Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Role of TRPV4 Channel in Human White Adipocytes Metabolic Activity
- Julio C. Sánchez, Aníbal Valencia-Vásquez, Andrés M. García
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):997-1006. Published online October 14, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1167

- 3,639 View
- 122 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Intracellular calcium (Ca2+) homeostasis plays an essential role in adipocyte metabolism and its alteration is associated with obesity and related disorders. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) channels are an important Ca2+ pathway in adipocytes and their activity is regulated by metabolic mediators such as insulin. In this study, we evaluated the role of TRPV4 channels in metabolic activity and adipokine secretion in human white adipocytes.
Methods
Human white adipocytes were freshly cultured and the effects of the activation and inhibition of TRPV4 channels on lipolysis, glucose uptake, lactate production, and leptin and adiponectin secretion were evaluated.
Results
Under basal and isoproterenol-stimulated conditions, TRPV4 activation by GSK1016709A decreased lipolysis whereas HC067047, an antagonist, increased lipolysis. The activation of TRPV4 resulted in increased glucose uptake and lactate production under both basal conditions and insulin-stimulated conditions; in contrast HC067047 decreased both parameters. Leptin production was increased, and adiponectin production was diminished by TRPV4 activation and its inhibition had the opposite effect.
Conclusion
Our results suggested that TRPV4 channels are metabolic mediators involved in proadipogenic processes and glucose metabolism in adipocyte biology. TRPV4 channels could be a potential pharmacological target to treat metabolic disorders. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Obesity, bone marrow adiposity, and leukemia: Time to act
Vijay Kumar, John H. Stewart
Obesity Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - TRP channels associated with macrophages as targets for the treatment of obese asthma
Wenzhao Zhu, Dinxi Bai, Wenting Ji, Jing Gao
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Multidisciplinary Advances Address the Challenges in Developing Drugs against Transient Receptor Potential Channels to Treat Metabolic Disorders
Yibing Wang
ChemMedChem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Ion channels regulate energy homeostasis and the progression of metabolic disorders: Novel mechanisms and pharmacology of their modulators
Wenyi Wu, Jianan Zheng, Ru Wang, Yibing Wang
Biochemical Pharmacology.2023; 218: 115863. CrossRef - Potential lipolytic regulators derived from natural products as effective approaches to treat obesity
Xi-Ding Yang, Xing-Cheng Ge, Si-Yi Jiang, Yong-Yu Yang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Adipokines: Deciphering the cardiovascular signature of adipose tissue
Joseph C. Galley, Shubhnita Singh, Wanessa M.C. Awata, Juliano V. Alves, Thiago Bruder-Nascimento
Biochemical Pharmacology.2022; 206: 115324. CrossRef
- Obesity, bone marrow adiposity, and leukemia: Time to act

- Obesity and Metabolism
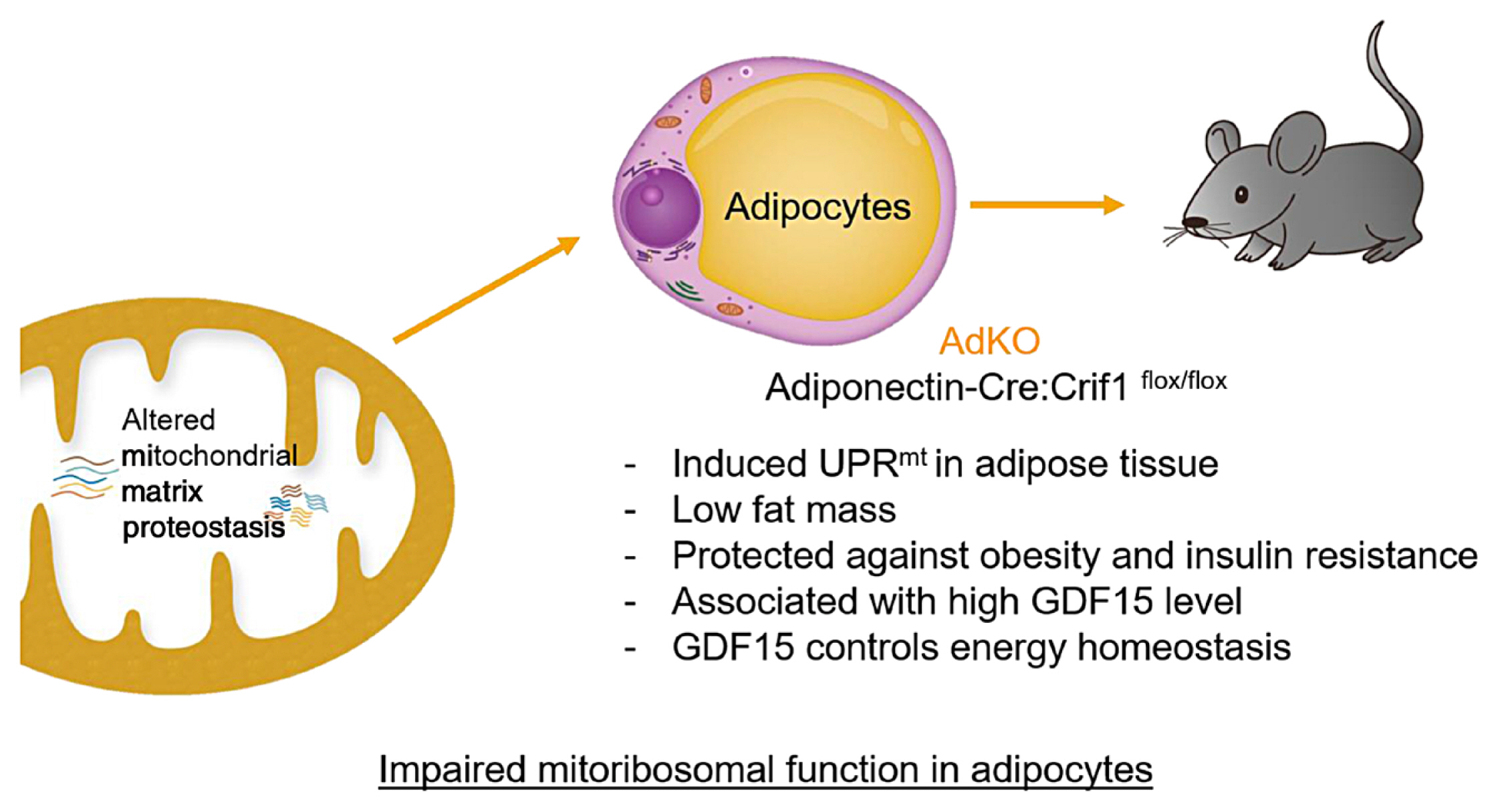
- Cellular and Intercellular Homeostasis in Adipose Tissue with Mitochondria-Specific Stress
- Min Jeong Choi, Saet-Byel Jung, Joon Young Chang, Minho Shong
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):1-11. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.956
- 5,487 View
- 228 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Paracrine interactions are imperative for the maintenance of adipose tissue intercellular homeostasis, and intracellular organelle dysfunction results in local and systemic alterations in metabolic homeostasis. It is currently accepted that mitochondrial proteotoxic stress activates the mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) in vitro and in vivo. The induction of mitochondrial chaperones and proteases during the UPRmt is a key cell-autonomous mechanism of mitochondrial quality control. The UPRmt also affects systemic metabolism through the secretion of cell non-autonomous peptides and cytokines (hereafter, metabokines). Mitochondrial function in adipose tissue plays a pivotal role in whole-body metabolism and human diseases. Despite continuing interest in the role of the UPRmt and quality control pathways of mitochondria in energy metabolism, studies on the roles of the UPRmt and metabokines in white adipose tissue are relatively sparse. Here, we describe the role of the UPRmt in adipose tissue, including adipocytes and resident macrophages, and the interactive roles of cell non-autonomous metabokines, particularly growth differentiation factor 15, in local adipose cellular homeostasis and systemic energy metabolism.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mitochondrial stress-induced GFRAL signaling controls diurnal food intake and anxiety-like behavior
Carla Igual Gil, Bethany M Coull, Wenke Jonas, Rachel N Lippert, Susanne Klaus, Mario Ost
Life Science Alliance.2022; 5(11): e202201495. CrossRef - Stress-induced FGF21 and GDF15 in obesity and obesity resistance
Susanne Keipert, Mario Ost
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 32(11): 904. CrossRef
- Mitochondrial stress-induced GFRAL signaling controls diurnal food intake and anxiety-like behavior

- Endocrine Research
- The Effects of High Fat Diet and Resveratrol on Mitochondrial Activity of Brown Adipocytes
- Cheol Ryong Ku, Yoon Hee Cho, Zhen-Yu Hong, Ha Lee, Sue Ji Lee, Seung-soo Hong, Eun Jig Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(2):328-335. Published online April 8, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.2.328
- 4,145 View
- 50 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 25 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Resveratrol (RSV) is a polyphenolic phytoalexin that has many effects on metabolic diseases such as diabetes and obesity. Given the importance of brown adipose tissue (BAT) for energy expenditure, we investigated the effects of RSV on brown adipocytes.
Methods For the
in vitro study, interscapular BAT was isolated from 7-week-old male Sprague Dawley rats. For thein vivo study, 7-week-old male Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats were divided into four groups and treated for 27 weeks with: standard diet (SD); SD+RSV (10 mg/kg body weight, daily); high fat diet (HFD); HFD+RSV. RSV was provided via oral gavage once daily during thein vivo experiments.Results RSV treatment of primary cultured brown preadipocytes promoted mitochondrial activity, along with over-expression of estrogen receptor α (ER-α). In OLETF rats, both HFD and RSV treatment increased the weight of BAT and the differentiation of BAT. However, only RSV increased the mitochondrial activity and ER-α expression of BAT in the HFD-fed group. Finally, RSV improved the insulin sensitivity of OLETF rats by increasing the mitochondrial activity of BAT, despite having no effects on white adipocytes and muscles in either diet group.
Conclusion RSV could improve insulin resistance, which might be associated with mitochondrial activity of brown adipocyte. Further studies evaluating the activity of RSV for both the differentiation and mitochondrial activity of BAT could be helpful in investigating the effects of RSV on metabolic parameters.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Natural Bioactive Compounds from Foods Inhibited Pigmentation Especially Potential Application of Fucoxanthin to Chloasma: a Mini-Review
Yida Wang, Hang Qi
Food Reviews International.2024; 40(1): 20. CrossRef - Resveratrol combats chronic diseases through enhancing mitochondrial quality
Weichu Tao, Hu Zhang, Xia Jiang, Ning Chen
Food Science and Human Wellness.2024; 13(2): 597. CrossRef - The Potential to Fight Obesity with Adipogenesis Modulating Compounds
Jiaqi Zhao, Ailin Zhou, Wei Qi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(4): 2299. CrossRef - Macrophage and Adipocyte Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Obesity-Induced Metabolic Diseases
Liwen Wang, Jie Hu, Haiyan Zhou
The World Journal of Men's Health.2021; 39(4): 606. CrossRef - Precision Nutrition to Activate Thermogenesis as a Complementary Approach to Target Obesity and Associated-Metabolic-Disorders
Marina Reguero, Marta Gómez de Cedrón, Sonia Wagner, Guillermo Reglero, José Carlos Quintela, Ana Ramírez de Molina
Cancers.2021; 13(4): 866. CrossRef - Natural Antioxidant Application on Fat Accumulation: Preclinical Evidence
Proshanta Roy, Daniele Tomassoni, Enea Traini, Ilenia Martinelli, Maria Vittoria Micioni Di Bonaventura, Carlo Cifani, Francesco Amenta, Seyed Khosrow Tayebati
Antioxidants.2021; 10(6): 858. CrossRef - Activation of Brown Adipose Tissue and Promotion of White Adipose Tissue Browning by Plant-based Dietary Components in Rodents: A Systematic Review
Francisco J Osuna-Prieto, Borja Martinez-Tellez, Antonio Segura-Carretero, Jonatan R Ruiz
Advances in Nutrition.2021; 12(6): 2147. CrossRef - Role of Dietary Polyphenols in Adipose Tissue Browning: A Narrative Review
Juan Salazar, Clímaco Cano, José L. Pérez, Ana Castro, María P. Díaz, Bermary Garrido, Rubén Carrasquero, Maricarmen Chacín, Manuel Velasco, Luis D´Marco, Joselyn Rojas-Quintero, Valmore Bermúdez
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2020; 26(35): 4444. CrossRef - Brown and Brite: The Fat Soldiers in the Anti-obesity Fight
Shireesh Srivastava, Richard L. Veech
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of resveratrol on adipokines and myokines involved in fat browning: Perspectives in healthy weight against obesity
Oh Yoen Kim, Ji Yeon Chung, Juhyun Song
Pharmacological Research.2019; 148: 104411. CrossRef - Ginsenoside Rb2 Alleviates Obesity by Activation of Brown Fat and Induction of Browning of White Fat
Yilian Hong, Yi Lin, Qiya Si, Lijuan Yang, Weisong Dong, Xuejiang Gu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Programming of the Beige Phenotype in White Adipose Tissue of Adult Mice by Mild Resveratrol and Nicotinamide Riboside Supplementations in Early Postnatal Life
Alba Serrano, Madhu Asnani-Kishnani, Ana María Rodríguez, Andreu Palou, Joan Ribot, María Luisa Bonet
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Polyphenols on Thermogenesis and Mitochondrial Biogenesis
Tanila Wood dos Santos, Quélita Cristina Pereira, Lucimara Teixeira, Alessandra Gambero, Josep A. Villena, Marcelo Lima Ribeiro
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(9): 2757. CrossRef - Programming mediated by fatty acids affects uncoupling protein 1 (UCP-1) in brown adipose tissue
Perla P. Argentato, Helena de Cássia César, Débora Estadella, Luciana P. Pisani
British Journal of Nutrition.2018; 120(6): 619. CrossRef - Effects of Genistein on Differentiation and Viability of Human Visceral Adipocytes
Elena Grossini, Serena Farruggio, Giulia Raina, David Mary, Giacomo Deiro, Sergio Gentilli
Nutrients.2018; 10(8): 978. CrossRef - A comprehensive review of the health perspectives of resveratrol
Abdur Rauf, Muhammad Imran, Hafiz Ansar Rasul Suleria, Bashir Ahmad, Dennis G. Peters, Mohammad S. Mubarak
Food & Function.2017; 8(12): 4284. CrossRef - The Role of Circulating Slit2, the One of the Newly Batokines, in Human Diabetes Mellitus
Yea Eun Kang, Sorim Choung, Ju Hee Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(3): 383. CrossRef - A nutritional perspective on UCP1-dependent thermogenesis
M. Luisa Bonet, Josep Mercader, Andreu Palou
Biochimie.2017; 134: 99. CrossRef - The Beneficial Effects of Quercetin, Curcumin, and Resveratrol in Obesity
Yueshui Zhao, Bo Chen, Jing Shen, Lin Wan, Yinxin Zhu, Tao Yi, Zhangang Xiao
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Antiobesity effects of resveratrol: which tissues are involved?
Alfredo Fernández‐Quintela, Iñaki Milton‐Laskibar, Marcela González, Maria P. Portillo
Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences.2017; 1403(1): 118. CrossRef - Resveratrol attenuates triglyceride accumulation associated with upregulation of Sirt1 and lipoprotein lipase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
Haruki Imamura, Daiji Nagayama, Noriko Ishihara, Syo Tanaka, Rena Watanabe, Yasuhiro Watanabe, Yuta Sato, Takashi Yamaguchi, Noriko Ban, Hidetoshi Kawana, Masahiro Ohira, Kei Endo, Atsuhito Saiki, Kohji Shirai, Ichiro Tatsuno
Molecular Genetics and Metabolism Reports.2017; 12: 44. CrossRef - Resveratrol has dose-dependent effects on DNA fragmentation and mitochondrial activity of ovine secondary follicles cultured in vitro
T.J.S. Macedo, V.R.P. Barros, A.P.O. Monte, B.B. Gouveia, M.É.S. Bezerra, A.Y.P. Cavalcante, R.S. Barberino, V.G. Menezes, M.H.T. Matos
Zygote.2017; 25(4): 434. CrossRef - Response: The Effects of High Fat Diet and Resveratrol on Mitochondrial Activity of Brown Adipocytes (Endocrinol Metab2016;31:328-35, Cheol Ryong Ku et al.)
Cheol Ryong Ku, Eun Jig Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(3): 482. CrossRef - Letter: The Effects of High Fat Diet and Resveratrol on Mitochondrial Activity of Brown Adipocytes (Endocrinol Metab2016;31:328-35, Cheol Ryong Ku et al.)
Ji-Young Cha
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(3): 480. CrossRef
- Natural Bioactive Compounds from Foods Inhibited Pigmentation Especially Potential Application of Fucoxanthin to Chloasma: a Mini-Review

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Attenuates Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Induced Lipolysis via Protection of Perilipin in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
- Seok-Woo Hong, Jinmi Lee, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(4):553-560. Published online December 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.553
- 3,406 View
- 26 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) are known to stimulate and repress lipolysis in adipocytes, respectively; however, the mechanisms regulating these processes have not been completely elucidated.
Methods The key factors and mechanism of action of TNF-α and AMPK in lipolysis were investigated by evaluating perilipin expression and activity of protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK)/eukaryotic initiation factor 2 α (eIF2α) by Western blot and an immunofluorescence assay in 24-hour TNF-α-treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes with artificial manipulation of AMPK activation.
Results Enhancement of AMPK activity by the addition of activator minoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR) suppressed TNF-α-induced lipolysis, whereas the addition of compound C, an inhibitor of AMPK phosphorylation, enhanced lipolysis. Perilipin, a lipid droplet-associated protein, was decreased by TNF-α and recovered following treatment with AICAR, showing a correlation with the antilipolytic effect of AICAR. Significant activation of PERK/eIF2α, a component of the unfolded protein response signaling pathway, was observed in TNF-α or vesicle-treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The antilipolytic effect and recovery of perilipin expression by AICAR in TNF-α-treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes were significantly diminished by treatment with 2-aminopurine, a specific inhibitor of eIF2α.
Conclusion These data indicated that AICAR-induced AMPK activation attenuates TNF-α-induced lipolysis via preservation of perilipin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. In addition, PERK/eIF2α activity is a novel mechanism of the anti-lipolytic effect of AICAR.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dysregulation of Lipid Droplet Protein Expression in Adipose Tissues and Association with Metabolic Risk Factors in Adult Females with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
Chan Yoon Park, Donguk Kim, Min Kyeong Seo, Jimin Kim, Han Choe, Jong-Hyeok Kim, Joon Pio Hong, Yeon Ji Lee, Yoonseok Heo, Hwa Jung Kim, Hye Soon Park, Yeon Jin Jang
The Journal of Nutrition.2023; 153(3): 691. CrossRef - Tschimganidine reduces lipid accumulation through AMPK activation and alleviates high-fat diet-induced metabolic diseases
Min-Seon Hwang, Jung-Hwan Baek, Jun-Kyu Song, In Hye Lee, Kyung-Hee Chun
BMB Reports.2023; 56(4): 246. CrossRef - Acetate stimulates lipogenesis via AMPKα signaling in rabbit adipose-derived stem cells
Lei Liu, Chunyan Fu, Yongxu Liu, Fuchang Li
General and Comparative Endocrinology.2021; 303: 113715. CrossRef - Docosahexaenoic acid-enriched phospholipids and eicosapentaenoic acid-enriched phospholipids inhibit tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes by activating sirtuin 1 pathways
Yu-Hong Yang, Yi-Ming Hao, Xiao-Fang Liu, Xiang Gao, Bao-Zhen Wang, Koretaro Takahashi, Lei Du
Food & Function.2021; 12(11): 4783. CrossRef - Role of the AMPK/ACC Signaling Pathway in TRPP2-Mediated Head and Neck Cancer Cell Proliferation
Kun Li, Lei Chen, Zhangying Lin, Junwei Zhu, Yang Fang, Juan Du, Bing Shen, Kaile Wu, Yehai Liu, Gianmarco Saponaro
BioMed Research International.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - GLUT12 and adipose tissue: Expression, regulation and its relation with obesity in mice
Eva Gil‐Iturbe, José Miguel Arbones‐Mainar, María J. Moreno‐Aliaga, María Pilar Lostao
Acta Physiologica.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Bilobalide Suppresses Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes via the AMPK Signaling Pathway
Su Bu, Chun Ying Yuan, Quan Xue, Ying Chen, Fuliang Cao
Molecules.2019; 24(19): 3503. CrossRef - Sulforaphane induces adipocyte browning and promotes glucose and lipid utilization
Hui Q. Zhang, Shi Y. Chen, An S. Wang, An J. Yao, Jian F. Fu, Jin S. Zhao, Fen Chen, Zu Q. Zou, Xiao H. Zhang, Yu J. Shan, Yong P. Bao
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research.2016; 60(10): 2185. CrossRef - Fyn phosphorylates AMPK to inhibit AMPK activity and AMP-dependent activation of autophagy
Eijiro Yamada, Shuichi Okada, Claire C. Bastie, Manu Vatish, Yasuyo Nakajima, Ryo Shibusawa, Atsushi Ozawa, Jeffrey E. Pessin, Masanobu Yamada
Oncotarget.2016; 7(46): 74612. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- Dysregulation of Lipid Droplet Protein Expression in Adipose Tissues and Association with Metabolic Risk Factors in Adult Females with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Association of Serum Adipocyte-Specific Fatty Acid Binding Protein with Fatty Liver Index as a Predictive Indicator of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Won Seon Jeon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(4):283-287. Published online December 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.4.283
- 3,419 View
- 33 Download
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Adipocyte-specific fatty acid-binding protein (A-FABP) is a cytoplasmic protein expressed in macrophages and adipocytes and it plays a role in insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Recently, the fatty liver index (FLI) was introduced as an indicator of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). In this study, we aimed to investigate the relationship between baseline serum A-FABP levels and FLI after 4 years in apparently healthy subjects.
Methods A total of 238 subjects without a past history of alcoholism or hepatitis were recruited from a medical check-up program. The NAFLD state was evaluated 4 years later in the same subjects using FLI. Fatty liver disease was diagnosed as diffusely increased echogenicity of the hepatic parenchyma compared to the kidneys, vascular blurring, and deep-echo attenuation. NAFLD was defined as subjects with fatty liver and no history of alcohol consumption (>20 g/day).
Results Baseline serum A-FABP levels were significantly associated with FLI after adjustment for age and sex (
P <0.001). The subjects with higher A-FABP levels had a higher mean FLI (P for trend=0.006). After adjusting for age and sex, serum A-FABP levels at baseline were shown to be significantly associated with FLI as a marker of development of NAFLD after 4 years (odds ratio, 2.68; 95% confidence interval, 1.24 to 5.80 for highest tertile vs. lowest tertile;P =0.012).Conclusion This study demonstrated that higher baseline serum A-FABP levels were associated with FLI as a predictive indicator of NAFLD after 4 years of follow-up in healthy Korean adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- FABP4 Expression in Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Is Independently Associated with Circulating Triglycerides in Obesity
Óscar Osorio-Conles, Ainitze Ibarzabal, José María Balibrea, Josep Vidal, Emilio Ortega, Ana de Hollanda
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(3): 1013. CrossRef - Unveiling the Role of the Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 in the Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Juan Moreno-Vedia, Josefa Girona, Daiana Ibarretxe, Lluís Masana, Ricardo Rodríguez-Calvo
Biomedicines.2022; 10(1): 197. CrossRef - Circulating level of fatty acid‐binding protein 4 is an independent predictor of metabolic dysfunction‐associated fatty liver disease in middle‐aged and elderly individuals
Marenao Tanaka, Satoko Takahashi, Yukimura Higashiura, Akiko Sakai, Masayuki Koyama, Shigeyuki Saitoh, Kazuaki Shimamoto, Hirofumi Ohnishi, Masato Furuhashi
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(5): 878. CrossRef - New Insights into Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Coronary Artery Disease: The Liver-Heart Axis
Georgiana-Diana Cazac, Cristina-Mihaela Lăcătușu, Cătălina Mihai, Elena-Daniela Grigorescu, Alina Onofriescu, Bogdan-Mircea Mihai
Life.2022; 12(8): 1189. CrossRef - Association between the liver fat score (LFS) and cardiovascular diseases in the national health and nutrition examination survey 1999–2016
Chun-On Lee, Hang-Long Li, Man-Fung Tsoi, Ching-Lung Cheung, Bernard Man Yung Cheung
Annals of Medicine.2021; 53(1): 1067. CrossRef - Relationship Between Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 and Liver Fat in Individuals at Increased Cardiometabolic Risk
Ricardo Rodríguez-Calvo, Juan Moreno-Vedia, Josefa Girona, Daiana Ibarretxe, Neus Martínez-Micaelo, Jordi Merino, Nuria Plana, Lluis Masana
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Diabetes: An Epidemiological Perspective
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(3): 226. CrossRef - Serum adipocyte fatty acid‐binding protein levels: An indicator of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease in Chinese individuals
Yiting Xu, Xiaojing Ma, Xiaoping Pan, Xingxing He, Yufei Wang, Yuqian Bao
Liver International.2019; 39(3): 568. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Based on Analyses from the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Eun-Jung Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2017; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - The relationship between serum fatty-acid binding protein 4 level and lung function in Korean subjects with normal ventilatory function
Hye-Jeong Park, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Seong Yong Lim, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
BMC Pulmonary Medicine.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Liver fatty acid-binding protein as a diagnostic marker for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Erdem Akbal, Erdem Koçak, Ömer Akyürek, Seyfettin Köklü, Hikmetullah Batgi, Mehmet Şenes
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift.2016; 128(1-2): 48. CrossRef - High‐methionine diets accelerate atherosclerosis by HHcy‐mediated FABP4 gene demethylation pathway via DNMT1 in ApoE−/− mice
An-Ning Yang, Hui-Ping Zhang, Yue Sun, Xiao-Ling Yang, Nan Wang, Guangrong Zhu, Hui Zhang, Hua Xu, Sheng-Chao Ma, Yue Zhang, Gui-Zhong Li, Yue-Xia Jia, Jun Cao, Yi-Deng Jiang
FEBS Letters.2015; 589(24PartB): 3998. CrossRef - Metabolic Health Is More Important than Obesity in the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A 4-Year Retrospective Study
Min-Kyung Lee, Eun-Jung Rhee, Min Chul Kim, Byung Sub Moon, Jeong In Lee, Young Seok Song, Eun Na Han, Hyo Sun Lee, Yoonjeong Son, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(4): 522. CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef - Noninvasive Markers for the Diagnosis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Sang Yong Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2013; 28(4): 280. CrossRef
- FABP4 Expression in Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Is Independently Associated with Circulating Triglycerides in Obesity


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



