Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Miscellaneous
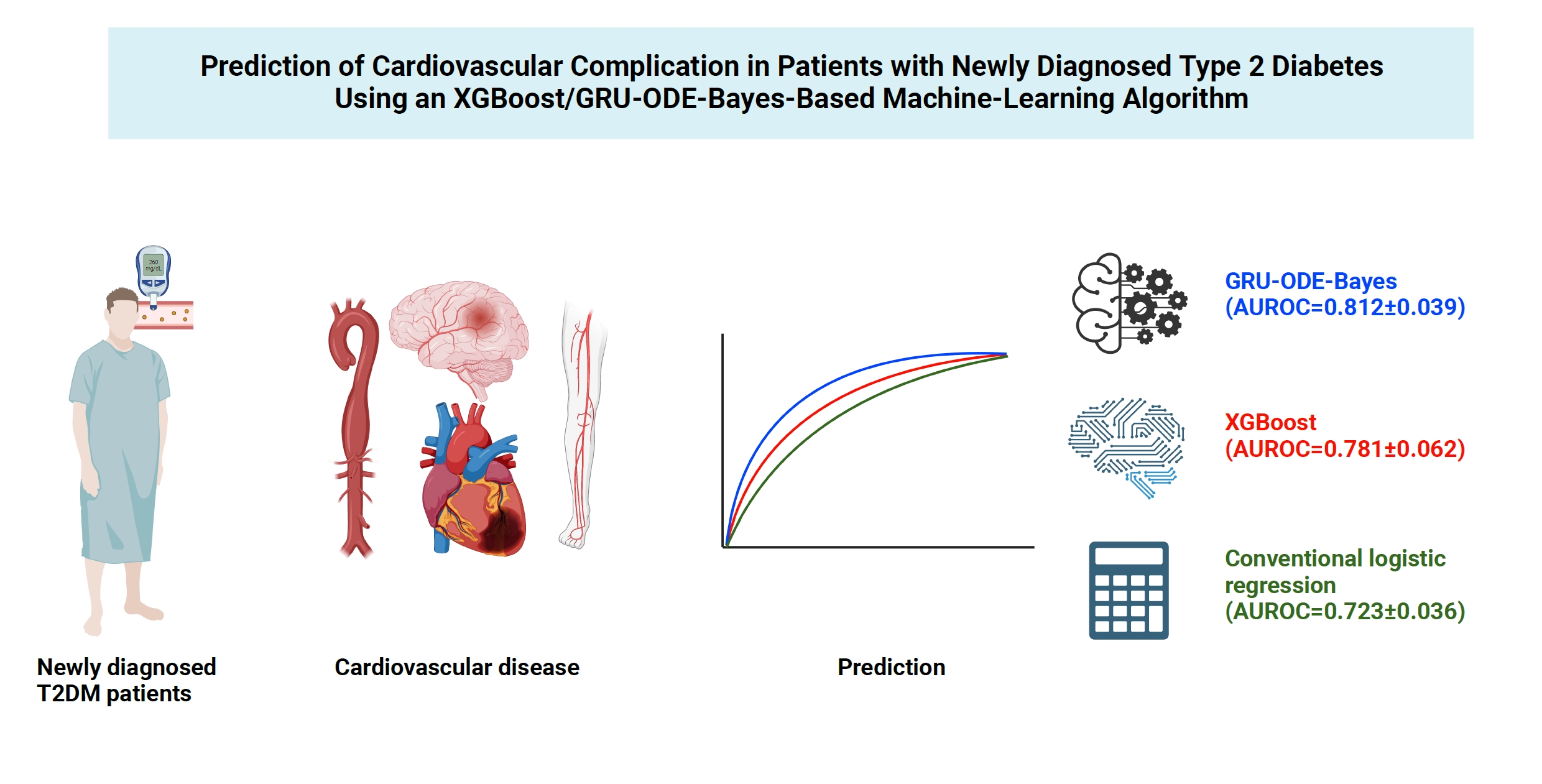
- Prediction of Cardiovascular Complication in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Using an XGBoost/GRU-ODE-Bayes-Based Machine-Learning Algorithm
- Joonyub Lee, Yera Choi, Taehoon Ko, Kanghyuck Lee, Juyoung Shin, Hun-Sung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):176-185. Published online November 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1739
- 1,223 View
- 60 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Cardiovascular disease is life-threatening yet preventable for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Because each patient with T2DM has a different risk of developing cardiovascular complications, the accurate stratification of cardiovascular risk is critical. In this study, we proposed cardiovascular risk engines based on machine-learning algorithms for newly diagnosed T2DM patients in Korea.
Methods
To develop the machine-learning-based cardiovascular disease engines, we retrospectively analyzed 26,166 newly diagnosed T2DM patients who visited Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital between July 2009 and April 2019. To accurately measure diabetes-related cardiovascular events, we designed a buffer (1 year), an observation (1 year), and an outcome period (5 years). The entire dataset was split into training and testing sets in an 8:2 ratio, and this procedure was repeated 100 times. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) was calculated by 10-fold cross-validation on the training dataset.
Results
The machine-learning-based risk engines (AUROC XGBoost=0.781±0.014 and AUROC gated recurrent unit [GRU]-ordinary differential equation [ODE]-Bayes=0.812±0.016) outperformed the conventional regression-based model (AUROC=0.723± 0.036).
Conclusion
GRU-ODE-Bayes-based cardiovascular risk engine is highly accurate, easily applicable, and can provide valuable information for the individualized treatment of Korean patients with newly diagnosed T2DM.

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
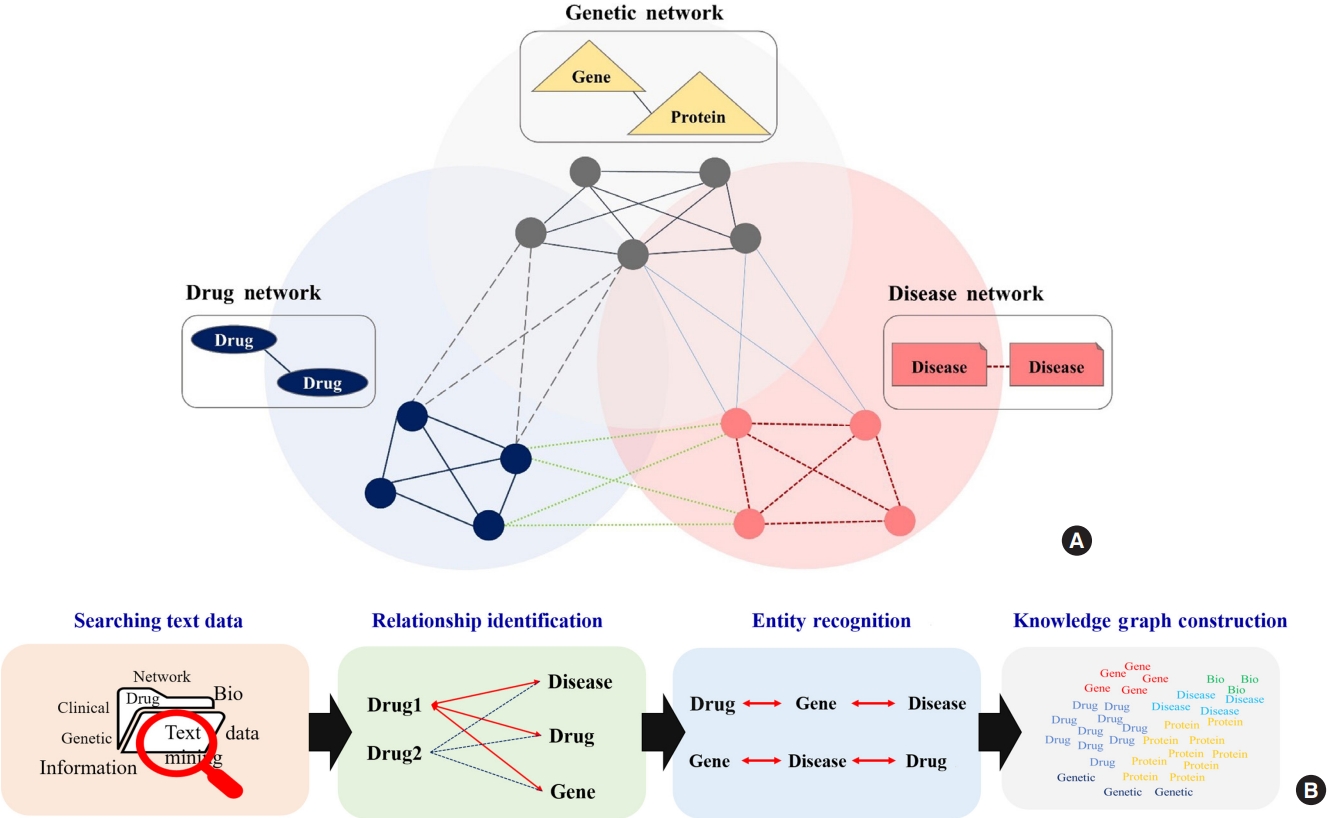
- A Study on Methodologies of Drug Repositioning Using Biomedical Big Data: A Focus on Diabetes Mellitus
- Suehyun Lee, Seongwoo Jeon, Hun-Sung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):195-207. Published online April 13, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1404
- 5,622 View
- 201 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Drug repositioning is a strategy for identifying new applications of an existing drug that has been previously proven to be safe. Based on several examples of drug repositioning, we aimed to determine the methodologies and relevant steps associated with drug repositioning that should be pursued in the future. Reports on drug repositioning, retrieved from PubMed from January 2011 to December 2020, were classified based on an analysis of the methodology and reviewed by experts. Among various drug repositioning methods, the network-based approach was the most common (38.0%, 186/490 cases), followed by machine learning/deep learningbased (34.3%, 168/490 cases), text mining-based (7.1%, 35/490 cases), semantic-based (5.3%, 26/490 cases), and others (15.3%, 75/490 cases). Although drug repositioning offers several advantages, its implementation is curtailed by the need for prior, conclusive clinical proof. This approach requires the construction of various databases, and a deep understanding of the process underlying repositioning is quintessential. An in-depth understanding of drug repositioning could reduce the time, cost, and risks inherent to early drug development, providing reliable scientific evidence. Furthermore, regarding patient safety, drug repurposing might allow the discovery of new relationships between drugs and diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Present and Future of Artificial Intelligence-Based Medical Image in Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Analytical Methods and Limitations of Clinical Use
Ji-Won Chun, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Present and Future of Artificial Intelligence-Based Medical Image in Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Analytical Methods and Limitations of Clinical Use

- Adrenal Gland
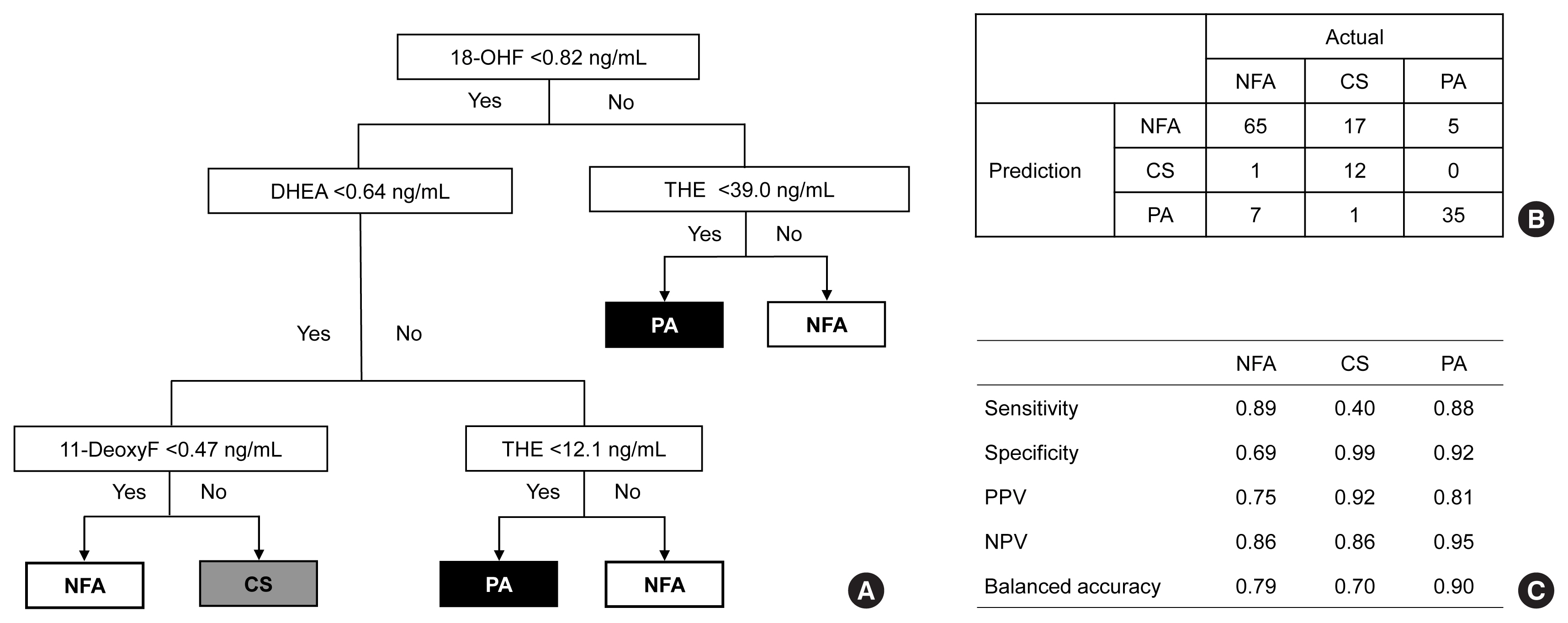
- Metabolic Subtyping of Adrenal Tumors: Prospective Multi-Center Cohort Study in Korea
- Eu Jeong Ku, Chaelin Lee, Jaeyoon Shim, Sihoon Lee, Kyoung-Ah Kim, Sang Wan Kim, Yumie Rhee, Hyo-Jeong Kim, Jung Soo Lim, Choon Hee Chung, Sung Wan Chun, Soon-Jib Yoo, Ohk-Hyun Ryu, Ho Chan Cho, A Ram Hong, Chang Ho Ahn, Jung Hee Kim, Man Ho Choi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1131-1141. Published online October 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1149
- 5,168 View
- 209 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Conventional diagnostic approaches for adrenal tumors require multi-step processes, including imaging studies and dynamic hormone tests. Therefore, this study aimed to discriminate adrenal tumors from a single blood sample based on the combination of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and machine learning algorithms in serum profiling of adrenal steroids.
Methods
The LC-MS-based steroid profiling was applied to serum samples obtained from patients with nonfunctioning adenoma (NFA, n=73), Cushing’s syndrome (CS, n=30), and primary aldosteronism (PA, n=40) in a prospective multicenter study of adrenal disease. The decision tree (DT), random forest (RF), and extreme gradient boost (XGBoost) were performed to categorize the subtypes of adrenal tumors.
Results
The CS group showed higher serum levels of 11-deoxycortisol than the NFA group, and increased levels of tetrahydrocortisone (THE), 20α-dihydrocortisol, and 6β-hydroxycortisol were found in the PA group. However, the CS group showed lower levels of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and its sulfate derivative (DHEA-S) than both the NFA and PA groups. Patients with PA expressed higher serum 18-hydroxycortisol and DHEA but lower THE than NFA patients. The balanced accuracies of DT, RF, and XGBoost for classifying each type were 78%, 96%, and 97%, respectively. In receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis for CS, XGBoost, and RF showed a significantly greater diagnostic power than the DT. However, in ROC analysis for PA, only RF exhibited better diagnostic performance than DT.
Conclusion
The combination of LC-MS-based steroid profiling with machine learning algorithms could be a promising one-step diagnostic approach for the classification of adrenal tumor subtypes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treating Primary Aldosteronism-Induced Hypertension: Novel Approaches and Future Outlooks
Nathan Mullen, James Curneen, Padraig T Donlon, Punit Prakash, Irina Bancos, Mark Gurnell, Michael C Dennedy
Endocrine Reviews.2024; 45(1): 125. CrossRef - Steroid profiling in adrenal disease
Danni Mu, Dandan Sun, Xia Qian, Xiaoli Ma, Ling Qiu, Xinqi Cheng, Songlin Yu
Clinica Chimica Acta.2024; 553: 117749. CrossRef - Plasma steroid profiling combined with machine learning for the differential diagnosis in mild autonomous cortisol secretion from nonfunctioning adenoma in patients with adrenal incidentalomas
Danni Mu, Xia Qian, Yichen Ma, Xi Wang, Yumeng Gao, Xiaoli Ma, Shaowei Xie, Lian Hou, Qi Zhang, Fang Zhao, Liangyu Xia, Liling Lin, Ling Qiu, Jie Wu, Songlin Yu, Xinqi Cheng
Endocrine Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mild autonomous cortisol secretion: pathophysiology, comorbidities and management approaches
Alessandro Prete, Irina Bancos
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum and hair steroid profiles in patients with nonfunctioning pituitary adenoma undergoing surgery: A prospective observational study
Seung Shin Park, Yong Hwy Kim, Ho Kang, Chang Ho Ahn, Dong Jun Byun, Man Ho Choi, Jung Hee Kim
The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.2023; 230: 106276. CrossRef - Recent Updates on the Management of Adrenal Incidentalomas
Seung Shin Park, Jung Hee Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 373. CrossRef - LC-MS based simultaneous profiling of adrenal hormones of steroids, catecholamines, and metanephrines
Jongsung Noh, Chaelin Lee, Jung Hee Kim, Seung Woon Myung, Man Ho Choi
Journal of Lipid Research.2023; 64(11): 100453. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Endocrine Society Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Primary Aldosteronism
Jeonghoon Ha, Jung Hwan Park, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Kyong Yeun Jung, Jeongmin Lee, Jong Han Choi, Seung Hun Lee, Namki Hong, Jung Soo Lim, Byung Kwan Park, Jung-Han Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Jooyoung Cho, Mi-kyung Kim, Choon Hee Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 597. CrossRef - Toward Systems-Level Metabolic Analysis in Endocrine Disorders and Cancer
Aliya Lakhani, Da Hyun Kang, Yea Eun Kang, Junyoung O. Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 619. CrossRef - Prevalence and Characteristics of Adrenal Tumors in an Unselected Screening Population
Ying Jing, Jinbo Hu, Rong Luo, Yun Mao, Zhixiao Luo, Mingjun Zhang, Jun Yang, Ying Song, Zhengping Feng, Zhihong Wang, Qingfeng Cheng, Linqiang Ma, Yi Yang, Li Zhong, Zhipeng Du, Yue Wang, Ting Luo, Wenwen He, Yue Sun, Fajin Lv, Qifu Li, Shumin Yang
Annals of Internal Medicine.2022; 175(10): 1383. CrossRef
- Treating Primary Aldosteronism-Induced Hypertension: Novel Approaches and Future Outlooks

- Miscellaneous
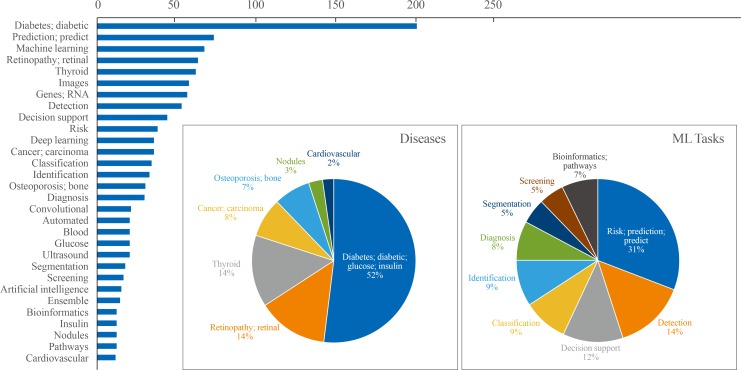
- Machine Learning Applications in Endocrinology and Metabolism Research: An Overview
- Namki Hong, Heajeong Park, Yumie Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):71-84. Published online March 19, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.71
- 15,550 View
- 205 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Machine learning (ML) applications have received extensive attention in endocrinology research during the last decade. This review summarizes the basic concepts of ML and certain research topics in endocrinology and metabolism where ML principles have been actively deployed. Relevant studies are discussed to provide an overview of the methodology, main findings, and limitations of ML, with the goal of stimulating insights into future research directions. Clear, testable study hypotheses stem from unmet clinical needs, and the management of data quality (beyond a focus on quantity alone), open collaboration between clinical experts and ML engineers, the development of interpretable high-performance ML models beyond the black-box nature of some algorithms, and a creative environment are the core prerequisites for the foreseeable changes expected to be brought about by ML and artificial intelligence in the field of endocrinology and metabolism, with actual improvements in clinical practice beyond hype. Of note, endocrinologists will continue to play a central role in these developments as domain experts who can properly generate, refine, analyze, and interpret data with a combination of clinical expertise and scientific rigor.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Artificial Intelligence for Predicting and Diagnosing Complications of Diabetes
Jingtong Huang, Andrea M. Yeung, David G. Armstrong, Ashley N. Battarbee, Jorge Cuadros, Juan C. Espinoza, Samantha Kleinberg, Nestoras Mathioudakis, Mark A. Swerdlow, David C. Klonoff
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2023; 17(1): 224. CrossRef - Expressions of Cushing’s syndrome in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1
William F. Simonds
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of machine learning and artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and classification of polycystic ovarian syndrome: a systematic review
Francisco J. Barrera, Ethan D.L. Brown, Amanda Rojo, Javier Obeso, Hiram Plata, Eddy P. Lincango, Nancy Terry, René Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, Janet E. Hall, Skand Shekhar
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of rituximab effect on modified Rodnan skin score in systemic sclerosis: a machine-learning analysis of the DesiReS trial
Satoshi Ebata, Koji Oba, Kosuke Kashiwabara, Keiko Ueda, Yukari Uemura, Takeyuki Watadani, Takemichi Fukasawa, Shunsuke Miura, Asako Yoshizaki-Ogawa, Asano Yoshihide, Ayumi Yoshizaki, Shinichi Sato
Rheumatology.2022; 61(11): 4364. CrossRef - Automating and improving cardiovascular disease prediction using Machine learning and EMR data features from a regional healthcare system
Qi Li, Alina Campan, Ai Ren, Wael E. Eid
International Journal of Medical Informatics.2022; 163: 104786. CrossRef - An Interactive Online App for Predicting Diabetes via Machine Learning from Environment-Polluting Chemical Exposure Data
Rosy Oh, Hong Kyu Lee, Youngmi Kim Pak, Man-Suk Oh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(10): 5800. CrossRef - Ensemble blood glucose prediction in diabetes mellitus: A review
M.Z. Wadghiri, A. Idri, Touria El Idrissi, Hajar Hakkoum
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2022; 147: 105674. CrossRef - The maze runner: navigating through basic kinetics to AI models of human metabolism pathology
Arina V. Martyshina, Oksana M. Tilinova, Anastasia A. Simanova, Olga S. Knyazeva, Irina V. Dokukina
Procedia Computer Science.2022; 213: 271. CrossRef - Applications of Machine Learning in Bone and Mineral Research
Sung Hye Kong, Chan Soo Shin
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 928. CrossRef - Facial Recognition Intensity in Disease Diagnosis Using Automatic Facial Recognition
Danning Wu, Shi Chen, Yuelun Zhang, Huabing Zhang, Qing Wang, Jianqiang Li, Yibo Fu, Shirui Wang, Hongbo Yang, Hanze Du, Huijuan Zhu, Hui Pan, Zhen Shen
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2021; 11(11): 1172. CrossRef - The Application of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Pituitary Adenomas
Congxin Dai, Bowen Sun, Renzhi Wang, Jun Kang
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Real World Data and Artificial Intelligence in Diabetology
Kwang Joon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 140. CrossRef - A Novel Detection Framework for Detecting Abnormal Human Behavior
Chengfei Wu, Zixuan Cheng, Yi-Zhang Jiang
Mathematical Problems in Engineering.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef
- Artificial Intelligence for Predicting and Diagnosing Complications of Diabetes

- Miscellaneous
- Medical Big Data Is Not Yet Available: Why We Need Realism Rather than Exaggeration
- Hun-Sung Kim, Dai-Jin Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(4):349-354. Published online December 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.4.349
- 5,840 View
- 140 Download
- 36 Web of Science
- 47 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Most people are now familiar with the concepts of big data, deep learning, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI) and have a vague expectation that AI using medical big data can be used to improve the quality of medical care. However, the expectation that big data could change the field of medicine is inconsistent with the current reality. The clinical meaningfulness of the results of research using medical big data needs to be examined. Medical staff needs to be clear about the purpose of AI that utilizes medical big data and to focus on the quality of this data, rather than the quantity. Further, medical professionals should understand the necessary precautions for using medical big data, as well as its advantages. No doubt that someday, medical big data will play an essential role in healthcare; however, at present, it seems too early to actively use it in clinical practice. The field continues to work toward developing medical big data and making it appropriate for healthcare. Researchers should continue to engage in empirical research to ensure that appropriate processes are in place to empirically evaluate the results of its use in healthcare.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current status of remote collaborative care for hypertension in medically underserved areas
Seo Yeon Baik, Kyoung Min Kim, Hakyoung Park, Jiwon Shinn, Hun-Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2024; 6(1): 33. CrossRef - Prediction of Cardiovascular Complication in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Using an XGBoost/GRU-ODE-Bayes-Based Machine-Learning Algorithm
Joonyub Lee, Yera Choi, Taehoon Ko, Kanghyuck Lee, Juyoung Shin, Hun-Sung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 176. CrossRef - Dark Data in Real-World Evidence: Challenges, Implications, and the Imperative of Data Literacy in Medical Research
Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative analysis: health data protection laws in Malaysia, Saudi Arabia and EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
Jawahitha Sarabdeen, Mohamed Mazahir Mohamed Ishak
International Journal of Law and Management.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Risk of Cardiovascular Disease Among Type 2 Diabetes Patients According to Average and Visit-to-Visit Variations of HbA1c Levels During the First 3 Years of Diabetes Diagnosis
Hyunah Kim, Da Young Jung, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Hyeon Woo Yim, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of cardiocerebrovascular disease incidence between angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor and angiotensin receptor blocker users in a real-world cohort
Suehyun Lee, Hyunah Kim, Hyeon Woo Yim, Kim Hun-Sung, Ju Han Kim
Journal of Applied Biomedicine.2023; 21(1): 7. CrossRef - Multi-Omics and Management of Follicular Carcinoma of the Thyroid
Thifhelimbilu Emmanuel Luvhengo, Ifongo Bombil, Arian Mokhtari, Maeyane Stephens Moeng, Demetra Demetriou, Claire Sanders, Zodwa Dlamini
Biomedicines.2023; 11(4): 1217. CrossRef - Correlation analysis of cancer incidence after pravastatin treatment
Jin Yu, Raeun Kim, Jiwon Shinn, Man Young Park, Hun-Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2023; 5(2): 61. CrossRef - A New Strategy for Evaluating the Quality of Laboratory Results for Big Data Research: Using External Quality Assessment Survey Data (2010–2020)
Eun-Jung Cho, Tae-Dong Jeong, Sollip Kim, Hyung-Doo Park, Yeo-Min Yun, Sail Chun, Won-Ki Min
Annals of Laboratory Medicine.2023; 43(5): 425. CrossRef - Weight loss and side-effects of liraglutide and lixisenatide in obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus
Jeongmin Lee, Raeun Kim, Min-Hee Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Jung Min Lee, Sang-Ah Jang, Hun-Sung Kim
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(5): 460. CrossRef - Cohort profile for development of machine learning models to predict healthcare-related adverse events (Demeter): clinical objectives, data requirements for modelling and overview of data set for 2016–2018
Svetlana Artemova, Ursula von Schenck, Rui Fa, Daniel Stoessel, Hadiseh Nowparast Rostami, Pierre-Ephrem Madiot, Jean-Marie Januel, Daniel Pagonis, Caroline Landelle, Meghann Gallouche, Christophe Cancé, Frederic Olive, Alexandre Moreau-Gaudry, Sigurd Pri
BMJ Open.2023; 13(8): e070929. CrossRef - The Present and Future of Artificial Intelligence-Based Medical Image in Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Analytical Methods and Limitations of Clinical Use
Ji-Won Chun, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Construction and application on the training course of information literacy for clinical nurses
Chao Wu, Yinjuan Zhang, Jing Wu, Linyuan Zhang, Juan Du, Lu Li, Nana Chen, Liping Zhu, Sheng Zhao, Hongjuan Lang
BMC Medical Education.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lightweight Histological Tumor Classification Using a Joint Sparsity-Quantization Aware Training Framework
Dina Aboutahoun, Rami Zewail, Keiji Kimura, Mostafa I. Soliman
IEEE Access.2023; 11: 119342. CrossRef - Long-Term Cumulative Exposure to High γ-Glutamyl Transferase Levels and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Han-Sang Baek, Bongseong Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Sang-Ah Chang, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 770. CrossRef - Comorbidity Patterns and Management in Inpatients with Endocrine Diseases by Age Groups in South Korea: Nationwide Data
Sung-Soo Kim, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 14(1): 42. CrossRef - Angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors versus angiotensin receptor blockers: New‐onset diabetes mellitus stratified by statin use
Juyoung Shin, Hyunah Kim, Hyeon Woo Yim, Ju Han Kim, Suehyun Lee, Hun‐Sung Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2022; 47(1): 97. CrossRef - Physician Knowledge Base: Clinical Decision Support Systems
Sira Kim, Eung-Hee Kim, Hun-Sung Kim
Yonsei Medical Journal.2022; 63(1): 8. CrossRef - Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor-Related Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Accuracy Verification of Operational Definition
Dong Yoon Kang, Hyunah Kim, SooJeong Ko, HyungMin Kim, Jiwon Shinn, Min-Gyu Kang, Sun-ju Byeon, Jeong-Hee Choi, Soo-Yong Shin, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Drug Repositioning: Exploring New Indications for Existing Drug-Disease Relationships
Hun-Sung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 62. CrossRef - A Study on Methodologies of Drug Repositioning Using Biomedical Big Data: A Focus on Diabetes Mellitus
Suehyun Lee, Seongwoo Jeon, Hun-Sung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 195. CrossRef - Development of a predictive model for the side effects of liraglutide
Jiyoung Min, Jiwon Shinn, Hun-Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(2): 87. CrossRef - Understanding and Utilizing Claim Data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) and Health Insurance Review & Assessment (HIRA) Database for Research
Dae-Sung Kyoung, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(2): 103. CrossRef - The Impact of the Association between Cancer and Diabetes Mellitus on Mortality
Sung-Soo Kim, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(7): 1099. CrossRef - Development of Various Diabetes Prediction Models Using Machine Learning Techniques
Juyoung Shin, Jaewon Kim, Chanjung Lee, Joon Young Yoon, Seyeon Kim, Seungjae Song, Hun-Sung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 650. CrossRef - Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Han-sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Jin Yu, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Jeonghoon Ha, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Dong-Jun Lim, Hun-Sung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 641. CrossRef - Retrospective cohort analysis comparing changes in blood glucose level and body composition according to changes in thyroid‐stimulating hormone level
Hyunah Kim, Da Young Jung, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Jae‐Hyoung Cho, Hyeon Woo Yim, Hun‐Sung Kim
Journal of Diabetes.2022; 14(9): 620. CrossRef - Long-Term Changes in HbA1c According to Blood Glucose Control Status During the First 3 Months After Visiting a Tertiary University Hospital
Hyunah Kim, Da Young Jung, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Hyeon Woo Yim, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Medication based machine learning to identify subpopulations of pediatric hemodialysis patients in an electronic health record database
Autumn M. McKnite, Kathleen M. Job, Raoul Nelson, Catherine M.T. Sherwin, Kevin M. Watt, Simon C. Brewer
Informatics in Medicine Unlocked.2022; 34: 101104. CrossRef - Improving Machine Learning Diabetes Prediction Models for the Utmost Clinical Effectiveness
Juyoung Shin, Joonyub Lee, Taehoon Ko, Kanghyuck Lee, Yera Choi, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(11): 1899. CrossRef - A Study on Weight Loss Cause as per the Side Effect of Liraglutide
Jin Yu, Jeongmin Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Hyung Cho, Hun-Sung Kim, Heng Zhou
Cardiovascular Therapeutics.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Risk Classification and Subphenotyping of Acute Kidney Injury: Concepts and Methodologies
Javier A. Neyra, Jin Chen, Sean M. Bagshaw, Jay L. Koyner
Seminars in Nephrology.2022; 42(3): 151285. CrossRef - Estimation of sodium‐glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor–related genital and urinary tract infections via electronic medical record–based common data model
SooJeong Ko, HyungMin Kim, Jiwon Shinn, Sun‐ju Byeon, Jeong‐Hee Choi, Hun‐Sung Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2021; 46(4): 975. CrossRef - Blood glucose levels and bodyweight change after dapagliflozin administration
Hyunah Kim, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, Jae‐Hyoung Cho, Kun‐Ho Yoon, Hun‐Sung Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2021; 12(9): 1594. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence in healthcare: possibilities of patent protection
T. N. Erivantseva, Yu. V. Blokhina
FARMAKOEKONOMIKA. Modern Pharmacoeconomic and Pharmacoepidemiology.2021; 14(2): 270. CrossRef - Lack of Acceptance of Digital Healthcare in the Medical Market: Addressing Old Problems Raised by Various Clinical Professionals and Developing Possible Solutions
Jong Il Park, Hwa Young Lee, Hyunah Kim, Jisan Lee, Jiwon Shinn, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prospect of Artificial Intelligence Based on Electronic Medical Records
Suehyun Lee, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2021; 10(3): 282. CrossRef - Data Pseudonymization in a Range That Does Not Affect Data Quality: Correlation with the Degree of Participation of Clinicians
Soo-Yong Shin, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a Predictive Model for Glycated Hemoglobin Values and Analysis of the Factors Affecting It
HyeongKyu Park, Da Young Lee, So young Park, Jiyoung Min, Jiwon Shinn, Dae Ho Lee, Soon Hyo Kwon, Hun-Sung Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2021; 3(4): 106. CrossRef - Modeling of Changes in Creatine Kinase after HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor Prescription
Hun-Sung Kim, Jiyoung Min, Jiwon Shinn, Oak-Kee Hong, Jang-Won Son, Seong-Su Lee, Sung-Rae Kim, Soon Jib Yoo
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2021; 3(4): 115. CrossRef - TRAINING IN BIG DATA TECHNOLOGIES OF MEDICAL UNIVERSITY STUDENTS
K.S ITINSON
AZIMUTH OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH: PEDAGOGY AND PSYCHOLOGY.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning Applications in Endocrinology and Metabolism Research: An Overview
Namki Hong, Heajeong Park, Yumie Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 71. CrossRef - Lessons from Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems in Digital Healthcare
Hun-Sung Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(3): 541. CrossRef - Apprehensions about Excessive Belief in Digital Therapeutics: Points of Concern Excluding Merits
Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Medical Ethics in the Era of Artificial Intelligence Based on Medical Big Data
Hae-Ran Na, Hun-Sung Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 126. CrossRef - Machine Learning Application in Diabetes and Endocrine Disorders
Namki Hong, Heajeong Park, Yumie Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 130. CrossRef - Real World Data and Artificial Intelligence in Diabetology
Kwang Joon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 140. CrossRef
- Current status of remote collaborative care for hypertension in medically underserved areas

- Thyroid
- Digital Medicine in Thyroidology: A New Era of Managing Thyroid Disease
- Jae Hoon Moon, Steven R. Steinhubl
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(2):124-131. Published online June 24, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.2.124
- 5,437 View
- 135 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Digital medicine has the capacity to affect all aspects of medicine, including disease prediction, prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and post-treatment management. In the field of thyroidology, researchers are also investigating potential applications of digital technology for the thyroid disease. Recent studies using artificial intelligence (AI)/machine learning (ML) have reported reasonable performance for the classification of thyroid nodules based on ultrasonographic (US) images. AI/ML-based methods have also shown good diagnostic accuracy for distinguishing between benign and malignant thyroid lesions based on cytopathologic findings. Assistance from AI/ML methods could overcome the limitations of conventional thyroid US and fine-needle aspiration cytology. A web-based database has been developed for thyroid cancer care. In addition to its role as a nationwide registry of thyroid cancer, it is expected to serve as a clinical platform to facilitate better thyroid cancer care and as a research platform providing comprehensive disease-specific big data. Evidence has been found that biosignal monitoring with wearable devices may predict thyroid dysfunction. This real-world thyroid function monitoring could aid in the management and early detection of thyroid dysfunction. In the thyroidology field, research involving the range of digital medicine technologies and their clinical applications is expected to be even more active in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- AI in Thyroid Cancer Diagnosis: Techniques, Trends, and Future Directions
Yassine Habchi, Yassine Himeur, Hamza Kheddar, Abdelkrim Boukabou, Shadi Atalla, Ammar Chouchane, Abdelmalik Ouamane, Wathiq Mansoor
Systems.2023; 11(10): 519. CrossRef - Empirical Method for Thyroid Disease Classification Using a Machine Learning Approach
Tahir Alyas, Muhammad Hamid, Khalid Alissa, Tauqeer Faiz, Nadia Tabassum, Aqeel Ahmad, Gulnaz Afzal
BioMed Research International.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Deep Learning Based Classification of Wrist Cracks from X-ray Imaging
Jahangir Jabbar, Muzammil Hussain, Hassaan Malik, Abdullah Gani, Ali Haider Khan, Muhammad Shiraz
Computers, Materials & Continua.2022; 73(1): 1827. CrossRef - Diagnostic Performance of Kwak, EU, ACR, and Korean TIRADS as Well as ATA Guidelines for the Ultrasound Risk Stratification of Non-Autonomously Functioning Thyroid Nodules in a Region with Long History of Iodine Deficiency: A German Multicenter Trial
Philipp Seifert, Simone Schenke, Michael Zimny, Alexander Stahl, Michael Grunert, Burkhard Klemenz, Martin Freesmeyer, Michael C. Kreissl, Ken Herrmann, Rainer Görges
Cancers.2021; 13(17): 4467. CrossRef - Association between Thyroid Function and Heart Rate Monitored by Wearable Devices in Patients with Hypothyroidism
Ki-Hun Kim, Juhui Lee, Chang Ho Ahn, Hyeong Won Yu, June Young Choi, Ho-Young Lee, Won Woo Lee, Jae Hoon Moon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 1121. CrossRef - Deep Learning based Classification of Thyroid Cancer using Different Medical Imaging Modalities : A Systematic Review
Maheen Ilyas, Hassaan Malik, Muhammad Adnan, Umair Bashir, Wajahat Anwaar Bukhari, Muhammad Imran Ali Khan, Adnan Ahmad
VFAST Transactions on Software Engineering.2021; 9(4): 1. CrossRef - Ultrasound risk stratification systems for thyroid nodule: between lights and shadows, we are moving towards a new era
Pierpaolo Trimboli, Cosimo Durante
Endocrine.2020; 69(1): 1. CrossRef - Associations of Thyroid Hormones and Resting Heart Rate in Patients
Referred to Coronary Angiography
Eva Steinberger, Stefan Pilz, Christian Trummer, Verena Theiler-Schwetz, Markus Reichhartinger, Thomas Benninger, Marlene Pandis, Oliver Malle, Martin H. Keppel, Nicolas Verheyen, Martin R. Grübler, Jakob Voelkl, Andreas Meinitzer, Winfried März
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2020; 52(12): 850. CrossRef
- AI in Thyroid Cancer Diagnosis: Techniques, Trends, and Future Directions


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



