Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Effectiveness of a Social Networking Site Based Automatic Mobile Message Providing System on Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Kyuho Kim, Jae-Seung Yun, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Minhan Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn, Jae Hyoung Cho, Seung-Hyun Ko
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(2):344-352. Published online December 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1871
- 1,168 View
- 40 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigated the effectiveness of a social networking site (SNS)-based automatic mobile message providing system on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
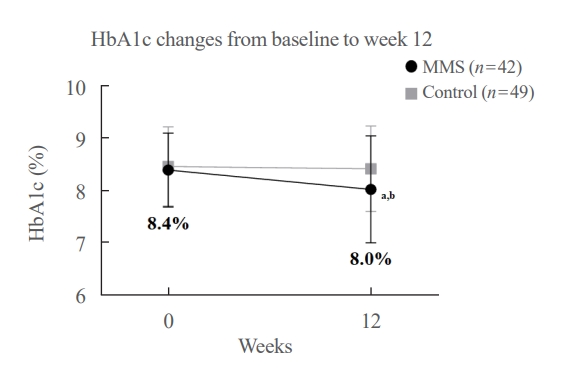
A 3-month, randomized, open-label, controlled, parallel-group trial was conducted. One hundred and ten participants with T2DM were randomized to a mobile message system (MMS) (n=55) or control group (n=55). The MMS group received protocolbased automated messages two times per day for 10 weeks regarding diabetes self-management through KakaoTalk SNS messenger. The primary outcome was the difference in the change in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels (%) from baseline to week 12.
Results
HbA1c levels were more markedly decreased in the MMS group (8.4%±0.7% to 8.0%±1.1%) than in the control group (8.5%±0.8% to 8.4%±0.8%), resulting in a significant between-group difference (P=0.027). No differences were observed in changes in fasting glucose levels, lipid profiles, and the number of participants who experienced hypoglycemia, or in changes in lifestyle behavior between groups. However, the self-monitoring of blood glucose frequency was significantly increased in the MMS group compared to the control group (P=0.003). In addition, sleep duration was increased in the MMS group, but was not changed in the control group.
Conclusion
An SNS-based automatic mobile message providing system was effective in improving glycemic control in patients in T2DM. Studies which based on a more individualized protocol, and investigate longer beneficial effect and sustainability will be required in the future.

- Clinical Study
- Romosozumab in Postmenopausal Korean Women with Osteoporosis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Efficacy and Safety Study
- Ki-Hyun Baek, Yoon-Sok Chung, Jung-Min Koh, In Joo Kim, Kyoung Min Kim, Yong-Ki Min, Ki Deok Park, Rajani Dinavahi, Judy Maddox, Wenjing Yang, Sooa Kim, Sang Jin Lee, Hyungjin Cho, Sung-Kil Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):60-69. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.848
- 6,897 View
- 391 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
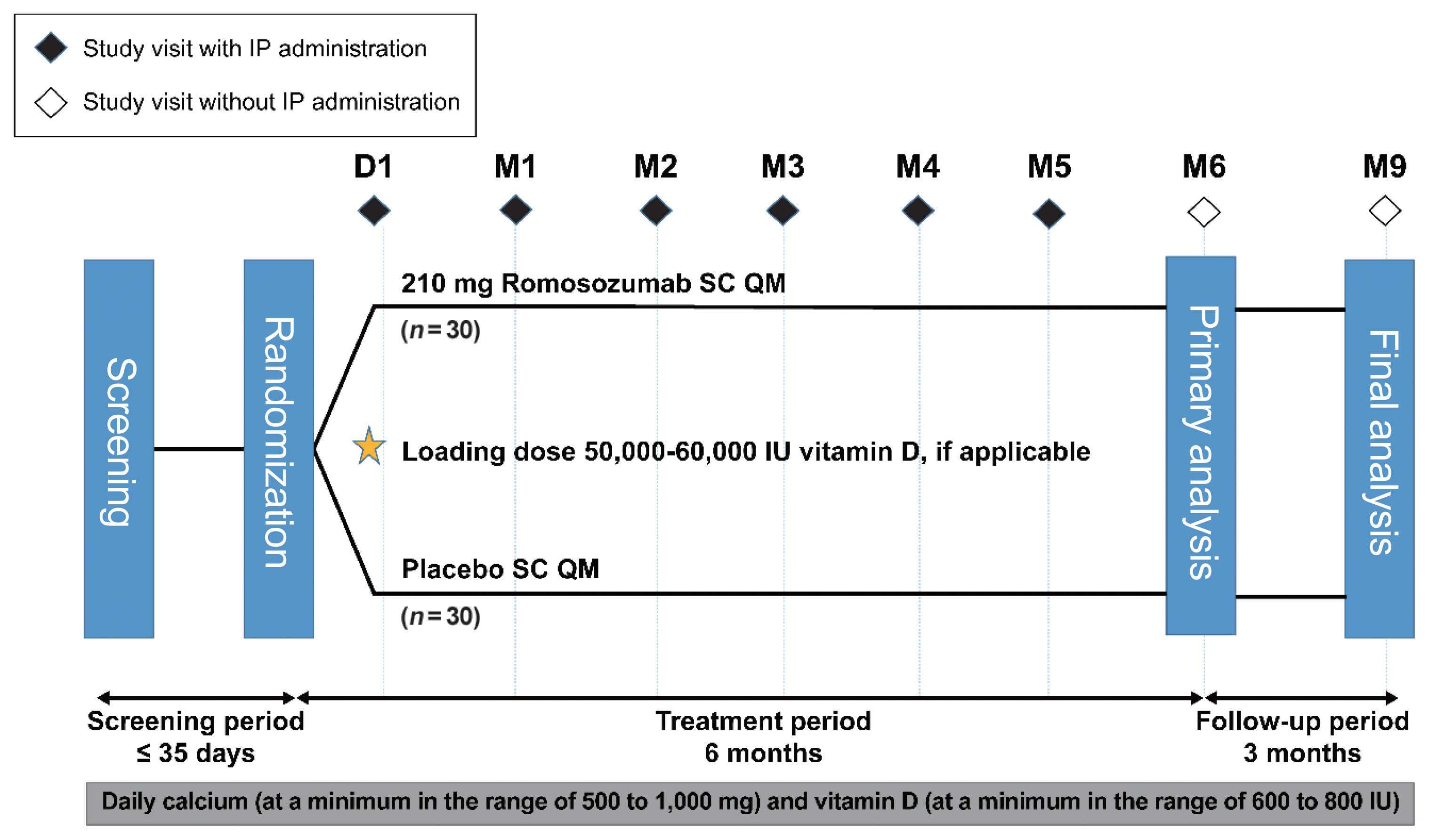
This phase 3 study evaluated the efficacy and safety of 6-month treatment with romosozumab in Korean postmenopausal women with osteoporosis.
Methods
Sixty-seven postmenopausal women with osteoporosis (bone mineral density [BMD] T-scores ≤–2.5 at the lumbar spine, total hip, or femoral neck) were randomized (1:1) to receive monthly subcutaneous injections of romosozumab (210 mg; n=34) or placebo (n=33) for 6 months.
Results
At month 6, the difference in the least square (LS) mean percent change from baseline in lumbar spine BMD (primary efficacy endpoint) between the romosozumab (9.5%) and placebo (–0.1%) groups was significant (9.6%; 95% confidence interval, 7.6 to 11.5; P<0.001). The difference in the LS mean percent change from baseline was also significant for total hip and femoral neck BMD (secondary efficacy endpoints). After treatment with romosozumab, the percent change from baseline in procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide transiently increased at months 1 and 3, while that in C-terminal telopeptide of type 1 collagen showed a sustained decrease. No events of cancer, hypocalcemia, injection site reaction, positively adjudicated atypical femoral fracture or osteonecrosis of the jaw, or positively adjudicated serious cardiovascular adverse events were observed. At month 9, 17.6% and 2.9% of patients in the romosozumab group developed binding and neutralizing antibodies, respectively.
Conclusion
Treatment with romosozumab for 6 months was well tolerated and significantly increased lumbar spine, total hip, and femoral neck BMD compared with placebo in Korean postmenopausal women with osteoporosis (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT02791516). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A pharmacovigilance analysis of FDA adverse event reporting system events for romosozumab
Zepeng Chen, Ming Li, Shuzhen Li, Yuxi Li, Junyan Wu, Kaifeng Qiu, Xiaoxia Yu, Lin Huang, Guanghui Chen
Expert Opinion on Drug Safety.2023; 22(4): 339. CrossRef - Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of romosozumab (evenity) for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture in postmenopausal women: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials (CDM‐J)
Wenbo Huang, Masashi Nagao, Naohiro Yonemoto, Sen Guo, Takeshi Tanigawa, Yuji Nishizaki
Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety.2023; 32(6): 671. CrossRef - Efficacy and Cardiovascular Safety of Romosozumab: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review
Seo-Yong Choi, Jeong-Min Kim, Sang-Hyeon Oh, Seunghyun Cheon, Jee-Eun Chung
Korean Journal of Clinical Pharmacy.2023; 33(2): 128. CrossRef - Clinical Studies On Romosozumab: An Alternative For Individuals With A High Risk Of Osteoporotic Fractures: A Current Concepts Review (Part I)
E. Carlos Rodriguez-Merchan, Alonso Moreno-Garcia, Hortensia De la Corte-Rodriguez
SurgiColl.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Romosozumab in osteoporosis: yesterday, today and tomorrow
Dong Wu, Lei Li, Zhun Wen, Guangbin Wang
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of anti-sclerostin antibodies in the treatment of osteoporosis: A meta-analysis and systematic review
Frideriki Poutoglidou, Efthimios Samoladas, Nikolaos Raikos, Dimitrios Kouvelas
Journal of Clinical Densitometry.2022; 25(3): 401. CrossRef - Benefits of lumican on human bone health: clinical evidence using bone marrow aspirates
Yun Sun Lee, So Jeong Park, Jin Young Lee, Eunah Choi, Beom-Jun Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2022; 37(4): 821. CrossRef - What is the risk of cardiovascular events in osteoporotic patients treated with romosozumab?
I. R. Reid
Expert Opinion on Drug Safety.2022; 21(12): 1441. CrossRef - Proxied Therapeutic Inhibition on Wnt Signaling Antagonists and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: Multi-Omics Analyses
Yu Qian, Cheng-Da Yuan, Saber Khederzadeh, Ming-Yu Han, Hai-Xia Liu, Mo-Chang Qiu, Jian-Hua Gao, Wei-Lin Wang, Yun-Piao Hou, Guo-Bo Chen, Ke-Qi Liu, Lin Xu, David Karasik, Shu-Yang Xie, Hou-Feng Zheng
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Multi-Omics Analyses Identify Pleiotropy and Causality Between Circulating Sclerostin and Atrial Fibrillation
Yu Qian, Peng-Lin Guan, Saber Khederzadeh, Ke-Qi Liu, Cheng-Da Yuan, Ming-Yu Han, Hai-Xia Liu, Mo-Chang Qiu, Jian-Hua Gao, Wei-Lin Wang, Yun-Piao Hou, Guo-Bo Chen, Lin Xu, David Karasik, Shu-Yang Xie, sheng zhifeng, Hou-Feng Zheng
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- A pharmacovigilance analysis of FDA adverse event reporting system events for romosozumab


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



