Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Clinical Study
- Efficacy and Safety of Pitavastatin in a Real-World Setting: Observational Study Evaluating SaFety in Patient Treated with Pitavastatin in Korea (PROOF Study)
- In-Kyung Jeong, Sung-Rae Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):882-891. Published online December 2, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.723
- 5,654 View
- 250 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
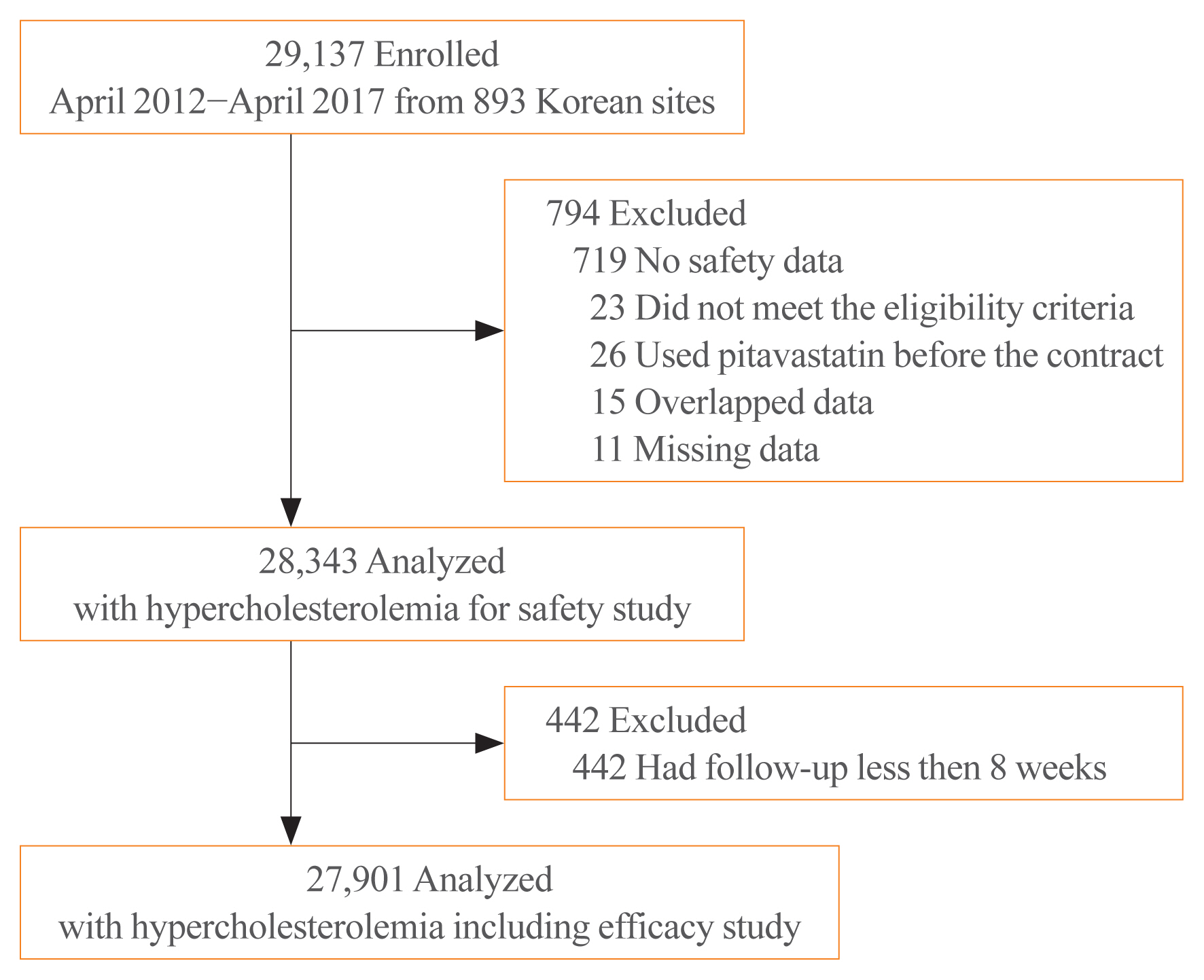
While randomized controlled trials provide useful information about drug safety and efficacy, they do not always reflect the observed results in the real world. The prospective, observational, non-comparative trial in South Korea was designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pitavastatin in clinical practice in 28,343 patients.
Methods
This study was conducted in 893 facilities in Korea from April 2, 2012 to April 1, 2017. This study was designed to administer 1, 2, or 4 mg pitavastatin to patients with hyperlipidemia at the age of 20 or older for at least 8 weeks.
Results
For 126 days of mean duration of administration of pitavastatin, the % change of low density lipoprotein cholesterol indicated a dose dependent reduction: –23.4%, –29.1%, and –35.2% in the 1, 2, and 4 mg groups, respectively in patients who have not been treated with lipid lowering medications prior to study. Only 1.74% (492/28,343) of pitavastatin-treated patients experienced adverse events, of which 0.43% (123/28,343) were adverse drug reactions. Less than 1% of patients experienced the grade 2 or more toxicity (Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events v4.03) in alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, serum creatinine, and serum creatine phosphokinase. Although there were no rhabdomyolysis in 28,343 patients, 0.04% of patients had been reported pitavastatin-related musculoskeletal disorders.
Conclusion
Overall, this observational study showed that pitavastatin was well tolerated and effectively modified the lipid profile, reducing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular risk in Korean patients with hypercholesterolemia in the real world. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level, Statin Use and Myocardial Infarction Risk in Young Adults
Heekyoung Jeong, Kyungdo Han, Soon Jib Yoo, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(3): 288. CrossRef
- Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level, Statin Use and Myocardial Infarction Risk in Young Adults

- Clinical Study
- Achievement of LDL-C Targets Defined by ESC/EAS (2011) Guidelines in Risk-Stratified Korean Patients with Dyslipidemia Receiving Lipid-Modifying Treatments
- Ye Seul Yang, Seo Young Lee, Jung-Sun Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Kang Wook Lee, Sang-Chol Lee, Jung Rae Cho, Seung-Jin Oh, Ji-Hyun Kim, Sung Hee Choi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):367-376. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.367

- 8,026 View
- 144 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study assessed the proportion of risk-stratified Korean patients with dyslipidemia achieving their low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) targets as defined by the European Society of Cardiology/European Atherosclerosis Society (ESC/EAS) (2011) guidelines while receiving lipid-modifying treatments (LMTs).
Methods
In this multicenter, cross-sectional, observational study, we evaluated data from Korean patients aged ≥19 years who were receiving LMTs for ≥3 months and had an LDL-C value within the previous 12 months on the same LMT. Data were collected for demographics, cardiovascular (CV) risk factors, medical history, and healthcare consumption. Patients were risk-stratified according to the ESC Systematic COronary Risk Evaluation (SCORE) chart and LDL-C target achievement rate was assessed.
Results
Guideline-based risk-stratification of the 1,034 patients showed the majority (72.2%) to be in the very high-risk category. Investigators’ assessment of risk was underestimated in 71.6% compared to ESC/EAS guidelines. Overall LDL-C target achievement rate was 44.3%; target achievement was the highest (66.0%) in moderate-risk patients and the lowest (39.0%) in very high-risk patients. Overall 97.1% patients were receiving statin therapy, mostly as a single-agent (89.2%). High-intensity statins and the highest permissible dose of high-intensity statins had been prescribed to only 9.1% and 7.3% patients in the very high-risk group, respectively. Physician satisfaction with patients’ LDL-C levels was the primary reason for non-intensification of statin therapy.
Conclusion
Achievement of target LDL-C level is suboptimal in Korean patients with dyslipidemia, especially in those at very high-risk of CV events. Current practices in LMTs need to be improved based on precise CV risk evaluation posed by dyslipidemia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Bempedoic Acid for Lipid Management in the Indian Population: An Expert Opinion
Jagdish Hiremath, J C Mohan, Prakash Hazra, JP S Sawhney, Ashwani Mehta, Sadanand Shetty, Abraham Oomman, Mahesh K Shah, Ganapathi Bantwal, Rajeev Agarwal, Rajiv Karnik, Peeyush Jain, Saumitra Ray, Sambit Das, Vibhuti Jadhao, Sachin Suryawanshi, Hanmant B
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimal implementation of the 2019 ESC/EAS dyslipidaemia guidelines in patients with and without atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease across Europe: a simulation based on the DA VINCI study
Julia Brandts, Sarah Bray, Guillermo Villa, Alberico L. Catapano, Neil R. Poulter, Antonio J. Vallejo-Vaz, Kausik K. Ray
The Lancet Regional Health - Europe.2023; 31: 100665. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - Target Low-Density Lipoprotein-Cholesterol and Secondary Prevention for Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Korean Nationwide Cohort Study
Ju Hyeon Kim, Jung-Joon Cha, Subin Lim, Jungseok An, Mi-Na Kim, Soon Jun Hong, Hyung Joon Joo, Jae Hyoung Park, Cheol Woong Yu, Do-Sun Lim, Kyeongmin Byeon, Sang-Wook Kim, Eun-Seok Shin, Kwang Soo Cha, Jei Keon Chae, Youngkeun Ahn, Myung Ho Jeong, Tae Hoo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2650. CrossRef - Current Status of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Achievement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Compared with Recent Guidelines
Soo Jin Yun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Ho Chan Cho, Sung Hee Choi, SungWan Chun, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Soo Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Gwanpyo Koh, Su Kyoung Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Sung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 464. CrossRef - There is urgent need to treat atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk earlier, more intensively, and with greater precision: A review of current practice and recommendations for improved effectiveness
Michael E. Makover, Michael D. Shapiro, Peter P. Toth
American Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2022; 12: 100371. CrossRef - Non-achievement of the Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Goal in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and a Very High Cardiovascular Disease Risk: A Multicenter Study in Vietnam
Huan Thanh Nguyen, Khang Pham Trong Ha, An Huu Nguyen, Thu Thanh Nguyen, Hang My Lam
Annals of Geriatric Medicine and Research.2021; 25(4): 278. CrossRef
- Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement

- Clinical Study
- Effects of a Portfolio-Mediterranean Diet and a Mediterranean Diet with or without a Sterol-Enriched Yogurt in Individuals with Hypercholesterolemia
- Yvelise Ferro, Elisa Mazza, Mariantonietta Salvati, Emma Santariga, Salvatore Giampà, Rocco Spagnuolo, Patrizia Doldo, Roberta Pujia, Adriana Coppola, Carmine Gazzaruso, Arturo Pujia, Tiziana Montalcini
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):298-307. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.298
- 6,795 View
- 142 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
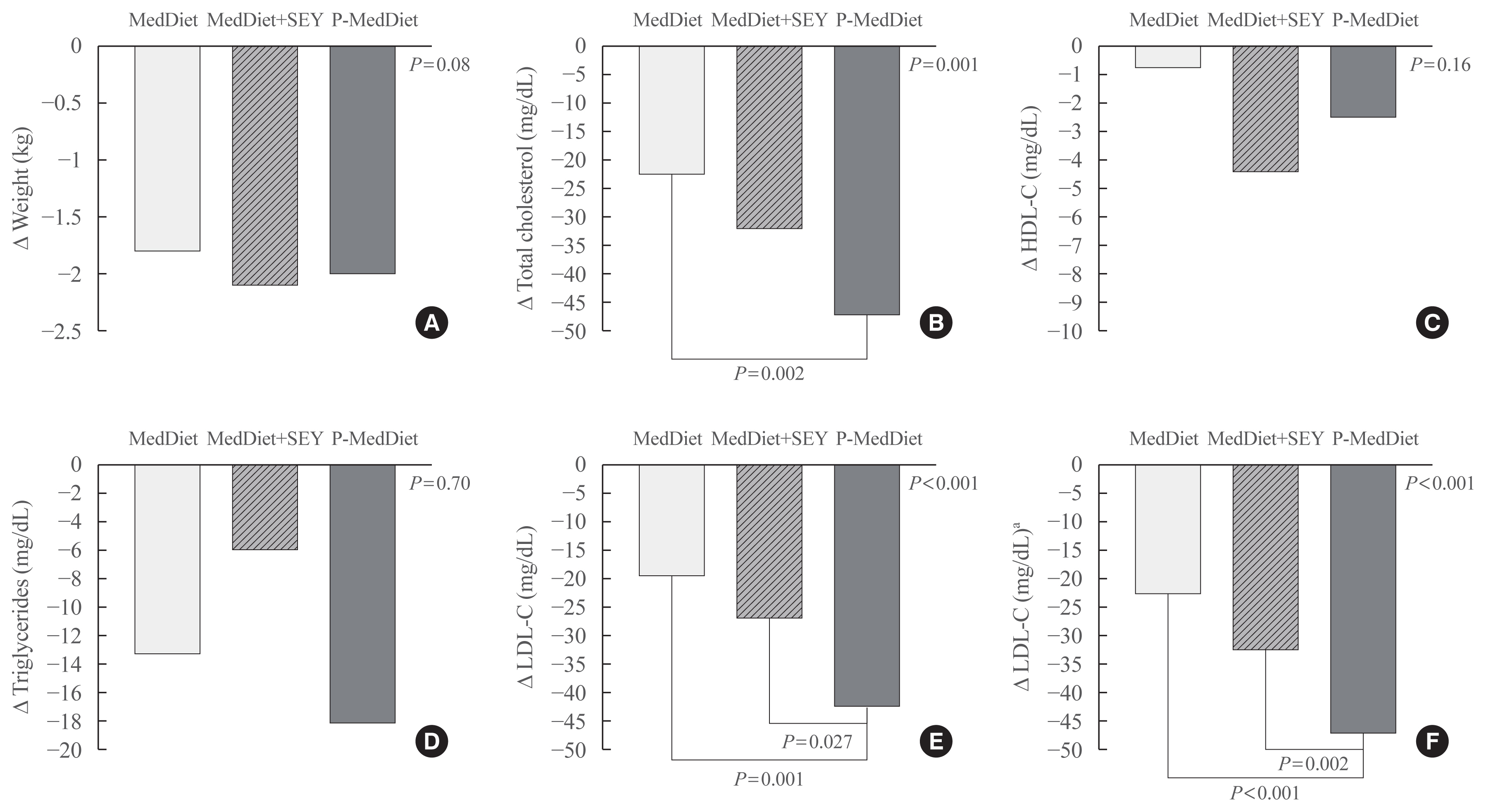
A growing number of functional foods have been proposed to reduce cholesterol levels and the Portfolio Diet, which includes a combination of plant sterols, fibres, nuts, and soy protein, reduces low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) from 20% to 30% in individuals with hyperlipidaemia. In this pilot study, the aim was to investigate whether a Mediterranean Diet incorporating a new and simple combination of cholesterol-lowering foods, excluding soy and nuts (namely the Portfolio-Mediterranean Diet), would reduce LDL-C levels, in the short-term, better than a Mediterranean Diet plus a sterol-enriched yogurt or a Mediterranean Diet alone.
Methods
We retrospectively evaluated 24 individuals on a Portfolio-Mediterranean Diet and 48 matched individuals on a Mediterranean Diet with or without a sterol-enriched yogurt (24 each groups) as controls.
Results
At follow-up (after 48±12 days), we observed an LDL reduction of 21±4, 23±4, and 44±4 mg/dL in the Mediterranean Diet alone, Mediterranean Diet plus yogurt and Portfolio-Mediterranean Diet respectively (P<0.001).
Conclusion
A Portfolio-Mediterranean Diet, incorporating a new combination of functional foods such as oats or barley, plant sterols, chitosan, and green tea but not soy and nuts, may reduce LDL of 25% in the short term in individuals with hypercholesterolemia. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intrinsic and environmental basis of aging: A narrative review
Carla Navarro, Juan Salazar, María P. Díaz, Maricarmen Chacin, Raquel Santeliz, Ivana Vera, Luis D′Marco, Heliana Parra, Mary Carlota Bernal, Ana Castro, Daniel Escalona, Henry García-Pacheco, Valmore Bermúdez
Heliyon.2023; 9(8): e18239. CrossRef - Application of small angle X‐ray scattering in exploring the effect of edible oils with different unsaturation FAs on bioaccessibility of stigmasterol oleate
Ying Wang, Tao Wang, Zhangtie Wang, Yiwen Guo, Ruijie Liu, Ming Chang
Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture.2023; 103(15): 7764. CrossRef - Phyto-Enrichment of Yogurt to Control Hypercholesterolemia: A Functional Approach
Harsh Kumar, Kanchan Bhardwaj, Natália Cruz-Martins, Ruchi Sharma, Shahida Anusha Siddiqui, Daljeet Singh Dhanjal, Reena Singh, Chirag Chopra, Adriana Dantas, Rachna Verma, Noura S. Dosoky, Dinesh Kumar
Molecules.2022; 27(11): 3479. CrossRef - Familial Hypercholesterolemia and Its Current Diagnostics and Treatment Possibilities: A Literature Analysis
Kristina Zubielienė, Gintarė Valterytė, Neda Jonaitienė, Diana Žaliaduonytė, Vytautas Zabiela
Medicina.2022; 58(11): 1665. CrossRef - Mediterranean Diet a Potential Strategy against SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Narrative Review
Yvelise Ferro, Roberta Pujia, Samantha Maurotti, Giada Boragina, Angela Mirarchi, Patrizia Gnagnarella, Elisa Mazza
Medicina.2021; 57(12): 1389. CrossRef
- Intrinsic and environmental basis of aging: A narrative review

Clinical Trial
- Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Low Density Lipoprotein Subfraction, Adiponectin and Apolipoprotein B in Type 2 Diabetic Patients.
- Haejung Jun, Junghae Ko, Hyesook Jung, Changshin Yoon, Taekyoon Kim, Minjeong Kwon, Soonhee Lee, Jihye Suk, Mikyung Kim, Dukkyu Kim, Jeong Hyun Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2011;26(3):218-224. Published online September 1, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2011.26.3.218
- 22,154 View
- 43 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Omega-3 fatty acids derived from fish oil have been reported to exert a beneficial effect on reducing cardiovascular disease. Reports about their mechanism have generated several interesting findings, including a change in small dense low density lipoprotein (sdLDL) cholesterol proportion, adiponectin, and apolipoprotein B (apoB), in addition to changes in the lipid profile. The principal objective of our study was to evaluate the effects of omega-3 fatty acids on plasma sdLDL, adiponectin, apoB100, and B48 in type 2 diabetic patients with hypertriglyceridemia. METHODS: We randomized 28 type 2 diabetic patients in a placebo-controlled, double-blind trial to receive either omega-3 fatty acids or placebo, both administered at a dose of 4 g daily for 12 weeks. LDL subfractions prior to and after treatment were separated via low-speed ultracentrifugation and analyzed via immunoelectrophoresis. Adiponectin, apoB100, and B48 levels were measured using an ELISA kit. RESULTS: sdLDL proportions were reduced in the omega-3 fatty acids group by 11% after 12 weeks of treatment (n = 17, P = 0.001), and were reduced by 4% in the control group (n = 11, P = 0.096). The patients receiving the omega-3 fatty acids evidenced a significant reduction in the levels of triglyceride (P = 0.001), apoB100, and B48 after 12 weeks (P = 0.038 and P = 0.009, respectively) relative to the baseline. Omega-3 fatty acids supplementation increased fasting blood glucose (P = 0.011), but the levels of HbA1c in each group did not change to a statistically significance degree. The adiponectin value was not reduced in the omega-3 fatty acids group (P = 0.133); by way of contrast, the placebo group evidenced a significant reduction in adiponectin value after 12 weeks (P = 0.002). CONCLUSION: Omega-3 fatty acid treatment proved effective in the reduction of atherogenic sdLDL and apoB in type 2 diabetic patients (Clinical trials reg. no. NCT 00758927, clinicaltrials.gov). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Blood Flow Improvement Effect of Bokbunja (Rubus coreanus) Seed Oil in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mouse Model
Hyelin Jeon, Sungmin Kwak, Su-Jin Oh, Hyun Soo Nam, Doo Won Han, Yoon Seok Song, Jinwoo Song, Kyung-Chul Choi
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2015; 44(8): 1105. CrossRef - Fatty Acid Compositions, Mineral and Vitamin Contents of the Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba)
Han-Soo Kim, Min-A Kim, Duan Yishan, Seong-Ho Jang, Dong-Soo Kang, Won-Ki Lee, Chun-Sik Lee, Jae-Young Ryu
Journal of Environmental Science International.2014; 23(1): 47. CrossRef
- Blood Flow Improvement Effect of Bokbunja (Rubus coreanus) Seed Oil in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mouse Model

Original Articles
- The Relationship between the Leptin Concentration and the Small Dense Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Concentration in Korean Type 2 Diabetic Patients.
- Wan Sub Shim, Hae Jin Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Yu Mie Rhee, Chul Woo Ahn, Sung Kil Lim, Hyun Chul Lee, Bong Soo Cha
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2006;21(4):319-327. Published online August 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.4.319
- 1,853 View
- 20 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Leptin has been suggested as a possible cause of atherosclerotic disease. The small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) has also been regarded as a new surrogate marker in atherosclerotic disease. The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationship between the leptin concentration and the small dense LDL-C concentration in Korean type 2 diabetic patients. METHODS: One hundred-ninety one type 2 diabetic patients, who did not use any medication that could affect the concentration of lipid such as statin, fibrate, thiazolidinediones and corticosteroid, were enrolled in this study. We analyzed the relationship between leptin, the small dense LDL-C and the other metabolic parameters. RESULTS: The small dense LDL-C concentrations were higher in the group with the highest tertile of the leptin value, both in males and females than those patients in the group with the lowest tertile of the leptin value. The small dense LDL-C concentrations were also higher in the group with the highest tertile of leptin divided by the BMI value both in males and females than those patients in the group with the lowest tertile of the leptin value. The leptin concentration was positively correlated with the small dense LDL-C, total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL-C, insulin and HOMAIR values after adjusting for age, gender and BMI. CONCLUSION: The association between leptin and small dense LDL-C could be a factor that explains the association between leptin and cardiovascular disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationships among Serum Adiponectin, Leptin and Vitamin D Concentrations and the Metabolic Syndrome in Farmers
Seo-Eun Yeon, Hee-Ryoung Son, Jung-Sook Choi, Eun-Kyung Kim
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2014; 19(1): 12. CrossRef - The Effect of Visceral Fat Area and Adipocytokines on Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Case-Control Study in Adult Korean Population
Kang-Kon Lee, Young-Sung Suh, Keun-Sang Yum
The Korean Journal of Obesity.2012; 21(1): 57. CrossRef
- Relationships among Serum Adiponectin, Leptin and Vitamin D Concentrations and the Metabolic Syndrome in Farmers

- Serum Lipoprotein (a) and Lipid Concentrations in Patients with Subelinical Hypothyroidism.
- Kyoung Ah Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Yeun Sun Kim, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Eun Mi Koh, Young Ki Min, Myung Shik Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Jong Hun Lee, Kwang Won Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1997;12(1):11-17. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,143 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Overt hypothyroidism is well-known cause of secondary hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis. However, there have been dissenting reports of abnormalities in serum lipid concentrations in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism (SH). Recently, it has been reported that serum Lp (a) concentration, an independent risk factor of atherosclerosis, was increased in patients with SH. Therefore, we analyzed serum Lp (a) and other lipid concentrations to investigate whether they are increased in patients with SH and the correlation between serum Lp (a) and TSH concentrations. METHODS: We undertook this study in 53 patients with SH (TSH > 6 uiU/ml) and 197 age-and sex-matched healthy control subjects, They had no abnormalities in liver function, BUN, creatinine, fasting blood glucose, urinalysis, and past medical histories. Serum T3, T4, and TSH concentrations were measured by RIA using commercial kits. Serum concentrations of Lp (a), total cholesterol, triglyceride (TG), and HDL cholesterol (HDL-C) were measured by rate nephelometry and enzyme assay, respectively. RESULTS: There were no significant differences of serum Lp (a), total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, TG, and HDL-C concentrations in 53 patients with SH and 197 control subjects (25.6+-3.8mg/dL vs. 25.4+-1.5mg/dL ; 204.0+-4.2mg/dL vs. 204.0+-2.4mg/dL ; 127.0+-3.9mg/dL vs. 125.0+-2.3 mg/dL ; 133.0+-8.5mg/dL vs. 130.0+-6.0mg/dL ; 50.0+-1.5mg/dL vs. 53.0+-0.9mg/dL). There was no correlation between Lp (a) and TSH concentrations in SH (r=0.12, p>0.05). CONCLUSION: Serum Lp (a) concentration as well as total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and TG was not increased in patients with SH. There was no correlation between serum Lp (a) and TSH levels in subclinical hypothyroidism.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



