Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Endocrine Research
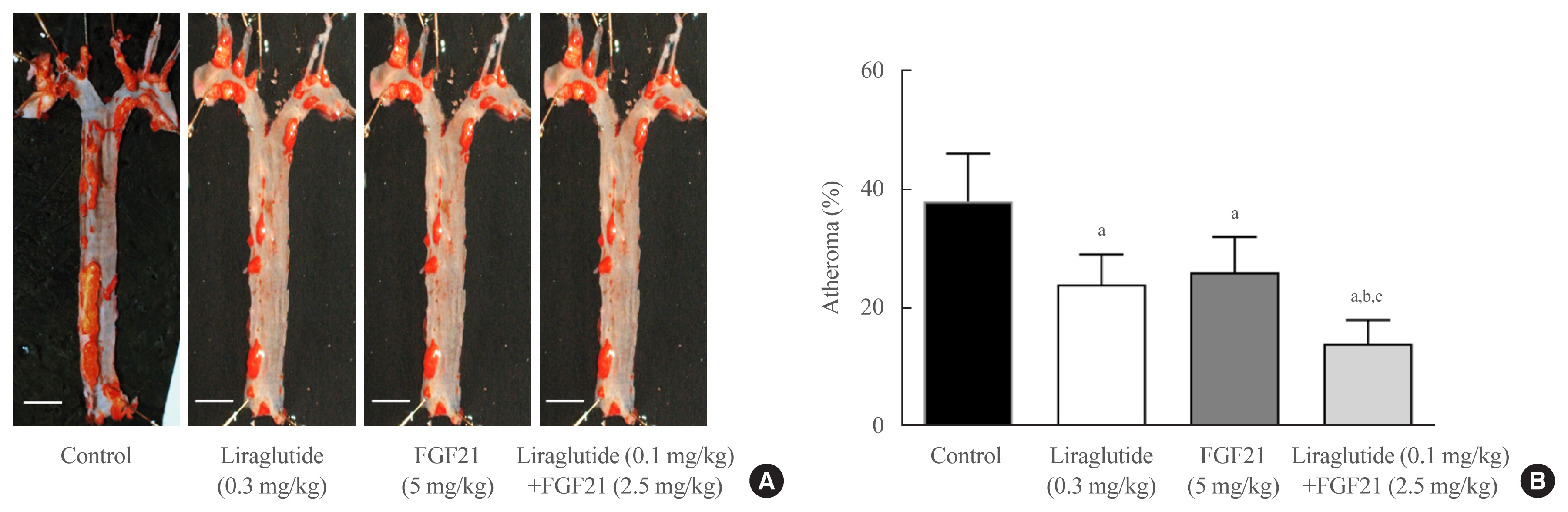
- Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Analogue and Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Combination on the Atherosclerosis-Related Process in a Type 2 Diabetes Mouse Model
- Jin Hee Kim, Gha Young Lee, Hyo Jin Maeng, Hoyoun Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyoung Min Kim, Soo Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):157-170. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.781
- 6,839 View
- 175 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogues regulate glucose homeostasis and have anti-inflammatory properties, but cause gastrointestinal side effects. The fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a hormonal regulator of lipid and glucose metabolism that has poor pharmacokinetic properties, including a short half-life. To overcome these limitations, we investigated the effect of a low-dose combination of a GLP-1 analogue and FGF21 on atherosclerosis-related molecular pathways.
Methods
C57BL/6J mice were fed a high-fat diet for 30 weeks followed by an atherogenic diet for 10 weeks and were divided into four groups: control (saline), liraglutide (0.3 mg/kg/day), FGF21 (5 mg/kg/day), and low-dose combination treatment with liraglutide (0.1 mg/kg/day) and FGF21 (2.5 mg/kg/day) (n=6/group) for 6 weeks. The effects of each treatment on various atherogenesisrelated pathways were assessed.
Results
Liraglutide, FGF21, and their low-dose combination significantly reduced atheromatous plaque in aorta, decreased weight, glucose, and leptin levels, and increased adiponectin levels. The combination treatment upregulated the hepatic uncoupling protein-1 (UCP1) and Akt1 mRNAs compared with controls. Matric mentalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) were downregulated and phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) and phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (p-ERK) were upregulated in liver of the liraglutide-alone and combination-treatment groups. The combination therapy also significantly decreased the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Caspase-3 was increased, whereas MMP-9, ICAM-1, p-Akt, and p-ERK1/2 were downregulated in the liraglutide-alone and combination-treatment groups.
Conclusion
Administration of a low-dose GLP-1 analogue and FGF21 combination exerts beneficial effects on critical pathways related to atherosclerosis, suggesting the synergism of the two compounds. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current status and future perspectives of FGF21 analogues in clinical trials
Zara Siu Wa Chui, Qing Shen, Aimin Xu
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Design and pharmaceutical evaluation of bifunctional fusion protein of FGF21 and GLP-1 in the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Xianlong Ye, Yingli Chen, Jianying Qi, Shenglong Zhu, Yuanyuan Wu, Jingjing Xiong, Fei Hu, Zhimou Guo, Xinmiao Liang
European Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 952: 175811. CrossRef - Use of FGF21 analogs for the treatment of metabolic disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Maria Paula Carbonetti, Fernanda Almeida-Oliveira, David Majerowicz
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the potential mechanism of Simiao Yongan decoction in the treatment of diabetic peripheral vascular disease based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology
Fang Cao, Yongkang Zhang, Yuan Zong, Xia Feng, Junlin Deng, Yuzhen Wang, Yemin Cao
Medicine.2023; 102(52): e36762. CrossRef - The Healing Capability of Clove Flower Extract (CFE) in Streptozotocin-Induced (STZ-Induced) Diabetic Rat Wounds Infected with Multidrug Resistant Bacteria
Rewaa Ali, Tarek Khamis, Gamal Enan, Gamal El-Didamony, Basel Sitohy, Gamal Abdel-Fattah
Molecules.2022; 27(7): 2270. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) and Atherosclerosis: Explaining Their Pathophysiology, Association and the Role of Incretin-Based Drugs
Eleftheria Galatou, Elena Mourelatou, Sophia Hatziantoniou, Ioannis S. Vizirianakis
Antioxidants.2022; 11(6): 1060. CrossRef - Unlocking the Therapeutic Potential of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Analogue and Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Combination for the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis in Type 2 Diabetes
Jang Won Son
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(1): 57. CrossRef - Effects of fasting on skeletal muscles and body fat of adult and old C57BL/6J mice
Mindaugas Kvedaras, Petras Minderis, Leonardo Cesanelli, Agne Cekanauskaite, Aivaras Ratkevicius
Experimental Gerontology.2021; 152: 111474. CrossRef - The Role of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Diabetic Cardiovascular Complications and Related Epigenetic Mechanisms
Mengjie Xiao, Yufeng Tang, Shudong Wang, Jie Wang, Jie Wang, Yuanfang Guo, Jingjing Zhang, Junlian Gu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Liraglutide Decreases Liver Fat Content and Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Levels in Newly Diagnosed Overweight Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Xinyue Li, Xiaojuan Wu, Yumei Jia, Jing Fu, Lin Zhang, Tao Jiang, Jia Liu, Guang Wang, Claudia Cardoso
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Differential importance of endothelial and hematopoietic cell GLP-1Rs for cardiometabolic versus hepatic actions of semaglutide
Brent A. McLean, Chi Kin Wong, Kiran Deep Kaur, Randy J. Seeley, Daniel J. Drucker
JCI Insight.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Current status and future perspectives of FGF21 analogues in clinical trials

- Bone Metabolism
- Association between Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Levels and Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women
- Hoon Sung Choi, Hyang Ah Lee, Sang-Wook Kim, Eun-Hee Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(2):273-277. Published online June 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.2.273
- 3,512 View
- 51 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Despite the beneficial effect of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) on metabolic disease, there are concerns about adverse effects on bone metabolism, supported by animal studies. However, a recent human study showed the positive association between serum FGF21 level and bone mineral density (BMD) in healthy premenopausal women. We undertook this study to examine the association between FGF21 level and BMD in healthy postmenopausal Korean women who are susceptible to osteoporosis.
Methods We used data of 115 participants from a cohort of healthy postmenopausal women (>50 years old) to examine the association between serum FGF21 level and BMD. The clinical characteristics were obtained from the participants, and blood testing and serum FGF21 testing were undertaken. BMD of the lumbar spine, femoral neck and total hip area, and bone markers were used in the analyses.
Results The mean age of the participants was 60.2±7.2 years. Serum FGF21 levels showed negative correlation with BMD and T-scores in all three areas, but there were no statistically significant differences. Multivariate analyses with adjustment for age and body mass index also did not show significant association between serum FGF21 level and BMD. In addition, serum FGF21 level also showed no correlation with osteocalcin and C-telopeptide levels.
Conclusion In our study, serum FGF21 level showed no significant correlation with BMD and T-scores.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fibroblast growth factor 21 and bone homeostasis
Yan Tang, Mei Zhang
Biomedical Journal.2023; 46(4): 100548. CrossRef - FGF21 negatively affects long-term female fertility in mice
Beat Moeckli, Thuy-Vy Pham, Florence Slits, Samuel Latrille, Andrea Peloso, Vaihere Delaune, Graziano Oldani, Stéphanie Lacotte, Christian Toso
Heliyon.2022; 8(11): e11490. CrossRef - Potential role of fibroblast growth factor 21 in the deterioration of bone quality in impaired glucose tolerance
D. T. W. Lui, C. H. Lee, V. W. K. Chau, C. H. Y. Fong, K. M. Y. Yeung, J. K. Y. Lam, A. C. H. Lee, W. S. Chow, K. C. B. Tan, Y. C. Woo, K. S. L. Lam
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2021; 44(3): 523. CrossRef - Skeletal Muscle and Bone – Emerging Targets of Fibroblast Growth Factor-21
Hui Sun, Matthew Sherrier, Hongshuai Li
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Age‐related bone loss is associated with FGF21 but not IGFBP1 in healthy adults
Shuen Yee Lee, Kai Deng Fam, Kar Ling Chia, Margaret M. C. Yap, Jorming Goh, Kwee Poo Yeo, Eric P. H. Yap, Sanjay H. Chotirmall, Chin Leong Lim
Experimental Physiology.2020; 105(4): 622. CrossRef - Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with Increased Plasma Levels of Fibroblast Growth Factors 19 and 21
Małgorzata Marchelek-Myśliwiec, Violetta Dziedziejko, Monika Nowosiad-Magda, Katarzyna Dołęgowska, Barbara Dołęgowska, Andrzej Pawlik, Krzysztof Safranow, Magda Wiśniewska, Joanna Stępniewska, Maciej Domański, Kazimierz Ciechanowski
Kidney and Blood Pressure Research.2019; 44(5): 1207. CrossRef
- Fibroblast growth factor 21 and bone homeostasis

- Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Mimetics for Treating Atherosclerosis
- Kelvin H. M. Kwok, Karen S. L. Lam
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(2):145-151. Published online May 19, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.2.145
- 4,181 View
- 43 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is an atypical member of the FGF family. Acting in an endocrine fashion, it increases glucose uptake, modulates lipid metabolism, and sensitizes insulin response in metabolically active organs, including the liver and adipose tissue. Emerging evidence shows a strong correlation between circulating FGF21 levels and the incidence and severity of atherosclerosis. Animal studies have demonstrated a beneficial role of FGF21 in protecting against aberrant lipid profile, while recent development in FGF21 mimetics has provided further insight into the lipid-lowering effects of FGF21 signaling. The present review summarizes the physiological roles of FGF21, and discusses major breakthroughs and limitations of FGF21 mimetic-based therapeutic strategies for treating atherosclerosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Higher fasting fibroblast growth factor 21 was associated with a greater decline in postprandial blood pressure
Jane Yu Ying Ong, Kaveri Pathak, Yun Zhao, Emily Calton, Christopher M. Reid, Mario J. Soares
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(2): 102720. CrossRef - Potential role of fibroblast growth factor 21 in the deterioration of bone quality in impaired glucose tolerance
D. T. W. Lui, C. H. Lee, V. W. K. Chau, C. H. Y. Fong, K. M. Y. Yeung, J. K. Y. Lam, A. C. H. Lee, W. S. Chow, K. C. B. Tan, Y. C. Woo, K. S. L. Lam
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2021; 44(3): 523. CrossRef - FGF21 induces autophagy‐mediated cholesterol efflux to inhibit atherogenesis via RACK1 up‐regulation
Lin Xiaolong, Guo Dongmin, Mihua Liu, Wang Zuo, Hu Huijun, Tan Qiufen, Hu XueMei, Lin Wensheng, Pan Yuping, Lin Jun, Zeng Zhaolin
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine.2020; 24(9): 4992. CrossRef - Two-hundred-liter scale fermentation, purification of recombinant human fibroblast growth factor-21, and its anti-diabetic effects on ob/ob mice
Qi Hui, Zhen Huang, Shucai Pang, Xuanxin Yang, Jinghang Li, Bingjie Yu, Lu Tang, Xiaokun Li, Xiaojie Wang
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology.2019; 103(2): 719. CrossRef - Protection Effect of Exogenous Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 on the Kidney Injury in Vascular Calcification Rats
Yu-Chen Shi, Wei-Wei Lu, Yue-Long Hou, Kun Fu, Feng Gan, Shu-Juan Cheng, Shao-Ping Wang, Yong-Fen Qi, Jing-Hua Liu
Chinese Medical Journal.2018; 131(5): 532. CrossRef
- Higher fasting fibroblast growth factor 21 was associated with a greater decline in postprandial blood pressure

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Novel Molecules Regulating Energy Homeostasis: Physiology and Regulation by Macronutrient Intake and Weight Loss
- Anna Gavrieli, Christos S. Mantzoros
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(3):361-372. Published online July 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.3.361
- 4,522 View
- 48 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Excess energy intake, without a compensatory increase of energy expenditure, leads to obesity. Several molecules are involved in energy homeostasis regulation and new ones are being discovered constantly. Appetite regulating hormones such as ghrelin, peptide tyrosine-tyrosine and amylin or incretins such as the gastric inhibitory polypeptide have been studied extensively while other molecules such as fibroblast growth factor 21, chemerin, irisin, secreted frizzle-related protein-4, total bile acids, and heme oxygenase-1 have been linked to energy homeostasis regulation more recently and the specific role of each one of them has not been fully elucidated. This mini review focuses on the above mentioned molecules and discusses them in relation to their regulation by the macronutrient composition of the diet as well as diet-induced weight loss.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extracts of Dunkelfelder Grape Seeds and Peel Increase the Metabolic Rate and Reduce Fat Deposition in Mice Maintained on a High-Fat Diet
Chenlu Yang, Xuelin Tian, Yulei Han, Xueqing Shi, Hua Wang, Hua Li
Foods.2023; 12(17): 3251. CrossRef - Insulin Resistance and Glucose Metabolism during Infection
Borros Arneth
Endocrines.2023; 4(4): 685. CrossRef - CMKLR1 senses chemerin/resolvin E1 to control adipose thermogenesis and modulate metabolic homeostasis
Zewei Zhao, Siqi Liu, Bingxiu Qian, Lin Zhou, Jianglin Shi, Junxi Liu, Lin Xu, Zhonghan Yang
Fundamental Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dissecting biological activities of fibroblast growth factor receptors by the coiled-coil-mediated oligomerization of FGF1
Natalia Porebska, Marta Pozniak, Mateusz Adam Krzyscik, Agata Knapik, Aleksandra Czyrek, Marika Kucinska, Kamil Jastrzebski, Malgorzata Zakrzewska, Jacek Otlewski, Lukasz Opalinski
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2021; 180: 470. CrossRef - Oral Semaglutide, the First Ingestible Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist: Could It Be a Magic Bullet for Type 2 Diabetes?
Hwi Seung Kim, Chang Hee Jung
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(18): 9936. CrossRef - Serum interleukin 15 in anorexia nervosa: Comparison to normal weight and obese girls
Wojciech Roczniak, Agata Mikołajczak-Będkowska, Elżbieta Świętochowska, Zofia Ostrowska, Katarzyna Ziora, Sylwia Balcerowicz, Karolina Górska-Flak, Magdalena Milan, Joanna Oświęcimska
The World Journal of Biological Psychiatry.2020; 21(3): 203. CrossRef - Physiology of energy homeostasis: Models, actors, challenges and the glucoadipostatic loop
Didier Chapelot, Keyne Charlot
Metabolism.2019; 92: 11. CrossRef - Correlates of zinc finger BED domain-containing protein 3 and ghrelin in metabolic syndrome patients with and without prediabetes
Rawan AbuZayed, Nailya Bulatova, Violet Kasabri, Maysa Suyagh, Lana Halaseh, Sundus AlAlawi
Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Pharmacotherapy of obesity: Available medications and drugs under investigation
Eleni Pilitsi, Olivia M. Farr, Stergios A. Polyzos, Nikolaos Perakakis, Eric Nolen-Doerr, Aimilia-Eirini Papathanasiou, Christos S. Mantzoros
Metabolism.2019; 92: 170. CrossRef - Link between chemerin, central obesity, and parameters of the Metabolic Syndrome: findings from a longitudinal study in obese children participating in a lifestyle intervention
Petra Niklowitz, Juliane Rothermel, Nina Lass, Andre Barth, Thomas Reinehr
International Journal of Obesity.2018; 42(10): 1743. CrossRef - The relationship between the leptin/ghrelin ratio and meals with various macronutrient contents in men with different nutritional status: a randomized crossover study
Edyta Adamska-Patruno, Lucyna Ostrowska, Joanna Goscik, Barbara Pietraszewska, Adam Kretowski, Maria Gorska
Nutrition Journal.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The Science of Obesity Management: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement
George A Bray, William E Heisel, Ashkan Afshin, Michael D Jensen, William H Dietz, Michael Long, Robert F Kushner, Stephen R Daniels, Thomas A Wadden, Adam G Tsai, Frank B Hu, John M Jakicic, Donna H Ryan, Bruce M Wolfe, Thomas H Inge
Endocrine Reviews.2018; 39(2): 79. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Weight loss technology for people with treated type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial
Kuat Oshakbayev, Bibazhar Dukenbayeva, Gulnar Togizbayeva, Aigul Durmanova, Meruyert Gazaliyeva, Abdul Sabir, Aliya Issa, Alisher Idrisov
Nutrition & Metabolism.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Salivary, gingival crevicular fluid and serum levels of ghrelin and chemerin in patients with periodontitis and overweight
H. F. R. Jentsch, N. Arnold, V. Richter, J. Deschner, T. Kantyka, S. Eick
Journal of Periodontal Research.2017; 52(6): 1050. CrossRef
- Extracts of Dunkelfelder Grape Seeds and Peel Increase the Metabolic Rate and Reduce Fat Deposition in Mice Maintained on a High-Fat Diet

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Transcriptional Regulation of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Expression
- Kwi-Hyun Bae, Jung-Guk Kim, Keun-Gyu Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(2):105-111. Published online June 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.2.105
- 4,415 View
- 60 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 24 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is an attractive target for treating metabolic disease due to its wide-ranging beneficial effects on glucose and lipid metabolism. Circulating FGF21 levels are increased in insulin-resistant states; however, endogenous FGF21 fails to improve glucose and lipid metabolism in obesity, suggesting that metabolic syndrome is an FGF21-resistant state. Therefore, transcription factors for FGF21 are potential drug targets that could increase FGF21 expression in obesity and reduce FGF21 resistance. Despite many studies on the metabolic effects of FGF21, the transcriptional regulation of FGF21 gene expression remains controversial and is not fully understood. As the FGF21 transcription factor pathway is one of the most promising targets for the treatment of metabolic syndrome, further investigation of FGF21 transcriptional regulation is required.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glucosamine Enhancement of Learning and Memory Functions by Promoting Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Production
Yu-Ming Chao, Hon-Yen Wu, Sin-Huei Yeh, Ding-I Yang, Lu-Shiun Her, Yuh-Lin Wu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(8): 4211. CrossRef - Relationship between FGF21 and drug or nondrug therapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chang Guo, Li Zhao, Yanyan Li, Xia Deng, Guoyue Yuan
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2021; 236(1): 55. CrossRef - Serum fibroblast growth factor 21 levels after out of hospital cardiac arrest are associated with neurological outcome
Pirkka T. Pekkarinen, Markus B. Skrifvars, Ville Lievonen, Pekka Jakkula, Laura Albrecht, Pekka Loisa, Marjaana Tiainen, Ville Pettilä, Matti Reinikainen, Johanna Hästbacka
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Epigenetic Regulation of Processes Related to High Level of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Obese Subjects
Teresa Płatek, Anna Polus, Joanna Góralska, Urszula Raźny, Agnieszka Dziewońska, Agnieszka Micek, Aldona Dembińska-Kieć, Bogdan Solnica, Małgorzata Malczewska-Malec
Genes.2021; 12(2): 307. CrossRef - Nutritional Regulation of Hepatic FGF21 by Dietary Restriction of Methionine
Han Fang, Kirsten P. Stone, Laura A. Forney, Desiree Wanders, Thomas W. Gettys
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Presence of Urinary Ketones according to Metabolic Status and Obesity
Bo-Reum Kim, Jeong Woo Seo, Sang Man Kim, Kyu-Nam Kim, Nam-Seok Joo
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - MS-275 induces hepatic FGF21 expression via H3K18ac-mediated CREBH signal
Qi Zhang, Qin Zhu, Ruyuan Deng, Feiye Zhou, Linlin Zhang, Shushu Wang, Kecheng Zhu, Xiao Wang, Libin Zhou, Qing Su
Journal of Molecular Endocrinology.2019; 62(4): 187. CrossRef - Spontaneous ketonuria and risk of incident diabetes: a 12 year prospective study
Gyuri Kim, Sang-Guk Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Ele Ferrannini, Yong-ho Lee, Nam H. Cho
Diabetologia.2019; 62(5): 779. CrossRef - Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 and the Adaptive Response to Nutritional Challenges
Úrsula Martínez-Garza, Daniel Torres-Oteros, Alex Yarritu-Gallego, Pedro F. Marrero, Diego Haro, Joana Relat
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(19): 4692. CrossRef - Berberine-induced activation of AMPK increases hepatic FGF21 expression via NUR77
Feiye Zhou, Mengyao Bai, Yuqing Zhang, Qin Zhu, Linlin Zhang, Qi Zhang, Shushu Wang, Kecheng Zhu, Yun Liu, Xiao Wang, Libin Zhou
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2018; 495(2): 1936. CrossRef - Practical prospects for boosting hepatic production of the “pro-longevity” hormone FGF21
Mark F. McCarty
Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The regulation of FGF21 gene expression by metabolic factors and nutrients
Anjeza Erickson, Régis Moreau
Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus and Sepsis
Silvia C. Trevelin, Daniela Carlos, Matteo Beretta, João S. da Silva, Fernando Q. Cunha
Shock.2017; 47(3): 276. CrossRef - The U-shaped relationship between fibroblast growth factor 21 and microvascular complication in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chan-Hee Jung, Sang-Hee Jung, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chul-Hee Kim, Sung-Koo Kang, Ji-Oh Mok
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(1): 134. CrossRef - Fibroblast Growth Factor 21—Metabolic Role in Mice and Men
Harald Staiger, Michaela Keuper, Lucia Berti, Martin Hrabě de Angelis, Hans-Ulrich Häring
Endocrine Reviews.2017; 38(5): 468. CrossRef - Anti-inflammatory effects of exercise training in adipose tissue do not require FGF21
Jay W Porter, Joe L Rowles, Justin A Fletcher, Terese M Zidon, Nathan C Winn, Leighton T McCabe, Young-Min Park, James W Perfield, John P Thyfault, R Scott Rector, Jaume Padilla, Victoria J Vieira-Potter
Journal of Endocrinology.2017; 235(2): 97. CrossRef - Hepatic Fgf21 Expression Is Repressed after Simvastatin Treatment in Mice
Panos Ziros, Zoi Zagoriti, George Lagoumintzis, Venetsana Kyriazopoulou, Ralitsa P. Iskrenova, Evagelia I. Habeos, Gerasimos P. Sykiotis, Dionysios V. Chartoumpekis, Ioannis G Habeos, Kostas Pantopoulos
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(9): e0162024. CrossRef - Association between insulin resistance and impairment of FGF21 signal transduction in skeletal muscles
Ja Young Jeon, Sung-E Choi, Eun Suk Ha, Tae Ho Kim, Jong Gab Jung, Seung Jin Han, Hae Jin Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Yup Kang, Kwan-Woo Lee
Endocrine.2016; 53(1): 97. CrossRef - Fibroblast growth factor 21 deficiency exacerbates chronic alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis and injury
Yanlong Liu, Cuiqing Zhao, Jian Xiao, Liming Liu, Min Zhang, Cuiling Wang, Guicheng Wu, Ming-Hua Zheng, Lan-Man Xu, Yong-Ping Chen, Moosa Mohammadi, Shao-Yu Chen, Matthew Cave, Craig McClain, Xiaokun Li, Wenke Feng
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Organokines on Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, and Atherosclerosis
Kyung Mook Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Physiological and Pharmacological Roles of FGF21 in Cardiovascular Diseases
Peng Cheng, Fangfang Zhang, Lechu Yu, Xiufei Lin, Luqing He, Xiaokun Li, Xuemian Lu, Xiaoqing Yan, Yi Tan, Chi Zhang
Journal of Diabetes Research.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Minireview: Roles of Fibroblast Growth Factors 19 and 21 in Metabolic Regulation and Chronic Diseases
Fangfang Zhang, Lechu Yu, Xiufei Lin, Peng Cheng, Luqing He, Xiaokun Li, Xuemian Lu, Yi Tan, Hong Yang, Lu Cai, Chi Zhang
Molecular Endocrinology.2015; 29(10): 1400. CrossRef - AMP-activated protein kinase suppresses the expression of LXR/SREBP-1 signaling-induced ANGPTL8 in HepG2 cells
Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2015; 414: 148. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- Glucosamine Enhancement of Learning and Memory Functions by Promoting Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Production


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



