Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Inhibition of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 during Serum Deprivation Increases Hepatic Gluconeogenesis via the AMPK/AKT/FOXO Signaling Pathway
- Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Min-Jeong Kim, Yu-Mi Lim, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):98-108. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1786
- 1,404 View
- 80 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) mediates glucose reabsorption in the renal proximal tubules, and SGLT2 inhibitors are used as therapeutic agents for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. This study aimed to elucidate the effects and mechanisms of SGLT2 inhibition on hepatic glucose metabolism in both serum deprivation and serum supplementation states.
Methods
Huh7 cells were treated with the SGLT2 inhibitors empagliflozin and dapagliflozin to examine the effect of SGLT2 on hepatic glucose uptake. To examine the modulation of glucose metabolism by SGLT2 inhibition under serum deprivation and serum supplementation conditions, HepG2 cells were transfected with SGLT2 small interfering RNA (siRNA), cultured in serum-free Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium for 16 hours, and then cultured in media supplemented with or without 10% fetal bovine serum for 8 hours.
Results
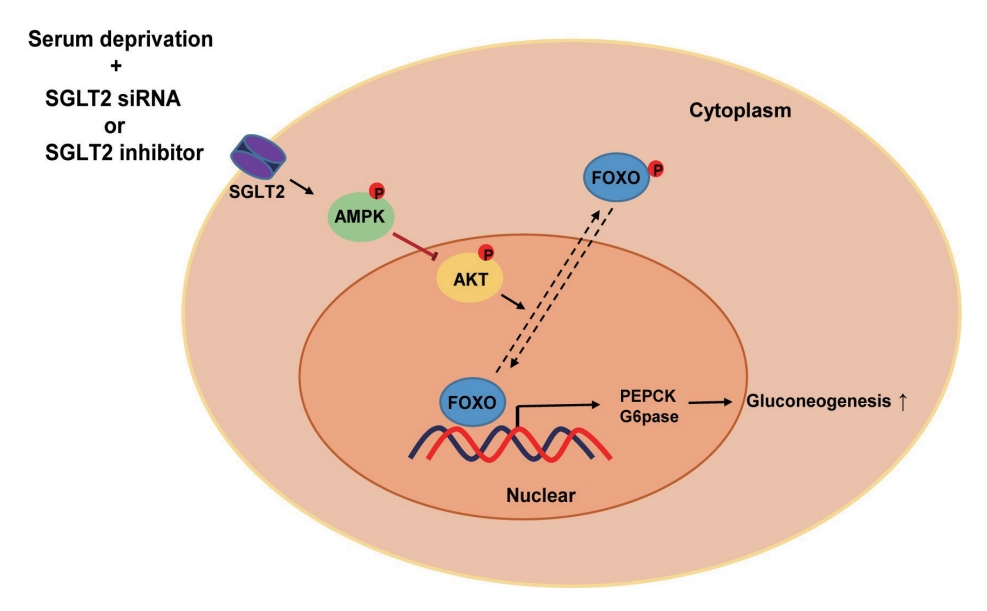
SGLT2 inhibitors dose-dependently decreased hepatic glucose uptake. Serum deprivation increased the expression levels of the gluconeogenesis genes peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma co-activator 1 alpha (PGC-1α), glucose 6-phosphatase (G6pase), and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK), and their expression levels during serum deprivation were further increased in cells transfected with SGLT2 siRNA. SGLT2 inhibition by siRNA during serum deprivation induces nuclear localization of the transcription factor forkhead box class O 1 (FOXO1), decreases nuclear phosphorylated-AKT (p-AKT), and p-FOXO1 protein expression, and increases phosphorylated-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (p-AMPK) protein expression. However, treatment with the AMPK inhibitor, compound C, reversed the reduction in the protein expression levels of nuclear p- AKT and p-FOXO1 and decreased the protein expression levels of p-AMPK and PEPCK in cells transfected with SGLT2 siRNA during serum deprivation.
Conclusion
These data show that SGLT2 mediates glucose uptake in hepatocytes and that SGLT2 inhibition during serum deprivation increases gluconeogenesis via the AMPK/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway.

- Calcium & bone metabolism
- MicroRNA-181a-5p Curbs Osteogenic Differentiation and Bone Formation Partially Through Impairing Runx1-Dependent Inhibition of AIF-1 Transcription
- Jingwei Liu, Xueying Chang, Daming Dong
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):156-173. Published online January 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1516
- 1,586 View
- 101 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Evidence has revealed the involvement of microRNAs (miRNAs) in modulating osteogenic differentiation, implying the promise of miRNA-based therapies for treating osteoporosis. This study investigated whether miR-181a-5p influences osteogenic differentiation and bone formation and aimed to establish the mechanisms in depth.
Methods
Clinical serum samples were obtained from osteoporosis patients, and MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with osteogenic induction medium (OIM) to induce osteogenic differentiation. miR-181a-5p-, Runt-related transcription factor 1 (Runx1)-, and/or allograft inflammatory factor-1 (AIF-1)-associated oligonucleotides or vectors were transfected into MC3T3-E1 cells to explore their function in relation to the number of calcified nodules, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining and activity, expression levels of osteogenesis-related proteins, and apoptosis. Luciferase activity, RNA immunoprecipitation, and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays were employed to validate the binding relationship between miR-181a-5p and Runx1, and the transcriptional regulatory relationship between Runx1 and AIF-1. Ovariectomy (OVX)-induced mice were injected with a miR-181a-5p antagonist for in vivo verification.
Results
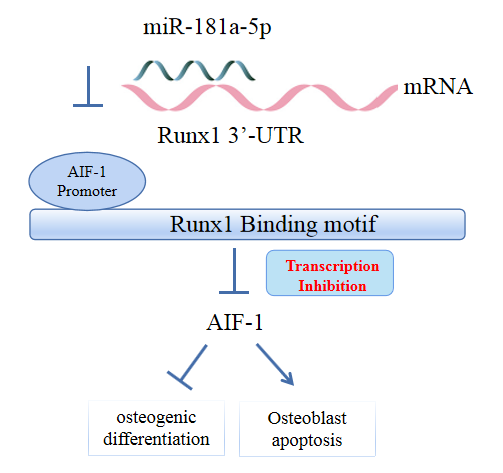
miR-181a-5p was highly expressed in the serum of osteoporosis patients. OIM treatment decreased miR-181a-5p and AIF-1 expression, but promoted Runx1 expression in MC3T-E1 cells. Meanwhile, upregulated miR-181a-5p suppressed OIM-induced increases in calcified nodules, ALP content, and osteogenesis-related protein expression. Mechanically, miR-181a-5p targeted Runx1, which acted as a transcription factor to negatively modulate AIF-1 expression. Downregulated Runx1 suppressed the miR-181a-5p inhibitor-mediated promotion of osteogenic differentiation, and downregulated AIF-1 reversed the miR-181a-5p mimic-induced inhibition of osteogenic differentiation. Tail vein injection of a miR-181a-5p antagonist induced bone formation in OVX-induced osteoporotic mice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, miR-181a-5p affects osteogenic differentiation and bone formation partially via the modulation of the Runx1/AIF-1 axis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Scopolamine regulates the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells through lactylation modification of RUNX2 protein
Ying Wu, Pan Gong
Pharmacology Research & Perspectives.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Scopolamine regulates the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells through lactylation modification of RUNX2 protein

- Thyroid
- The Role of Thyroid Hormone in the Regulation of Cerebellar Development
- Sumiyasu Ishii, Izuki Amano, Noriyuki Koibuchi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):703-716. Published online August 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1150
- 4,508 View
- 170 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
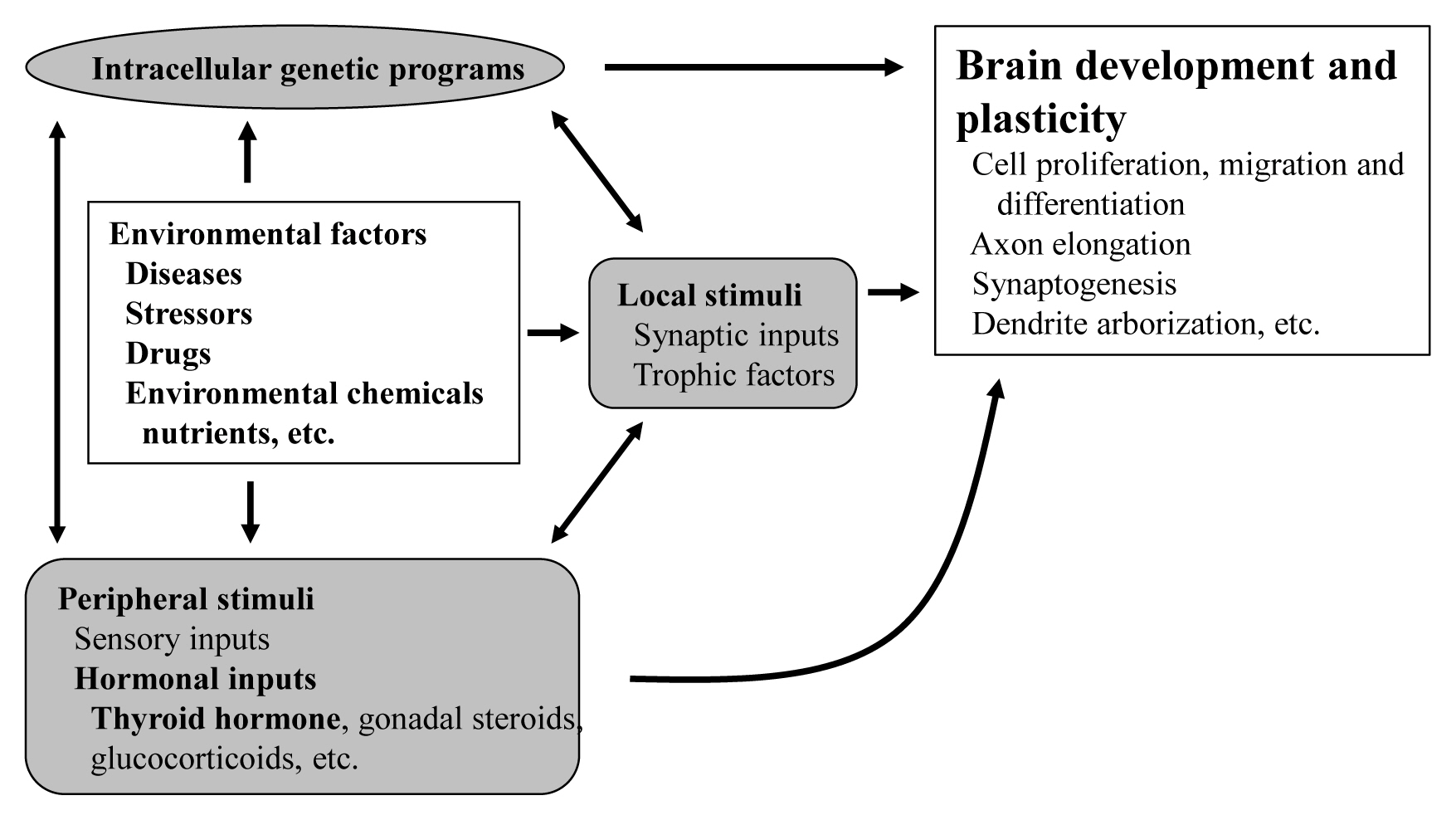
ePub - The proper organized expression of specific genes in time and space is responsible for the organogenesis of the central nervous system including the cerebellum. The epigenetic regulation of gene expression is tightly regulated by an intrinsic intracellular genetic program, local stimuli such as synaptic inputs and trophic factors, and peripheral stimuli from outside of the brain including hormones. Some hormone receptors are expressed in the cerebellum. Thyroid hormones (THs), among numerous circulating hormones, are well-known major regulators of cerebellar development. In both rodents and human, hypothyroidism during the postnatal developmental period results in abnormal morphogenesis or altered function. THs bind to the thyroid hormone receptors (TRs) in the nuclei and with the help of transcriptional cofactors regulate the transcription of target genes. Gene regulation by TR induces cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation, which are necessary for brain development and plasticity. Thus, the lack of TH action mediators may directly cause aberrant cerebellar development. Various kinds of animal models have been established in a bid to study the mechanism of TH action in the cerebellum. Interestingly, the phenotypes differ greatly depending on the models. Herein we summarize the actions of TH and TR particularly in the developing cerebellum.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Neuropeptides and Their Roles in the Cerebellum
Zi-Hao Li, Bin Li, Xiao-Yang Zhang, Jing-Ning Zhu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(4): 2332. CrossRef - Exploring the underlying molecular mechanism of tri(1,3-dichloropropyl) phosphate-induced neurodevelopmental toxicity via thyroid hormone disruption in zebrafish by multi-omics analysis
Ying Xu, Lei Yang, Yanguo Teng, Jian Li, Na Li
Aquatic Toxicology.2023; 258: 106510. CrossRef - Association of Maternal TSH, FT4 With Children's BMI Trajectories, and Obesity: A Birth Cohort Study
Mengting Yang, Shanshan Zhang, Yuzhu Teng, Xue Ru, Linlin Zhu, Yan Han, Xingyong Tao, Hui Cao, Shuangqin Yan, Fangbiao Tao, Kun Huang
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 109(1): e190. CrossRef - Thyroid hormone receptor beta: Relevance in human health and diseases
Ghausiya Rehman, Neha Kumari, Farhad Bano, Rakesh K. Tyagi
Endocrine and Metabolic Science.2023; 13: 100144. CrossRef - Targeting Thyroid Hormone/Thyroid Hormone Receptor Axis: An Attractive Therapy Strategy in Liver Diseases
Qianyu Tang, Min Zeng, Linxi Chen, Nian Fu
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Histone Deacetylase 3 Inhibitor Alleviates Cerebellar Defects in Perinatal Hypothyroid Mice by Stimulating Histone Acetylation and Transcription at Thyroid Hormone-Responsive Gene Loci
Alvin Susetyo, Sumiyasu Ishii, Yuki Fujiwara, Izuki Amano, Noriyuki Koibuchi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(14): 7869. CrossRef - Selection-driven adaptation to the extreme Antarctic environment in the Emperor penguin
Federica Pirri, Lino Ometto, Silvia Fuselli, Flávia A. N. Fernandes, Lorena Ancona, Nunzio Perta, Daniele Di Marino, Céline Le Bohec, Lorenzo Zane, Emiliano Trucchi
Heredity.2022; 129(6): 317. CrossRef - Long-term depression–inductive stimulation causes long-term potentiation in mouse Purkinje cells with a mutant thyroid hormone receptor
Ayane Ninomiya, Izuki Amano, Michifumi Kokubo, Yusuke Takatsuru, Sumiyasu Ishii, Hirokazu Hirai, Nobutake Hosoi, Noriyuki Koibuchi
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Neuropeptides and Their Roles in the Cerebellum

- Clinical Study
- Molecular Correlates and Nuclear Features of Encapsulated Follicular-Patterned Thyroid Neoplasms
- Chan Kwon Jung, Andrey Bychkov, Dong Eun Song, Jang-Hee Kim, Yun Zhu, Zhiyan Liu, Somboon Keelawat, Chiung-Ru Lai, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Kaori Kameyama, Kennichi Kakudo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):123-133. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.860

- 5,108 View
- 150 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Assessing nuclear features is diagnostically challenging in the aspect of thyroid pathology. The aim of this study was to determine whether pathologists could distinguish BRAF-like and RAS-like nuclear features morphologically and identify morphological features to differentiate thyroid tumors with RAS-like mutations from encapsulated papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) with predominant follicular growth and BRAFV600E mutation.
Methods
Representative whole slide images of 16 encapsulated thyroid tumors with predominant follicular growth were reviewed by 12 thyroid pathologists using a web browser-based image viewer. Total nuclear score was calculated from semi-quantitatively scored eight nuclear features. The molecular profile of RAS and BRAF genes was determined by Sanger sequencing.
Results
Total nuclear score ranging 0 to 24 could differentiate BRAF-like tumors from RAS-like tumors with a cut-off value of score 14. The interobserver agreement was the highest for the assessment of nuclear pseudoinclusions (NPIs) but the lowest for nuclear elongation and sickle-shaped nuclei. NPIs were found in tumors with BRAFV600E mutation, but not in tumors with RAS-like mutations. Total nuclear scores were significantly higher for tumors with BRAFV600E than for those with RAS-like mutations (P<0.001).
Conclusion
Our results suggest that NPIs and high nuclear scores have diagnostic utility as rule-in markers for differentiating PTC with BRAFV600E mutation from benign or borderline follicular tumors with RAS-like mutations. Relaxation of rigid criteria for nuclear features resulted in an overdiagnosis of PTC. Immunostaining or molecular testing for BRAFV600E mutation is a useful adjunct for cases with high nuclear scores to identify true PTC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differentiating BRAF V600E- and RAS-like alterations in encapsulated follicular patterned tumors through histologic features: a validation study
Chankyung Kim, Shipra Agarwal, Andrey Bychkov, Jen-Fan Hang, Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Kennichi Kakudo, Somboon Keelawat, Chih-Yi Liu, Zhiyan Liu, Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Chanchal Rana, Huy Gia Vuong, Yun Zhu, Chan Kwon Jung
Virchows Archiv.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Presence of Typical “BRAFV600E-Like” Atypia in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma is Highly Specific for the Presence of the BRAFV600E Mutation
John Turchini, Loretta Sioson, Adele Clarkson, Amy Sheen, Leigh Delbridge, Anthony Glover, Mark Sywak, Stan Sidhu, Anthony J. Gill
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(1): 112. CrossRef - Could Oxidative Stress Play a Role in the Development and Clinical Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer?
Maria Kościuszko, Angelika Buczyńska, Adam Jacek Krętowski, Anna Popławska-Kita
Cancers.2023; 15(12): 3182. CrossRef - Pitfalls in thyroid pathology and the medicolegal aspects of error
David N Poller
Diagnostic Histopathology.2023; 29(11): 495. CrossRef - Developing Models to Predict BRAFV600E and RAS Mutational Status in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Using Clinicopathological Features and pERK1/2 Immunohistochemistry Expression
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Imam Subekti, Sonar Soni Panigoro, Asmarinah, Lisnawati, Retno Asti Werdhani, Hasrayati Agustina, Dina Khoirunnisa, Mutiah Mutmainnah, Fajar Lamhot Gultom, Abdillah Hasbi Assadyk, Maria Francisca Ham
Biomedicines.2023; 11(10): 2803. CrossRef - The Asian Thyroid Working Group, from 2017 to 2023
Kennichi Kakudo, Chan Kwon Jung, Zhiyan Liu, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Andrey Bychkov, Huy Gia Vuong, Somboon Keelawat, Radhika Srinivasan, Jen-Fan Hang, Chiung-Ru Lai
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(6): 289. CrossRef - Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclear Features (NIFTP): Tumour Entity with a Short History. A Review on Challenges in Our Microscopes, Molecular and Ultrasonographic Profile
Ivana Kholová, Elina Haaga, Jaroslav Ludvik, David Kalfert, Marie Ludvikova
Diagnostics.2022; 12(2): 250. CrossRef - Update from the 2022 World Health Organization Classification of Thyroid Tumors: A Standardized Diagnostic Approach
Chan Kwon Jung, Andrey Bychkov, Kennichi Kakudo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(5): 703. CrossRef - Different Threshold of Malignancy for RAS-like Thyroid Tumors Causes Significant Differences in Thyroid Nodule Practice
Kennichi Kakudo
Cancers.2022; 14(3): 812. CrossRef - The Incidence of Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features: A Meta-Analysis Assessing Worldwide Impact of the Reclassification
Chanchal Rana, Huy Gia Vuong, Thu Quynh Nguyen, Hoang Cong Nguyen, Chan Kwon Jung, Kennichi Kakudo, Andrey Bychkov
Thyroid.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Differentiating BRAF V600E- and RAS-like alterations in encapsulated follicular patterned tumors through histologic features: a validation study

- Endocrine Research
- Danshen Extracts Prevents Obesity and Activates Mitochondrial Function in Brown Adipose Tissue
- Yoon Hee Cho, Cheol Ryong Ku, Young-Suk Choi, Hyeon Jeong Lee, Eun Jig Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):185-195. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.835
- 4,616 View
- 132 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Danshen has been widely used in oriental medicine to improve body function. The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of water-soluble Danshen extract (DE) on weight loss and on activation proteins involved in mitochondrial biogenesis in brown adipose tissue (BAT) in obese mice.
Methods
BAT was isolated from 7-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats, and expression of proteins related to mitochondrial biogenesis was confirmed in both brown preadipocytes and mature brown adipocytes treated with DE. For the in vivo study, low-density lipoprotein receptor knock out mice were divided into three groups and treated for 17 weeks with: standard diet; high fat diet (HFD); HFD+DE. Body weight was measured every week, and oral glucose tolerance test was performed after DE treatment in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. To observe the changes in markers related to thermogenesis and adipogenesis in the BAT, white adipose tissue (WAT) and liver of experimental animals, tissues were removed and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen.
Results
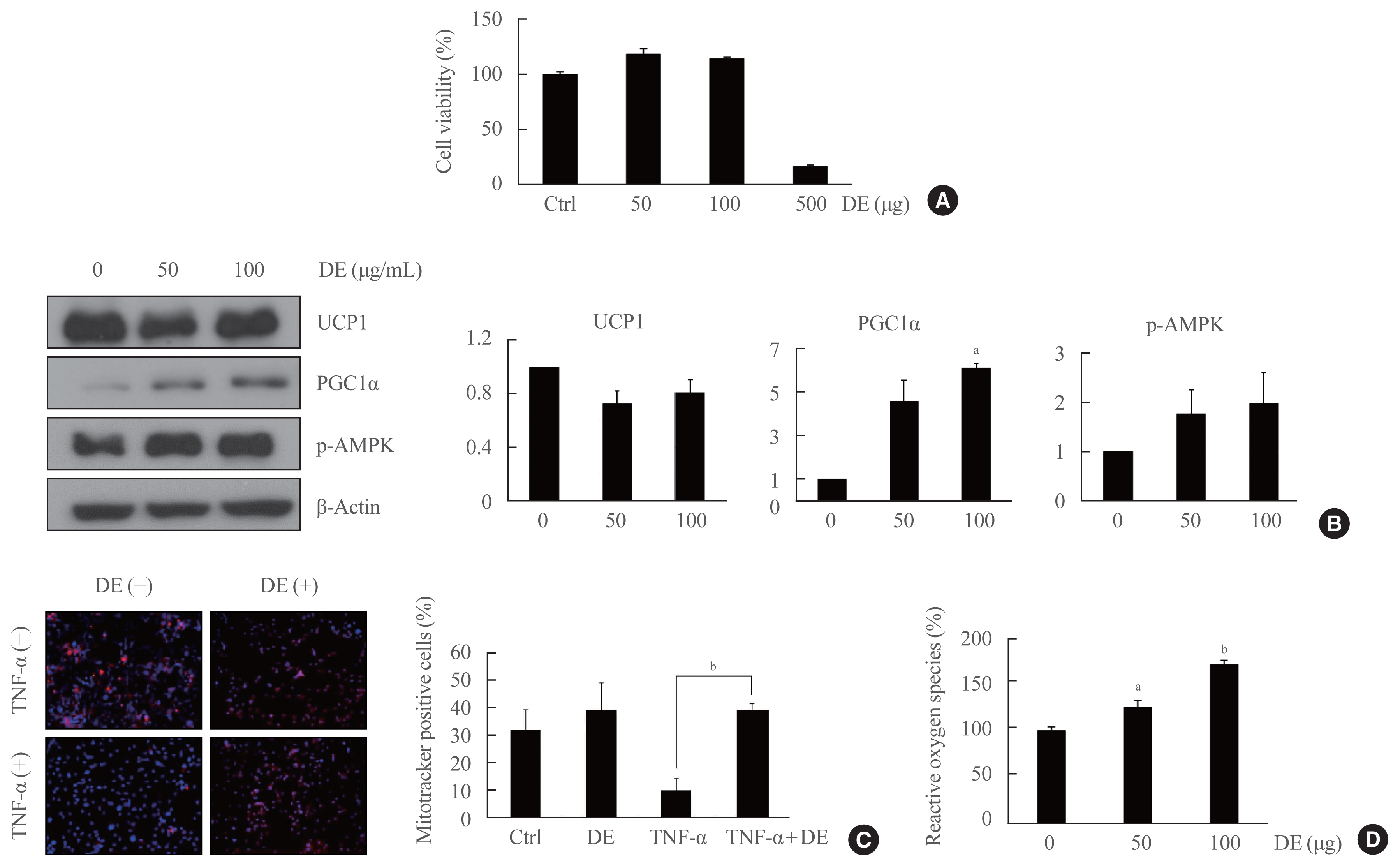
DE increased the expression of uncoupling protein 1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha in brown preadipocytes, and also promoted the brown adipocyte differentiation and mitochondrial function in the mature brown adipocytes. Reactive oxygen species production in brown preadipocytes was increased depending on the concentration of DE. DE activates thermogenesis in BAT and normalizes increased body weight and adipogenesis in the liver due to HFD. Browning of WAT was increased in WAT of DE treatment group.
Conclusion
DE protects against obesity and activates mitochondrial function in BAT. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pharmacological Benefits and Underlying Mechanisms of Salvia miltiorrhiza against Molecular Pathology of Various Liver Diseases: A Review
Cho Hyun Hwang, Eungyeong Jang, Jang-Hoon Lee
The American Journal of Chinese Medicine.2023; 51(07): 1675. CrossRef
- Pharmacological Benefits and Underlying Mechanisms of Salvia miltiorrhiza against Molecular Pathology of Various Liver Diseases: A Review

- Clinical Study
- Identification of Novel Genetic Variants Related to Trabecular Bone Score in Community-Dwelling Older Adults
- Sung Hye Kong, Ji Won Yoon, Jung Hee Kim, JooYong Park, Jiyeob Choi, Ji Hyun Lee, A Ram Hong, Nam H. Cho, Chan Soo Shin
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):801-810. Published online November 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.735

- 4,621 View
- 112 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
As the genetic variants of trabecular bone microarchitecture are not well-understood, we performed a genome-wide association study to identify genetic determinants of bone microarchitecture analyzed by trabecular bone score (TBS).
Methods
TBS-associated genes were discovered in the Ansung cohort (discovery cohort), a community-based rural cohort in Korea, and then validated in the Gene-Environment Interaction and Phenotype (GENIE) cohort (validation cohort), consisting of subjects who underwent health check-up programs. In the discovery cohort, 2,451 participants were investigated for 1.42 million genotyped and imputed markers.
Results
In the validation cohort, identified as significant variants were evaluated in 2,733 participants. An intronic variant in iroquois homeobox 3 (IRX3), rs1815994, was significantly associated with TBS in men (P=3.74E-05 in the discovery cohort, P=0.027 in the validation cohort). Another intronic variant in mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 5 (MAP2K5), rs11630730, was significantly associated with TBS in women (P=3.05E-09 in the discovery cohort, P=0.041 in the validation cohort). Men with the rs1815994 variant and women with the rs11630730 variant had lower TBS and lumbar spine bone mineral density. The detrimental effects of the rs1815994 variant in men and rs11630730 variant in women were also identified in association analysis (β=–0.0281, β=–0.0465, respectively).
Conclusion
In this study, the rs1815994 near IRX3 in men and rs11630730 near MAP2K5 in women were associated with deterioration of the bone microarchitecture. It is the first study to determine the association of genetic variants with TBS. Further studies are needed to confirm our findings and identify additional variants contributing to the trabecular bone microarchitecture.

- Endocrine Research
- Serotonin Regulates De Novo Lipogenesis in Adipose Tissues through Serotonin Receptor 2A
- Ko Eun Shong, Chang-Myung Oh, Jun Namkung, Sangkyu Park, Hail Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):470-479. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.470
- Correction in: Endocrinol Metab 2020;35(3):672
- 8,481 View
- 262 Download
- 21 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Obesity is defined as excessive fat mass and is a major cause of many chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. Increasing energy expenditure and regulating adipose tissue metabolism are important targets for the treatment of obesity. Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptophan [5-HT]) is a monoamine metabolite of the essential amino acid tryptophan. Here, we demonstrated that 5-HT in mature adipocytes regulated energy expenditure and lipid metabolism.
Methods
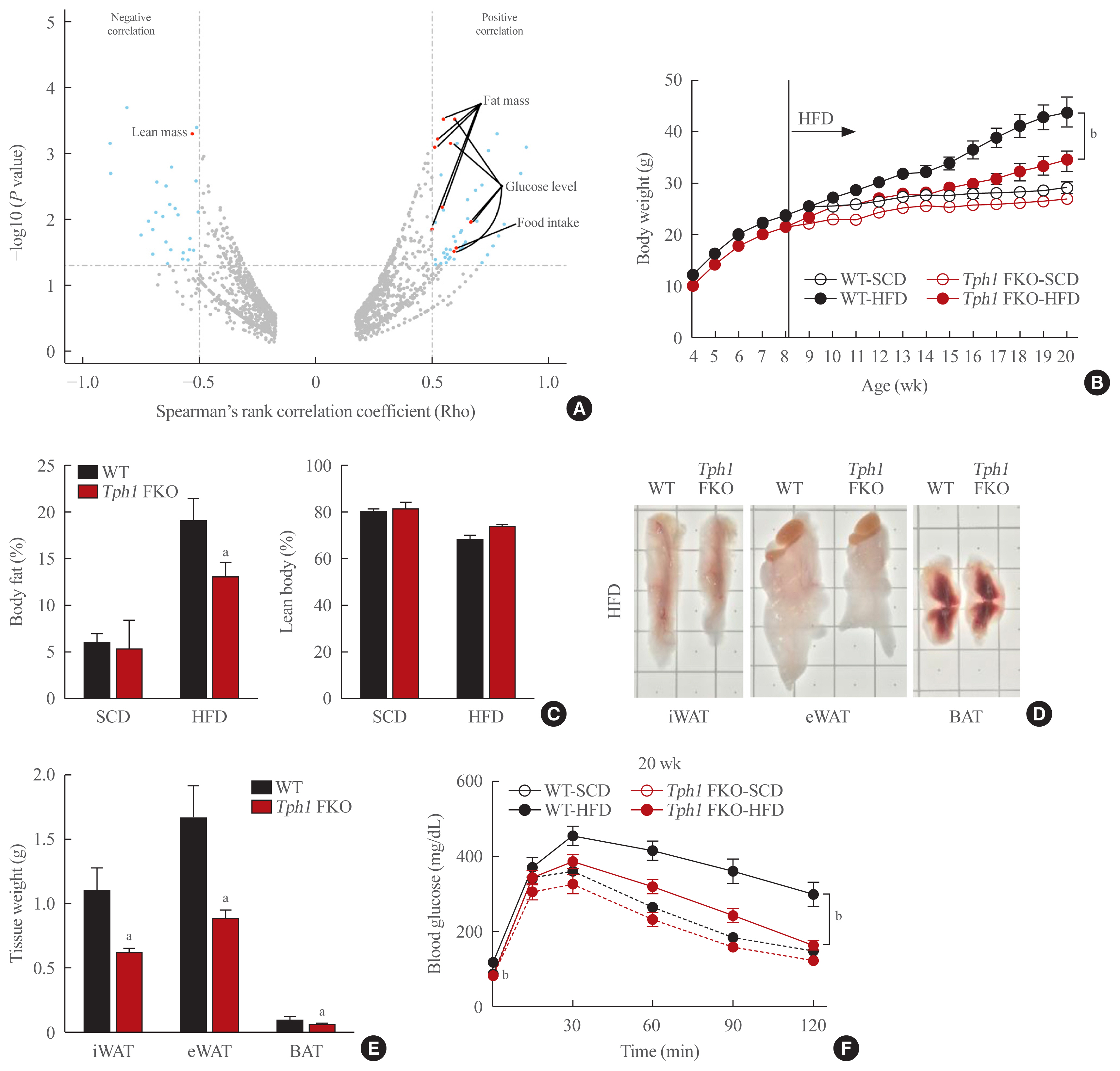
Tryptophan hydroxylase 1 (TPH1) is the rate-limiting enzyme during 5-HT synthesis in non-neural peripheral tissues. We generated adipose tissue-specific Tph1 knockout (Tph1 FKO) mice and adipose tissue-specific serotonin receptor 2A KO (Htr2a FKO) mice and analyzed their phenotypes during high-fat diet (HFD) induced obesity.
Results
Tph1 FKO mice fed HFD exhibited reduced lipid accumulation, increased thermogenesis, and resistance to obesity. In addition, Htr2a FKO mice fed HFD showed reduced lipid accumulation in white adipose tissue and resistance to obesity.
Conclusion
These data suggest that the inhibition of serotonin signaling might be an effective strategy in obesity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gut microbiota dysbiosis and decreased levels of acetic and propionic acid participate in glucocorticoid-induced glycolipid metabolism disorder
Qin Zhang, Gaopeng Guan, Jie Liu, Wenmu Hu, Ping Jin, Yung-Fu Chang
mBio.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Chain-Mediating Effect of Obesity, Depressive Symptoms on the Association between Dietary Quality and Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Shuai Zhang, Limei E, Zhonghai Lu, Yingying Yu, Xuebin Yang, Yao Chen, Xiubo Jiang
Nutrients.2023; 15(3): 629. CrossRef - Metabolic and Molecular Response to High-Fat Diet Differs between Rats with Constitutionally High and Low Serotonin Tone
Petra Baković, Maja Kesić, Darko Kolarić, Jasminka Štefulj, Lipa Čičin-Šain
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(3): 2169. CrossRef - Linking serotonin homeostasis to gut function: Nutrition, gut microbiota and beyond
Lili Jiang, Dandan Han, Youling Hao, Zhuan Song, Zhiyuan Sun, Zhaolai Dai
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Serotonin transporter-deficient mice display enhanced adipose tissue inflammation after chronic high-fat diet feeding
Johannes Hoch, Niklas Burkhard, Shanshan Zhang, Marina Rieder, Timoteo Marchini, Vincent Geest, Krystin Krauel, Timm Zahn, Nicolas Schommer, Muataz Ali Hamad, Carolina Bauer, Nadine Gauchel, Daniela Stallmann, Claus Normann, Dennis Wolf, Rüdiger Eberhard
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of serotonin in prenatal ontogenesis
Inna I. Evsyukova
Journal of obstetrics and women's diseases.2023; 72(4): 81. CrossRef - Genome-wide survey and functional analysis reveal TCF21 promotes chicken preadipocyte differentiation by directly upregulating HTR2A
Xinyang Zhang, Bohan Cheng, Yanyan Ma, Yumeng Liu, Ning Wang, Hui Zhang, Yumao Li, Yuxiang Wang, Peng Luan, Zhiping Cao, Hui Li
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2022; 587: 131. CrossRef - Maternal Metabolic State and Fetal Sex and Genotype Modulate Methylation of the Serotonin Receptor Type 2A Gene (HTR2A) in the Human Placenta
Marina Horvatiček, Maja Perić, Ivona Bečeheli, Marija Klasić, Maja Žutić, Maja Kesić, Gernot Desoye, Sandra Nakić Radoš, Marina Ivanišević, Dubravka Hranilovic, Jasminka Štefulj
Biomedicines.2022; 10(2): 467. CrossRef - Synthesis and biological evaluation of tyrosine derivatives as peripheral 5HT2A receptor antagonists for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Minhee Kim, Wonil Choi, Jihyeon Yoon, Byung-kwan Jeong, Suvarna H. Pagire, Haushabhau S. Pagire, Jungsun Park, Jung Eun Nam, Chang Joo Oh, Jae-Han Jeon, Seong Soon Kim, Byung Hoi Lee, Jin Sook Song, Myung Ae Bae, In-Kyu Lee, Hail Kim, Jin Hee Ahn
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2022; 239: 114517. CrossRef - Serotonin in the regulation of systemic energy metabolism
Joon Ho Moon, Chang‐Myung Oh, Hail Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(10): 1639. CrossRef - Traumatic brain injury alters the gut-derived serotonergic system and associated peripheral organs
Natosha M. Mercado, Guanglin Zhang, Zhe Ying, Fernando Gómez-Pinilla
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2022; 1868(11): 166491. CrossRef - Modulation of adipose tissue metabolism by microbial-derived metabolites
Wenyun Liu, Ge Yang, Pinyi Liu, Xin Jiang, Ying Xin
Frontiers in Microbiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Risperidone Exacerbates Glucose Intolerance, Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, and Renal Impairment in Obese Mice
Hsiao-Pei Tsai, Po-Hsun Hou, Frank-Chiahung Mao, Chia-Chia Chang, Wei-Cheng Yang, Ching-Feng Wu, Huei-Jyuan Liao, Tzu-Chun Lin, Lan-Szu Chou, Li-Wei Hsiao, Geng-Ruei Chang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(1): 409. CrossRef - Pancreatic Sirtuin 3 Deficiency Promotes Hepatic Steatosis by Enhancing 5-Hydroxytryptamine Synthesis in Mice With Diet-Induced Obesity
Xing Ming, Arthur C.K. Chung, Dandan Mao, Huanyi Cao, Baoqi Fan, Willy K.K. Wong, Chin Chung Ho, Heung Man Lee, Kristina Schoonjans, Johan Auwerx, Guy A. Rutter, Juliana C.N. Chan, Xiao Yu Tian, Alice P.S. Kong
Diabetes.2021; 70(1): 119. CrossRef - Peripheral Selective Oxadiazolylphenyl Alanine Derivatives as Tryptophan Hydroxylase 1 Inhibitors for Obesity and Fatty Liver Disease
Eun Jung Bae, Won Gun Choi, Haushabhau S. Pagire, Suvarna H. Pagire, Saravanan Parameswaran, Jun-Ho Choi, Jihyeon Yoon, Won-il Choi, Ji Hun Lee, Jin Sook Song, Myung Ae Bae, Mijin Kim, Jae-Han Jeon, In-Kyu Lee, Hail Kim, Jin Hee Ahn
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2021; 64(2): 1037. CrossRef - A Systems Biology Approach to Investigating the Interaction between Serotonin Synthesis by Tryptophan Hydroxylase and the Metabolic Homeostasis
Suhyeon Park, Yumin Kim, Jibeom Lee, Jeong Yun Lee, Hail Kim, Sunjae Lee, Chang-Myung Oh
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(5): 2452. CrossRef - Metabolic Disturbances in Rat Sublines with Constitutionally Altered Serotonin Homeostasis
Maja Kesić, Petra Baković, Ranko Stojković, Jasminka Štefulj, Lipa Čičin-Šain
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(10): 5400. CrossRef - The Mechanism of Secretion and Metabolism of Gut-Derived 5-Hydroxytryptamine
Ning Liu, Shiqiang Sun, Pengjie Wang, Yanan Sun, Qingjuan Hu, Xiaoyu Wang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(15): 7931. CrossRef - Inhibiting serotonin signaling through HTR2B in visceral adipose tissue improves obesity-related insulin resistance
Won Gun Choi, Wonsuk Choi, Tae Jung Oh, Hye-Na Cha, Inseon Hwang, Yun Kyung Lee, Seung Yeon Lee, Hyemi Shin, Ajin Lim, Dongryeol Ryu, Jae Myoung Suh, So-Young Park, Sung Hee Choi, Hail Kim
Journal of Clinical Investigation.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Serotonergic Regulation of Hepatic Energy Metabolism
Jiwon Park, Wooju Jeong, Chahyeon Yun, Hail Kim, Chang-Myung Oh
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(6): 1151. CrossRef
- Gut microbiota dysbiosis and decreased levels of acetic and propionic acid participate in glucocorticoid-induced glycolipid metabolism disorder

- Endocrine Research
- Transformation of Mature Osteoblasts into Bone Lining Cells and RNA Sequencing-Based Transcriptome Profiling of Mouse Bone during Mechanical Unloading
- A Ram Hong, Kwangsoo Kim, Ji Yeon Lee, Jae-Yeon Yang, Jung Hee Kim, Chan Soo Shin, Sang Wan Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):456-469. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.456
- Correction in: Endocrinol Metab 2021;36(6):1314
- 7,610 View
- 172 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We investigated RNA sequencing-based transcriptome profiling and the transformation of mature osteoblasts into bone lining cells (BLCs) through a lineage tracing study to better understand the effect of mechanical unloading on bone loss.
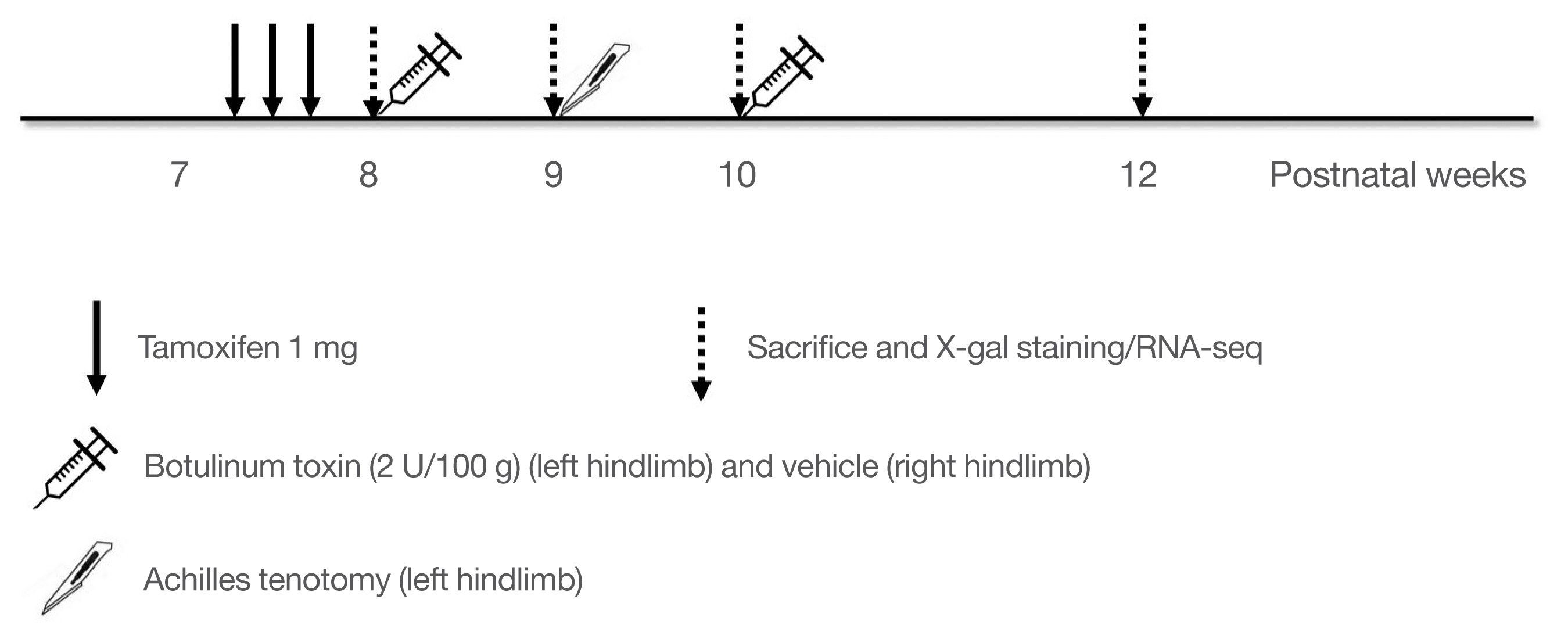
Methods
Dmp1-CreERt2(+):Rosa26R mice were injected with 1 mg of 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen three times a week starting at postnatal week 7, and subjected to a combination of botulinum toxin injection with left hindlimb tenotomy starting at postnatal week 8 to 10. The animals were euthanized at postnatal weeks 8, 9, 10, and 12. We quantified the number and thickness of X-gal(+) cells on the periosteum of the right and left femoral bones at each time point.
Results
Two weeks after unloading, a significant decrease in the number and a subtle change in the thickness of X-gal(+) cells were observed in the left hindlimbs compared with the right hindlimbs. At 4 weeks after unloading, the decrease in the thickness was accelerated in the left hindlimbs, although the number of labeled cells was comparable. RNA sequencing analysis showed downregulation of 315 genes in the left hindlimbs at 2 and 4 weeks after unloading. Of these, Xirp2, AMPD1, Mettl11b, NEXN, CYP2E1, Bche, Ppp1r3c, Tceal7, and Gadl1 were upregulated during osteoblastogenic/osteocytic and myogenic differentiation in vitro.
Conclusion
These findings demonstrate that mechanical unloading can accelerate the transformation of mature osteoblasts into BLCs in the early stages of bone loss in vivo. Furthermore, some of the genes involved in this process may have a pleiotropic effect on both bone and muscle. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Insights and implications of sexual dimorphism in osteoporosis
Yuan-Yuan Zhang, Na Xie, Xiao-Dong Sun, Edouard C. Nice, Yih-Cherng Liou, Canhua Huang, Huili Zhu, Zhisen Shen
Bone Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - METTLing in Stem Cell and Cancer Biology
John G. Tooley, James P. Catlin, Christine E. Schaner Tooley
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports.2023; 19(1): 76. CrossRef - Three's a crowd – why did three N-terminal methyltransferases evolve for one job?
Meghan M. Conner, Christine E. Schaner Tooley
Journal of Cell Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Unlocking the mysteries of alpha-N-terminal methylation and its diverse regulatory functions
Panyue Chen, Rong Huang, Tony R. Hazbun
Journal of Biological Chemistry.2023; 299(7): 104843. CrossRef - Examining Mechanisms for Voltage-Sensitive Calcium Channel-Mediated Secretion Events in Bone Cells
Perla C. Reyes Fernandez, Christian S. Wright, Mary C. Farach-Carson, William R. Thompson
Calcified Tissue International.2023; 113(1): 126. CrossRef - Reactivation of Bone Lining Cells are Attenuated Over Repeated Anti-sclerostin Antibody Administration
A Ram Hong, Jae-Yeon Yang, Ji Yeon Lee, Joonho Suh, Yun-Sil Lee, Jung-Eun Kim, Sang Wan Kim
Calcified Tissue International.2022; 111(5): 495. CrossRef - Purine metabolism in the development of osteoporosis
Keda Yang, Jie Li, Lin Tao
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 155: 113784. CrossRef - Effects of Gabapentin and Pregabalin on Calcium Homeostasis: Implications for Physical Rehabilitation of Musculoskeletal Tissues
Perla C. Reyes Fernandez, Christian S. Wright, Stuart J. Warden, Julia Hum, Mary C. Farach-Carson, William R. Thompson
Current Osteoporosis Reports.2022; 20(6): 365. CrossRef - Calvaria Bone Transcriptome in Mouse Models of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Pierre Moffatt, Iris Boraschi-Diaz, Juliana Marulanda, Ghalib Bardai, Frank Rauch
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(10): 5290. CrossRef - Age-related neurodegeneration and cognitive impairments of NRMT1 knockout mice are preceded by misregulation of RB and abnormal neural stem cell development
James P. Catlin, Leandro N. Marziali, Benjamin Rein, Zhen Yan, M. Laura Feltri, Christine E. Schaner Tooley
Cell Death & Disease.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Insights and implications of sexual dimorphism in osteoporosis

- Miscellaneous
- Rare PTH Gene Mutations Causing Parathyroid Disorders: A Review
- Joon-Hyop Lee, Munkhtugs Davaatseren, Sihoon Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):64-70. Published online March 19, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.64

- 5,090 View
- 107 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Since parathyroid hormone (PTH) was first isolated and its gene (
PTH ) was sequenced, only eightPTH mutations have been discovered. The C18R mutation inPTH , discovered in 1990, was the first to be reported. This autosomal dominant mutation induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and subsequent apoptosis in parathyroid cells. The next mutation, which was reported in 1992, is associated with exon skipping. The substitution of G with C in the first nucleotide of the second intron results in the exclusion of the second exon; since this exon includes the initiation codon, translation initiation is prevented. An S23P mutation and an S23X mutation at the same residue were reported in 1999 and 2012, respectively. Both mutations resulted in hypoparathyroidism. In 2008, a somatic R83X mutation was detected in a parathyroid adenoma tissue sample collected from a patient with hyperparathyroidism. In 2013, a heterozygous p.Met1_Asp6del mutation was incidentally discovered in a case-control study. Two years later, the R56C mutation was reported; this is the only reported hypoparathyroidism-causing mutation in the mature bioactive part ofPTH . In 2017, another heterozygous mutation, M14K, was detected. The discovery of these eight mutations in thePTH gene has provided insights into its function and broadened our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying mutation progression. Further attempts to detect other such mutations will help elucidate the functions of PTH in a more sophisticated manner.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Intricacies of Renal Phosphate Reabsorption—An Overview
Valerie Walker
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(9): 4684. CrossRef - Molecular and Clinical Spectrum of Primary Hyperparathyroidism
Smita Jha, William F Simonds
Endocrine Reviews.2023; 44(5): 779. CrossRef - Rare cause of persistent hypocalcaemia in infancy due to PTH gene mutation
Savita Khadse, Vrushali Satish Takalikar, Radha Ghildiyal, Nikhil Shah
BMJ Case Reports.2023; 16(9): e256358. CrossRef - Homozygous Ser-1 to Pro-1 mutation in parathyroid hormone identified in hypocalcemic patients results in secretion of a biologically inactive pro-hormone
Patrick Hanna, Ashok Khatri, Shawn Choi, Severine Brabant, Matti L. Gild, Marie L. Piketty, Bruno Francou, Dominique Prié, John T. Potts, Roderick J. Clifton-Bligh, Agnès Linglart, Thomas J. Gardella, Harald Jüppner
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Genetics of monogenic disorders of calcium and bone metabolism
Paul J. Newey, Fadil M. Hannan, Abbie Wilson, Rajesh V. Thakker
Clinical Endocrinology.2022; 97(4): 483. CrossRef - Homozygous missense variant of PTH (c.166C>T, p.(Arg56Cys)) as the cause of familial isolated hypoparathyroidism in a three-year-old child
Stine Linding Andersen, Anja Lisbeth Frederiksen, Astrid Bruun Rasmussen, Mette Madsen, Ann-Margrethe Rønholt Christensen
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 35(5): 691. CrossRef - Novel PTH Gene Mutations Causing Isolated Hypoparathyroidism
Colin P Hawkes, Jamal M Al Jubeh, Dong Li, Susan E Tucker, Tara Rajiyah, Michael A Levine
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(6): e2449. CrossRef
- The Intricacies of Renal Phosphate Reabsorption—An Overview

- A Case of Thyroid Hemiagenesis with Papillary Adenocarcinoma.
- Je Ho Han, Bong Yun Cha, Ho Young Son, Yoo Bae Ahn, Kwang Woo Lee, Sung Koo Kang, Se Jeong Oh, Jong Soon Na, Sang Ah Jang, Moo Il Kang
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(4):385-389. Published online November 6, 2019
- 1,122 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Variation in the gross anatomy of the thyroid is relatively common. Although thyroid hemiagenesis is considered to be a rare congenital anomaly, its incidence is probably underestimated because the diagnosis is usually incidental.We present the case of a 26-year-old woman with right thyroid hemiagenesis associated with papillary adenocarcinoma. The diagnosis of hemiagenesis was established by isotope imaging, which showed hot nodule, thyroid ultrasonography and surgical exploration for proper management of a nodule in the left lobe of thyroid gland. As she was diagnosed to have papillary adenocarcinoma, total thyroidectomy was performed and at present she remains disease-free.

- Endocrine Research
- Expression of NF2 Modulates the Progression of BRAFV600E Mutated Thyroid Cancer Cells
- Mi-Hyeon You, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(2):203-212. Published online June 24, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.2.203
- 5,043 View
- 66 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background We previously reported the frequent neurofibromatosis 2 (
NF2 ) gene mutations in anaplastic thyroid cancers in association with theBRAF V600E mutation. We aimed to investigate the role ofNF2 in thyroid cancer withBRAF mutation.Methods To identify the function of
NF2 in thyroid cancers, we investigated the changes in cell proliferation, colon formation, migration and invasion of thyroid cancer cells (8505C, BHT101, and KTC-1) withBRAF V600E mutation after overexpression and knock-down ofNF2 . We also examined how cell proliferation changed whenNF2 was mutagenized. HumanNF2 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) was analyzed using the The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data.Results First,
NF2 was overexpressed in 8505C and KTC-1 cells. Compared to control,NF2 overexpressed group of both thyroid cancer cells showed significant inhibition in cell proliferation and colony formation. These results were also confirmed by cell migration and invasion assay. After knock-down ofNF2 in 8505C cells, there were no significant changes in cell proliferation and colony formation, compared with the control group. However, after mutagenized S288* and Q470* sites ofNF2 gene, the cell proliferation increased compared toNF2 overexpression group. In the analysis of TCGA data, the mRNA expression ofNF2 was significantly decreased in PTCs with lateral cervical lymph node (LN) metastasis compared with PTCs without LN metastasis.Conclusion Our study suggests that
NF2 might play a role as a tumor suppressor in thyroid cancer withBRAF mutation. More studies are needed to elucidate the mechanism howNF2 acts in thyroid cancer withBRAF mutation.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mechanistic Insights of Thyroid Cancer Progression
Luis Javier Leandro-García, Iñigo Landa
Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gene Editing with CRISPR/Cas Methodology and Thyroid Cancer: Where Are We?
Cesar Seigi Fuziwara, Diego Claro de Mello, Edna Teruko Kimura
Cancers.2022; 14(3): 844. CrossRef - Extracellular Vesicles as Signal Carriers in Malignant Thyroid Tumors?
Małgorzata Grzanka, Anna Stachurska-Skrodzka, Anna Adamiok-Ostrowska, Ewa Gajda, Barbara Czarnocka
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(6): 3262. CrossRef - Mitofusin-2 modulates the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in thyroid cancer progression
Mi-Hyeon You, Min Ji Jeon, Seong ryeong Kim, Woo Kyung Lee, Sheue-yann Cheng, Goo Jang, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - High Phosphoglycerate Dehydrogenase Expression Induces Stemness and Aggressiveness in Thyroid Cancer
Min Ji Jeon, Mi-Hyeon You, Ji Min Han, Soyoung Sim, Hyun Ju Yoo, Woo Kyung Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Dong Eun Song, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim, Won Bae Kim
Thyroid.2020; 30(11): 1625. CrossRef
- Mechanistic Insights of Thyroid Cancer Progression

- Miscellaneous
- Search for Novel Mutational Targets in Human Endocrine Diseases
- So Young Park, Myeong Han Seo, Sihoon Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(1):23-28. Published online March 21, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.1.23
- 3,840 View
- 81 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub The identification of disease-causing genetic variations is an important goal in the field of genetics. Advancements in genetic technology have changed scientific knowledge and made it possible to determine the basic mechanism and pathogenesis of human disorders rapidly. Many endocrine disorders are caused by genetic variations of a single gene or by mixed genetic factors. Various genetic testing methods are currently available, enabling a more precise diagnosis of many endocrine disorders and facilitating the development of a concrete therapeutic plan. In this review article, we discuss genetic testing technologies for genetic endocrine disorders, with relevant examples. We additionally describe our research on implementing genetic analysis strategies to identify novel causal mutations in hypocalcemia-related disorders.

- Bone Metabolism
- Recent Topics in Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva
- Takenobu Katagiri, Sho Tsukamoto, Yutaka Nakachi, Mai Kuratani
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(3):331-338. Published online September 18, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.3.331
- 5,069 View
- 79 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) is a rare genetic disease that is characterized by the formation of heterotopic bone tissues in soft tissues, such as skeletal muscle, ligament, and tendon. It is difficult to remove such heterotopic bones via internal medicine or invasive procedures. The identification of activin A receptor, type I (
ACVR1 )/ALK2 gene mutations associated with FOP has allowed the genetic diagnosis of FOP. TheACVR1 /ALK2 gene encodes the ALK2 protein, which is a transmembrane kinase receptor in the transforming growth factor-β family. The relevant mutations activate intracellular signalingin vitro and induce heterotopic bone formationin vivo . Activin A is a potential ligand that activates mutant ALK2 but not wild-type ALK2. Various types of small chemical and biological inhibitors of ALK2 signaling have been developed to establish treatments for FOP. Some of these are in clinical trials in patients with FOP.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How Activin A Became a Therapeutic Target in Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva
Dushyanth Srinivasan, Martin Arostegui, Erich J. Goebel, Kaitlin N. Hart, Senem Aykul, John B. Lees-Shepard, Vincent Idone, Sarah J. Hatsell, Aris N. Economides
Biomolecules.2024; 14(1): 101. CrossRef - Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva Mimics Generalized Dystonia Disorder: A Case Report
Seraj Makkawi, Osama Khojah, Reema Abualnaja, Abdulaziz Qashqari, Nawaf A Alahmadi, Abdullatif G Bshnaq, Abdulrahman Alharthi, Hashem H Al-Hashemi, Aiman M Shawli
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploration of marine natural resources in Indonesia and development of efficient strategies for the production of microbial halogenated metabolites
Hiroyuki Yamazaki
Journal of Natural Medicines.2022; 76(1): 1. CrossRef - A Novel De Novo Frameshift Pathogenic Variant in the FAM111B Resulting in Progressive Osseous Heteroplasia Phenotype
Anna Ryabets-Lienhard, Panadeekarn Panjawatanan, Kyle Vogt, Jianling Ji, Senta Georgia, Pisit Pitukcheewanont
Calcified Tissue International.2022; 112(4): 518. CrossRef - Inhibitory effects of sesquiterpene lactones from the Indonesian marine sponge Lamellodysidea cf. herbacea on bone morphogenetic protein-induced osteoblastic differentiation
Satoshi Ohte, Hiroyuki Yamazaki, Ohgi Takahashi, Henki Rotinsulu, Defny S. Wewengkang, Deiske A. Sumilat, Delfly B. Abdjul, Wilmar Maarisit, Magie M. Kapojos, Huiping Zhang, Fumiaki Hayashi, Michio Namikoshi, Takenobu Katagiri, Hiroshi Tomoda, Ryuji Uchid
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters.2021; 35: 127783. CrossRef - Genomic Context and Mechanisms of the ACVR1 Mutation in Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva
Roberto Ravazzolo, Renata Bocciardi
Biomedicines.2021; 9(2): 154. CrossRef - New insights on fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: discussion of an autoptic case report and brief literature review
Vittorio Bolcato, Claudia Carelli, Silvia Damiana Visonà, Marcella Reguzzoni, Maja Di Rocco, Alessandra Radogna, Livio Pietro Tronconi, Matteo Moretti
Intractable & Rare Diseases Research.2021; 10(2): 136. CrossRef - Accumulated Knowledge of Activin Receptor-Like Kinase 2 (ALK2)/Activin A Receptor, Type 1 (ACVR1) as a Target for Human Disorders
Takenobu Katagiri, Sho Tsukamoto, Mai Kuratani
Biomedicines.2021; 9(7): 736. CrossRef - Cytoskeleton Reorganization in EndMT—The Role in Cancer and Fibrotic Diseases
Wojciech Michał Ciszewski, Marta Ewelina Wawro, Izabela Sacewicz-Hofman, Katarzyna Sobierajska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(21): 11607. CrossRef - Alendronate disturbs femoral growth due to changes during immunolocalization of transforming growth factor-β1 and bone morphogenetic protein-2 in epiphyseal plate
Juliana Souza Vieira, Emanuelle Juliana Cunha, Juliana Feltrin de Souza, Luis Henrique Koeler Chaves, Jessica Lakes de Souza, Allan Fernando Giovanini
World Journal of Experimental Medicine.2020; 10(1): 1. CrossRef - ALK2: A Therapeutic Target for Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva and Diffuse Intrinsic Pontine Glioma
Katsuhiko Sekimata, Tomohiro Sato, Naoki Sakai
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin.2020; 68(3): 194. CrossRef - Role of Signal Transduction Pathways and Transcription Factors in Cartilage and Joint Diseases
Riko Nishimura, Kenji Hata, Yoshifumi Takahata, Tomohiko Murakami, Eriko Nakamura, Maki Ohkawa, Lerdluck Ruengsinpinya
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(4): 1340. CrossRef - Design of primers for direct sequencing of nine coding exons in the human ACVR1 gene
Masaru Matsuoka, Sho Tsukamoto, Yuta Orihara, Rieko Kawamura, Mai Kuratani, Nobuhiko Haga, Kenji Ikebuchi, Takenobu Katagiri
Bone.2020; 138: 115469. CrossRef - A new diketopiperazine-like inhibitor of bone morphogenetic protein-induced osteoblastic differentiation produced by marine-derived Aspergillus sp. BFM-0085
Satoshi Ohte, Takehiro Shiokawa, Nobuhiro Koyama, Takenobu Katagiri, Chiaki Imada, Hiroshi Tomoda
The Journal of Antibiotics.2020; 73(8): 554. CrossRef - Penicillic Acid Congener, a New Inhibitor of BMP-Induced Alkaline Phosphatase Activity in Myoblasts, Produced by the Fungus Penicillium sp. BF-0343
Nobuhiro Koyama, Yasuhiro Otoguro, Satoshi Ohte, Takenobu Katagiri, Hiroshi Tomoda
Natural Product Communications.2020; 15(9): 1934578X2094265. CrossRef - Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: current concepts from bench to bedside
Arun-Kumar Kaliya-Perumal, Tom J. Carney, Philip W. Ingham
Disease Models & Mechanisms.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Aspects and Current Therapeutic Approaches for FOP
Hiroshi Kitoh
Biomedicines.2020; 8(9): 325. CrossRef - Screening for Small Molecule Inhibitors of BMP-Induced Osteoblastic Differentiation from Indonesian Marine Invertebrates
Hiroyuki Yamazaki, Satoshi Ohte, Henki Rotinsulu, Defny S. Wewengkang, Deiske A. Sumilat, Delfly B. Abdjul, Wilmar Maarisit, Magie M. Kapojos, Michio Namikoshi, Takenobu Katagiri, Hiroshi Tomoda, Ryuji Uchida
Marine Drugs.2020; 18(12): 606. CrossRef - Propranolol and ascorbic acid in control of fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva flare-ups due to accidental falls
Durval Batista Palhares, Deborah Ribeiro Nascimento, Marilene Garcia Palhares, Suzana Lopes Bomfim Balaniuc, Liane de Rosso Giuliani, Paula Cristhina Niz Xavier, José Mauro Goulart Brum, Fabiana Alves, Francisco Oliveira Vieira, Elaine Maria Souza-Fagunde
Intractable & Rare Diseases Research.2019; 8(1): 24. CrossRef - Late-onset fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva with atypical presentation: A case report
Conor M. Cunningham, J. Matthew Royeca, Samuel W. King, Hemant Pandit
Case Reports in Women's Health.2019; 23: e00134. CrossRef - Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva: lessons learned from a rare disease
Gulseren Akyuz, Kardelen Gencer-Atalay, Pinar Ata
Current Opinion in Pediatrics.2019; 31(6): 716. CrossRef - Discovery of Heterotopic Bone-Inducing Activity in Hard Tissues and the TGF-β Superfamily
Takenobu Katagiri, Sho Tsukamoto, Yutaka Nakachi, Mai Kuratani
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(11): 3586. CrossRef
- How Activin A Became a Therapeutic Target in Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva

- Thyroid
- Combined Effects of Baicalein and Docetaxel on Apoptosis in 8505c Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cells via Downregulation of the ERK and Akt/mTOR Pathways
- Chan Ho Park, Se Eun Han, Il Seong Nam-Goong, Young Il Kim, Eun Sook Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(1):121-132. Published online March 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.1.121
- 5,011 View
- 63 Download
- 41 Web of Science
- 35 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC) is one of the most lethal human malignancies. Docetaxel, a microtubule stabilizer, is a common chemotherapeutic agent used to treat various metastatic cancers. However, prolonged use results in various side effects and drug resistance. Flavonoids, such as baicalein, are accepted chemotherapeutic and dietary chemopreventive agents with many advantages, such as greater accessibility, affordability, and lower toxicity, compared with traditional chemotherapy agents. In this study, we evaluated whether baicalein enhances the effects of docetaxel on apoptosis and metastasis in 8505c ATC cells.
Methods The 8505c cells were treated with baicalein or docetaxel individually and in combination. Cell viability was measured by MTT (thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide) assay, and apoptosis was detected by fluorescence microscopy of Hoechst-stained cells. The expression of apoptotic (Bax and caspase-3), anti-apoptotic (Bcl-2), angiogenic (vascular endothelial growth factor [VEGF], transforming growth factor β [TGF-β], E-cadherin, and N-cadherin), and signaling (extracellular signal-regulated kinase [ERK] mitogen activated protein kinase [MAPK], Akt, and mammalian target of rapamycin [mTOR]) proteins was determined by Western blot analysis.
Results The combination of baicalein (50 or 100 µM) and docetaxel (10 nM) significantly inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis compared with monotherapies. The combination treatment significantly inhibited the expression of Bax, caspase-3, VEGF, TGF-β1, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and mTOR, but decreased the expression of Bcl-2 and significantly decreased the phosphorylation of ERK and Akt.
Conclusion The combination of baicalein and docetaxel effectively induced apoptosis and inhibited metastasis in 8505c cells through downregulation of apoptotic and angiogenic protein expression and blocking of the ERK and Akt/mTOR pathways in 8505c cells. These results suggest that baicalein enhances the anticancer effects of docetaxel in ATC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 signaling pathways in cancer angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis by natural compounds: a comprehensive and critical review
Sajad Fakhri, Seyed Zachariah Moradi, Farahnaz Faraji, Leila Kooshki, Kassidy Webber, Anupam Bishayee
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews.2024; 43(1): 501. CrossRef - Baicalein Alleviates Arsenic-induced Oxidative Stress through
Activation of the Keap1/Nrf2 Signalling Pathway in Normal Human
Liver Cells
Qi Wang, Aihua Zhang
Current Molecular Medicine.2024; 24(3): 355. CrossRef - Natural products reverse cancer multidrug resistance
Jia-Yu Zou, Qi-Lei Chen, Xiao-Ci Luo, Davaadagva Damdinjav, Usama Ramadan Abdelmohsen, Hong-Yan Li, Tungalag Battulga, Hu-Biao Chen, Yu-Qing Wang, Jian-Ye Zhang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of novel characteristic biomarkers and immune infiltration profile for the anaplastic thyroid cancer via machine learning algorithms
C. Li, X. Dong, Q. Yuan, G. Xu, Z. Di, Y. Yang, J. Hou, L. Zheng, W. Chen, G. Wu
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2023; 46(8): 1633. CrossRef - Promising Role of the Scutellaria baicalensis Root Hydroxyflavone–Baicalein in the Prevention and Treatment of Human Diseases
Marcelina Chmiel, Monika Stompor-Gorący
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(5): 4732. CrossRef - STEAP1 Knockdown Decreases the Sensitivity of Prostate Cancer Cells to Paclitaxel, Docetaxel and Cabazitaxel
Sandra M. Rocha, Daniel Nascimento, Rafaella S. Coelho, Ana Margarida Cardoso, Luís A. Passarinha, Sílvia Socorro, Cláudio J. Maia
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(7): 6643. CrossRef - Baicalein as Promising Anticancer Agent: A Comprehensive Analysis on Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Perspectives
A K M Helal Morshed, Supti Paul, Arafat Hossain, Tuli Basak, Md. Sanower Hossain, Md. Mehedi Hasan, Md. Al Hasibuzzaman, Tanjim Ishraq Rahaman, Md. Abdur Rashid Mia, Pollob Shing, Md Sohel, Shabana Bibi, Dipta Dey, Partha Biswas, Md. Nazmul Hasan, Long Ch
Cancers.2023; 15(7): 2128. CrossRef - The role of flavonoids in the regulation of epithelial‐mesenchymal transition in cancer: A review on targeting signaling pathways and metastasis
Carina Proença, Marisa Freitas, Daniela Ribeiro, Ana T. Rufino, Eduarda Fernandes, José Miguel P. Ferreira de Oliveira
Medicinal Research Reviews.2023; 43(6): 1878. CrossRef - Developing a ternary conductive hydrogel of polyacrylamide, polyaniline, and carbon nanotube: A potential chemiresistive gas sensor
Mohsen Peykari, Saeed Pourmahdian
Journal of Composite Materials.2023; 57(27): 4291. CrossRef - Inhibiting MEK1 R189 citrullination enhances the chemosensitivity of docetaxel to multiple tumour cells
Teng Xue, Shujia Fei, Jian Gu, Nan Li, Pengxue Zhang, Xiaoqiu Liu, Paul R Thompson, Xuesen Zhang
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Baicalein improves the chemoresistance of ovarian cancer through regulation of CirSLC7A6
Shuqing Li, Zhihui Yi, Mingqing Li, Zhiling Zhu
Journal of Ovarian Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary cell cultures for the personalized therapy in aggressive thyroid cancer of follicular origin
Poupak Fallahi, Silvia Martina Ferrari, Giusy Elia, Francesca Ragusa, Armando Patrizio, Sabrina Rosaria Paparo, Gianni Marone, Maria Rosaria Galdiero, Giovanni Guglielmi, Rudy Foddis, Alfonso Cristaudo, Alessandro Antonelli
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2022; 79: 203. CrossRef - Synergistic effects of BAY606583 on docetaxel in esophageal cancer through modulation of ERK1/2
Zinab Mohammadi, Jahanbakhsh Asadi, Seyyed Mehdi Jafari
Cell Biochemistry and Function.2022; 40(6): 569. CrossRef - Regulation of Cell Signaling Pathways and Non-Coding RNAs by Baicalein in Different Cancers
Ammad Ahmad Farooqi, Gulnara Kapanova, Sundetgali Kalmakhanov, Gulnur Tanbayeva, Kairat S. Zhakipbekov, Venera S. Rakhmetova, Marat K. Syzdykbayev
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(15): 8377. CrossRef - Crosstalk between xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibiting and cancer chemotherapeutic properties of comestible flavonoids- a comprehensive update
Md Sohanur Rahaman, Md Afjalus Siraj, Md Arman Islam, Prayas Chakma Shanto, Ordha Islam, Md Amirul Islam, Jesus Simal-Gandara
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2022; 110: 109147. CrossRef - Anticancer effects of natural phytochemicals in anaplastic thyroid cancer (Review)
Yitian Li, Jing Zhang, Huihui Zhou, Zhen Du
Oncology Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Multifaceted Role of Baicalein in Cancer Management through Modulation of Cell Signalling Pathways
Arshad Husain Rahmani, Ahmad Almatroudi, Amjad Ali Khan, Ali Yousif Babiker, Malak Alanezi, Khaled S. Allemailem
Molecules.2022; 27(22): 8023. CrossRef - Ouabain Effects on Human Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma 8505C Cells
Mariana Pires Teixeira, Natalia Ferreira Haddad, Eliza Freitas Passos, Marcelle Novaes Andrade, Maria Luisa Arantes Campos, Joyle Moreira Carvalho da Silva, Camila Saggioro de Figueiredo, Elizabeth Giestal-de-Araujo, Denise Pires de Carvalho, Leandro Mira
Cancers.2022; 14(24): 6168. CrossRef - Baicalein Represses Cervical Cancer Cell Growth, Cell Cycle Progression and Promotes Apoptosis via Blocking AKT/mTOR Pathway by the Regulation of circHIAT1/miR-19a-3p Axis
Jiaojiao Hu, Runkun Wang, Yi Liu, Jianbo Zhou, Ka Shen, Yun Dai
OncoTargets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 905. CrossRef - Phytochemicals in thyroid cancer: analysis of the preclinical studies
Stefania Bulotta, Francesca Capriglione, Marilena Celano, Valeria Pecce, Diego Russo, Valentina Maggisano
Endocrine.2021; 73(1): 8. CrossRef - Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in thyroid papillary carcinoma: molecular networks and interactions
Jeehoon Ham, Bin Wang, Joseph William Po, Amandeep Singh, Navin Niles, Cheok Soon Lee
Journal of Clinical Pathology.2021; 74(12): 759. CrossRef - Clinical Study of Virtual Reality Augmented Technology Combined with Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound in the Assessment of Thyroid Cancer
Qinghua Liu, Jian Cheng, Jingjing Li, Lei Liu, Hongbo Li, Zhihan Lv
Journal of Healthcare Engineering.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Potential of baicalein in the prevention and treatment of cancer: A scientometric analyses based review
Elika Verma, Aviral Kumar, Uzini Devi Daimary, Dey Parama, Sosmitha Girisa, Gautam Sethi, Ajaikumar B. Kunnumakkara
Journal of Functional Foods.2021; 86: 104660. CrossRef - E-cadherin on epithelial–mesenchymal transition in thyroid cancer
Xiaoyu Zhu, Xiaoping Wang, Yifei Gong, Junlin Deng
Cancer Cell International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Combinatorial Therapies in Thyroid Cancer: An Overview of Preclinical and Clinical Progresses
Gheysen Laetitia, Saussez Sven, Journe Fabrice
Cells.2020; 9(4): 830. CrossRef - Preclinical and clinical combination therapies in the treatment of anaplastic thyroid cancer
Daniela Gentile, Paola Orlandi, Marta Banchi, Guido Bocci
Medical Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Interleukin-22 enhances chemoresistance of lung adenocarcinoma cells to paclitaxel
Zhiliang Huang, Yu Gao, Dianchen Hou
Human Cell.2020; 33(3): 850. CrossRef - Plant natural products with anti-thyroid cancer activity
Javad Sharifi-Rad, Sadegh Rajabi, Miquel Martorell, Maria Dolores López, María Trinidad Toro, Susi Barollo, Decio Armanini, Patrick Valere Tsouh Fokou, Giuseppe Zagotto, Giovanni Ribaudo, Raffaele Pezzani
Fitoterapia.2020; 146: 104640. CrossRef - Baicalein: A metabolite with promising antineoplastic activity
Hardeep Singh Tuli, Vaishali Aggarwal, Jagjit Kaur, Diwakar Aggarwal, Gaurav Parashar, Nidarshana Chaturvedi Parashar, Muobarak Tuorkey, Ginpreet Kaur, Raj Savla, Katrin Sak, Manoj Kumar
Life Sciences.2020; 259: 118183. CrossRef - Impact of Antioxidant Natural Compounds on the Thyroid Gland and Implication of the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway
Ana Paunkov, Dionysios V. Chartoumpekis, Panos G. Ziros, Niki Chondrogianni, Thomas W. Kensler, Gerasimos P. Sykiotis
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2019; 25(16): 1828. CrossRef - Reversal of Multidrug Resistance in Cancer by Multi-Functional Flavonoids
Qingmei Ye, Kai Liu, Qun Shen, Qingyue Li, Jinghui Hao, Fangxuan Han, Ren-Wang Jiang
Frontiers in Oncology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibition of Cancer Stem-Like Phenotype by Curcumin and Deguelin in CAL-62 Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Cells
Mehmet A. Kocdor, Hakan Cengiz, Halil Ates, Hilal Kocdor
Anti-Cancer Agents in Medicinal Chemistry.2019; 19(15): 1887. CrossRef - Induction of apoptotic but not autophagic cell death by Cinnamomum cassia extracts on human oral cancer cells
Ching‐Han Yu, Shu‐Chen Chu, Shun‐Fa Yang, Yih‐Shou Hsieh, Chih‐Yi Lee, Pei‐Ni Chen
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2019; 234(4): 5289. CrossRef - Licochalcone A induces apoptotic cell death via JNK/p38 activation in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
Chun‐Yi Chuang, Cheng‐Ming Tang, Hsin‐Yu Ho, Chung‐Han Hsin, Chia‐Jui Weng, Shun‐Fa Yang, Pei‐Ni Chen, Chiao‐Wen Lin
Environmental Toxicology.2019; 34(7): 853. CrossRef - Rab23 contributes to the progression of colorectal cancer via protein kinase B and extracellular signal‑regulated kinase signaling pathways
Tongbi Zhao, Dong Han, Huan Meng
Oncology Letters.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 signaling pathways in cancer angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis by natural compounds: a comprehensive and critical review

- The SCAP/SREBP Pathway: A Mediator of Hepatic Steatosis
- Young-Ah Moon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(1):6-10. Published online January 19, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.1.6
- 7,536 View
- 208 Download
- 74 Web of Science
- 72 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is strongly associated with insulin resistance, obesity, and dyslipidemia. NAFLD encompasses a wide range of states from the simple accumulation of triglycerides in the hepatocytes to serious states accompanied by inflammation and fibrosis in the liver.
De novo lipogenesis has been shown to be a significant factor in the development of hepatic steatosis in insulin-resistant states. Sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) is the main transcription factor that mediates the activation of lipogenesis, and SREBP cleavage activating protein (SCAP) is required for the activation of SREBPs. Here, recent animal studies that suggest SCAP as a therapeutic target for hepatic steatosis and hypertriglyceridemia are discussed.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- SREBPs as the potential target for solving the polypharmacy dilemma
Xue Wang, Yanqiu Chen, Heyu Meng, Fanbo Meng
Frontiers in Physiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of SCAP/SREBP as Central Regulators of Lipid Metabolism in Hepatic Steatosis
Preethi Chandrasekaran, Ralf Weiskirchen
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(2): 1109. CrossRef - Expression and correlation analysis of silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1), sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 (SREBP1), and pyroptosis factor in gestational diabetes mellitus
Ning Han, Xin-yuan Chang, Zi-li Yuan, Yi-zhan Wang
The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Uxi (Endopleura uchi (Huber) Cuatrec) bark extract mitigates HFD-induced adiposity in rats via targeting oxidative stress, and lipogenic genes expression
Eman A.R. Abdelghffar, Zuhair M. Mohammedsaleh, Raha Osailan, Aisha Elaimi, Wafae Ouchari, Mohamed A.O. Abdelfattah, Mona F. Mahmoud, Mansour Sobeh
Journal of Functional Foods.2024; 114: 106034. CrossRef - Robinetin Alleviates Metabolic Failure in Liver through Suppression of p300–CD38 Axis
Ji-Hye Song, Hyo-Jin Kim, Jangho Lee, Seung-Pyo Hong, Min-Yu Chung, Yu-Geun Lee, Jae Ho Park, Hyo-Kyoung Choi, Jin-Taek Hwang
Biomolecules & Therapeutics.2024; 32(2): 214. CrossRef - Regeneration of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Cells Using Chimeric FGF21/HGFR: A Novel Therapeutic Approach
Sung-Jun Kim, So-Jung Kim, Jeongeun Hyun, Hae-Won Kim, Jun-Hyeog Jang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(6): 3092. CrossRef - Evolutionary analysis of buffalo sterol regulatory element-binding factor (SREBF) family genes and their affection on milk traits
Tingzhu Ye, Jing Yuan, Sayed Haidar Abbas Raza, Tingxian Deng, Lv Yang, Muhammad Jamil Ahmad, Seyed Mahdi Hosseini, Xinxin Zhang, Muna O Alamoudi, Qwait AlGabbani, Youssef S Alghamdi, Chao Chen, Aixin Liang, Nicola M. Schreurs, Liguo Yang
Animal Biotechnology.2023; 34(7): 2082. CrossRef - Hepatic Pin1 Expression, Particularly in Nuclei, Is Increased in NASH Patients in Accordance with Evidence of the Role of Pin1 in Lipid Accumulation Shown in Hepatoma Cell Lines
Machi Kanna, Yusuke Nakatsu, Takeshi Yamamotoya, Akifumi Kushiyama, Midori Fujishiro, Hideyuki Sakoda, Hiraku Ono, Koji Arihiro, Tomoichiro Asano
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(10): 8847. CrossRef - Dietary acetate promotes growth and nutrients deposition in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) through increasing acetyl-CoA-triggered energy production
Wen-Hao Zhou, Samwel M. Limbu, Yuan Luo, Rui-Xin Li, Jiong Ren, Fang Qiao, Mei-Ling Zhang, Zhen-Yu Du
Aquaculture.2023; 575: 739750. CrossRef - Palmitate로 유발된 비알코올성 지방간 세포 모델에서 블랙커런트 초임계 추출물의 지방증 개선효과
수정 이, 은숙 양, 영호 김, 혜연 김, 혜란 최, 석 김, 태호 류
Korean Journal of Food and Cookery Science.2023; 39(3): 178. CrossRef - PM2.5 induced liver lipid metabolic disorders in C57BL/6J mice
Chenxiao Zhang, Tengfei Ma, Chang Liu, Ding Ma, Jian Wang, Meng Liu, Jinjun Ran, Xueting Wang, Xiaobei Deng
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - High Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) Oolong Tea Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Disorders in Mice
Monthana Weerawatanakorn, Sang He, Chun-Han Chang, Yen-Chun Koh, Meei-Ju Yang, Min-Hsiung Pan
ACS Omega.2023; 8(37): 33997. CrossRef - MicroRNA-19a regulates milk fat metabolism by targeting SYT1 in bovine mammary epithelial cells
Baojun Yu, Jiamin Liu, Zhengyun Cai, Tong Mu, Di Zhang, Xiaofang Feng, Yaling Gu, Juan Zhang
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2023; 253: 127096. CrossRef - SREBP Regulation of Lipid Metabolism in Liver Disease, and Therapeutic Strategies
Na Li, Xiaodan Li, Yifu Ding, Xiao Liu, Karin Diggle, Tatiana Kisseleva, David A. Brenner
Biomedicines.2023; 11(12): 3280. CrossRef - Daidzein stimulates fatty acid-induced fat deposition in C2C12 myoblast cells via the G protein-coupled receptor 30 pathway
Chengjian Zhou, Ping Li, Meihong Han, Xuejun Gao
Animal Biotechnology.2022; 33(5): 851. CrossRef - Hepatocyte steatosis inhibits hepatitis B virus secretion via induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress
Qichuang Liu, Maoyuan Mu, Huan Chen, Guoyuan Zhang, Yanqing Yang, Jun Chu, Ying Li, Fangwan Yang, Shide Lin
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2022; 477(11): 2481. CrossRef - The cholesterol pathway: impact on immunity and cancer
Ryan J. King, Pankaj K. Singh, Kamiya Mehla
Trends in Immunology.2022; 43(1): 78. CrossRef - Hepatic retinaldehyde dehydrogenases are modulated by tocopherol supplementation in mice with hepatic steatosis
Amanda D'Espessailles, Valeria Campos, Nevenka Juretić, Gladys S. Tapia, Paulina Pettinelli
Nutrition.2022; 94: 111539. CrossRef - CD36 promotes de novo lipogenesis in hepatocytes through INSIG2-dependent SREBP1 processing
Han Zeng, Hong Qin, Meng Liao, Enze Zheng, Xiaoqing Luo, Anhua Xiao, Yiyu Li, Lin Chen, Li Wei, Lei Zhao, Xiong Z. Ruan, Ping Yang, Yaxi Chen
Molecular Metabolism.2022; 57: 101428. CrossRef - Biogenesis and Breakdown of Lipid Droplets in Pathological Conditions
Claudio M. Fader Kaiser, Patricia S. Romano, M. Cristina Vanrell, Cristian A. Pocognoni, Julieta Jacob, Benjamín Caruso, Laura R. Delgui
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of an orally administered DGAT2 inhibitor alone or coadministered with a liver-targeted ACC inhibitor in adults with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): rationale and design of the phase II, dose-ranging, dose-finding, randomised, pl
Neeta B Amin, Amanda Darekar, Quentin M Anstee, Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, Frank Tacke, Manoli Vourvahis, Douglas S Lee, Michael Charlton, Naim Alkhouri, Atsushi Nakajima, Carla Yunis
BMJ Open.2022; 12(3): e056159. CrossRef - Identification of microRNA Transcriptome Involved in Bovine Intramuscular Fat Deposition
Susan K. Duckett, Maslyn A. Greene
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Camellia (Camellia oleifera bel.) seed oil reprograms gut microbiota and alleviates lipid accumulation in high fat-fed mice through the mTOR pathway
Jing Gao, Li Ma, Jie Yin, Gang Liu, Jie Ma, SiTing Xia, SaiMing Gong, Qi Han, TieJun Li, YongZhong Chen, YuLong Yin
Food & Function.2022; 13(9): 4977. CrossRef - The Perirenal Fat Thickness Was Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yuxian Yang, Shuting Li, Yuechao Xu, Jing Ke, Dong Zhao
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 1505. CrossRef - Vanadium(IV)-Chlorodipicolinate Protects against Hepatic Steatosis by Ameliorating Lipid Peroxidation, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Inflammation
Yuanli Wang, Rulong Chen, Jingyi Li, Guodong Zeng, Juntao Yuan, Jingran Su, Chunyan Wu, Zhongbing Lu, Fang Zhang, Wenjun Ding
Antioxidants.2022; 11(6): 1093. CrossRef - Inhibiting SCAP/SREBP exacerbates liver injury and carcinogenesis in murine nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Satoshi Kawamura, Yuki Matsushita, Shigeyuki Kurosaki, Mizuki Tange, Naoto Fujiwara, Yuki Hayata, Yoku Hayakawa, Nobumi Suzuki, Masahiro Hata, Mayo Tsuboi, Takahiro Kishikawa, Hiroto Kinoshita, Takuma Nakatsuka, Masaya Sato, Yotaro Kudo, Yujin Hoshida, At
Journal of Clinical Investigation.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Baicalein Prevents Fructose-Induced Hepatic Steatosis in Rats: In the Regulation of Fatty Acid De Novo Synthesis, Fatty Acid Elongation and Fatty Acid Oxidation
Pan Li, Ruoyu Zhang, Meng Wang, Yuwei Chen, Zhiwei Chen, Xiumei Ke, Ling Zuo, Jianwei Wang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification and validation of immune related core transcription factors GTF2I in NAFLD
Minbo Zhang, Yu Zhang, Xiaoxiao Jiao, Linying Lai, Yiting Qian, Bo Sun, Wenzhuo Yang
PeerJ.2022; 10: e13735. CrossRef - Lipid-lowering effect of microencapsulated peptides from brewer's spent grain in high-sucrose diet-fed rats
M.R. Ferreira, A.G. Garzón, M.E. Oliva, R.E. Cian, S.R. Drago, M.E. D'Alessandro
Food Bioscience.2022; 49: 101981. CrossRef - The SREBP-dependent regulation of cyclin D1 coordinates cell proliferation and lipid synthesis
Arwa Aldaalis, Maria T. Bengoechea-Alonso, Johan Ericsson
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Targets of statins intervention in LDL-C metabolism: Gut microbiota
ChangXin Sun, ZePing Wang, LanQing Hu, XiaoNan Zhang, JiYe Chen, ZongLiang Yu, LongTao Liu, Min Wu
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Regulation of lipid droplet (LD) formation in hepatocytes via regulation of SREBP1c by non-coding RNAs
Shereen A. El Sobky, Nourhan K. Aboud, Nihal M. El Assaly, Injie O. Fawzy, Nada El-Ekiaby, Ahmed I. Abdelaziz
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Aspalathin-rich green rooibos tea in combination with glyburide and atorvastatin enhances lipid metabolism in a db/db mouse model
Oelfah Patel, Christo J. F. Muller, Elizabeth Joubert, Bernd Rosenkranz, Johan Louw, Charles Awortwe
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Capparis spinosa improves non-alcoholic steatohepatitis through down-regulating SREBP-1c and a PPARα-independent pathway in high-fat diet-fed rats
Rasoul Akbari, Hamid Yaghooti, Mohammad Taha Jalali, Laya Sadat Khorsandi, Narges Mohammadtaghvaei
BMC Research Notes.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Gypenosides counteract hepatic steatosis and intestinal barrier injury in rats with metabolic associated fatty liver disease by modulating the adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase and Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor kappa B pathways
Shuhua Shen, Kungen Wang, Yihui Zhi, Yue Dong
Pharmaceutical Biology.2022; 60(1): 1949. CrossRef - CYP51-mediated cholesterol biosynthesis is required for the proliferation of CD4+ T cells in Sjogren’s syndrome
Junhao Yin, Jiayao Fu, Yanxiong Shao, Jiabao Xu, Hui Li, Changyu Chen, Yijie Zhao, Zhanglong Zheng, Chuangqi Yu, Lingyan Zheng, Baoli Wang
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2022; 23(5): 1691. CrossRef - Differential TM4SF5‐mediated SIRT1 modulation and metabolic signaling in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis progression
Jihye Ryu, Eunmi Kim, Min‐Kyung Kang, Dae‐Geun Song, Eun‐Ae Shin, Haesong Lee, Jae Woo Jung, Seo Hee Nam, Ji Eon Kim, Hye‐Jin Kim, Taekwon Son, Semi Kim, Hwi Young Kim, Jung Weon Lee
The Journal of Pathology.2021; 253(1): 55. CrossRef - Changes in Glutathione Content in Liver Diseases: An Update
Mariapia Vairetti, Laura Giuseppina Di Pasqua, Marta Cagna, Plinio Richelmi, Andrea Ferrigno, Clarissa Berardo
Antioxidants.2021; 10(3): 364. CrossRef - Metreleptin therapy for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Open-label therapy interventions in two different clinical settings
Baris Akinci, Angela Subauste, Nevin Ajluni, Nazanene H. Esfandiari, Rasimcan Meral, Adam H. Neidert, Akin Eraslan, Rita Hench, Diana Rus, Barbara Mckenna, Hero K. Hussain, Thomas L. Chenevert, Marwan K. Tayeh, Amit R. Rupani, Jeffrey W. Innis, Christos S
Med.2021; 2(7): 814. CrossRef - Prediction of Srebp-1 as a Key Target of Qing Gan San Against MAFLD in Rats via RNA-Sequencing Profile Analysis
Bendong Yang, Jingyue Sun, Shufei Liang, Peixuan Wu, Rui Lv, Yanping He, Deqi Li, Wenlong Sun, Xinhua Song
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Structural insights into the mechanism of human NPC1L1-mediated cholesterol uptake
Miaoqing Hu, Fan Yang, Yawen Huang, Xin You, Desheng Liu, Shan Sun, Sen-Fang Sui
Science Advances.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification and Optimization of a Minor Allele-Specific siRNA to Prevent PNPLA3 I148M-Driven Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Justin K. Murray, Jason Long, Lei Liu, Shivani Singh, Danielle Pruitt, Michael Ollmann, Elissa Swearingen, Miki Hardy, Oliver Homann, Bin Wu, Jerry Ryan Holder, Kelvin Sham, Brad Herberich, Mei-Chu Lo, Hui Dou, Artem Shkumatov, Monica Florio, Ingrid C. Ru
Nucleic Acid Therapeutics.2021; 31(5): 324. CrossRef - Molecular mechanism of DLBS3733, a bioactive fraction of Lagerstroemia speciosa (L.) Pers., on ameliorating hepatic lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells
Olivia M. Tandrasasmita, Guntur Berlian, Raymond R. Tjandrawinata
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2021; 141: 111937. CrossRef - The Role of Gut Microbiota on Cholesterol Metabolism in Atherosclerosis
Margaret Vourakis, Gaétan Mayer, Guy Rousseau
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(15): 8074. CrossRef - Inhibition of Atherosclerosis and Liver Steatosis by Agmatine in Western Diet-Fed apoE-Knockout Mice Is Associated with Decrease in Hepatic De Novo Lipogenesis and Reduction in Plasma Triglyceride/High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio
Anna Wiśniewska, Aneta Stachowicz, Katarzyna Kuś, Magdalena Ulatowska-Białas, Justyna Totoń-Żurańska, Anna Kiepura, Kamila Stachyra, Maciej Suski, Mariusz Gajda, Jacek Jawień, Rafał Olszanecki
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(19): 10688. CrossRef - Therapeutic Targeting of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Downregulating SREBP-1C Expression via AMPK-KLF10 Axis
Yu-Chi Chen, Rong-Jane Chen, Szu-Yuan Peng, Winston C. Y. Yu, Vincent Hung-Shu Chang
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Regulation of Key Genes for Milk Fat Synthesis in Ruminants
Tong Mu, Honghong Hu, Yanfen Ma, Xiaofang Feng, Juan Zhang, Yaling Gu
Frontiers in Nutrition.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Visceral-to-Subcutaneous Abdominal Fat Ratio Is Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis
Chan-Hee Jung, Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyemi Kwon, Yoosoo Chang, Seungho Ryu, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 165. CrossRef - Lipidomic profiling analysis of the phospholipid molecules in SCAP-induced lipid droplet formation in bovine mammary epithelial cells
Liqiang Han, Kun Pang, Xiu ling Li, Juan J Loor, Guo yu Yang, Tengyun Gao
Prostaglandins & Other Lipid Mediators.2020; 149: 106420. CrossRef - Sexual Dimorphism of NAFLD in Adults. Focus on Clinical Aspects and Implications for Practice and Translational Research
Amedeo Lonardo, Ayako Suzuki
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(5): 1278. CrossRef - Smurf1 aggravates non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease by stabilizing SREBP‐1c in an E3 activity‐independent manner
Xin Zhang, Yutao Zhan, Wenjun Lin, Fei Zhao, Chaojing Guo, Yujiao Chen, Mengge Du, Dongnian Li, Lingqiang Zhang, Wei An, Hong‐Rui Wang, Ping Xie
The FASEB Journal.2020; 34(6): 7631. CrossRef - Beneficial Effects of SREBP Decoy Oligodeoxynucleotide in an Animal Model of Hyperlipidemia
Hyun-Jin An, Jung-Yeon Kim, Mi-Gyeong Gwon, Hyemin Gu, Hyun-Ju Kim, Jaechan Leem, Sung Won Youn, Kwan-Kyu Park
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(2): 552. CrossRef - Lack of Augmenter of Liver Regeneration Disrupts Cholesterol Homeostasis of Liver in Mice by Inhibiting the AMPK Pathway
Xin Wang, Ling‐yue Dong, Qu‐jing Gai, Wei‐lun Ai, Yuan Wu, Wei‐chun Xiao, Jing Zhang, Wei An
Hepatology Communications.2020; 4(8): 1149. CrossRef - HESA-A Attenuates Hepatic Steatosis in NAFLD Rat Model Through the Suppression of SREBP-1c and NF-kβ
M. Efati, M. Khorrami, Z. Jangravi, A. Z. Mahmoudabadi, M. Raeiszadeh, J. R. Sarshoori
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics.2020; 26(3): 1283. CrossRef - Prevention of Nonalcoholic Hepatic Steatosis by Shenling Baizhu Powder: Involvement of Adiponectin-Induced Inhibition of Hepatic SREBP-1c
Kairui Tang, Yuanjun Deng, Chuiyang Zheng, Huan Nie, Maoxing Pan, Runsen Chen, Jiqian Xie, Qinhe Yang, Yupei Zhang
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - (−)-Epicatechin and the comorbidities of obesity
Eleonora Cremonini, Dario E. Iglesias, Jiye Kang, Giovanni E. Lombardo, Zahra Mostofinejad, Ziwei Wang, Wei Zhu, Patricia I. Oteiza
Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics.2020; 690: 108505. CrossRef - microRNAs targeting cellular cholesterol: implications for combating anticancer drug resistance
Bernice Monchusi, Mandeep Kaur
Genes & Cancer.2020; 11(1-2): 20. CrossRef - Cellular acidosis triggers human MondoA transcriptional activity by driving mitochondrial ATP production
Blake R Wilde, Zhizhou Ye, Tian-Yeh Lim, Donald E Ayer
eLife.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Differential Recovery Speed of Activity and Metabolic Rhythms in Rats After an Experimental Protocol of Shift-Work
Nadia Saderi, Adrián Báez-Ruiz, Lucia E. Azuara-Álvarez, Carolina Escobar, Roberto C. Salgado-Delgado
Journal of Biological Rhythms.2019; 34(2): 154. CrossRef - Genetically modified mouse models to study hepatic neutral lipid mobilization
Guenter Haemmerle, Achim Lass
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2019; 1865(5): 879. CrossRef - Preventive effect of trans-chalcone on non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: Improvement of hepatic lipid metabolism
Elham Karimi-Sales, Abbas Ebrahimi-Kalan, Mohammad Reza Alipour
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2019; 109: 1306. CrossRef - A new pathway to eSCAPe lipotoxicity
Fadila Benhamed, Catherine Postic
Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology.2018; 42(1): 3. CrossRef - Overexpression of SREBF chaperone (SCAP) enhances nuclear SREBP1 translocation to upregulate fatty acid synthase (FASN) gene expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells
L.Q. Han, T.Y. Gao, G.Y. Yang, J.J. Loor
Journal of Dairy Science.2018; 101(7): 6523. CrossRef - Statin use and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients at high risk: A nationwide nested case-control study
Gyuri Kim, Suk-Yong Jang, Chung Mo Nam, Eun Seok Kang
Journal of Hepatology.2018; 68(3): 476. CrossRef - Changes of the Fatty Acid Profile in Erythrocyte Membranes of Patients following 6-Month Dietary Intervention Aimed at the Regression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Dominika Maciejewska, Wojciech Marlicz, Karina Ryterska, Marcin Banaszczak, Dominika Jamioł-Milc, Ewa Stachowska
Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Systems Analysis of the Liver Transcriptome in Adult Male Zebrafish Exposed to the Plasticizer (2-Ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP)
Matthew Huff, Willian A. da Silveira, Oliana Carnevali, Ludivine Renaud, Gary Hardiman
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Inactivation of ceramide synthase 2 catalytic activity in mice affects transcription of genes involved in lipid metabolism and cell division
Andreas Bickert, Paul Kern, Martina van Uelft, Stefanie Herresthal, Thomas Ulas, Katharina Gutbrod, Bernadette Breiden, Joachim Degen, Konrad Sandhoff, Joachim L. Schultze, Peter Dörmann, Dieter Hartmann, Reinhard Bauer, Klaus Willecke
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids.2018; 1863(7): 734. CrossRef - Paradoxical Protective Effect of Perfluorooctanesulfonic Acid Against High-Fat Diet–Induced Hepatic Steatosis in Mice
Ian Huck, Kevin Beggs, Udayan Apte
International Journal of Toxicology.2018; 37(5): 383. CrossRef - Developmental and extrahepatic physiological functions of SREBP pathway genes in mice
Luke J. Engelking, Mary Jo Cantoria, Yanchao Xu, Guosheng Liang
Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology.2018; 81: 98. CrossRef - Herbacetin, a flaxseed flavonoid, ameliorates high percent dietary fat induced insulin resistance and lipid accumulation through the regulation of hepatic lipid metabolizing and lipid-regulating enzymes
Chinnadurai Veeramani, Mohammed A. Alsaif, Khalid S. Al-Numair
Chemico-Biological Interactions.2018; 288: 49. CrossRef - Isocaloric Dietary Changes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High Cardiometabolic Risk Individuals
Giuseppe Della Pepa, Claudia Vetrani, Gianluca Lombardi, Lutgarda Bozzetto, Giovanni Annuzzi, Angela Rivellese
Nutrients.2017; 9(10): 1065. CrossRef - MDG-1, a Potential Regulator of PPARα and PPARγ, Ameliorates Dyslipidemia in Mice
Xu Wang, Linlin Shi, Sun Joyce, Yuan Wang, Yi Feng
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2017; 18(9): 1930. CrossRef
- SREBPs as the potential target for solving the polypharmacy dilemma


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



