
- 19. Gao Y, Zhao L, Son JS, Liu X, Chen Y, Deavila JM, et al. Maternal exercise before and during pregnancy facilitates embryonic myogenesis by enhancing thyroid hormone signaling. Thyroid 2022;32:581–93.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. Straczkowski M, Nikolajuk A, Stefanowicz M, Matulewicz N, Fernandez-Real JM, Karczewska-Kupczewska M. Adipose tissue and skeletal muscle expression of genes associated with thyroid hormone action in obesity and insulin resistance. Thyroid 2022;32:206–14.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Kojima Y, Kondo Y, Fujishita T, Mishiro-Sato E, Kajino-Sakamoto R, Taketo MM, et al. Stromal iodothyronine deiodinase 2 (DIO2) promotes the growth of intestinal tumors in ApcΔ716 mutant mice. Cancer Sci 2019;110:2520–8.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 22. Yu G, Tzouvelekis A, Wang R, Herazo-Maya JD, Ibarra GH, Srivastava A, et al. Thyroid hormone inhibits lung fibrosis in mice by improving epithelial mitochondrial function. Nat Med 2018;24:39–49.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 23. Meyer EL, Goemann IM, Dora JM, Wagner MS, Maia AL. Type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase is highly expressed in medullary thyroid carcinoma. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2008;289:16–22.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Kim BW, Daniels GH, Harrison BJ, Price A, Harney JW, Larsen PR, et al. Overexpression of type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase in follicular carcinoma as a cause of low circulating free thyroxine levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003;88:594–8.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Tannahill LA, Visser TJ, McCabe CJ, Kachilele S, Boelaert K, Sheppard MC, et al. Dysregulation of iodothyronine deiodinase enzyme expression and function in human pituitary tumours. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2002;56:735–43.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 26. Nauman P, Bonicki W, Michalik R, Warzecha A, Czernicki Z. The concentration of thyroid hormones and activities of iodothyronine deiodinases are altered in human brain gliomas. Folia Neuropathol 2004;42:67–73.PubMed
- 27. Zhou Z, Wang H, Zhang X, Song M, Yao S, Jiang P, et al. Defective autophagy contributes to endometrial epithelialmesenchymal transition in intrauterine adhesions. Autophagy 2022;18:2427–42.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 28. Ma SF, Xie L, Pino-Yanes M, Sammani S, Wade MS, Letsiou E, et al. Type 2 deiodinase and host responses of sepsis and acute lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2011;45:1203–11.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. An X, Ogawa-Wong A, Carmody C, Ambrosio R, Cicatiello AG, Luongo C, et al. A type 2 deiodinase-dependent increase in Vegfa mediates myoblast-endothelial cell cross-talk during skeletal muscle regeneration. Thyroid 2021;31:115–27.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Adu-Gyamfi EA, Lamptey J, Chen XM, Li FF, Li C, Ruan LL, et al. Iodothyronine deiodinase 2 (DiO2) regulates trophoblast cell line cycle, invasion and apoptosis; and its downregulation is associated with early recurrent miscarriage. Placenta 2021;111:54–68.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Arnaldi LA, Borra RC, Maciel RM, Cerutti JM. Gene expression profiles reveal that DCN, DIO1, and DIO2 are underexpressed in benign and malignant thyroid tumors. Thyroid 2005;15:210–21.ArticlePubMed
- 32. Murakami M, Araki O, Morimura T, Hosoi Y, Mizuma H, Yamada M, et al. Expression of type II iodothyronine deiodinase in brain tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2000;85:4403–6.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Davey JC, Becker KB, Schneider MJ, St Germain DL, Galton VA. Cloning of a cDNA for the type II iodothyronine deiodinase. J Biol Chem 1995;270:26786–9.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Croteau W, Davey JC, Galton VA, St Germain DL. Cloning of the mammalian type II iodothyronine deiodinase: a selenoprotein differentially expressed and regulated in human and rat brain and other tissues. J Clin Invest 1996;98:405–17.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Araki O, Murakami M, Morimura T, Kamiya Y, Hosoi Y, Kato Y, et al. Assignment of type II iodothyronine deiodinase gene (DIO2) to human chromosome band 14q24.2-->q24.3 by in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet 1999;84:73–4.PubMed
- 36. Buettner C, Harney JW, Larsen PR. The role of selenocysteine 133 in catalysis by the human type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase. Endocrinology 2000;141:4606–12.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Callebaut I, Curcio-Morelli C, Mornon JP, Gereben B, Buettner C, Huang S, et al. The iodothyronine selenodeiodinases are thioredoxin-fold family proteins containing a glycoside hydrolase clan GH-A-like structure. J Biol Chem 2003;278:36887–96.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Dentice M, Bandyopadhyay A, Gereben B, Callebaut I, Christoffolete MA, Kim BW, et al. The Hedgehog-inducible ubiquitin ligase subunit WSB-1 modulates thyroid hormone activation and PTHrP secretion in the developing growth plate. Nat Cell Biol 2005;7:698–705.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 39. Zavacki AM, Drigo RAE, Freitas BC, Chung M, Harney JW, Egri P, et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase TEB4 mediates degradation of type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase. Mol Cell Biol 2009;29:5339–47.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 40. Drigo RAE, Bianco AC. Type 2 deiodinase at the crossroads of thyroid hormone action. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2011;43:1432–41.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 41. Zeold A, Pormuller L, Dentice M, Harney JW, Curcio-Morelli C, Tente SM, et al. Metabolic instability of type 2 deiodinase is transferable to stable proteins independently of subcellular localization. J Biol Chem 2006;281:31538–43.ArticlePubMed
- 42. Baqui MM, Gereben B, Harney JW, Larsen PR, Bianco AC. Distinct subcellular localization of transiently expressed types 1 and 2 iodothyronine deiodinases as determined by immunofluorescence confocal microscopy. Endocrinology 2000;141:4309–12.ArticlePubMed
- 43. McAninch EA, Jo S, Preite NZ, Farkas E, Mohacsik P, Fekete C, et al. Prevalent polymorphism in thyroid hormone-activating enzyme leaves a genetic fingerprint that underlies associated clinical syndromes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015;100:920–33.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 44. Bianco AC, Kim BS. Pathophysiological relevance of deiodinase polymorphism. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 2018;25:341–6.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 45. Chaker L, Bianco AC, Jonklaas J, Peeters RP. Hypothyroidism. Lancet 2017;390:1550–62.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 46. Jonklaas J, Bianco AC, Bauer AJ, Burman KD, Cappola AR, Celi FS, et al. Guidelines for the treatment of hypothyroidism: prepared by the American Thyroid Association task force on thyroid hormone replacement. Thyroid 2014;24:1670–751.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 47. Rastoldo G, Marouane E, El-Mahmoudi N, Pericat D, Watabe I, Lapotre A, et al. L-thyroxine improves vestibular compensation in a rat model of acute peripheral vestibulopathy: cellular and behavioral aspects. Cells 2022;11:684.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 48. Ettleson MD, Bianco AC. Individualized therapy for hypothyroidism: is T4 enough for everyone? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2020;105:e3090–104.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 49. Williams GR, Bassett JH. Deiodinases: the balance of thyroid hormone: local control of thyroid hormone action: role of type 2 deiodinase. J Endocrinol 2011;209:261–72.PubMed
- 50. Shakir MK, Brooks DI, McAninch EA, Fonseca TL, Mai VQ, Bianco AC, et al. Comparative effectiveness of levothyroxine, desiccated thyroid extract, and levothyroxine+liothyronine in hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2021;106:e4400–13.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 51. Ahmed ZS, Sherin RP, Fonseca TL, Hoang TD, Shakir MK. Improvement of depression in a patient with hypothyroidism and deiodinase polymorphism with LT3 Therapy. Clin Case Rep 2022;10:e05651.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 52. Wolff TM, Dietrich JW, Muller MA. Optimal hormone replacement therapy in hypothyroidism: a model predictive control approach. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2022;13:884018.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 53. Maino F, Cantara S, Forleo R, Pilli T, Castagna MG. Clinical significance of type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase polymorphism. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab 2018;13:273–7.ArticlePubMed
- 54. Drigo RAE, Fonseca TL, Werneck-de-Castro JP, Bianco AC. Role of the type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase (D2) in the control of thyroid hormone signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013;1830:3956–64.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 55. Silva JE, Larsen PR. Adrenergic activation of triiodothyronine production in brown adipose tissue. Nature 1983;305:712–3.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 56. Schneider MJ, Fiering SN, Pallud SE, Parlow AF, St Germain DL, Galton VA. Targeted disruption of the type 2 selenodeiodinase gene (DIO2) results in a phenotype of pituitary resistance to T4. Mol Endocrinol 2001;15:2137–48.ArticlePubMed
- 57. Christoffolete MA, Linardi CC, de Jesus L, Ebina KN, Carvalho SD, Ribeiro MO, et al. Mice with targeted disruption of the Dio2 gene have cold-induced overexpression of the uncoupling protein 1 gene but fail to increase brown adipose tissue lipogenesis and adaptive thermogenesis. Diabetes 2004;53:577–84.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 58. Yau WW, Singh BK, Lesmana R, Zhou J, Sinha RA, Wong KA, et al. Thyroid hormone (T3) stimulates brown adipose tissue activation via mitochondrial biogenesis and MTOR-mediated mitophagy. Autophagy 2019;15:131–50.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 59. Galton VA, Wood ET, St Germain EA, Withrow CA, Aldrich G, St Germain GM, et al. Thyroid hormone homeostasis and action in the type 2 deiodinase-deficient rodent brain during development. Endocrinology 2007;148:3080–8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 60. Morte B, Bernal J. Thyroid hormone action: astrocyte-neuron communication. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2014;5:82.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 61. Barez-Lopez S, Montero-Pedrazuela A, Bosch-Garcia D, Venero C, Guadano-Ferraz A. Increased anxiety and fear memory in adult mice lacking type 2 deiodinase. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017;84:51–60.ArticlePubMed
- 62. Bocco BM, Werneck-de-Castro JP, Oliveira KC, Fernandes GW, Fonseca TL, Nascimento BP, et al. Type 2 deiodinase disruption in astrocytes results in anxiety-depressive-like behavior in male mice. Endocrinology 2016;157:3682–95.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 63. Uter JC, Kramer UM, Schols L, Rodriguez-Fornells A, Gobel A, Heldmann M, et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in thyroid hormone transporter genes MCT8, MCT10 and deiodinase DIO2 contribute to inter-individual variance of executive functions and personality traits. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2020;128:573–81.ArticlePubMed
- 64. Nascimento BP, Bocco BM, Fernandes GW, Fonseca TL, McAninch EA, Cardoso CV, et al. Induction of type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase after status epilepticus modifies hippocampal gene expression in male mice. Endocrinology 2018;159:3090–104.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 65. Sabatino L, Federighi G, Del Seppia C, Lapi D, Costagli C, Scuri R, et al. Thyroid hormone deiodinases response in brain of spontaneausly hypertensive rats after hypotensive effects induced by mandibular extension. Endocrine 2021;74:100–7.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 66. Barez-Lopez S, Grijota-Martinez C, Auso E, Fernandez-de Frutos M, Montero-Pedrazuela A, Guadano-Ferraz A. Adult mice lacking Mct8 and Dio2 proteins present alterations in peripheral thyroid hormone levels and severe brain and motor skill impairments. Thyroid 2019;29:1669–82.ArticlePubMed
- 67. Dora JM, Machado WE, Rheinheimer J, Crispim D, Maia AL. Association of the type 2 deiodinase Thr92Ala polymorphism with type 2 diabetes: case-control study and meta-analysis. Eur J Endocrinol 2010;163:427–34.ArticlePubMed
- 68. Mentuccia D, Proietti-Pannunzi L, Tanner K, Bacci V, Pollin TI, Poehlman ET, et al. Association between a novel variant of the human type 2 deiodinase gene Thr92Ala and insulin resistance: evidence of interaction with the Trp64Arg variant of the beta-3-adrenergic receptor. Diabetes 2002;51:880–3.PubMed
- 69. Nair S, Muller YL, Ortega E, Kobes S, Bogardus C, Baier LJ. Association analyses of variants in the DIO2 gene with early-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus in Pima Indians. Thyroid 2012;22:80–7.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 70. Canani LH, Capp C, Dora JM, Meyer EL, Wagner MS, Harney JW, et al. The type 2 deiodinase A/G (Thr92Ala) polymorphism is associated with decreased enzyme velocity and increased insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005;90:3472–8.ArticlePubMed
- 71. Grarup N, Andersen MK, Andreasen CH, Albrechtsen A, Borch-Johnsen K, Jorgensen T, et al. Studies of the common DIO2 Thr92Ala polymorphism and metabolic phenotypes in 7342 Danish white subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007;92:363–6.ArticlePubMed
- 72. Gumieniak O, Perlstein TS, Williams JS, Hopkins PN, Brown NJ, Raby BA, et al. Ala92 type 2 deiodinase allele increases risk for the development of hypertension. Hypertension 2007;49:461–6.ArticlePubMed
- 73. van der Deure WM, Peeters RP, Uitterlinden AG, Hofman A, Breteler MM, Witteman J, et al. Impact of thyroid function and polymorphisms in the type 2 deiodinase on blood pressure: the Rotterdam Study and the Rotterdam Scan Study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2009;71:137–44.ArticlePubMed
- 74. Dhanunjaya Y, Dolia PB, Chitraa R. Type II 5’deiodinase Thr92Ala polymorphism is associated with CVD risk among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. J Diabetes Mellitus 2016;6:58–68.ArticlePDF
- 75. Meulenbelt I, Min JL, Bos S, Riyazi N, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, van der Wijk HJ, et al. Identification of DIO2 as a new susceptibility locus for symptomatic osteoarthritis. Hum Mol Genet 2008;17:1867–75.ArticlePubMed
- 76. Luo M, Zhou XH, Zou T, Keyim K, Dong LM. Type II deiodinase polymorphisms and serum thyroid hormone levels in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Genet Mol Res 2015;14:5407–16.ArticlePubMed
- 77. Hoftijzer HC, Heemstra KA, Visser TJ, le Cessie S, Peeters RP, Corssmit EP, et al. The type 2 deiodinase ORFa-Gly3Asp polymorphism (rs12885300) influences the set point of the hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis in patients treated for differentiated thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011;96:E1527–33.ArticlePubMed
- 78. Peltsverger MY, Butler PW, Alberobello AT, Smith S, Guevara Y, Dubaz OM, et al. The -258A/G (SNP rs12885300) polymorphism of the human type 2 deiodinase gene is associated with a shift in the pattern of secretion of thyroid hormones following a TRH-induced acute rise in TSH. Eur J Endocrinol 2012;166:839–45.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 79. Sarzo B, Ballesteros V, Iniguez C, Manzano-Salgado CB, Casas M, Llop S, et al. Maternal perfluoroalkyl substances, thyroid hormones, and DIO genes: a Spanish cross-sectional study. Environ Sci Technol 2021;55:11144–54.Article
- 80. Bunevicius A, Laws ER, Saudargiene A, Tamasauskas A, Iervasi G, Deltuva V, et al. Common genetic variations of deiodinase genes and prognosis of brain tumor patients. Endocrine 2019;66:563–72.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 81. Waarsing JH, Kloppenburg M, Slagboom PE, Kroon HM, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, Weinans H, et al. Osteoarthritis susceptibility genes influence the association between hip morphology and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2011;63:1349–54.ArticlePubMed
- 82. He B, Li J, Wang G, Ju W, Lu Y, Shi Y, et al. Association of genetic polymorphisms in the type II deiodinase gene with bipolar disorder in a subset of Chinese population. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2009;33:986–90.ArticlePubMed
- 83. Galecka E, Talarowska M, Orzechowska A, Gorski P, Bienkiewicz M, Szemraj J. Association of the DIO2 gene single nucleotide polymorphisms with recurrent depressive disorder. Acta Biochim Pol 2015;62:297–302.ArticlePubMed
- 84. Jin T, Wang L, He X, Liu M, Bai M, Rong H, et al. Association between DIO2 polymorphism and the risk of Kashin-Beck disease in the Tibetan population. J Gene Med 2019;21:e3123.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 85. Zhang RQ, Zhang DD, Zhang D, Yang XL, Li Q, Wang C, et al. Crosstalk between CpG methylation and polymorphisms (CpG-SNPs) in the promotor region of DIO2 in Kashin-Beck disease. Chin Med Sci J 2022;37:52–9.PubMed
- 86. Shahida B, Planck T, Asman P, Lantz M. Study of deiodinase type 2 polymorphisms in Graves’ disease and ophthalmopathy in a Swedish population. Eur Thyroid J 2018;7:289–93.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 87. Leiria LB, Dora JM, Wajner SM, Estivalet AA, Crispim D, Maia AL. The rs225017 polymorphism in the 3’UTR of the human DIO2 gene is associated with increased insulin resistance. PLoS One 2014;9:e103960.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 88. Guo TW, Zhang FC, Yang MS, Gao XC, Bian L, Duan SW, et al. Positive association of the DIO2 (deiodinase type 2) gene with mental retardation in the iodine-deficient areas of China. J Med Genet 2004;41:585–90.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 89. Gereben B, McAninch EA, Ribeiro MO, Bianco AC. Scope and limitations of iodothyronine deiodinases in hypothyroidism. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2015;11:642–52.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 90. Wouters HJ, van Loon HC, van der Klauw MM, Elderson MF, Slagter SN, Kobold AM, et al. No effect of the Thr92Ala polymorphism of deiodinase-2 on thyroid hormone parameters, health-related quality of life, and cognitive functioning in a large population-based cohort study. Thyroid 2017;27:147–55.ArticlePubMed
- 91. Cantara S, Ricci C, Maino F, Marzocchi C, Pacini F, Castagna MG. Variants in MCT10 protein do not affect FT3 levels in athyreotic patients. Endocrine 2019;66:551–6.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 92. Comarella AP, Vilagellin D, Bufalo NE, Euflauzino JF, de Souza Teixeira E, Miklos AB, et al. The polymorphic inheritance of DIO2 rs225014 may predict body weight variation after Graves’ disease treatment. Arch Endocrinol Metab 2021;64:787–95.ArticlePubMed
- 93. de Lima Beltrao FE, de Almeida Beltrao DC, Carvalhal G, de Lima Beltrao FE, de Souza Braga Filho J, de Brito Oliveira J, et al. Heterozygote advantage of the type II deiodinase Thr92Ala polymorphism on intrahospital mortality of COVID-19. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2022;107:e2488–501.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 94. Jo S, Fonseca TL, Bocco BM, Fernandes GW, McAninch EA, Bolin AP, et al. Type 2 deiodinase polymorphism causes ER stress and hypothyroidism in the brain. J Clin Invest 2019;129:230–45.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 95. Wang X, Chen K, Zhang C, Wang H, Li J, Wang C, et al. The type 2 deiodinase Thr92Ala polymorphism is associated with higher body mass index and fasting glucose levels: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int 2021;2021:9914009.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 96. Heemstra KA, Hoftijzer H, van der Deure WM, Peeters RP, Hamdy NA, Pereira A, et al. The type 2 deiodinase Thr92Ala polymorphism is associated with increased bone turnover and decreased femoral neck bone mineral density. J Bone Miner Res 2010;25:1385–91.ArticlePubMed
- 97. Kang YE, Kang YM, Park B, Shong M, Yi HS. Type 2 deiodinase Thr92Ala polymorphism is associated with a reduction in bone mineral density: a community-based Korean genome and epidemiology study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2020;93:238–47.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 98. Panicker V, Saravanan P, Vaidya B, Evans J, Hattersley AT, Frayling TM, et al. Common variation in the DIO2 gene predicts baseline psychological well-being and response to combination thyroxine plus triiodothyronine therapy in hypothyroid patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009;94:1623–9.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 99. Castagna MG, Dentice M, Cantara S, Ambrosio R, Maino F, Porcelli T, et al. DIO2 Thr92Ala reduces deiodinase-2 activity and serum-T3 levels in thyroid-deficient patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2017;102:1623–30.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 100. Kerkhof HJ, Lories RJ, Meulenbelt I, Jonsdottir I, Valdes AM, Arp P, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies an osteoarthritis susceptibility locus on chromosome 7q22. Arthritis Rheum 2010;62:499–510.PubMedPMC
- 101. Evangelou E, Kerkhof HJ, Styrkarsdottir U, Ntzani EE, Bos SD, Esko T, et al. A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies novel variants associated with osteoarthritis of the hip. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:2130–6.PubMed
- 102. Butterfield NC, Curry KF, Steinberg J, Dewhurst H, Komla-Ebri D, Mannan NS, et al. Accelerating functional gene discovery in osteoarthritis. Nat Commun 2021;12:467.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 103. Yu FF, Sun L, Zhou GY, Ping ZG, Guo X, Ba Y. Meta-analysis of association studies of selenoprotein gene polymorphism and Kashin-Beck disease: an updated systematic review. Biol Trace Elem Res 2022;200:543–50.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 104. McAninch EA, Rajan KB, Evans DA, Jo S, Chaker L, Peeters RP, et al. A common DIO2 polymorphism and Alzheimer disease dementia in African and European Americans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2018;103:1818–26.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 105. E Marcondes AA, Gomez TG, Ravache TT, Batistuzzo A, Lorena FB, de Paula CS, et al. Assessment of children in the autistic spectrum disorder that carry the Thr92Ala-DIO2 polymorphism. J Endocrinol Invest 2021;44:1775–82.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 106. Janowska M, Potocka N, Paszek S, Skrzypa M, Zulewicz K, Kluz M, et al. An assessment of GPX1 (rs1050450), DIO2 (rs225014) and SEPP1 (rs7579) gene polymorphisms in women with endometrial cancer. Genes (Basel) 2022;13:188.ArticlePubMedPMC
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Noncatalytic Reductive Deiodination of Thyroid Hormones. Electrochemistry and Quantum Chemical Calculations
Piotr P. Romańczyk, Stefan S. Kurek
ChemElectroChem.2024;[Epub] CrossRef

 KES
KES
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite