Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Thyroid
- The Role of Thyroid Hormone in the Regulation of Cerebellar Development
- Sumiyasu Ishii, Izuki Amano, Noriyuki Koibuchi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):703-716. Published online August 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1150
- 4,546 View
- 170 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
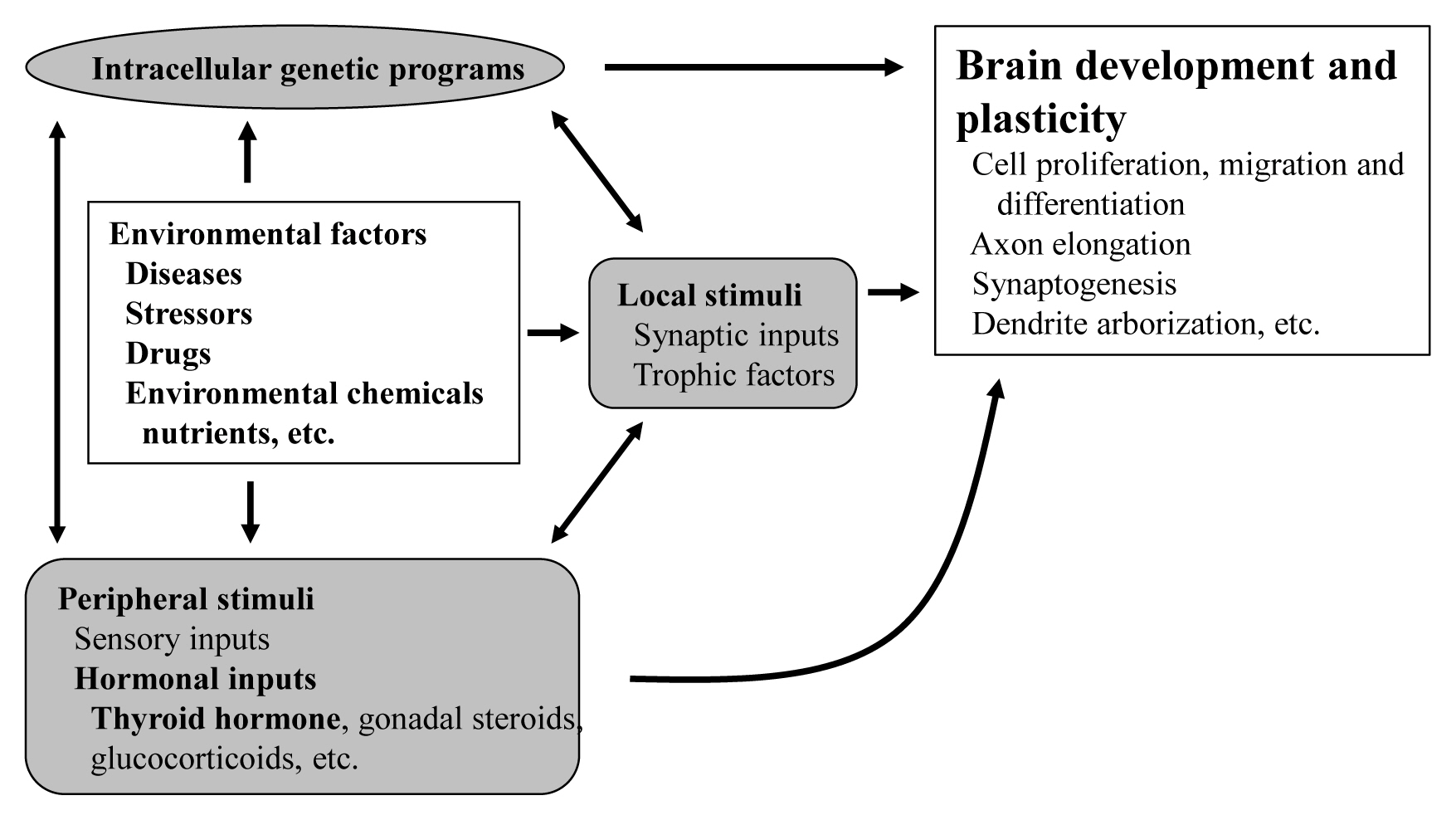
ePub - The proper organized expression of specific genes in time and space is responsible for the organogenesis of the central nervous system including the cerebellum. The epigenetic regulation of gene expression is tightly regulated by an intrinsic intracellular genetic program, local stimuli such as synaptic inputs and trophic factors, and peripheral stimuli from outside of the brain including hormones. Some hormone receptors are expressed in the cerebellum. Thyroid hormones (THs), among numerous circulating hormones, are well-known major regulators of cerebellar development. In both rodents and human, hypothyroidism during the postnatal developmental period results in abnormal morphogenesis or altered function. THs bind to the thyroid hormone receptors (TRs) in the nuclei and with the help of transcriptional cofactors regulate the transcription of target genes. Gene regulation by TR induces cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation, which are necessary for brain development and plasticity. Thus, the lack of TH action mediators may directly cause aberrant cerebellar development. Various kinds of animal models have been established in a bid to study the mechanism of TH action in the cerebellum. Interestingly, the phenotypes differ greatly depending on the models. Herein we summarize the actions of TH and TR particularly in the developing cerebellum.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Neuropeptides and Their Roles in the Cerebellum
Zi-Hao Li, Bin Li, Xiao-Yang Zhang, Jing-Ning Zhu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(4): 2332. CrossRef - Exploring the underlying molecular mechanism of tri(1,3-dichloropropyl) phosphate-induced neurodevelopmental toxicity via thyroid hormone disruption in zebrafish by multi-omics analysis
Ying Xu, Lei Yang, Yanguo Teng, Jian Li, Na Li
Aquatic Toxicology.2023; 258: 106510. CrossRef - Association of Maternal TSH, FT4 With Children's BMI Trajectories, and Obesity: A Birth Cohort Study
Mengting Yang, Shanshan Zhang, Yuzhu Teng, Xue Ru, Linlin Zhu, Yan Han, Xingyong Tao, Hui Cao, Shuangqin Yan, Fangbiao Tao, Kun Huang
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 109(1): e190. CrossRef - Thyroid hormone receptor beta: Relevance in human health and diseases
Ghausiya Rehman, Neha Kumari, Farhad Bano, Rakesh K. Tyagi
Endocrine and Metabolic Science.2023; 13: 100144. CrossRef - Targeting Thyroid Hormone/Thyroid Hormone Receptor Axis: An Attractive Therapy Strategy in Liver Diseases
Qianyu Tang, Min Zeng, Linxi Chen, Nian Fu
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Histone Deacetylase 3 Inhibitor Alleviates Cerebellar Defects in Perinatal Hypothyroid Mice by Stimulating Histone Acetylation and Transcription at Thyroid Hormone-Responsive Gene Loci
Alvin Susetyo, Sumiyasu Ishii, Yuki Fujiwara, Izuki Amano, Noriyuki Koibuchi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(14): 7869. CrossRef - Selection-driven adaptation to the extreme Antarctic environment in the Emperor penguin
Federica Pirri, Lino Ometto, Silvia Fuselli, Flávia A. N. Fernandes, Lorena Ancona, Nunzio Perta, Daniele Di Marino, Céline Le Bohec, Lorenzo Zane, Emiliano Trucchi
Heredity.2022; 129(6): 317. CrossRef - Long-term depression–inductive stimulation causes long-term potentiation in mouse Purkinje cells with a mutant thyroid hormone receptor
Ayane Ninomiya, Izuki Amano, Michifumi Kokubo, Yusuke Takatsuru, Sumiyasu Ishii, Hirokazu Hirai, Nobutake Hosoi, Noriyuki Koibuchi
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Neuropeptides and Their Roles in the Cerebellum

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Receptor-Mediated Muscle Homeostasis as a Target for Sarcopenia Therapeutics
- Jong Hyeon Yoon, Ki-Sun Kwon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):478-490. Published online June 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1081
- 8,922 View
- 337 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
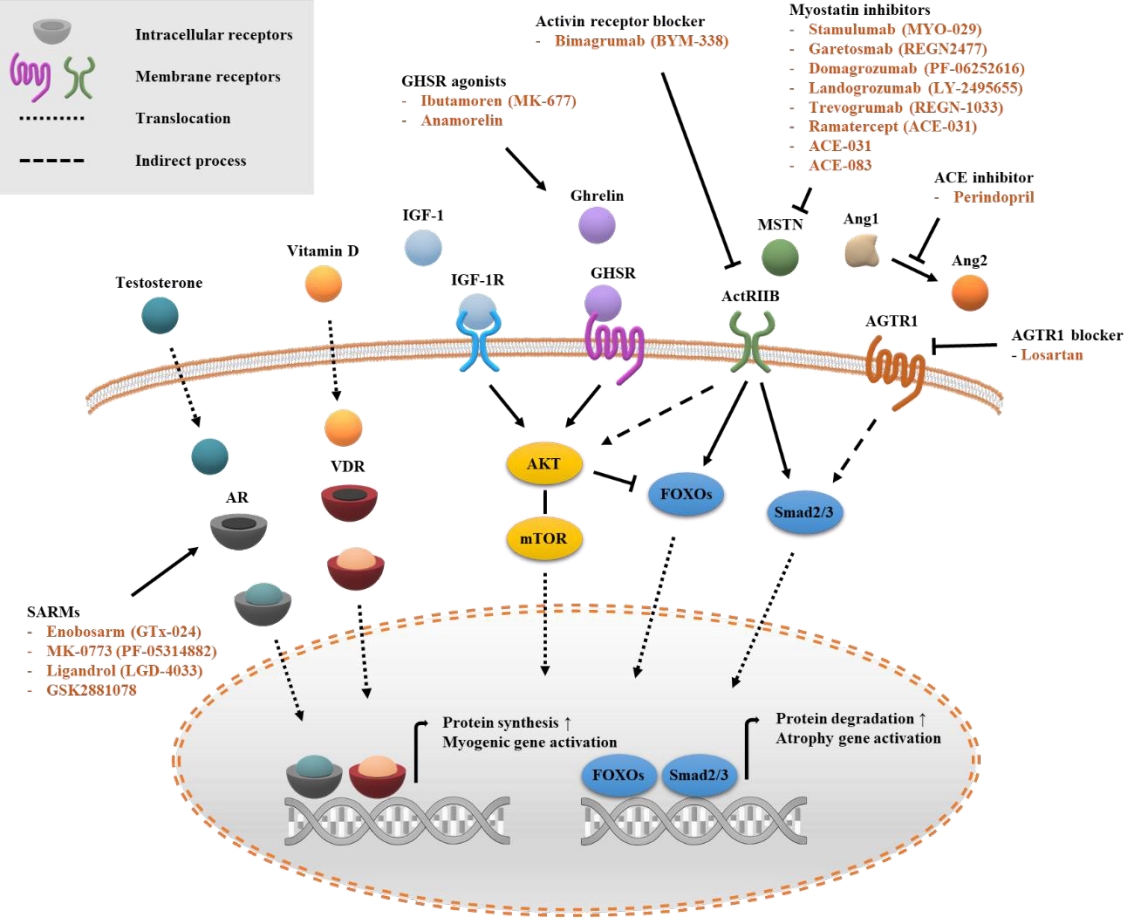
ePub - Sarcopenia is a disease characterized by age-related decline of skeletal muscle mass and function. The molecular mechanisms of the pathophysiology of sarcopenia form a complex network due to the involvement of multiple interconnected signaling pathways. Therefore, signaling receptors are major targets in pharmacological strategies in general. To provide a rationale for pharmacological interventions for sarcopenia, we herein describe several druggable signaling receptors based on their role in skeletal muscle homeostasis and changes in their activity with aging. A brief overview is presented of the efficacy of corresponding drug candidates under clinical trials. Strategies targeting the androgen receptor, vitamin D receptor, Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor, and ghrelin receptor primarily focus on promoting anabolic action using natural ligands or mimetics. Strategies involving activin receptors and angiotensin receptors focus on inhibiting catabolic action. This review may help to select specific targets or combinations of targets in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Current Landscape of Pharmacotherapies for Sarcopenia
Gulistan Bahat, Serdar Ozkok
Drugs & Aging.2024; 41(2): 83. CrossRef - Associations of micronutrient dietary patterns with sarcopenia among US adults: a population-based study
Yining Liu, Xiangliang Liu, Linnan Duan, Yixin Zhao, Yuwei He, Wei Li, Jiuwei Cui
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Vitamin D Level on Sarcopenia in Elderly People: A Critical Review
Saniya Khan, Sunil Kumar, Sourya Acharya, Anil Wanjari
Journal of Health and Allied Sciences NU.2023; 13(04): 453. CrossRef - Novel Potential Targets for Function-Promoting Therapies: Orphan Nuclear Receptors, Anti-inflammatory Drugs, Troponin Activators, Mas Receptor Agonists, and Urolithin A
Waly Dioh, Vihang Narkar, Anurag Singh, Fady Malik, Luigi Ferrucci, Cendrine Tourette, Jean Mariani, Rob van Maanen, Roger A Fielding, Lewis A Lipsitz
The Journals of Gerontology: Series A.2023; 78(Supplement): 44. CrossRef - Alverine citrate promotes myogenic differentiation and ameliorates muscle atrophy
Jong Hyeon Yoon, Seung-Min Lee, Younglang Lee, Min Ju Kim, Jae Won Yang, Jeong Yi Choi, Ju Yeon Kwak, Kwang-Pyo Lee, Yong Ryoul Yang, Ki-Sun Kwon
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2022; 586: 157. CrossRef - Adeno-associated virus-mediated expression of an inactive CaMKIIβ mutant enhances muscle mass and strength in mice
Takahiro Eguchi, Yuji Yamanashi
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2022; 589: 192. CrossRef - Gastric Mobility and Gastrointestinal Hormones in Older Patients with Sarcopenia
Hsien-Hao Huang, Tse-Yao Wang, Shan-Fan Yao, Pei-Ying Lin, Julia Chia-Yu Chang, Li-Ning Peng, Liang-Kung Chen, David Hung-Tsang Yen
Nutrients.2022; 14(9): 1897. CrossRef - Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness and Sarcopenia
Marcela Kanova, Pavel Kohout
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(15): 8396. CrossRef
- The Current Landscape of Pharmacotherapies for Sarcopenia

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Bile Acid Nuclear Receptor Farnesoid X Receptor: Therapeutic Target for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Sun-Gi Kim, Byung-Kwon Kim, Kyumin Kim, Sungsoon Fang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(4):500-504. Published online December 20, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.4.500
- 5,815 View
- 74 Download
- 32 Web of Science
- 33 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is one of the causes of fatty liver, occurring when fat is accumulated in the liver without alcohol consumption. NAFLD is the most common liver disorder in advanced countries. NAFLD is a spectrum of pathology involving hepatic steatosis with/without inflammation and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with accumulation of hepatocyte damage and hepatic fibrosis. Recent studies have revealed that NAFLD results in the progression of cryptogenic cirrhosis that leads to hepatocarcinoma and cardiovascular diseases such as heart failure. The main causes of NAFLD have not been revealed yet, metabolic syndromes including obesity and insulin resistance are widely accepted for the critical risk factors for the pathogenesis of NAFLD. Nuclear receptors (NRs) are transcriptional factors that sense environmental or hormonal signals and regulate expression of genes, involved in cellular growth, development, and metabolism. Several NRs have been reported to regulate genes involved in energy and xenobiotic metabolism and inflammation. Among various NRs, farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is abundantly expressed in the liver and a key regulator to control various metabolic processes in the liver. Recent studies have shown that NAFLD is associated with inappropriate function of FXR. The impact of FXR transcriptional activity in NAFLD is likely to be potential therapeutic strategy, but still requires to elucidate underlying potent therapeutic mechanisms of FXR for the treatment of NAFLD. This article will focus the physiological roles of FXR and establish the correlation between FXR transcriptional activity and the pathogenesis of NAFLD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Geniposide plus chlorogenic acid reverses non-alcoholic steatohepatitis via regulation of gut microbiota and bile acid signaling in a mouse model in vivo
Hongshan Li, Yingfei Xi, Xin Xin, Qin Feng, Yiyang Hu
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - DOT1L Epigenetically Regulates Autophagy and Mitochondria Fusion in Cell Lines of Renal Cancer
Yanguang Hou, Jiachen Liu, Shiyu Huang, Lei Wang, Juncheng Hu, Xiuheng Liu
Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Insights into the molecular targets and emerging pharmacotherapeutic interventions for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Chander K. Negi, Pavel Babica, Lola Bajard, Julie Bienertova-Vasku, Giovanni Tarantino
Metabolism.2022; 126: 154925. CrossRef - FXR: structures, biology, and drug development for NASH and fibrosis diseases
Si-yu Tian, Shu-ming Chen, Cheng-xi Pan, Yong Li
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.2022; 43(5): 1120. CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease development: A multifactorial pathogenic phenomena
Aamir Bashir, Ajay Duseja, Arka De, Manu Mehta, Pramil Tiwari
Liver Research.2022; 6(2): 72. CrossRef - The effects of quercetin on the expression of SREBP-1c mRNA in high-fat diet-induced NAFLD in mice
Jamal Nasser Saleh Al-maamari, Mahardian Rahmadi, Sisca Melani Panggono, Devita Ardina Prameswari, Eka Dewi Pratiwi, Chrismawan Ardianto, Santhra Segaran Balan, Budi Suprapti
Journal of Basic and Clinical Physiology and Pharmacology.2021; 32(4): 637. CrossRef - Co‑administration of obeticholic acid and simvastatin protects against high‑fat diet‑induced non‑alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice
Wen-Cong Li, Su-Xian Zhao, Wei-Guang Ren, Yu-Guo Zhang, Rong-Qi Wang, Ling-Bo Kong, Qing-Shan Zhang, Yue-Min Nan
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Gypenosides regulate farnesoid X receptor-mediated bile acid and lipid metabolism in a mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Hongshan Li, Yingfei Xi, Xin Xin, Huajie Tian, Yiyang Hu
Nutrition & Metabolism.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms of hepatic insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and potential treatment strategies
Chang-hua Zhang, Bu-gao Zhou, Jun-qing Sheng, Yang Chen, Ying-qian Cao, Chen Chen
Pharmacological Research.2020; 159: 104984. CrossRef - Farnesoid X Receptor Activation Protects Liver From Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Up‐Regulating Small Heterodimer Partner in Kupffer Cells
Dan Jin, Tianfei Lu, Ming Ni, Han Wang, Jiang Zhang, Chenpeng Zhong, Chuan Shen, Jun Hao, Ronald W. Busuttil, Jerzy W. Kupiec‐Weglinski, Jianjun Zhang, Ning Xu, Yuan Zhai
Hepatology Communications.2020; 4(4): 540. CrossRef - Salidroside improves high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by regulating the gut microbiota–bile acid–farnesoid X receptor axis
Hongshan Li, Yingfei Xi, Xin Xin, Huajie Tian, Yiyang Hu
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2020; 124: 109915. CrossRef - An Overview of Lipid Metabolism and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Ke Pei, Ting Gui, Dongfang Kan, Huichao Feng, Yanqiang Jin, Ying Yang, Qian Zhang, Ziwei Du, Zhibo Gai, Jibiao Wu, Yunlun Li
BioMed Research International.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Intestinal Barrier Function–Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Interactions and Possible Role of Gut Microbiota
Yizhe Cui, Qiuju Wang, Renxu Chang, Xiaocui Zhou, Chuang Xu
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.2019; 67(10): 2754. CrossRef - A novel ASBT inhibitor, IMB17-15, repressed nonalcoholic fatty liver disease development in high-fat diet-fed Syrian golden hamsters
Mao-xu Ge, Wei-xiao Niu, Jin-feng Ren, Shi-ying Cai, Dong-ke Yu, Hong-tao Liu, Na Zhang, Yi-xuan Zhang, Yu-cheng Wang, Rong-guang Shao, Ju-xian Wang, Hong-wei He
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.2019; 40(7): 895. CrossRef - Consenso mexicano de la enfermedad por hígado graso no alcohólico
R. Bernal-Reyes, G. Castro-Narro, R. Malé-Velázquez, R. Carmona-Sánchez, M.S. González-Huezo, I. García-Juárez, N. Chávez-Tapia, C. Aguilar-Salinas, I. Aiza-Haddad, M.A. Ballesteros-Amozurrutia, F. Bosques-Padilla, M. Castillo-Barradas, J.A. Chávez-Barrer
Revista de Gastroenterología de México.2019; 84(1): 69. CrossRef - Fish oil alleviates circadian bile composition dysregulation in male mice with NAFLD
Yang Liu, Qi Li, Hualin Wang, Xiuju Zhao, Na Li, Hongyu Zhang, Guoxun Chen, Zhiguo Liu
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2019; 69: 53. CrossRef - Effects of sanshoamides and capsaicinoids on plasma and liver lipid metabolism in hyperlipidemic rats
Zhaojun Chen, Yongxiang Liu, Hui Wang, Zhongai Chen, Jia Liu, Hui Liu
Food Science and Biotechnology.2019; 28(2): 519. CrossRef - The Mexican consensus on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
R. Bernal-Reyes, G. Castro-Narro, R. Malé-Velázquez, R. Carmona-Sánchez, M.S. González-Huezo, I. García-Juárez, N. Chávez-Tapia, C. Aguilar-Salinas, I. Aiza-Haddad, M.A. Ballesteros-Amozurrutia, F. Bosques-Padilla, M. Castillo-Barradas, J.A. Chávez-Barrer
Revista de Gastroenterología de México (English Edition).2019; 84(1): 69. CrossRef - Role of bile acids in the diagnosis and progression of liver cirrhosis: A prospective observational study
Ning Liu, Jiao Feng, Yang Lv, Qing Liu, Jingfan Deng, Yujing Xia, Chuanyong Guo, Yingqun Zhou
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Essential role of nuclear receptors for the evaluation of the benefits of bioactive herbal extracts on liver function
Fengling Wang, Yifan Wu, Xiaoting Xie, Jing Sun, Weidong Chen
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2018; 99: 798. CrossRef - Maternal obesity has sex‐dependent effects on insulin, glucose and lipid metabolism and the liver transcriptome in young adult rat offspring
Consuelo Lomas‐Soria, Luis A. Reyes‐Castro, Guadalupe L. Rodríguez‐González, Carlos A. Ibáñez, Claudia J. Bautista, Laura A. Cox, Peter W. Nathanielsz, Elena Zambrano
The Journal of Physiology.2018; 596(19): 4611. CrossRef - Protective effect of dioscin against thioacetamide-induced acute liver injury via FXR/AMPK signaling pathway in vivo
Lingli Zheng, Lianhong Yin, Lina Xu, Yan Qi, Hua Li, Youwei Xu, Xu Han, Kexin Liu, Jinyong Peng
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2018; 97: 481. CrossRef - New therapeutic perspectives in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Javier Ampuero, Yolanda Sánchez-Torrijos, Virginia Aguilera, Francisco Bellido, Manuel Romero-Gómez
Gastroenterología y Hepatología (English Edition).2018; 41(2): 128. CrossRef - Hepatic farnesoid X receptor protein level and circulating fibroblast growth factor 19 concentration in children with NAFLD
Valerio Nobili, Anna Alisi, Antonella Mosca, Claudia Della Corte, Silvio Veraldi, Rita De Vito, Cristiano De Stefanis, Valentina D'Oria, Joerg Jahnel, Evelyn Zohrer, Eleonora Scorletti, Christopher D. Byrne
Liver International.2018; 38(2): 342. CrossRef - The use of obeticholic acid for the management of non-viral liver disease: current clinical practice and future perspectives
Stefano Gitto, Valeria Guarneri, Alessandro Sartini, Pietro Andreone
Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2018; 12(2): 165. CrossRef - Natural products as modulators of the nuclear receptors and metabolic sensors LXR, FXR and RXR
Verena Hiebl, Angela Ladurner, Simone Latkolik, Verena M. Dirsch
Biotechnology Advances.2018; 36(6): 1657. CrossRef - Nuevas perspectivas terapéuticas en la esteatohepatitis no alcohólica
Javier Ampuero, Yolanda Sánchez-Torrijos, Virginia Aguilera, Francisco Bellido, Manuel Romero-Gómez
Gastroenterología y Hepatología.2018; 41(2): 128. CrossRef - Bile acid regulation: A novel therapeutic strategy in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Qinwei Yu, Zhenzhou Jiang, Luyong Zhang
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2018; 190: 81. CrossRef - Hippocampal FXR plays a role in the pathogenesis of depression: A preliminary study based on lentiviral gene modulation
Wei-Guan Chen, Jia-Xuan Zheng, Xi Xu, Yu-Ming Hu, Yu-Min Ma
Psychiatry Research.2018; 264: 374. CrossRef - Bile acid receptors and the kidney
Michal Herman-Edelstein, Talia Weinstein, Moshe Levi
Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension.2018; 27(1): 56. CrossRef - Effects of resveratrol, exercises and their combination on Farnesoid X receptor, Liver X receptor and Sirtuin 1 gene expression and apoptosis in the liver of elderly rats with nonalcoholic fatty liver
Amir Hajighasem, Parvin Farzanegi, Zohreh Mazaheri, Marjan Naghizadeh, Ghoncheh Salehi
PeerJ.2018; 6: e5522. CrossRef - Gut–Liver Axis Derangement in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Marco Poeta, Luca Pierri, Pietro Vajro
Children.2017; 4(8): 66. CrossRef - Farnesoid X Receptor Agonist as a new treatment option for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver disease: A Review
S Singh, KK Kharbanda
Archives of Hepatitis Research.2017; 3(1): 029. CrossRef
- Geniposide plus chlorogenic acid reverses non-alcoholic steatohepatitis via regulation of gut microbiota and bile acid signaling in a mouse model in vivo


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



