Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Efficacy and Safety of Omarigliptin, a Novel Once-Weekly Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor, in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- A.B.M. Kamrul-Hasan, Muhammad Shah Alam, Samir Kumar Talukder, Deep Dutta, Shahjada Selim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):109-126. Published online January 23, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1839

- 1,241 View
- 40 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
No recent meta-analysis has holistically analyzed and summarized the efficacy and safety of omarigliptin in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We conducted a meta-analysis to address this knowledge gap.
Methods
Electronic databases were searched to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that included patients with T2DM who received omarigliptin in the intervention arm. The control arm consisted of either a placebo (passive control group [PCG]) or an active comparator (active control group [ACG]). The primary outcome assessed was changes in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), while secondary outcomes included variations in glucose levels, achievement of glycemic targets, adverse events (AEs), and hypoglycemic events.
Results
From 332 initially screened articles, data from 16 RCTs involving 8,804 subjects were analyzed. Omarigliptin demonstrated superiority over placebo in reducing HbA1c levels (mean difference, –0.58%; 95% confidence interval, –0.75 to –0.40; P<0.00001; I2=91%). Additionally, omarigliptin outperformed placebo in lowering fasting plasma glucose, 2-hour postprandial glucose, and in the percentage of participants achieving HbA1c levels below 7.0% and 6.5%. The glycemic efficacy of omarigliptin was similar to that of the ACG across all measures. Although the omarigliptin group experienced a higher incidence of hypoglycemic events compared to the PCG, the overall AEs, serious AEs, hypoglycemia, and severe hypoglycemia were comparable between the omarigliptin and control groups (PCG and ACG).
Conclusion
Omarigliptin has a favorable glycemic efficacy and safety profile for managing T2DM.

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Effectiveness of a Social Networking Site Based Automatic Mobile Message Providing System on Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Kyuho Kim, Jae-Seung Yun, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Minhan Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn, Jae Hyoung Cho, Seung-Hyun Ko
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(2):344-352. Published online December 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1871
- 1,156 View
- 38 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigated the effectiveness of a social networking site (SNS)-based automatic mobile message providing system on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
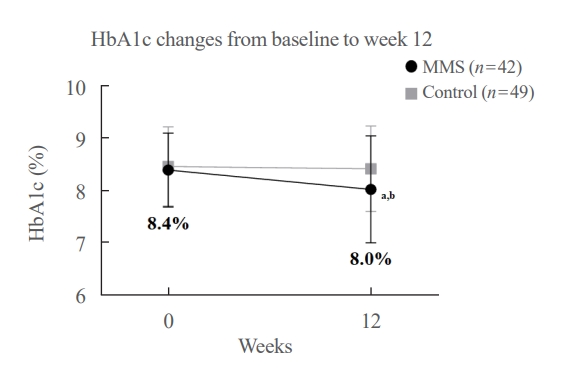
A 3-month, randomized, open-label, controlled, parallel-group trial was conducted. One hundred and ten participants with T2DM were randomized to a mobile message system (MMS) (n=55) or control group (n=55). The MMS group received protocolbased automated messages two times per day for 10 weeks regarding diabetes self-management through KakaoTalk SNS messenger. The primary outcome was the difference in the change in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels (%) from baseline to week 12.
Results
HbA1c levels were more markedly decreased in the MMS group (8.4%±0.7% to 8.0%±1.1%) than in the control group (8.5%±0.8% to 8.4%±0.8%), resulting in a significant between-group difference (P=0.027). No differences were observed in changes in fasting glucose levels, lipid profiles, and the number of participants who experienced hypoglycemia, or in changes in lifestyle behavior between groups. However, the self-monitoring of blood glucose frequency was significantly increased in the MMS group compared to the control group (P=0.003). In addition, sleep duration was increased in the MMS group, but was not changed in the control group.
Conclusion
An SNS-based automatic mobile message providing system was effective in improving glycemic control in patients in T2DM. Studies which based on a more individualized protocol, and investigate longer beneficial effect and sustainability will be required in the future.

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Year-Long Trend in Glycated Hemoglobin Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes during the COVID-19 Pandemic
- Jonghwa Jin, Seong Wook Lee, Won-Ki Lee, Jae-Han Jeon, Jung-Guk Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Keun-Gyu Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1142-1146. Published online October 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1154
- 3,913 View
- 148 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
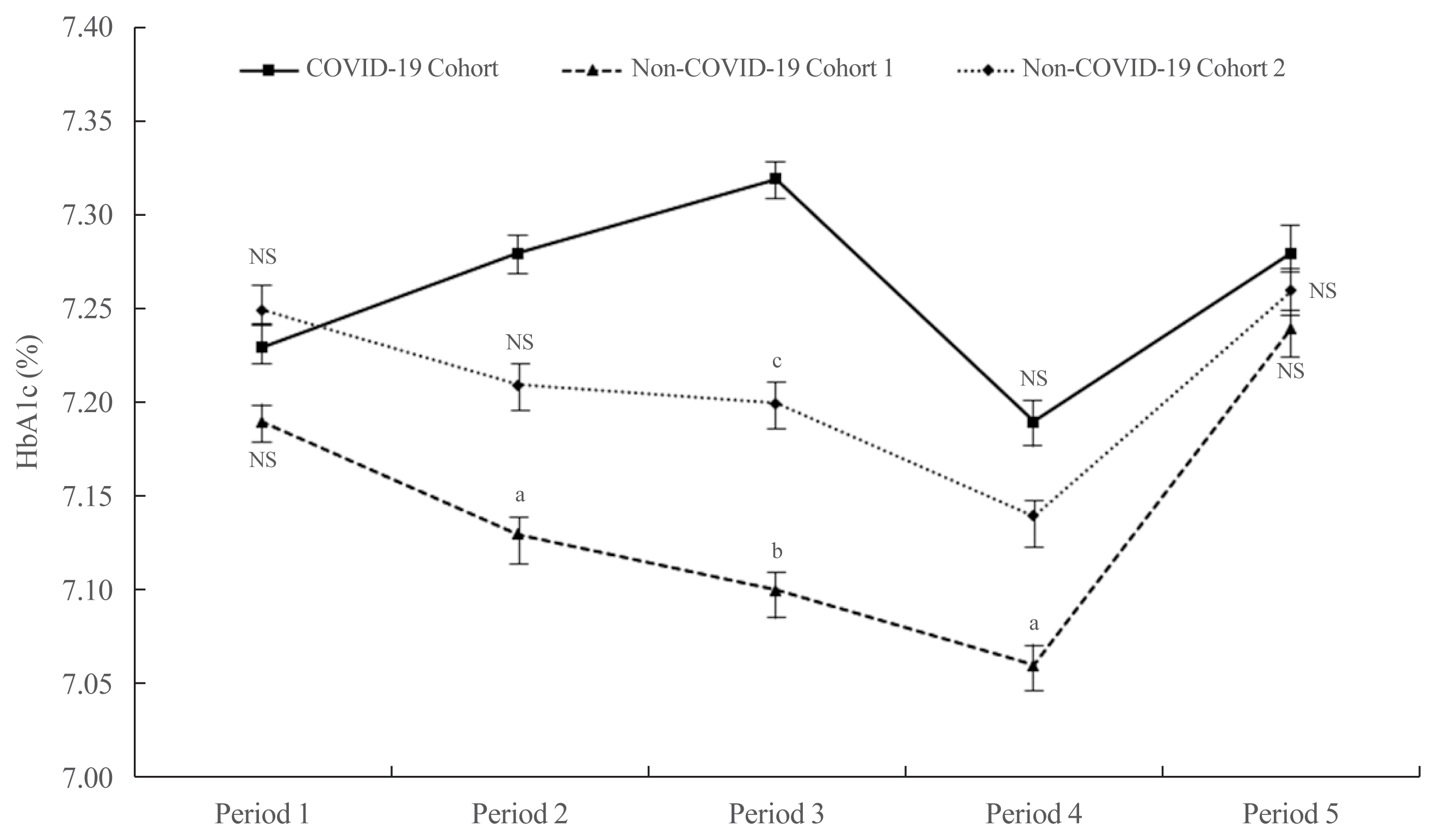
ePub - It has been suggested that the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has had a negative impact on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, no study has examined yearly trends in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels after the start of the COVID-19 outbreak. Here, we performed a retrospective analysis of HbA1c concentrations during the early period of the COVID-19 outbreak (COVID-19 cohort) and then compared the yearly trend in the mean HbA1c level, along with fluctuations in HbA1c levels, with those during previous years (non-COVID-19 cohorts). We observed that the mean HbA1c level in patients with T2DM increased during the first 6 months of the COVID-19 outbreak. After 6 months, HbA1c levels in the COVID-19 cohort returned to levels seen in the non-COVID-19 cohorts. The data suggest that vulnerable patients with T2DM should be monitored closely during the early period of a pandemic to ensure they receive appropriate care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Physical and Mental Health Characteristics of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients with and without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Turkey
Abdulbari Bener, Murat Atmaca, Abdulla O. A. A. Al-Hamaq, Antonio Ventriglio
Brain Sciences.2024; 14(4): 377. CrossRef - A Hybrid Model of In-Person and Telemedicine Diabetes Education and Care for Management of Patients with Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Findings and Implications from a Multicenter Prospective Study
Ayla M. Tourkmani, Turki J. Alharbi, Abdulaziz M. Bin Rsheed, Azzam F. Alotaibi, Mohammed S. Aleissa, Sultan Alotaibi, Amal S. Almutairi, Jancy Thomson, Ahlam S. Alshahrani, Hadil S. Alroyli, Hend M. Almutairi, Mashael A. Aladwani, Eman R. Alsheheri, Hyfa
Telemedicine Reports.2024; 5(1): 46. CrossRef - The indirect impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on people with type 2 diabetes mellitus and without COVID-19 infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis
Zhuoran Hu, Hin Moi Youn, Jianchao Quan, Lily Luk Siu Lee, Ivy Lynn Mak, Esther Yee Tak Yu, David Vai-Kiong Chao, Welchie Wai Kit Ko, Ian Chi Kei Wong, Gary Kui Kai Lau, Chak Sing Lau, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam, Eric Yuk Fai Wan
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(3): 229. CrossRef - Evaluating Effects of Virtual Diabetes Group Visits in Community Health Centers During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Tracy Dinh, Erin M Staab, Daisy Nuñez, Mengqi Zhu, Wen Wan, Cynthia T Schaefer, Amanda Campbell, Michael Quinn, Arshiya A Baig
Journal of Patient Experience.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiovascular-related health behavior changes: lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic and post-pandemic challenges
Inha Jung, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2023; 5(4): 99. CrossRef
- Physical and Mental Health Characteristics of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients with and without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Turkey

- Clinical Study
- Efficacy and Safety of the Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Gemigliptin in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis
- Deep Dutta, Anshita Agarwal, Indira Maisnam, Rajiv Singla, Deepak Khandelwal, Meha Sharma
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(2):374-387. Published online April 6, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.818
- 6,441 View
- 226 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 26 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
No meta-analysis has holistically analysed and summarised the efficacy and safety of gemigliptin in type 2 diabetes. The meta-analysis addresses this knowledge gap.
Methods
Electronic databases were searched for randomised controlled trials (RCTs) involving diabetes patients receiving gemigliptin in the intervention arm and placebo/active comparator in the control arm. The primary outcome was change in haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). The secondary outcomes were alterations in glucose, glycaemic targets, lipids, insulin resistance, and adverse events.
Results
Data from 10 RCTs involving 1,792 patients were analysed. Four had an active control group (ACG), with metformin/dapagliflozin/sitagliptin/glimepiride as the active comparator; six had a passive control group (PCG), with placebo/rosuvastatin as controls. HbA1c reduction by gemigliptin at 24 weeks was comparable to ACG (mean difference [MD], 0.09%; 95% confidence interval [CI], –0.06 to 0.23; P=0.24; I2=0%; moderate certainty of evidence [MCE]), but superior to PCG (MD, –0.91%; 95% CI, –1.18 to –0.63); P<0.01; I2=89%; high certainty of evidence [HCE]). Gemigliptin was superior to PCG regarding achieving HbA1c <7% (12 weeks: odds ratio [OR], 5.91; 95% CI, 1.34 to 26.08; P=0.02; I2=74%; 24 weeks: OR, 4.48; 95% CI, 2.09 to 9.60; P<0.01; I2=69%; HCE). Gemigliptin was comparable to ACG regarding achieving HbA1c <7% after 24 weeks (OR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.52 to 1.63; P=0.77; I2=66%; MCE). Adverse events were similar between the gemigliptin and control groups (risk ratio [RR], 1.06; 95% CI, 0.82 to 1.36; P=0.66; I2=35%; HCE). The gemigliptin group did not have increased hypoglycaemia (RR, 1.19; 95% CI, 0.62 to 2.28; P=0.61; I2=19%; HCE).
Conclusion
Gemigliptin has good glycaemic efficacy and is well-tolerated over 6 months of use. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hyperprolactinemia Due to Prolactinoma has an Adverse Impact on Bone Health with Predominant Impact on Trabecular Bone: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Lakshmi Nagendra, Deep Dutta, Sunetra Mondal, Nitin Kapoor, Ameya Joshi, Saptarshi Bhattacharya
Journal of Clinical Densitometry.2024; 27(1): 101453. CrossRef - Impact of early initiation of ezetimibe in patients with acute coronary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Kunal Mahajan, Lakshmi Nagendra, Anil Dhall, Deep Dutta
European Journal of Internal Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of dorzagliatin, a novel glucokinase activators, in the treatment of T2DM: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Yuqian Wu, Kai Wang, Jingyang Su, Xin Liu
Medicine.2024; 103(8): e36916. CrossRef - Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Post-bariatric Surgery Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, Lakshmi Nagendra, Ameya Joshi, Suryashri Krishnasamy, Meha Sharma, Naresh Parajuli
Obesity Surgery.2024; 34(5): 1653. CrossRef - Orforglipron, a novel non‐peptide oral daily glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor agonist as an anti‐obesity medicine: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Deep Dutta, Lakshmi Nagendra, Beatrice Anne, Manoj Kumar, Meha Sharma, A. B. M. Kamrul‐Hasan
Obesity Science & Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Safety and tolerability of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in children and young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Lakshmi Nagendra, Deep Dutta, Harish Bukkasagar Girijashankar, Deepak Khandelwal, Tejal Lathia, Meha Sharma
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 29(2): 82. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of novel dual glucokinase activator dorzagliatin in type-2 diabetes A meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, Deepak Khandelwal, Manoj Kumar, Meha Sharma
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(1): 102695. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of novel thiazolidinedione lobeglitazone for managing type-2 diabetes a meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Manoj Kumar, Priyankar K. Datta, Ritin Mohindra, Meha Sharma
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(1): 102697. CrossRef - Effects of Initial Combinations of Gemigliptin Plus Metformin Compared with Glimepiride Plus Metformin on Gut Microbiota and Glucose Regulation in Obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: The INTESTINE Study
Soo Lim, Minji Sohn, Jose C. Florez, Michael A. Nauck, Jiyoung Ahn
Nutrients.2023; 15(1): 248. CrossRef - Systematic review and meta-analysis of teneligliptin for treatment of type 2 diabetes
R. Pelluri, S. Kongara, V. R. Nagasubramanian, S. Mahadevan, J. Chimakurthy
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2023; 46(5): 855. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin added to metformin plus gemigliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind, randomized, comparator-active study: ENHANCE-D study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Kyung Ah Han, Tae Nyun Kim, Cheol-Young Park, Jung Hwan Park, Sang Yong Kim, Yong Hyun Kim, Kee Ho Song, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Sik Kim, Gwanpyo Koh, Jun Goo Kang, Mi Kyung Kim, Ji Min Han, Nan Hee Kim, Ji Oh Mok, Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Lim, Sang S
Diabetes & Metabolism.2023; 49(4): 101440. CrossRef - Verapamil improves One-Year C-Peptide Levels in Recent Onset Type-1 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis
Deep Dutta, Lakshmi Nagendra, Nishant Raizada, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Meha Sharma
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 27(3): 192. CrossRef - Role of novel sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor enavogliflozin in type-2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, B.G. Harish, Beatrice Anne, Lakshmi Nagendra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(8): 102816. CrossRef - Semaglutide and cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Lakshmi Nagendra, Harish BG, Meha Sharma, Deep Dutta
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(9): 102834. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Novel Thiazolidinedione Rivoglitazone in Type-2 Diabetes a Meta-Analysis
Deep Dutta, Jyoti Kadian, Indira Maisnam, Ashok Kumar, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Meha Sharma
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 27(4): 286. CrossRef - Impact of early initiation of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitors in patients with acute coronary syndrome: A systematic review meta-analysis
Lakshmi Nagendra, Kunal Mahajan, Gunjan Gupta, Deep Dutta
Indian Heart Journal.2023; 75(6): 416. CrossRef - Optimal use of once weekly icodec insulin in type-2 diabetes: An updated meta-analysis of phase-2 and phase-3 randomized controlled trials
Deep Dutta, Lakshmi Nagendra, Sowrabha Bhat, Ritin Mohindra, Vineet Surana, Anoop Misra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(10): 102877. CrossRef - Impact of Enhanced External Counter-pulsation Therapy on Glycaemic Control in People With Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Lakshmi Nagendra, Deep Dutta, Meha Sharma, Harish Bg
touchREVIEWS in Endocrinology.2023; 19(2): 8. CrossRef - Role of Novel Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Analogue Polyethylene Glycol Loxenatide in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, Subhankar Chatterjee, Priyankar K. Datta, Ritin Mohindra, Meha Sharma
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 27(5): 377. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Ultra-rapid Lispro Insulin in Managing Type-1 and Type-2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Deep Dutta, Lakshmi Nagendra, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Meha Sharma
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 27(6): 467. CrossRef - Safety and efficacy of once weekly dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 inhibitor trelagliptin in type-2 diabetes: A meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, Ritin Mohindra, Vineet Surana, Meha Sharma
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2022; 16(4): 102469. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of hydroxychloroquine for managing glycemia in type-2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
D Dutta, R Jindal, D Mehta, M Kumar, M Sharma
Journal of Postgraduate Medicine.2022; 68(2): 85. CrossRef - Gemigliptin exerts protective effects against doxorubicin-induced hepatotoxicity by inhibiting apoptosis via the regulation of fibroblast growth factor 21 expression
Kyeong-Min Lee, Yeo Jin Hwang, Gwon-Soo Jung
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2022; 626: 135. CrossRef - Reporting and methodological quality of systematic reviews of DPP-4 inhibitors for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: an evidence-based mapping
Zouxi Du, Tingting Lu, Mingdong Gao, Limin Tian
Acta Diabetologica.2022; 59(12): 1539. CrossRef - Ranirestat improves electrophysiologic but not clinical measures of diabetic polyneuropathy: A meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, Ritin Mohindra, Manoj Kumar, Ashok Kumar, Meha Sharma
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 26(5): 399. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of novel twincretin tirzepatide a dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist in the management of type-2 diabetes: A Cochrane meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, Vineet Surana, Rajiv Singla, Sameer Aggarwal, Meha Sharma
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 25(6): 475. CrossRef
- Hyperprolactinemia Due to Prolactinoma has an Adverse Impact on Bone Health with Predominant Impact on Trabecular Bone: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis

- Clinical Study
- Predictive Performance of Glycated Hemoglobin for Incident Diabetes Compared with Glucose Tolerance Test According to Central Obesity
- Suji Yoo, Jaehoon Jung, Hosu Kim, Kyoung Young Kim, Soo Kyoung Kim, Jungwha Jung, Jong Ryeal Hahm, Jong Ha Baek
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):873-881. Published online December 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.798

- 3,862 View
- 102 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To examine whether glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) test would be a suitable screening tool for detecting high-risk subjects for diabetes compared to oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) according to accompanied central obesity.
Methods
In this prospective population-based cohort study, both OGTT and HbA1c tests were performed and continued every 2 years up to 12 years among individuals with non-diabetic state at baseline (aged 40 to 69 years, n=7,512). Incident diabetes was established by a doctor, HbA1c ≥6.5%, and/or fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥126 mg/dL, and/or 2-hour postprandial glucose (2hPG) level based on OGTT ≥200 mg/dL. Discriminative capacities of high HbA1c (≥5.7%) versus high 2hPG (≥140 mg/dL) for predicting incident diabetes were compared using Cox-proportional hazard regression and C-index.
Results
During the median 11.5 years of follow-up period, 1,341 (17.6%) developed diabetes corresponding to an incidence of 22.1 per 1,000 person-years. Isolated high 2hPG was associated with higher risk for incident diabetes (hazard ratio [HR], 4.29; 95% confidence interval [CI], 3.56 to 5.17) than isolated high HbA1c (HR, 2.79; 95% CI, 2.40 to 3.26; P<0.05). In addition, high 2hPG provided better discriminatory capacity than high HbA1c (C-index 0.79 vs. 0.75, P<0.05). Meanwhile, in subjects with central obesity, the HR (3.95 [95% CI, 3.01 to 5.18] vs. 2.82 [95% CI, 2.30 to 3.46]) and discriminatory capacity of incident diabetes (C-index 0.75 vs. 0.75) between two subgroups became comparable.
Conclusion
Even though the overall inferior predictive capacity of HbA1c test than OGTT, HbA1c test might plays a complementary role in identifying high risk for diabetes especially in subjects with central obesity with increased sensitivity.

- Clinical Study
- Relationships between Thigh and Waist Circumference, Hemoglobin Glycation Index, and Carotid Plaque in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Myung Ki Yoon, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm, Kap Bum Huh, Chul Sik Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):319-328. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.319
- 8,371 View
- 145 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigated the relationships of thigh and waist circumference with the hemoglobin glycation index (HGI) and carotid atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods
This observational study included 3,075 Korean patients with type 2 diabetes, in whom anthropometric measurements and carotid ultrasonography were conducted. HGI was defined as the measured hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level minus the predicted HbA1c level, which was calculated using the linear relationship between HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose levels. Carotid atherosclerosis was defined as a clearly isolated focal plaque or focal wall thickening >50% of the surrounding intima-media thickness.
Results
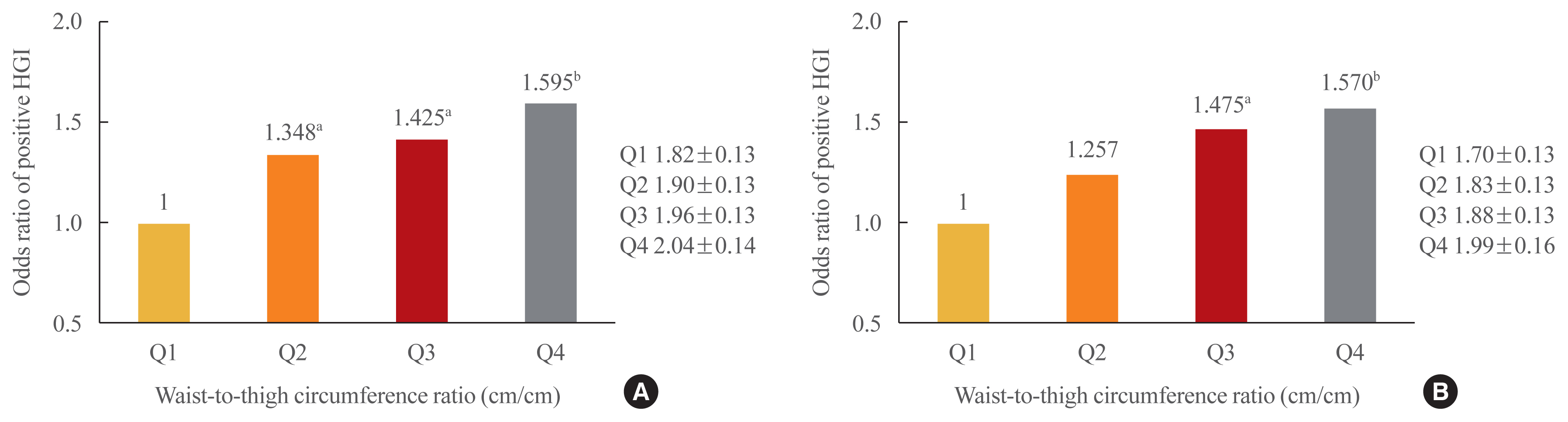
The frequency of a positive HGI decreased with increasing thigh circumference in men and increased with increasing waist circumference in women after adjusting for potential confounding variables. Thigh and waist circumference had a combined augmentative effect on the likelihood of positive HGI, which was dramatically higher in patients in higher waist-to-thigh ratio quartiles (adjusted odds ratios for the highest compared to the lowest quartile: 1.595 in men and 1.570 in women). Additionally, the larger the thigh circumference, the lower the risk of carotid atherosclerosis, although in women, this relationship lacked significance after adjustment for potential confounders.
Conclusion
HGI was associated with thigh circumference in men and waist circumference in women. In addition, the combination of low thigh circumference and high waist circumference was strongly associated with a higher HGI in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes. In particular, thigh circumference was associated with carotid atherosclerosis in men. However, further longitudinal studies are warranted. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between hemoglobin glycation index and subclinical myocardial injury in the general population free from cardiovascular disease
Zhenwei Wang, Yihai Liu, Jing Xie, Nai-Feng Liu
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2022; 32(2): 469. CrossRef - Association of Hemoglobin Glycation Index With Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography: A Retrospective Study
Zhezhe Chen, Duanbin Li, Maoning Lin, Hangpan Jiang, Tian Xu, Yu Shan, Guosheng Fu, Min Wang, Wenbin Zhang
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of continuous glucose monitoring-assessed glucose variability with intima-media thickness and ultrasonic tissue characteristics of the carotid arteries: a cross-sectional analysis in patients with type 2 diabetes
Naohiro Taya, Naoto Katakami, Tomoya Mita, Yosuke Okada, Satomi Wakasugi, Hidenori Yoshii, Toshihiko Shiraiwa, Akihito Otsuka, Yutaka Umayahara, Kayoko Ryomoto, Masahiro Hatazaki, Tetsuyuki Yasuda, Tsunehiko Yamamoto, Masahiko Gosho, Iichiro Shimomura, Hi
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between hemoglobin glycation index and subclinical myocardial injury in the general population free from cardiovascular disease

- Clinical Study
- Fasting and Postprandial Hyperglycemia: Their Predictors and Contributions to Overall Hyperglycemia in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Jaecheol Moon, Ji Young Kim, Soyeon Yoo, Gwanpyo Koh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):290-297. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.290
- 6,921 View
- 201 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to identify factors that affect fasting hyperglycemia (FHG) and postprandial hyperglycemia (PPG) and their contributions to overall hyperglycemia in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
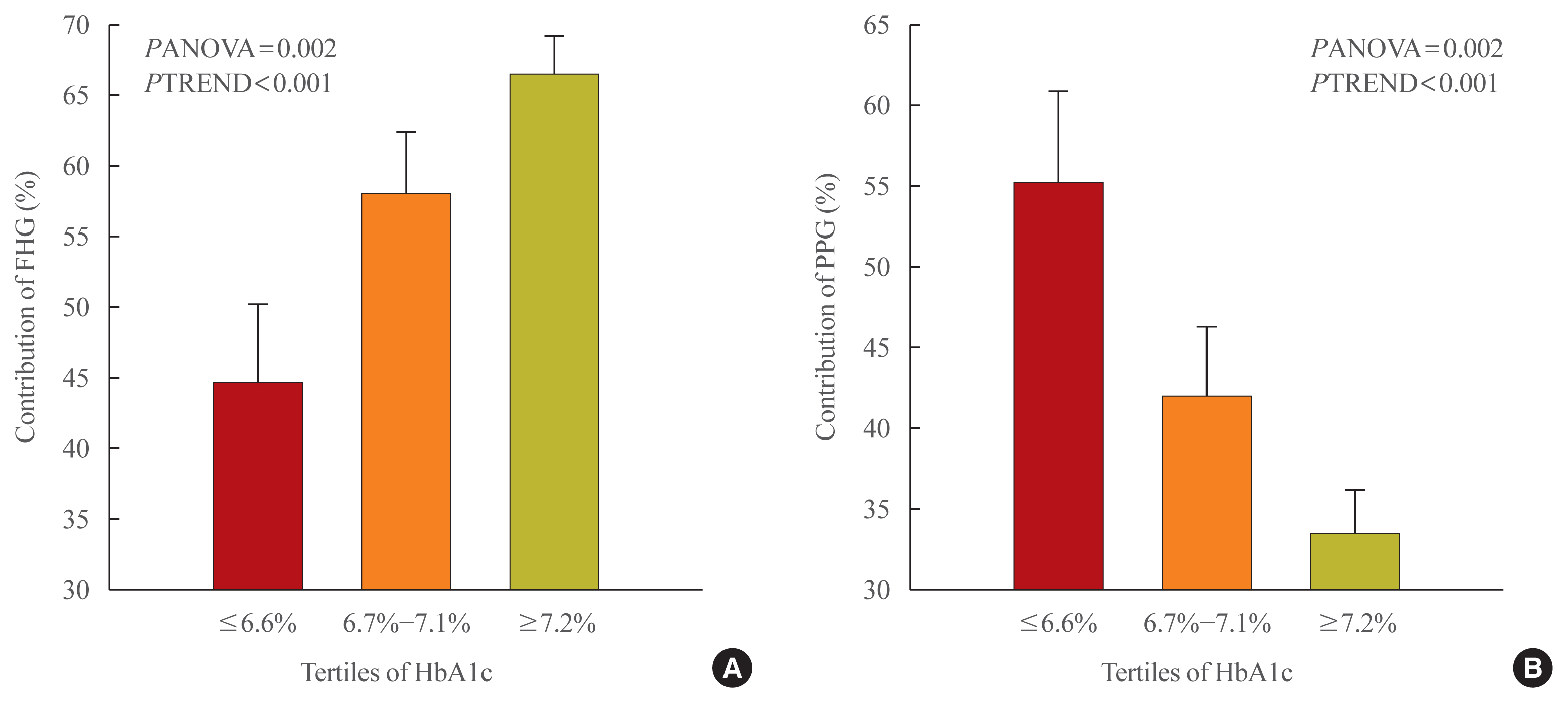
This was a retrospective study conducted on 194 Korean T2DM patients with 7-point self-monitoring blood glucose (SMBG) profiles plotted in 4 days in 3 consecutive months. We calculated the areas corresponding to FHG and PPG (area under the curve [AUC]FHG and AUCPPG) and contributions (%) in the graph of the 7-point SMBG data. The levels of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) were categorized by tertiles, and the contributions of FHG and PPG were compared.
Results
The relative contribution of FHG increased (44.7%±5.6%, 58.0%±4.4%, 66.5%±2.8%; PANOVA=0.002, PTREND <0.001), while that of PPG decreased (55.3%±5.5%, 42.0%±4.4%, 33.5%±2.8%; PANOVA=0.002, PTREND <0.001) with the elevated HbA1c. Multivariate analysis showed that HbA1c (β=0.615, P<0.001), waist circumference (β=0.216, P=0.042), and triglyceride (β=0.121, P=0.048) had a significant association with AUCFHG. Only HbA1c (β=0.231, P=0.002) and age (β=0.196, P=0.009) was significantly associated with AUCPPG.
Conclusion
The data suggested that in Korean T2DM patients, FHG predominantly contributed to overall hyperglycemia at higher HbA1c levels, whereas it contributed to PPG at lower HbA1c levels. It is recommended that certain factors, namely age, degree of glycemic control, obesity, or triglyceride levels, should be considered when prescribing medications for T2DM patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prospective study of the association between chronotype and cardiometabolic risk among Chinese young adults
Tingting Li, Yang Xie, Shuman Tao, Liwei Zou, Yajuan Yang, Fangbiao Tao, Xiaoyan Wu
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of mulberry twig alkaloids(Sangzhi alkaloids) and metformin on blood glucose fluctuations in combination with premixed insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes
Ziyu Meng, Chengye Xu, Haoling Liu, Xinyuan Gao, Xinyu Li, Wenjian Lin, Xuefei Ma, Changwei Yang, Ming Hao, Kangqi Zhao, Yuxin Hu, Yi Wang, Hongyu Kuang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating Triglyceride and Glucose Index as a Simple and Easy-to-Calculate Marker for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of General Internal Medicine.2022; 37(16): 4153. CrossRef - A new approach for investigating the relative contribution of basal glucose and postprandial glucose to HbA1C
Jing Ma, Hua He, Xiaojie Yang, Dawei Chen, Cuixia Tan, Li Zhong, Qiling Du, Xiaohua Wu, Yunyi Gao, Guanjian Liu, Chun Wang, Xingwu Ran
Nutrition & Diabetes.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A National Health Information Database Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 628. CrossRef
- Prospective study of the association between chronotype and cardiometabolic risk among Chinese young adults

- Diabetes
- Association between White Blood Cell Counts within Normal Range and Hemoglobin A1c in a Korean Population
- Jae Won Hong, Jung Hyun Noh, Dong-Jun Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(1):79-87. Published online January 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.1.79
- 4,615 View
- 51 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background We examined whether white blood cell (WBC) count levels within normal range, could be associated with hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels.
Methods Among the 11,472 people (≥19 years of age) who participated in the 2011 to 2012 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination, subjects with chronic disease or illness, including 807 patients with diabetes currently taking anti-diabetic medications and/or 1,149 subjects with WBC levels <4,000 or >10,000/µL were excluded.
Results Overall, adjusted HbA1c levels increased across the WBC quartiles (5.55%±0.01%, 5.58%±0.01%, 5.60%±0.01%, and 5.65%±0.01%,
P <0.001) after adjusting for confounding factors, such as age, gender, fasting plasma glucose, college graduation, smoking history, waist circumference, presence of hypertension, serum total cholesterol, serum triglyceride, and presence of anemia. The adjusted proportions (%) of HbA1c levels of ≥5.7%, ≥6.1%, and ≥6.5% showed significant increases across WBC quartiles (P <0.001,P =0.002, andP =0.022, respectively). Logistic regression analyses of WBC quartiles for the risk of HbA1c levels of ≥5.7%, ≥6.1%, and ≥6.5%, using the variables above as covariates, showed that the odds ratios of the fourth quartile of WBCs were 1.59 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.35 to 1.89;P <0.001), 1.78 (95% CI, 1.31 to 2.42;P <0.001), and 2.03 (95% CI, 1.13 to 3.64;P =0.018), using the first quartile of WBCs as the reference.Conclusion HbA1c levels were positively associated with WBC levels within normal range in a general adult population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Vitamin D supplementation modulates glycated hemoglobin (HBA1c) in diabetes mellitus
Asma Akhter, Sultan Alouffi, Uzma Shahab, Rihab Akasha, Mohd Fazal-Ur-Rehman, Mohamed E. Ghoniem, Naved Ahmad, Kirtanjot Kaur, Ramendra Pati Pandey, Ahmed Alshammari, Firoz Akhter, Saheem Ahmad
Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics.2024; 753: 109911. CrossRef - Glucose indices as inflammatory markers in children with acute surgical abdomen: a cross-sectional study
Hoda Atef Abdelsattar Ibrahim, Sherif Kaddah, Sara Mohamed Elkhateeb, Abeer Aboalazayem, Aya Ahmed Amin, Mahmoud Marei Marei
Annals of Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with relative muscle strength in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chiao-Nan Chen, Ting-Chung Chen, Shiow-Chwen Tsai, Chii-Min Hwu
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2021; 95: 104384. CrossRef - Non-vascular contributing factors of diabetic foot ulcer severity in national referral hospital of Indonesia
Em Yunir, Dicky L. Tahapary, Tri Juli Edi Tarigan, Dante Saksono Harbuwono, Yoga Dwi Oktavianda, Melly Kristanti, Eni Iswati, Angela Sarumpaet, Pradana Soewondo
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(1): 805. CrossRef - Association between Inflammatory Markers and Glycemic Control in Korean Diabetic Patients
Min Kang, Seok-Joon Sohn
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(3): 247. CrossRef - Prediabetes Is Independently Associated with Subclinical Carotid Atherosclerosis: An Observational Study in a Non-Urban Mediterranean Population
Maria Belén Vilanova, Josep Franch-Nadal, Mireia Falguera, Josep Ramon Marsal, Sílvia Canivell, Esther Rubinat, Neus Miró, Àngels Molló, Manel Mata-Cases, Mònica Gratacòs, Esmeralda Castelblanco, Dídac Mauricio
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(7): 2139. CrossRef
- Vitamin D supplementation modulates glycated hemoglobin (HBA1c) in diabetes mellitus


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



