Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Obesity and Metabolism
- Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Normal Weight and Obesity
- Norbert Stefan
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):487-493. Published online August 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.301
- 9,149 View
- 439 Download
- 31 Web of Science
- 32 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
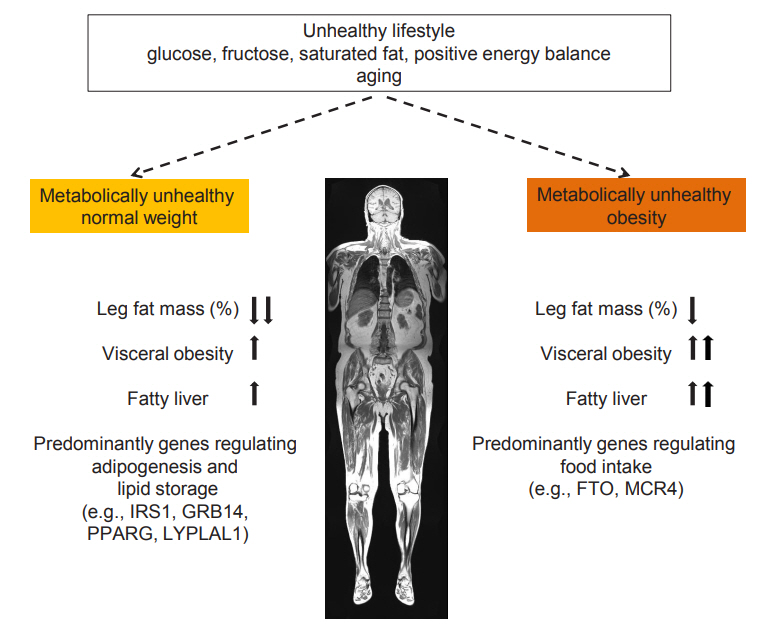
ePub - Increased fat mass is an established risk factor for the cardiometabolic diseases type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (CVD) and is associated with increased risk of all-cause and CVD mortality. However, also very low fat mass associates with such an increased risk. Whether impaired metabolic health, characterized by hypertension, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and subclinical inflammation, may explain part of the elevated risk of cardiometabolic diseases that is found in many subjects with very low fat mass, as it does in many obese subjects, is unknown. An important pathomechanism of impaired metabolic health is disproportionate fat distribution. In this article the risk of cardiometabolic diseases and mortality in subjects with metabolically healthy and unhealthy normal weight and obesity is summarized. Furthermore, the change of metabolic health during a longer period of follow-up and its impact on cardiometabolic diseases is being discussed. Finally, the implementation of the concept of metabolic health in daily clinical practice is being highlighted.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Phenotyping obesity: A focus on metabolically healthy obesity and metabolically unhealthy normal weight
Rachel Agius, Nikolai P. Pace, Stephen Fava
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing verum and sham acupoint catgut embedding for adults with obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Jin-huan Yue, Xiao-ling Li, Yu-ying Zhang, Guan-hu Yang, Jeffrey Zhong-xue Mah, Ang Li, Wei-wei Zhao, Yu-lin Wang, Qin-hong Zhang, Jia-qi Huang
Medicine.2024; 103(4): e36653. CrossRef - Association between Weight Change and Incidence of Dyslipidemia in Young Adults: A Retrospective Cohort Study of Korean Male Soldiers
Joon-Young Yoon, Won Ju Park, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Cheol-Kyu Park, Wonsuk Choi
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2024; 33(1): 36. CrossRef - Dietary intake of methyl donor nutrients in relation to metabolic health status, serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and adropin
Donya Poursalehi, Keyhan Lotfi, Farnaz Shahdadian, Zahra Hajhashemy, Parisa Rouhani, Parvane Saneei
Clinical Nutrition.2024; 43(6): 1353. CrossRef - Metabolically Healthy Obesity: An Eye-opener
Purushothaman Padmanabhan, Nagendram Dinakaran, Somnath Verma, S Keerthana
Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Endoscopy Practice.2023; 3(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of metabolic health and obesity on all-cause death and CVD incidence in Korean adults: a retrospective cohort study
Ye-Seul Kim, Sang-Jun Shin, Yonghwan Kim, Joungyoun Kim, Hee-Taik Kang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Coffee and metabolic phenotypes: A cross-sectional analysis of the Japan multi-institutional collaborative cohort (J-MICC) study
Takeshi Watanabe, Kokichi Arisawa, Tien Van Nguyen, Masashi Ishizu, Sakurako Katsuura-Kamano, Asahi Hishida, Takashi Tamura, Yasufumi Kato, Rieko Okada, Rie Ibusuki, Chihaya Koriyama, Sadao Suzuki, Takahiro Otani, Teruhide Koyama, Satomi Tomida, Kiyonori
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2023; 33(3): 620. CrossRef - Metabolically unhealthy phenotype in adults with normal weight: Is cardiometabolic health worse off when compared to adults with obesity?
Myong-Won Seo, Joon Young Kim
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2023; 17(2): 116. CrossRef - Association between metabolic obesity phenotypes and multiple myeloma hospitalization burden: A national retrospective study
Yue Zhang, Xiude Fan, Chunhui Zhao, Zinuo Yuan, Yiping Cheng, Yafei Wu, Junming Han, Zhongshang Yuan, Yuanfei Zhao, Keke Lu
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolically healthy obesity: Misleading phrase or healthy phenotype?
Cem Tanriover, Sidar Copur, Abduzhappar Gaipov, Batu Ozlusen, Rustu E. Akcan, Masanari Kuwabara, Mads Hornum, Daniel H. Van Raalte, Mehmet Kanbay
European Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 111: 5. CrossRef - Prevalence of combined metabolic health and weight status by various diagnosis criteria and association with cardiometabolic disease in Korean adults
Myong-Won Seo, Jung-Min Lee, Hyun Chul Jung
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2023; 17(2): 137. CrossRef - Precision medicine in complex diseases—Molecular subgrouping for improved prediction and treatment stratification
Åsa Johansson, Ole A. Andreassen, Søren Brunak, Paul W. Franks, Harald Hedman, Ruth J. F. Loos, Benjamin Meder, Erik Melén, Craig E. Wheelock, Bo Jacobsson
Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 294(4): 378. CrossRef - Lipid droplet biogenesis and functions in health and disease
Armella Zadoorian, Ximing Du, Hongyuan Yang
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2023; 19(8): 443. CrossRef - Molecular Mechanisms for the Vicious Cycle between Insulin Resistance and the Inflammatory Response in Obesity
Dariusz Szukiewicz
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(12): 9818. CrossRef - Insulin Resistance Is the Main Characteristic of Metabolically Unhealthy Obesity (MUO) Associated with NASH in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery
Sophia M. Schmitz, Sebastian Storms, Alexander Koch, Christine Stier, Andreas Kroh, Karl P. Rheinwalt, Sandra Schipper, Karim Hamesch, Tom F. Ulmer, Ulf P. Neumann, Patrick H. Alizai
Biomedicines.2023; 11(6): 1595. CrossRef - Hyperleptinemia as a marker of various phenotypes of obesity and overweight in women with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus
L. V. Kondrateva, Yu. N. Gorbunova, T. A. Panafidina, T. V. Popkova
Rheumatology Science and Practice.2023; 61(3): 339. CrossRef - Predictable Representation of Metabolic Synthesis Pathways of Vitamins and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Obese Adults
A. V. Shestopalov, L. A. Ganenko, I. M. Kolesnikova, T. V. Grigoryeva, I. Yu. Vasilyev, Yu. L. Naboka, N. I. Volkova, O. V. Borisenko, S. A. Roumiantsev
Journal of Evolutionary Biochemistry and Physiology.2023; 59(5): 1510. CrossRef - PREDICTION OF VITAMINS AND SHORT-CHAIN FATTY ACIDS SYNTHESIS PATHWAYS IN OBESE ADULTS
A. V. Shestopalov, L. A. Ganenko, I. M. Kolesnikova, T. V. Grigoryeva, I. Yu. Vasilyev, Yu. L. Naboka, N. I. Volkova, O. V Borisenko, S. A. Roumiantsev
Журнал эволюционной биохимии и физиологии.2023; 59(5): 389. CrossRef - Metabolically unhealthy individuals, either with obesity or not, have a higher risk of critical coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes than metabolically healthy individuals without obesity
Nam Hoon Kim, Kyeong Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim
Metabolism.2022; 128: 154894. CrossRef - Associations between obesity, metabolic syndrome, and endometrial cancer risk in East Asian women
Boyoung Park
Journal of Gynecologic Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin and cancer: a tangled web
Brooks P. Leitner, Stephan Siebel, Ngozi D. Akingbesote, Xinyi Zhang, Rachel J. Perry
Biochemical Journal.2022; 479(5): 583. CrossRef - Relationships Between Metabolic Body Composition Status and Rapid Kidney Function Decline in a Community-Based Population: A Prospective Observational Study
Shao-Chi Chu, Po-Hsi Wang, Kuan-Ying Lu, Chia-Chun Ko, Yun-Hsuan She, Chin-Chan Lee, I-Wen Wu, Chiao-Yin Sun, Heng-Jung Hsu, Heng-Chih Pan
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dissecting the clinical relevance of polygenic risk score for obesity—a cross-sectional, longitudinal analysis
Eun Kyung Choe, Manu Shivakumar, Seung Mi Lee, Anurag Verma, Dokyoon Kim
International Journal of Obesity.2022; 46(9): 1686. CrossRef - Metabolic and Obesity Phenotype Trajectories in Taiwanese Medical Personnel
Hsin-Yun Chang, Jer-Hao Chang, Yin-Fan Chang, Chih-Hsing Wu, Yi-Ching Yang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(13): 8184. CrossRef - Sex Differences in Cardiovascular Impact of Early Metabolic Impairment: Interplay between Dysbiosis and Adipose Inflammation
Haneen S. Dwaib, Ibrahim AlZaim, Ghina Ajouz, Ali H. Eid, Ahmed El-Yazbi
Molecular Pharmacology.2022; 102(1): 60. CrossRef - Reduced leukocyte mitochondrial copy number in metabolic syndrome and metabolically healthy obesity
Rachel Agius, Nikolai Paul Pace, Stephen Fava
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in BMI and physical activity from youth to adulthood distinguish normal-weight, metabolically obese adults from those who remain healthy
A. Viitasalo, K. Pahkala, T. Lehtimäki, JSA. Viikari, TH. Tammelin, O. Raitakari, TO. Kilpeläinen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathogenesis, Murine Models, and Clinical Implications of Metabolically Healthy Obesity
Yun Kyung Cho, Yoo La Lee, Chang Hee Jung
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(17): 9614. CrossRef - Metabolically healthy obesity: it is time to consider its dynamic changes
Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(4): 123. CrossRef - Obesity as a Risk Factor for Breast Cancer—The Role of miRNA
Karolina Hanusek, Jakub Karczmarski, Anna Litwiniuk, Katarzyna Urbańska, Filip Ambrozkiewicz, Andrzej Kwiatkowski, Lidia Martyńska, Anita Domańska, Wojciech Bik, Agnieszka Paziewska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(24): 15683. CrossRef - Propensity Score–Matching Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG) vs. Gastric Bypass (RYGB) in Patients ≥ 60 Years
Omar Thaher, Stefanie Wolf, Martin Hukauf, Christine Stroh
Obesity Surgery.2021; 31(6): 2682. CrossRef - Associations between obesity, metabolic health, and the risk of breast cancer in East Asian women
Boyoung Park, Soyeoun Kim, Hayoung Kim, Chihwan Cha, Min Sung Chung
British Journal of Cancer.2021; 125(12): 1718. CrossRef
- Phenotyping obesity: A focus on metabolically healthy obesity and metabolically unhealthy normal weight

Original Article
- Prevalence and Characteristics of Metabolically Obese but Normal Weight and Metabolically Healthy but Obese in Middle-aged Koreans: the Chungju Metabolic Disease Cohort (CMC) Study.
- Seung Hwan Lee, Hee Sung Ha, Young Jun Park, Jin Hee Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, Kun Ho Yoon, Moo Il Kang, Won Chul Lee, Ho Young Son, Yong Moon Park, Hyuk Sang Kwon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2011;26(2):133-141. Published online June 1, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2011.26.2.133
- 2,386 View
- 35 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
We attempted to determine the prevalence and characteristics of metabolically obese but normal weight (MONW) and metabolically healthy but obese (MHO) individuals in a large cohort of middle-aged Koreans. METHODS: 8,987 non-diabetic subjects were selected from the Chungju Metabolic disease Cohort Study performed in 2003-2006. MONW was defined as a body mass index (BMI) > or = 18.5 and < 23 kg/m2 with a homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) in the highest quartile. MHO was defined as BMI > or = 25 kg/m2 with HOMA-IR in the lowest quartile. RESULTS: The mean age of the subjects was 62.3 +/- 10.5 years (men 40.4%). The age-adjusted prevalence of MONW and MHO were 4.3% (5.3% men, 3.7% women) and 5.6% (3.6% men, 7.0% women), respectively. 14.2% of men and 12.9% of women were classified as MONW among the normal weight population, whereas 10.7% of men and 14.5% of women were classified as MHO among the obese subjects. The prevalence of prediabetes was significantly higher in the MONW group than in the MHO group (34.7 vs. 12.5%, P < 0.0001 in men; 23.1 vs. 8.8%, P < 0.0001 in women). The MONW group evidenced an equivalent risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) relative to the MHO group (10.77 +/- 0.68 vs. 10.22 +/- 0.90% in men; 7.02 +/- 0.34 vs. 7.26 +/- 0.26% in women, means +/- standard error [SE]). CONCLUSION: The subjects in the MONW group are characterized by a high risk of diabetes and CHD, despite their normal weights. Their substantial prevalence in the population emphasizes the importance of identifying subjects in the MONW group, and warrants more intensive risk management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Obesity, metabolic health, and mortality in adults: a nationwide population-based study in Korea
Hae Kyung Yang, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Yong-Moon Park, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Moo-Il Kang, Bong-Yun Cha, Seung-Hwan Lee
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - The Definition of Metabolically Healthy Obesity
Hae Kyung Yang, Seung-Hwan Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2014; 15(1): 17. CrossRef
- Obesity, metabolic health, and mortality in adults: a nationwide population-based study in Korea


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



