Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Miscellaneous
- Clinical Value of Serum Mitochondria-Inhibiting Substances in Assessing Renal Hazards: A Community-Based Prospective Study in Korea
- Hoon Sung Choi, Jin Taek Kim, Hong Kyu Lee, Wook Ha Park, Youngmi Kim Pak, Sung Woo Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1298-1306. Published online November 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1226
- 3,312 View
- 95 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Mitochondrial dysfunction is strongly associated with several kidney diseases. However, no studies have evaluated the potential renal hazards of serum mitochondria-inhibiting substance (MIS) and aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand (AhRL) levels.
Methods
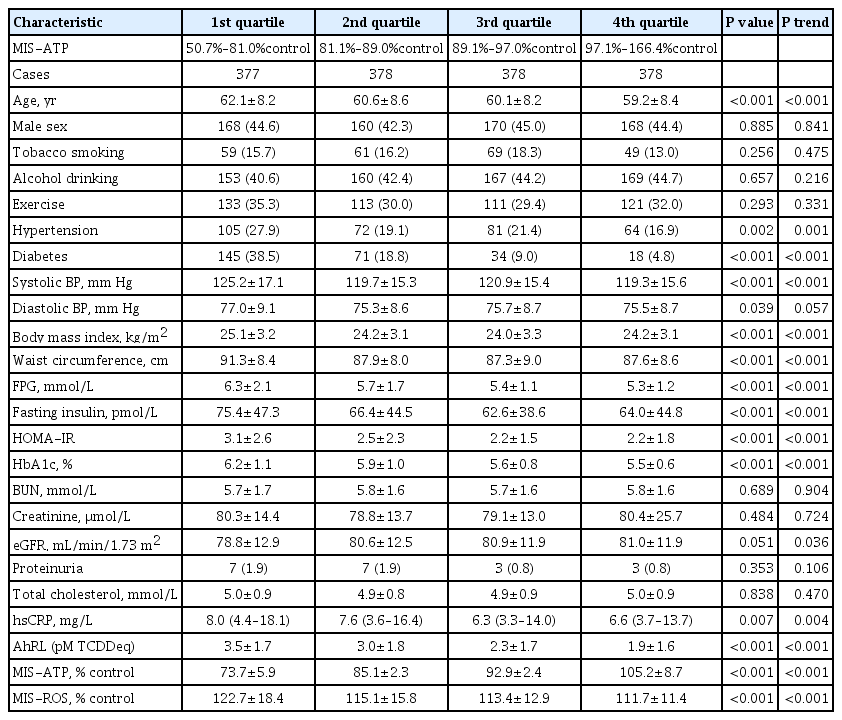
We used serum level of MIS and AhRL and clinical renal outcomes from 1,511 participants of a prospective community-based cohort in Ansung. MIS was evaluated based on intracellular adenosine triphosphate (MIS-ATP) or reactive oxygen species (MIS-ROS) generation measured using cell-based assays.
Results
During a mean 6.9-year follow-up, 84 participants (5.6%) developed a rapid decline in kidney function. In the lowest quartile group of MIS-ATP, patients were older and had metabolically deleterious parameters. In multivariate logistic regression analysis, higher MIS-ATP was associated with decreased odds for rapid decline: the odds ratio (OR) of 1% increase was 0.977 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.957 to 0.998; P=0.031), while higher MIS-ROS was marginally associated with increased odds for rapid decline (OR, 1.014; 95% CI, 0.999 to 1.028; P=0.055). However, serum AhRL was not associated with the rapid decline in kidney function. In subgroup analysis, the renal hazard of MIS was particularly evident in people with hypertension and low baseline kidney function.
Conclusion
Serum MIS was independently associated with a rapid decline in kidney function, while serum AhRL was not. The clinical implication of renal hazard on serum MIS requires further evaluation in future studies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Interactive Online App for Predicting Diabetes via Machine Learning from Environment-Polluting Chemical Exposure Data
Rosy Oh, Hong Kyu Lee, Youngmi Kim Pak, Man-Suk Oh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(10): 5800. CrossRef
- An Interactive Online App for Predicting Diabetes via Machine Learning from Environment-Polluting Chemical Exposure Data


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



