Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Association among Current Smoking, Alcohol Consumption, Regular Exercise, and Lower Extremity Amputation in Patients with Diabetic Foot: Nationwide Population-Based Study
- Yoon Jae Lee, Kyung-Do Han, Jun Hyeok Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(5):770-780. Published online October 12, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1519

- 3,288 View
- 202 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The present study investigates whether modifiable behavioral factors of current cigarette smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, and regular exercise are associated with risk of lower extremity amputation (LEA) in diabetic patients.
Methods
A total of 2,644,440 diabetic patients (aged ≥20 years) was analyzed using the database of the Korean National Health Insurance Service. Cox proportional hazard regression was used to assess adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) for the behavioral factors with risk of LEA under adjustment for potential confounders.
Results
The risk of LEA was significantly increased by current cigarette smoking and heavy alcohol consumption (HR, 1.436; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.367 to 1.508 and HR, 1.082; 95% CI, 1.011 to 1.158) but significantly decreased with regular exercise (HR, 0.745; 95% CI, 0.706 to 0.786) after adjusting for age, sex, smoking, alcohol consumption, exercise, low income, hypertension, dyslipidemia, body mass index, using insulin or oral antidiabetic drugs, and diabetic duration. A synergistically increased risk of LEA was observed with larger number of risky behaviors.
Conclusion
Modification of behaviors of current smoking, heavy alcohol intake, and exercise prevents LEA and can improve physical, emotional, and social quality of life in diabetic patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adjuvant effect of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers: A case series
Rita de Cassia Ferreira, Rebeca Boltes Cecatto, Silvana Torres Perez, Raquel Agnelli Mesquita‐Ferrari, Sandra Kalil Bussadori, Cinthya Cosme Duran, Anna Carolina Tempestini Horliana, Kristianne Porta Santos Fernandes
Journal of Biophotonics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with diabetic foot ulcers and lower limb amputations in type 1 and type 2 diabetes supported by real‐world data from the German/Austrian DPV registry
Alexander J. Eckert, Stefan Zimny, Marcus Altmeier, Ana Dugic, Anton Gillessen, Latife Bozkurt, Gabriele Götz, Wolfram Karges, Frank J. Wosch, Stephan Kress, Reinhard W. Holl
Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigating Diabetic Foot Pathophysiology and Amputation Prevention Strategies through Behavioral Modification
Jun Hyeok Kim
Journal of Wound Management and Research.2023; 19(3): 167. CrossRef
- Adjuvant effect of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers: A case series

- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
- Development of a Spine X-Ray-Based Fracture Prediction Model Using a Deep Learning Algorithm
- Sung Hye Kong, Jae-Won Lee, Byeong Uk Bae, Jin Kyeong Sung, Kyu Hwan Jung, Jung Hee Kim, Chan Soo Shin
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(4):674-683. Published online August 5, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1461

- 3,896 View
- 212 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Since image-based fracture prediction models using deep learning are lacking, we aimed to develop an X-ray-based fracture prediction model using deep learning with longitudinal data.
Methods
This study included 1,595 participants aged 50 to 75 years with at least two lumbosacral radiographs without baseline fractures from 2010 to 2015 at Seoul National University Hospital. Positive and negative cases were defined according to whether vertebral fractures developed during follow-up. The cases were divided into training (n=1,416) and test (n=179) sets. A convolutional neural network (CNN)-based prediction algorithm, DeepSurv, was trained with images and baseline clinical information (age, sex, body mass index, glucocorticoid use, and secondary osteoporosis). The concordance index (C-index) was used to compare performance between DeepSurv and the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) and Cox proportional hazard (CoxPH) models.
Results
Of the total participants, 1,188 (74.4%) were women, and the mean age was 60.5 years. During a mean follow-up period of 40.7 months, vertebral fractures occurred in 7.5% (120/1,595) of participants. In the test set, when DeepSurv learned with images and clinical features, it showed higher performance than FRAX and CoxPH in terms of C-index values (DeepSurv, 0.612; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.571 to 0.653; FRAX, 0.547; CoxPH, 0.594; 95% CI, 0.552 to 0.555). Notably, the DeepSurv method without clinical features had a higher C-index (0.614; 95% CI, 0.572 to 0.656) than that of FRAX in women.
Conclusion
DeepSurv, a CNN-based prediction algorithm using baseline image and clinical information, outperformed the FRAX and CoxPH models in predicting osteoporotic fracture from spine radiographs in a longitudinal cohort. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Automated detection of vertebral fractures from X-ray images: A novel machine learning model and survey of the field
Li-Wei Cheng, Hsin-Hung Chou, Yu-Xuan Cai, Kuo-Yuan Huang, Chin-Chiang Hsieh, Po-Lun Chu, I-Szu Cheng, Sun-Yuan Hsieh
Neurocomputing.2024; 566: 126946. CrossRef - Application of radiomics model based on lumbar computed tomography in diagnosis of elderly osteoporosis
Baisen Chen, Jiaming Cui, Chaochen Li, Pengjun Xu, Guanhua Xu, Jiawei Jiang, Pengfei Xue, Yuyu Sun, Zhiming Cui
Journal of Orthopaedic Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Spinal Injury: A Narrative Review of Algorithms in Diagnosis and Prognosis
Satoshi Maki, Takeo Furuya, Masahiro Inoue, Yasuhiro Shiga, Kazuhide Inage, Yawara Eguchi, Sumihisa Orita, Seiji Ohtori
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(3): 705. CrossRef - A CT-based Deep Learning Model for Predicting Subsequent Fracture Risk in Patients with Hip Fracture
Yisak Kim, Young-Gon Kim, Jung-Wee Park, Byung Woo Kim, Youmin Shin, Sung Hye Kong, Jung Hee Kim, Young-Kyun Lee, Sang Wan Kim, Chan Soo Shin
Radiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Novel QCT-Based Deep Transfer Learning Approach for Predicting Stiffness Tensor of Trabecular Bone Cubes
Pengwei Xiao, Tinghe Zhang, Yufei Huang, Xiaodu Wang
IRBM.2024; 45(2): 100831. CrossRef - Deep learning in the radiologic diagnosis of osteoporosis: a literature review
Yu He, Jiaxi Lin, Shiqi Zhu, Jinzhou Zhu, Zhonghua Xu
Journal of International Medical Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Convolutional Neural Network Model to Predict a Pathologic Fracture in the Proximal Femur Using Abdomen and Pelvis CT Images of Patients With Advanced Cancer
Min Wook Joo, Taehoon Ko, Min Seob Kim, Yong-Suk Lee, Seung Han Shin, Yang-Guk Chung, Hong Kwon Lee
Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research.2023; 481(11): 2247. CrossRef - Automated Opportunistic Trabecular Volumetric Bone Mineral Density Extraction Outperforms Manual Measurements for the Prediction of Vertebral Fractures in Routine CT
Sophia S. Goller, Jon F. Rischewski, Thomas Liebig, Jens Ricke, Sebastian Siller, Vanessa F. Schmidt, Robert Stahl, Julian Kulozik, Thomas Baum, Jan S. Kirschke, Sarah C. Foreman, Alexandra S. Gersing
Diagnostics.2023; 13(12): 2119. CrossRef - Machine learning‐based prediction of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women with clinical examined features: A quantitative clinical study
Kainat A. Ullah, Faisal Rehman, Muhammad Anwar, Muhammad Faheem, Naveed Riaz
Health Science Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Skeletal Fracture Detection with Deep Learning: A Comprehensive Review
Zhihao Su, Afzan Adam, Mohammad Faidzul Nasrudin, Masri Ayob, Gauthamen Punganan
Diagnostics.2023; 13(20): 3245. CrossRef - Deep learning system for automated detection of posterior ligamentous complex injury in patients with thoracolumbar fracture on MRI
Sang Won Jo, Eun Kyung Khil, Kyoung Yeon Lee, Il Choi, Yu Sung Yoon, Jang Gyu Cha, Jae Hyeok Lee, Hyunggi Kim, Sun Yeop Lee
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Vertebra Segmentation Based Vertebral Compression Fracture Determination from Reconstructed Spine X-Ray Images
Srinivasa Rao Gadu, Chandra Sekhar Potala
International Journal of Electrical and Electronics Research.2023; 11(4): 1225. CrossRef - Computer Vision in Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture Risk Prediction: A Systematic Review
Anthony K. Allam, Adrish Anand, Alex R. Flores, Alexander E. Ropper
Neurospine.2023; 20(4): 1112. CrossRef - A Meaningful Journey to Predict Fractures with Deep Learning
Jeonghoon Ha
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 617. CrossRef - New Horizons: Artificial Intelligence Tools for Managing Osteoporosis
Hans Peter Dimai
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Automated detection of vertebral fractures from X-ray images: A novel machine learning model and survey of the field

- Clinical Study
- Development of a Non-Invasive Liver Fibrosis Score Based on Transient Elastography for Risk Stratification in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Chi-Ho Lee, Wai-Kay Seto, Kelly Ieong, David T.W. Lui, Carol H.Y. Fong, Helen Y. Wan, Wing-Sun Chow, Yu-Cho Woo, Man-Fung Yuen, Karen S.L. Lam
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):134-145. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.887

- 4,504 View
- 132 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
In non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), transient elastography (TE) is an accurate non-invasive method to identify patients at risk of advanced fibrosis (AF). We developed a diabetes-specific, non-invasive liver fibrosis score based on TE to facilitate AF risk stratification, especially for use in diabetes clinics where TE is not readily available.
Methods
Seven hundred sixty-six adults with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD were recruited and randomly divided into a training set (n=534) for the development of diabetes fibrosis score (DFS), and a testing set (n=232) for internal validation. DFS identified patients with AF on TE, defined as liver stiffness (LS) ≥9.6 kPa, based on a clinical model comprising significant determinants of LS with the lowest Akaike information criteria. The performance of DFS was compared with conventional liver fibrosis scores (NFS, FIB-4, and APRI), using area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values (NPV).
Results
DFS comprised body mass index, platelet, aspartate aminotransferase, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and albuminuria, five routine measurements in standard diabetes care. Derived low and high DFS cut-offs were 0.1 and 0.3, with 90% sensitivity and 90% specificity, respectively. Both cut-offs provided better NPVs of >90% than conventional fibrosis scores. The AUROC of DFS for AF on TE was also higher (P<0.01) than the conventional fibrosis scores, being 0.85 and 0.81 in the training and testing sets, respectively.
Conclusion
Compared to conventional fibrosis scores, DFS, with a high NPV, more accurately identified diabetes patients at-risk of AF, who need further evaluation by hepatologists. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Implementation of a liver health check in people with type 2 diabetes
Kushala W M Abeysekera, Luca Valenti, Zobair Younossi, John F Dillon, Alina M Allen, Mazen Noureddin, Mary E Rinella, Frank Tacke, Sven Francque, Pere Ginès, Maja Thiele, Philip N Newsome, Indra Neil Guha, Mohammed Eslam, Jörn M Schattenberg, Saleh A Alqa
The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2024; 9(1): 83. CrossRef - Sequential algorithm to stratify liver fibrosis risk in overweight/obese metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease
Chi-Ho Lee, David Tak-Wai Lui, Raymond Hang-Wun Li, Michele Mae-Ann Yuen, Carol Ho-Yi Fong, Ambrose Pak-Wah Leung, Justin Chiu-Man Chu, Loey Lung-Yi Mak, Tai-Hing Lam, Jean Woo, Yu-Cho Woo, Aimin Xu, Hung-Fat Tse, Kathryn Choon-Beng Tan, Bernard Man-Yung
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-Invasive Measurement of Hepatic Fibrosis by Transient Elastography: A Narrative Review
Luca Rinaldi, Chiara Giorgione, Andrea Mormone, Francesca Esposito, Michele Rinaldi, Massimiliano Berretta, Raffaele Marfella, Ciro Romano
Viruses.2023; 15(8): 1730. CrossRef - Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease — How relevant is this to primary care physicians and diabetologists?
Chi-Ho Lee
Primary Care Diabetes.2022; 16(2): 245. CrossRef - Non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: An update
Chi‐H Lee, David TW Lui, Karen SL Lam
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(6): 930. CrossRef - Ultrasound-Based Hepatic Elastography in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Focus on Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Georgiana-Diana Cazac, Cristina-Mihaela Lăcătușu, Cătălina Mihai, Elena-Daniela Grigorescu, Alina Onofriescu, Bogdan-Mircea Mihai
Biomedicines.2022; 10(10): 2375. CrossRef
- Implementation of a liver health check in people with type 2 diabetes

- Clinical Study
- Achievement of LDL-C Targets Defined by ESC/EAS (2011) Guidelines in Risk-Stratified Korean Patients with Dyslipidemia Receiving Lipid-Modifying Treatments
- Ye Seul Yang, Seo Young Lee, Jung-Sun Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Kang Wook Lee, Sang-Chol Lee, Jung Rae Cho, Seung-Jin Oh, Ji-Hyun Kim, Sung Hee Choi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):367-376. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.367

- 8,000 View
- 144 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study assessed the proportion of risk-stratified Korean patients with dyslipidemia achieving their low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) targets as defined by the European Society of Cardiology/European Atherosclerosis Society (ESC/EAS) (2011) guidelines while receiving lipid-modifying treatments (LMTs).
Methods
In this multicenter, cross-sectional, observational study, we evaluated data from Korean patients aged ≥19 years who were receiving LMTs for ≥3 months and had an LDL-C value within the previous 12 months on the same LMT. Data were collected for demographics, cardiovascular (CV) risk factors, medical history, and healthcare consumption. Patients were risk-stratified according to the ESC Systematic COronary Risk Evaluation (SCORE) chart and LDL-C target achievement rate was assessed.
Results
Guideline-based risk-stratification of the 1,034 patients showed the majority (72.2%) to be in the very high-risk category. Investigators’ assessment of risk was underestimated in 71.6% compared to ESC/EAS guidelines. Overall LDL-C target achievement rate was 44.3%; target achievement was the highest (66.0%) in moderate-risk patients and the lowest (39.0%) in very high-risk patients. Overall 97.1% patients were receiving statin therapy, mostly as a single-agent (89.2%). High-intensity statins and the highest permissible dose of high-intensity statins had been prescribed to only 9.1% and 7.3% patients in the very high-risk group, respectively. Physician satisfaction with patients’ LDL-C levels was the primary reason for non-intensification of statin therapy.
Conclusion
Achievement of target LDL-C level is suboptimal in Korean patients with dyslipidemia, especially in those at very high-risk of CV events. Current practices in LMTs need to be improved based on precise CV risk evaluation posed by dyslipidemia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Bempedoic Acid for Lipid Management in the Indian Population: An Expert Opinion
Jagdish Hiremath, J C Mohan, Prakash Hazra, JP S Sawhney, Ashwani Mehta, Sadanand Shetty, Abraham Oomman, Mahesh K Shah, Ganapathi Bantwal, Rajeev Agarwal, Rajiv Karnik, Peeyush Jain, Saumitra Ray, Sambit Das, Vibhuti Jadhao, Sachin Suryawanshi, Hanmant B
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimal implementation of the 2019 ESC/EAS dyslipidaemia guidelines in patients with and without atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease across Europe: a simulation based on the DA VINCI study
Julia Brandts, Sarah Bray, Guillermo Villa, Alberico L. Catapano, Neil R. Poulter, Antonio J. Vallejo-Vaz, Kausik K. Ray
The Lancet Regional Health - Europe.2023; 31: 100665. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - Target Low-Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol and Secondary Prevention for Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Korean Nationwide Cohort Study
Ju Hyeon Kim, Jung-Joon Cha, Subin Lim, Jungseok An, Mi-Na Kim, Soon Jun Hong, Hyung Joon Joo, Jae Hyoung Park, Cheol Woong Yu, Do-Sun Lim, Kyeongmin Byeon, Sang-Wook Kim, Eun-Seok Shin, Kwang Soo Cha, Jei Keon Chae, Youngkeun Ahn, Myung Ho Jeong, Tae Hoo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2650. CrossRef - Current Status of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Achievement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Compared with Recent Guidelines
Soo Jin Yun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Ho Chan Cho, Sung Hee Choi, SungWan Chun, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Soo Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Gwanpyo Koh, Su Kyoung Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Sung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 464. CrossRef - There is urgent need to treat atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk earlier, more intensively, and with greater precision: A review of current practice and recommendations for improved effectiveness
Michael E. Makover, Michael D. Shapiro, Peter P. Toth
American Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2022; 12: 100371. CrossRef - Non-achievement of the Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Goal in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and a Very High Cardiovascular Disease Risk: A Multicenter Study in Vietnam
Huan Thanh Nguyen, Khang Pham Trong Ha, An Huu Nguyen, Thu Thanh Nguyen, Hang My Lam
Annals of Geriatric Medicine and Research.2021; 25(4): 278. CrossRef
- Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement

- Clinical Study
- Low Predictive Value of FRAX Adjusted by Trabecular Bone Score for Osteoporotic Fractures in Korean Women: A Community-Based Cohort Study
- Hana Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Min Joo Kim, A Ram Hong, HyungJin Choi, EuJeong Ku, Ji Hyun Lee, Chan Soo Shin, Nam H. Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):359-366. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.359
- 5,944 View
- 132 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
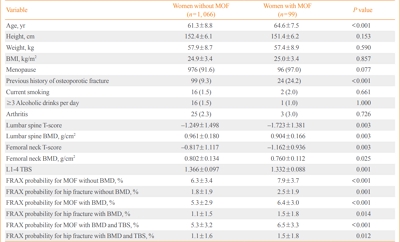
The value of the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) and the trabecular bone score (TBS) for assessing osteoporotic fracture risk has not been fully elucidated in Koreans. We conducted this study to clarify the predictive value of FRAX adjusted by TBS for osteoporotic fractures in Korean women.
Methods
After screening 7,192 eligible subjects from the Ansung cohort, 1,165 women aged 45 to 76 years with available bone mineral density (BMD) and TBS data were enrolled in this study. We assessed their clinical risk factors for osteoporotic fractures and evaluated the predictive value of FRAX with or without BMD and TBS.
Results
During the mean follow-up period of 7.5 years, 99 (8.5%) women suffered major osteoporotic fractures (MOFs) and 28 (2.4%) experienced hip fractures. FRAX without BMD, BMD-adjusted FRAX, and TBS-adjusted FRAX were significantly associated with the risk of MOFs (hazard ratio [HR] per percent increase, 1.08; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.03 to 1.14; HR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.03 to 1.15; and HR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.02 to 1.13, respectively). However, BMD-adjusted FRAX and TBS-adjusted FRAX did not predict MOFs better than FRAX without BMD based on the Harrell’s C statistic. FRAX probabilities showed limited value for predicting hip fractures. The cut-off values of FRAX without BMD, FRAX with BMD, and FRAX with BMD adjusted by TBS for predicting MOFs were 7.2%, 5.0%, and 6.7%, respectively.
Conclusion
FRAX with BMD and TBS adjustment did not show better predictive value for osteoporotic fractures in this study than FRAX without adjustment. Moreover, the cut-off values of FRAX probabilities for treatment might be lower in Korean women than in other countries. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Update on the utility of trabecular bone score (TBS) in clinical practice for the management of osteoporosis: a systematic review by the Egyptian Academy of Bone and Muscle Health
Yasser El Miedany, Walaa Elwakil, Mohammed Hassan Abu-Zaid, Safaa Mahran
Egyptian Rheumatology and Rehabilitation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of predictive value of FRAX, trabecular bone score, and bone mineral density for vertebral fractures in systemic sclerosis: A cross-sectional study
Kyung-Ann Lee, Hyun-Joo Kim, Hyun-Sook Kim
Medicine.2023; 102(2): e32580. CrossRef - Screening for the primary prevention of fragility fractures among adults aged 40 years and older in primary care: systematic reviews of the effects and acceptability of screening and treatment, and the accuracy of risk prediction tools
Michelle Gates, Jennifer Pillay, Megan Nuspl, Aireen Wingert, Ben Vandermeer, Lisa Hartling
Systematic Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Chronic airway disease as a major risk factor for fractures in osteopenic women: Nationwide cohort study
Sung Hye Kong, Ae Jeong Jo, Chan Mi Park, Kyun Ik Park, Ji Eun Yun, Jung Hee Kim
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Update on the clinical use of trabecular bone score (TBS) in the management of osteoporosis: results of an expert group meeting organized by the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Disease
Enisa Shevroja, Jean-Yves Reginster, Olivier Lamy, Nasser Al-Daghri, Manju Chandran, Anne-Laurence Demoux-Baiada, Lynn Kohlmeier, Marie-Paule Lecart, Daniel Messina, Bruno Muzzi Camargos, Juraj Payer, Sansin Tuzun, Nicola Veronese, Cyrus Cooper, Eugene V.
Osteoporosis International.2023; 34(9): 1501. CrossRef - Comparison of HU histogram analysis and BMD for proximal femoral fragility fracture assessment: a retrospective single-center case–control study
Sun-Young Park, Hong Il Ha, Injae Lee, Hyun Kyung Lim
European Radiology.2022; 32(3): 1448. CrossRef - Association of Trabecular Bone Score-Adjusted Fracture Risk Assessment Tool with Coronary Artery Calcification in Women
Tzyy-Ling Chuang, Yuh-Feng Wang, Malcolm Koo, Mei-Hua Chuang
Diagnostics.2022; 12(1): 178. CrossRef - Risk of osteoporotic fracture in women using the FRAX tool with and without bone mineral density score in patients followed at a tertiary outpatient clinic ‒ An observational study
Maria Helena Sampaio Favarato, Maria Flora de Almeida, Arnaldo Lichtenstein, Milton de Arruda Martins, Mario Ferreira Junior
Clinics.2022; 77: 100015. CrossRef - Comparison of Trabecular Bone Score–Adjusted Fracture Risk Assessment (TBS-FRAX) and FRAX Tools for Identification of High Fracture Risk among Taiwanese Adults Aged 50 to 90 Years with or without Prediabetes and Diabetes
Tzyy-Ling Chuang, Mei-Hua Chuang, Yuh-Feng Wang, Malcolm Koo
Medicina.2022; 58(12): 1766. CrossRef - Application of the Trabecular Bone Score in Clinical Practice
Sung Hye Kong, Namki Hong, Jin-Woo Kim, Deog Yoon Kim, Jung Hee Kim
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2021; 28(2): 101. CrossRef
- Update on the utility of trabecular bone score (TBS) in clinical practice for the management of osteoporosis: a systematic review by the Egyptian Academy of Bone and Muscle Health

Review Article
- Diabetes
- Recent Updates on Vascular Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Chan-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):260-271. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.260
- 7,621 View
- 282 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
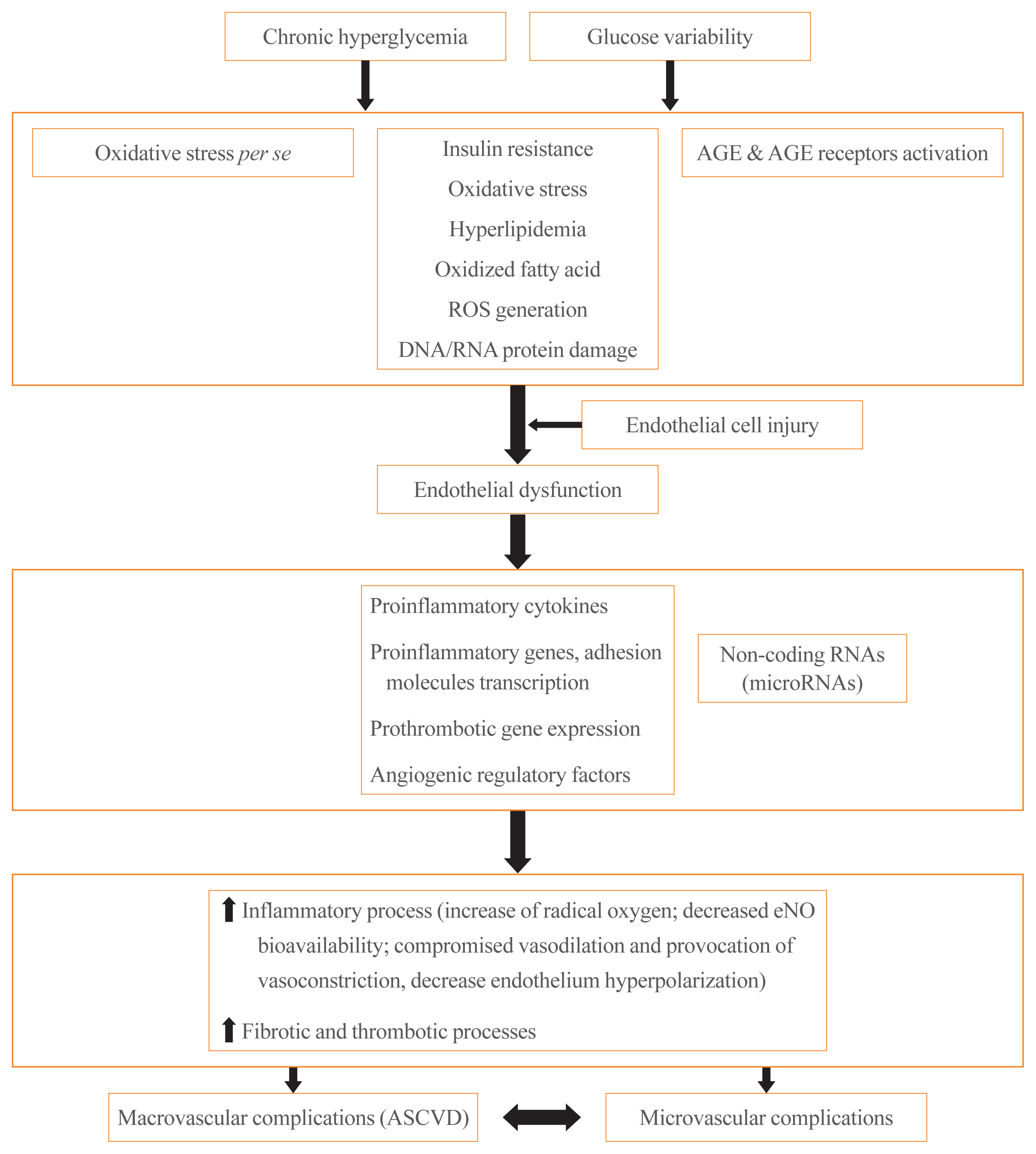
ePub - It is well known that patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are at an increased risk of morbidity and mortality from atherosclerotic cardiovascular (CV) complications. Previously, the concept that diabetes mellitus (DM) is a “coronary artery disease (CAD) risk equivalent” was widely accepted, implying that all DM patients should receive intensive management. However, considerable evidence exist for wide heterogeneity in the risk of CV events among T2DM patients and the concept of a “CAD risk equivalent” has changed. Recent guidelines recommend further CV risk stratification in T2DM patients, with treatment tailored to the risk level. Although imaging modalities for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) have been used to improve risk prediction, there is currently no evidence that imaging-oriented therapy improves clinical outcomes. Therefore, controversy remains whether we should screen for CVD in asymptomatic T2DM. The coexistence of T2DM and heart failure (HF) is common. Based on recent CV outcome trials, sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and glucagon like peptide-1 receptor agonists are recommended who have established ASCVD, indicators of high risk, or HF because of their demonstrated benefits for CVD. These circumstances have led to an increasing emphasis on ASCVD and HF in T2DM patients. In this review, we examine the literature published within the last 5 years on the risk assessment of CVD in asymptomatic T2DM patients. In particular, we review recent guidelines regarding screening for CVD and research focusing on the role of coronary artery calcium, coronary computed tomography angiography, and carotid intima-media thickness in asymptomatic T2DM patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pathways of Coagulopathy and Inflammatory Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Orsolya-Zsuzsa Akácsos-Szász, Sándor Pál, Kinga-Ilona Nyulas, Enikő Nemes-Nagy, Ana-Maria Fárr, Lóránd Dénes, Mónika Szilveszter, Erika-Gyöngyi Bán, Mariana Cornelia Tilinca, Zsuzsánna Simon-Szabó
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(5): 4319. CrossRef - Increased soluble endoglin levels in newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients are associated with endothelial dysfunction
Xiaobing Dou, Xiujing Wang, Xiuhua Yu, Jiaqi Yao, Huiling Shen, Yao Xu, Bojing Zheng, Zhenying Zhang, Qingying Tan, Tianxiao Hu
Endocrine Journal.2023; 70(7): 711. CrossRef - Effects of hypertension on subcortical nucleus morphological alternations in patients with type 2 diabetes
Feng Cui, Zhi-Qiang Ouyang, Yi-Zhen Zeng, Bing-Bing Ling, Li Shi, Yun Zhu, He-Yi Gu, Wan-Lin Jiang, Ting Zhou, Xue-Jin Sun, Dan Han, Yi Lu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Coronary Artery Calcium Score as a Sensitive Indicator of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Long-Term Cohort Study
Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Sang Min Lee, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Rae Cho, Young-Hoon Jeong, Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 568. CrossRef - Exploring Endothelial Colony-Forming Cells to Better Understand the Pathophysiology of Disease: An Updated Review
Qiuwang Zhang, Anthony Cannavicci, Michael J. B. Kutryk, Giuseppe Mandraffino
Stem Cells International.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Recent Insights into the Nutritional Antioxidant Therapy in Prevention and Treatment of Diabetic Vascular Complications: A Comprehensive Review
Narasimha M. Beeraka, Irina K. Tomilova, Galina A. Batrak, Maria V. Zhaburina, Vladimir N. Nikolenko, Mikhail Y. Sinelnikov, Liudmila M. Mikhaleva
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2022; 29(11): 1920. CrossRef - Topical Reappraisal of Molecular Pharmacological Approaches to Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus Angiopathy
Constantin Munteanu, Mariana Rotariu, Marius-Alexandru Turnea, Aurelian Anghelescu, Irina Albadi, Gabriela Dogaru, Sînziana Calina Silișteanu, Elena Valentina Ionescu, Florentina Carmen Firan, Anca Mirela Ionescu, Carmen Oprea, Gelu Onose
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2022; 44(8): 3378. CrossRef - Visfatin is negatively associated with coronary artery lesions in subjects with impaired fasting glucose
Fei Xu, Xiang Ning, Tong Zhao, Qinghua Lu, Huiqiang Chen
Open Medicine.2022; 17(1): 1405. CrossRef - Effects of dulaglutide on endothelial progenitor cells and arterial elasticity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Dandan Xie, Yutong Li, Murong Xu, Xiaotong Zhao, Mingwei Chen
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum netrin and VCAM-1 as biomarker for Egyptian patients with type IΙ diabetes mellitus
Maher M. Fadel, Faten R. Abdel Ghaffar, Shimaa K. Zwain, Hany M. Ibrahim, Eman AE. badr
Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports.2021; 27: 101045. CrossRef - Decoding the chemical composition and pharmacological mechanisms of Jiedu Tongluo Tiaogan Formula using high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with network pharmacology-based investigation
Qi Zhang, Chunli Piao, Wenqi Jin, De Jin, Han Wang, Cheng Tang, Xiaohua Zhao, Naiwen Zhang, Shengnan Gao, Fengmei Lian
Aging.2021; 13(21): 24290. CrossRef
- Pathways of Coagulopathy and Inflammatory Response in SARS-CoV-2 Infection among Type 2 Diabetic Patients


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



