Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - The Effects of Glucose Lowering Agents on the Secondary Prevention of Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):977-987. Published online October 14, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1046
- 4,047 View
- 175 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
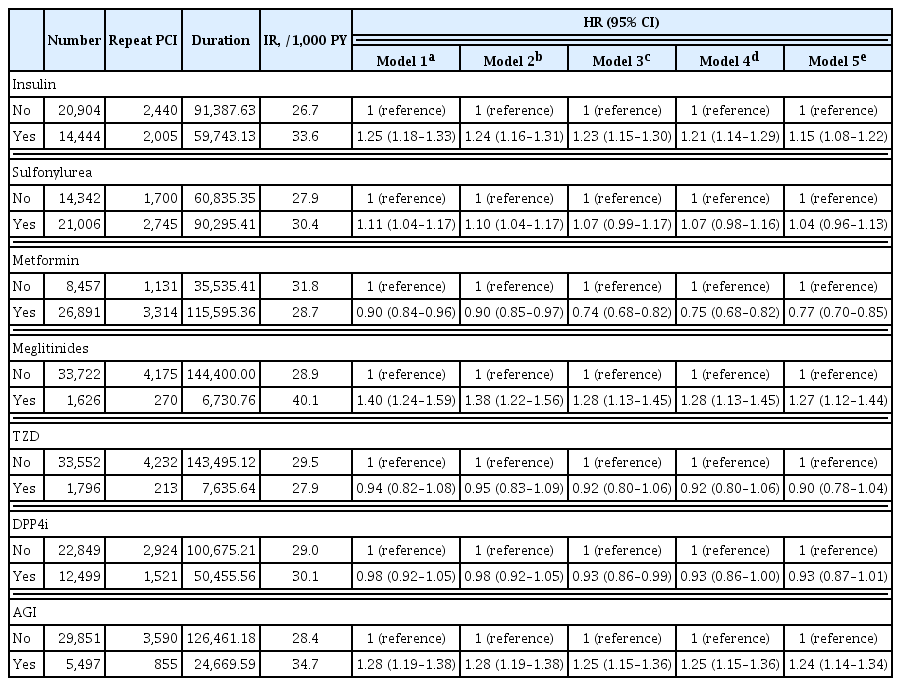
Patients with diabetes have a higher risk of requiring repeated percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) than non-diabetic patients. We aimed to evaluate and compare the effects of anti-diabetic drugs on the secondary prevention of myocardial infarction among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Methods
We analyzed the general health check-up dataset and claims data of the Korean National Health Insurance Service of 199,714 participants (age ≥30 years) who underwent PCIs between 2010 and 2013. Those who underwent additional PCI within 1 year of their first PCI (n=3,325) and those who died within 1 year (n=1,312) were excluded. Patients were classified according to their prescription records for glucose-lowering agents. The primary endpoint was the incidence rate of coronary revascularization.
Results
A total of 35,348 patients were included in the study. Metformin significantly decreased the risk of requiring repeat PCI in all patients (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.77). In obese patients with body mass index (BMI) ≥25 kg/m2, patients treated with thiazolidinedione (TZD) exhibited a decreased risk of requiring repeat revascularization than those who were not treated with TZD (aHR, 0.77; 95% confidence interval, 0.63 to 0.95). Patients treated with metformin showed a decreased risk of requiring revascularization regardless of their BMI. Insulin, meglitinide, and alpha-glucosidase inhibitor were associated with increased risk of repeated PCI.
Conclusion
The risk of requiring repeat revascularization was lower in diabetic patients treated with metformin and in obese patients treated with TZD. These results suggest that physicians should choose appropriate glucose-lowering agents for the secondary prevention of coronary artery disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Application of systemic inflammation indices and lipid metabolism-related factors in coronary artery disease
Zhuoyan Zhao, Huan Lian, Yixiang Liu, Lixian Sun, Ying Zhang
Coronary Artery Disease.2023; 34(5): 306. CrossRef - Effect of metformin on adverse outcomes in T2DM patients: Systemic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Zhicheng Xu, Haidong Zhang, Chenghui Wu, Yuxiang Zheng, Jingzhou Jiang
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Establishment of a Predictive Model for Poor Prognosis of Incomplete Revascularization in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease and Multivessel Disease
Huan Lian, Zhuoyan Zhao, Kelin Ma, Zhenjiang Ding, Lixian Sun, Ying Zhang
Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis.2022; 28: 107602962211392. CrossRef
- Application of systemic inflammation indices and lipid metabolism-related factors in coronary artery disease

- Clinical Study
- Association of Hyperparathyroidism and Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
- Chaiho Jeong, Hye In Kwon, Hansang Baek, Hun-Sung Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Jeonghoon Ha, Moo Il Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):925-932. Published online December 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.725

- 5,386 View
- 184 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Concomitant papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) and hyperparathyroidism (HPT) have been reported in several studies. Our study aimed to investigate the incidence of concomitant PTC in HPT patients upon preoperative diagnosis and present a clinical opinion on detecting thyroid malignancy in case of parathyroidectomy.
Methods
Patients who underwent parathyroidectomy between January 2009 and December 2019 in two medical centers were included. Of the 279 participants 154 were diagnosed as primary hyperparathyroidism (pHPT) and 125 as secondary hyperparathyroidism (sHPT). The incidence of concomitant PTC and its clinical characteristics were compared with 98 patients who underwent thyroidectomy and were diagnosed with classical PTC during the same period.
Results
Concurrent PTC was detected in 14 patients (9.1%) with pHPT and in nine patients (7.2%) with sHPT. Ten (71.4%) and seven (77.8%) PTCs were microcarcinomas in the pHPT and sHPT cases respectively. In the pHPT patients, vitamin D was lower in the pHPT+PTC group (13.0±3.7 ng/mL) than in the pHPT-only group (18.5±10.4 ng/mL; P=0.01). Vitamin D levels were also lower in the sHPT+PTC group (12.3±5.6 ng/mL) than in the sHPT-only group (18.0±10.2 ng/mL; P=0.12). In the concomitant PTC group, lymph node ratio was higher than in the classical PTC group (P=0.00).
Conclusion
A high prevalence of concomitant PTC was seen in patients with pHPT and sHPT. Those concomitant PTCs were mostly microcarcinomas and had more aggressive features, suggesting that efforts should be made to detect concomitant malignancies in the preoperative parathyroidectomy evaluation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The unexpected effect of parathyroid adenoma on inflammation
Ahmet Tarik Harmantepe, Belma Kocer, Zulfu Bayhan, Emre Gonullu, Ugur Can Dulger
Updates in Surgery.2024; 76(2): 589. CrossRef - Evaluation of Nodular Goiter and Papillary Thyroid Cancer Coincidence in Patients with Primary Hyperparathyroidism
Mustafa ÇALIŞKAN, Hasret CENGİZ, Taner DEMİRCİ
Düzce Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi.2023; 25(2): 200. CrossRef - Papillary thyroid carcinoma coexisting with benign thyroid and parathyroid pathology: clinical and pathomorphological features
A. Dinets, M. Gorobeiko, V. Hoperia, A. Lovin, S. Tarasenko
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2023; 19(4): 274. CrossRef - The Nexus of Hyperparathyroidism and Thyroid Carcinoma: Insights into Pathogenesis and Diagnostic Challenges—A Narrative Review
Gregorio Scerrino, Nunzia Cinzia Paladino, Giuseppina Orlando, Giuseppe Salamone, Pierina Richiusa, Stefano Radellini, Giuseppina Melfa, Giuseppa Graceffa
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(1): 147. CrossRef - Is preoperative parathyroid localization necessary for tertiary hyperparathyroidism?
Rongzhi Wang, Peter Abraham, Brenessa Lindeman, Herbert Chen, Jessica Fazendin
The American Journal of Surgery.2022; 224(3): 918. CrossRef - Papillary thyroid carcinoma prevalence and its predictors in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism
Elif Tutku DURMUŞ, Ayşegül ATMACA, Mehmet KEFELİ, Ramis ÇOLAK, Buğra DURMUŞ, Cafer POLAT
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2022; 5(5): 1499. CrossRef - Association of Hyperparathyroidism and Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Multicenter Retrospective Study (Endocrinol Metab 2020;35:925-32, Chaiho Jeong et al.)
Chaiho Jeong, Jeonghoon Ha, Moo Il Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(1): 205. CrossRef - Association of Hyperparathyroidism and Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Multicenter Retrospective Study (Endocrinol Metab 2020;35:925-32, Chaiho Jeong et al.)
Burcu Candemir, Coşkun Meriç
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(1): 203. CrossRef
- The unexpected effect of parathyroid adenoma on inflammation

- Clinical Study
- Impact of Subtotal Parathyroidectomy on Clinical Parameters and Quality of Life in Hemodialysis Patients with Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
- Mohamed Mimi Abd Elgawwad El-kholey, Ghada El-said Ibrahim, Osama Ibrahim Elshahat, Ghada El-Kannishy
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(4):367-373. Published online December 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.4.367
- 4,452 View
- 81 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Impairment of quality of life (QOL) is a key clinical characteristic of patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), and can be especially severe in the presence of secondary hyperparathyroidism (SHPT). Despite the proven success of parathyroidectomy (PTX) in controlling biochemical parameters in patients with severe SHPT, evidence is lacking regarding the effects of PTX on various clinical outcomes, including QOL.
Methods Twenty ESRD patients on maintenance hemodialysis with SHPT who underwent subtotal PTX were included in an observational longitudinal study. All studied patients underwent history-taking, clinical examinations, and laboratory investigations, including a complete blood count and measurements of serum calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, parathyroid hormone (PTH), and albumin levels preoperatively and at 3 months postoperatively. QOL was assessed before surgery and at 3 months after surgery using the Kidney Disease Quality of Life 36-Item Short-Form instrument.
Results After PTX, significant decreases in serum PTH and phosphorus levels were observed, as well as a significant increase in serum magnesium levels. Significant weight gain and improvements of QOL were also detected postoperatively.
Conclusion Subtotal PTX seems to be an efficient alternative to medical management in uncontrolled cases of SHPT, as it is capable of controlling the biochemical derangements that occur in hyperparathyroidism. Furthermore, PTX had a beneficial effect on clinical outcomes, as shown by weight gain and improvements in all QOL scales.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Abnormalities of serum magnesium levels in dialysis patients undergoing parathyroidectomy
Chi-Yu Kuo, Chung-Hsin Tsai, Jie-Jen Lee, Shih-Ping Cheng
Updates in Surgery.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Parathyroidectomy on Quality of Life Among Patients Undergoing Dialysis
Lin Wang, Ming-Hui Xin, Yan Ma, Yu Wang, Meng-Yuan Hu, Qiang-Qiang Liu, Jin-Bor Chen
International Journal of General Medicine.2022; Volume 15: 1185. CrossRef - Paricalcitol versus Calcitriol + Cinacalcet for the Treatment of Secondary Hyperparathyroidism in Chronic Kidney Disease in China: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Zhuolin Zhang, Lele Cai, Hong Wu, Xinglu Xu, Wenqing Fang, Xuan He, Xiao Wang, Xin Li
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Abnormalities of serum magnesium levels in dialysis patients undergoing parathyroidectomy

- A Case of Kallmann's Syndrome Mildly Presenting as Secondary Amenorrhea.
- Na Rae Joo, Cheol Young Park, Hong Ju Moon, Jun Goo Kang, Sung Hee Ihm, Moon Gi Choi, Hyung Joon Yoo, Yul Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung woo Park
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007;22(2):130-134. Published online April 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.2.130
- 2,123 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Kallmann's syndrome is very rare congenital defect in GnRH (gonadotrophin releasing hormone) secretion involving both sexes. The mode of inheritance has not been fully understood. But, including X-linked inheritance, the ratio of incidence between male versus female is 5:1, and there is a few case reports of female Kallmann's syndrome in Korea, especially in internal medicine department. We report a case of 35 year-old female Kallmann's syndrome presenting secondary amenorrhea as a mild presentation.

- A Case of Pituitary Macroadenoma Accompanied with CRH Deficiency.
- Yoo Jung Nahm, Jin Soo Kim, Keun Jong Cho, Uk Hyun Kil, Sung Yong Woo, Sung Rae Kim, Soon Jib Yoo, Sung Koo Kang, Ho Young Son
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(2):153-157. Published online April 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.2.153
- 1,677 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Pituitary tumor can be accompanied with various pituitary hormone abnormalities. Pituitary tumors can be divided into functioning or nonfunctioning tumors. A functioning pituitary tumor, via the oversecretion of pituitary hormones, causes diverse clinical features. A nonfunctioning pituitary tumor can be accompanied with pituitary dysfunction and this may be due to compression or destruction of normal pituitary tissue, suppression of the pituitary portal system or direct damage to the hypothalamus. Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) deficiency, which is caused by defects in the synthesis or release of CRH, is a cause of secondary adrenocortical insufficiency. The clinical presentations are hypoglycemia, weight loss, anemia, weakness, nausea, vomiting and hyponatremia. Acquired CRH deficiency has also been suggested to occur based on a lack of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia, but there is a normal ACTH response to exogenous CRH. We experienced a case of a woman with pituitary macroadenoma accompanied with CRH deficiency. We report here on this case with the review of the literature.

- Determination of Glucocorticoid Replacement Therapy and Adequate Maintenance Dose in Patients with Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency.
- Sang Wan Kim, Hye Seung Jung, Seong Hee Kwon, Do Joon Park, Chan Soo Shin, Kyung Soo Park, Seong Yeon Kim, Bo Youn Cho, Hong Kyu Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2003;18(5):456-464. Published online October 1, 2003
- 1,083 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Determination of the adequate dose of glucocorticoid replacement therapy, in patients with secondary adrenal insufficiency, is of great importance to avoid the consequences of under or over treatment. The aims of this study were: 1) to assess the value of adrenal cortical function tests in determining whether glucocorticoid replacement should be given, and 2) to investigate the adequate maintenance dose of glucocorticoid in patients with secondary adrenal insufficiency. METHODS: Forty patients, with secondary adrenal insufficiency, confirmed by the insulin-induced hypoglycemia test (IHT), were studied. All subjects underwent basal serum cortisol measurement, IHT and 250 g rapid ACTH stimulation tests (AST). The clinical usefulness of these tests, for the determination of glucocorticoid replacement therapy, was evaluated in patients with secondary adrenal insufficiency. 26 of the 40 patients had received prednisolone (Pd) (5 mg per day) replacement due to symptoms from adrenal insufficiency. The dose of Pd was serially changed from 5 to 3.75, and then to 6.25 mg per day, every 3 month. The measured lipid parameters, serum osteocalcin and urinary N-telopeptide were measured and the quality of life evaluated by the administration of an Addisonian questionnaire, both before and after the dose changes. RESULTS: 1) For all tests, cut-offs were selected that would provide adequate specificity and sensitivity. When the cut-offs were set to provide 95% specificity, the corresponding sensitivitycut-off values, obtained with basal serum cortisol, peak serum cortisol in IHT and AST were: 88.4% <5 microgram/dL, 80.7% <11 microgram/dL and 76.9% <16 microgram/dL. 2) The urinary type I collagen N-telopeptide, total cholesterol, HDL- and LDL-cholesterol levels were significantly increased, and the serum osteocalcin levels significantly decreased when the daily dose of Pd was increased to 6.25 from 3.75 or 5 mg. The LDL-cholesterol levels especially, were significantly increased, even though the change in the Pd from 3.75 to 5 mg per day was subtle. CONCLUSION: The basal cortisol levels, HPA axis tests and the symptoms of patients may be helpful to determine whether prednisolone replacement therapy should be given. It is suggest that an adequate dose of glucocorticoid replacement therapy should be not exceed Pd 5mg per day, so as not to have adverse effects on the bone and lipid metabolisms.

- Usefullness of Urinary Free Cortisol Measurement in Diagnosis of Iatrogenic Cushing Syndrome.
- Yong Hyun Kim, Sang Jin Kim, Dong Seop Choi
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2000;15(2):162-169. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,058 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Although insulin induced hypoglycemia test is a standard diagnostic method in assessment of hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis, rapid ACTH stimulation test using 250microgram has been used as a first line diagnostic test especially in secondary adrenal insufficiency due to iatrogenic Cushing syndrome because it is easy and safe. However, it was suggested that a maximal cortisol response can be achieved with a much lower ACTH dose and 1microgram ACTH enhances the sensitivity without decreasing specificity of test. Also recently, there was a report that midnight to morning urine cortisol increment is more accurate, noninvasive method can be used for measurement of hypothalmo-pituitary-adrenal axis. In this study, we compared the 1microgram ACTH stimulation test with midnight to morning urinary free cortisol increment in secondary adrenal insufficiency due to iatrogenic Cushing syndrome to study the agreement of two test and accuracy of increment of urinary free cortisol in diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency. METHODS: Double voided urine sample were collected at midnight and 8 A.M. in 12 patients who have Cushing-like feature and history of taking glucocorticoids and in 12 normal controls. Urinary free cortisol was measured and cortisol increment was defined as the morning urine free cortisol minus the midnight urine free cortisol. The 1microgram ACTH stimulation test was performed in 12 iatrogenic Cushing syndrome patients at the same day and compard with the result of cortisol increment. RESULTS: Using the results of 12 controls, normal urine free cortisol increment was defined as greater than 165.5nmol/L(6.0microgram/dL). Subnormal cortisol response in 1microgram ACTH stimulation test was noted in 8 out of 12 patients group and urinary free cortisol increment was not observed in 7 out of 8 subnormal response group. Normal cortisol response in 1microgram ACTH stimulation test was noted in 4 out of 12 patients group and urinary free cortisol increment was observed in 3 out of 4 normal response group. So 83% of concordance rate between 1microgram ACTH stimulation test and urine free cortisol increment was recorded. CONCLUSION: Urinary free cortisol increment has high concordance rate with 1microgram ACTH stimulation test and simple, easy test in diagnosing secondary adrenal insufficiency due to iatrogenic Cushing syndrome. Further study including more patients will be helpful to know the adequacy and reliability of test in evaluation of hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



