Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
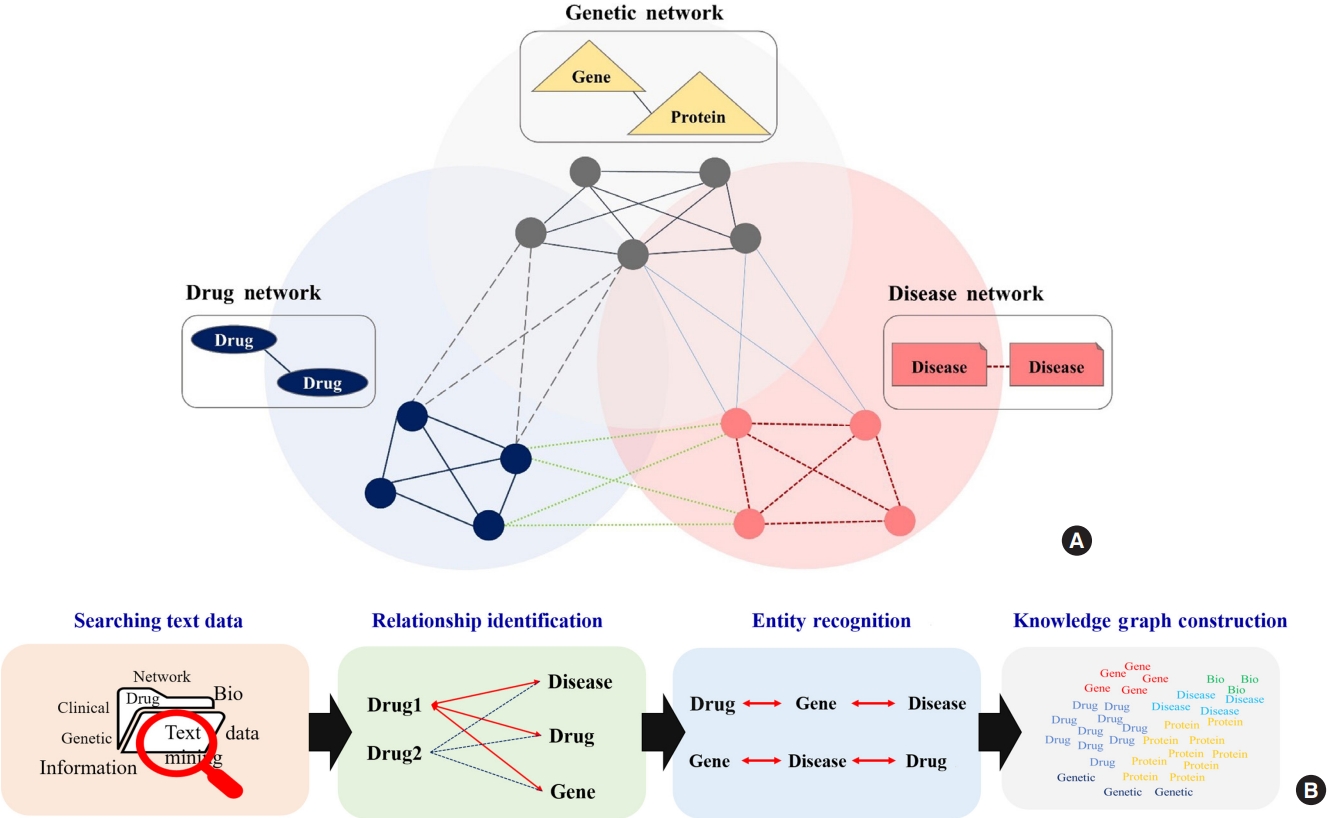
- A Study on Methodologies of Drug Repositioning Using Biomedical Big Data: A Focus on Diabetes Mellitus
- Suehyun Lee, Seongwoo Jeon, Hun-Sung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):195-207. Published online April 13, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1404
- 5,614 View
- 201 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Drug repositioning is a strategy for identifying new applications of an existing drug that has been previously proven to be safe. Based on several examples of drug repositioning, we aimed to determine the methodologies and relevant steps associated with drug repositioning that should be pursued in the future. Reports on drug repositioning, retrieved from PubMed from January 2011 to December 2020, were classified based on an analysis of the methodology and reviewed by experts. Among various drug repositioning methods, the network-based approach was the most common (38.0%, 186/490 cases), followed by machine learning/deep learningbased (34.3%, 168/490 cases), text mining-based (7.1%, 35/490 cases), semantic-based (5.3%, 26/490 cases), and others (15.3%, 75/490 cases). Although drug repositioning offers several advantages, its implementation is curtailed by the need for prior, conclusive clinical proof. This approach requires the construction of various databases, and a deep understanding of the process underlying repositioning is quintessential. An in-depth understanding of drug repositioning could reduce the time, cost, and risks inherent to early drug development, providing reliable scientific evidence. Furthermore, regarding patient safety, drug repurposing might allow the discovery of new relationships between drugs and diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Present and Future of Artificial Intelligence-Based Medical Image in Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Analytical Methods and Limitations of Clinical Use
Ji-Won Chun, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Present and Future of Artificial Intelligence-Based Medical Image in Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Analytical Methods and Limitations of Clinical Use

Original Article
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Drug Repositioning Using Temporal Trajectories of Accompanying Comorbidities in Diabetes Mellitus
- Namgi Park, Ja Young Jeon, Eugene Jeong, Soyeon Kim, Dukyong Yoon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):65-73. Published online February 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1275

- 3,784 View
- 164 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Most studies of systematic drug repositioning have used drug-oriented data such as chemical structures, gene expression patterns, and adverse effect profiles. As it is often difficult to prove repositioning candidates’ effectiveness in real-world clinical settings, we used patient-centered real-world data for screening repositioning candidate drugs for multiple diseases simultaneously, especially for diabetic complications.
Methods
Using the National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort (2002 to 2013), we analyzed claims data of 43,048 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (age ≥40 years). To find repositioning candidate disease-drug pairs, a nested case-control study was used for 29 pairs of diabetic complications and the drugs that met our criteria. To validate this study design, we conducted an external validation for a selected candidate pair using electronic health records.
Results
We found 24 repositioning candidate disease-drug pairs. In the external validation study for the candidate pair cerebral infarction and glycopyrrolate, we found that glycopyrrolate was associated with decreased risk of cerebral infarction (hazard ratio, 0.10; 95% confidence interval, 0.02 to 0.44).
Conclusion
To reduce risks of diabetic complications, it would be possible to consider these candidate drugs instead of other drugs, given the same indications. Moreover, this methodology could be applied to diseases other than diabetes to discover their repositioning candidates, thereby offering a new approach to drug repositioning. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Drug Repositioning: Exploring New Indications for Existing Drug-Disease Relationships
Hun-Sung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 62. CrossRef
- Drug Repositioning: Exploring New Indications for Existing Drug-Disease Relationships


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



