Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Thyroid
- The Diagnostic Role of Repeated Biopsy of Thyroid Nodules with Atypia of Undetermined Significance with Architectural Atypia on Core-Needle Biopsy
- Hye Hyeon Moon, Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Tae-Yon Sung, Dong Eun Song, Tae Yong Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee, Jung Hwan Baek
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(2):300-309. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1818

- 451 View
- 31 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We aimed to evaluate the utility of repeat biopsy of thyroid nodules classified as atypia of undetermined significance with architectural atypia (IIIB) on core-needle biopsy (CNB).
Methods
This retrospective study evaluated patients with thyroid nodules categorized as IIIB on CNB between 2013 and 2015. Demographic characteristics, subsequent biopsy results, and ultrasound (US) images were evaluated. The malignancy rates of nodules according to number of CNBs and the number of IIIB diagnoses was compared. Demographic and US features were evaluated to determine factors predictive of malignancy.
Results
Of 1,003 IIIB nodules on CNB, the final diagnosis was determined for 328 (32.7%) nodules, with 121 of them confirmed as malignant, resulting in a malignancy rate of 36.9% (95% confidence interval, 31.7% to 42.1%). Repeat CNB was performed in 248 nodules (24.7%), with 75 (30.2%), 131 (52.8%), 13 (5.2%), 26 (10.5%), one (0.4%), and two (0.8%) reclassified into categories II, IIIB, IIIA, IV, V, and VI, respectively. Malignancy rates were not significantly affected by the number of CNBs (P=0.291) or the number of IIIB diagnoses (P=0.473). None of the nodules confirmed as category II on repeat CNB was malignant. US features significantly associated with malignancy (P<0.003) included solid composition, irregular margins, microcalcifications, and high suspicion on the US risk stratification system.
Conclusion
Repeat biopsy of nodules diagnosed with IIIB on CNB did not increase the detection of malignancy but can potentially reduce unnecessary surgery. Repeat biopsy should be performed selectively, with US features guiding the choice between repeat biopsy and diagnostic surgery.

- Thyroid
Thyroid Cancer Screening - Diagnostic Performance of Ultrasound-Based Risk Stratification Systems for Thyroid Nodules: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Leehi Joo, Min Kyoung Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Eun Ju Ha, Dong Gyu Na
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):117-128. Published online February 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1670

- 2,208 View
- 167 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigated the diagnostic performance of biopsy criteria in four society ultrasonography risk stratification systems (RSSs) for thyroid nodules, including the 2021 Korean (K)-Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TIRADS).
Methods
The Ovid-MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane, and KoreaMed databases were searched and a manual search was conducted to identify original articles investigating the diagnostic performance of biopsy criteria for thyroid nodules (≥1 cm) in four widely used society RSSs.
Results
Eleven articles were included. The pooled sensitivity and specificity were 82% (95% confidence interval [CI], 74% to 87%) and 60% (95% CI, 52% to 67%) for the American College of Radiology (ACR)-TIRADS, 89% (95% CI, 85% to 93%) and 34% (95% CI, 26% to 42%) for the American Thyroid Association (ATA) system, 88% (95% CI, 81% to 92%) and 42% (95% CI, 22% to 67%) for the European (EU)-TIRADS, and 96% (95% CI, 94% to 97%) and 21% (95% CI, 17% to 25%) for the 2016 K-TIRADS. The sensitivity and specificity were 76% (95% CI, 74% to 79%) and 50% (95% CI, 49% to 52%) for the 2021 K-TIRADS1.5 (1.5-cm size cut-off for intermediate-suspicion nodules). The pooled unnecessary biopsy rates of the ACR-TIRADS, ATA system, EU-TIRADS, and 2016 K-TIRADS were 41% (95% CI, 32% to 49%), 65% (95% CI, 56% to 74%), 68% (95% CI, 60% to 75%), and 79% (95% CI, 74% to 83%), respectively. The unnecessary biopsy rate was 50% (95% CI, 47% to 53%) for the 2021 K-TIRADS1.5.
Conclusion
The unnecessary biopsy rate of the 2021 K-TIRADS1.5 was substantially lower than that of the 2016 K-TIRADS and comparable to that of the ACR-TIRADS. The 2021 K-TIRADS may help reduce potential harm due to unnecessary biopsies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- To Screen or Not to Screen?
Do Joon Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 69. CrossRef - The 2017 United States Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation for Thyroid Cancer Screening Is No Longer the Gold Standard
Ka Hee Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 72. CrossRef - Thyroid Cancer Screening: How to Maximize Its Benefits and Minimize Its Harms
Jung Hwan Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 75. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Patients with Thyroid Nodules
Young Joo Park, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Soo Hwan Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Seung-Kuk Baek, So Won Oh, Min Kyoung Lee, Sang-Woo Lee, Young Ah Lee, Yong Sang Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Leehi Joo, Yuh-Seog Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2023; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Appropriateness of Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration
Lairce Cristina Ribeiro Brito, Iara Beatriz De Carvalho Botêlho, Lanna Matos Silva Fernandes, Nayze Lucena Sangreman Aldeman, Uziel Nunes Silva
International Journal for Innovation Education and Research.2023; 11(6): 8. CrossRef
- To Screen or Not to Screen?

- Thyroid
Thyroid Cancer Screening - Survival Comparison of Incidentally Found versus Clinically Detected Thyroid Cancers: An Analysis of a Nationwide Cohort Study
- Shinje Moon, Eun Kyung Lee, Hoonsung Choi, Sue K. Park, Young Joo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):81-92. Published online February 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1668

- 1,718 View
- 154 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The true benefit of thyroid cancer screening is incompletely understood. This study investigated the impact of ultrasound screening on thyroid cancer outcomes through a comparison with symptomatic thyroid cancer using data from a nationwide cohort study in Korea.
Methods
Cox regression analysis was performed to assess the hazard ratios (HRs) for all-cause and thyroid cancer-specific mortality. Considering the possible bias arising from age, sex, year of thyroid cancer registration, and confounding factors for mortality (including smoking/drinking status, diabetes, and hypertension), all analyses were conducted with stabilized inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) according to the route of detection.
Results
Of 5,796 patients with thyroid cancer, 4,145 were included and 1,651 were excluded due to insufficient data. In comparison with the screening group, the clinical suspicion group was associated with large tumors (17.2±14.6 mm vs. 10.4±7.9 mm), advanced T stage (3–4) (odds ratio [OR], 1.24; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.09 to 1.41), extrathyroidal extension (OR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.02 to 1.32), and advanced stage (III–IV) (OR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.00 to 1.35). In IPTW-adjusted Cox regression analysis, the clinical suspicion group had significantly higher risks of all-cause mortality (HR, 1.43; 95% CI, 1.14 to 1.80) and thyroid cancer-specific mortality (HR, 3.07; 95% CI, 1.77 to 5.29). Mediation analysis showed that the presence of thyroid-specific symptoms was directly associated with a higher risk of cancer-specific mortality. Thyroid-specific symptoms also indirectly affected thyroid cancer-specific mortality, mediated by tumor size and advanced clinicopathologic status.
Conclusion
Our findings provide important evidence for the survival benefit of early detection of thyroid cancer compared to symptomatic thyroid cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Characteristics, Diagnostic Approach and Outcome of Thyroid Incidental Findings vs. Clinically Overt Thyroid Nodules: An Observational Single-Centre Study
Tom Jansen, Nike Stikkelbroeck, Annenienke van de Ven, Ilse van Engen-van Grunsven, Marcel Janssen, Han Bonenkamp, Martin Gotthardt, Romana T. Netea-Maier
Cancers.2023; 15(8): 2350. CrossRef - Lower Thyroid Cancer Mortality in Patients Detected by Screening: A Meta-Analysis
Shinje Moon, Young Shin Song, Kyong Yeun Jung, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Joo Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 93. CrossRef - To Screen or Not to Screen?
Do Joon Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 69. CrossRef - The 2017 United States Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation for Thyroid Cancer Screening Is No Longer the Gold Standard
Ka Hee Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 72. CrossRef - Thyroid Cancer Screening: How to Maximize Its Benefits and Minimize Its Harms
Jung Hwan Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 75. CrossRef
- Clinical Characteristics, Diagnostic Approach and Outcome of Thyroid Incidental Findings vs. Clinically Overt Thyroid Nodules: An Observational Single-Centre Study

- Thyroid
Thyroid Cancer Screening - Lower Thyroid Cancer Mortality in Patients Detected by Screening: A Meta-Analysis
- Shinje Moon, Young Shin Song, Kyong Yeun Jung, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Joo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):93-103. Published online February 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1667
- 2,170 View
- 117 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Thyroid cancer screening has contributed to the skyrocketing prevalence of thyroid cancer. However, the true benefit of thyroid cancer screening is not fully understood. This study aimed to evaluate the impact of screening on the clinical outcomes of thyroid cancer by comparing incidental thyroid cancer (ITC) with non-incidental thyroid cancer (NITC) through a meta-analysis.
Methods
PubMed and Embase were searched from inception to September 2022. We estimated and compared the prevalence of high-risk features (aggressive histology of thyroid cancer, extrathyroidal extension, metastasis to regional lymph nodes or distant organs, and advanced tumor-node-metastasis [TNM] stage), thyroid cancer-specific death, and recurrence in the ITC and NITC groups. We also calculated pooled risks and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of the outcomes derived from these two groups.
Results
From 1,078 studies screened, 14 were included. In comparison to NITC, the ITC group had a lower incidence of aggressive histology (odds ratio [OR], 0.46; 95% CI, 0.31 to 0.7), smaller tumors (mean difference, −7.9 mm; 95% CI, −10.2 to −5.6), lymph node metastasis (OR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.48 to 0.86), and distant metastasis (OR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.23 to 0.77). The risks of recurrence and thyroid cancer-specific mortality were also lower in the ITC group (OR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.25 to 0.71 and OR, 0.46; 95% CI, 0.28 to 0.74) than in the NITC group.
Conclusion
Our findings provide important evidence of a survival benefit from the early detection of thyroid cancer compared to symptomatic thyroid cancer. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- To Screen or Not to Screen?
Do Joon Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 69. CrossRef - The 2017 United States Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation for Thyroid Cancer Screening Is No Longer the Gold Standard
Ka Hee Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 72. CrossRef - Thyroid Cancer Screening: How to Maximize Its Benefits and Minimize Its Harms
Jung Hwan Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 75. CrossRef - Delayed Surgery for and Outcomes of Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Is the Pendulum Still Swinging?
Giorgio Grani
Clinical Thyroidology.2023; 35(5): 192. CrossRef
- To Screen or Not to Screen?

- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
- Update on Preoperative Parathyroid Localization in Primary Hyperparathyroidism
- Hye-Sun Park, Namki Hong, Jong Ju Jeong, Mijin Yun, Yumie Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(5):744-755. Published online October 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1589

- 3,983 View
- 352 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Parathyroidectomy is the treatment of choice for primary hyperparathyroidism when the clinical criteria are met. Although bilateral neck exploration is traditionally the standard method for surgery, minimally invasive parathyroidectomy (MIP), or focused parathyroidectomy, has been widely accepted with comparable curative outcomes. For successful MIP, accurate preoperative localization of parathyroid lesions is essential. However, no consensus exists on the optimal approach for localization. Currently, ultrasonography and technetium-99m-sestamibi–single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography are widely accepted in most cases. However, exact localization cannot always be achieved, especially in cases with multiglandular disease, ectopic glands, recurrent disease, and normocalcemic primary hyperparathyroidism. Therefore, new modalities for preoperative localization have been developed and evaluated. Positron emission tomography/computed tomography and parathyroid venous sampling have demonstrated improvements in sensitivity and accuracy. Both anatomical and functional information can be obtained by combining these methods. As each approach has its advantages and disadvantages, the localization study should be deliberately chosen based on each patient’s clinical profile, costs, radiation exposure, and the availability of experienced experts. In this review, we summarize various methods for the localization of hyperfunctioning parathyroid tissues in primary hyperparathyroidism.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expression of the Calcium-Sensing Receptor on Normal and Abnormal Parathyroid and Thyroid Tissue
Anne L. Worth, Mesrop Ayrapetyan, Susan J. Maygarden, Zibo Li, Zhanhong Wu, Chris B. Agala, Lawrence T. Kim
Journal of Surgical Research.2024; 293: 618. CrossRef - A Rare Case of Hyperfunctioning Lipoadenoma Presenting as a Cystic Pararthyroid Lesion
Jinyoung Kim, Ohjoon Kwon, Tae-Jung Kim, So Lyung Jung, Eun Ji Han, Ki-Ho Song
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2023; 30(2): 201. CrossRef - Role of 18F-Fluorocholine Positron Emission Tomography (PET)/Computed Tomography (CT) in Diagnosis of Elusive Parathyroid Adenoma
Janan R Badier, Pokhraj P Suthar, Jagadeesh S Singh, Miral D Jhaveri
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pitfalls of DualTracer 99m-Technetium (Tc) Pertechnetate and Sestamibi Scintigraphy before Parathyroidectomy: Between Primary-Hyperparathyroidism-Associated Parathyroid Tumour and Ectopic Thyroid Tissue
Mara Carsote, Mihaela Stanciu, Florina Ligia Popa, Oana-Claudia Sima, Eugenia Petrova, Anca-Pati Cucu, Claudiu Nistor
Medicina.2023; 60(1): 15. CrossRef - Diagnostic Performance of Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Parathyroid Localization of Primary Hyperparathyroidism: A Systematic Review
Max H. M. C. Scheepers, Zaid Al-Difaie, Lloyd Brandts, Andrea Peeters, Bjorn Winkens, Mahdi Al-Taher, Sanne M. E. Engelen, Tim Lubbers, Bas Havekes, Nicole D. Bouvy, Alida A. Postma
Diagnostics.2023; 14(1): 25. CrossRef
- Expression of the Calcium-Sensing Receptor on Normal and Abnormal Parathyroid and Thyroid Tissue

- Thyroid
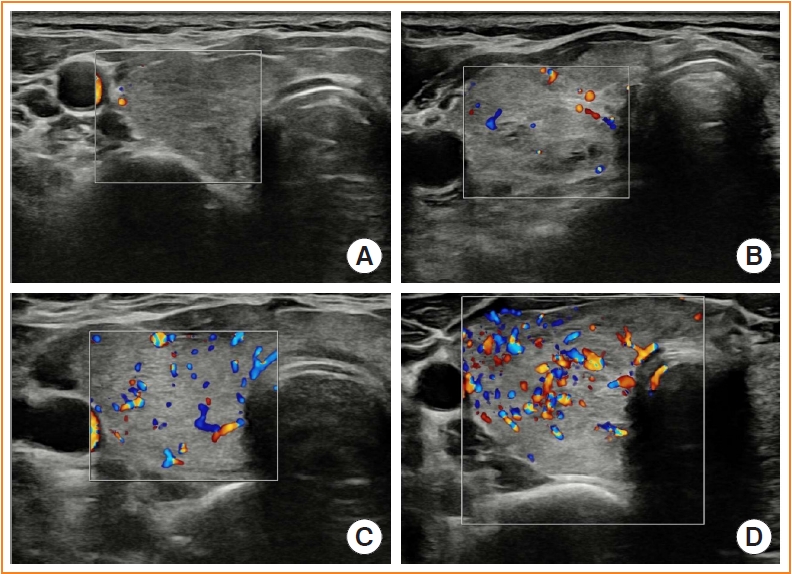
- Usefulness of Real-Time Quantitative Microvascular Ultrasonography for Differentiation of Graves’ Disease from Destructive Thyroiditis in Thyrotoxic Patients
- Han-Sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Chai-Ho Jeong, Jeonghoon Ha, Moo Il Kang, Dong-Jun Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):323-332. Published online April 13, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1413
- 3,665 View
- 143 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Microvascular ultrasonography (MVUS) is a third-generation Doppler technique that was developed to increase sensitivity compared to conventional Doppler. The purpose of this study was to compare MVUS with conventional color Doppler (CD) and power Doppler (PD) imaging to distinguish Graves’ disease (GD) from destructive thyroiditis (DT).
Methods
This prospective study included 101 subjects (46 GDs, 47 DTs, and eight normal controls) from October 2020 to November 2021. All ultrasonography examinations were performed using microvascular flow technology (MV-Flow). The CD, PD, and MVUS images were semi-quantitatively graded according to blood flow patterns. On the MVUS images, vascularity indices (VIs), which were the ratio (%) of color pixels in the total grayscale pixels in a defined region of interest, were obtained automatically. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was performed to verify the diagnostic performance of MVUS. The interclass correlation coefficient and Cohen’s kappa analysis were used to analyze the reliability of MVUS (ClinicalTrials.gov:NCT04879173).
Results
The area under the curve (AUC) for CD, PD, MVUS, and MVUS-VI was 0.822, 0.844, 0.808, and 0.852 respectively. The optimal cutoff value of the MVUS-VI was 24.95% for distinguishing GD and DT with 87% sensitivity and 80.9% specificity. We found a significant positive correlation of MVUS-VI with thyrotropin receptor antibody (r=0.554) and with thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin bioassay (r=0.841). MVUS showed high intra- and inter-observer reliability from various statistical method.
Conclusion
In a real time and quantitative manner, MVUS-VI could be helpful to differentiate GD from thyroiditis in thyrotoxic patients, with less inter-observer variability. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of autoimmune thyroid disease with type 1 diabetes mellitus and its ultrasonic diagnosis and management
Jin Wang, Ke Wan, Xin Chang, Rui-Feng Mao
World Journal of Diabetes.2024; 15(3): 348. CrossRef - The Early Changes in Thyroid-Stimulating Immunoglobulin Bioassay over Anti-Thyroid Drug Treatment Could Predict Prognosis of Graves’ Disease
Jin Yu, Han-Sang Baek, Chaiho Jeong, Kwanhoon Jo, Jeongmin Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Min Hee Kim, Jungmin Lee, Dong-Jun Lim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(3): 338. CrossRef - Duplex Hemodynamic Parameters of Both Superior and Inferior Thyroid Arteries in Evaluation of Thyroid Hyperfunction Disorders
Maha Assem Hussein, Alaa Abdel Hamid, Rasha M Abdel Samie, Elshaymaa Hussein, Shereen Sadik Elsawy
International Journal of General Medicine.2022; Volume 15: 7131. CrossRef - Case 5: A 41-Year-Old Woman With Palpitation
Jiwon Yang, Kabsoo Shin, Jeongmin Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Dong-Jun Lim, Han-Sang Baek
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Microvascular assessment of fascio-cutaneous flaps by ultrasound: A large animal study
Guillaume Goudot, Yanis Berkane, Eloi de Clermont-Tonnerre, Claire Guinier, Irina Filz von Reiterdank, Antonia van Kampen, Korkut Uygun, Curtis L. Cetrulo, Basak E. Uygun, Anahita Dua, Alexandre G. Lellouch
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association of autoimmune thyroid disease with type 1 diabetes mellitus and its ultrasonic diagnosis and management

- Thyroid
- Clinicopathological Characteristics and Disease-Free Survival in Patients with Hürthle Cell Carcinoma: A Multicenter Cohort Study in South Korea
- Meihua Jin, Eun Sook Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Hee Kyung Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Mijin Kim, Won Gu Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1078-1085. Published online October 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1151

- 3,874 View
- 110 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Hürthle cell carcinoma (HCC), a type of thyroid carcinoma, is rare in South Korea, and few studies have investigated its prognosis.
Methods
This long-term multicenter retrospective cohort study evaluated the clinicopathological features and clinical outcomes in patients with HCC who underwent thyroid surgery between 1996 and 2009.
Results
The mean age of the 97 patients included in the study was 50.3 years, and 26.8% were male. The mean size of the primary tumor was 3.2±1.8 cm, and three (3.1%) patients had distant metastasis at initial diagnosis. Ultrasonographic findings were available for 73 patients; the number of nodules with low-, intermediate-, and high suspicion was 28 (38.4%), 27 (37.0%), and 18 (24.7%), respectively, based on the Korean-Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System. Preoperatively, follicular neoplasm (FN) or suspicion for FN accounted for 65.2% of the cases according to the Bethesda category, and 13% had malignancy or suspicious for malignancy. During a median follow-up of 8.5 years, eight (8.2%) patients had persistent/recurrent disease, and none died of HCC. Older age, gross extrathyroidal extension (ETE), and widely invasive types of tumors were significantly associated with distant metastasis (all P<0.01). Gross ETE (hazard ratio [HR], 27.7; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.2 to 346.4; P=0.01) and widely invasive classification (HR, 6.5; 95% CI, 1.1 to 39.4; P=0.04) were independent risk factors for poor disease-free survival (DFS).
Conclusion
The long-term prognosis of HCC is relatively favorable in South Korea from this study, although this is not a nation-wide data, and gross ETE and widely invasive cancer are significant prognostic factors for DFS. The diagnosis of HCC by ultrasonography and cytopathology remains challenging. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Molecular Alterations and Comprehensive Clinical Management of Oncocytic Thyroid Carcinoma
Lindsay A. Bischoff, Ian Ganly, Laura Fugazzola, Erin Buczek, William C. Faquin, Bryan R. Haugen, Bryan McIver, Caitlin P. McMullen, Kate Newbold, Daniel J. Rocke, Marika D. Russell, Mabel Ryder, Peter M. Sadow, Eric Sherman, Maisie Shindo, David C. Shonk
JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery.2024; 150(3): 265. CrossRef - Oncocytic carcinoma of the thyroid: Conclusions from a 20‐year patient cohort
Nelson R. Gruszczynski, Shahzeb S. Hasan, Ana G. Brennan, Julian De La Chapa, Adithya S. Reddy, David N. Martin, Prem P. Batchala, Edward B. Stelow, Eric M. Dowling, Katherine L. Fedder, Jonathan C. Garneau, David C. Shonka
Head & Neck.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hurthle cell carcinoma: a rare variant of thyroid malignancy – a case report
Yuvraj Adhikari, Anupama Marasini, Nawaraj Adhikari, Laxman D. Paneru, Binit Upadhaya Regmi, Manita Raut
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2023; 85(5): 1940. CrossRef - Hürthle Cell Carcinoma: Single Center Analysis and Considerations for Surgical Management Based on the Recent Literature
Costanza Chiapponi, Milan J.M. Hartmann, Matthias Schmidt, Michael Faust, Christiane J. Bruns, Anne M. Schultheis, Hakan Alakus
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Molecular Alterations and Comprehensive Clinical Management of Oncocytic Thyroid Carcinoma

- Clinical Study
- Effectiveness of Injecting Cold 5% Dextrose into Patients with Nerve Damage Symptoms during Thyroid Radiofrequency Ablation
- Min Kyoung Lee, Jung Hwan Baek, Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):407-415. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.407

- 6,080 View
- 140 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Although radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a safe treatment for thyroid tumors, nerve damage is a frequent complication. A previous retrospective study suggested that an injection of cold 5% dextrose in water (5% DW) can reduce nerve damage during RFA. This study validated the efficacy of injecting cold 5% DW for management of nerve damage during RFA.
Methods
Between November 2017 and December 2018, 242 patients underwent 291 RFA sessions for treatment of benign thyroid nodules or recurrent thyroid cancers. Using a standardized technique, cold (0°C to 4°C) 5% DW was immediately injected around the damaged nerve into patients with any symptoms suggesting nerve damage. The incidence of nerve damage, the volume of 5% DW injected, symptom recovery time and the incidence of permanent nerve damage were evaluated.
Results
Nineteen patients experienced nerve damage symptoms related to 21 RFA sessions, including 17 patients during 19 sessions and two patients on the day after two sessions. Patients with nerve damage symptoms detected during RFA were treated by injection of a mean 41 mL (range, 3 to 260) cold 5% DW, but the two patients who experienced symptoms the next day did not receive cold 5% DW injections. Immediate recovery was observed after 15 RFA sessions in 14 patients. No patient experienced permanent nerve damage.
Conclusion
Injection of cold 5% DW is effective in managing nerve damage during RFA of thyroid lesions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Radiofrequency Ablation in Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules
Meghal Shah, Catherine McManus
Surgical Clinics of North America.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and Economic Evaluation of Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation vs. Parathyroidectomy for Patients with Primary Hyperparathyroidism: A Cohort Study
Hui-hui Chai, Zhan-jing Dai, Bai Xu, Qiao-hong Hu, Hong-feng He, Ying Xin, Wen-wen Yue, Cheng-zhong Peng
Academic Radiology.2023; 30(11): 2647. CrossRef - Efficacy of single-session radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in rendering euthyroidism for persistent/relapsed Graves’ disease, a pilot study
Man Him Matrix Fung, Brian Hung Hin Lang
European Radiology.2023; 33(9): 6534. CrossRef - Radiofrequency Ablation of Cervical Thyroid Cancer Metastases—Experience of Endocrinology Practices in the United States
Shahzad Ahmad, Jules Aljammal, Ian Orozco, Sheharyar Raashid, Fizza Zulfiqar, Sean P Nikravan, Iram Hussain
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules: the value of anterolateral hydrodissection
So Yeong Jeong, Jung Hwan Baek, Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Ki-Wook Chung, Tae Yong Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee
Ultrasonography.2023; 42(3): 432. CrossRef - Effective and Safe Application of Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodules
Jin Yong Sung
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2023; 84(5): 985. CrossRef - Assessment of thyroid-specific quality of life in patients with benign symptomatic thyroid nodules treated with radiofrequency or ethanol ablation: a prospective multicenter study
So Yeong Jeong, Eun Ju Ha, Jung Hwan Baek, Tae Yong Kim, Yu-Mi Lee, Jeong Hyun Lee, Jeonghun Lee
Ultrasonography.2022; 41(1): 204. CrossRef - Management of Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Injury During Radiofrequency Ablation of Thyroid Nodules
Jules Aljammal, Iram Hussain, Shahzad Ahmad
AACE Clinical Case Reports.2022; 8(2): 102. CrossRef - Thermal Ablation for the Management of Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma in the Era of Active Surveillance and Hemithyroidectomy
Sae Rom Chung, Jung Hwan Baek, Young Jun Choi, Jeong Hyun Lee
Current Oncology Reports.2022; 24(8): 1045. CrossRef - Improving Voice Outcomes after Thyroid Surgery and Ultrasound-Guided Ablation Procedures
Pia Pace-Asciak, Jon O. Russell, Ralph P. Tufano
Frontiers in Surgery.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Using Intra‐Operative Laryngeal Ultrasonography as a Real‐Time Tool in Assessing Vocal Cord Function During Radiofrequency Ablation of the Thyroid Gland
Matrix Man Him Fung, Brian Hung Hin Lang
World Journal of Surgery.2022; 46(9): 2206. CrossRef - Long-term outcome of microwave ablation for benign thyroid nodules: Over 48-month follow-up study
Jia-Rui Du, Wen-Hui Li, Cheng-Hai Quan, Hui Wang, Deng-Ke Teng
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Continuous neuromonitoring during radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules provides objective evidence of laryngeal nerve safety
Catherine F. Sinclair, Maria J. Téllez, Roberto Peláez-Cruz, Alba Díaz-Baamonde, Sedat Ulkatan
The American Journal of Surgery.2021; 222(2): 354. CrossRef - Future Considerations and Directions for Thermal Ablative Technologies
Jonathon Russell, Catherine F. Sinclair
Current Otorhinolaryngology Reports.2021; 9(2): 210. CrossRef
- The Role of Radiofrequency Ablation in Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules

- Clinical Study
- Revisiting Rupture of Benign Thyroid Nodules after Radiofrequency Ablation: Various Types and Imaging Features
- Sae Rom Chung, Jung Hwan Baek, Jin Yong Sung, Ji Hwa Ryu, So Lyung Jung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(4):415-421. Published online December 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.4.415
- 5,796 View
- 96 Download
- 22 Web of Science
- 24 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background To evaluate the imaging features, clinical manifestations, and prognosis of patients with thyroid nodule rupture after radiofrequency ablation (RFA).
Methods The records of 12 patients who experienced thyroid nodule rupture after RFA at four Korean thyroid centers between March 2010 and July 2017 were retrospectively reviewed. Clinical data evaluated included baseline patient characteristics, treatment methods, initial presenting symptoms, imaging features, treatment, and prognosis.
Results The most common symptoms of post-RFA nodule rupture were sudden neck bulging and pain. Based on imaging features, the localization of nodule rupture was classified into three types: anterior, posterolateral, and medial types. The anterior type is the most often, followed by posterolateral and medial type. Eight patients recovered completely after conservative treatment. Four patients who did not improve with conservative management required invasive procedures, including incision and drainage or aspiration.
Conclusion Thyroid nodule rupture after RFA can be classified into three types based on its localization: anterior, posterolateral, and medial types. Because majority of thyroid nodule ruptures after RFA can be managed conservatively, familiarity with these imaging features is essential in avoiding unnecessary imaging workup or invasive procedures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing the efficacy of thyroid nodule radiofrequency ablation using patient-reported outcome measures
Ege Akgun, Gustavo Romero-Velez, Eren Berber
Surgery.2024; 175(3): 654. CrossRef - The Comparison of Efficacy and Safety between Radiofrequency Ablation Alone and Ethanol Ablation Followed by Radiofrequency Ablation in the Treatment of Mixed Cystic and Solid Thyroid Nodule
Min Gang Jo, Min Kyoung Lee, Jae Ho Shin, Min Guk Seo, So Lyung Jung
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cutaneous fistula formation after thyroid nodule rupture: A rare complication after radiofrequency ablation
Amanda J. Bastien, Luv Amin, Jeffrey Moses, Wendy Sacks, Allen S. Ho
Head & Neck.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Thyroid nodule rupture after radiofrequency ablation: case report and literature review
Tatiana Ferraro, Sameeha Sajid, Steven P. Hodak, Chelsey K. Baldwin
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodules: Radiology In Training
Ningcheng Li, Timothy C. Huber
Radiology.2023; 306(1): 54. CrossRef - A Case of Thyroid Abscess Following Ethanol Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodule
Heungrae Cho, Dongbin Ahn, Ji Hye Kwak, Gil Joon Lee
Korean Journal of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery.2023; 66(9): 624. CrossRef - Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodules
Julia E Noel, Catherine F Sinclair
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 109(1): e12. CrossRef - 2022 Taiwan clinical multicenter expert consensus and recommendations for thyroid radiofrequency ablation
Wei-Che Lin, Wen-Chieh Chen, Pei-Wen Wang, Yi-Chia Chan, Yen-Hsiang Chang, Harn-Shen Chen, Szu-Tah Chen, Wei-Chih Chen, Kai-Lun Cheng, Shun-Yu Chi, Pi-Ling Chiang, Chen-Kai Chou, Feng-Fu Chou, Shun-Chen Huang, Feng-Hsuan Liu, Sheng-Dean Luo, Fen-Yu Tseng,
Ultrasonography.2023; 42(3): 357. CrossRef - Effective and Safe Application of Radiofrequency Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodules
Jin Yong Sung
Journal of the Korean Society of Radiology.2023; 84(5): 985. CrossRef - General Principles for the Safe Performance, Training, and Adoption of Ablation Techniques for Benign Thyroid Nodules: An American Thyroid Association Statement
Catherine F. Sinclair, Jung Hwan Baek, Kathleen E. Hands, Steven P. Hodak, Timothy C. Huber, Iram Hussain, Brian Hung-Hin Lang, Julia E. Noel, Maria Papaleontiou, Kepal N. Patel, Gilles Russ, Jonathon Russell, Stefano Spiezia, Jennifer H. Kuo
Thyroid®.2023; 33(10): 1150. CrossRef - Radiofrequency ablation and thyroid cancer: review of the current literature
Haris Muhammad, Aniqa Tehreem, Jonathon O. Russell
American Journal of Otolaryngology.2022; 43(1): 103204. CrossRef - Microwave Ablation Vs Traditional Thyroidectomy for Benign Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective, Non-Randomized Cohort Study
Shaokun Li, Mingfeng Yang, Haipeng Guo, Muyuan Liu, Shaowei Xu, Hanwei Peng
Academic Radiology.2022; 29(6): 871. CrossRef - Radiofrequency ablation and related ultrasound‐guided ablation technologies for treatment of benign and malignant thyroid disease: An international multidisciplinary consensus statement of the American Head and Neck Society Endocrine Surgery Section with
Lisa A. Orloff, Julia E. Noel, Brendan C. Stack, Marika D. Russell, Peter Angelos, Jung Hwan Baek, Kevin T. Brumund, Feng‐Yu Chiang, Mary Beth Cunnane, Louise Davies, Andrea Frasoldati, Anne Y. Feng, Laszlo Hegedüs, Ayaka J. Iwata, Emad Kandil, Jennifer K
Head & Neck.2022; 44(3): 633. CrossRef - Thyroid Nodule Radiofrequency Ablation: Complications and Clinical Follow Up
James Y. Lim, Jennifer H. Kuo
Techniques in Vascular and Interventional Radiology.2022; 25(2): 100824. CrossRef - Minimally-invasive treatments for benign thyroid nodules: recommendations for information to patients and referring physicians by the Italian Minimally-Invasive Treatments of the Thyroid group
Giovanni Mauri, Stella Bernardi, Andrea Palermo, Roberto Cesareo, Enrico Papini, Luigi Solbiati, Daniele Barbaro, Salvatore Monti, Maurilio Deandrea, Laura Fugazzola, Giovanni Gambelunghe, Roberto Negro, Stefano Spiezia, Fulvio Stacul, Luca Maria Sconfien
Endocrine.2022; 76(1): 1. CrossRef - American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Disease State Clinical Review: The Clinical Utility of Minimally Invasive Interventional Procedures in the Management of Benign and Malignant Thyroid Lesions
Sina Jasim, Kepal N. Patel, Gregory Randolph, Stephanie Adams, Roberto Cesareo, Edward Condon, Tara Henrichsen, Malak Itani, Maria Papaleontiou, Leonardo Rangel, John Schmitz, Marius N. Stan
Endocrine Practice.2022; 28(4): 433. CrossRef - Radiofrequency Ablation of Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules
Patrick J. Navin, Scott M. Thompson, Anil N. Kurup, Robert A. Lee, Matthew R. Callstrom, M. Regina Castro, Marius N. Stan, Brian T. Welch, John J. Schmitz
RadioGraphics.2022; 42(6): 1812. CrossRef - SFE-AFCE-SFMN 2022 consensus on the management of thyroid nodules: Thermal ablation
Adrien Ben Hamou, Edouard Ghanassia, Arnaud Muller, Miriam Ladsous, Nunzia Cinzia Paladino, Laurent Brunaud, Laurence Leenhardt, Gilles Russ
Annales d'Endocrinologie.2022; 83(6): 423. CrossRef - Complications of RFA for Thyroid Nodules: Prevention and Management
Rahul K. Sharma, Jennifer H Kuo
Current Otorhinolaryngology Reports.2021; 9(1): 79. CrossRef - Ultrasonographic characteristics of thyroid nodule rupture after microwave ablation
Peng Tian, Wenyan Du, Xiaoxi Liu, Yiwen Ding, Zekai Zhang, Jing Li, Yanzhen Wang
Medicine.2021; 100(9): e25070. CrossRef - Symptomatic aseptic necrosis of benign thyroid lesions after microwave ablation: risk factors and clinical significance
Jian-ping Dou, Jie Yu, Zhi-gang Cheng, Fang-yi Liu, Xiao-ling Yu, Qi-di Hou, Fang Liu, Zhi-yu Han, Ping Liang
International Journal of Hyperthermia.2021; 38(1): 815. CrossRef - The Importance of Nodule Size in the Management of Ruptured Thyroid Nodule After Radiofrequency Ablation: A Retrospective Study and Literature Review
Wen-Chieh Chen, Sheng-Dean Luo, Wei-Chih Chen, Chen-Kai Chou, Yen-Hsiang Chang, Kai-Lun Cheng, Wei-Che Lin
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Follow-Up of Single-Fiber Multiple Low-Intensity Energy Laser Ablation Technique of Benign Thyroid Nodules
Mattia Squarcia, Mireia Mora, Gloria Aranda, Enrique Carrero, Daniel Martínez, Ramona Jerez, Ricard Valero, Joan Berenguer, Irene Halperin, Felicia A. Hanzu
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Injecting Cold 5% Dextrose into Patients with Nerve Damage Symptoms during Thyroid Radiofrequency Ablation
Min Kyoung Lee, Jung Hwan Baek, Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Jeong Hyun Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 407. CrossRef
- Assessing the efficacy of thyroid nodule radiofrequency ablation using patient-reported outcome measures

- Clinical Study
- Does Radiofrequency Ablation Induce Neoplastic Changes in Benign Thyroid Nodules: A Preliminary Study
- Su Min Ha, Jun Young Shin, Jung Hwan Baek, Dong Eun Song, Sae Rom Chung, Young Jun Choi, Jeong Hyun Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(2):169-178. Published online May 15, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.2.169
- 5,622 View
- 81 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background To evaluate the clinical feasibility of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of benign thyroid nodules along with cytomorphological alteration, and any malignant transformation through biopsy.
Methods The data were retrospectively collected between April 2008 and June 2013 and core needle biopsy (CNB) was performed on 16 benign thyroid nodules previously treated using RFA. The parameters of the patients were compared, between the time of enrollment and the last follow-up examination, using linear mixed model statistical analysis.
Results No atypical cells or neoplastic transformation were detected in the undertreated peripheral portion of treated benign nodules on the CNB specimen. RFA altered neither the thyroid capsule nor the thyroid tissue adjacent to the treated area. On histopathological examinations, we observed 81.2% acellular hyalinization, which was the most common finding. After a mean follow-up period of over 5 years, the mean volume of thyroid nodule had decreased to 6.4±4.2 mL, with a reduction rate of 81.3%±5.8% (
P <0.0001).Conclusion RFA is a technically feasible treatment method for benign thyroid nodules, with no carcinogenic effect or tissue damage of the normal thyroid tissue adjacent to the RFA-treated zone.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of the Therapeutic Efficacy and Technical Outcomes between Conventional Fixed Electrodes and Adjustable Electrodes in the Radiofrequency Ablation of Benign Thyroid Nodules
Jae Ho Shin, Minkook Seo, Min Kyoung Lee, So Lyung Jung
Korean Journal of Radiology.2024; 25(2): 199. CrossRef - Thermoablation of thyroid nodules reveals excellent results with low morbidity
Robert M. Eisele, Philipp R. Scherber, Monika Schlüter, Thorsten Drews, Matthias Glanemann, Gereon Gäbelein
Technology and Health Care.2022; 30(3): 683. CrossRef - Radiofrequency ablation and related ultrasound‐guided ablation technologies for treatment of benign and malignant thyroid disease: An international multidisciplinary consensus statement of the American Head and Neck Society Endocrine Surgery Section with
Lisa A. Orloff, Julia E. Noel, Brendan C. Stack, Marika D. Russell, Peter Angelos, Jung Hwan Baek, Kevin T. Brumund, Feng‐Yu Chiang, Mary Beth Cunnane, Louise Davies, Andrea Frasoldati, Anne Y. Feng, Laszlo Hegedüs, Ayaka J. Iwata, Emad Kandil, Jennifer K
Head & Neck.2022; 44(3): 633. CrossRef - Thyroid Nodule Radiofrequency Ablation: Complications and Clinical Follow Up
James Y. Lim, Jennifer H. Kuo
Techniques in Vascular and Interventional Radiology.2022; 25(2): 100824. CrossRef - American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Disease State Clinical Review: The Clinical Utility of Minimally Invasive Interventional Procedures in the Management of Benign and Malignant Thyroid Lesions
Sina Jasim, Kepal N. Patel, Gregory Randolph, Stephanie Adams, Roberto Cesareo, Edward Condon, Tara Henrichsen, Malak Itani, Maria Papaleontiou, Leonardo Rangel, John Schmitz, Marius N. Stan
Endocrine Practice.2022; 28(4): 433. CrossRef - Efficacy of radiofrequency and laser thermal ablation in solving thyroid nodule-related symptoms and cosmetic concerns. A systematic review and meta-analysis
Roberto Cesareo, Silvia Egiddi, Anda M. Naciu, Gaia Tabacco, Andrea Leoncini, Nicola Napoli, Andrea Palermo, Pierpaolo Trimboli
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2022; 23(5): 1051. CrossRef - Comparison of ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation versus thyroid lobectomy for T1bN0M0 papillary thyroid carcinoma
Lin Yan, Xinyang Li, Yingying Li, Jing Xiao, Mingbo Zhang, Yukun Luo
European Radiology.2022; 33(1): 730. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta-analysis comparing tumor progression and complications between radiofrequency ablation and thyroidectomy for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Yuan-dong Sun, Hao Zhang, Hai-tao Zhu, Chun-xue Wu, Miao-ling Chen, Jian-jun Han
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - RFA and benign thyroid nodules: Review of the current literature
Haris Muhammad, Prasanna Santhanam, Jonathon O. Russell, Jennifer H. Kuo
Laryngoscope Investigative Otolaryngology.2021; 6(1): 155. CrossRef - Radiofrequency ablation and thyroid nodules: updated systematic review
Haris Muhammad, Prasanna Santhanam, Jonathon O. Russell
Endocrine.2021; 72(3): 619. CrossRef - Complications of RFA for Thyroid Nodules: Prevention and Management
Rahul K. Sharma, Jennifer H Kuo
Current Otorhinolaryngology Reports.2021; 9(1): 79. CrossRef - Long-Term Results of Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Benign Thyroid Nodules: State of the Art and Future Perspectives—A Systematic Review
Hervé Monpeyssen, Ahmad Alamri, Adrien Ben Hamou
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Outcomes of Thermal Ablation for Benign Thyroid Nodules: The Issue of Regrowth
Jung Suk Sim, Jung Hwan Baek, Rosaria Meccariello
International Journal of Endocrinology.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation Versus Thyroid Lobectomy for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Propensity-Matched Cohort Study of 884 Patients
Lin Yan, Mingbo Zhang, Qing Song, Yukun Luo
Thyroid.2021; 31(11): 1662. CrossRef - Clinical Effects of Microwave Ablation in the Treatment of Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinomas and Related Histopathological Changes
Chenya Lu, Xingjia Li, Xiaoqiu Chu, Ruiping Li, Jie Li, Jianhua Wang, Yalin Wang, Yang Xu, Guofang Chen, Shuhang Xu, Chao Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Ultrasound-Guided Thermal Ablation of Thyroid Nodules: Technicalities Progress and Clinical Applications, Especially in Malignant Thyroid Nodules
Enock Adjei Agyekum, Jian-hua Fu, Fei-Ju Xu, Yong-Zhen Ren, Debora Akortia, Qing Chen, Xiao-Qin Qian, Yuguo Wang, Xian Wang
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison Between Radiofrequency Ablation and Microwave Ablation in the Treatment for Benign Thyroid Nodules: a Meta-analysis
Jing Wu, Junguo Liu, Li Liu
Indian Journal of Surgery.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - 2020 European Thyroid Association Clinical Practice Guideline for the Use of Image-Guided Ablation in Benign Thyroid Nodules
Enrico Papini, Hervé Monpeyssen, Andrea Frasoldati, Laszlo Hegedüs
European Thyroid Journal.2020; 9(4): 172. CrossRef - Response: Long-Term Outcomes Following Thermal Ablation of Benign Thyroid Nodules as an Alternative to Surgery: The Importance of Controlling Regrowth (Endocrinol Metab 2019;34:117–23, Jung Suk Sim et al.)
Jung Suk Sim, Jung Hwan Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(3): 325. CrossRef
- Comparison of the Therapeutic Efficacy and Technical Outcomes between Conventional Fixed Electrodes and Adjustable Electrodes in the Radiofrequency Ablation of Benign Thyroid Nodules

- Thyroid
- The Validity of Ultrasonography-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy in Thyroid Nodules 4 cm or Larger Depends on Ultrasonography Characteristics
- Jin Hwa Kim, Na Kyung Kim, Young Lyun Oh, Hye Jeong Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Sun Wook Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(4):545-552. Published online December 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.545
- 3,692 View
- 31 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The objective of this study was to evaluate the validity of fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) according to ultrasonography (US) characteristics in thyroid nodules 4 cm and larger.
Methods We retrospectively reviewed the cases of 263 patients who underwent thyroid surgery for thyroid nodules larger than 4 cm between January 2001 and December 2010.
Results The sensitivity of US-FNAB was significantly higher in nodules with calcifications (micro- or macro-) than those without (97.9% vs. 87.%
P <0.05). The accuracy of US-FNAB was higher in large thyroid nodules with US features suspicious of malignancy, such as a solid component, ill-defined margin, hypoechogenicity or marked hypoechogenicity, or any calcifications (micro- or macro-) compared to thyroid nodules with none of these features. Furthermore, the accuracy improved as the number of these features increased. The overall false negative rate (FNR) was 11.9%. The FNR of thyroid nodules that appeared benign on US, such as mixed nodules (7.7%) or nodules without calcification (9.8%), trended toward being lower than that of solid nodules (17.9%) or nodules with any microcalcification or macrocalcification (33.3%). In nodules without suspicious features of malignancy, the FNR of US-FNAB was 0% (0/15).Conclusion We suggest individualized strategies for large thyroid nodules according to US features. Patients with benign FNAB can be followed in the absence of any malignant features in US. However, if patients exhibit any suspicious features, potential false negative results of FNAB should be kept in mind and surgery may be considered.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of malignancy and diagnostic accuracy of fine-needle aspiration biopsy in thyroid nodules with diameters greater than 4 centimeters
Rafaela N. Barcelos, Cléber P. Camacho, Maria da Conceição de O. C. Mamone, Elza S. Ikejiri, Felipe A. B. Vanderlei, Ji H. Yang, Rosália P. Padovani, Leandro A. L. Martins, Rosa Paula M. Biscolla, Danielle Macellaro, Susan C. Lindsey, Rui M. B. Maciel, Jo
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The comparison of accuracy of ultrasonographic features versus ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology in diagnosis of malignant thyroid nodules
Mehrdad Nabahati, Zoleika Moazezi, Soude Fartookzadeh, Rahele Mehraeen, Naser Ghaemian, Majid Sharbatdaran
Journal of Ultrasound.2019; 22(3): 315. CrossRef - False negative rate of fine‐needle aspiration in thyroid nodules: impact of nodule size and ultrasound pattern
Hye Shin Ahn, Dong Gyu Na, Jung Hwan Baek, Jin Yong Sung, Ji‐Hoon Kim
Head & Neck.2019; 41(4): 967. CrossRef - Thyroid nodules over 4 cm do not have higher malignancy or benign cytology false-negative rates
Muhammed Kizilgul, Rupendra Shrestha, Angela Radulescu, Maria R. Evasovich, Lynn A. Burmeister
Endocrine.2019; 66(2): 249. CrossRef - Large Cytologically Benign Thyroid Nodules Do Not Have High Rates of Malignancy or False-Negative Rates and Clinical Observation Should be Considered: A Meta-Analysis
Nicole A. Cipriani, Michael G. White, Peter Angelos, Raymon H. Grogan
Thyroid.2018; 28(12): 1595. CrossRef - Risk of Malignancy in Thyroid Nodules 4 cm or Larger
Uchechukwu C. Megwalu
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 77. CrossRef - Usefulness of NRAS codon 61 mutation analysis and core needle biopsy for the diagnosis of thyroid nodules previously diagnosed as atypia of undetermined significance
Eun Kyung Jang, Won Gu Kim, Eui Young Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Yun Mi Choi, Min Ji Jeon, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Jene Choi, Dong Eun Song, Won Bae Kim
Endocrine.2016; 52(2): 305. CrossRef - Association between neck ultrasonographic findings and clinico‐pathological features in the follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma
Eun Kyung Jang, Won Gu Kim, Yun Mi Choi, Min Ji Jeon, Hyemi Kwon, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Dong Eun Song, Won Bae Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2015; 83(6): 968. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- Risk of malignancy and diagnostic accuracy of fine-needle aspiration biopsy in thyroid nodules with diameters greater than 4 centimeters

- Thyroid
- Clinicopathological, Biochemical, and Sonographic Features of Thyroid Nodule Predictive of Malignancy among Adult Filipino Patients in a Tertiary Hospital in the Philippines
- Edwin Jadulco Cañete, Cherrie Mae Sison-Peña, Cecilia Alegado Jimeno
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(4):489-497. Published online December 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.489
- 4,587 View
- 38 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Thyroid nodules may harbor cancer in 5% to 15% of cases. Specific clinical and sonographic features predictive of malignancy have been investigated in various populations, but due to differences in epidemiology, risk factors and iodine nutrition status, these predictors may not be valid in the Philippines. This study determined the clinicopathological, biochemical, and sonographic features of thyroid nodules predictive of malignancy among adult Filipino patients at the University of the Philippines-Philippine General Hospital (UP-PGH).
Methods We reviewed the medical records of Filipino patients ≥19 years of age who underwent thyroid surgery in UP-PGH from 2008 to 2011.
Results A total of 837 of 1,670 patients (50.1%) were enrolled in the study, which included 417 benign and 420 malignant tumors. The mean age at diagnosis was 38±11 years, with female predominance. Multiple logistic regression analysis showed that the presence of a hard or firm nodule (odds ratio [OR], 58.8,
P <0.001; OR, 12.8,P <0.001), presence of microcalcifications (OR, 11.1;P <0.001), irregular margins on ultrasound (OR, 4.5;P <0.001), and absence of associated symptoms (OR, 2.3;P <0.002) increased significantly the likelihood of thyroid malignancy.Conclusion Similar to international data, the absence of associated symptoms, firm to hard thyroid nodules, and the presence of microcalcifications and irregular margins were significant predictors of thyroid malignancy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Detection of Thyroid Nodule Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors in Southwest China: A Study of 45,023 Individuals Undergoing Physical Examinations
Yi Liang, Xiaohong Li, Fang Wang, Zongting Yan, Yuhuan Sang, Yuan Yuan, Yun Qin, Xuefei Zhang, Mei Ju
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 1697. CrossRef - Diagnostic performance of the EU TI‐RADS and ACR TI‐RADS scoring systems in predicting thyroid malignancy
Hiba‐Allah Chatti, Ibtissem Oueslati, Aymen Azaiez, Jihen Marrakchi, Seif Boukriba, Habiba Mizouni, Slim Haouet, Ghazi Besbes, Meriem Yazidi, Melika Chihaoui
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Behaviour and epidemiology of differentiated thyroid cancer among filipinos in and outside the Philippines: Comparison between Qatar, Canada and Philippines
Mohamed Said Ghali, Walid El Ansari, Abdelrahman Abdelaal, Mohamed S. Al Hassan
Annals of Medicine and Surgery.2022; 81: 104202. CrossRef - Association Between Thyroid Nodules and Volume and Metabolic Syndrome in an Iodine-Adequate Area: A Large Community-Based Population Study
Yue Su, Yan-ling Zhang, Meng Zhao, Hai-qing Zhang, Xu Zhang, Qing-bo Guan, Chun-xiao Yu, Shan-shan Shao, Jin Xu
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2019; 17(4): 217. CrossRef - Accuracy of ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration cytology and significance of non-diagnostic cytology in the preoperative detection of thyroid malignancy
JSL Chieng, CH Lee, AA Karandikar , JPN Goh, SSS Tan
Singapore Medical Journal.2019; 60(4): 193. CrossRef - Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Practice in the Philippines
Agustina D. Abelardo
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2017; 51(6): 555. CrossRef - An Epidemiological Study of Risk Factors of Thyroid Nodule and Goiter in Chinese Women
Lei Zheng, Wenhua Yan, Yue Kong, Ping Liang, Yiming Mu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2015; 12(9): 11608. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- Detection of Thyroid Nodule Prevalence and Associated Risk Factors in Southwest China: A Study of 45,023 Individuals Undergoing Physical Examinations

- Preoperative Localization and Intraoperative Parathyroid Hormone Assay in Korean Patients with Primary Hyperparathyroidism
- Eirie Cho, Jung Mi Chang, Seok Young Yoon, Gil Tae Lee, Yun Hyi Ku, Hong Il Kim, Myung-Chul Lee, Guk Haeng Lee, Min Joo Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(4):464-469. Published online December 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.464
- 3,522 View
- 32 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The intraoperative parathyroid hormone (IOPTH) assay is widely used in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT). We investigated the usefulness of the IOPTH assay in Korean patients with PHPT.
Methods We retrospectively reviewed the data of 33 patients with PHPT who underwent parathyroidectomy. Neck ultrasonography (US) and 99mTc-sestamibi scintigraphy (MIBI scan) were performed preoperatively and IOPTH assays were conducted.
Results The sensitivity of neck US and MIBI scans were 91% and 94%, respectively. A 50% decrease in parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels 10 minutes after excision of the parathyroid gland was obtained in 91% (30/33) of patients and operative success was achieved in 97% (32/33) of patients. The IOPTH assay was 91% true-positive, 3% true-negative, 0% false-positive, and 6% false-negative. The overall accuracy of the IOPTH assay was 94%. In five cases with discordant neck US and MIBI scan results, a sufficient decrease in IOPTH levels helped the surgeon confirm the complete excision of the parathyroid gland with no additional neck exploration.
Conclusion The IOPTH assay is an accurate tool for localizing hyperfunctioning parathyroid glands and is helpful for evaluating cases with discordant neck US and MIBI scan results.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Single-Center Experience of Parathyroidectomy Using Intraoperative Parathyroid Hormone Monitoring
Seong Hoon Kim, Si Yeon Lee, Eun Ah Min, Young Mi Hwang, Yun Suk Choi, Jin Wook Yi
Medicina.2022; 58(10): 1464. CrossRef - The natural history and hip geometric changes of primary hyperparathyroidism without parathyroid surgery
Kyong Yeun Jung, A. Ram Hong, Dong Hwa Lee, Jung Hee Kim, Kyoung Min Kim, Chan Soo Shin, Seong Yeon Kim, Sang Wan Kim
Journal of Bone and Mineral Metabolism.2017; 35(3): 278. CrossRef - The utility of the radionuclide probe in parathyroidectomy for primary hyperparathyroidism
MS Lim, M Jinih, CH Ngai, NM Foley, HP Redmond
The Annals of The Royal College of Surgeons of England.2017; 99(5): 369. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- Single-Center Experience of Parathyroidectomy Using Intraoperative Parathyroid Hormone Monitoring

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Association of Serum Adipocyte-Specific Fatty Acid Binding Protein with Fatty Liver Index as a Predictive Indicator of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Won Seon Jeon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(4):283-287. Published online December 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.4.283
- 3,416 View
- 33 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Adipocyte-specific fatty acid-binding protein (A-FABP) is a cytoplasmic protein expressed in macrophages and adipocytes and it plays a role in insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Recently, the fatty liver index (FLI) was introduced as an indicator of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In this study, we aimed to investigate the relationship between baseline serum A-FABP levels and FLI after 4 years in apparently healthy subjects.
Methods A total of 238 subjects without a past history of alcoholism or hepatitis were recruited from a medical check-up program. The NAFLD state was evaluated 4 years later in the same subjects using FLI. Fatty liver disease was diagnosed as diffusely increased echogenicity of the hepatic parenchyma compared to the kidneys, vascular blurring, and deep-echo attenuation. NAFLD was defined as subjects with fatty liver and no history of alcohol consumption (>20 g/day).
Results Baseline serum A-FABP levels were significantly associated with FLI after adjustment for age and sex (
P <0.001). The subjects with higher A-FABP levels had a higher mean FLI (P for trend=0.006). After adjusting for age and sex, serum A-FABP levels at baseline were shown to be significantly associated with FLI as a marker of development of NAFLD after 4 years (odds ratio, 2.68; 95% confidence interval, 1.24 to 5.80 for highest tertile vs. lowest tertile;P =0.012).Conclusion This study demonstrated that higher baseline serum A-FABP levels were associated with FLI as a predictive indicator of NAFLD after 4 years of follow-up in healthy Korean adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- FABP4 Expression in Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Is Independently Associated with Circulating Triglycerides in Obesity
Óscar Osorio-Conles, Ainitze Ibarzabal, José María Balibrea, Josep Vidal, Emilio Ortega, Ana de Hollanda
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(3): 1013. CrossRef - Unveiling the Role of the Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 in the Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Juan Moreno-Vedia, Josefa Girona, Daiana Ibarretxe, Lluís Masana, Ricardo Rodríguez-Calvo
Biomedicines.2022; 10(1): 197. CrossRef - Circulating level of fatty acid‐binding protein 4 is an independent predictor of metabolic dysfunction‐associated fatty liver disease in middle‐aged and elderly individuals
Marenao Tanaka, Satoko Takahashi, Yukimura Higashiura, Akiko Sakai, Masayuki Koyama, Shigeyuki Saitoh, Kazuaki Shimamoto, Hirofumi Ohnishi, Masato Furuhashi
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(5): 878. CrossRef - New Insights into Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Coronary Artery Disease: The Liver-Heart Axis
Georgiana-Diana Cazac, Cristina-Mihaela Lăcătușu, Cătălina Mihai, Elena-Daniela Grigorescu, Alina Onofriescu, Bogdan-Mircea Mihai
Life.2022; 12(8): 1189. CrossRef - Association between the liver fat score (LFS) and cardiovascular diseases in the national health and nutrition examination survey 1999–2016
Chun-On Lee, Hang-Long Li, Man-Fung Tsoi, Ching-Lung Cheung, Bernard Man Yung Cheung
Annals of Medicine.2021; 53(1): 1067. CrossRef - Relationship Between Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 and Liver Fat in Individuals at Increased Cardiometabolic Risk
Ricardo Rodríguez-Calvo, Juan Moreno-Vedia, Josefa Girona, Daiana Ibarretxe, Neus Martínez-Micaelo, Jordi Merino, Nuria Plana, Lluis Masana
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Diabetes: An Epidemiological Perspective
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(3): 226. CrossRef - Serum adipocyte fatty acid‐binding protein levels: An indicator of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease in Chinese individuals
Yiting Xu, Xiaojing Ma, Xiaoping Pan, Xingxing He, Yufei Wang, Yuqian Bao
Liver International.2019; 39(3): 568. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Based on Analyses from the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Eun-Jung Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2017; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - The relationship between serum fatty-acid binding protein 4 level and lung function in Korean subjects with normal ventilatory function
Hye-Jeong Park, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Seong Yong Lim, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
BMC Pulmonary Medicine.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Liver fatty acid-binding protein as a diagnostic marker for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Erdem Akbal, Erdem Koçak, Ömer Akyürek, Seyfettin Köklü, Hikmetullah Batgi, Mehmet Şenes
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift.2016; 128(1-2): 48. CrossRef - High‐methionine diets accelerate atherosclerosis by HHcy‐mediated FABP4 gene demethylation pathway via DNMT1 in ApoE−/− mice
An-Ning Yang, Hui-Ping Zhang, Yue Sun, Xiao-Ling Yang, Nan Wang, Guangrong Zhu, Hui Zhang, Hua Xu, Sheng-Chao Ma, Yue Zhang, Gui-Zhong Li, Yue-Xia Jia, Jun Cao, Yi-Deng Jiang
FEBS Letters.2015; 589(24PartB): 3998. CrossRef - Metabolic Health Is More Important than Obesity in the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A 4-Year Retrospective Study
Min-Kyung Lee, Eun-Jung Rhee, Min Chul Kim, Byung Sub Moon, Jeong In Lee, Young Seok Song, Eun Na Han, Hyo Sun Lee, Yoonjeong Son, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(4): 522. CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef - Noninvasive Markers for the Diagnosis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Sang Yong Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2013; 28(4): 280. CrossRef
- FABP4 Expression in Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Is Independently Associated with Circulating Triglycerides in Obesity

- Thyroid
- Delayed Surgery for Parathyroid Adenoma Misdiagnosed as a Thyroid Nodule and Treated with Radiofrequency Ablation
- Ho-Su Kim, Bong Hoi Choi, Jung Rang Park, Jong Ryeal Hahm, Jung Hwa Jung, Soo Kyoung Kim, Sungsu Kim, Kyong-Young Kim, Soon Il Chung, Tae Sik Jung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(3):231-235. Published online September 13, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.3.231
- 4,118 View
- 38 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Primary hyperparathyroidism occurs as a result of isolated parathyroid adenoma in 80% to 85% of all cases. A 99mtechnetium (99mTc) sestamibi scan or neck ultrasonography is used to localize the neoplasm prior to surgical intervention. A 53-year-old female was referred for the exclusion of metabolic bone disease. She presented with low back pain that had persisted for the past 6 months and elevated serum alkaline phosphatase (1,253 IU/L). Four years previously, she had been diagnosed at a local hospital with a 2.3-cm thyroid nodule, which was determined to be pathologically benign. Radiofrequency ablation was performed at the same hospital because the nodule was still growing during the follow-up period 2 years before the visit to our hospital, and the procedure was unsuccessful in reducing the size of the nodule. The results of the laboratory tests in our hospital were as follows: serum calcium, 14.6 mg/dL; phosphorus, 3.5 mg/dL; and intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH), 1,911 pg/mL. Neck ultrasonography and 99mTc sestamibi scan detected a 5-cm parathyroid neoplasm in the left lower lobe of the patient's thyroid; left parathyroidectomy was performed. This case indicated that thyroid ultrasonographers and pathologists need to be experienced enough to differentiate a parathyroid neoplasm from a thyroid nodule; 99mTc sestamibi scan, serum calcium, and iPTH levels can help to establish the diagnosis of parathyroid neoplasm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Complications after radiofrequency ablation of hyperparathyroidism secondary to chronic kidney disease
Li-Ping Lin, Miao Lin, Song-Song Wu, Wei-hua Liu, Li Zhang, Yi-ping Ruan, Mei-zhu Gao, Fu-Yuan Hong
Renal Failure.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk factors influencing cure of ultrasound-guided microwave ablation for primary hyperparathyroidism
Fangyi Liu, Li Zang, Yang Liu, Xiaoling Yu, Zhigang Cheng, Zhiyu Han, Jie Yu, Ping Liang
International Journal of Hyperthermia.2022; 39(1): 258. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of radiofrequency ablation versus parathyroidectomy for secondary hyperparathyroidism in dialysis patients: a single-center retrospective study
Mian Ren, Danna Zheng, Juan Wu, Yueming Liu, Chengzhong Peng, Wei Shen, Bo Lin
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiofrequency Ablation of Parathyroid Adenoma: A Novel Treatment Option for Primary Hyperparathyroidism
Iram Hussain, Shahzad Ahmad, Jules Aljammal
AACE Clinical Case Reports.2021; 7(3): 195. CrossRef - Efficacy of Ultrasound-guided Radiofrequency Ablation of Parathyroid Hyperplasia: Single Session vs. Two-Session for Effect on Hypocalcemia
Zeng Zeng, Cheng-Zhong Peng, Ji-Bin Liu, Yi-Wen Li, Hong-Feng He, Qiao-Hong Hu, Bo Lin, Xiao-Gang Shen
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of microwave ablation for ectopic secondary hyperparathyroidism: a feasibility study
Xin Li, Ying Wei, Hongzeng Shao, Lili Peng, Chao An, Ming-An Yu
International Journal of Hyperthermia.2019; 36(1): 646. CrossRef - US-guided Microwave Ablation of Hyperplastic Parathyroid Glands: Safety and Efficacy in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease—A Pilot Study
Li Zhuo, Li-li Peng, Yu-mei Zhang, Zhi-hong Xu, Gu-ming Zou, Xin Wang, Wen-ge Li, Ming-de Lu, Ming-an Yu
Radiology.2017; 282(2): 576. CrossRef - Safety and efficiency of microwave ablation for recurrent and persistent secondary hyperparathyroidism after parathyroidectomy: A retrospective pilot study
Ming-An Yu, Li Yao, Ling Zhang, Lili Peng, Li Zhuo, Yumei Zhang, Wenge Li, Ming-De Lv
International Journal of Hyperthermia.2016; 32(2): 180. CrossRef - A nonfunctioning parathyroid carcinoma misdiagnosed as a follicular thyroid nodule
Filomena Cetani, Gianluca Frustaci, Liborio Torregrossa, Silvia Magno, Fulvio Basolo, Alberto Campomori, Paolo Miccoli, Claudio Marcocci
World Journal of Surgical Oncology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef
- Complications after radiofrequency ablation of hyperparathyroidism secondary to chronic kidney disease


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



