Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Renal Protection of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist, Finerenone, in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Dong-Lim Kim, Seung-Eun Lee, Nan Hee Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):43-55. Published online February 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1629
- 5,646 View
- 766 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
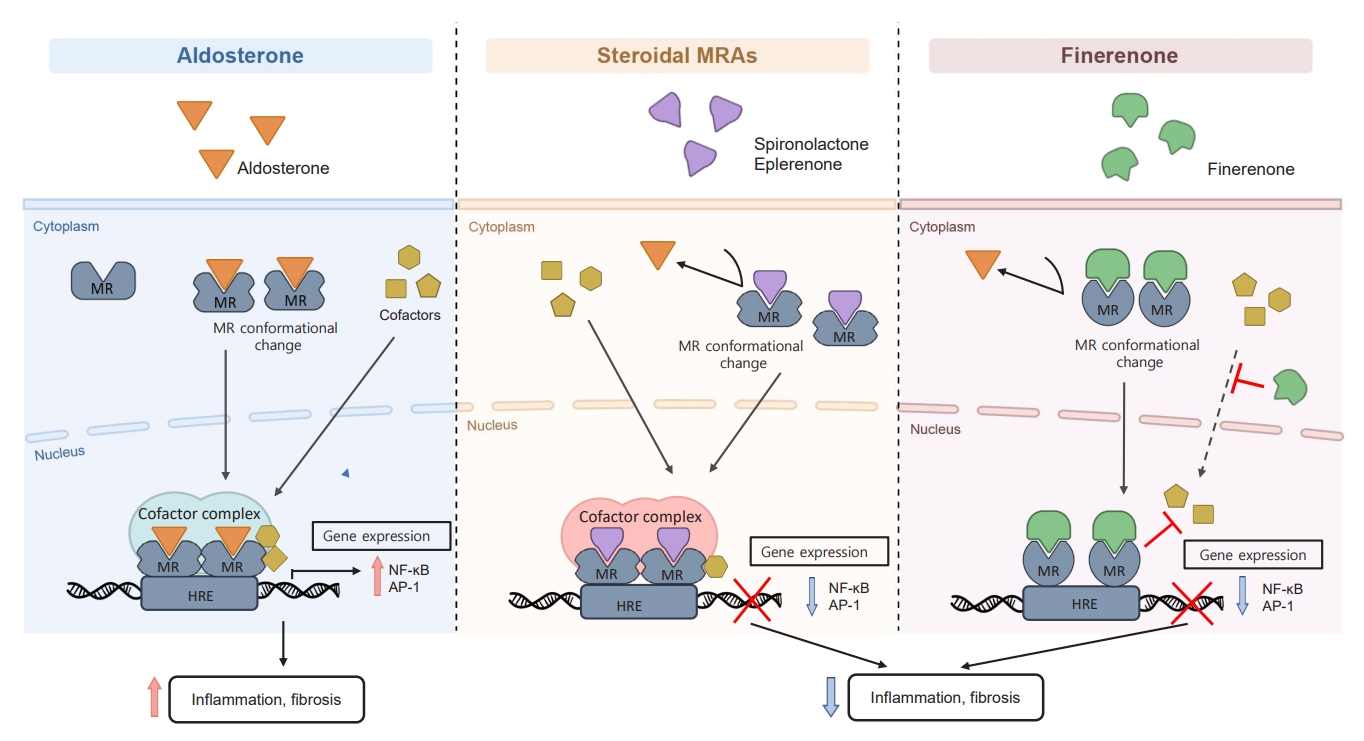
ePub - Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the most common cause of end-stage renal disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). CKD increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases; therefore, its prevention and treatment are important. The prevention of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) can be achieved through intensive glycemic control and blood pressure management. Additionally, DKD treatment aims to reduce albuminuria and improve kidney function. In patients with T2DM, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors, sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists can delay the progression of DKD. Hence, there is a need for novel treatments that can effectively suppress DKD progression. Finerenone is a first-in-class nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist with clinically proven efficacy in improving albuminuria, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and risk of cardiovascular events in early and advanced DKD. Therefore, finerenone is a promising treatment option to delay DKD progression. This article reviews the mechanism of renal effects and major clinical outcomes of finerenone in DKD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Neue Antihypertensiva im Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosteron-System
Markus van der Giet
CardioVasc.2024; 24(1): 33. CrossRef -
Chicoric acid
advanced PAQR3 ubiquitination to ameliorate ferroptosis in diabetes nephropathy through the relieving of the interaction between PAQR3 and P110α pathway
Weiwei Zhang, Yong Liu, Jiajun Zhou, Teng Qiu, Haitang Xie, Zhichen Pu
Clinical and Experimental Hypertension.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endothelial CXCR2 deficiency attenuates renal inflammation and glycocalyx shedding through NF-κB signaling in diabetic kidney disease
Siyuan Cui, Xin Chen, Jiayu Li, Wei Wang, Deqi Meng, Shenglong Zhu, Shiwei Shen
Cell Communication and Signaling.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular Targets of Novel Therapeutics for Diabetic Kidney Disease: A New Era of Nephroprotection
Alessio Mazzieri, Francesca Porcellati, Francesca Timio, Gianpaolo Reboldi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3969. CrossRef - Epigenetic modification in diabetic kidney disease
Zhe Liu, Jiahui Liu, Wanning Wang, Xingna An, Ling Luo, Dehai Yu, Weixia Sun
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel Approaches in Chronic Renal Failure without Renal Replacement Therapy: A Review
Sandra Martínez-Hernández, Martín Muñoz-Ortega, Manuel Ávila-Blanco, Mariana Medina-Pizaño, Javier Ventura-Juárez
Biomedicines.2023; 11(10): 2828. CrossRef - Finerenone and other future therapeutic options for Alport syndrome
Helen Pearce, Holly Mabillard
Journal of Rare Diseases.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Neue Antihypertensiva im Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosteron-System

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Therapy: From Discovery to Type 2 Diabetes and Beyond
- Adie Viljoen, Stephen C. Bain
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):25-33. Published online February 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1642
- 2,789 View
- 307 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The therapeutic benefits of the incretin hormone, glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP1), for people with type 2 diabetes and/or obesity, are now firmly established. The evidence-base arising from head-to-head comparative effectiveness studies in people with type 2 diabetes, as well as the recommendations by professional guidelines suggest that GLP1 receptor agonists should replace more traditional treatment options such as sulfonylureas and dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitors. Furthermore, their benefits in reducing cardiovascular events in people with type 2 diabetes beyond improvements in glycaemic control has led to numerous clinical trials seeking to translate this benefit beyond type 2 diabetes. Following early trial results their therapeutic benefit is currently being tested in other conditions including fatty liver disease, kidney disease, and Alzheimer’s disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Road towards Triple Agonists: Glucagon-Like Peptide 1, Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide and Glucagon Receptor - An Update
Agnieszka Jakubowska, Carel W. le Roux, Adie Viljoen
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 12. CrossRef - Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: cardiovascular benefits and mechanisms of action
John R. Ussher, Daniel J. Drucker
Nature Reviews Cardiology.2023; 20(7): 463. CrossRef - A new class of glucose-lowering therapy for type 2 diabetes: the latest development in the incretin arena
Stephen C Bain, Thinzar Min
The Lancet.2023; 402(10401): 504. CrossRef - Flattening the biological age curve by improving metabolic health: to taurine or not to taurine, that’ s the question
Kwok M. Ho, Anna Lee, William Wu, Matthew T.V. Chan, Lowell Ling, Jeffrey Lipman, Jason Roberts, Edward Litton, Gavin M. Joynt, Martin Wong
Journal of Geriatric Cardiology.2023; 20(11): 813. CrossRef
- The Road towards Triple Agonists: Glucagon-Like Peptide 1, Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide and Glucagon Receptor - An Update

- Thyroid
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Graves’ Disease and the Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease: A Korean Population-Based Study
- Yoon Young Cho, Bongseong Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Hye Ryoun Jang, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chan-Hee Jung, Jae Hyeon Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Kyungdo Han, Tae Hyuk Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):281-289. Published online April 6, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1333

- 3,896 View
- 134 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Hyperthyroidism is associated with an increased glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in the hyperdynamic state, which is reversible after restoring euthyroidism. However, long-term follow-up of renal dysfunction in patients with hyperthyroidism has not been performed.
Methods
This was a retrospective cohort study using the Korean National Health Insurance database and biannual health checkup data. We included 41,778 Graves’ disease (GD) patients and 41,778 healthy controls, matched by age and sex. The incidences of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) were calculated in GD patients and controls. The cumulative dose and duration of antithyroid drugs (ATDs) were calculated for each patient and categorized into the highest, middle, and lowest tertiles.
Results
Among 41,778 GD patients, 55 ESRD cases occurred during 268,552 person-years of follow-up. Relative to the controls, regardless of smoking, drinking, or comorbidities, including chronic kidney disease, GD patients had a 47% lower risk of developing ESRD (hazard ratio [HR], 0.53; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.37 to 0.76). In particular, GD patients with a higher baseline GFR (≥90 mL/min/1.73 m2; HR, 0.33; 95% CI, 0.11 to 0.99), longer treatment duration (>33 months; HR, 0.31; 95% CI, 0.17 to 0.58) or higher cumulative dose (>16,463 mg; HR, 0.29; 95% CI, 0.15 to 0.57) of ATDs had a significantly reduced risk of ESRD.
Conclusion
This was the first epidemiological study on the effect of GD on ESRD, and we demonstrated that GD population had a reduced risk for developing ESRD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Renal function changes in patients with subclinical hyperthyroidism: a novel postulated mechanism
Magdy Mohamed Allam, Hanaa Tarek El-Zawawy, Tarek Hussein El-Zawawy
Endocrine.2023; 82(1): 78. CrossRef - Effect of Hyperthyroidism on Preventing Renal Insufficiency
Tae Yong Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 220. CrossRef - Effects and Clinical Value of Peritoneal Dialysis on Water and Water Balance, Adverse Reactions, Quality of Life, and Clinical Prognosis in Patients with Decompensated Chronic Nephropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Xichao Wang, Miaomiao Zhang, Na Sun, Wenxiu Chang, Gang Chen
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef
- Renal function changes in patients with subclinical hyperthyroidism: a novel postulated mechanism

- Miscellaneous
- Clinical Value of Serum Mitochondria-Inhibiting Substances in Assessing Renal Hazards: A Community-Based Prospective Study in Korea
- Hoon Sung Choi, Jin Taek Kim, Hong Kyu Lee, Wook Ha Park, Youngmi Kim Pak, Sung Woo Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1298-1306. Published online November 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1226
- 3,280 View
- 95 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Mitochondrial dysfunction is strongly associated with several kidney diseases. However, no studies have evaluated the potential renal hazards of serum mitochondria-inhibiting substance (MIS) and aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand (AhRL) levels.
Methods
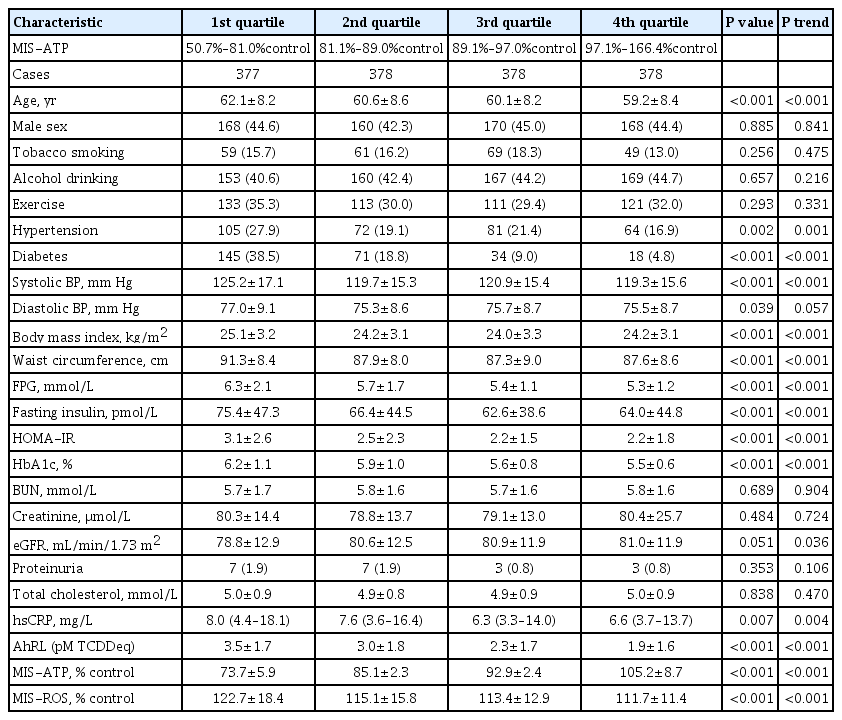
We used serum level of MIS and AhRL and clinical renal outcomes from 1,511 participants of a prospective community-based cohort in Ansung. MIS was evaluated based on intracellular adenosine triphosphate (MIS-ATP) or reactive oxygen species (MIS-ROS) generation measured using cell-based assays.
Results
During a mean 6.9-year follow-up, 84 participants (5.6%) developed a rapid decline in kidney function. In the lowest quartile group of MIS-ATP, patients were older and had metabolically deleterious parameters. In multivariate logistic regression analysis, higher MIS-ATP was associated with decreased odds for rapid decline: the odds ratio (OR) of 1% increase was 0.977 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.957 to 0.998; P=0.031), while higher MIS-ROS was marginally associated with increased odds for rapid decline (OR, 1.014; 95% CI, 0.999 to 1.028; P=0.055). However, serum AhRL was not associated with the rapid decline in kidney function. In subgroup analysis, the renal hazard of MIS was particularly evident in people with hypertension and low baseline kidney function.
Conclusion
Serum MIS was independently associated with a rapid decline in kidney function, while serum AhRL was not. The clinical implication of renal hazard on serum MIS requires further evaluation in future studies. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Interactive Online App for Predicting Diabetes via Machine Learning from Environment-Polluting Chemical Exposure Data
Rosy Oh, Hong Kyu Lee, Youngmi Kim Pak, Man-Suk Oh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(10): 5800. CrossRef
- An Interactive Online App for Predicting Diabetes via Machine Learning from Environment-Polluting Chemical Exposure Data

- Diabetes
- Cardiorenal Protection in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Jason F. Lee, Ecaterina Berzan, Vikas S. Sridhar, Ayodele Odutayo, David Z.I. Cherney
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(2):256-269. Published online April 19, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.987
- 5,738 View
- 300 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
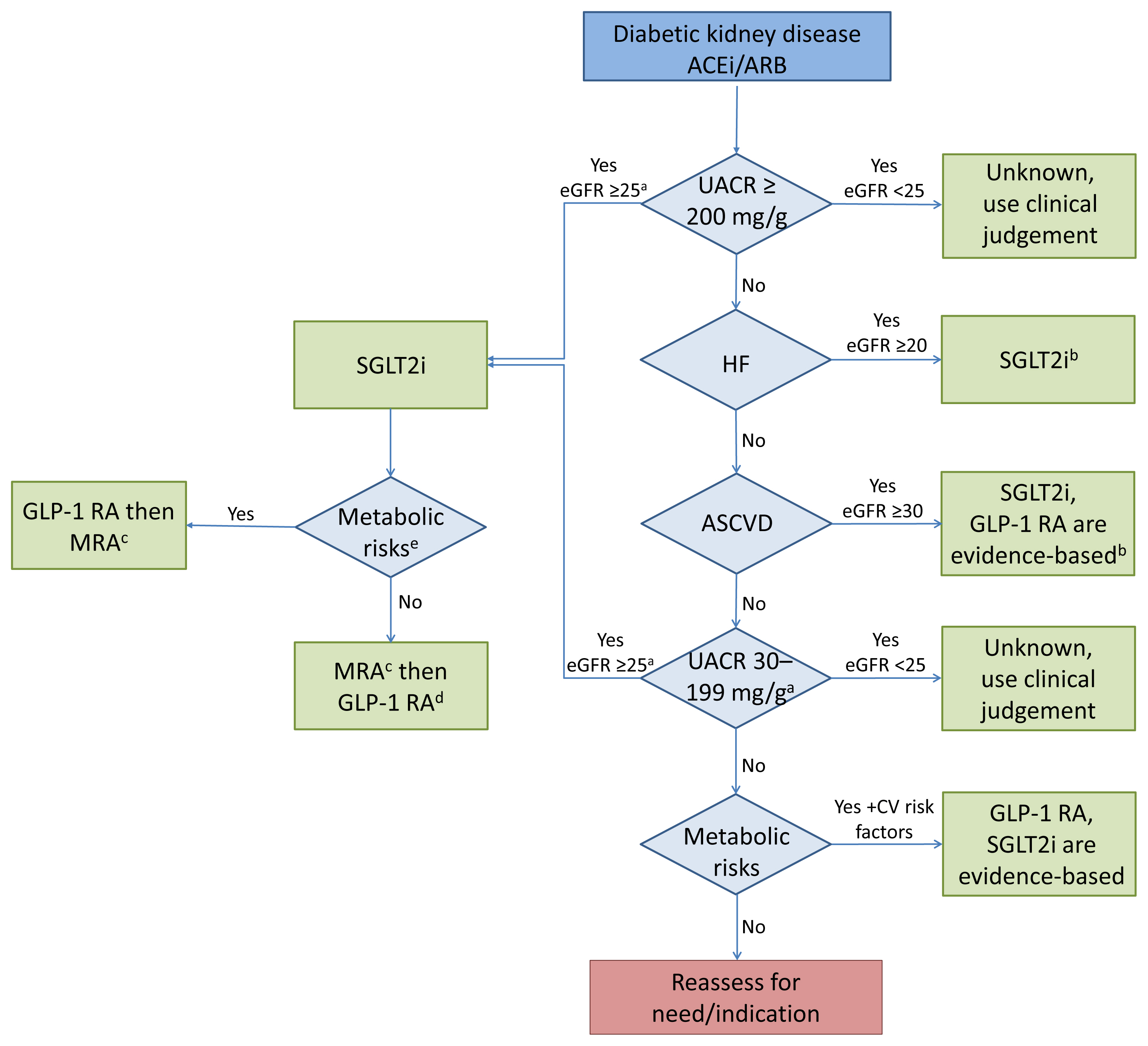
ePub - Over the last 5 years there have been many new developments in the management of diabetic kidney disease. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors were initially used for glycemic control, but more recent studies have now shown that their benefits extend to cardiovascular and kidney outcomes. The recent addition of data on the novel mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) gives us another approach to further decrease the residual risk of diabetic kidney disease progression. In this review we describe the mechanism of action, key studies, and possible adverse effects related to these three classes of medications. The management of type 2 diabetes now includes an increasing number of medications for the management of comorbidities in a patient population at significant risk of cardiovascular disease and progression of chronic kidney disease. It is from this perspective that we seek to outline the rationale for the sequential and/or combined use of SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 RA and MRAs in patients with type 2 diabetes for heart and kidney protection.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relative and Absolute Risks of Adverse Events with Real-World Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in CKD
Ayodele Odutayo, Adeera Levin
Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.2023; 18(5): 557. CrossRef - Renal Protection of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist, Finerenone, in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Dong-Lim Kim, Seung-Eun Lee, Nan Hee Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 43. CrossRef - Intrarenal Mechanisms of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors on Tubuloglomerular Feedback and Natriuresis
Eun Sil Koh, Gheun-Ho Kim, Sungjin Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 359. CrossRef - SGLT2 and DPP4 inhibitors improve Alzheimer’s disease–like pathology and cognitive function through distinct mechanisms in a T2D–AD mouse model
A Young Sim, Da Hyun Choi, Jong Youl Kim, Eun Ran Kim, A-ra Goh, Yong-ho Lee, Jong Eun Lee
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 168: 115755. CrossRef - Narrative review investigating the nephroprotective mechanisms of sodium glucose cotransporter type 2 inhibitors in diabetic and nondiabetic patients with chronic kidney disease
Emma S. Speedtsberg, Martin Tepel
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of CKD
Nimrit Goraya, Jennifer D. Moran
Nephrology Self-Assessment Program.2022; 21(2): 146. CrossRef - Nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonism for cardiovascular and renal disorders − New perspectives for combination therapy
Peter Kolkhof, Amer Joseph, Ulrich Kintscher
Pharmacological Research.2021; 172: 105859. CrossRef - Sodium‐Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors, All‐Cause Mortality, and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Bayesian Meta‐Analysis and Meta‐Regression
Ayodele Odutayo, Bruno R. da Costa, Tiago V. Pereira, Vinay Garg, Samir Iskander, Fatimah Roble, Rahim Lalji, Cesar A. Hincapié, Aquila Akingbade, Myanca Rodrigues, Arnav Agarwal, Bishoy Lawendy, Pakeezah Saadat, Jacob A. Udell, Francesco Cosentino, Peter
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Finerenone: A Potential Treatment for Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Luis D’Marco, María Jesús Puchades, Lorena Gandía, Claudia Forquet, Elena Giménez-Civera, Nayara Panizo, Javier Reque, Isabel Juan-García, Valmore Bermúdez, José Luis Gorriz
touchREVIEWS in Endocrinology.2021; 17(2): 84. CrossRef - Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Mechanisms of Action: A Review
Jorge I. Fonseca-Correa, Ricardo Correa-Rotter
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Relative and Absolute Risks of Adverse Events with Real-World Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in CKD

- Clinical Study
- Comparative Renal Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Individual Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- Jae Hyun Bae, Eun-Gee Park, Sunhee Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Seokyung Hahn, Nam Hoon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(2):388-400. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.912
- 6,365 View
- 361 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To compare the renal effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on individual outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods
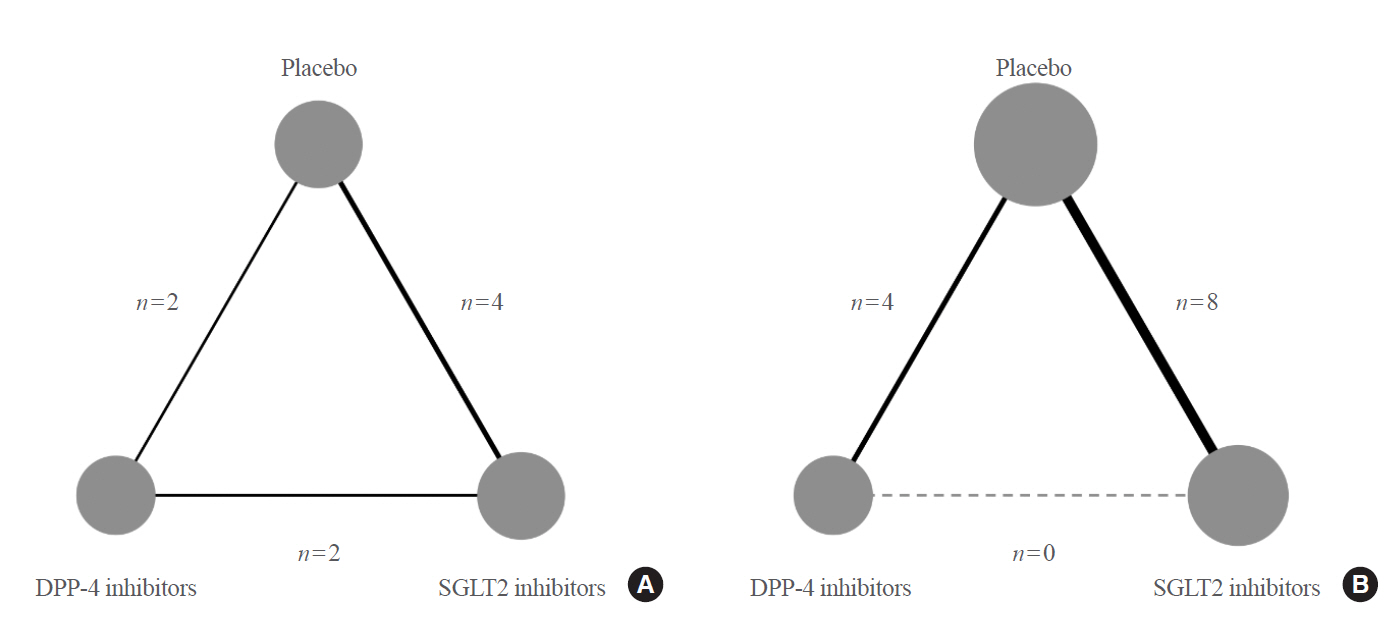
We searched electronic databases (MEDLINE, Embase, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials) from inception to June 2019 to identity eligible randomized controlled trials of DPP-4 inhibitors or SGLT2 inhibitors that reported at least one kidney outcome in patients with type 2 diabetes. Outcomes of interest were microalbuminuria, macroalbuminuria, worsening nephropathy, and end-stage kidney disease (ESKD). We performed an arm-based network meta-analysis using Bayesian methods and calculated absolute risks and rank probabilities of each treatment for the outcomes.
Results
Seventeen studies with 87,263 patients were included. SGLT2 inhibitors significantly lowered the risks of individual kidney outcomes, including microalbuminuria (odds ratio [OR], 0.64; 95% credible interval [CrI], 0.41 to 0.93), macroalbuminuria (OR, 0.48; 95% CrI, 0.24 to 0.72), worsening nephropathy (OR, 0.65; 95% CrI, 0.44 to 0.91), and ESKD (OR, 0.65; 95% CrI, 0.46 to 0.98) as compared with placebo. However, DPP-4 inhibitors did not lower the risks. SGLT2 inhibitors were considerably associated with higher absolute risk reductions in all kidney outcomes than DPP-4 inhibitors, although the benefits were statistically insignificant. The rank probabilities showed that SGLT2 inhibitors were better treatments for lowering the risk of albuminuria and ESKD than placebo or DPP-4 inhibitors.
Conclusion
SGLT2 inhibitors were superior to DPP-4 inhibitors in reducing the risk of albuminuria and ESKD in patients with type 2 diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Therapie des Typ-2-Diabetes
Rüdiger Landgraf, Jens Aberle, Andreas L. Birkenfeld, Baptist Gallwitz, Monika Kellerer, Harald H. Klein, Dirk Müller-Wieland, Michael A. Nauck, Tobias Wiesner, Erhard Siegel
Die Diabetologie.2024; 20(2): 212. CrossRef - Ipragliflozin and sitagliptin differentially affect lipid and apolipoprotein profiles in type 2 diabetes: the SUCRE study
Mototsugu Nagao, Jun Sasaki, Kyoko Tanimura-Inagaki, Ichiro Sakuma, Hitoshi Sugihara, Shinichi Oikawa
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Effect of Glucose-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Stroke Prevention: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Ji Soo Kim, Gyeongsil Lee, Kyung-Il Park, Seung-Won Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 312. CrossRef - Therapy of Type 2 Diabetes
Rüdiger Landgraf, Jens Aberle, Andreas L. Birkenfeld, Baptist Gallwitz, Monika Kellerer, Harald H. Klein, Dirk Müller-Wieland, Michael A. Nauck, Tobias Wiesner, Erhard Siegel
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Therapie des Typ-2-Diabetes
Rüdiger Landgraf, Jens Aberle, Andreas L. Birkenfeld, Baptist Gallwitz, Monika Kellerer, Harald H. Klein, Dirk Müller-Wieland, Michael A. Nauck, Tobias Wiesner, Erhard Siegel
Die Diabetologie.2023; 19(5): 658. CrossRef - Renoprotective Effect of Thai Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with SGLT-2 Inhibitors versus DPP-4 Inhibitors: A Real-World Observational Study
Apichaya Chanawong, Suriyon Uitrakul, Supatcha Incomenoy, Natnicha Poonchuay, Rizky Abdulah
Advances in Pharmacological and Pharmaceutical Sciences.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Different nursing interventions on sleep quality among critically ill patients: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Daijin Huang, Yumei Li, Jing Ye, Chang Liu, Dongyan Shen, Yunhui Lv
Medicine.2023; 102(52): e36298. CrossRef - New trends in the approach to the treatment of type 2 diabetes - observations and benefits in the outpatient practice of a diabetologist
Pavel Weber, Hana Meluzínová, Dana Weberová
Klinická farmakologie a farmacie.2022; 35(4): 118. CrossRef - Comparative efficacy of novel antidiabetic drugs on cardiovascular and renal outcomes in patients with diabetic kidney disease: A systematic review and network meta‐analysis
Hongwei Cao, Tao Liu, Li Wang, Qiuhe Ji
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(8): 1448. CrossRef - Therapie des Typ-2-Diabetes
Rüdiger Landgraf, Jens Aberle, Andreas L. Birkenfeld, Baptist Gallwitz, Monika Kellerer, Harald H. Klein, Dirk Müller-Wieland, Michael A. Nauck, Tobias Wiesner, Erhard Siegel
Die Diabetologie.2022; 18(5): 623. CrossRef - Significant reduction in chronic kidney disease progression with sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitors compared to dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors in adults with type 2 diabetes in a UK clinical setting: An observational outcomes study based on inte
Iskandar Idris, Ruiqi Zhang, Jil B. Mamza, Mike Ford, Tamsin Morris, Amitava Banerjee, Kamlesh Khunti
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(11): 2138. CrossRef - Therapy of Type 2 Diabetes
Rüdiger Landgraf, Jens Aberle, Andreas L. Birkenfeld, Baptist Gallwitz, Monika Kellerer, Harald Klein, Dirk Müller-Wieland, Michael A. Nauck, Tobias Wiesner, Erhard Siegel
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2022; 130(S 01): S80. CrossRef - Molecular Mechanistic Pathways Targeted by Natural Compounds in the Prevention and Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Kaixuan Zhou, Xue Zi, Jiayu Song, Qiulu Zhao, Jia Liu, Huiwei Bao, Lijing Li
Molecules.2022; 27(19): 6221. CrossRef - Lower risk of gout in sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors versus dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitors in type-2 diabetes
Jiandong Zhou, Xuejin Liu, Oscar Hou-In Chou, Lifang Li, Sharen Lee, Wing Tak Wong, Qingpeng Zhang, Carlin Chang, Tong Liu, Gary Tse, Fengshi Jing, Bernard Man Yung Cheung
Rheumatology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - New Era for Renal-Protective Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes: Better Renal Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Taking Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors versus Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors
Chan-Hee Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(2): 339. CrossRef - Efficacy / safety balance of DPP-4 inhibitors versus SGLT2 inhibitors in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes
André J. Scheen
Diabetes & Metabolism.2021; 47(6): 101275. CrossRef
- Therapie des Typ-2-Diabetes

- A Case of Propylthiouracil - Induced Hepatitis; Showed Chronic Active Hepatitis by Pathologic Finding.
- Yoon Sok Chung, Hyeon Man Kim, Deok Bae Park, Kwang Hwa Park, Chull Sim, Min Kyung Song, Heui Chul Chung
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;10(3):289-294. Published online November 6, 2019
- 913 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 15-year old girl developed propylthiouracil-induced hepatitis documented as chronic active hepatitis by liver biopsy, who had suffered from Graves' disease for 1 year and treated with propylthiouracil. The result of lymphocyte transformation test was negative which was performed after 3 months of onset of hepatitis.

- Diabetes
- Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors on Renal Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Jae Hyun Bae, Sunhee Kim, Eun-Gee Park, Sin Gon Kim, Seokyung Hahn, Nam Hoon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(1):80-92. Published online March 21, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.1.80
- 7,632 View
- 267 Download
- 36 Web of Science
- 38 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background To investigate the effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors on renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods MEDLINE, Embase, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were searched to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of DPP-4 inhibitors from inception to September 2017. We selected eligible RCTs comparing DPP-4 inhibitors with placebo or other antidiabetic agents and reporting at least one renal outcome. A meta-analysis was conducted to calculate standardized mean differences, weighted mean differences (WMDs), relative risks (RRs), and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for each renal outcome.
Results We included 23 RCTs with 19 publications involving 41,359 patients. Overall changes in urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio were comparable between DPP-4 inhibitors and controls (
P =0.150). However, DPP-4 inhibitors were associated with significantly lower risk of incident microalbuminuria (RR, 0.89; 95% CI, 0.80 to 0.98;P =0.022) and macroalbuminuria (RR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.61 to 0.97;P =0.027), as well as higher rates of regression of albuminuria (RR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.10 to 1.35;P <0.001) compared with controls. Although DPP-4 inhibitors were associated with small but significantly lower estimated glomerular filtration rate (WMD, −1.11 mL/min/1.73 m2; 95% CI, −1.78 to −0.44;P =0.001), there was no difference in the risk of end-stage renal disease between two groups (RR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.76 to 1.14;P =0.475).Conclusion DPP-4 inhibitors had beneficial renal effects mainly by reducing the risk of development or progression of albuminuria compared with placebo or other antidiabetic agents.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ipragliflozin and sitagliptin differentially affect lipid and apolipoprotein profiles in type 2 diabetes: the SUCRE study
Mototsugu Nagao, Jun Sasaki, Kyoko Tanimura-Inagaki, Ichiro Sakuma, Hitoshi Sugihara, Shinichi Oikawa
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of glucose‐lowering agents on cardiovascular and renal outcomes in subjects with type 2 diabetes: An updated meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials with external adjudication of events
Edoardo Mannucci, Marco Gallo, Andrea Giaccari, Riccardo Candido, Basilio Pintaudi, Giovanni Targher, Matteo Monami
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(2): 444. CrossRef - Sitagliptin Mitigates Diabetic Nephropathy in a Rat Model of Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes: Possible Role of PTP1B/JAK-STAT Pathway
Sarah M. AL-Qabbaa, Samaher I. Qaboli, Tahani K. Alshammari, Maha A. Alamin, Haya M. Alrajeh, Lama A. Almuthnabi, Rana R. Alotaibi, Asma S. Alonazi, Anfal F. Bin Dayel, Nawal M. Alrasheed, Nouf M. Alrasheed
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(7): 6532. CrossRef - Take an individualized and multipronged approach when managing older adults with type 2 diabetes
Sheridan M. Hoy
Drugs & Therapy Perspectives.2023; 39(5): 171. CrossRef - Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes With Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors Combination Therapy: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Cardiovascular Outcome Trials
Awadhesh Kumar Singh, Akriti Singh, Ritu Singh
Endocrine Practice.2023; 29(7): 509. CrossRef - Sodium‐glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors versus dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors on new‐onset overall cancer in Type 2 diabetes mellitus: A population‐based study
Cheuk To Chung, Ishan Lakhani, Oscar Hou In Chou, Teddy Tai Loy Lee, Edward Christopher Dee, Kenrick Ng, Wing Tak Wong, Tong Liu, Sharen Lee, Qingpeng Zhang, Bernard Man Yung Cheung, Gary Tse, Jiandong Zhou
Cancer Medicine.2023; 12(11): 12299. CrossRef - Comparative Effects of Glucose-Lowering Medications on Kidney Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes
Deborah J. Wexler, Ian H. de Boer, Alokananda Ghosh, Naji Younes, Ionut Bebu, Silvio E. Inzucchi, Janet B. McGill, Sunder Mudaliar, David Schade, Michael W. Steffes, William V. Tamborlane, Meng H. Tan, Faramarz Ismail-Beigi, Jill P. Crandall, Melissa Dian
JAMA Internal Medicine.2023; 183(7): 705. CrossRef - SAFETY PROFILE OF DIPEPTIDYL PEPTIDASE-4 INHIBITORS
M. Ganeva
Trakia Journal of Sciences.2023; 21(1): 54. CrossRef - Chronic Kidney Disease and SGLT2 Inhibitors: A Review of the Evolving Treatment Landscape
Christian W. Mende
Advances in Therapy.2022; 39(1): 148. CrossRef - Management of Hyperglycemia in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
Gunjan Y. Gandhi, Arshag D. Mooradian
Drugs & Aging.2022; 39(1): 39. CrossRef - Pharmacoeconomic evaluation of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic literature review
Zhen Ruan, Huimin Zou, Qing Lei, Carolina Oi Lam Ung, Honghao Shi, Hao Hu
Expert Review of Pharmacoeconomics & Outcomes Research.2022; 22(4): 555. CrossRef - Effect of Anagliptin versus Sitagliptin on Renal Function: Subanalyzes from the REASON Trial
Hiroki Teragawa, Takeshi Morimoto, Yuichi Fujii, Tomohiro Ueda, Mio Sakuma, Michio Shimabukuro, Osamu Arasaki, Koichi Node, Takashi Nomiyama, Shinichiro Ueda
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 685. CrossRef - Glomerular filtration rate as a kidney outcome of diabetic kidney disease: a focus on new antidiabetic drugs
Hyo Jin Kim, Sang Soo Kim, Sang Heon Song
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2022; 37(3): 502. CrossRef - The Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors on Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Wan-Chia Hsu, Chun-Sheng Lin, Jung-Fu Chen, Chih-Min Chang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2653. CrossRef - Treatment of diabetes mellitus has borne much fruit in the prevention of cardiovascular disease
Hiroaki Yagyu, Hitoshi Shimano
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(9): 1472. CrossRef - Finerenone, a Novel and Safer Approach toward Management of Diabetic Kidney Disease with Heart Failure
Ayesha Abdul Qadir Memon, Sarmad Iqbal
Global Journal of Medical, Pharmaceutical, and Biomedical Update.2022; 17: 12. CrossRef - The effects of dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors on kidney outcomes
Daniel V. O'Hara, Thomas R. Parkhill, Sunil V. Badve, Min Jun, Meg J. Jardine, Vlado Perkovic
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(3): 763. CrossRef - Urinary DPP4 correlates with renal dysfunction, and DPP4 inhibition protects against the reduction in megalin and podocin expression in experimental CKD
Acaris Benetti, Flavia Letícia Martins, Letícia Barros Sene, Maria Heloisa M. Shimizu, Antonio C. Seguro, Weverton M. Luchi, Adriana C. C. Girardi
American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology.2021; 320(3): F285. CrossRef - Incretin-based drugs and the kidney in type 2 diabetes: choosing between DPP-4 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists
Johannes F.E. Mann, Marcel H.A. Muskiet
Kidney International.2021; 99(2): 314. CrossRef - Renoprotective Effects of DPP-4 Inhibitors
Daiji Kawanami, Yuichi Takashi, Hiroyuki Takahashi, Ryoko Motonaga, Makito Tanabe
Antioxidants.2021; 10(2): 246. CrossRef - Danegaptide Prevents TGFβ1-Induced Damage in Human Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells of the Kidney
Paul E. Squires, Gareth W. Price, Ulrik Mouritzen, Joe A. Potter, Bethany M. Williams, Claire E. Hills
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(6): 2809. CrossRef - Comparative Renal Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Individual Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Jae Hyun Bae, Eun-Gee Park, Sunhee Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Seokyung Hahn, Nam Hoon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(2): 388. CrossRef - Consensus Recommendations by the Asian Pacific Society of Cardiology: Optimising Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Jack Wei Chieh Tan, David Sim, Junya Ako, Wael Almahmeed, Mark E Cooper, Jamshed J Dalal, Chaicharn Deerochanawong, David Wei Chun Huang, Sofian Johar, Upendra Kaul, Sin Gon Kim, Natalie Koh, Alice Pik-Shan Kong, Rungroj Krittayaphong, Bernard Kwok, Bien
European Cardiology Review.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes and kidney disease: emphasis on treatment with SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists
Francesco Prattichizzo, Paola de Candia, Antonio Ceriello
Metabolism.2021; 120: 154799. CrossRef - SGLT2 Inhibitors and Other Novel Therapeutics in the Management of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Robert C. Stanton
Seminars in Nephrology.2021; 41(2): 85. CrossRef - Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Nina Vodošek Hojs, Sebastjan Bevc, Robert Ekart, Nejc Piko, Tadej Petreski, Radovan Hojs
Pharmaceuticals.2021; 14(6): 561. CrossRef - Podocyte Glucocorticoid Receptors Are Essential for Glomerular Endothelial Cell Homeostasis in Diabetes Mellitus
Swayam Prakash Srivastava, Han Zhou, Ocean Setia, Alan Dardik, Carlos Fernandez‐Hernando, Julie Goodwin
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Coronavirus Disease (COVID)-19 and Diabetic Kidney Disease
Swayam Prakash Srivastava, Rohit Srivastava, Subhash Chand, Julie E. Goodwin
Pharmaceuticals.2021; 14(8): 751. CrossRef - Effects of DPP4 inhibitors on renal outcomes in diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
SaikatK Dalui, Raja Chakraverty, Nafisha Yasmin, Smita Pattanaik, Kaushik Pandit, Suparna Chatterjee
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 25(4): 283. CrossRef - Comparison of Adverse Kidney Outcomes With Empagliflozin and Linagliptin Use in Patients With Type 2 Diabetic Patients in a Real-World Setting
Yueh-Ting Lee, Chien-Ning Hsu, Chung-Ming Fu, Shih-Wei Wang, Chiang-Chi Huang, Lung-Chih Li
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of DPP-4 Inhibitors in Type-2 Diabetes Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
Mishal Yousef Alqurashi, Khalid Faisal Alharthi, Abdulaziz Abdulrahman Alshehri, Yazeed Khalid Alharbi, Mohammad Abdulmunem Sanousi, Anas Abdullah Almazyed, Khulud Saeed Alghamdi, Sarah Musaad Alrashidi, Waad Abdullah Qaeed, Amjad Aedh Alasmari
Pharmacophore.2021; 12(3): 91. CrossRef - Type 2 diabetes mellitus management in patients with chronic kidney disease: an update
Zoi Kleinaki, Stella Kapnisi, Sofia-Andriani Theodorelou-Charitou, Ilias P. Nikas, Stavroula A. Paschou
Hormones.2020; 19(4): 467. CrossRef - Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes: A Review of Cardiovascular and Renal Outcome Trials
David M. Williams, Asif Nawaz, Marc Evans
Diabetes Therapy.2020; 11(2): 369. CrossRef - Favorable pleiotropic effects of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: head-to-head comparisons with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes patients
Shih-Chieh Shao, Kai-Cheng Chang, Swu-Jane Lin, Rong-Nan Chien, Ming-Jui Hung, Yuk-Ying Chan, Yea-Huei Kao Yang, Edward Chia-Cheng Lai
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel therapeutic agents for the treatment of diabetic kidney disease
Rachel E. Hartman, P.S.S. Rao, Mariann D. Churchwell, Susan J. Lewis
Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs.2020; 29(11): 1277. CrossRef - Renal protection with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists
Martina Vitale, Jonida Haxhi, Tiziana Cirrito, Giuseppe Pugliese
Current Opinion in Pharmacology.2020; 54: 91. CrossRef - Loss of Mitochondrial Control Impacts Renal Health
Swayam Prakash Srivastava, Keizo Kanasaki, Julie E. Goodwin
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Renal Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Jae Hyun Bae, Eun-Gee Park, Sunhee Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Seokyung Hahn, Nam Hoon Kim
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Ipragliflozin and sitagliptin differentially affect lipid and apolipoprotein profiles in type 2 diabetes: the SUCRE study

- Comparison between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin in Renal Function Decline among Patients with Diabetes
- Eugene Han, Gyuri Kim, Ji-Yeon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Beom Seok Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(2):274-280. Published online June 23, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.2.274
- 5,248 View
- 175 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Although the beneficial effects of statin treatment in dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis have been well studied, there is limited information regarding the renal effects of statins in diabetic nephropathy. We aimed to investigate whether, and which, statins affected renal function in Asian patients with diabetes.
Methods We enrolled 484 patients with diabetes who received statin treatment for more than 12 months. We included patients treated with moderate-intensity dose statin treatment (atorvastatin 10 to 20 mg/day or rosuvastatin 5 to 10 mg/day). The primary outcome was a change in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) during the 12-month statin treatment, and rapid renal decline was defined as a >3% reduction in eGFR in a 1-year period.
Results In both statin treatment groups, patients showed improved serum lipid levels and significantly reduced eGFRs (from 80.3 to 78.8 mL/min/1.73 m2 for atorvastatin [
P =0.012], from 79.1 to 76.1 mL/min/1.73 m2 for rosuvastatin [P =0.001]). A more rapid eGFR decline was observed in the rosuvastatin group than in the atorvastatin group (48.7% vs. 38.6%,P =0.029). Multiple logistic regression analyses demonstrated more rapid renal function loss in the rosuvastatin group than in the atorvastatin group after adjustment for other confounding factors (odds ratio, 1.60; 95% confidence interval, 1.06 to 2.42).Conclusion These results suggest that a moderate-intensity dose of atorvastatin has fewer detrimental effects on renal function than that of rosuvastatin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with telmisartan, rosuvastatin, and ezetimibe in patients with dyslipidemia and hypertension: A randomized, double‐blind, multicenter, therapeutic confirmatory, phase III clinical trial
Chan Joo Lee, Woong Chol Kang, Sang Hyun Ihm, Il Suk Sohn, Jong Shin Woo, Jin Won Kim, Soon Jun Hong, Jung Hyun Choi, Jung‐Won Suh, Jae‐Bin Seo, Joon‐Hyung Doh, Jung‐Woo Son, Jae‐Hyeong Park, Ju‐Hee Lee, Young Joon Hong, Jung Ho Heo, Jinho Shin, Seok‐Min
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2024; 26(3): 262. CrossRef - Anti-hyperglycemic, anti-hyperlipidemic, and anti-inflammatory effect of the drug Guggulutiktaka ghrita on high-fat diet-induced obese rats
Samreen M. Sheik, Pugazhandhi Bakthavatchalam, Revathi P. Shenoy, Basavaraj S. Hadapad, Deepak Nayak M, Monalisa Biswas, Varashree Bolar Suryakanth
Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine.2022; 13(3): 100583. CrossRef - The challenge of reducing residual cardiovascular risk in patients with chronic kidney disease
Stefan Mark Nidorf
European Heart Journal.2022; 43(46): 4845. CrossRef - Diabetic Kidney Disease in Older People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Improving Prevention and Treatment Options
Ahmed H. Abdelhafiz
Drugs & Aging.2020; 37(8): 567. CrossRef - Intracellular Mechanism of Rosuvastatin-Induced Decrease in Mature hERG Protein Expression on Membrane
Pan-Feng Feng, Bo Zhang, Lei Zhao, Qing Fang, Yan Liu, Jun-Nan Wang, Xue-Qi Xu, Hui Xue, Yang Li, Cai-Chuan Yan, Xin Zhao, Bao-Xin Li
Molecular Pharmaceutics.2019; 16(4): 1477. CrossRef - The problem of safety of lipid-lowering therapy
M V. Zykov
Kardiologiia.2019; 59(5S): 13. CrossRef - Regional evidence and international recommendations to guide lipid management in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes with special reference to renal dysfunction
Titus WL Lau, Kevin E.K. Tan, Jason C.J. Choo, Tsun‐Gun Ng, Subramaniam Tavintharan, Juliana C.N. Chan
Journal of Diabetes.2018; 10(3): 200. CrossRef - Lipids: a personal view of the past decade
Niki Katsiki, Dimitri P Mikhailidis
Hormones.2018; 17(4): 461. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with telmisartan, rosuvastatin, and ezetimibe in patients with dyslipidemia and hypertension: A randomized, double‐blind, multicenter, therapeutic confirmatory, phase III clinical trial

- Clinical Study
- Eligibility for Statin Treatment in Korean Subjects with Reduced Renal Function: An Observational Study
- Byung Sub Moon, Jongho Kim, Ji Hyun Kim, Young Youl Hyun, Se Eun Park, Hyung-Geun Oh, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Kyu-Beck Lee, Hyang Kim, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(3):402-409. Published online August 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.3.402
- 3,934 View
- 33 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between statin eligibility and the degree of renal dysfunction using the Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III and the American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines in Korean adults.
Methods Renal function was assessed in 18,746 participants of the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study from January 2011 to December 2012. Subjects were divided into three groups according to estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR): stage 1, eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m2; stage 2, eGFR 60 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m2; and stages 3 to 5, eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2. Statin eligibility in these groups was determined using the ATP III and ACC/AHA guidelines, and the risk for 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) was calculated using the Framingham Risk Score (FRS) and Pooled Cohort Equation (PCE).
Results There were 3,546 (18.9%) and 4,048 (21.5%) statin-eligible subjects according to ATP III and ACC/AHA guidelines, respectively. The proportion of statin-eligible subjects increased as renal function deteriorated. Statin eligibility by the ACC/AHA guidelines showed better agreement with the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) recommendations compared to the ATP III guidelines in subjects with stage 3 to 5 chronic kidney disease (CKD) (κ value, 0.689 vs. 0.531). When the 10-year ASCVD risk was assessed using the FRS and PCE, the mean risk calculated by both equations significantly increased as renal function declined.
Conclusions The proportion of statin-eligible subjects significantly increased according to worsening renal function in this Korean cohort. ACC/AHA guideline showed better agreement for statin eligibility with that recommended by KDIGO guideline compared to ATP III in subjects with CKD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases risk and renal outcome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Honghong Ren, Lijun Zhao, Yutong Zou, Yiting Wang, Junlin Zhang, Yucheng Wu, Rui Zhang, Tingli Wang, Jiali Wang, Yitao Zhu, Ruikun Guo, Huan Xu, Lin Li, Mark E. Cooper, Fang Liu
Renal Failure.2021; 43(1): 477. CrossRef - Long-term effects of various types of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors on changes in glomerular filtration rate in Korea
Seo Yeon Baik, Hyunah Kim, So Jung Yang, Tong Min Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Hun-Sung Kim
Frontiers of Medicine.2019; 13(6): 713. CrossRef - Analysis and comparison of the cost-effectiveness of statins according to the baseline low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level in Korea
Y. J. Jeong, H. Kim, S. J. Baik, T. M. Kim, S. J. Yang, S.-H. Lee, J.-H. Cho, H. Lee, H. W. Yim, I. Y. Choi, K.-H. Yoon, H.-S. Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2017; 42(3): 292. CrossRef - Comparison between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin in Renal Function Decline among Patients with Diabetes
Eugene Han, Gyuri Kim, Ji-Yeon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Beom Seok Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(2): 274. CrossRef
- Association between atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases risk and renal outcome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Current Challenges in Diabetic Nephropathy: Early Diagnosis and Ways to Improve Outcomes
- Sang Soo Kim, Jong Ho Kim, In Joo Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(2):245-253. Published online May 27, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.2.245
- 6,157 View
- 94 Download
- 51 Web of Science
- 45 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Diabetes is often associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and is the primary cause of kidney failure in half of patients who receive dialysis therapy. Given the increasing prevalence of diabetes and its high morbidity and mortality, diabetic nephropathy is a serious drawback in individual patients and a tremendous socioeconomic burden on society. Despite growing concern for the management of diabetic nephropathy, the prevalence of CKD with diabetes is the same today as it was 20 years ago. The current strategy to manage diabetic nephropathy, including the control of hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and blood pressure and the wide-spread use of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors, is well established to be beneficial in the early stages of diabetic nephropathy. However, the effects are uncertain in patients with relatively progressed CKD. Therefore, early diagnosis or risk verification is extremely important in order to reduce the individual and socioeconomic burdens associated with diabetic nephropathy by providing appropriate management to prevent the development and progression of this condition. This review focuses on recent research and guidelines regarding risk assessment, advances in medical treatment, and challenges of and future treatments for diabetic nephropathy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Polymorphisms in the Risk of Development and Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy
Magdalena Król-Kulikowska, Nikita Abramenko, Milan Jakubek, Mirosław Banasik, Marta Kepinska
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(4): 995. CrossRef - Diagnostic utility of renal shear wave elastography and renal Doppler findings in diabetic nephropathy: a case–control study
Ahmed Abdelrahman Baz, Eman Muhammad Abdeen, Mona Yousry Helmy, Abo El-Magd Al-Bohy
Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Gestione perioperatoria del paziente diabetico adulto
M. Raucoules-Aimé, T. Thierry Nessan Ouattara
EMC - Anestesia-Rianimazione.2023; 28(1): 1. CrossRef - Pyruvate Kinase M2: A New Biomarker for the Early Detection of Diabetes-Induced Nephropathy
Yeon Su Park, Joo Hee Han, Jae Hyeon Park, Ji Soo Choi, Seung Hyeon Kim, Hyung Sik Kim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(3): 2683. CrossRef - Tratamiento perioperatorio del paciente diabético adulto
M. Raucoules-Aimé, T. Thierry Nessan Ouattara
EMC - Anestesia-Reanimación.2023; 49(1): 1. CrossRef - Renal Protection of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist, Finerenone, in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Dong-Lim Kim, Seung-Eun Lee, Nan Hee Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 43. CrossRef - The role of tubulointerstitial markers in differential diagnosis and prognosis in patients with type 2 diabetes and biopsy proven diabetic kidney disease
Xijian Wang, Liang Ren, Ying Huang, Zhengang Feng, Guangdi Zhang, Houyong Dai
Clinica Chimica Acta.2023; 547: 117448. CrossRef - Network pharmacology and molecular docking technology-based predictive study of the active ingredients and potential targets of rhubarb for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy
Shaojie Fu, Yena Zhou, Cong Hu, Zhonggao Xu, Jie Hou
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Acrolein plays a culprit role in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy in vitro and in vivo
Zhen-Jie Tong, Chin-Wei Kuo, Po-Cheng Yen, Chih-Ching Lin, Ming-Tsun Tsai, Shing-Hwa Lu, Yi-Ping Chang, Wen-Sheng Liu, Han-Hsing Tsou, Hsiao-Wei Cheng, Hsiang-Tsui Wang
European Journal of Endocrinology.2022; 187(4): 579. CrossRef - Probiotics ameliorates glycemic control of patients with diabetic nephropathy: A randomized clinical study
Hongyang Jiang, Yan Zhang, Dongyan Xu, Qing Wang
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent (BOLD) MRI in Glomerular Disease
Daniel R. Nemirovsky, Puneet Gupta, Sophia Hu, Raymond Wong, Avnesh S. Thakor
Transplantology.2021; 2(2): 109. CrossRef - Amelioration of STZ-induced nephropathy in diabetic rats by saffron hydro alcoholic extract
Jamal Amri, Mona Alaee, Seyed Amirhossein Latifi, Abbas Alimoradian, Mehdi Salehi
Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation.2021; 42(4): 411. CrossRef - Exosomes: Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets of Diabetic Vascular Complications
Anqi Chen, Hailing Wang, Ying Su, Chunlin Zhang, Yanmei Qiu, Yifan Zhou, Yan Wan, Bo Hu, Yanan Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors benefit to kidney and cardiovascular outcomes for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease 3b-4: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Haiyan Cao, Youxia Liu, Zhixia Tian, Yuhang Lian, Junya Jia, Ming Liu, Dong Li
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 180: 109033. CrossRef - Proteinuria as a significant predictive factor for the progression of carotid artery atherosclerosis in non-albuminuric type 2 diabetes
Young-eun Kim, Minyoung Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 181: 109082. CrossRef - The Role of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles in Diabetes and Its Chronic Complications
Fu-Xing-Zi Li, Xiao Lin, Feng Xu, Su-Kang Shan, Bei Guo, Li-Min Lei, Ming-Hui Zheng, Yi Wang, Qiu-Shuang Xu, Ling-Qing Yuan
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Preparation of Ergosterol-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers for Enhancing Oral Bioavailability and Antidiabetic Nephropathy Effects
Zhonghua Dong, Sajid Iqbal, Zhongxi Zhao
AAPS PharmSciTech.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Carbon dots as fluorescent nanoprobe for the determination of N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase activity
Jimei Ma, Heng Zhang, Fangfang Peng, Xiaoqing Yang, Zi-Long Li, Linhao Sun, Hong Jiang
Analytica Chimica Acta.2020; 1101: 129. CrossRef - Coffee Consumption is Associated with a Decreased Risk of Incident Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Cohort Studies
Thatsaphan Srithongkul, Patompong Ungprasert
European Journal of Internal Medicine.2020; 77: 111. CrossRef - Understanding molecular upsets in diabetic nephropathy to identify novel targets and treatment opportunities
Nidhi Raval, Akshant Kumawat, Dnyaneshwar Kalyane, Kiran Kalia, Rakesh K. Tekade
Drug Discovery Today.2020; 25(5): 862. CrossRef - A meta-analysis of serum Hcy in diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy
Xiaoling Zhou, Aijie Shi, Xiao Zhou
Pteridines.2020; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Link between ACE I/D gene polymorphism and dyslipidemia in diabetic nephropathy: A case-control study from Hyderabad, India
UmmeNajiya Mahwish, KamakshiChaithri Ponnaluri, Babi Heera, SatishReddy Alavala, KRudrama Devi, SreeBhushan Raju, GSuman Latha, Parveen Jahan
Indian Journal of Nephrology.2020; 30(2): 77. CrossRef - Assessment of urinary NGAL for differential diagnosis and progression of diabetic kidney disease
Suyan Duan, Jiajia Chen, Lin Wu, Guangyan Nie, Lianqin Sun, Chengning Zhang, Zhimin Huang, Changying Xing, Bo Zhang, Yanggang Yuan
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2020; 34(10): 107665. CrossRef - Urinary proteins detected using modern proteomics intervene in early type 2 diabetic kidney disease – a pilot study
Alina Golea-Secara, Cristian Munteanu, Mirela Sarbu, Octavian M Cretu, Silvia Velciov, Adrian Vlad, Flaviu Bob, Florica Gadalean, Cristina Gluhovschi, Oana Milas, Anca Simulescu, Maria Mogos-Stefan, Mihaela Patruica, Ligia Petrica, Alina D Zamfir
Biomarkers in Medicine.2020; 14(16): 1521. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of Shenkang injection as adjuvant therapy in patients with diabetic nephropathy
Yanping Wang, Mingzhu Li, Chenyun Li, Sheng Xu, Jiangfeng Wu, Gaochuan Zhang, Yuanyuan Cai
Medicine.2020; 99(52): e23821. CrossRef - A Nucleoside/Nucleobase-Rich Extract from Cordyceps Sinensis Inhibits the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Protects against Renal Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy
Zhonghua Dong, Yueyue Sun, Guangwei Wei, Siying Li, Zhongxi Zhao
Molecules.2019; 24(22): 4119. CrossRef - Lack of Association between Past Helicobacter pylori Infection and Diabetes: A Two-Cohort Study
Jeung Hui Pyo, Hyuk Lee, Sung Chul Choi, Soo Jin Cho, Yoon-Ho Choi, Yang Won Min, Byung-Hoon Min, Jun Haeng Lee, Heejin Yoo, Kyunga Kim, Jae J. Kim
Nutrients.2019; 11(8): 1874. CrossRef - Serum Homocysteine, cystatin C as Biomarkers for Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy
Weihai Xu, Suhua Tang, Meijuan Xiang, Jianyun Peng
Pteridines.2019; 30(1): 183. CrossRef - Serum leptin in diabetic nephropathy male patients from Gaza Strip
Maged M. Yassin, Ayman M. AbuMustafa, Mohamed M. Yassin
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(2): 1245. CrossRef - Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Renal Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Jae Hyun Bae, Eun-Gee Park, Sunhee Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Seokyung Hahn, Nam Hoon Kim
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between nonalbumin proteinuria and renal tubular damage of N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase and its clinical relevance in patients with type 2 diabetes without albuminuria
Eugene Han, Mi-Kyung Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Hye Soon Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2019; 33(3): 255. CrossRef - Supplementation of Abelmoschus manihot Ameliorates Diabetic Nephropathy and Hepatic Steatosis by Activating Autophagy in Mice
Hwajin Kim, Theodomir Dusabimana, So Kim, Jihyun Je, Kyuho Jeong, Min Kang, Kye Cho, Hye Kim, Sang Park
Nutrients.2018; 10(11): 1703. CrossRef - Perioperative management of adult diabetic patients. Preoperative period
Gaëlle Cheisson, Sophie Jacqueminet, Emmanuel Cosson, Carole Ichai, Anne-Marie Leguerrier, Bogdan Nicolescu-Catargi, Alexandre Ouattara, Igor Tauveron, Paul Valensi, Dan Benhamou
Anaesthesia Critical Care & Pain Medicine.2018; 37: S9. CrossRef - Practical management of diabetes patients before, during and after surgery: A joint French diabetology and anaesthesiology position statement
E. Cosson, B. Catargi, G. Cheisson, S. Jacqueminet, C. Ichai, A.-M. Leguerrier, A. Ouattara, I. Tauveron, E. Bismuth, D. Benhamou, P. Valensi
Diabetes & Metabolism.2018; 44(3): 200. CrossRef - MicroRNA‐326‐3p ameliorates high glucose and ox‐LDL‐IC‐ induced fibrotic injury in renal mesangial cells by targeting FcγRIII
Yiting Wang, Rui Zhang, Junlin Zhang, Fang Liu
Nephrology.2018; 23(11): 1031. CrossRef - Urinary Extracellular Vesicle
Wei-Cheng Xu, Ge Qian, Ai-Qun Liu, Yong-Qiang Li, He-Qun Zou
Chinese Medical Journal.2018; 131(11): 1357. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Comparison between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin in Renal Function Decline among Patients with Diabetes
Eugene Han, Gyuri Kim, Ji-Yeon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Beom Seok Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(2): 274. CrossRef - WITHDRAWN: Salvianolate attenuates renal fibrosis in rat models of diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress mechanisms
Chongxiang Xiong, Jianrao Lu, Xinhua Wang, Monica V. Masucci
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Diffusion tensor imaging of the renal cortex in diabetic patients: correlation with urinary and serum biomarkers
Ahmed Abdel Khalek Abdel Razek, Mohammad Alsayed Abd Alhamid Al-Adlany, Alhadidy Mohammed Alhadidy, Mohammed Ali Atwa, Naglaa Elsayed Abass Abdou
Abdominal Radiology.2017; 42(5): 1493. CrossRef - Texte 2 : période préopératoire
Gaëlle Cheisson, Sophie Jacqueminet, Emmanuel Cosson, Carole Ichai, Anne-Marie Leguerrier, Bogdan Nicolescu-Catargi, Alexandre Ouattara, Igor Tauveron, Paul Valensi, Dan Benhamou
Anesthésie & Réanimation.2017; 3(3): 218. CrossRef - Global Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes of Reduced GFR
Bernadette Thomas, Kunihiro Matsushita, Kalkidan Hassen Abate, Ziyad Al-Aly, Johan Ärnlöv, Kei Asayama, Robert Atkins, Alaa Badawi, Shoshana H. Ballew, Amitava Banerjee, Lars Barregård, Elizabeth Barrett-Connor, Sanjay Basu, Aminu K. Bello, Isabela Bensen
Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.2017; 28(7): 2167. CrossRef - Salvia miltiorrhiza Lipophilic Fraction Attenuates Oxidative Stress in Diabetic Nephropathy through Activation of Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2
Lin An, Mei Zhou, Faiz M. M. T. Marikar, Xue-Wen Hu, Qiu-Yun Miao, Ping Li, Jun Chen
The American Journal of Chinese Medicine.2017; 45(07): 1441. CrossRef - Addition of nonalbumin proteinuria to albuminuria improves prediction of type 2 diabetic nephropathy progression
Jong Ho Kim, Seo Young Oh, Eun Heui Kim, Min Jin Lee, Yun Kyung Jeon, Bo Hyun Kim, Jin Mi Kim, Yong Ki Kim, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Reversal of Early Diabetic Nephropathy by Islet Transplantation under the Kidney Capsule in a Rat Model
Yunqiang He, Ziqiang Xu, Mingshi Zhou, Minmin Wu, Xuehai Chen, Silu Wang, Kaiyan Qiu, Yong Cai, Hongxing Fu, Bicheng Chen, Mengtao Zhou
Journal of Diabetes Research.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef
- The Role of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Polymorphisms in the Risk of Development and Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy

- Age Is the Strongest Effector for the Relationship between Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate and Coronary Artery Calcification in Apparently Healthy Korean Adults
- Hyun Beom Chae, Shin Yeoung Lee, Nam Hee Kim, Ki Joong Han, Tae Hoon Lee, Choel Min Jang, Kyung Mo Yoo, Hae Jung Park, Min Kyung Lee, Won Seon Jeon, Se Eun Park, Heui-Soo Moon, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(3):312-319. Published online September 25, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.3.312
- 3,735 View
- 33 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is considered one of the most common risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Coronary artery calcification (CAC) is a potential mechanism that explains the association between renal function and cardiovascular mortality. We aimed to evaluate the association between renal function and CAC in apparently healthy Korean subjects.
Methods A total of 23,617 participants in a health-screening program at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital were included in the study. Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was assessed using the Cockcroft-Gault equation. Coronary artery calcium score (CACS) was measured via multidetector computed tomography. Subjects were divided into three groups according to the CKD Staging system with eGFR grade: stage 1, eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m2; stage 2, eGFR 60 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m2; and stage 3, eGFR 30 to 59 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Results The mean age of the participants was 41.4 years and the mean eGFR was 103.6±21.7 mL/min/1.73 m2. Hypertension and diabetes were noted in 43.7% and 5.5% of the participants, respectively. eGFR showed a weakly negative but significant association with CACS in bivariate correlation analysis (
r =-0.076,P <0.01). Mean CACS significantly increased from CKD stage 1 to 3. The proportion of subjects who had CAC significantly increased from CKD stage 1 to 3. Although the odds ratio for CAC significantly increased from stage 1 to 3 after adjustment for confounding factors, this significance was reversed when age was included in the model.Conclusion In early CKD, renal function negatively correlated with the degree of CAC in Korean subjects. Age was the strongest effector for this association.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Coronary artery calcium and risk of chronic kidney disease in young and middle-aged adults
Yejin Kim, Jeonggyu Kang, Yoosoo Chang, Young Youl Hyun, Kyu-Beck Lee, Hocheol Shin, Sarah H Wild, Christopher D Byrne, Seungho Ryu
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation.2023; 38(6): 1439. CrossRef - New Model for Predicting the Presence of Coronary Artery Calcification
Samel Park, Min Hong, HwaMin Lee, Nam-jun Cho, Eun-Young Lee, Won-Young Lee, Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyo-Wook Gil
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(3): 457. CrossRef - Long-term effects of various types of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors on changes in glomerular filtration rate in Korea
Seo Yeon Baik, Hyunah Kim, So Jung Yang, Tong Min Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Hun-Sung Kim
Frontiers of Medicine.2019; 13(6): 713. CrossRef - Chronic kidney disease and coronary artery calcification in the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA‐Brasil)
Cheng Suh‐Chiou, Rosa M. Moysés, Marcio S. Bittencourt, Isabela M. Bensenor, Paulo A. Lotufo
Clinical Cardiology.2017; 40(12): 1309. CrossRef - Eligibility for Statin Treatment in Korean Subjects with Reduced Renal Function: An Observational Study
Byung Sub Moon, Jongho Kim, Ji Hyun Kim, Young Youl Hyun, Se Eun Park, Hyung-Geun Oh, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Kyu-Beck Lee, Hyang Kim, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(3): 402. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- Coronary artery calcium and risk of chronic kidney disease in young and middle-aged adults

- A Case of Primary Hyperparathyroidism Associated with Gall-bladder Stone and Chronic Cholecystitis.
- Jin Hyung Lee, Pil Moon Jung, Chong Whan Kim, Myeong Sang Shin, Hong Jun Park, Soo Min Nam, Mi Young Lee, Jang Hyun Koh, Mee Yoen Cho, Jang Yel Shin, Choon Hee Chung, Young Goo Shin
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007;22(6):470-474. Published online December 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.6.470
- 2,100 View
- 27 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Primary hyperparathyroidism is caused mainly by a parathyroid adenoma or hyperplasia, and is characterized by hypercalcemia and hypophosphatemia induced by an increased level of parathyroid hormone (PTH). Patients with primary hyperparathyroidism are usually asymptomatic and the disease is most often detected incidentally. However, patients can present with symptoms of renal stones, peptic ulcer disease, muscle weakness, depression, constipation, and pancreatitis. In addition, it has been reported that choletithiasis can be combined with primary hyperparathyroidism. We report a case of a 49-year-old man with primary hyperparathyroidism accompanied with chronic cholecystitis caused by a gallbladder (GB) stone. The chief complaint was nausea, poor oral intake, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Abdominal sonography was performed and chronic cholecystitis with a GB stone was diagnosed. The serum calcium level was 18.5 mg/dL and the intact parathyroid hormone level was 1,777 pg/mL. A parathyroid mass was detected by neck-computed tomography, neck ultrasonography and a (99m)Tc-Tetrofosmin parathyroid scan. The parathyroid mass was removed and the mass was confirmed as a parathyroid adenoma. Cholecystectomy was performed and the diagnosis of chronic cholecystitis was confirmed. After the surgical procedure, the symptoms improved and the calcium level was normalized.

- A Case of Thyroid MALT Lymphoma without Autoimmune Thyroiditis.
- Ok Nyu Kong, Sang Hyen Joo, Sun Hye Shin, Min Ah Na, Jun Hyeop An, Yang Ho Kang, Do Youn Park, Seok Man Son, In Ju Kim, Yong Ki Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2005;20(3):268-272. Published online June 1, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2005.20.3.268
- 1,829 View
- 18 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A primary thyroid lymphoma is rare among all types of thyroid malignancy. Usually, a thyroid lymphoma is associated with underlying chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. Recently, we experienced a primary thyroid mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue(MALT) lymphoma, with an incidental micropapillary thyroid carcinoma, but lacking evidence of autoimmune thyroiditis. A female patient visited our hospital for further evaluation of a rapidly enlarging, painless thyroid mass which had been stable for 8 years. Lymphocytic thyroiditis or a lymphoma was suspected from fine needle aspiration performed at another hospital. The thyroid function test and other routine laboratory tests were normal. The histopathological findings after a total thyroidectomy revealed a MALT lymphoma with a micropapillary thyroid carcinoma. There was no evidence of chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. This is, to the best of our knowledge, the first case report of a MALT lymphoma arising from the thyroid gland without evidence of chronic autoimmune thyroiditis in Korea
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

- A Case of Calciphylaxis Mimicking Dermatomyositis.
- Jeung Hun Han, Sin Won Lee, Gui Hwa Jung, Chang Hoon Choi, Soon Hee Lee, Jung Guk Kim, Sung Woo Ha, Jong Myung Lee, Nung Soo Kim, Bo Wan Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2002;17(2):297-301. Published online April 1, 2002
- 1,010 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Calciphylaxis is a rare, but fatal, condition that is characterized by a rapidly progressive ischemic necrosis of the skin, underlying tissue and other organs, as well as rapid vascular calcification. It results in death due to sepsis, heart or respiratory failure. A 67-year old female was admitted to hospital with the chief complaint of constant pain to both lower legs of 1 week duration. She was treated with calcitonin-salmon due to a prior unexplained hypercalcemia of 2 weeks. On the third day post admission. pain and weakness in the lower legs were aggravated, became painful, with violaceous skin lesions developing on the thigh with findings similar to those of rhabdomyolysis. Because she was suspected of having dermatomyositis, she was treated with methylpredrisolone. However, the skin lesions and symptoms were aggravated, and she died of sepsis due to a skin infection. About 160 cases of calciphylaxis have been reported, with most of these cases being associated with secondary hyperparathyroidism due to end-stage renal disease, but cases of calciphylaxis without renal failure are very rare. We now report a case of calciphylaxis without renal failure, mimicking dermatomyositis, and present a brief review of the pathophysiology and treatments of calciphylaxis inform the relevant literature.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



