Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Thyroid
- Phospholipase C-γ as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Graves’ Orbitopathy
- Tae Hoon Roh, Min Kyung Chae, Jae Sang Ko, Don O. Kikkawa, Sun Young Jang, Jin Sook Yoon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):739-749. Published online November 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1780
- 1,577 View
- 95 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
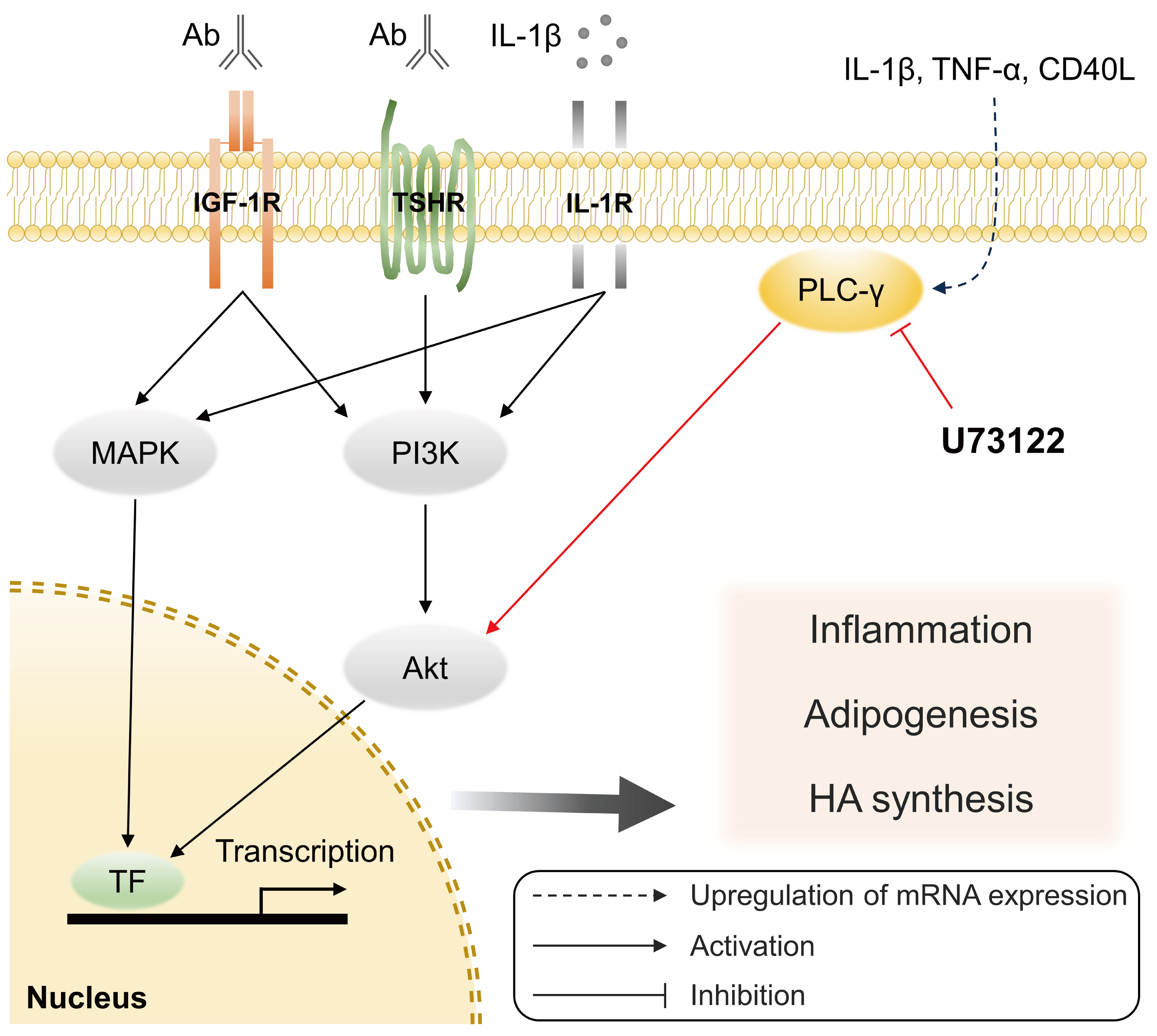
Phospholipase C-γ (PLC-γ) plays a crucial role in immune responses and is related to the pathogenesis of various inflammatory disorders. In this study, we investigated the role of PLC-γ and the therapeutic effect of the PLC-specific inhibitor U73122 using orbital fibroblasts from patients with Graves’ orbitopathy (GO).
Methods
The expression of phospholipase C gamma 1 (PLCG1) and phospholipase C gamma 2 (PLCG2) was evaluated using polymerase chain reaction in GO and normal orbital tissues/fibroblasts. The primary cultures of orbital fibroblasts were treated with non-toxic concentrations of U73122 with or without interleukin (IL)-1β to determine its therapeutic efficacy. The proinflammatory cytokine levels and activation of downstream signaling molecules were determined using Western blotting.
Results
PLCG1 and PLCG2 mRNA expression was significantly higher in GO orbital tissues than in controls (P<0.05). PLCG1 and PLCG2 mRNA expression was significantly increased (P<0.05) in IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α, and a cluster of differentiation 40 ligand-stimulated GO fibroblasts. U73122 significantly inhibited the IL-1β-induced expression of proinflammatory molecules, including IL-6, IL-8, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, cyclooxygenase-2, and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), and phosphorylated protein kinase B (p-Akt) and p38 (p-p38) kinase in GO fibroblasts, whereas it inhibited IL-6, IL-8, and ICAM-1, and p-Akt and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (p-JNK) in normal fibroblasts (P<0.05).
Conclusion
PLC-γ-inhibiting U73122 suppressed the production of proinflammatory cytokines and the phosphorylation of Akt and p38 kinase in GO fibroblasts. This study indicates the implications of PLC-γ in GO pathogenesis and its potential as a therapeutic target for GO.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
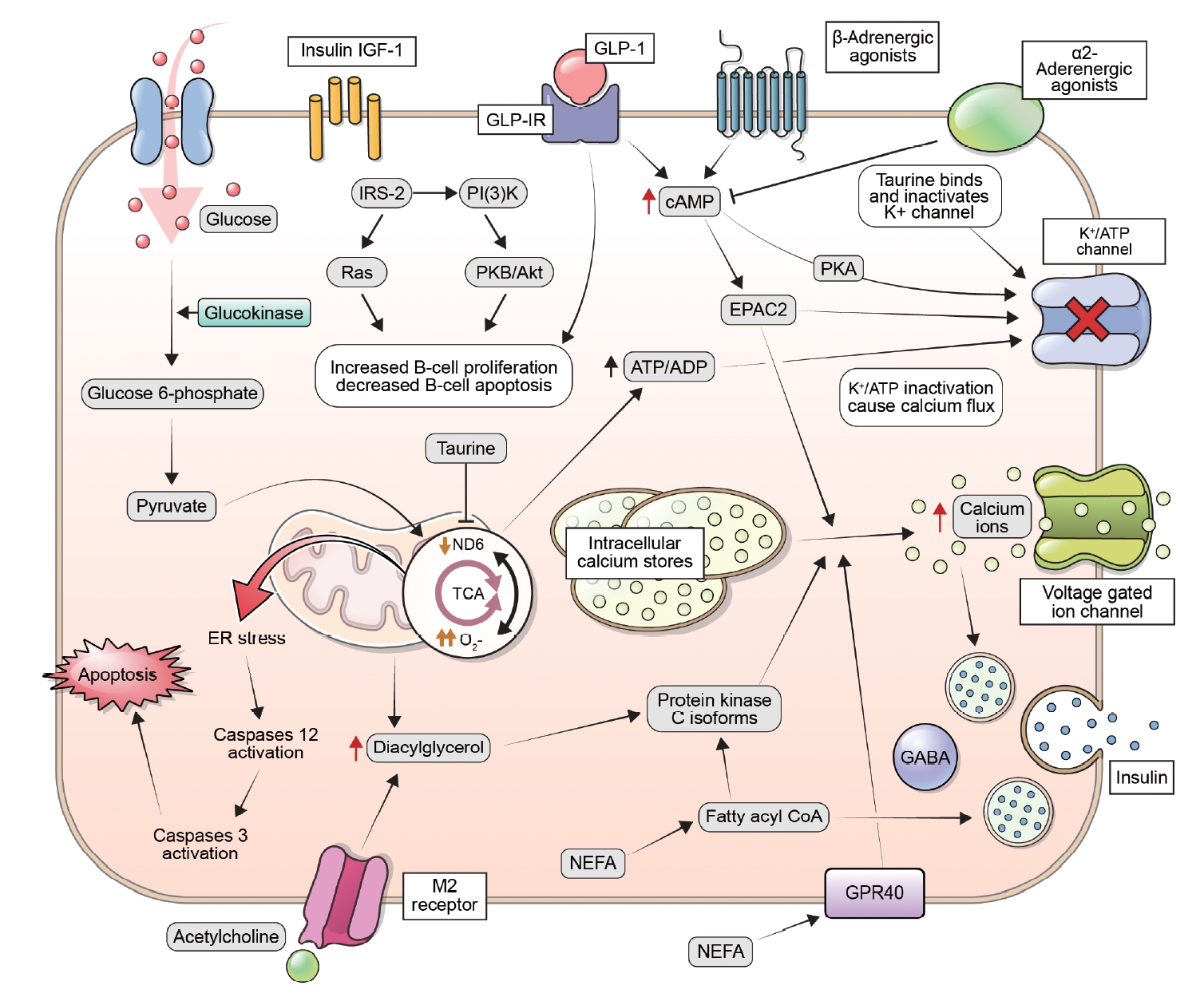
- The Impact of Taurine on Obesity-Induced Diabetes Mellitus: Mechanisms Underlying Its Effect
- Kainat Ahmed, Ha-Neul Choi, Jung-Eun Yim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):482-492. Published online October 17, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1776
- 2,681 View
- 158 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - This review explores the potential benefits of taurine in ameliorating the metabolic disorders of obesity and type 2 diabetes (T2D), highlighting the factors that bridge these associations. Relevant articles and studies were reviewed to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the relationship between obesity and the development of T2D and the effect of taurine on those conditions. The loss of normal β-cell function and development of T2D are associated with obesity-derived insulin resistance. The occurrence of diabetes has been linked to the low bioavailability of taurine, which plays critical roles in normal β-cell function, anti-oxidation, and anti-inflammation. The relationships among obesity, insulin resistance, β-cell dysfunction, and T2D are complex and intertwined. Taurine may play a role in ameliorating these metabolic disorders through different pathways, but further research is needed to fully understand its effects and potential as a therapeutic intervention.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of a Very Low-Calorie Diet on Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory and Metabolomic Profile in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Obese Subjects
Neus Bosch-Sierra, Carmen Grau-del Valle, Christian Salom, Begoña Zaragoza-Villena, Laura Perea-Galera, Rosa Falcón-Tapiador, Susana Rovira-Llopis, Carlos Morillas, Daniel Monleón, Celia Bañuls
Antioxidants.2024; 13(3): 302. CrossRef
- Effect of a Very Low-Calorie Diet on Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory and Metabolomic Profile in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Obese Subjects

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Association between Serum Amyloid A Levels and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Ting Liu, Meng Li, Chunying Cui, Jielin Zhou
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(3):315-327. Published online June 7, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1621
- 2,155 View
- 105 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
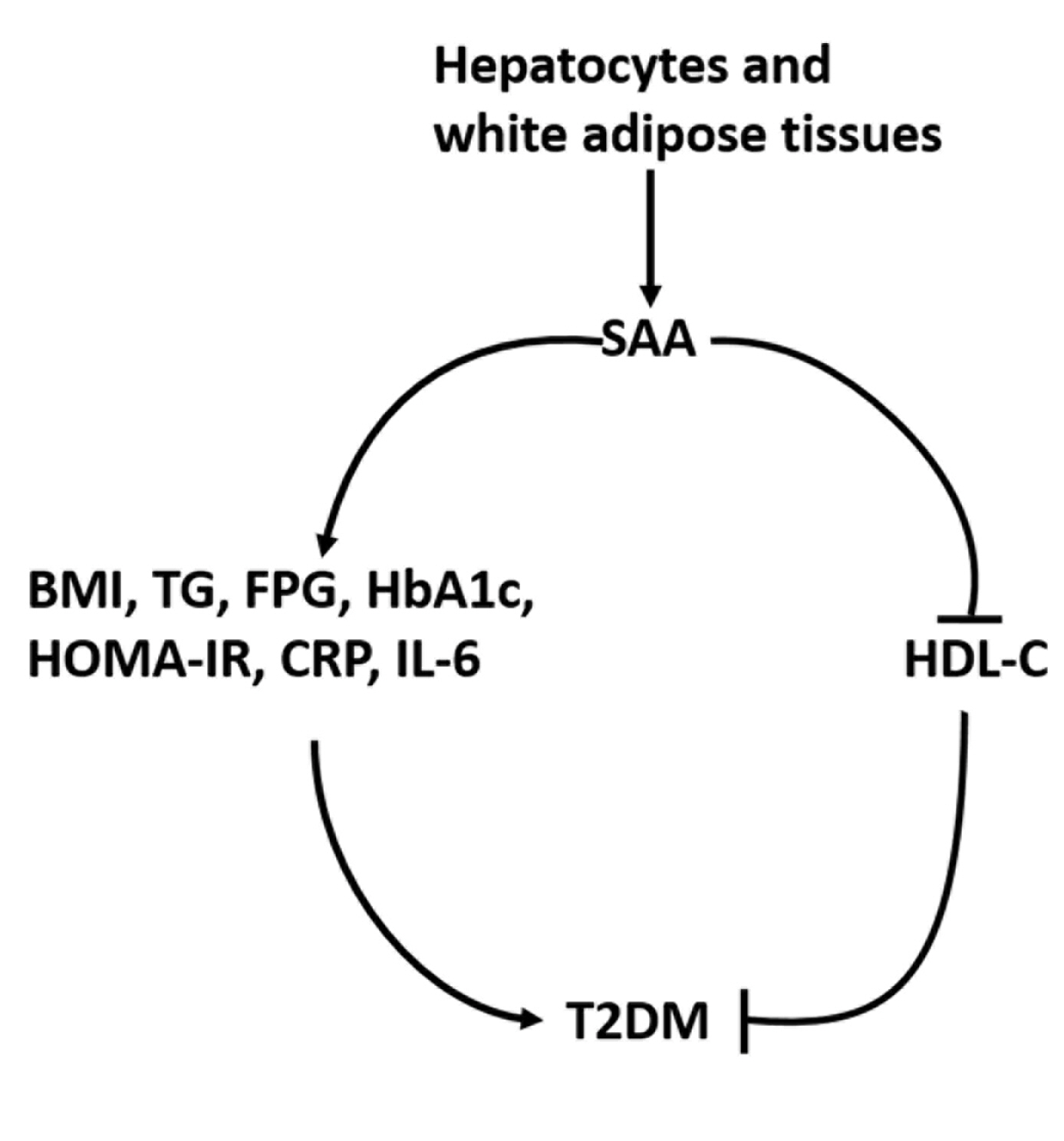
To date, consistent data have not been reported on the association between serum amyloid A (SAA) levels and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The purpose of this study was to systematically summarize their relationship.
Methods
Databases including PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, Web of Science, and MEDLINE were searched until August 2021. Cross-sectional and case-control studies were included.
Results
Twenty-one studies with 1,780 cases and 2,070 controls were identified. SAA levels were significantly higher in T2DM patients than in healthy groups (standardized mean difference [SMD], 0.68; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.39 to 0.98). A subgroup analysis showed that the mean age of participants and the continent that participants were from were related to differences in SAA levels between cases and controls. Furthermore, in T2DM patients, SAA levels were positively associated with body mass index (r=0.34; 95% CI, 0.03 to 0.66), triglycerides (r=0.12; 95% CI, 0.01 to 0.24), fasting plasma glucose (r=0.26; 95% CI, 0.07 to 0.45), hemoglobin A1c (r=0.24; 95% CI, 0.16 to 0.33), homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance (r=0.22; 95% CI, 0.10 to 0.34), C-reactive protein (r=0.77; 95% CI, 0.62 to 0.91), and interleukin-6 (r=0.42; 95% CI, 0.31 to 0.54), but negatively linked with highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol (r=–0.23; 95% CI, –0.44 to –0.03).
Conclusion
The meta-analysis suggests that high SAA levels may be associated with the presence of T2DM, as well as lipid metabolism homeostasis and the inflammatory response. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Correlation between insulin resistance and the rate of neutrophils-lymphocytes, monocytes-lymphocytes, platelets-lymphocytes in type 2 diabetic patients
Yuanyuan Zhang, Huaizhen Liu
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Functions of High-Density Lipoprotein in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Damien Denimal
Antioxidants.2023; 13(1): 57. CrossRef
- Correlation between insulin resistance and the rate of neutrophils-lymphocytes, monocytes-lymphocytes, platelets-lymphocytes in type 2 diabetic patients

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Stimulation of Alpha-1-Adrenergic Receptor Ameliorates Obesity-Induced Cataracts by Activating Glycolysis and Inhibiting Cataract-Inducing Factors
- Yong-Jik Lee, Yoo-Na Jang, Hyun-Min Kim, Yoon-Mi Han, Hong Seog Seo, Youngsub Eom, Jong-suk Song, Ji Hoon Jeong, Tae Woo Jung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):221-232. Published online March 23, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1237
- 3,625 View
- 137 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
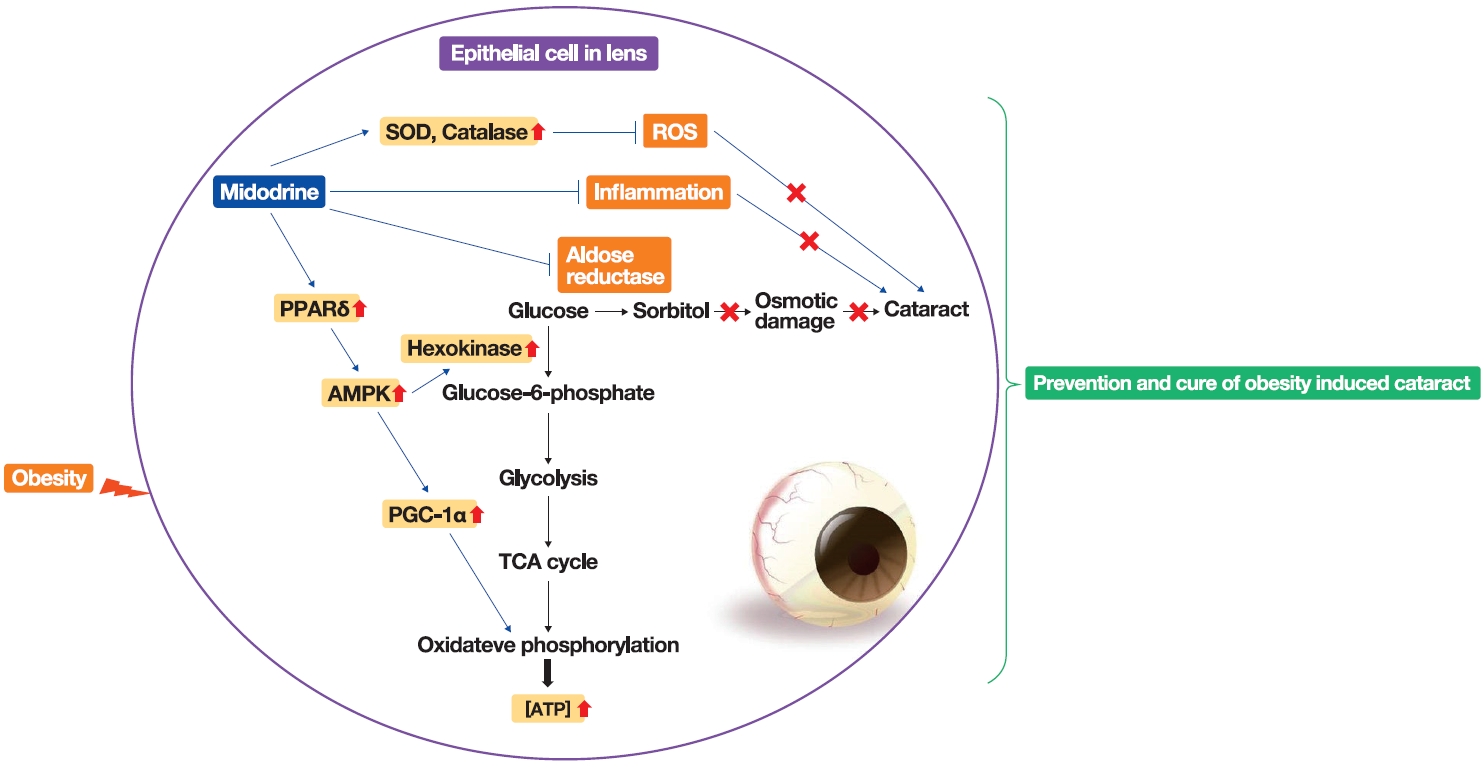
Obesity, the prevalence of which is increasing due to the lack of exercise and increased consumption of Westernized diets, induces various complications, including ophthalmic diseases. For example, obesity is involved in the onset of cataracts.
Methods
To clarify the effects and mechanisms of midodrine, an α1-adrenergic receptor agonist, in cataracts induced by obesity, we conducted various analytic experiments in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats, a rat model of obesity.
Results
Midodrine prevented cataract occurrence and improved lens clearance in OLETF rats. In the lenses of OLETF rats treated with midodrine, we observed lower levels of aldose reductase, tumor necrosis factor-α, and sorbitol, but higher levels of hexokinase, 5’-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase-alpha, adenosine 5´-triphosphate, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptordelta, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha, superoxide dismutase, and catalase.
Conclusion
The ameliorating effects of midodrine on cataracts in the OLETF obesity rat model are exerted via the following three mechanisms: direct inhibition of the biosynthesis of sorbitol, which causes cataracts; reduction of reactive oxygen species and inflammation; and (3) stimulation of normal aerobic glycolysis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- α1-Adrenergic Receptors: Insights into Potential Therapeutic Opportunities for COVID-19, Heart Failure, and Alzheimer’s Disease
Dianne M. Perez
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 4188. CrossRef - A new use for old drugs: identifying compounds with an anti-obesity effect using a high through-put semi-automated Caenorhabditis elegans screening platform
Freek Haerkens, Charlotte Kikken, Laurens Kirkels, Monique van Amstel, Willemijn Wouters, Els van Doornmalen, Christof Francke, Samantha Hughes
Heliyon.2022; 8(8): e10108. CrossRef
- α1-Adrenergic Receptors: Insights into Potential Therapeutic Opportunities for COVID-19, Heart Failure, and Alzheimer’s Disease

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Risk of Diabetes in Subjects with Positive Fecal Immunochemical Test: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
- Kwang Woo Kim, Hyun Jung Lee, Kyungdo Han, Jung Min Moon, Seung Wook Hong, Eun Ae Kang, Jooyoung Lee, Hosim Soh, Seong-Joon Koh, Jong Pil Im, Joo Sung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1069-1077. Published online October 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1119

- 3,629 View
- 97 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Positive fecal immunochemical test (FIT) results have been recently suggested as a risk factor for systemic inflammation. Diabetes induces inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract via several ways. We investigated the association between FIT results and the incidence of diabetes.
Methods
A total of 7,946,393 individuals aged ≥50 years from the National Cancer Screening Program database who underwent FIT for colorectal cancer (CRC) screening from 2009 to 2012 were enrolled. The primary outcome was newly diagnosed diabetes based on the International Classification of Disease 10th revision codes and administration of anti-diabetic medication during the follow-up period.
Results
During a mean follow-up of 6.5 years, the incidence rates of diabetes were 11.97, 13.60, 14.53, and 16.82 per 1,000 personyears in the FIT negative, one-positive, two-positive, and three-positive groups, respectively. The hazard ratios (HRs) for the incidence of diabetes were 1.14 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.12 to 1.16; HR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.16 to 1.27; and HR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.28 to 1.55) in the one-positive, two-positive, and three-positive FIT groups compared with the FIT negative group, respectively. The effect was consistent in individuals with normal fasting blood glucose (adjusted HR 1.55 vs. 1.14, P for interaction <0.001).
Conclusion
Positive FIT results were associated with a significantly higher risk of diabetes, suggesting that the FIT can play a role not only as a CRC screening tool, but also as a surrogate marker of systemic inflammation; thus, increasing the diabetes risk. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Uncovering a dose-response relationship between positive fecal immunochemical test (FIT) and all-cause, cardiovascular and cancer-related mortality
Chi Pang Wen, Min Kuang Tsai, June Han Lee, Hung Yi Chiou, Christopher Wen, Ta-Wei David Chu, Chien Hua Chen
European Journal of Internal Medicine.2024; 120: 69. CrossRef - Faecal haemoglobin concentrations are associated with all-cause mortality and cause of death in colorectal cancer screening
Lasse Kaalby, Ulrik Deding, Issam Al-Najami, Gabriele Berg-Beckhoff, Thomas Bjørsum-Meyer, Tinne Laurberg, Aasma Shaukat, Robert J. C. Steele, Anastasios Koulaouzidis, Morten Rasmussen, Morten Kobaek-Larsen, Gunnar Baatrup
BMC Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Positive Results from the Fecal Immunochemical Test Can Be Related to Dementia: A Nationwide Population-Based Study in South Korea
Yu Kyung Jun, Seung Woo Lee, Kwang Woo Kim, Jung Min Moon, Seong-Joon Koh, Hyun Jung Lee, Joo Sung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Jong Pil Im
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2023; 91(4): 1515. CrossRef - Faecal Haemoglobin Estimated by Faecal Immunochemical Tests—An Indicator of Systemic Inflammation with Real Clinical Potential
Karen N. Barnett, Gavin R. C. Clark, Robert J. C. Steele, Callum G. Fraser
Diagnostics.2021; 11(11): 2093. CrossRef
- Uncovering a dose-response relationship between positive fecal immunochemical test (FIT) and all-cause, cardiovascular and cancer-related mortality

- Endocrine Research
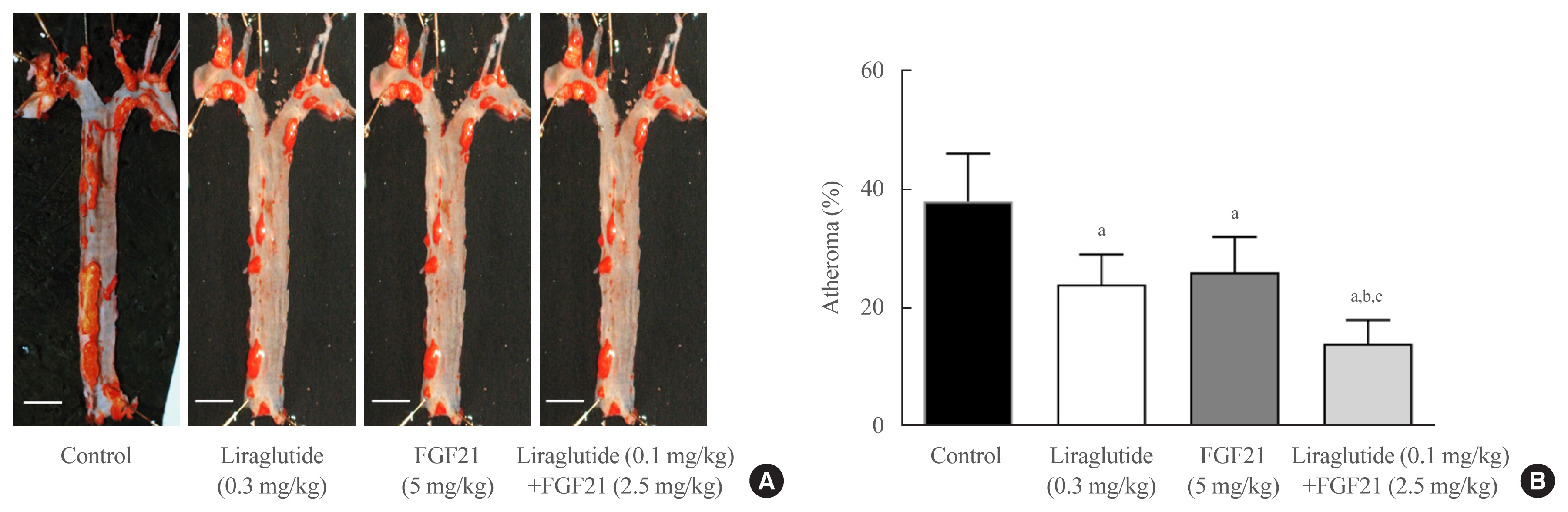
- Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Analogue and Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Combination on the Atherosclerosis-Related Process in a Type 2 Diabetes Mouse Model
- Jin Hee Kim, Gha Young Lee, Hyo Jin Maeng, Hoyoun Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyoung Min Kim, Soo Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):157-170. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.781
- 6,861 View
- 176 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogues regulate glucose homeostasis and have anti-inflammatory properties, but cause gastrointestinal side effects. The fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a hormonal regulator of lipid and glucose metabolism that has poor pharmacokinetic properties, including a short half-life. To overcome these limitations, we investigated the effect of a low-dose combination of a GLP-1 analogue and FGF21 on atherosclerosis-related molecular pathways.
Methods
C57BL/6J mice were fed a high-fat diet for 30 weeks followed by an atherogenic diet for 10 weeks and were divided into four groups: control (saline), liraglutide (0.3 mg/kg/day), FGF21 (5 mg/kg/day), and low-dose combination treatment with liraglutide (0.1 mg/kg/day) and FGF21 (2.5 mg/kg/day) (n=6/group) for 6 weeks. The effects of each treatment on various atherogenesisrelated pathways were assessed.
Results
Liraglutide, FGF21, and their low-dose combination significantly reduced atheromatous plaque in aorta, decreased weight, glucose, and leptin levels, and increased adiponectin levels. The combination treatment upregulated the hepatic uncoupling protein-1 (UCP1) and Akt1 mRNAs compared with controls. Matric mentalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) were downregulated and phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt) and phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (p-ERK) were upregulated in liver of the liraglutide-alone and combination-treatment groups. The combination therapy also significantly decreased the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Caspase-3 was increased, whereas MMP-9, ICAM-1, p-Akt, and p-ERK1/2 were downregulated in the liraglutide-alone and combination-treatment groups.
Conclusion
Administration of a low-dose GLP-1 analogue and FGF21 combination exerts beneficial effects on critical pathways related to atherosclerosis, suggesting the synergism of the two compounds. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Current status and future perspectives of FGF21 analogues in clinical trials
Zara Siu Wa Chui, Qing Shen, Aimin Xu
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Design and pharmaceutical evaluation of bifunctional fusion protein of FGF21 and GLP-1 in the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Xianlong Ye, Yingli Chen, Jianying Qi, Shenglong Zhu, Yuanyuan Wu, Jingjing Xiong, Fei Hu, Zhimou Guo, Xinmiao Liang
European Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 952: 175811. CrossRef - Use of FGF21 analogs for the treatment of metabolic disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Maria Paula Carbonetti, Fernanda Almeida-Oliveira, David Majerowicz
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the potential mechanism of Simiao Yongan decoction in the treatment of diabetic peripheral vascular disease based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology
Fang Cao, Yongkang Zhang, Yuan Zong, Xia Feng, Junlin Deng, Yuzhen Wang, Yemin Cao
Medicine.2023; 102(52): e36762. CrossRef - The Healing Capability of Clove Flower Extract (CFE) in Streptozotocin-Induced (STZ-Induced) Diabetic Rat Wounds Infected with Multidrug Resistant Bacteria
Rewaa Ali, Tarek Khamis, Gamal Enan, Gamal El-Didamony, Basel Sitohy, Gamal Abdel-Fattah
Molecules.2022; 27(7): 2270. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) and Atherosclerosis: Explaining Their Pathophysiology, Association and the Role of Incretin-Based Drugs
Eleftheria Galatou, Elena Mourelatou, Sophia Hatziantoniou, Ioannis S. Vizirianakis
Antioxidants.2022; 11(6): 1060. CrossRef - Unlocking the Therapeutic Potential of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Analogue and Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Combination for the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis in Type 2 Diabetes
Jang Won Son
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(1): 57. CrossRef - Effects of fasting on skeletal muscles and body fat of adult and old C57BL/6J mice
Mindaugas Kvedaras, Petras Minderis, Leonardo Cesanelli, Agne Cekanauskaite, Aivaras Ratkevicius
Experimental Gerontology.2021; 152: 111474. CrossRef - The Role of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Diabetic Cardiovascular Complications and Related Epigenetic Mechanisms
Mengjie Xiao, Yufeng Tang, Shudong Wang, Jie Wang, Jie Wang, Yuanfang Guo, Jingjing Zhang, Junlian Gu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Liraglutide Decreases Liver Fat Content and Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Levels in Newly Diagnosed Overweight Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Xinyue Li, Xiaojuan Wu, Yumei Jia, Jing Fu, Lin Zhang, Tao Jiang, Jia Liu, Guang Wang, Claudia Cardoso
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Differential importance of endothelial and hematopoietic cell GLP-1Rs for cardiometabolic versus hepatic actions of semaglutide
Brent A. McLean, Chi Kin Wong, Kiran Deep Kaur, Randy J. Seeley, Daniel J. Drucker
JCI Insight.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Current status and future perspectives of FGF21 analogues in clinical trials

- Obesity and Metabolism
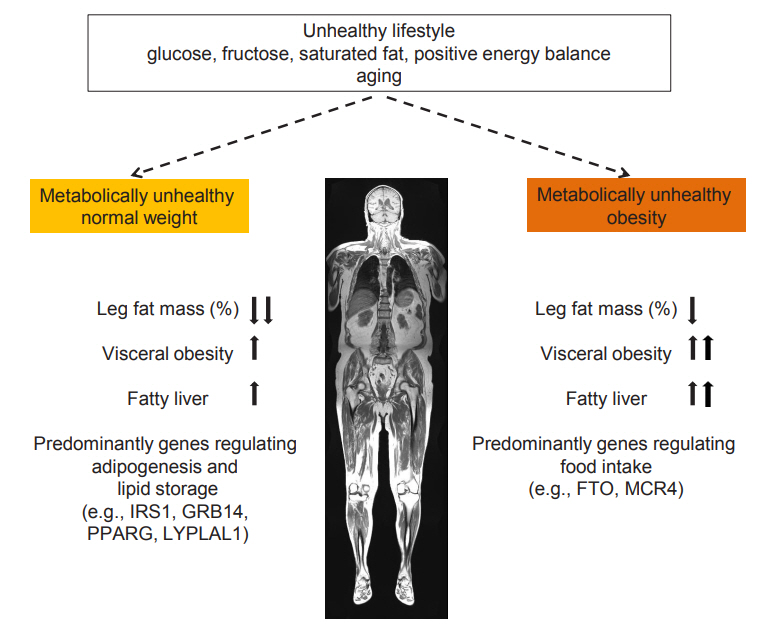
- Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Normal Weight and Obesity
- Norbert Stefan
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):487-493. Published online August 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.301
- 9,090 View
- 437 Download
- 31 Web of Science
- 30 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Increased fat mass is an established risk factor for the cardiometabolic diseases type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (CVD) and is associated with increased risk of all-cause and CVD mortality. However, also very low fat mass associates with such an increased risk. Whether impaired metabolic health, characterized by hypertension, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and subclinical inflammation, may explain part of the elevated risk of cardiometabolic diseases that is found in many subjects with very low fat mass, as it does in many obese subjects, is unknown. An important pathomechanism of impaired metabolic health is disproportionate fat distribution. In this article the risk of cardiometabolic diseases and mortality in subjects with metabolically healthy and unhealthy normal weight and obesity is summarized. Furthermore, the change of metabolic health during a longer period of follow-up and its impact on cardiometabolic diseases is being discussed. Finally, the implementation of the concept of metabolic health in daily clinical practice is being highlighted.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Phenotyping obesity: A focus on metabolically healthy obesity and metabolically unhealthy normal weight
Rachel Agius, Nikolai P. Pace, Stephen Fava
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing verum and sham acupoint catgut embedding for adults with obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Jin-huan Yue, Xiao-ling Li, Yu-ying Zhang, Guan-hu Yang, Jeffrey Zhong-xue Mah, Ang Li, Wei-wei Zhao, Yu-lin Wang, Qin-hong Zhang, Jia-qi Huang
Medicine.2024; 103(4): e36653. CrossRef - Association between Weight Change and Incidence of Dyslipidemia in Young Adults: A Retrospective Cohort Study of Korean Male Soldiers
Joon-Young Yoon, Won Ju Park, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Cheol-Kyu Park, Wonsuk Choi
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2024; 33(1): 36. CrossRef - Metabolically Healthy Obesity: An Eye-opener
Purushothaman Padmanabhan, Nagendram Dinakaran, Somnath Verma, S Keerthana
Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Endoscopy Practice.2023; 3(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of metabolic health and obesity on all-cause death and CVD incidence in Korean adults: a retrospective cohort study
Ye-Seul Kim, Sang-Jun Shin, Yonghwan Kim, Joungyoun Kim, Hee-Taik Kang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Coffee and metabolic phenotypes: A cross-sectional analysis of the Japan multi-institutional collaborative cohort (J-MICC) study
Takeshi Watanabe, Kokichi Arisawa, Tien Van Nguyen, Masashi Ishizu, Sakurako Katsuura-Kamano, Asahi Hishida, Takashi Tamura, Yasufumi Kato, Rieko Okada, Rie Ibusuki, Chihaya Koriyama, Sadao Suzuki, Takahiro Otani, Teruhide Koyama, Satomi Tomida, Kiyonori
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2023; 33(3): 620. CrossRef - Metabolically unhealthy phenotype in adults with normal weight: Is cardiometabolic health worse off when compared to adults with obesity?
Myong-Won Seo, Joon Young Kim
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2023; 17(2): 116. CrossRef - Association between metabolic obesity phenotypes and multiple myeloma hospitalization burden: A national retrospective study
Yue Zhang, Xiude Fan, Chunhui Zhao, Zinuo Yuan, Yiping Cheng, Yafei Wu, Junming Han, Zhongshang Yuan, Yuanfei Zhao, Keke Lu
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolically healthy obesity: Misleading phrase or healthy phenotype?
Cem Tanriover, Sidar Copur, Abduzhappar Gaipov, Batu Ozlusen, Rustu E. Akcan, Masanari Kuwabara, Mads Hornum, Daniel H. Van Raalte, Mehmet Kanbay
European Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 111: 5. CrossRef - Prevalence of combined metabolic health and weight status by various diagnosis criteria and association with cardiometabolic disease in Korean adults
Myong-Won Seo, Jung-Min Lee, Hyun Chul Jung
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2023; 17(2): 137. CrossRef - Precision medicine in complex diseases—Molecular subgrouping for improved prediction and treatment stratification
Åsa Johansson, Ole A. Andreassen, Søren Brunak, Paul W. Franks, Harald Hedman, Ruth J. F. Loos, Benjamin Meder, Erik Melén, Craig E. Wheelock, Bo Jacobsson
Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 294(4): 378. CrossRef - Lipid droplet biogenesis and functions in health and disease
Armella Zadoorian, Ximing Du, Hongyuan Yang
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2023; 19(8): 443. CrossRef - Molecular Mechanisms for the Vicious Cycle between Insulin Resistance and the Inflammatory Response in Obesity
Dariusz Szukiewicz
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(12): 9818. CrossRef - Insulin Resistance Is the Main Characteristic of Metabolically Unhealthy Obesity (MUO) Associated with NASH in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery
Sophia M. Schmitz, Sebastian Storms, Alexander Koch, Christine Stier, Andreas Kroh, Karl P. Rheinwalt, Sandra Schipper, Karim Hamesch, Tom F. Ulmer, Ulf P. Neumann, Patrick H. Alizai
Biomedicines.2023; 11(6): 1595. CrossRef - Hyperleptinemia as a marker of various phenotypes of obesity and overweight in women with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus
L. V. Kondrateva, Yu. N. Gorbunova, T. A. Panafidina, T. V. Popkova
Rheumatology Science and Practice.2023; 61(3): 339. CrossRef - Predictable Representation of Metabolic Synthesis Pathways of Vitamins and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Obese Adults
A. V. Shestopalov, L. A. Ganenko, I. M. Kolesnikova, T. V. Grigoryeva, I. Yu. Vasilyev, Yu. L. Naboka, N. I. Volkova, O. V. Borisenko, S. A. Roumiantsev
Journal of Evolutionary Biochemistry and Physiology.2023; 59(5): 1510. CrossRef - Metabolically unhealthy individuals, either with obesity or not, have a higher risk of critical coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes than metabolically healthy individuals without obesity
Nam Hoon Kim, Kyeong Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim
Metabolism.2022; 128: 154894. CrossRef - Associations between obesity, metabolic syndrome, and endometrial cancer risk in East Asian women
Boyoung Park
Journal of Gynecologic Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin and cancer: a tangled web
Brooks P. Leitner, Stephan Siebel, Ngozi D. Akingbesote, Xinyi Zhang, Rachel J. Perry
Biochemical Journal.2022; 479(5): 583. CrossRef - Relationships Between Metabolic Body Composition Status and Rapid Kidney Function Decline in a Community-Based Population: A Prospective Observational Study
Shao-Chi Chu, Po-Hsi Wang, Kuan-Ying Lu, Chia-Chun Ko, Yun-Hsuan She, Chin-Chan Lee, I-Wen Wu, Chiao-Yin Sun, Heng-Jung Hsu, Heng-Chih Pan
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dissecting the clinical relevance of polygenic risk score for obesity—a cross-sectional, longitudinal analysis
Eun Kyung Choe, Manu Shivakumar, Seung Mi Lee, Anurag Verma, Dokyoon Kim
International Journal of Obesity.2022; 46(9): 1686. CrossRef - Metabolic and Obesity Phenotype Trajectories in Taiwanese Medical Personnel
Hsin-Yun Chang, Jer-Hao Chang, Yin-Fan Chang, Chih-Hsing Wu, Yi-Ching Yang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(13): 8184. CrossRef - Sex Differences in Cardiovascular Impact of Early Metabolic Impairment: Interplay between Dysbiosis and Adipose Inflammation
Haneen S. Dwaib, Ibrahim AlZaim, Ghina Ajouz, Ali H. Eid, Ahmed El-Yazbi
Molecular Pharmacology.2022; 102(1): 60. CrossRef - Reduced leukocyte mitochondrial copy number in metabolic syndrome and metabolically healthy obesity
Rachel Agius, Nikolai Paul Pace, Stephen Fava
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in BMI and physical activity from youth to adulthood distinguish normal-weight, metabolically obese adults from those who remain healthy
A. Viitasalo, K. Pahkala, T. Lehtimäki, JSA. Viikari, TH. Tammelin, O. Raitakari, TO. Kilpeläinen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathogenesis, Murine Models, and Clinical Implications of Metabolically Healthy Obesity
Yun Kyung Cho, Yoo La Lee, Chang Hee Jung
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(17): 9614. CrossRef - Metabolically healthy obesity: it is time to consider its dynamic changes
Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(4): 123. CrossRef - Obesity as a Risk Factor for Breast Cancer—The Role of miRNA
Karolina Hanusek, Jakub Karczmarski, Anna Litwiniuk, Katarzyna Urbańska, Filip Ambrozkiewicz, Andrzej Kwiatkowski, Lidia Martyńska, Anita Domańska, Wojciech Bik, Agnieszka Paziewska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(24): 15683. CrossRef - Propensity Score–Matching Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG) vs. Gastric Bypass (RYGB) in Patients ≥ 60 Years
Omar Thaher, Stefanie Wolf, Martin Hukauf, Christine Stroh
Obesity Surgery.2021; 31(6): 2682. CrossRef - Associations between obesity, metabolic health, and the risk of breast cancer in East Asian women
Boyoung Park, Soyeoun Kim, Hayoung Kim, Chihwan Cha, Min Sung Chung
British Journal of Cancer.2021; 125(12): 1718. CrossRef
- Phenotyping obesity: A focus on metabolically healthy obesity and metabolically unhealthy normal weight

- Miscellaneous
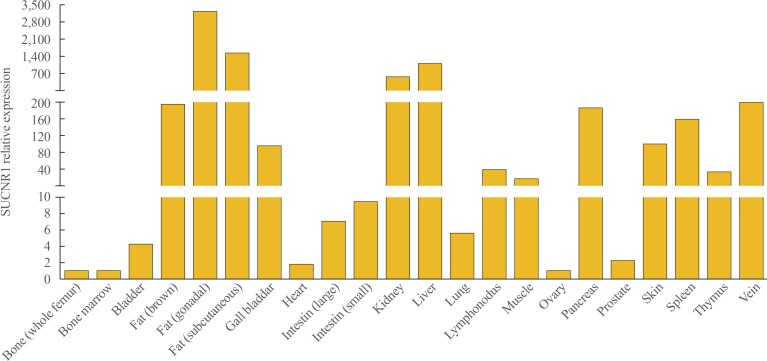
- Multifaceted Actions of Succinate as a Signaling Transmitter Vary with Its Cellular Locations
- Yuqi Guo, Sun Wook Cho, Deepak Saxena, Xin Li
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):36-43. Published online March 19, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.36
- 7,677 View
- 198 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 24 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Since the identification of succinate's receptor in 2004, studies supporting the involvement of succinate signaling through its receptor in various diseases have accumulated and most of these investigations have highlighted succinate's pro-inflammatory role. Taken with the fact that succinate is an intermediate metabolite in the center of mitochondrial activity, and considering its potential regulation of protein succinylation through succinyl-coenzyme A, a review on the overall multifaceted actions of succinate to discuss whether and how these actions relate to the cellular locations of succinate is much warranted. Mechanistically, it is important to consider the sources of succinate, which include somatic cellular released succinate and those produced by the microbiome, especially the gut microbiota, which is an equivalent, if not greater contributor of succinate levels in the body. Continue learning the critical roles of succinate signaling, known and unknown, in many pathophysiological conditions is important. Furthermore, studies to delineate the regulation of succinate levels and to determine how succinate elicits various types of signaling in a temporal and spatial manner are also required.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Type 2 diabetes and succinate: unmasking an age-old molecule
Sonia Fernández-Veledo, Anna Marsal-Beltran, Joan Vendrell
Diabetologia.2024; 67(3): 430. CrossRef - Metabolism Serves as a Bridge Between Cardiomyocytes and Immune Cells in Cardiovascular Diseases
Lixiao Hang, Ying Zhang, Zheng Zhang, Haiqiang Jiang, Lin Xia
Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle as a Central Regulator of the Rate of Aging: Implications for Metabolic Interventions
Jonathan M. Borkum
Advanced Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dysregulation of metabolic pathways in pulmonary fibrosis
Rishi Rajesh, Reham Atallah, Thomas Bärnthaler
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2023; 246: 108436. CrossRef - Succinate metabolism and membrane reorganization drives the endotheliopathy and coagulopathy of traumatic hemorrhage
Sarah Abdullah, Michael Ghio, Aaron Cotton-Betteridge, Aditya Vinjamuri, Robert Drury, Jacob Packer, Oguz Aras, Jessica Friedman, Mardeen Karim, David Engelhardt, Emma Kosowski, Kelby Duong, Farhana Shaheen, Patrick R. McGrew, Charles T. Harris, Robert Re
Science Advances.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pharmacokinetics of Succinate in Rats after Intravenous Administration of Mexidol
A. V. Shchulkin, P. Yu. Mylnikov, I. V. Chernykh, A. S. Esenina, E. N. Yakusheva
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine.2023; 175(1): 54. CrossRef - Complex II Biology in Aging, Health, and Disease
Eric Goetzman, Zhenwei Gong, Bob Zhang, Radhika Muzumdar
Antioxidants.2023; 12(7): 1477. CrossRef - The Influence of the Microbiome on Urological Malignancies: A Systematic Review
Joao G. Porto, Maria Camila Suarez Arbelaez, Brandon Pena, Archan Khandekar, Ankur Malpani, Bruno Nahar, Sanoj Punnen, Chad R. Ritch, Mark L. Gonzalgo, Dipen J. Parekh, Robert Marcovich, Hemendra N. Shah
Cancers.2023; 15(20): 4984. CrossRef - The Gut Microbiome, Metformin, and Aging
Sri Nitya Reddy Induri, Payalben Kansara, Scott C. Thomas, Fangxi Xu, Deepak Saxena, Xin Li
Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology.2022; 62(1): 85. CrossRef - Tissue- and substrate-dependent mitochondrial responses to acute hypoxia–reoxygenation stress in a marine bivalve (Crassostrea gigas
)
Linda Adzigbli, Eugene P. Sokolov, Siriluck Ponsuksili, Inna M. Sokolova
Journal of Experimental Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Acute Succinate Administration Increases Oxidative Phosphorylation and Skeletal Muscle Explosive Strength via SUCNR1
Guli Xu, Yexian Yuan, Pei Luo, Jinping Yang, Jingjing Zhou, Canjun Zhu, Qingyan Jiang, Gang Shu
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrated bioinformatics analysis identifies established and novel TGFβ1-regulated genes modulated by anti-fibrotic drugs
Ava C. Wilson, Joe Chiles, Shah Ashish, Diptiman Chanda, Preeti L. Kumar, James A. Mobley, Enid R. Neptune, Victor J. Thannickal, Merry-Lynn N. McDonald
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - SUCNR1 Mediates the Priming Step of the Inflammasome in Intestinal Epithelial Cells: Relevance in Ulcerative Colitis
Cristina Bauset, Lluis Lis-Lopez, Sandra Coll, Laura Gisbert-Ferrándiz, Dulce C. Macias-Ceja, Marta Seco-Cervera, Francisco Navarro, Juan V. Esplugues, Sara Calatayud, Dolores Ortiz-Masia, Maria D. Barrachina, Jesús Cosín-Roger
Biomedicines.2022; 10(3): 532. CrossRef - Succinate as a New Actor in Pluripotency and Early Development?
Damien Detraux, Patricia Renard
Metabolites.2022; 12(7): 651. CrossRef - Succinate Dehydrogenase, Succinate, and Superoxides: A Genetic, Epigenetic, Metabolic, Environmental Explosive Crossroad
Paule Bénit, Judith Goncalves, Riyad El Khoury, Malgorzata Rak, Judith Favier, Anne-Paule Gimenez-Roqueplo, Pierre Rustin
Biomedicines.2022; 10(8): 1788. CrossRef - Aqueous, Non-Polymer-Based Perovskite Quantum Dots for Bioimaging: Conserving Fluorescence and Long-Term Stability via Simple and Robust Synthesis
Sanjayan C G, Jyothi Mannekote Shivanna, Jessica D. Schiffman, Sakar Mohan, Srinivasa Budagumpi, R. Geetha Balakrishna
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.2022; 14(34): 38471. CrossRef - Targeting the succinate receptor effectively inhibits periodontitis
Yuqi Guo, Fangxi Xu, Scott C. Thomas, Yanli Zhang, Bidisha Paul, Satish Sakilam, Sungpil Chae, Patty Li, Caleb Almeter, Angela R. Kamer, Paramjit Arora, Dana T. Graves, Deepak Saxena, Xin Li
Cell Reports.2022; 40(12): 111389. CrossRef - Gemigliptin Alleviates Succinate-Induced Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation by Ameliorating Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Giang Nguyen, So Young Park, Dinh Vinh Do, Dae-Hee Choi, Eun-Hee Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 918. CrossRef - Succinate at the Crossroad of Metabolism and Angiogenesis: Roles of SDH, HIF1α and SUCNR1
Reham Atallah, Andrea Olschewski, Akos Heinemann
Biomedicines.2022; 10(12): 3089. CrossRef - Divulging a Pleiotropic Role of Succinate Receptor SUCNR1 in Renal Cell Carcinoma Microenvironment
Rania Najm, Mahmood Yaseen Hachim, Richard K. Kandasamy
Cancers.2022; 14(24): 6064. CrossRef - Succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors: in silico flux analysis and in vivo metabolomics investigations show no severe metabolic consequences for rats and humans
H. Kamp, J. Wahrheit, S. Stinchcombe, T. Walk, F. Stauber, B.v. Ravenzwaay
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2021; 150: 112085. CrossRef - Can polarization of macrophage metabolism enhance cardiac regeneration?
Connor Lantz, Amanda Becker, Edward B. Thorp
Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology.2021; 160: 87. CrossRef - Ethylmethylhydroxypyridine Succinate Induces Anti-inflammatory Polarization of Microglia in the Brain of Aging Rat
Y. I. Kirova, F. M. Shakova, T. A. Voronina
Biochemistry (Moscow), Supplement Series A: Membrane and Cell Biology.2021; 15(4): 356. CrossRef - Model systems in SDHx-related pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma
Krisztina Takács-Vellai, Zsolt Farkas, Fanni Ősz, Gordon W. Stewart
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews.2021; 40(4): 1177. CrossRef
- Type 2 diabetes and succinate: unmasking an age-old molecule

- Diabetes
- Pioglitazone Attenuates Palmitate-Induced Inflammation and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Pancreatic β-Cells
- Seok-Woo Hong, Jinmi Lee, Jung Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(1):105-113. Published online March 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.1.105
- 6,245 View
- 96 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background The nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activator gamma (PPARγ) is a useful therapeutic target for obesity and diabetes, but its role in protecting β-cell function and viability is unclear.
Methods To identify the potential functions of PPARγ in β-cells, we treated mouse insulinoma 6 (MIN6) cells with the PPARγ agonist pioglitazone in conditions of lipotoxicity, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and inflammation.
Results Palmitate-treated cells incubated with pioglitazone exhibited significant improvements in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and the repression of apoptosis, as shown by decreased caspase-3 cleavage and poly (adenosine diphosphate [ADP]-ribose) polymerase activity. Pioglitazone also reversed the palmitate-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor α, interleukin 6 [IL-6], and IL-1β) and ER stress markers (phosphor-eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α, glucose-regulated protein 78 [GRP78], cleaved-activating transcription factor 6 [ATF6], and C/EBP homologous protein [CHOP]), and pioglitazone significantly attenuated inflammation and ER stress in lipopolysaccharide- or tunicamycin-treated MIN6 cells. The protective effect of pioglitazone was also tested in pancreatic islets from high-fat-fed KK-Ay mice administered 0.02% (wt/wt) pioglitazone or vehicle for 6 weeks. Pioglitazone remarkably reduced the expression of ATF6α, GRP78, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, prevented α-cell infiltration into the pancreatic islets, and upregulated glucose transporter 2 (Glut2) expression in β-cells. Moreover, the preservation of β-cells by pioglitazone was accompanied by a significant reduction of blood glucose levels.
Conclusion Altogether, these results support the proposal that PPARγ agonists not only suppress insulin resistance, but also prevent β-cell impairment via protection against ER stress and inflammation. The activation of PPARγ might be a new therapeutic approach for improving β-cell survival and insulin secretion in patients with diabetes mellitus
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nr1h4 and Thrb ameliorate ER stress and provide protection in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s
Nancy Ahuja, Shalini Gupta, Rashmi Arora, Ella Bhagyaraj, Drishti Tiwari, Sumit Kumar, Pawan Gupta
Life Science Alliance.2024; 7(7): e202302416. CrossRef - Prosthetic vascular grafts engineered to combat calcification: Progress and future directions
Taylor K. Brown, Sara Alharbi, Karen J. Ho, Bin Jiang
Biotechnology and Bioengineering.2023; 120(4): 953. CrossRef - Obesity, diabetes mellitus, and cardiometabolic risk: An Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) Clinical Practice Statement (CPS) 2023
Harold Edward Bays, Shagun Bindlish, Tiffany Lowe Clayton
Obesity Pillars.2023; 5: 100056. CrossRef - Metformin promotes osteogenic differentiation and prevents hyperglycaemia-induced osteoporosis by suppressing PPARγ expression
Lifeng Zheng, Ximei Shen, Yun Xie, Hong Lian, Sunjie Yan, Shizhong Wang
Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica.2023; 55(3): 394. CrossRef - Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors as targets to treat metabolic diseases: Focus on the adipose tissue, liver, and pancreas
Henrique Souza-Tavares, Carolline Santos Miranda, Isabela Macedo Lopes Vasques-Monteiro, Cristian Sandoval, Daiana Araujo Santana-Oliveira, Flavia Maria Silva-Veiga, Aline Fernandes-da-Silva, Vanessa Souza-Mello
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 29(26): 4136. CrossRef - Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase upregulation contributes to palmitate-elicited peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor transactivation in hepatocytes
Qing Song, Jun Wang, Alexandra Griffiths, Samuel Man Lee, Iredia D. Iyamu, Rong Huang, Jose Cordoba-Chacon, Zhenyuan Song
American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology.2023; 325(1): C29. CrossRef - The global perspective on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) in ectopic fat deposition: A review
Yanhao Qiu, Mailin Gan, Xingyu Wang, Tianci Liao, Qiuyang Chen, Yuhang Lei, Lei Chen, Jinyong Wang, Ye Zhao, Lili Niu, Yan Wang, Shunhua Zhang, Li Zhu, Linyuan Shen
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2023; 253: 127042. CrossRef - Chemical inducer of regucalcin attenuates lipopolysaccharide‐induced inflammatory responses in pancreatic MIN6 β‐cells and RAW264.7 macrophages
Tomiyasu Murata, Kazunori Hashimoto, Susumu Kohno, Chiaki Takahashi, Masayoshi Yamaguchi, Chihiro Ito, Itoigawa Masataka, Roji Kojima, Kiyomi Hikita, Norio Kaneda
FEBS Open Bio.2022; 12(1): 175. CrossRef - Targets for rescue from fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity in pancreatic beta cells
Seok-Woo Hong, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(2): 57. CrossRef - Analysis of changes in the proteomic profile of porcine corpus luteum during different stages of the oestrous cycle: effects of PPAR gamma ligands
Zuzanna Kunicka, Karol Mierzejewski, Aleksandra Kurzyńska, Robert Stryiński, Jesús Mateos, Mónica Carrera, Monika Golubska, Iwona Bogacka, Xiaolong Wang
Reproduction, Fertility and Development.2022; 34(11): 776. CrossRef - Activation of PPARγ Protects Obese Mice from Acute Lung Injury by Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Promoting Mitochondrial Biogenesis
Yin Tang, Ke Wei, Ling Liu, Jingyue Ma, Siqi Wu, Wenjing Tang, Stéphane Mandard
PPAR Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Effect of Pioglitazone on endoplasmic reticulum stress regarding in situ perfusion rat model
Vivien Telek, Luca Erlitz, Ibitamuno Caleb, Tibor Nagy, Mónika Vecsernyés, Bálint Balogh, György Sétáló, Péter Hardi, Gábor Jancsó, Ildikó Takács
Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation.2021; 79(2): 311. CrossRef - Inflammation in Metabolic Diseases and Insulin Resistance
Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2021; 3(2): 31. CrossRef - Current Status of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Type II Diabetes
Sagir Mustapha, Mustapha Mohammed, Ahmad Khusairi Azemi, Abubakar Ibrahim Jatau, Aishatu Shehu, Lukman Mustapha, Ibrahim Muazzamu Aliyu, Rabi’u Nuhu Danraka, Abdulbasit Amin, Auwal Adam Bala, Wan Amir Nizam Wan Ahmad, Aida Hanum Ghulam Rasool, Mohd Rais M
Molecules.2021; 26(14): 4362. CrossRef - JunD Regulates Pancreatic β-Cells Function by Altering Lipid Accumulation
Kexin Wang, Yixin Cui, Peng Lin, Zhina Yao, Yu Sun
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Pioglitazone even at low dosage improves NAFLD in type 2 diabetes: clinical and pathophysiological insights from a subgroup of the TOSCA.IT randomised trial
Giuseppe Della Pepa, Marco Russo, Marilena Vitale, Fabrizia Carli, Claudia Vetrani, Maria Masulli, Gabriele Riccardi, Olga Vaccaro, Amalia Gastaldelli, Angela A. Rivellese, Lutgarda Bozzetto
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 178: 108984. CrossRef - Radioprotective Effect of Pioglitazone Against Genotoxicity Induced by Ionizing Radiation in Healthy Human Lymphocytes
Roya Kazemi, Seyed J. Hosseinimehr
Cardiovascular & Hematological Agents in Medicinal Chemistry .2021; 19(1): 72. CrossRef - Recent Insights Into Mechanisms of β-Cell Lipo- and Glucolipotoxicity in Type 2 Diabetes
Maria Lytrivi, Anne-Laure Castell, Vincent Poitout, Miriam Cnop
Journal of Molecular Biology.2020; 432(5): 1514. CrossRef - Artemisinin and dihydroartemisinin promote β-cell apoptosis induced by palmitate via enhancing ER stress
Ke Chen, Hu Hua, Ziyang Zhu, Tong Wu, Zhanjun Jia, Qianqi Liu
Apoptosis.2020; 25(3-4): 192. CrossRef - Mechanisms of impaired pancreatic β‑cell function in high‑fat diet‑induced obese mice: The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress
Xiaoqing Yi, Xuan Cai, Sisi Wang, Yanfeng Xiao
Molecular Medicine Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Docosahexaenoic and Eicosapentaenoic Acids Prevent Altered-Muc2 Secretion Induced by Palmitic Acid by Alleviating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in LS174T Goblet Cells
Quentin Escoula, Sandrine Bellenger, Michel Narce, Jérôme Bellenger
Nutrients.2019; 11(9): 2179. CrossRef - PPAR-γ agonist, pioglitazone, reduced oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress associated with L-NAME-induced hypertension in rats
Eman Soliman, Shereen F. Behairy, Nabila N. El-maraghy, Shimaa M. Elshazly
Life Sciences.2019; 239: 117047. CrossRef - Changes of MODY signal pathway genes in the endoplasmic reticulum stress in INS-1-3 cells
Yanan Dong, Shirui Li, Wenhui Zhao, Yanlei Wang, Tingting Ge, Jianzhong Xiao, Yukun Li, Herve Le Stunff
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(6): e0198614. CrossRef
- Nr1h4 and Thrb ameliorate ER stress and provide protection in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s

- Small Heterodimer Partner and Innate Immune Regulation
- Jae-Min Yuk, Hyo Sun Jin, Eun-Kyeong Jo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(1):17-24. Published online March 16, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.1.17
- 4,513 View
- 57 Download
- 21 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader The nuclear receptor superfamily consists of the steroid and non-steroid hormone receptors and the orphan nuclear receptors. Small heterodimer partner (SHP) is an orphan family nuclear receptor that plays an essential role in the regulation of glucose and cholesterol metabolism. Recent studies reported a previously unidentified role for SHP in the regulation of innate immunity and inflammation. The innate immune system has a critical function in the initial response against a variety of microbial and danger signals. Activation of the innate immune response results in the induction of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines to promote anti-microbial effects. An excessive or uncontrolled inflammatory response is potentially harmful to the host, and can cause tissue damage or pathological threat. Therefore, the innate immune response should be tightly regulated to enhance host defense while preventing unwanted immune pathologic responses. In this review, we discuss recent studies showing that SHP is involved in the negative regulation of toll-like receptor-induced and NLRP3 (NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3)-mediated inflammatory responses in innate immune cells. Understanding the function of SHP in innate immune cells will allow us to prevent or modulate acute and chronic inflammation processes in cases where dysregulated innate immune activation results in damage to normal tissues.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Upregulation of Anti-Angiogenic miR-106b-3p Correlates Negatively with IGF-1 and Vascular Health Parameters in a Model of Subclinical Cardiovascular Disease: Study with Metformin Therapy
Sherin Bakhashab, Josie O’Neill, Rosie Barber, Catherine Arden, Jolanta U. Weaver
Biomedicines.2024; 12(1): 171. CrossRef - Role of sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) in HBV-induced hepatitis: Opportunities for developing novel therapeutics
Zhentao Zhang, Qi Zhang, Yiwen Zhang, Yutao Lou, Luqi Ge, Wanli Zhang, Wen Zhang, Feifeng Song, Ping Huang
Biochemical Pharmacology.2024; 219: 115956. CrossRef - Chlorpyrifos induces apoptosis and necroptosis via the activation of CYP450s pathway mediated by nuclear receptors in LMH cells
Xinyu Zhang, Kexin Sun, Xu Wang, Xu Shi, Duqiang Gong
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2023; 30(1): 1060. CrossRef - A perspective study of the possible impact of obeticholic acid against SARS-CoV-2 infection
Gaber El-Saber Batiha, Hayder M. Al-kuraishy, Ali I. Al-Gareeb, Fadia S. Youssef, Suzy A. El-Sherbeni, Walaa A. Negm
Inflammopharmacology.2023; 31(1): 9. CrossRef - Is Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 a Target for the Intervention of Cytokine Storms?
Zihang Liu, Panpan Deng, Shengnan Liu, Yiying Bian, Yuanyuan Xu, Qiang Zhang, Huihui Wang, Jingbo Pi
Antioxidants.2023; 12(1): 172. CrossRef - Small Heterodimer Partner Modulates Macrophage Differentiation during Innate Immune Response through the Regulation of Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor Gamma, Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase, and Nuclear Factor Kappa B Pathways
Forkan Ahamed, Natalie Eppler, Elizabeth Jones, Lily He, Yuxia Zhang
Biomedicines.2023; 11(9): 2403. CrossRef - Natural products modulate NLRP3 in ulcerative colitis
Jia-Chen Xue, Shuo Yuan, Xiao-Ting Hou, Huan Meng, Bao-Hong Liu, Wen-Wen Cheng, Ming Zhao, Hong-Ben Li, Xue-Fen Guo, Chang Di, Min-Jie Li, Qing-Gao Zhang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The effectiveness of small heterodimer partner and FGF 19 levels in prediction of perinatal morbidity in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
Mehmet Bayram, Kader Irak, Sami Cifci, Ali Riza Koksal, Cemal Kazezoglu, Zuat Acar, Halil Onur Ozarı, Huseyin Alkim
Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.2022; 42(5): 1174. CrossRef - Nuclear Receptors as Multiple Regulators of NLRP3 Inflammasome Function
Ahmad Alatshan, Szilvia Benkő
Frontiers in Immunology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Orphan Nuclear Receptor Gene NR0B2 Is a Favorite Prognosis Factor Modulated by Multiple Cellular Signal Pathways in Human Liver Cancers
Runzhi Zhu, Yanjie Tu, Jingxia Chang, Haixia Xu, Jean C. Li, Wang Liu, Ahn-Dao Do, Yuxia Zhang, Jinhu Wang, Benyi Li
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Small heterodimer partner as a predictor of neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy response and survival in patients with rectal cancer: A preliminary study
Sup Kim, Mina Joo, Min-Kyung Yeo, Moon-June Cho, Jun-Sang Kim, Eun-Kyeong Jo, Jin-Man Kim
Oncology Letters.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - LPS Stimulation Induces Small Heterodimer Partner Expression Through the AMPK-NRF2 Pathway in Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea)
Jianlong Du, Xiaojun Xiang, Dan Xu, Kun Cui, Yuning Pang, Wei Xu, Kangsen Mai, Qinghui Ai
Frontiers in Immunology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Host Transcription Factors in Hepatitis B Virus RNA Synthesis
Kristi L. Turton, Vanessa Meier-Stephenson, Maulik D. Badmalia, Carla S. Coffin, Trushar R. Patel
Viruses.2020; 12(2): 160. CrossRef - Farnesoid X Receptor Activation Protects Liver From Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Up‐Regulating Small Heterodimer Partner in Kupffer Cells
Dan Jin, Tianfei Lu, Ming Ni, Han Wang, Jiang Zhang, Chenpeng Zhong, Chuan Shen, Jun Hao, Ronald W. Busuttil, Jerzy W. Kupiec‐Weglinski, Jianjun Zhang, Ning Xu, Yuan Zhai
Hepatology Communications.2020; 4(4): 540. CrossRef - Toll-like receptors in sepsis-associated cytokine storm and their endogenous negative regulators as future immunomodulatory targets
V. Kumar
International Immunopharmacology.2020; 89: 107087. CrossRef - Small Heterodimer Partner Controls the Virus-Mediated Antiviral Immune Response by Targeting CREB-Binding Protein in the Nucleus
Jae-Hoon Kim, Ji-Eun Yoon, Chamilani Nikapitiya, Tae-Hwan Kim, Md Bashir Uddin, Hyun-Cheol Lee, Yong-Hoon Kim, Jung Hwan Hwang, Kiramage Chathuranga, W.A. Gayan Chathuranga, Hueng-Sik Choi, Chul-Joong Kim, Jae U. Jung, Chul-Ho Lee, Jong-Soo Lee
Cell Reports.2019; 27(7): 2105. CrossRef - Glycogen synthase kinase 3β promotes liver innate immune activation by restraining AMP-activated protein kinase activation
Haoming Zhou, Han Wang, Ming Ni, Shi Yue, Yongxiang Xia, Ronald W. Busuttil, Jerzy W. Kupiec-Weglinski, Ling Lu, Xuehao Wang, Yuan Zhai
Journal of Hepatology.2018; 69(1): 99. CrossRef - Cholangiocyte‐derived exosomal long noncoding RNA H19 promotes cholestatic liver injury in mouse and humans
Xiaojiaoyang Li, Runping Liu, Zhiming Huang, Emily C. Gurley, Xuan Wang, Juan Wang, Hongliang He, Hu Yang, Guanhua Lai, Luyong Zhang, Jasmohan S. Bajaj, Melanie White, William M. Pandak, Phillip B. Hylemon, Huiping Zhou
Hepatology.2018; 68(2): 599. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Emerging roles of orphan nuclear receptors in regulation of innate immunity
Hyo Sun Jin, Tae Sung Kim, Eun-Kyeong Jo
Archives of Pharmacal Research.2016; 39(11): 1491. CrossRef
- Upregulation of Anti-Angiogenic miR-106b-3p Correlates Negatively with IGF-1 and Vascular Health Parameters in a Model of Subclinical Cardiovascular Disease: Study with Metformin Therapy

- Obesity and Metabolism
- The Impact of Organokines on Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, and Atherosclerosis
- Kyung Mook Choi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(1):1-6. Published online March 16, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.1.1
- 4,926 View
- 66 Download
- 39 Web of Science
- 42 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Immoderate energy intake, a sedentary lifestyle, and aging have contributed to the increased prevalence of obesity, sarcopenia, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. There is an urgent need for the development of novel pharmacological interventions that can target excessive fat accumulation and decreased muscle mass and/or strength. Adipokines, bioactive molecules derived from adipose tissue, are involved in the regulation of appetite and satiety, inflammation, energy expenditure, insulin resistance and secretion, glucose and lipid metabolism, and atherosclerosis. Recently, there is emerging evidence that skeletal muscle and the liver also function as endocrine organs that secrete myokines and hepatokines, respectively. Novel discoveries and research into these organokines (adipokines, myokines, and hepatokines) may lead to the development of promising biomarkers and therapeutics for cardiometabolic disease. In this review, I summarize recent data on these organokines and focus on the role of adipokines, myokines, and hepatokines in the regulation of insulin resistance, inflammation, and atherosclerosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cardiometabolic diseases and early cognitive decline: Mitigated by integrated active lifestyle for brain health
Haowei Li, Shige Qi, Shengshu Wang, Shanshan Yang, Shaohua Liu, Shimin Chen, Xuehang Li, Rongrong Li, Junhan Yang, Huaihao Li, Yinghui Bao, Yueting Shi, Zhihui Wang, Miao Liu, Yao He
Journal of Affective Disorders.2024; 350: 155. CrossRef - Current status and future perspectives of FGF21 analogues in clinical trials
Zara Siu Wa Chui, Qing Shen, Aimin Xu
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Organokinler ve Biyokimyasal Etkileri
Ahmet İlhan, Umut Kökbaş
Arşiv Kaynak Tarama Dergisi.2024; 33(1): 71. CrossRef - The Significance of Selected Myokines in Predicting the Length of Rehabilitation of Patients after COVID-19 Infection
Alicja Mińko, Agnieszka Turoń-Skrzypińska, Aleksandra Rył, Katarzyna Mańkowska, Aneta Cymbaluk-Płoska, Iwona Rotter
Biomedicines.2024; 12(4): 836. CrossRef - Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes and the impact of altered metabolic interorgan crosstalk
Jose Marcos Sanches, Li Na Zhao, Albert Salehi, Claes B. Wollheim, Philipp Kaldis
The FEBS Journal.2023; 290(3): 620. CrossRef - Research Progress on the Mechanism of Obesity-Induced Cardiovascular Disease
文清 刘
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(08): 12887. CrossRef - The Pan-liver Network Theory: From Traditional Chinese Medicine to Western Medicine
Yaxing Zhang, Xian-Ming Fang
Chinese Journal of Physiology.2023; 66(6): 401. CrossRef - Higher serum level of CTRP15 in patients with coronary artery disease is associated with disease severity, body mass index and insulin resistance
Abolfazl Shokoohi Nahrkhalaji, Reza Ahmadi, Reza Fadaei, Ghodratollah Panahi, Malihe Razzaghi, Soudabeh Fallah
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2022; 128(1): 276. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) and Organokines: What Is Now and What Will Be in the Future
João Paulo Margiotti dos Santos, Mariana Canevari de Maio, Monike Alves Lemes, Lucas Fornari Laurindo, Jesselina Francisco dos Santos Haber, Marcelo Dib Bechara, Pedro Sidnei do Prado, Eduardo Costa Rauen, Fernando Costa, Barbara Cristina de Abreu Pereira
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(1): 498. CrossRef - Hepatic PTEN Signaling Regulates Systemic Metabolic Homeostasis through Hepatokines-Mediated Liver-to-Peripheral Organs Crosstalk
Flavien Berthou, Cyril Sobolewski, Daniel Abegg, Margot Fournier, Christine Maeder, Dobrochna Dolicka, Marta Correia de Sousa, Alexander Adibekian, Michelangelo Foti
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(7): 3959. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Metabolic Syndrome in Women: Effects of Lifestyle Modifications
Maria Teresa Guagnano, Damiano D'Ardes, Rossi Ilaria, Francesca Santilli, Cosima Schiavone, Marco Bucci, Francesco Cipollone
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(10): 2759. CrossRef - Contribution of organokines in the development of NAFLD/NASH associated hepatocellular carcinoma
Meenakshi Vachher, Savita Bansal, Bhupender Kumar, Sandeep Yadav, Taruna Arora, Nalini Moza Wali, Archana Burman
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.2022; 123(10): 1553. CrossRef - Organokines, Sarcopenia, and Metabolic Repercussions: The Vicious Cycle and the Interplay with Exercise
Giulia Minniti, Letícia Maria Pescinini-Salzedas, Guilherme Almeida dos Santos Minniti, Lucas Fornari Laurindo, Sandra Maria Barbalho, Renata Vargas Sinatora, Lance Alan Sloan, Rafael Santos de Argollo Haber, Adriano Cressoni Araújo, Karina Quesada, Jesse
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(21): 13452. CrossRef - CURRENT CONCEPTS ON LEPTIN-MEDIATED REGULATION OF METABOLISM
R. B. Aliiev
Bulletin of Problems Biology and Medicine.2022; 1(4): 9-1. CrossRef - Inflammatory biomarkers and prediction of insulin resistance in Congolese adults
Reine Freudlendrich Eboka-Loumingou Sakou, Benjamin Longo-Mbenza, Mûnka Nkalla-Lambi, Etienne Mokondjimobe, Henry Germain Monabeka, Donatien Moukassa, Ange Antoine Abena, Mia Pamela Mekieje Tumchou, Venant Tchokonte-Nana
Heliyon.2021; 7(2): e06139. CrossRef - Adipokines, Myokines, and Hepatokines: Crosstalk and Metabolic Repercussions
Ana Rita de Oliveira dos Santos, Bárbara de Oliveira Zanuso, Vitor Fernando Bordin Miola, Sandra Maria Barbalho, Patrícia C. Santos Bueno, Uri Adrian Prync Flato, Claudia Rucco P. Detregiachi, Daniela Vieira Buchaim, Rogério Leone Buchaim, Ricardo José To
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(5): 2639. CrossRef - The Effects of Two Different Intensities of Combined Training on C1q/TNF-Related Protein 3 (CTRP3) and Insulin Resistance in Women with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Somayeh Rajabi, Roya Askari, Amir Hossein Haghighi, Nasrin Razavianzadeh
Hepatitis Monthly.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Handgrip and sex-specific cardiometabolic risk factors in Hispanic/Latino migrant farmworkers
Anas Raed, Jessica Bilz, Miriam Cortez-Cooper, Lufei Young, Li Chen, Pamela Cromer, Haidong Zhu, Andrew Mazzoli, Samip Parikh, Jigar Bhagatwala, Yutong Dong, Zhuo Sun, Debbie Layman, Yanbin Dong
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Crossing the Antarctica: Exploring the Effects of Appetite-Regulating Hormones and Indicators of Nutrition Status during a 93-Day Solo-Expedition
Bjørn Helge Johnsen, Guttorm Brattebø, Terry M. Phillips, Rune Gjeldnes, Paul T. Bartone, Hans-Olav Neteland Monsen, Julian F. Thayer
Nutrients.2021; 13(6): 1777. CrossRef - Irisin in atherosclerosis
Zhe-Bin Cheng, Liang Huang, Xuan Xiao, Jia-Xiang Sun, Zi-Kai Zou, Jie-Feng Jiang, Cong Lu, Hai-Ya Zhang, Chi Zhang
Clinica Chimica Acta.2021; 522: 158. CrossRef - Pilates and TRX training methods can improve insulin resistance in overweight women by increasing an exercise-hormone, Irisin
Marzyeh Rahimi, Parvaneh Nazarali, Rostam Alizadeh
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(2): 1455. CrossRef - Effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists on myokine levels and pro-inflammatory cytokines in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Valentina Guarnotta, Maria J. Bianco, Enrica Vigneri, Felicia Panto’, Bruna Lo Sasso, Marcello Ciaccio, Giuseppe Pizzolanti, Carla Giordano
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2021; 31(11): 3193. CrossRef - Hepatokines and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Linking Liver Pathophysiology to Metabolism
Tae Hyun Kim, Dong-Gyun Hong, Yoon Mee Yang
Biomedicines.2021; 9(12): 1903. CrossRef - Higher circulating levels of ANGPTL8 are associated with body mass index, triglycerides, and endothelial dysfunction in patients with coronary artery disease
Reza Fadaei, Hossein Shateri, Johanna K. DiStefano, Nariman Moradi, Mohammad Mohammadi, Farzad Emami, Hassan Aghajani, Nasrin Ziamajidi
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2020; 469(1-2): 29. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular disease phenotypes
Giandomenico Bisaccia, Fabrizio Ricci, Cesare Mantini, Claudio Tana, Gian Luca Romani, Cosima Schiavone, Sabina Gallina
SAGE Open Medicine.2020; 8: 205031212093380. CrossRef - Dysregulated Autophagy Mediates Sarcopenic Obesity and Its Complications via AMPK and PGC1α Signaling Pathways: Potential Involvement of Gut Dysbiosis as a Pathological Link
Ji Yeon Ryu, Hyung Muk Choi, Hyung-In Yang, Kyoung Soo Kim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(18): 6887. CrossRef - Fetuin-A as a Potential Biomarker of Metabolic Variability Following 60 Days of Bed Rest
Kiera Ward, Edwin Mulder, Petra Frings-Meuthen, Donal J. O’Gorman, Diane Cooper
Frontiers in Physiology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Moderate Aerobic Exercise on Serum Levels of FGF21 and Fetuin A in Women with Type 2 Diabetes
Exir Vizvari, Parvin farzanegi, Hajar Abbas Zade
Medical Laboratory Journal.2020; 14(6): 17. CrossRef - The implication of hepatokines in metabolic syndrome
Maryam Esfahani, Mostafa Baranchi, Mohammad Taghi Goodarzi
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(4): 2477. CrossRef - The Role of Adipose Tissue and Adipokines in Sepsis: Inflammatory and Metabolic Considerations, and the Obesity Paradox
Irene Karampela, Gerasimos Socrates Christodoulatos, Maria Dalamaga
Current Obesity Reports.2019; 8(4): 434. CrossRef - Sarcopenia and myokines profile as risk factors in cardiovascular diseases?
Mariusz Ciołkiewicz, Anna Kuryliszyn-Moskal, Anna Hryniewicz, Karol Kamiński
Postępy Higieny i Medycyny Doświadczalnej.2019; 73: 550. CrossRef - Pathophysiological Implication of Fetuin-A Glycoprotein in the Development of Metabolic Disorders: A Concise Review
Lynda Bourebaba, Krzysztof Marycz
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(12): 2033. CrossRef - Loss of Glycine N-Methyltransferase Associates with Angiopoietin-Like Protein 8 Expression in High Fat-Diet-Fed Mice
Jian-Wei Huang, Chao-Ju Chen, Chia-Hung Yen, Yi-Ming Arthur Chen, Yu-Peng Liu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(17): 4223. CrossRef - Recent advances in biosensor technology in assessment of early diabetes biomarkers
Armin Salek-Maghsoudi, Faezeh Vakhshiteh, Raheleh Torabi, Shokoufeh Hassani, Mohammad Reza Ganjali, Parviz Norouzi, Morteza Hosseini, Mohammad Abdollahi
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2018; 99: 122. CrossRef - Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in skeletal muscle, adipose tissue and liver: a positron emission tomography study
Miikka-Juhani Honka, Aino Latva-Rasku, Marco Bucci, Kirsi A Virtanen, Jarna C Hannukainen, Kari K Kalliokoski, Pirjo Nuutila
European Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 178(5): 523. CrossRef - Magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes as nanocarrier tags for sensitive determination of fetuin in saliva
Esther Sánchez-Tirado, Araceli González-Cortés, Paloma Yáñez-Sedeño, José M. Pingarrón
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2018; 113: 88. CrossRef - Decreased muscle mass in Korean subjects with intracranial arterial stenosis: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Ho-Jung Jung, Hwanseok Jung, Taeyoung Lee, Jongho Kim, Jongsin Park, Hacsoo Kim, Junghwan Cho, Won-Young Lee, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyung-Geun Oh
Atherosclerosis.2017; 256: 89. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Low muscle mass and risk of type 2 diabetes in middle-aged and older adults: findings from the KoGES
Jang Won Son, Seong Su Lee, Sung Rae Kim, Soon Jib Yoo, Bong Yun Cha, Ho Young Son, Nam H. Cho
Diabetologia.2017; 60(5): 865. CrossRef - Effects of chlorogenic acid on intracellular calcium regulation in lysophosphatidylcholine-treated endothelial cells
Hye-Jin Jung, Seung-Soon Im, Dae-Kyu Song, Jae-Hoon Bae
BMB Reports.2017; 50(6): 323. CrossRef - Irisin: A Potential Link between Physical Exercise and Metabolism—An Observational Study in Differently Trained Subjects, from Elite Athletes to Sedentary People
Stefano Benedini, Elena Dozio, Pietro Luigi Invernizzi, Elena Vianello, Giuseppe Banfi, Ileana Terruzzi, Livio Luzi, Massimiliano Marco Corsi Romanelli
Journal of Diabetes Research.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Serum Vaspin Concentration in Elderly Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Differing Body Mass Index: A Cross-Sectional Study
Wei Yang, Yun Li, Tian Tian, Li Wang
BioMed Research International.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef
- Cardiometabolic diseases and early cognitive decline: Mitigated by integrated active lifestyle for brain health

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Helicobacter pylori Stool Antigen Levels and Serological Biomarkers of Gastric Inflammation are Associated with Cardio-Metabolic Risk Factors in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Zahra Bahadoran, Parvin Mirmiran, Maryam Zarif-yeaganeh, Homayoun Zojaji, Fereidoun Azizi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(3):280-287. Published online May 18, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.3.280
- 3,284 View
- 30 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Helicobacter pylori infection and subsequent gastric inflammation have been proposed as risk factors for the development of insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease. In this study we assessed the possible association ofH. pylori bacterial load, and serum biomarker of gastric inflammation with cardiometabolic risk factors in diabetic patients.Methods In this cross-sectional study, 84
H. pylori -infected type 2 diabetic patients were assessed for anthropometrics, biochemical and clinical measurements. Pearson correlation test, linear, and logarithmic regression curve estimation models were used to assess the association ofH. pylori stool antigen (HpSAg) levels, and pepsinogen I (PGI) to pepsinogen II (PGII) ratio with fasting serum glucose, insulin, serum lipid and lipoprotein parameters, malondialdehyde, high-sensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), systolic and diastolic blood pressure, body weight, waist circumference and lipid accumulation product (LAP) index.Results The mean age of participants was 54±10 years, and 44% were men. Mean HpSAg levels and PGI/PGII ratio were 0.24±0.23 µg/mL and 9.9±9.0, respectively. Higher HpSAg as well as lower PGI/PGII was correlated with higher anthropometric measures and LAP. A significant negative correlation between PGI/PGII ratio and blood pressure (
r =-0.21 andr =-0.22, systolic and diastolic, respectively,P <0.05), serum insulin (r =-0.17,P =0.05), and hs-CRP (r =-0.17,P =0.05) was observed. A significant linear association between PGI/PGII ratio with serum triglycerides (β=-0.24,P <0.05), serum high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C; β=0.43,P <0.01), and triglycerides/HDL-C ratio (β=-0.28,P <0.05) were observed.Conclusion Higher
H. pylori bacterial load and lower PGI/PGII ratio was associated with higher levels of cardiometabolic risk factors inH. pylori infected type 2 diabetic patients.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Both diet and Helicobacter pylori infection contribute to atherosclerosis in pre- and postmenopausal cynomolgus monkeys
Traci L. Testerman, Cristina Semino-Mora, Jennifer A. Cann, Beidi Qiang, Edsel A. Peña, Hui Liu, Cara H. Olsen, Haiying Chen, Susan E. Appt, Jay R. Kaplan, Thomas C. Register, D. Scott Merrell, Andre Dubois, Xianwu Cheng
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(9): e0222001. CrossRef - Associations of Helicobacter pylori infection and peptic disease with diabetic mellitus: Results from a large population-based study
Saeda Haj, Gabriel Chodick, Rotem Refaeli, Sophy Goren, Varda Shalev, Khitam Muhsen, David M. Ojcius
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(8): e0183687. CrossRef - Helicobacter Pylori Infection Is Associated with Dyslipidemia and Increased Levels of Oxidized LDL in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
Mohamed Hasan Mukhtar, Wesam Ahmed Nasif, Abdullatif Taha Babakr
Journal of Diabetes Mellitus.2016; 06(03): 185. CrossRef - Update on prevention and treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection
Zhao-Chun Chi
World Chinese Journal of Digestology.2016; 24(16): 2454. CrossRef
- Both diet and Helicobacter pylori infection contribute to atherosclerosis in pre- and postmenopausal cynomolgus monkeys

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Lipid Accumulation Product Is Associated with Insulin Resistance, Lipid Peroxidation, and Systemic Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Parvin Mirmiran, Zahra Bahadoran, Fereidoun Azizi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(4):443-449. Published online December 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.443
- 4,160 View
- 42 Download
- 45 Web of Science
- 44 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Lipid accumulation product (LAP) is a novel biomarker of central lipid accumulation related to risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. In this study, we assessed the association of LAP with glucose homeostasis, lipid and lipid peroxidation, and subclinical systemic inflammation in diabetic patients.
Methods Thirty-nine male and 47 female type 2 diabetic patients were assessed for anthropometrics and biochemical measurements. LAP was calculated as [waist circumference (cm)-65]×[triglycerides (mmol/L)] in men, and [waist circumference (cm)-58]×[triglycerides (mmol/L)] in women. Associations of LAP with fasting glucose, insulin, insulin resistance index, lipid and lipoprotein levels, malondialdehyde, and high-sensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) were assessed.
Results Mean age and LAP index were 53.6±9.6 and 51.9±31.2 years, respectively. After adjustments for age, sex and body mass index status, a significant positive correlation was observed between LAP index and fasting glucose (
r =0.39,P <0.001), and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (r =0.31,P <0.05). After additional adjustment for fasting glucose levels, antidiabetic and antilipidemic drugs, the LAP index was also correlated to total cholesterol (r =0.45,P <0.001), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels (r =-0.29,P <0.05), triglycerides to HDL-C ratio (r =0.89,P <0.001), malondialdehyde (r =0.65,P <0.001), and hs-CRP levels (r =0.27,P <0.05).Conclusion Higher central lipid accumulation in diabetic patients was related to higher insulin resistance, oxidative stress and systemic inflammation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between lipid accumulation products and osteoarthritis among adults in the United States: A cross-sectional study, NHANES 2017-2020
Jie Huang, Jiaheng Han, Rigbat Rozi, Bensheng Fu, Zhengcao Lu, Jiang Liu, Yu Ding
Preventive Medicine.2024; 180: 107861. CrossRef - Impacts of a 12-week aerobic, resistance, and combined exercise training on serum FAM19A5, glucose homeostasis, and novel cardiovascular risk factors among adults with obesity
Ehsan Mir, Alireza Shamseddini, Najmeh Rahimi, Behzad Bazgir
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - High-Intensity Interval Versus Moderate-Intensity Continuous Exercise Training on Glycemic Control, Beta Cell Function, and Aerobic Fitness in Women with Type 2 Diabetes
Arghavan Niyazi, Seyed Mohammad Ali Yasrebi, Mohtaram Yazdanian, Gholam Rasul Mohammad Rahimi
Biological Research For Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasma carnitine, choline, γ-butyrobetaine, and trimethylamine-N-oxide, but not zonulin, are reduced in overweight/obese patients with pre/diabetes or impaired glycemia
Alia Snouper, Violet Kasabri, Nailya Bulatova, Maysa Suyagh, Monther Sadder, Khaldoun Shnewer, Ismail Yousef
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2023; 43(4): 592. CrossRef - Association of low-carbohydrate diet score and carbohydrate quality with visceral adiposity and lipid accumulation product
Fatemeh Gholami, Fahime Martami, Parivash Ghorbaninezhad, Amin Mirrafiei, Mojdeh Ebaditabar, Samira Davarzani, Nadia Babaei, Kurosh Djafarian, Sakineh Shab-Bidar
British Journal of Nutrition.2023; 129(5): 843. CrossRef - Role of ferroptosis inhibitors in the management of diabetes
Krishna Prasad M, Sundhar Mohandas, Ramkumar Kunka Mohanram
BioFactors.2023; 49(2): 270. CrossRef - Leveraging the future of diagnosis and management of diabetes: From old indexes to new technologies
Maria João Meneses, Rita Susana Patarrão, Tomás Pinheiro, Inês Coelho, Nuno Carriço, Ana Carolina Marques, Artur Romão, João Nabais, Elvira Fortunato, João Filipe Raposo, Maria Paula Macedo
European Journal of Clinical Investigation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sex difference in the associations among obesity-related indices with incidence of diabetes mellitus in a large Taiwanese population follow-up study
Tung-Ling Chung, Yi-Hsueh Liu, Pei-Yu Wu, Jiun-Chi Huang, Szu-Chia Chen
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Body adiposity markers and insulin resistance in patients with type 1 diabetes
Camila Lemos Marques, Mileni Vanti Beretta, Raquel Eccel Prates, Jussara Carnevale de Almeida, Ticiana da Costa Rodrigues
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of insulin resistance indices in predicting albuminuria among patients with type 2 diabetes
Seyed Ali Nabipoorashrafi, Azam Adeli, Seyed Arsalan Seyedi, Soghra Rabizadeh, Razman Arabzadeh Bahri, Fatemeh Mohammadi, Amirhossein Yadegar, Manouchehr Nakhjavani, Alireza Esteghamati
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipid accumulation product and visceral adiposity index: two indices to predict metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance in chronic kidney disease patients
Ahmed Mohamed Fahmy, Nelly El Shall, Ibrahim Kabbash, Loai El Ahwal, Amal Selim
Endocrine Regulations.2023; 57(1): 99. CrossRef - The effect of DASH diet on atherogenic indices, pro-oxidant-antioxidant balance, and liver steatosis in obese adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A double-blind controlled randomized clinical trial
Taghi Badali, Sara Arefhosseini, Farnaz Rooholahzadegan, Helda Tutunchi, Mehrangiz Ebrahimi-Mameghani
Health Promotion Perspectives.2023; 13(1): 77. CrossRef - Sex Difference in the Associations among Obesity-Related Indices with Hyperuricemia in a Large Taiwanese Population Study
Shih-Yao Su, Tsung-Han Lin, Yi-Hsueh Liu, Pei-Yu Wu, Jiun-Chi Huang, Ho-Ming Su, Szu-Chia Chen
Nutrients.2023; 15(15): 3419. CrossRef - Interrelation between the lipid accumulation product index and diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Min Tang, Shuangshuang Yao, Han Cao, Xiaohui Wei, Qin Zhen, Yijiong Tan, Fang Liu, Yufan Wang, Yongde Peng, Nengguang Fan
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cut-off values and clinical efficacy of body roundness index and other novel anthropometric indices in identifying metabolic syndrome and its components among Southern-Indian adults
Chiranjeevi Kumar Endukuru, Girwar Singh Gaur, Yerrabelli Dhanalakshmi, Jayaprakash Sahoo, Balasubramaniyan Vairappan
Diabetology International.2022; 13(1): 188. CrossRef - Effect of Exercise Training on Spexin Level, Appetite, Lipid Accumulation Product, Visceral Adiposity Index, and Body Composition in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes
Arash Mohammadi, Nahid Bijeh, Mahtab Moazzami, Kazem khodaei, Najmeh Rahimi
Biological Research For Nursing.2022; 24(2): 152. CrossRef - Carminic acid mitigates fructose-triggered hepatic steatosis by inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammatory reaction
Ling Li, Bo Fang, Yinglei Zhang, Liuqing Yan, Yuxin He, Linfeng Hu, Qifei Xu, Qiang Li, Xianling Dai, Qin Kuang, Minxuan Xu, Jun Tan, Chenxu Ge
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 145: 112404. CrossRef - Relationship between Visceral Adipose Index, Lipid Accumulation Product and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
停停 陈
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(04): 3350. CrossRef - The Relationship between Lipid Accumulation Product, Insulin Resistance and Obesity in Korean Adults
Hyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2022; 54(2): 149. CrossRef - Association of lipid accumulation product with type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Shaghayegh Khanmohammadi, Hamed Tavolinejad, Arya Aminorroaya, Yasaman Rezaie, Haleh Ashraf, Ali Vasheghani-Farahani
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2022; 21(2): 1943. CrossRef - The visceral adiposity index and lipid accumulation product as predictors of cardiovascular events in normal weight subjects
Susan Darroudi, Sara Saffar Soflaee, Zeinab Sadat Hosseini, Maryam Safari Farmad, Hassan Mirshafiei, Mohammad Sobhan Sheikh Andalibi, Mostafa Eslamiyeh, Ghazaleh Donyadideh, Reihaneh Aryan, Mansoureh Sadat Ekhteraee Toosi, Nasrin Talkhi, Habibollah Esmail
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2022; 52: 190. CrossRef - The association of red meat intake with inflammation and circulating intermediate biomarkers of type 2 diabetes is mediated by central adiposity
Mohsen Mazidi, Andre Pascal Kengne, Elena S. George, Mario Siervo
British Journal of Nutrition.2021; 125(9): 1043. CrossRef - Sprint interval training vs. combined aerobic + resistance training in overweight women with type 2 diabetes
Ebrahim BANITALEBI, Majid MARDANIYAN GHAHFARROKHI, Mohammad FARAMARZI, Conrad P. EARNEST
The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin resistance as a predictor of cardiovascular diseases
Neuza Domingues
Revista Portuguesa de Cardiologia.2021; 40(8): 545. CrossRef - Insulin resistance as a predictor of cardiovascular diseases
Neuza Domingues
Revista Portuguesa de Cardiologia (English Edition).2021; 40(8): 545. CrossRef - Visceral Adiposity Index, Triglyceride/High-Density Lipoprotein Ratio, and Lipid Accumulation Product Index to Discriminate Metabolic Syndrome Among Adult Type 1 Diabetes Patients
Savas Karatas, Selvihan Beysel
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2021; 19(9): 507. CrossRef - Association of Dietary Patterns with Visceral Adiposity, Lipid Accumulation Product, and Triglyceride-Glucose Index in Iranian Adults
Mohammad Reza Amini, Hossein Shahinfar, Nadia Babaei, Samira Davarzani, Mojdeh Ebaditabar, Kurosh Djafarian, Cain C. T. Clark, Sakineh Shab-Bidar
Clinical Nutrition Research.2020; 9(2): 145. CrossRef - Growth differentiation factor 15 protects against the aging‐mediated systemic inflammatory response in humans and mice
Ji Sun Moon, Ludger J. E. Goeminne, Jung Tae Kim, Jing Wen Tian, Seok‐Hwan Kim, Ha Thi Nga, Seul Gi Kang, Baeki E. Kang, Jin‐Seok Byun, Young‐Sun Lee, Jae‐Han Jeon, Minho Shong, Johan Auwerx, Dongryeol Ryu, Hyon‐Seung Yi
Aging Cell.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Accumulation of Cerebrospinal Fluid Glycerophospholipids and Sphingolipids in Cognitively Healthy Participants With Alzheimer’s Biomarkers Precedes Lipolysis in the Dementia Stage
Alfred N. Fonteh, Abby J. Chiang, Xianghong Arakaki, Sarah P. Edminster, Michael G Harrington
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of disorders of carbohydrate and fat metabolism in children under conditions of oral exposure to organochlorine compounds
Konstantin P. Luzhetskiy, Vladimir M. Chigvintsev, Svetlana A. Vekovshinina, Alexandra Yu. Vandysheva, Daria A. Eisfeld
Hygiene and sanitation.2020; 99(11): 1263. CrossRef - Assessment of adiposity distribution and its association with diabetes and insulin resistance: a population-based study
Kan Sun, Diaozhu Lin, Qiling Feng, Feng Li, Yiqin Qi, Wanting Feng, Chuan Yang, Li Yan, Meng Ren, Dan Liu
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of measures of central fat accumulation indices with body fat distribution and metabolic, hormonal, and inflammatory parameters in women with polycystic ovary syndrome
Victor Barbosa Ribeiro, Gislaine Satyko Kogure, Iris Palma Lopes, Rafael Costa Silva, Daiana Cristina Chielli Pedroso, Rui Alberto Ferriani, Cristiana Libardi Miranda Furtado, Rosana Maria dos Reis
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Mechanism of Dyslipidemia in Obesity—Unique Regulation of Ileal Villus Cell Brush Border Membrane Sodium–Bile Acid Cotransport
Sundaram, Palaniappan, Nepal, Chaffins, Sundaram, Arthur
Cells.2019; 8(10): 1197. CrossRef - Vibrational spectroscopy-based quantification of liver steatosis
E. Szafraniec, S. Tott, E. Kus, D. Augustynska, A. Jasztal, A. Filipek, S. Chlopicki, M. Baranska
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2019; 1865(11): 165526. CrossRef - Lipid accumulation product (LAP) index as a potential risk assessment for cardiovascular risk stratification among type II diabetes mellitus in a Ghanaian population: A cross-sectional study
Evans Asamoah Adu, Christian Obirikorang, Emmanuel Acheampong, Aaron Siaw Kwakye, Foster Fokuoh, Yaa Obirikorang, Enoch Odame Anto, Emmanuella Nsenbah Batu, Brodrick Yeboah Amoah, Patience N. Ansong, Joseph Fomusi Ndisang
Cogent Medicine.2019; 6(1): 1639880. CrossRef - Lipid accumulation product and triglycerides/glucose index are useful predictors of insulin resistance
Mohsen Mazidi, Andre-Pascal Kengne, Niki Katsiki, Dimitri P. Mikhailidis, Maciej Banach
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2018; 32(3): 266. CrossRef - Lipid accumulation product and visceral adiposity index are associated with dietary patterns in adult Americans
Mohsen Mazidi, Hong-kai Gao, Andre Pascal Kengne
Medicine.2018; 97(19): e0322. CrossRef - Rapamycin improves insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in type 2 diabetes rats through activation of autophagy
Wan Zhou, Shandong Ye
Cell Biology International.2018; 42(10): 1282. CrossRef - Three novel obese indicators perform better in monitoring management of metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetes
Chun-Ming Ma, Na Lu, Rui Wang, Xiao-Li Liu, Qiang Lu, Fu-Zai Yin
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between the Lipid Accumulation Product Index and Alanine Aminotransferase in Korean Adult Men
Kyung-A Shin
The Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2017; 49(4): 374. CrossRef - Visceral adiposity index, lipid accumulation product and intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis in middle-aged and elderly Chinese
Rui Li, Qi Li, Min Cui, Zegang Ying, Lin Li, Tingting Zhong, Yingchao Huo, Peng Xie
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Atorvastatin on Growth Differentiation Factor-15 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Dyslipidemia
Ji Min Kim, Min Kyung Back, Hyon-Seung Yi, Kyong Hye Joung, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(1): 70. CrossRef - Renoprotective effect of berberine on type 2 diabetic nephropathy in rats
Si‐Fan Sun, Ting‐Ting Zhao, Hao‐Jun Zhang, Xiao‐Ru Huang, Wei‐Ku Zhang, Lei Zhang, Mei‐Hua Yan, Xi Dong, Hua Wang, Yu‐Min Wen, Xin‐Ping Pan, Hui Yao Lan, Ping Li
Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology.2015; 42(6): 662. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- Association between lipid accumulation products and osteoarthritis among adults in the United States: A cross-sectional study, NHANES 2017-2020

- Adrenal gland
- Herpes Virus Entry Mediator Signaling in the Brain Is Imperative in Acute Inflammation-Induced Anorexia and Body Weight Loss
- Kwang Kon Kim, Sung Ho Jin, Byung Ju Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(3):214-220. Published online September 13, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.3.214
- 3,023 View
- 30 Download
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Reduced appetite and body weight loss are typical symptoms of inflammatory diseases. A number of inflammatory stimuli are responsible for the imbalance in energy homeostasis, leading to metabolic disorders. The herpes virus entry mediator (HVEM) protein plays an important role in the development of various inflammatory diseases, such as intestinal inflammation and diet-induced obesity. However, the role of HVEM in the brain is largely unknown. This study aims to investigate whether HVEM signaling in the brain is involved in inflammation-induced anorexia and body weight loss.
Methods Food intake and body weight were measured at 24 hours after intraperitoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or intracerebroventricular injection of recombinant mouse LIGHT (also called tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily 14, TNFSF14), an HVEM ligand, into 8- to 10-week-old male C57BL/6 mice and mice lacking HVEM expression (HVEM-/-). We also assessed LPS-induced change in hypothalamic expression of HVEM using immunohistochemistry.
Results Administration of LPS significantly reduced food intake and body weight, and moreover, increased expression of HVEM in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus. However, LPS induced only minor decreases in food intake and body weight in HVEM-/- mice. Administration of LIGHT into the brain was very effective at decreasing food intake and body weight in wild-type mice, but was less effective in HVEM-/- mice.
Conclusion Activation of brain HVEM signaling is responsible for inflammation-induced anorexia and body weight loss.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pediatric traumatic brain injury and a subsequent transient immune challenge independently influenced chronic outcomes in male mice
Rishabh Sharma, Pablo M. Casillas-Espinosa, Larissa K. Dill, Sarah S.J. Rewell, Matthew R. Hudson, Terence J. O'Brien, Sandy R. Shultz, Bridgette D. Semple
Brain, Behavior, and Immunity.2022; 100: 29. CrossRef - Bodyweight, locomotion, and behavioral responses of the naked mole rat (Heterocephalus glaber) to lipopolysaccharide administration
Mosiany Letura Kisipan, Rodi Omondi Ojoo, Titus Ikusya Kanui, Klas S. P. Abelson
Journal of Comparative Physiology A.2022; 208(4): 493. CrossRef - Intestinal Epithelial Toll-like Receptor 4 Deficiency Modifies the Response to the Activity-Based Anorexia Model in a Sex-Dependent Manner: A Preliminary Study
Pauline Tirelle, Colin Salaün, Alexandre Kauffmann, Christine Bôle-Feysot, Charlène Guérin, Marion Huré, Alexis Goichon, Asma Amamou, Jonathan Breton, Jean-Luc do Rego, Pierre Déchelotte, Najate Achamrah, Moïse Coëffier
Nutrients.2022; 14(17): 3607. CrossRef - A systemic immune challenge to model hospital-acquired infections independently regulates immune responses after pediatric traumatic brain injury
Rishabh Sharma, Akram Zamani, Larissa K. Dill, Mujun Sun, Erskine Chu, Marcus J. Robinson, Terence J. O’Brien, Sandy R. Shultz, Bridgette D. Semple
Journal of Neuroinflammation.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Inflammation-induced alterations in maternal-fetal Heme Oxygenase (HO) are associated with sustained innate immune cell dysregulation in mouse offspring
Maide Ozen, Hui Zhao, Flora Kalish, Yang Yang, Lauren L. Jantzie, Ronald J. Wong, David K. Stevenson, Leticia Reyes
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(6): e0252642. CrossRef - Treatment With Lipopolysaccharide Induces Distinct Changes in Metabolite Profile and Body Weight in 129Sv and Bl6 Mouse Strains
Maria Piirsalu, Egon Taalberg, Kersti Lilleväli, Li Tian, Mihkel Zilmer, Eero Vasar
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Systemic effects in naïve mice injected with immunomodulatory lectin ArtinM
Patrícia Kellen Martins Oliveira Brito, Thiago Eleutério Gonçalves, Fabrício Freitas Fernandes, Camila Botelho Miguel, Wellington Francisco Rodrigues, Javier Emílio Lazo Chica, Maria Cristina Roque-Barreira, Thiago Aparecido da Silva, Sujit Kumar Bhutia
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(10): e0187151. CrossRef - Corosolic acid ameliorates acute inflammation through inhibition of IRAK-1 phosphorylation in macrophages
Seung-Jae Kim, Ji-Young Cha, Hye Suk Kang, Jae-Ho Lee, Ji Yoon Lee, Jae-Hyung Park, Jae-Hoon Bae, Dae-Kyu Song, Seung-Soon Im
BMB Reports.2016; 49(5): 276. CrossRef - Patent Highlights April–May 2016
Hermann AM Mucke
Pharmaceutical Patent Analyst.2016; 5(5): 301. CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef - Overexpression of CCN3 Inhibits Inflammation and Progression of Atherosclerosis in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice
Jun Liu, Yingang Ren, Li Kang, Lihua Zhang, Philip Michael Bauer
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(4): e94912. CrossRef
- Pediatric traumatic brain injury and a subsequent transient immune challenge independently influenced chronic outcomes in male mice

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Tumor Necrosis Factor-α as a Predictor for the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A 4-Year Follow-Up Study
- Yun Yong Seo, Yong Kyun Cho, Ji-Cheol Bae, Mi Hae Seo, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(1):41-45. Published online March 25, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.1.41
- 4,538 View
- 34 Download
- 60 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α is associated with insulin resistance and systemic inflammatory responses. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between TNF-α and the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in a longitudinal study.
Methods Three hundred and sixty-three apparently healthy subjects (mean age, 40.5±6.1 years; male, 57.6%) without NAFLD were enrolled in 2003. Anthropometric and laboratory measurements were performed. The participants were grouped into tertiles according to their serum TNF-α levels from samples taken in 2003. At a 4-year follow-up, we compared the odds ratios (ORs) of the development of NAFLD according to the tertiles of TNF-α levels measured in 2003.
Results At the 4-year follow-up, the cumulative incidence of NAFLD was 29.2% (106/363). The group that developed NAFLD had higher levels of TNF-α than those in the group without NAFLD (3.65±1.79 pg/mL vs. 3.15±1.78 pg/mL;
P =0.016). When the 2003 serum TNF-α levels were categorized into tertiles: incidence of NAFLD observed in 2007 was significantly higher with increasing tertiles (22.6%, 35.8%, and 41.5%, respectively;P <0.05). The risk of developing NAFLD was significantly greater in the highest tertile of TNF-α than in the lowest tertile after adjusting for age, smoking, and BMI (OR, 2.20; 95% confidence interval, 1.12 to 4.01;P <0.05).Conclusion Higher serum TNF-α levels in subjects without NAFLD were associated with the development of NAFLD. The results of study might suggest a pathologic role of inflammation in NAFLD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nigella sativa Efficacy in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Mechanisms and Clinical Effects
A.A. Sangouni, A. Jamalzehi, M. Moradpour, H. Mozaffari-Khosravi
Journal of Herbal Medicine.2024; 43: 100833. CrossRef - Berberine prevents NAFLD and HCC by modulating metabolic disorders
Xinyue Lin, Juanhong Zhang, Yajun Chu, Qiuying Nie, Junmin Zhang
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2024; 254: 108593. CrossRef - Antitumor Mechanisms of Lycium barbarum Fruit: An Overview of In Vitro and In Vivo Potential
Maria Rosaria Miranda, Vincenzo Vestuto, Giuseppina Amodio, Michele Manfra, Giacomo Pepe, Pietro Campiglia
Life.2024; 14(3): 420. CrossRef - Theabrownin alleviates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting the intestinal farnesoid X receptor–ceramide axis
Jieyi Wang, Dan Zheng, Kun Ge, Fengjie Huang, Yang Li, Xiaojiao Zheng, Wei Jia, Aihua Zhao
Food Frontiers.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Necroptosis contributes to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease pathoetiology with promising diagnostic and therapeutic functions
Hong-Ju Sun, Bo Jiao, Yan Wang, Yue-Hua Zhang, Ge Chen, Zi-Xuan Wang, Hong Zhao, Qing Xie, Xiao-Hua Song
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 30(14): 1968. CrossRef - RGS7-ATF3-Tip60 Complex Promotes Hepatic Steatosis and Fibrosis by Directly Inducing TNFα
Madhuri Basak, Kiran Das, Tarun Mahata, Abhishek Singh Sengar, Sumit Kumar Verma, Sayan Biswas, Kakali Bhadra, Adele Stewart, Biswanath Maity
Antioxidants & Redox Signaling.2023; 38(1-3): 137. CrossRef - The capsaicinoid nonivamide suppresses the inflammatory response and attenuates the progression of steatosis in a NAFLD‐rat model
Naruemon Wikan, Jiraporn Tocharus, Chio Oka, Sivanan Sivasinprasasn, Waraluck Chaichompoo, Apichart Suksamrarn, Chainarong Tocharus
Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermoneutral housing shapes hepatic inflammation and damage in mouse models of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Jarren R. Oates, Keisuke Sawada, Daniel A. Giles, Pablo C. Alarcon, Michelle S.M.A. Damen, Sara Szabo, Traci E. Stankiewicz, Maria E. Moreno-Fernandez, Senad Divanovic
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol down-regulates 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfur transferase and caspase-3 in rat model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Maher N. Ibrahim, Abeer A. Khalifa, Dalia A. Hemead, Amira Ebrahim Alsemeh, Marwa A. Habib
Journal of Molecular Histology.2023; 54(2): 119. CrossRef - Effects of Resveratrol Supplementation on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Management
Arefe Nemati, Zeinab Nikniaz, Ali Mota
Topics in Clinical Nutrition.2023; 38(2): 144. CrossRef - The effects of chicory supplementation on liver enzymes and lipid profiles in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical evidence
Elham Maleki, Ali Sadeghpour, Erfan Taherifard, Bahareh Izadi, Mehdi Pasalar, Maryam Akbari
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2023; 55: 447. CrossRef - Using bioinformatics and systems biology methods to identify the mechanism of interaction between COVID-19 and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Wenbo Dong, Yan Jin, Hongshuo Shi, Xuecheng Zhang, Jinshu Chen, Hongling Jia, Yongchen Zhang
Medicine.2023; 102(23): e33912. CrossRef - The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Ilias D. Vachliotis, Stergios A. Polyzos
Current Obesity Reports.2023; 12(3): 191. CrossRef - NAFLD Is Associated With Quiescent Rather Than Active Crohn’s Disease
Scott McHenry, Matthew Glover, Ali Ahmed, Quazim Alayo, Maria Zulfiqar, Daniel R Ludwig, Matthew A Ciorba, Nicholas O Davidson, Parakkal Deepak
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gene-regulation modules in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease revealed by single-nucleus ATAC-seq
Fumihiko Takeuchi, Yi-Qiang Liang, Hana Shimizu-Furusawa, Masato Isono, Mia Yang Ang, Kotaro Mori, Taizo Mori, Eiji Kakazu, Sachiyo Yoshio, Norihiro Kato
Life Science Alliance.2023; 6(10): e202301988. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Evolution Using In Vivo and In Vitro Studies: A Systematic Review
Cristian Sandoval, Carolina Reyes, Pamela Rosas, Karina Godoy, Vanessa Souza-Mello, Jorge Farías
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(21): 15728. CrossRef - Maternal betaine supplementation ameliorates fatty liver disease in offspring mice by inhibiting hepatic NLRP3 inflammasome activation
Lun Li, Liuqiao Sun, Xiaoping Liang, Qian Ou, Xuying Tan, Fangyuan Li, Zhiwei Lai, Chenghe Ding, Hangjun Chen, Xinxue Yu, Qiongmei Wu, Jun Wei, Feng Wu, Lijun Wang
Nutrition Research and Practice.2023; 17(6): 1084. CrossRef - Association of Inflammatory Cytokines With Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Yamei Duan, Xiongfeng Pan, Jiayou Luo, Xiang Xiao, Jingya Li, Prince L. Bestman, Miyang Luo
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A potential link between plasma short‑chain fatty acids, TNF‑α level and disease progression in non‑alcoholic fatty liver disease: A retrospective study
Jing Xiong, Xia Chen, Zhijing Zhao, Ying Liao, Ting Zhou, Qian Xiang
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Update on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Associated Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Their Involvement in Liver Steatosis, Inflammation, and Fibrosis: A Narrative Review
Fajar Dwi Astarini, Neneng Ratnasari, Widya Wasityastuti
Iranian Biomedical Journal.2022; 26(4): 252. CrossRef - Clinical significance of epicardial fat assessment in hypertensive patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
M. Е. Statsenko, A. M. Streltsova
"Arterial’naya Gipertenziya" ("Arterial Hypertension").2022; 28(3): 260. CrossRef - The biological clock enhancer nobiletin ameliorates steatosis in genetically obese mice by restoring aberrant hepatic circadian rhythm
Sebastian Larion, Caleb A. Padgett, Joshua T. Butcher, James D. Mintz, David J. Fulton, David W. Stepp
American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology.2022; 323(4): G387. CrossRef - Effect of Fiber Supplementation on Systemic Inflammation and Liver Steatosis in Mice Fed with High-Carbohydrate Diets
Cacilda Rocha Hildebrand Budke, Débora Marchetti Chaves Thomaz, Rodrigo Juliano de Oliveira, Rita de Cássia Avellaneda Guimarães, Amariles Diniz Ramires, Doroty Mesquita Dourado, Elisvânia Freitas dos Santos, Adriana Conceicon Guercio Menezes, Andréia Con
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2022; 20(10): 558. CrossRef - Association between inflammatory markers and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obese children
Yamei Duan, Jiayou Luo, Xiongfeng Pan, Jia Wei, Xiang Xiao, Jingya Li, Miyang Luo
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of resveratrol supplementation in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials
Sahar Rafiee, Hamed Mohammadi, Abed Ghavami, Erfan Sadeghi, Zahra Safari, Gholamreza Askari
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2021; 42: 101281. CrossRef - Association of xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes (GSTM1 and GSTT 1), and pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6) genetic polymorphisms with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Narges Damavandi, Sirous Zeinali
Molecular Biology Reports.2021; 48(2): 1225. CrossRef - Potential protective effect of curcumin in high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats
AhmedM M. Mahmouda, NohaA.-R A. El-Hagag, HusseinI El-Bitar, Abdel-HalimM Afifi
Journal of Current Medical Research and Practice.2021; 6(1): 92. CrossRef - Current innovations in nutraceuticals and functional foods for intervention of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Mengyao Zhao, Shumin Chen, Xiaoguo Ji, Xin Shen, Jiangshan You, Xinyi Liang, Hao Yin, Liming Zhao
Pharmacological Research.2021; 166: 105517. CrossRef - Inflammation in Metabolic Diseases and Insulin Resistance
Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2021; 3(2): 31. CrossRef - Cellular Mechanisms of Liver Fibrosis
Pragyan Acharya, Komal Chouhan, Sabine Weiskirchen, Ralf Weiskirchen
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of insulin resistance and systemic inflammation in reducing the elasticity of the main arteries in patients with arterial hypertension and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
M.E. Statsenko, A.M. Streltsova, M.I. Turovets
Profilakticheskaya meditsina.2021; 24(5): 60. CrossRef - Validation of an adipose-liver human-on-a-chip model of NAFLD for preclinical therapeutic efficacy evaluation
Victoria L. Slaughter, John W. Rumsey, Rachel Boone, Duaa Malik, Yunqing Cai, Narasimhan Narasimhan Sriram, Christopher J. Long, Christopher W. McAleer, Stephen Lambert, Michael L. Shuler, J. J. Hickman
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - L-ergothioneine and metformin alleviates liver injury in experimental type-2 diabetic rats via reduction of oxidative stress, inflammation, and hypertriglyceridemia
Ayobami Dare, Mahendra L. Channa, Anand Nadar
Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology.2021; 99(11): 1137. CrossRef - Patchouli alcohol ameliorates skeletal muscle insulin resistance and NAFLD via AMPK/SIRT1-mediated suppression of inflammation
Do Hyeon Pyun, Tae Jin Kim, Seung Yeon Park, Hyun Jung Lee, A.M. Abd El-Aty, Ji Hoon Jeong, Tae Woo Jung
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2021; 538: 111464. CrossRef - Low Vitamin D Level was Associated with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Vahid Sheikhi, Zahra Heidari
Shiraz E-Medical Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Inflammation and Fibrogenesis in MAFLD: Role of the Hepatic Immune System
Pietro Torre, Benedetta Maria Motta, Roberta Sciorio, Mario Masarone, Marcello Persico
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef Sarcopenia Is an Independent Risk Factor for NAFLD in COPD: A Nationwide Survey (KNHANES 2008–2011)
Kyung Soo Hong, Min Cheol Kim, June Hong Ahn
International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.2020; Volume 15: 1005. CrossRef- A multi-targeting strategy to ameliorate high-fat-diet- and fructose-induced (western diet-induced) non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with supplementation of a mixture of legume ethanol extracts
Yen-Chun Koh, Yen-Cheng Lin, Pei-Sheng Lee, Ting-Jang Lu, Kai-Yi Lin, Min-Hsiung Pan
Food & Function.2020; 11(9): 7545. CrossRef - The effect of adiponectin in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and the potential role of polyphenols in the modulation of adiponectin signaling
Samukelisiwe C. Shabalala, Phiwayinkosi V. Dludla, Lawrence Mabasa, Abidemi P. Kappo, Albertus K. Basson, Carmen Pheiffer, Rabia Johnson
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2020; 131: 110785. CrossRef - Redox Regulation by Protein S-Glutathionylation: From Molecular Mechanisms to Implications in Health and Disease
Aysenur Musaogullari, Yuh-Cherng Chai
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(21): 8113. CrossRef - Long-Term Soy Protein Isolate Consumption Reduces Liver Steatosis Through Changes in Global Transcriptomics in Obese Zucker Rats
Melisa Kozaczek, Walter Bottje, Byungwhi Kong, Sami Dridi, Diyana Albataineh, Kentu Lassiter, Reza Hakkak
Frontiers in Nutrition.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Lycopene Modulates Pathophysiological Processes of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Obese Rats
Mariane Róvero Costa, Jéssica Leite Garcia, Carol Cristina Vágula de Almeida Silva, Artur Junio Togneri Ferron, Fabiane Valentini Francisqueti-Ferron, Fabiana Kurokawa Hasimoto, Cristina Schmitt Gregolin, Dijon Henrique Salomé de Campos, Cleverton Roberto
Antioxidants.2019; 8(8): 276. CrossRef - A new method to induce nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in mice
Feryal Savari, Seyyed Ali Mard, Mohammad Badavi, Anahita Rezaie, Mohammad Kazem Gharib-Naseri
BMC Gastroenterology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Zeaxanthin Dipalmitate in the Treatment of Liver Disease
Nisma Lena Bahaji Azami, Mingyu Sun
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - A narrative review on effects of vitamin D on main risk factors and severity of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abbas Ali Sangouni, Saeid Ghavamzadeh, Atena Jamalzehi
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(3): 2260. CrossRef - ABO blood group and risk of newly diagnosed nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A case-control study in Han Chinese population
Guo-Chao Zhong, Shan Liu, Yi-Lin Wu, Mei Xia, Jin-Xian Zhu, Fa-Bao Hao, Lun Wan, Pavel Strnad
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(12): e0225792. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Diabetes: An Epidemiological Perspective
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(3): 226. CrossRef - Telmisartan improves the metabolic, hematological and inflammasome indices in non-alcoholic fatty liver infiltration: A pilot open-label placebo-controlled study
Marwan S.M. Al-Nimer, Vian A.W. Esmail, O. Mohammad
Electronic Journal of General Medicine.2019; 16(3): em142. CrossRef - TRUSS Exacerbates NAFLD Development by Promoting IκBα Degradation in Mice
Chang‐Jiang Yu, Qiu‐Shi Wang, Ming‐Ming Wu, Bin‐Lin Song, Chen Liang, Jie Lou, Liang‐Liang Tang, Xiao‐Di Yu, Na Niu, Xu Yang, Bao‐Long Zhang, Yao Qu, Yang Liu, Zhi‐Chao Dong, Zhi‐Ren Zhang
Hepatology.2018; 68(5): 1769. CrossRef - Association Between Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and the Risk of Hepatic Events: A Median 3 Years Follow-Up Study
Zhi Zhu, Shuofeng Li
Hepatitis Monthly.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Based on Analyses from the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Eun-Jung Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2017; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - Ezetimibe alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through the miR-16 inhibiting mTOR/p70S6K1 pathway
Xiang Wang, Yunbing Meng, Junrong Zhang
RSC Advances.2017; 7(60): 37967. CrossRef - Relationship between adipose tissue dysfunction, vitamin D deficiency and the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Flavia A Cimini, Ilaria Barchetta, Simone Carotti, Laura Bertoccini, Marco G Baroni, Umberto Vespasiani-Gentilucci, Maria-Gisella Cavallo, Sergio Morini
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2017; 23(19): 3407. CrossRef - Omega-3 Fatty Acids Protect Fatty and Lean Mouse Livers After Major Hepatectomy
Michael Linecker, Perparim Limani, Patryk Kambakamba, Philipp Kron, Christoph Tschuor, Nicolas Calo, Michelangelo Foti, Jean-François Dufour, Rolf Graf, Bostjan Humar, Pierre-Alain Clavien
Annals of Surgery.2017; 266(2): 324. CrossRef - Exogenous administration of DLK1 ameliorates hepatic steatosis and regulates gluconeogenesis via activation of AMPK
Y-h Lee, M R Yun, H M Kim, B H Jeon, B-C Park, B-W Lee, E S Kang, H C Lee, Y W Park, B-S Cha
International Journal of Obesity.2016; 40(2): 356. CrossRef - Immune Imbalances in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: From General Biomarkers and Neutrophils to Interleukin-17 Axis Activation and New Therapeutic Targets
Feliciano Chanana Paquissi
Frontiers in Immunology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Serum Adipocytokine Levels according to Metabolic Health and Obesity Status
Tae Hoon Lee, Won Seon Jeon, Ki Joong Han, Shin Yeoung Lee, Nam Hee Kim, Hyun Beom Chae, Choel Min Jang, Kyung Mo Yoo, Hae Jung Park, Min Kyung Lee, Se Eun Park, Hyung Geun Oh, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(2): 185. CrossRef - Metabolic Health Is More Important than Obesity in the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A 4-Year Retrospective Study
Min-Kyung Lee, Eun-Jung Rhee, Min Chul Kim, Byung Sub Moon, Jeong In Lee, Young Seok Song, Eun Na Han, Hyo Sun Lee, Yoonjeong Son, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(4): 522. CrossRef - Adipokines and proinflammatory cytokines, the key mediators in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Sanja Stojsavljević
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2014; 20(48): 18070. CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef
- Nigella sativa Efficacy in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Mechanisms and Clinical Effects


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



