Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Frequency of Exposure to Impaired Fasting Glucose and Risk of Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes
- Seung-Hwan Lee, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Mee Kyoung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1007-1015. Published online October 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1218
- 3,838 View
- 126 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Metabolic abnormalities, such as impaired fasting glucose (IFG), are dynamic phenomena; however, it is unclear whether the timing of IFG exposure and cumulative exposure to IFG are related to cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality risk.
Methods
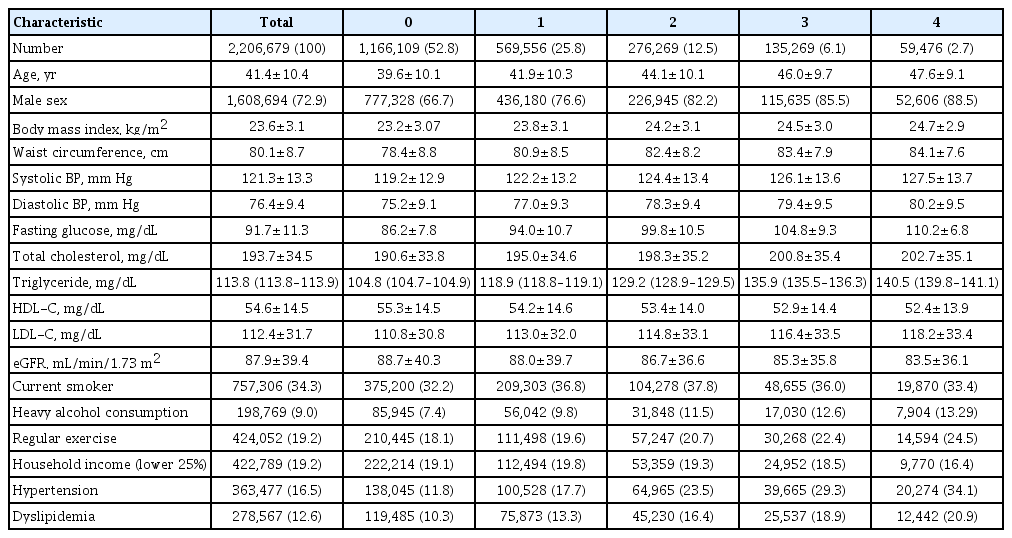
Data were extracted from a nationwide population-based cohort in South Korea for adults (n=2,206,679) who were free of diabetes and had 4 years of consecutive health examination data. Fasting blood glucose levels of 100 to 125 mg/dL were defined as IFG, and the number of IFG diagnoses for each adult in the 4-year period was tabulated as the IFG exposure score (range, 0 to 4). Adults with persistent IFG for the 4-year period received a score of 4.
Results
The median follow-up was 8.2 years. There were 24,820 deaths, 13,502 cases of stroke, and 13,057 cases of myocardial infarction (MI). IFG exposure scores of 1, 2, 3, and 4 were associated with all-cause mortality (multivariable-adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.11; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.08 to 1.15; aHR, 1.16; 95% CI, 1.12 to 1.20; aHR, 1.20; 95% CI, 1.15 to 1.25; aHR, 1.18; 95% CI, 1.11 to 1.25, respectively) compared with an IFG exposure score of 0. Adjusting for hypertension and dyslipidemia attenuated the slightly increased risk of MI or stroke associated with high IFG exposure scores, but significant associations for allcause mortality remained.
Conclusion
The intensity of IFG exposure was associated with an elevated risk of all-cause mortality, independent of cardiovascular risk factors. The association between IFG exposure and CVD risk was largely mediated by the coexistence of dyslipidemia and hypertension. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A nationwide cohort study on diabetes severity and risk of Parkinson disease
Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Seung Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
npj Parkinson's Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes severity is strongly associated with the risk of active tuberculosis in people with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide cohort study with a 6-year follow-up
Ji Young Kang, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
Respiratory Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Construction and Validation of a Model for Predicting Impaired Fasting Glucose Based on More Than 4000 General Population
Cuicui Wang, Xu Zhang, Chenwei Li, Na Li, Xueni Jia, Hui Zhao
International Journal of General Medicine.2023; Volume 16: 1415. CrossRef - Factors Affecting High Body Weight Variability
Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 163. CrossRef - Exposure to perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances and risk of stroke in adults: a meta-analysis
Min Cheol Chang, Seung Min Chung, Sang Gyu Kwak
Reviews on Environmental Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cumulative effect of impaired fasting glucose on the risk of dementia in middle-aged and elderly people: a nationwide cohort study
Jin Yu, Kyu-Na Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A Longitudinal Retrospective Observational Study on Obesity Indicators and the Risk of Impaired Fasting Glucose in Pre- and Postmenopausal Women
Myung Ji Nam, Hyunjin Kim, Yeon Joo Choi, Kyung-Hwan Cho, Seon Mee Kim, Yong-Kyun Roh, Kyungdo Han, Jin-Hyung Jung, Yong-Gyu Park, Joo-Hyun Park, Do-Hoon Kim
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(10): 2795. CrossRef - Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 552. CrossRef - Lipid cutoffs for increased cardiovascular disease risk in non-diabetic young people
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hun-Sung Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hwan Lee
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2022; 29(14): 1866. CrossRef - Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level, Statin Use and Myocardial Infarction Risk in Young Adults
Heekyoung Jeong, Kyungdo Han, Soon Jib Yoo, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(3): 288. CrossRef - Additive interaction of diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease in cancer patient mortality risk
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- A nationwide cohort study on diabetes severity and risk of Parkinson disease

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Differences in Abdominal Body Composition According to Glycemic Status: An Inverse Probability Treatment Weighting Analysis
- Seungbong Han, Young-Jee Jeon, Gyung-Min Park, Tae Young Lee, Soon Eun Park, Gyeongseok Yu, Byung Ju Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):855-864. Published online August 11, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1086
- 3,218 View
- 111 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Several studies have reported that abdominal fat and muscle changes occur in diabetic patients. However, there are few studies about such changes among prediabetic patients. In this study, we evaluated the differences in abdominal fat and muscles based on abdominopelvic computed tomography in prediabetic and diabetic subjects compared to normal subjects.
Methods
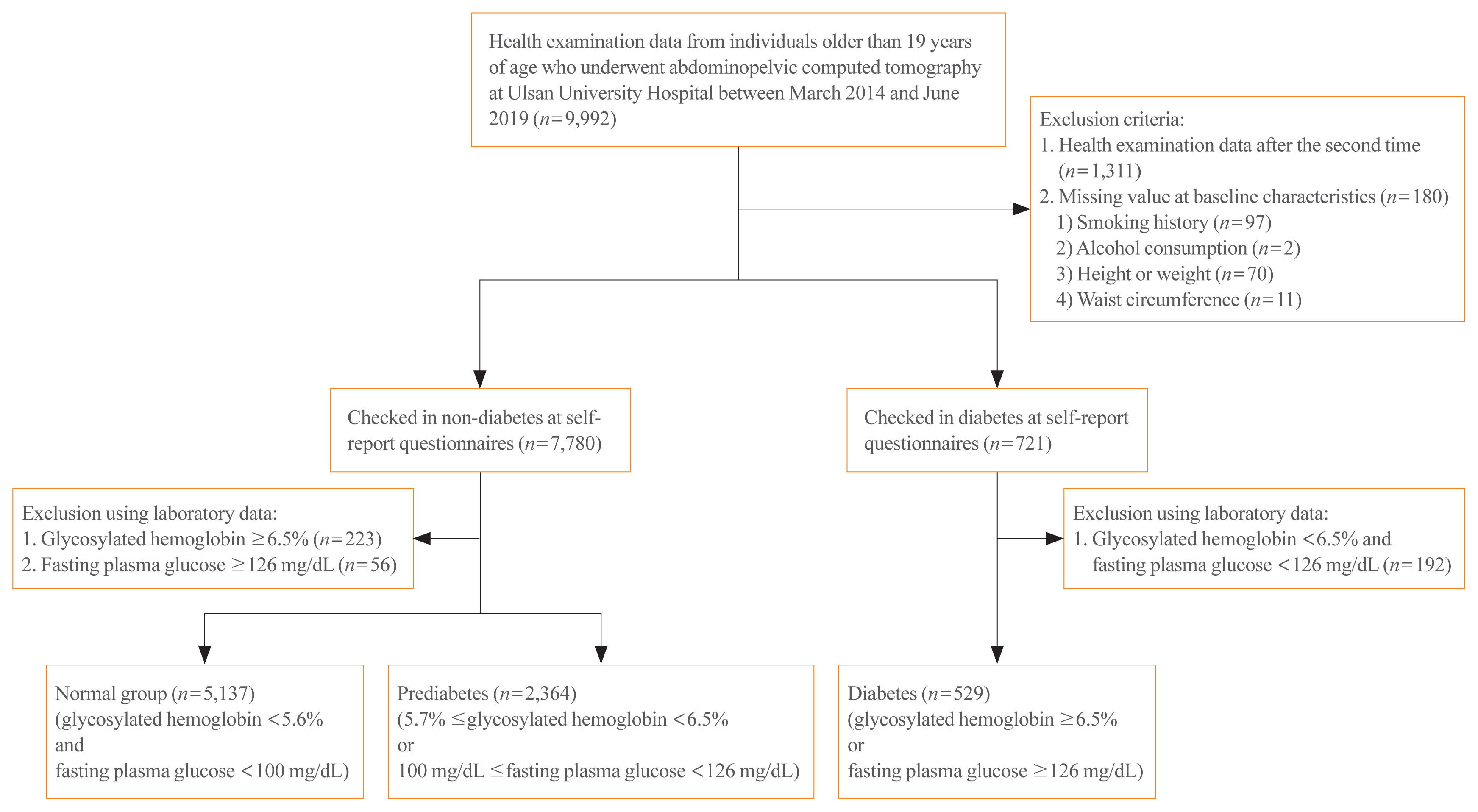
We performed a cross-sectional study using health examination data from March 2014 to June 2019 at Ulsan University Hospital and classified subjects into normal, prediabetic, and diabetic groups. We analyzed the body mass index corrected area of intra-abdominal components among the three groups using inverse probability treatment weighting (IPTW) analysis.
Results
Overall, 8,030 subjects were enrolled; 5,137 (64.0%), 2,364 (29.4%), and 529 (6.6%) subjects were included in the normal, prediabetic, and diabetic groups, respectively. After IPTW adjustment of baseline characteristics, there were significant differences in log visceral adipose tissue index (VATI; 1.22±0.64 cm2/[kg/m2] vs. 1.30±0.63 cm2/[kg/m2] vs. 1.47±0.64 cm2/[kg/m2], P<0.001) and low-attenuation muscle index (LAMI; 1.02±0.36 cm2/[kg/m2] vs. 1.03±0.36 cm2/[kg/m2] vs. 1.09±0.36 cm2/[kg/m2], P<0.001) among the normal, prediabetic, and diabetic groups. Prediabetic subjects had higher log VATI (estimated coefficient= 0.082, P<0.001), and diabetic subjects had higher log VATI (estimated coefficient=0.248, P<0.001) and LAMI (estimated coefficient=0.078, P<0.001) compared to normal subjects.
Conclusion
Considering that VATI and LAMI represented visceral fat and lipid-rich skeletal muscle volumes, respectively, visceral obesity was identified in both prediabetic and diabetic subjects compared to normal subjects in this study. However, intra-muscular fat infiltration was observed in diabetic subjects only. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Testosterone is associated with abdominal body composition derived from computed tomography: a large cross sectional study
Seungbong Han, Young-Jee Jeon, Tae Young Lee, Gyung-Min Park, Sungchan Park, Seong Cheol Kim
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Testosterone is associated with abdominal body composition derived from computed tomography: a large cross sectional study

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Association of Protein Z with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes
- Yun-Ui Bae, Ji Hong You, Nan Hee Cho, Leah Eunjung Kim, Hye Min Shim, Jae-Hyung Park, Ho Chan Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):637-646. Published online June 2, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.962

- 5,175 View
- 147 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a progressive metabolic disease. Early detection of prediabetes is important to reduce the risk of T2DM. Some cytokines are known to be associated with T2DM. Therefore, we aimed to identify cytokines as novel biomarkers of glucose dysmetabolism.
Methods
The first stage of the study included 43 subjects (13 subjects with newly diagnosed T2DM, 13 with prediabetes, and 16 with normoglycemia) for cytokine microarray analysis. Blood samples of the subjects were assessed for 310 cytokines to identify potential indicators of prediabetes. The second stage included 142 subjects (36 subjects with T2DM, 35 with prediabetes, and 71 with normoglycemia) to validate the potential cytokines associated with prediabetes.
Results
We identified 41 cytokines that differed by 1.5-fold or more in at least one out of the three comparisons (normoglycemia vs. prediabetes, normoglycemia vs. T2DM, and prediabetes vs. T2DM) among 310 cytokines. Finally, we selected protein Z (PROZ) and validated this finding to determine its association with prediabetes. Plasma PROZ levels were found to be decreased in patients with prediabetes (1,490.32±367.19 pg/mL) and T2DM (1,583.34±465.43 pg/mL) compared to those in subjects with normoglycemia (1,864.07±450.83 pg/mL) (P<0.001). There were significantly negative correlations between PROZ and fasting plasma glucose (P=0.001) and hemoglobin A1c (P=0.010).
Conclusion
PROZ levels were associated with prediabetes and T2DM. We suggest that PROZ may be a promising biomarker for the early detection of prediabetes. Further large-scale studies are needed to evaluate the relationship and mechanism between PROZ and prediabetes and T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- On the human health benefits of microalgal phytohormones: An explorative in silico analysis
Angelo Del Mondo, Annamaria Vinaccia, Luigi Pistelli, Christophe Brunet, Clementina Sansone
Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal.2023; 21: 1092. CrossRef - Role of F-box WD Repeat Domain Containing 7 in Type 1 Diabetes
Sarah W. Mohammed, Zainab M. Qassam, Ekhlass M. Taha, Nameer M. Salih
Ibn AL-Haitham Journal For Pure and Applied Sciences.2023; 36(3): 167. CrossRef - Identification of Protein Z as a Potential Novel Biomarker for the Diagnosis of Prediabetes
Seung-Hoi Koo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 572. CrossRef - Association of Protein Z with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2021;36:637-46, Yun-Ui Bae et al.)
Ji Hong You, Yun-Ui Bae, Ho Chan Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 1149. CrossRef - Association of Protein Z with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2021;36:637-46, Yun-Ui Bae et al.)
Tiffany Pascreau, Maia Tchikviladze, Emilie Jolly, Sara Zia-Chahabi, Bertrand Lapergue, Marc Vasse
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 1147. CrossRef
- On the human health benefits of microalgal phytohormones: An explorative in silico analysis

- Diabetes
- Comparison of Serum PCSK9 Levels in Subjects with Normoglycemia, Impaired Fasting Glucose, and Impaired Glucose Tolerance
- Eugene Han, Nan Hee Cho, Seong-Su Moon, Hochan Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):480-483. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.480
- 4,952 View
- 115 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - We investigated proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) concentrations in individuals with normoglycemia, impaired fasting glucose (IFG), and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT). This was a pilot, cross-sectional study including 92 individuals who had not been diagnosed with or treated for diabetes. We measured PCSK9 levels in three groups of subjects; namely, normoglycemia (n=57), IFG (n=21), and IGT (n=14). Individuals with IFG and IGT showed higher PCSK9 concentrations than those in the normoglycemic group, with the highest serum PCSK9 concentrations found in individuals with IGT (55.25±15.29 ng/mL for normoglycemia, 63.47±17.78 ng/mL for IFG, 72.22±15.46 ng/mL for IGT, analysis of variance P=0.001). There were no significant differences in high- or low-density lipoprotein cholesterol among groups. Serum PCSK9 levels are increased in patients with prediabetes compared to subjects with normoglycemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Emerging Insights on the Diverse Roles of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) in Chronic Liver Diseases: Cholesterol Metabolism and Beyond
Thomas Grewal, Christa Buechler
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(3): 1070. CrossRef - Insight into the Evolving Role of PCSK9
Mateusz Maligłówka, Michał Kosowski, Marcin Hachuła, Marcin Cyrnek, Łukasz Bułdak, Marcin Basiak, Aleksandra Bołdys, Grzegorz Machnik, Rafał Jakub Bułdak, Bogusław Okopień
Metabolites.2022; 12(3): 256. CrossRef - Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) levels are not associated with severity of liver disease and are inversely related to cholesterol in a cohort of thirty eight patients with liver cirrhosis
Susanne Feder, Reiner Wiest, Thomas S. Weiss, Charalampos Aslanidis, Doris Schacherer, Sabrina Krautbauer, Gerhard Liebisch, Christa Buechler
Lipids in Health and Disease.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Emerging Insights on the Diverse Roles of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) in Chronic Liver Diseases: Cholesterol Metabolism and Beyond

- Obesity and Metabolism
- The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea
- Junghyun Noh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(3):349-353. Published online August 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.3.349
- 6,292 View
- 50 Download
- 51 Web of Science
- 53 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Diabetes is one of the foremost public health issues worldwide that can lead to complications in many organ systems, and has become a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in Korea. According to data from the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS), about 2.7 million Koreans (8.0%) aged 30 years or older had type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in 2013. The prevalence of T2DM increased with age and rose from 5.6% in 2006 to 8.0% in 2013. Using data based on The Health Screening Service of the NHIS, 25% of Korean adults were reported to have prediabetes in 2013. The prevalence of an impaired fasting glucose tended to increase over time from 21.5% in 2006 to 25.0% in 2013. Even though nationwide health screening has been regularly conducted as a public service, the proportion of undiagnosed cases of diabetes was still reported to be on the higher side in the latest study. Based on the results of these epidemic studies, further actions will be needed to effectively implement lifestyle changes on a social level and increase measures for the early detection of diabetes to stem the tide of the epidemic.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Nationwide Population‐Based Study for the Recurrence and Comorbidities in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Hye Yeon Ko, Hae Jeong Nam, Min Hee Kim
The Laryngoscope.2024; 134(3): 1417. CrossRef - Real-World Outcomes of Individualized Targeted Therapy with Insulin Glargine 300 Units/mL in Insulin-Naïve Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes: TOBE Study
Eun-Gyoung Hong, Kyung-Wan Min, Jung Soo Lim, Kyu-Jeung Ahn, Chul Woo Ahn, Jae-Myung Yu, Hye Soon Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Won Kim, Dong Han Kim, Hak Chul Jang
Advances in Therapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer risk according to fasting blood glucose trajectories: a population-based cohort study
Thi Minh Thu Khong, Thi Tra Bui, Hee-Yeon Kang, Jinhee Lee, Eunjung Park, Jin-Kyoung Oh
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2024; 12(1): e003696. CrossRef - Nomenclature Dilemma of Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): Considerable Proportions of MAFLD Are Metabolic Healthy
Huiyul Park, Eileen L. Yoon, Mimi Kim, Seon Cho, Eun-Hee Nah, Dae Won Jun
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2023; 21(4): 1041. CrossRef - Efficacy of Polydeoxyribonucleotide in Promoting the Healing of Diabetic Wounds in a Murine Model of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes: A Pilot Experiment
Jiyoung Yun, SaeGwang Park, Ha Young Park, Kyung Ah Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(3): 1932. CrossRef - Influence of Fasting Glucose Level on Gastric Cancer Incidence in a Prospective Cohort Study
Tao Thi Tran, Jeonghee Lee, Madhawa Gunathilake, Hyunsoon Cho, Jeongseon Kim
Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.2022; 31(1): 254. CrossRef - A Comparative analysis of type 2 diabetes management quality indicators in cancer survivors
Eun J. Ko, Su J. Lee
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 9(11): 100116. CrossRef - Comparative Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor and Thiazolidinedione Treatment on Risk of Stroke among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Seung Eun Lee, Hyewon Nam, Han Seok Choi, Hoseob Kim, Dae-Sung Kyoung, Kyoung-Ah Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 567. CrossRef - Prevalence and diagnosis experience of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women over 50: Focusing on socioeconomic factors
Min Hyeok Choi, Ji Hee Yang, Jae Seung Seo, Yoon-ji Kim, Suk-Woong Kang, Jose M. Moran
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(3): e0248020. CrossRef - Effect of Teneligliptin versus Sulfonylurea on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Real-World Study in Korea
Da Hea Seo, Kyoung Hwa Ha, So Hun Kim, Dae Jung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(1): 70. CrossRef - A nationwide study of patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance with a 10-year follow-up in South Korea
Ka-Won Kang, Ji Eun Song, Byung-Hyun Lee, Min Ji Jeon, Eun Sang Yu, Dae Sik Kim, Se Ryeon Lee, Hwa Jung Sung, Chul Won Choi, Yong Park, Byung Soo Kim
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Fibrosis Burden of Missed and Added Populations According to the New Definition of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver
Huiyul Park, Eileen L. Yoon, Mimi Kim, Jung-Hwan Kim, Seon Cho, Dae Won Jun, Eun-Hee Nah
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(19): 4625. CrossRef - The Effects of Glucose Lowering Agents on the Secondary Prevention of Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 977. CrossRef - Decreased Vagal Activity and Deviation in Sympathetic Activity Precedes Development of Diabetes
Da Young Lee, Mi Yeon Lee, Jung Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Won-Young Lee, Sung-Woo Park, Seungho Ryu, Se Eun Park
Diabetes Care.2020; 43(6): 1336. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of ertugliflozin in East/Southeast Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Jie Liu, Shrita Patel, Nilo B. Cater, Larry Wu, Susan Huyck, Steven G. Terra, Anne Hickman, Amanda Darekar, Annpey Pong, Ira Gantz
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2020; 22(4): 574. CrossRef - Outcomes for Inappropriate Renal Dose Adjustment of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Population-Based Study
Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Mayo Clinic Proceedings.2020; 95(1): 101. CrossRef - Longitudinal Study of Diabetic Differences between International Migrants and Natives among the Asian Population
Heng Piao, Jae Moon Yun, Aesun Shin, Belong Cho
Biomolecules & Therapeutics.2020; 28(1): 110. CrossRef - Risk of active tuberculosis development in contacts exposed to infectious tuberculosis in congregate settings in Korea
Shin Young Park, Sunmi Han, Young-Man Kim, Jieun Kim, Sodam Lee, Jiyeon Yang, Un-Na Kim, Mi-sun Park
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Combined Impact of Chronic Kidney Disease and Diabetes on the Risk of Colorectal Cancer Depends on Sex: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Hyung Jung Oh, Hye Ah Lee, Chang Mo Moon, Dong-Ryeol Ryu
Yonsei Medical Journal.2020; 61(6): 506. CrossRef - Coffee Consumption, Genetic Polymorphisms, and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Pooled Analysis of Four Prospective Cohort Studies
An Na Kim, Hyun Jeong Cho, Jiyoung Youn, Taiyue Jin, Moonil Kang, Joohon Sung, Jung Eun Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(15): 5379. CrossRef - Current findings of kidney biopsy including nephropathy associated with hypertension and diabetes mellitus in Korea
Kipyo Kim, Sang Ho Lee, Sung Woo Lee, Jung Pyo Lee, Ho Jun Chin
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2020; 35(5): 1173. CrossRef - A Diabetes-Related Dietary Pattern Is Associated with Incident Diabetes in Obese Men in the Korean Genome Epidemiology Study
Hye Ah Lee, NaYeong Son, Won Kyung Lee, Hyesook Park
The Journal of Nutrition.2019; 149(2): 323. CrossRef - Associations of postmenopausal hormone therapy with metabolic syndrome among diabetic and non-diabetic women
Ji-Eun Kim, Jaesung Choi, JooYong Park, Jong-koo Lee, Aesun Shin, Sang Min Park, Daehee Kang, Ji-Yeob Choi
Maturitas.2019; 121: 76. CrossRef - The changing epidemiology of herpes zoster over a decade in South Korea, 2006–2015
Jae-Ki Choi, Sun Hee Park, Sanghyun Park, Sung-Yeon Cho, Hyo-Jin Lee, Si-Hyun Kim, Su-Mi Choi, Dong-Gun Lee, Jung-Hyun Choi, Jin-Hong Yoo
Vaccine.2019; 37(36): 5153. CrossRef - Prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes and pre-diabetes and its associated risk factors in Vietnam
Van Dat Nguyen, Quang Mai Vien, Thai Hung Do, Cong Danh Phan, Huu Chau Nguyen, Van Tuyen Nguyen, Dinh Luong Nguyen, Won Seok Sir, Yun Chon
Journal of Global Health Science.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Heterogeneous Trajectories of Cognitive Function in Older Adults with Diabetes: Findings from the Korean Longitudinal Study of Aging (KLoSA)
Chanhee Kim, Min Jung Kim, Chang Gi Park
Stress.2019; 27(1): 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Coffee Consumption on the Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus: The 2012–2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yejee Lim, Youngmi Park, Sun Kyu Choi, Soyeon Ahn, Jung Hun Ohn
Nutrients.2019; 11(10): 2377. CrossRef - Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on diabetic retinopathy and its progression: A real-world Korean study
Yoo-Ri Chung, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kihwang Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Ping-Hsun Wu
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(10): e0224549. CrossRef - Letter: Projection of Diabetes Prevalence in Korean Adults for the Year 2030 Using Risk Factors Identified from National Data (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:90–6)
Bo Kyung Koo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(2): 242. CrossRef - Changes of computed tomography‐based body composition after adrenalectomy in patients with endogenous hypercortisolism
Namki Hong, Jooyeon Lee, Cheol Ryong Ku, Kichang Han, Cho Rok Lee, Sang Wook Kang, Yumie Rhee
Clinical Endocrinology.2019; 90(2): 267. CrossRef - Estimating Lifetime Duration of Diabetes by Age and Gender in the Korean Population Using a Markov Model
Seung Woo Cho, Seon Ha Kim, Young-Eun Kim, Seok-Jun Yoon, Min-Woo Jo
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Hospital-Based Korean Diabetes Prevention Study: A Prospective, Multi-Center, Randomized, Open-Label Controlled Study
Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Jeong-Taek Woo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(1): 49. CrossRef - Medical Big Data Is Not Yet Available: Why We Need Realism Rather than Exaggeration
Hun-Sung Kim, Dai-Jin Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(4): 349. CrossRef - Implementation of the Chronic Disease Care System and its association with health care costs and continuity of care in Korean adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Woorim Kim, Yoon Soo Choy, Sang Ah Lee, Eun-Cheol Park
BMC Health Services Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in diabetes prevalence among Korean adults based on Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys III–VI
Jae-woo Lee, Hee-Taik Kang, Hyoung-Ji Lim, Byoungjin Park
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 138: 57. CrossRef - Insulin Resistance and the Risk of Diabetes and Dysglycemia in Korean General Adult Population
Jong Ha Baek, Hosu Kim, Kyong Young Kim, Jaehoon Jung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(4): 296. CrossRef - Relationship Between Circulating Netrin-1 Concentration, Impaired Fasting Glucose, and Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes
Jisook Yim, Gyuri Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Jeong-Ho Kim, Jin Won Cho, Sang-Guk Lee, Yong-ho Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum metabolite profile associated with incident type 2 diabetes in Koreans: findings from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Soo Jin Yang, So-Young Kwak, Garam Jo, Tae-Jin Song, Min-Jeong Shin
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in the prevalence of metabolic syndrome and its components in South Korea: Findings from the Korean National Health Insurance Service Database (2009–2013)
Seung Eun Lee, Kyungdo Han, Yu Mi Kang, Seon-Ok Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Kyung Soo Ko, Joong-Yeol Park, Ki-Up Lee, Eun Hee Koh, Ying-Mei Feng
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(3): e0194490. CrossRef - Effect of Change in Total Cholesterol Levels on Cardiovascular Disease Among Young Adults
Su‐Min Jeong, Seulggie Choi, Kyuwoong Kim, Sung Min Kim, Gyeongsil Lee, Seong Yong Park, Yeon‐Yong Kim, Joung Sik Son, Jae‐Moon Yun, Sang Min Park
Journal of the American Heart Association.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Age, sex, and the association of chronic kidney disease with all-cause mortality in Buddhist priests
Hyo Jin Kim, Yunmi Kim, Sejoong Kim, Ho Jun Chin, Hajeong Lee, Jung Pyo Lee, Dong Ki Kim, Kook-Hwan Oh, Kwon Wook Joo, Yon Su Kim, Deuk-Young Nah, Sung Joon Shin, Kyung Soo Kim, Jae Yoon Park, Kyung Don Yoo
Medicine.2018; 97(45): e13099. CrossRef - Association of change in total cholesterol level with mortality: A population-based study
Su-Min Jeong, Seulggie Choi, Kyuwoong Kim, Sung-Min Kim, Gyeongsil Lee, Joung Sik Son, Jae-Moon Yun, Sang Min Park, Katriina Aalto-Setala
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(4): e0196030. CrossRef - High hemoglobin levels are associated with decreased risk of diabetic retinopathy in Korean type 2 diabetes
Min-Kyung Lee, Kyung-Do Han, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Seo-Young Sohn, Jee-Sun Jeong, Mee-Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of systemic inflammation on the relationship between insulin resistance and all-cause and cancer-related mortality
Da Young Lee, Eun-Jung Rhee, Yoosoo Chang, Chong Il Sohn, Ho-Cheol Shin, Seungho Ryu, Won-Young Lee
Metabolism.2018; 81: 52. CrossRef - The two isoforms of matrix metalloproteinase- 2 have distinct renal spatial and temporal distributions in murine models of types 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus
Il Young Kim, Sang Soo Kim, Hye Won Lee, Sun Sik Bae, Hong Koo Ha, Eun Soon Jung, Min Young Lee, Miyeun Han, Harin Rhee, Eun Young Seong, Dong Won Lee, Soo Bong Lee, David H. Lovett, Sang Heon Song
BMC Nephrology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The optimal cut-off of blood pressure related to left ventricular diastolic dysfunction and remodeling in Asian diabetic patients
Ju Young Jung, Sung Keun Park, Jae-Hong Ryoo, Chang-Mo Oh, Jeong Gyu Kang, Kanghee Moon, Keum Ok Lee, Joong-Myung Choi
Journal of Cardiology.2018; 71(1): 16. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Smoking Cessation Intention among Current Smokers with Diabetes: Analysis of the 2013 Community Health Survey in Korea
Young-Hoon Lee, Jum Suk Ko
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2017; 17(3): 184. CrossRef - The differences in the incidence of diabetes mellitus and prediabetes according to the type of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors prescribed in Korean patients
Tong Min Kim, Hyunah Kim, Yoo Jin Jeong, Sun Jung Baik, So Jung Yang, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, In Young Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon, Hun-Sung Kim
Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety.2017; 26(10): 1156. CrossRef - Analysis and comparison of the cost-effectiveness of statins according to the baseline low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level in Korea
Y. J. Jeong, H. Kim, S. J. Baik, T. M. Kim, S. J. Yang, S.-H. Lee, J.-H. Cho, H. Lee, H. W. Yim, I. Y. Choi, K.-H. Yoon, H.-S. Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2017; 42(3): 292. CrossRef - Associations of Dietary Antioxidants and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: Data from the 2007–2012 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Dan Quansah, Kyungho Ha, Shinyoung Jun, Seong-Ah Kim, Sangah Shin, Gyung-Ah Wie, Hyojee Joung
Molecules.2017; 22(10): 1664. CrossRef - Accuracy of Capillary Blood Glucose Test When Fasting in Diabetes Patients or General Population: Performance Evaluation of G300 Based on ISO 15197:2013 Standards
Young-min Jee, Min-hee Seo, Byung-wook Yoo, Sung-ho Hong, Choo-yon Cho, Yong-jin Cho, Jung-eun Oh, Kyung-suk Shin
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2017; 17(4): 259. CrossRef - Increased Vascular Disease Mortality Risk in Prediabetic Korean Adults Is Mainly Attributable to Ischemic Stroke
Nam Hoon Kim, Tae Yeon Kwon, Sungwook Yu, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Yousung Park, Sin Gon Kim
Stroke.2017; 48(4): 840. CrossRef
- A Nationwide Population‐Based Study for the Recurrence and Comorbidities in Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Plasma Adiponectin Levels in Elderly Patients with Prediabetes
- Si Eun Kong, Yea Eun Kang, Kyong Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Bon Jeong Ku
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(3):326-333. Published online August 4, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.3.326
- 3,232 View
- 36 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The significance of adiponectin levels in elderly individuals with prediabetes has yet to be determined. Thus, the present study was performed to evaluate the relationships between adiponectin levels and anthropometric variables, body composition parameters, insulin sensitivity, and lipid profiles in elderly prediabetic patients.
Methods The present study included 120 subjects with prediabetes who were >65 years of age and were selected from among 1,993 subjects enrolled in the Korea Rural Genomic Cohort Study. All subjects underwent a 75 g oral glucose tolerance test and tests for measurement of insulin sensitivity. All diagnoses of prediabetes satisfied the criteria of the American Diabetes Association.
Results Plasma adiponectin levels were lower in elderly prediabetic subjects than elderly subjects with normal glucose tolerance (
P <0.01) as well as in elderly prediabetic patients with metabolic syndrome (MetS) than in those without MetS (P <0.02). When the subjects were categorized into two groups according to plasma adiponectin levels, the waist-to-hip ratio and 2-hour insulin levels were significantly lower in individuals with high plasma adiponectin levels than in those with low plasma adiponectin levels. Additionally, the plasma adiponectin levels of elderly prediabetic subject were inversely correlated with body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), waist-to-hip ratio, visceral fat, visceral fat ratio, and 2-hour insulin levels.Conclusion The present findings demonstrated that the major factors correlated with adiponectin levels in elderly prediabetic subjects were BMI, WC, waist-to-hip ratio, visceral fat, visceral fat ratio, and 2-hour insulin levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differential Association of Selected Adipocytokines, Adiponectin, Leptin, Resistin, Visfatin and Chemerin, with the Pathogenesis and Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in the Asir Region of Saudi Arabia: A Case Control Study
Mohammad Muzaffar Mir, Rashid Mir, Mushabab Ayed Abdullah Alghamdi, Javed Iqbal Wani, Zia Ul Sabah, Mohammed Jeelani, Vijaya Marakala, Shahzada Khalid Sohail, Mohamed O’haj, Muffarah Hamid Alharthi, Mohannad Mohammad S. Alamri
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(5): 735. CrossRef - Postloading insulinemia is independently associated with arterial stiffness in young Japanese persons
Norimitsu Murai, Naoko Saito, Sayuri Nii, Yuto Nishikawa, Asami Suzuki, Eriko Kodama, Tatsuya Iida, Kentaro Mikura, Hideyuki Imai, Mai Hashizume, Yasuyoshi Kigawa, Rie Tadokoro, Chiho Sugisawa, Kei Endo, Toru Iizaka, Fumiko Otsuka, Shun Ishibashi, Shoichi
Hypertension Research.2021; 44(11): 1515. CrossRef - Association of Adiponectin and rs1501299 of the ADIPOQ Gene with Prediabetes in Jordan
Mahmoud Alfaqih, Faheem Al-Mughales, Othman Al-Shboul, Mohammad Al Qudah, Yousef Khader, Muhammad Al-Jarrah
Biomolecules.2018; 8(4): 117. CrossRef
- Differential Association of Selected Adipocytokines, Adiponectin, Leptin, Resistin, Visfatin and Chemerin, with the Pathogenesis and Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in the Asir Region of Saudi Arabia: A Case Control Study


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



