Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Triglyceride-Glucose Index Predicts Future Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases: A 16-Year Follow-up in a Prospective, Community-Dwelling Cohort Study
- Joon Ho Moon, Yongkang Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Jae Hoon Moon, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi, Nam H. Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):406-417. Published online August 3, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1703

- 2,673 View
- 166 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
While the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index is a measure of insulin resistance, its association with cardiovascular disease (CVD) has not been well elucidated. We evaluated the TyG index for prediction of CVDs in a prospective large communitybased cohort.
Methods
Individuals 40 to 70 years old were prospectively followed for a median 15.6 years. The TyG index was calculated as the Ln [fasting triglycerides (mg/dL)×fasting glucose (mg/dL)/2]. CVDs included any acute myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease or cerebrovascular disease. We used a Cox proportional hazards model to estimate CVD risks according to quartiles of the TyG index and plotted the receiver operating characteristics curve for the incident CVD.
Results
Among 8,511 subjects (age 51.9±8.8 years; 47.5% males), 931 (10.9%) had incident CVDs during the follow-up. After adjustment for age, sex, body mass index, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, total cholesterol, smoking, alcohol, exercise, and C-reactive protein, subjects in the highest TyG quartile had 36% increased risk of incident CVD compared with the lowest TyG quartile (hazard ratio, 1.36; 95% confidence interval, 1.10 to 1.68). Carotid plaque, assessed by ultrasonography was more frequent in subjects in the higher quartile of TyG index (P for trend=0.049 in men and P for trend <0.001 in women). The TyG index had a higher predictive power for CVDs than the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) (area under the curve, 0.578 for TyG and 0.543 for HOMA-IR). Adding TyG index on diabetes or hypertension alone gave sounder predictability for CVDs.
Conclusion
The TyG index is independently associated with future CVDs in 16 years of follow-up in large, prospective Korean cohort. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Construction and validation of a nomogram for predicting diabetes remission at 3 months after bariatric surgery in patients with obesity combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Kaisheng Yuan, Bing Wu, Ruiqi Zeng, Fuqing Zhou, Ruixiang Hu, Cunchuan Wang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(1): 169. CrossRef - Association between the triglyceride glucose index and chronic total coronary occlusion: A cross-sectional study from southwest China
Kaiyong Xiao, Huili Cao, Bin Yang, Zhe Xv, Lian Xiao, Jianping Wang, Shuiqing Ni, Hui Feng, Zhongwei He, Lei Xv, Juan Li, Dongmei Xv
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024; 34(4): 850. CrossRef - The association between TyG and all-cause/non-cardiovascular mortality in general patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus is modified by age: results from the cohort study of NHANES 1999–2018
Younan Yao, Bo Wang, Tian Geng, Jiyan Chen, Wan Chen, Liwen Li
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index predicts type 2 diabetes mellitus more effectively than oral glucose tolerance test-derived insulin sensitivity and secretion markers
Min Jin Lee, Ji Hyun Bae, Ah Reum Khang, Dongwon Yi, Mi Sook Yun, Yang Ho Kang
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111640. CrossRef - Evaluation of the novel three lipid indices for predicting five- and ten-year incidence of cardiovascular disease: findings from Kerman coronary artery disease risk factors study (KERCADRS)
Alireza Jafari, Hamid Najafipour, Mitra Shadkam, Sina Aminizadeh
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Construction and validation of a nomogram for predicting diabetes remission at 3 months after bariatric surgery in patients with obesity combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- The Impact of Insulin Resistance on Hepatic Fibrosis among United States Adults with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: NHANES 2017 to 2018
- Ji Cheol Bae, Lauren A. Beste, Kristina M. Utzschneider
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):455-465. Published online June 21, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1434
- 4,197 View
- 135 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We aimed to investigate the association of hepatic steatosis with liver fibrosis and to assess the interactive effects of hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance on liver fibrosis in a nationally representative sample of United States adults.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional analysis using data from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2017 to 2018, which for the first time included transient elastography to assess liver stiffness and hepatic steatosis. We evaluated the association between hepatic steatosis (using controlled attenuation parameter [CAP]) and clinically significant liver fibrosis (defined as liver stiffness ≥7.5 kPa) using logistic regression with an interaction term for hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance (defined as homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance ≥3.0).
Results
Among adults undergoing transient elastography (n=2,023), 45.9% had moderate or greater hepatic steatosis and 11.3% had clinically significant liver fibrosis. After adjustment for demographic and metabolic factors, the odds of significant liver fibrosis increased as CAP score rose (odds ratio, 1.35 per standard deviation increment; 95% confidence interval, 1.11 to 1.64). We detected a significant interaction effect between CAP score and insulin resistance on the probability of significant liver fibrosis (P=0.016 for interaction). The probability of significant liver fibrosis increased in the presence of insulin resistance with increasing CAP score, while those without insulin resistance had low probability of significant liver fibrosis, even with high CAP scores.
Conclusion
Individuals with hepatic steatosis had higher odds of fibrosis when insulin resistance was present. Our findings emphasize the importance of the metabolic aspects of the disease on fibrosis risk and suggest a need to better identify patients with metabolic associated fatty liver disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of insulin resistance indicators with hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in patients with metabolic syndrome
Tzu-chia Kuo, Yang-bor Lu, Chieh-lun Yang, Bin Wang, Lin-xin Chen, Ching-ping Su
BMC Gastroenterology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - No More NAFLD: The Term Is Now MASLD
Ji Cheol Bae
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 92. CrossRef - Insulin Resistance/Sensitivity Measures as Screening Indicators of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis
Mohammad E. Khamseh, Mojtaba Malek, Soodeh Jahangiri, Sohrab Nobarani, Azita Hekmatdoost, Marieh Salavatizadeh, Samira Soltanieh, Haleh Chehrehgosha, Hoda Taheri, Zeinab Montazeri, Fereshteh Attaran, Faramarz Ismail-Beigi, Fariba Alaei-Shahmiri
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The association of Neuromedin U levels and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A comparative analysis
Murat Keskin, Sercan Avul, Aylin Beyaz, Nizameddin Koca
Heliyon.2024; 10(5): e27291. CrossRef - Oral Insulin Alleviates Liver Fibrosis and Reduces Liver Steatosis in Patients With Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatohepatitis and Type 2 Diabetes: Results of Phase II Randomized, Placebo-controlled Feasibility Clinical Trial
Yuval Ishay, Joel Neutel, Yotam Kolben, Ram Gelman, Orly Sneh Arbib, Oliver Lopez, Helena Katchman, Rizwana Mohseni, Miriam Kidron, Yaron Ilan
Gastro Hep Advances.2024; 3(3): 417. CrossRef - Comparative and Predictive Significance of Serum Leptin Levels in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Mehwish Qamar, Abeer Fatima, Ambreen Tauseef, Muhammad I Yousufzai, Ibrahim Liaqat, Qanbar Naqvi
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Greater Severity of Steatosis Is Associated with a Higher Risk of Incident Diabetes: A Retrospective Longitudinal Study
Ji Min Han, Jung Hwan Cho, Hye In Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Yu-Ji Lee, Jung Won Lee, Kwang Min Kim, Ji Cheol Bae
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 418. CrossRef - Hepatic T-cell senescence and exhaustion are implicated in the progression of fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes and mouse model with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Byeong Chang Sim, Yea Eun Kang, Sun Kyoung You, Seong Eun Lee, Ha Thi Nga, Ho Yeop Lee, Thi Linh Nguyen, Ji Sun Moon, Jingwen Tian, Hyo Ju Jang, Jeong Eun Lee, Hyon-Seung Yi
Cell Death & Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Familial clustering of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in first‐degree relatives of adults with lean nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Sorachat Niltwat, Chanin Limwongse, Natthinee Charatcharoenwitthaya, Duangkamon Bunditvorapoom, Wimolrak Bandidniyamanon, Phunchai Charatcharoenwitthaya
Liver International.2023; 43(12): 2713. CrossRef - Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance Is Inversely Related to Incident Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Jun-Hyuk Lee, Yu-Jin Kwon, Kyongmin Park, Hye Sun Lee, Hoon-Ki Park, Jee Hye Han, Sang Bong Ahn
Nutrients.2022; 14(15): 3039. CrossRef - DPP-4 Inhibitor in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patient with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Achieving Two Goals at Once?
Ji Cheol Bae
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 858. CrossRef
- Association of insulin resistance indicators with hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in patients with metabolic syndrome

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Changes in Insulin Resistance Index and the Risk of Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease without Diabetes: Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
- Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Inha Jung, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1016-1028. Published online October 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1110
- 4,149 View
- 128 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
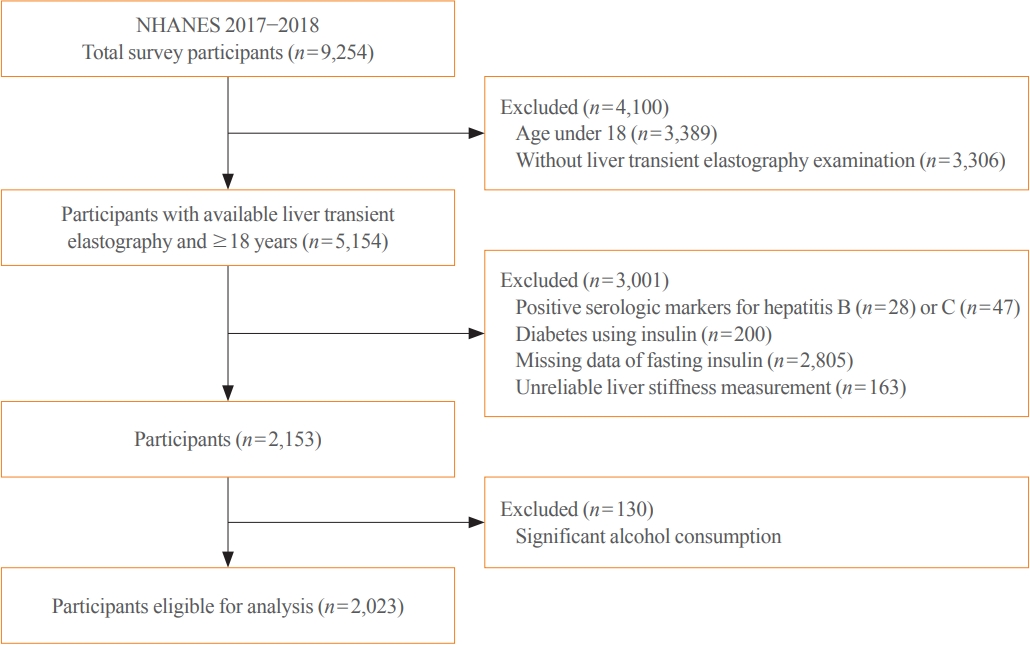
Fibrosis is the most important prognostic factor for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Insulin resistance plays a key role of fibrosis progression. We evaluated the association between changes in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) values and changes in fibrosis status in NAFLD.
Methods
We analyzed the data of 15,728 participants with NAFLD (86% men, mean age 40.5 years) who had no diabetes at baseline and visited our centers for health check-ups both in 2012 and 2016. The participants were classified into four groups according to the degree of change in HOMA-IR values from baseline to the end of follow-up: G1 (<0), G2 (0–0.50), G3 (0.51–1.00), and G4 (>1.00). NAFLD was assessed by ultrasonography, and fibrosis status was evaluated by the NAFLD fibrosis score (NFS) and the aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index (APRI).
Results
After the 4-year follow-up, the multivariable-adjusted odds ratio (OR) for progression of fibrosis probability increased with increasing HOMA-IR values (OR, 2.25; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.87 to 2.71 for NFS; and OR, 2.55; 95% CI, 2.05 to 3.18 for APRI, G4). This tendency remained consistent throughout the subgroup analyses, except in those for female sex and a body mass index <25 kg/m2. The OR for regression of fibrosis probability decreased with increasing HOMA-IR values (OR, 0.33; 95% CI, 0.25 to 0.43 for NFS, G4).
Conclusion
Changes in HOMA-IR values were associated with changes in fibrosis status in patients with NAFLD without diabetes, which underscores the role of insulin resistance in liver fibrosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Insulin Resistance/Sensitivity Measures as Screening Indicators of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis
Mohammad E. Khamseh, Mojtaba Malek, Soodeh Jahangiri, Sohrab Nobarani, Azita Hekmatdoost, Marieh Salavatizadeh, Samira Soltanieh, Haleh Chehrehgosha, Hoda Taheri, Zeinab Montazeri, Fereshteh Attaran, Faramarz Ismail-Beigi, Fariba Alaei-Shahmiri
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2024; 69(4): 1430. CrossRef - Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction: A 7-year retrospective cohort study of 3,496 adults using serial echocardiography
Gyuri Kim, Tae Yang Yu, Jae Hwan Jee, Ji Cheol Bae, Mira Kang, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism.2024; : 101534. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Liver Fibrosis in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Yu Luo, Cuiyu Wang, Tian Zhang, Xiaoyu He, Jianan Hao, Andong Shen, Hang Zhao, Shuchun Chen, Luping Ren
International Journal of General Medicine.2023; Volume 16: 293. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance in Adults: A before and after Pandemic Lockdown Longitudinal Study
Ángel Arturo López-González, Bárbara Altisench Jané, Luis Masmiquel Comas, Sebastiana Arroyo Bote, Hilda María González San Miguel, José Ignacio Ramírez Manent
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2795. CrossRef - Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance Is Inversely Related to Incident Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Jun-Hyuk Lee, Yu-Jin Kwon, Kyongmin Park, Hye Sun Lee, Hoon-Ki Park, Jee Hye Han, Sang Bong Ahn
Nutrients.2022; 14(15): 3039. CrossRef - Machine learning models including insulin resistance indexes for predicting liver stiffness in United States population: Data from NHANES
Kexing Han, Kexuan Tan, Jiapei Shen, Yuting Gu, Zilong Wang, Jiayu He, Luyang Kang, Weijie Sun, Long Gao, Yufeng Gao
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The crosstalk between insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: a culprit or a consequence?
Dae-Jeong Koo, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(4): 132. CrossRef
- Insulin Resistance/Sensitivity Measures as Screening Indicators of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Musclin Is Related to Insulin Resistance and Body Composition, but Not to Body Mass Index or Cardiorespiratory Capacity in Adults
- Yeliana L. Sánchez, Manuela Yepes-Calderón, Luis Valbuena, Andrés F. Milán, María C. Trillos-Almanza, Sergio Granados, Miguel Peña, Mauricio Estrada-Castrillón, Juan C. Aristizábal, Raúl Narvez-Sanchez, Jaime Gallo-Villegas, Juan C. Calderón
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1055-1068. Published online October 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1104
- 5,064 View
- 137 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We studied whether musclin function in humans is related to glycemic control, body composition, and cardiorespiratory capacity.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was performed in sedentary adults with or without metabolic syndrome (MS). Serum musclin was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Insulin resistance (IR) was evaluated by the homeostatic model assessment (HOMA-IR). Body composition was determined by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and muscle composition by measuring carnosine in the thigh, a surrogate of fiber types, through proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Cardiorespiratory capacity was assessed through direct ergospirometry.
Results
The control (n=29) and MS (n=61) groups were comparable in age (51.5±6.5 years old vs. 50.7±6.1 years old), sex (72.4% vs. 70.5% women), total lean mass (58.5%±7.4% vs. 57.3%±6.8%), and peak oxygen consumption (VOpeak) (31.0±5.8 mL O2./kg.min vs. 29.2±6.3 mL O2/kg.min). Individuals with MS had higher body mass index (BMI) (30.6±4.0 kg/m2 vs. 27.4± 3.6 kg/m2), HOMA-IR (3.5 [95% confidence interval, CI, 2.9 to 4.6] vs. 1.7 [95% CI, 1.1 to 2.0]), and musclin (206.7 pg/mL [95% CI, 122.7 to 387.8] vs. 111.1 pg/mL [95% CI, 63.2 to 218.5]) values than controls (P˂0.05). Musclin showed a significant relationship with HOMA-IR (β=0.23; 95% CI, 0.12 to 0.33; P˂0.01), but not with VOpeak, in multiple linear regression models adjusted for age, sex, fat mass, lean mass, and physical activity. Musclin was significantly associated with insulin, glycemia, visceral fat, and regional muscle mass, but not with BMI, VCO2peak, maximum heart rate, maximum time of work, or carnosine.
Conclusion
In humans, musclin positively correlates with insulinemia, IR, and a body composition profile with high visceral adiposity and lean mass, but low body fat percentage. Musclin is not related to BMI or cardiorespiratory capacity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Musclin Mitigates the Attachment of HUVECs to THP-1 Monocytes in Hyperlipidemic Conditions through PPARα/HO-1-Mediated Attenuation of Inflammation
Wonjun Cho, Heeseung Oh, Sung Woo Choi, A. M. Abd El-Aty, Fatma Yeşilyurt, Ji Hoon Jeong, Tae Woo Jung
Inflammation.2024; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Glucose restriction enhances oxidative fiber formation: A multi-omic signal network involving AMPK and CaMK2
Kaiyi Zhang, Ning Xie, Huaqiong Ye, Jiakun Miao, Boce Xia, Yu Yang, Huanqi Peng, Shuang Xu, Tianwen Wu, Cong Tao, Jinxue Ruan, Yanfang Wang, Shulin Yang
iScience.2024; 27(1): 108590. CrossRef - Myokines: metabolic regulation in obesity and type 2 diabetes
Zhi-Tian Chen, Zhi-Xuan Weng, Jiandie D Lin, Zhuo-Xian Meng
Life Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiological, mechanistic, and practical bases for assessment of cardiorespiratory fitness and muscle status in adults in healthcare settings
Jaime A. Gallo-Villegas, Juan C. Calderón
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2023; 123(5): 945. CrossRef - Serum Levels of Myonectin Are Lower in Adults with Metabolic Syndrome and Are Negatively Correlated with Android Fat Mass
Jorge L. Petro, María Carolina Fragozo-Ramos, Andrés F. Milán, Juan C. Aristizabal, Jaime A. Gallo-Villegas, Juan C. Calderón
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(8): 6874. CrossRef - The correlation of serum musclin with diabetic nephropathy
Jie Zhang, Jing Shi, Zengguang Cheng, Wenchao Hu
Cytokine.2023; 167: 156211. CrossRef - Efficacy of high-intensity interval- or continuous aerobic-training on insulin resistance and muscle function in adults with metabolic syndrome: a clinical trial
Jaime Gallo-Villegas, Leonardo A. Castro-Valencia, Laura Pérez, Daniel Restrepo, Oscar Guerrero, Sergio Cardona, Yeliana L. Sánchez, Manuela Yepes-Calderón, Luis H. Valbuena, Miguel Peña, Andrés F. Milán, Maria C. Trillos-Almanza, Sergio Granados, Juan C.
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2022; 122(2): 331. CrossRef - Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species (RONS) and Cytokines—Myokines Involved in Glucose Uptake and Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle
Paola Llanos, Jesus Palomero
Cells.2022; 11(24): 4008. CrossRef
- Musclin Mitigates the Attachment of HUVECs to THP-1 Monocytes in Hyperlipidemic Conditions through PPARα/HO-1-Mediated Attenuation of Inflammation

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Increased Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Individuals with High Weight Variability
- Inha Jung, Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):845-854. Published online August 27, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1098
- 4,916 View
- 140 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
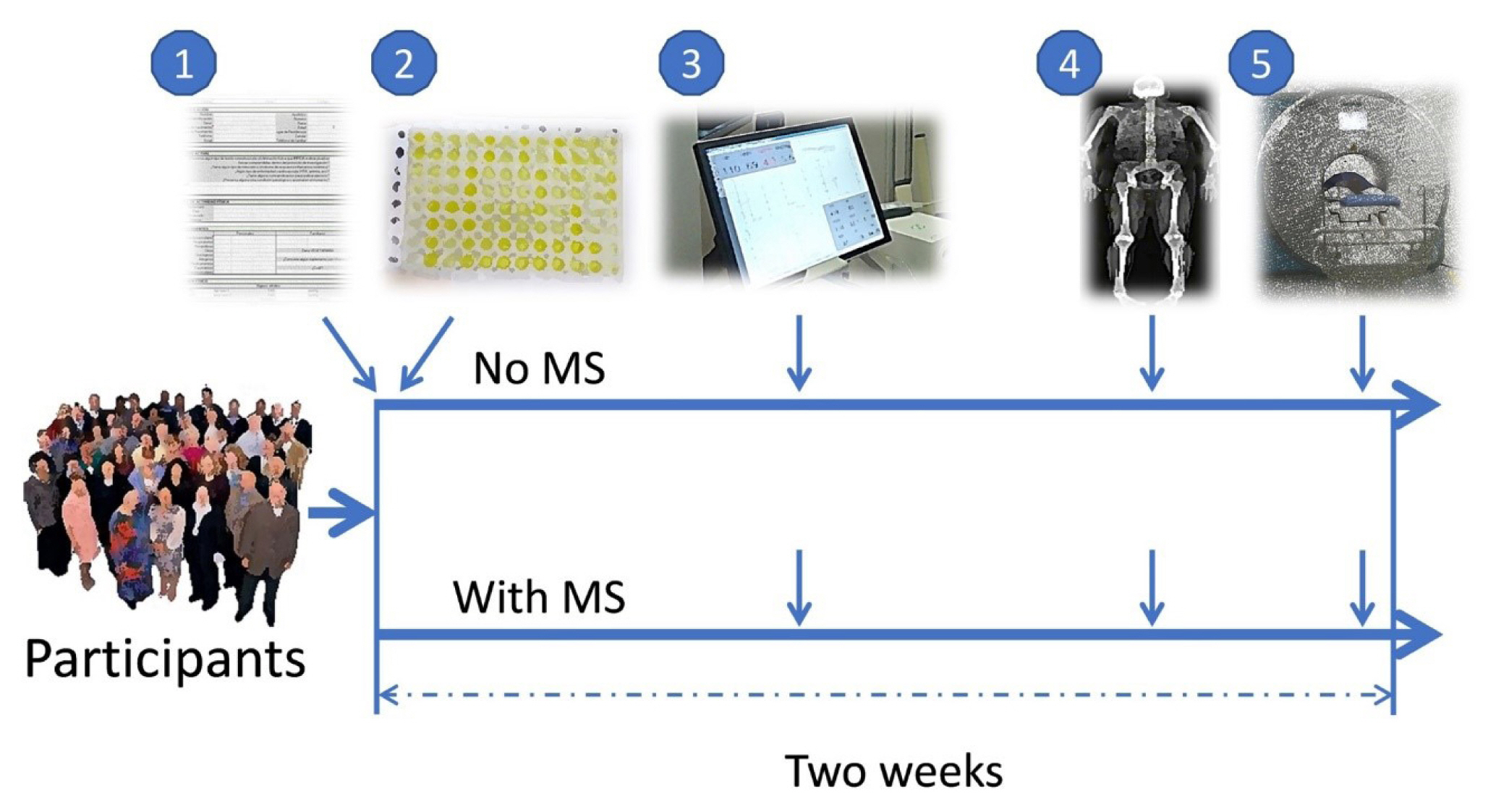
Weight loss through lifestyle modification is recommended for patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Recent studies have suggested that repeated loss and gain of weight is associated with worse health outcomes. This study aimed to examine the association between weight variability and the risk of NAFLD in patients without diabetes.
Methods
We examined the health-checkup data of 30,708 participants who had undergone serial examinations between 2010 and 2014. Weight variability was assessed using coefficient of variation and the average successive variability of weight (ASVW), which was defined as the sum of absolute weight changes between successive years over the 5-year period divided by 4. The participants were classified according to the baseline body mass index and weight difference over 4 years.
Results
On dividing the participants into four groups according to ASVW quartile groups, those in the highest quartile showed a significantly increased risk of NAFLD compared to those in the lowest quartile (odds ratio [OR], 1.89; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.63 to 2.19). Among participants without obesity at baseline, individuals with high ASVW showed increased risk of NAFLD (OR, 1.80; 95% CI, 1.61 to 2.01). Participants with increased weight over 4 years and high ASVW demonstrated higher risk of NAFLD compared to those with stable weight and low ASVW (OR, 4.87; 95% CI, 4.29 to 5.53).
Conclusion
Regardless of participant baseline obesity status, high weight variability was associated with an increased risk of developing NAFLD. Our results suggest that further effort is required to minimize weight fluctuations after achieving a desirable body weight. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Changes in Macronutrients during Dieting Lead to Weight Cycling and Metabolic Complications in Mouse Model
Anouk Charlot, Anthony Bringolf, Léa Debrut, Joris Mallard, Anne-Laure Charles, Emilie Crouchet, Delphine Duteil, Bernard Geny, Joffrey Zoll
Nutrients.2024; 16(5): 646. CrossRef - Weight variability, physical functioning and incident disability in older adults
Katie J. McMenamin, Tamara B. Harris, Joshua F. Baker
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(4): 1648. CrossRef - Dulaglutide Ameliorates Palmitic Acid-Induced Hepatic Steatosis by Activating FAM3A Signaling Pathway
Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Min-Jeong Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 74. CrossRef - Triglyceride and glucose index is a simple and easy‐to‐calculate marker associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung‐Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong‐Yup Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park
Obesity.2022; 30(6): 1279. CrossRef - Metabolic (dysfunction)-associated fatty liver disease in individuals of normal weight
Mohammed Eslam, Hashem B. El-Serag, Sven Francque, Shiv K. Sarin, Lai Wei, Elisabetta Bugianesi, Jacob George
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2022; 19(10): 638. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance in Adults: A before and after Pandemic Lockdown Longitudinal Study
Ángel Arturo López-González, Bárbara Altisench Jané, Luis Masmiquel Comas, Sebastiana Arroyo Bote, Hilda María González San Miguel, José Ignacio Ramírez Manent
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2795. CrossRef - Higher Weight Variability Could Bring You a Fatty Liver
Yeoree Yang, Jae-Hyoung Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 766. CrossRef - Autonomic Imbalance Increases the Risk for Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Inha Jung, Da Young Lee, Mi Yeon Lee, Hyemi Kwon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Won-Young Lee, Sung-Woo Park, Se Eun Park
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Changes in Macronutrients during Dieting Lead to Weight Cycling and Metabolic Complications in Mouse Model

- Diabetes
- In Vivo and In Vitro Quantification of Glucose Kinetics: From Bedside to Bench
- Il-Young Kim, Sanghee Park, Yeongmin Kim, Yewon Chang, Cheol Soo Choi, Sang-Hoon Suh, Robert R. Wolfe
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):733-749. Published online December 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.406

- 7,515 View
- 293 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Like other substrates, plasma glucose is in a dynamic state of constant turnover (i.e., rates of glucose appearance [Ra glucose] into and disappearance [Rd glucose] from the plasma) while staying within a narrow range of normal concentrations, a physiological priority. Persistent imbalance of glucose turnover leads to elevations (i.e., hyperglycemia, Ra>Rd) or falls (i.e., hypoglycemia, Ra<Rd) in the pool size, leading to clinical conditions such as diabetes. Endogenous Ra glucose is divided into hepatic glucose production via glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis (GNG) and renal GNG. On the other hand, Rd glucose, the summed rate of glucose uptake by tissues/organs, involves various intracellular metabolic pathways including glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, and oxidation at varying rates depending on the metabolic status. Despite the dynamic nature of glucose metabolism, metabolic studies typically rely on measurements of static, snapshot information such as the abundance of mRNAs and proteins and (in)activation of implicated signaling networks without determining actual flux rates. In this review, we will discuss the importance of obtaining kinetic information, basic principles of stable isotope tracer methodology, calculations of in vivo glucose kinetics, and assessments of metabolic flux in experimental models in vivo and in vitro.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Postabsorptive and postprandial glucose and fat metabolism in postmenopausal women with breast cancer—Preliminary data after chemotherapy compared to healthy controls
Kristian Buch-Larsen, Linn Gillberg, Haboon Ismail Ahmed, Simone Diedrichsen Marstrand, Michael Andersson, Gerrit van Hall, Charlotte Brøns, Peter Schwarz
Nutrition.2024; 122: 112394. CrossRef - Essential Amino Acid-Enriched Diet Alleviates Dexamethasone-Induced Loss of Muscle Mass and Function through Stimulation of Myofibrillar Protein Synthesis and Improves Glucose Metabolism in Mice
Yeongmin Kim, Sanghee Park, Jinseok Lee, Jiwoong Jang, Jiyeon Jung, Jin-Ho Koh, Cheol Soo Choi, Robert R. Wolfe, Il-Young Kim
Metabolites.2022; 12(1): 84. CrossRef - Exploring Human Muscle Dynamics In Vivo Using Stable Isotope Tracers
Il-Young Kim, Sanghee Park, Jiwoong Jang, Yeongmin Kim, Hee-Joo Kim
Annals of Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism.2022; 14(2): 40. CrossRef
- Postabsorptive and postprandial glucose and fat metabolism in postmenopausal women with breast cancer—Preliminary data after chemotherapy compared to healthy controls

- Clinical Study
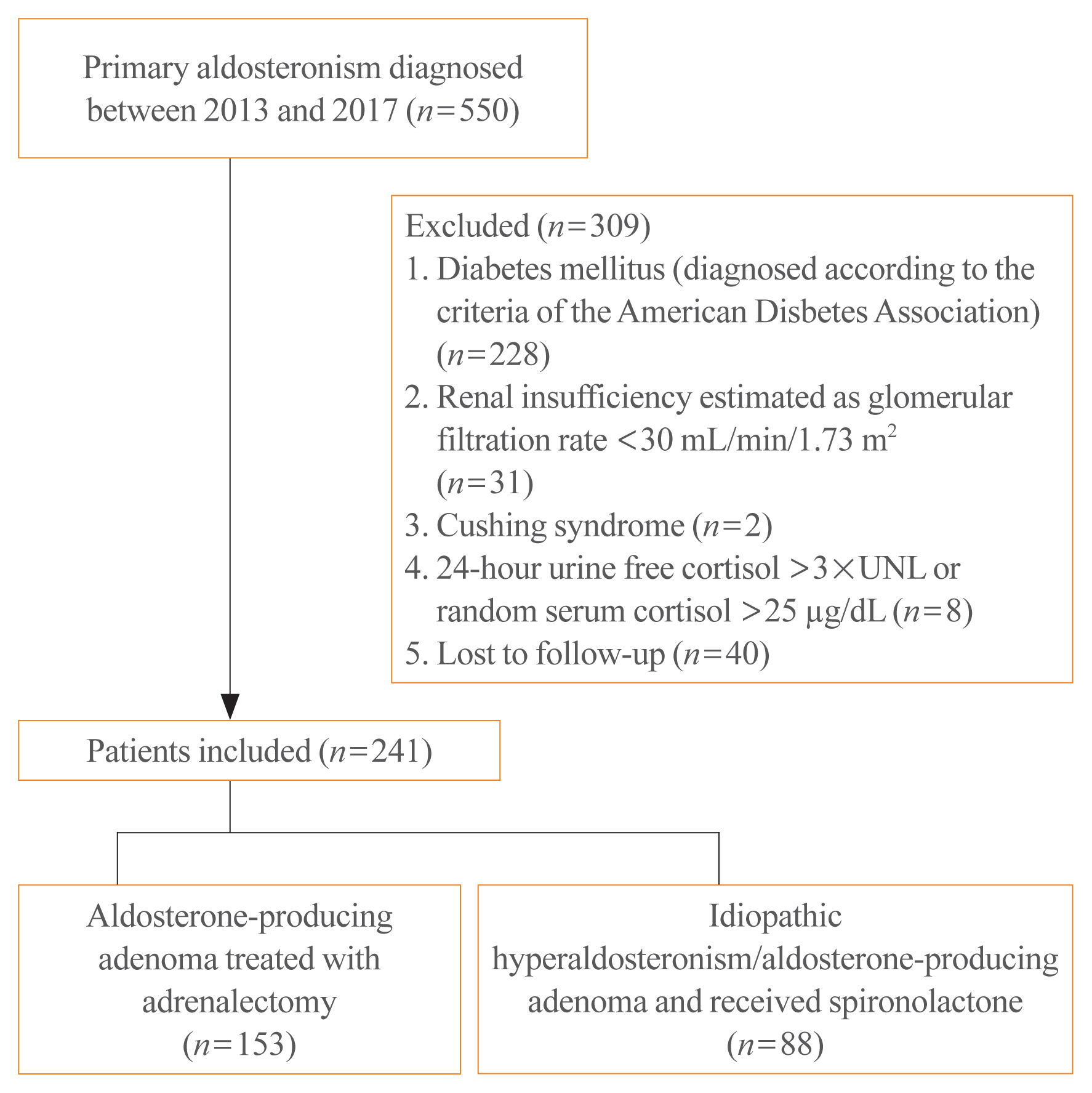
- Changes in Glucose Metabolism after Adrenalectomy or Treatment with a Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist for Primary Aldosteronism
- Yu-Fang Lin, Kang-Yung Peng, Chia-Hui Chang, Ya-Hui Hu, Vin-Cent Wu, Shiu-Dong Chung, Taiwan Primary Aldosteronism Investigation (TAIPAI) Study Group
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):838-846. Published online December 2, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.797
- 5,135 View
- 131 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Data on the effects of excess aldosterone on glucose metabolism are inconsistent. This study compared the changes in glucose metabolism in patients with primary aldosteronism (PA) after adrenalectomy or treatment with a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA).
Methods
Overall, 241 patients were enrolled; 153 underwent adrenalectomy and 88 received an MRA. Fasting glucose, homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), and homeostatic model assessment of β-cell function (HOMA-β) were compared between the treatment groups after 1 year. Plasma aldosterone concentration (PAC) and factors determining HOMA-IR and PAC were evaluated.
Results
No baseline differences were observed between the groups. Fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, and HOMA-β increased in both groups and there were no significant differences in fasting glucose following treatment. Multiple regression analysis showed associations between PAC and HOMA-IR (β=0.172, P=0.017) after treatment. Treatment with spironolactone was the only risk factor associated with PAC >30 ng/dL (odds ratio, 5.2; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.7 to 10; P<0.001) and conferred a 2.48-fold risk of insulin resistance after 1 year compared with surgery (95% CI, 1.3 to 4.8; P=0.007).
Conclusion
Spironolactone treatment might increase insulin resistance in patients with PA. This strengthened the current recommendation that adrenalectomy is the preferred strategy for patient with positive lateralization test. Achieving a post-treatment PAC of <30 ng/dL for improved insulin sensitivity may be appropriate. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How should anti-hypertensive medications be adjusted before screening for primary aldosteronism?
Jin-Ying Lu, Yi-Yao Chang, Ting-Wei Lee, Ming-Hsien Wu, Zheng-Wei Chen, Yen-Ta Huang, Tai-Shuan Lai, Leay Kiaw Er, Yen-Hung Lin, Vin-Cent Wu, Hao-Min Cheng, Hsien-Li Kao, Charles Jia-Yin Hou, Kwan-Dun Wu, Szu-Tah Chen, Feng-Hsuan Liu
Journal of the Formosan Medical Association.2024; 123: S91. CrossRef - Diabete e sindrome metabolica nel paziente con iperaldosteronismo primario
Stella Bernardi, Valerio Velardi, Federica De Luca, Giulia Zuolo, Veronica Calabrò, Riccardo Candido, Bruno Fabris
L'Endocrinologo.2024; 25(1): 48. CrossRef - Prevalence, risk factors and evolution of diabetes mellitus after treatment in primary aldosteronism. Results from the SPAIN-ALDO registry
M. Araujo-Castro, M. Paja Fano, B. Pla Peris, M. González Boillos, E. Pascual-Corrales, A. M. García Cano, P. Parra Ramírez, P. Martín Rojas-Marcos, J. G. Ruiz-Sanchez, A. Vicente Delgado, E. Gómez Hoyos, R. Ferreira, I. García Sanz, M. Recasens Sala, R.
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2023; 46(11): 2343. CrossRef - Estimated glomerular filtration rate-dip after medical target therapy associated with increased mortality and cardiovascular events in patients with primary aldosteronism
Jia-Yuh Sheu, Shuo-Meng Wang, Vin-Cent Wu, Kuo-How Huang, Chi-Shin Tseng, Yuan-Ju Lee, Yao-Chou Tsai, Yen-Hung Lin, Jeff S. Chueh
Journal of Hypertension.2023; 41(9): 1401. CrossRef - Risk of dementia in primary aldosteronism compared with essential hypertension: a nationwide cohort study
Namki Hong, Kyoung Jin Kim, Min Heui Yu, Seong Ho Jeong, Seunghyun Lee, Jung Soo Lim, Yumie Rhee
Alzheimer's Research & Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Secondary diabetes mellitus due to primary aldosteronism
Melpomeni Moustaki, Stavroula A. Paschou, Eleni C. Vakali, Andromachi Vryonidou
Endocrine.2022; 79(1): 17. CrossRef - Serum Cystatin C Levels Could Predict Rapid Kidney Function Decline in A Community-Based Population
Wei-Ching Fang, Hsing-Yu Chen, Shao-Chi Chu, Po-Hsi Wang, Chin-Chan Lee, I-Wen Wu, Chiao-Yin Sun, Heng-Jung Hsu, Chun-Yu Chen, Yung-Chang Chen, Vin-Cent Wu, Heng-Chih Pan
Biomedicines.2022; 10(11): 2789. CrossRef - Recovery from diabetes mellitus in primary aldosteronism patients after adrenalectomy
Yu Liu, Lede Lin, Chi Yuan, Sikui Shen, Yin Tang, Zhihong Liu, Yuchun Zhu, Liang Zhou
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- How should anti-hypertensive medications be adjusted before screening for primary aldosteronism?

- Clinical Study
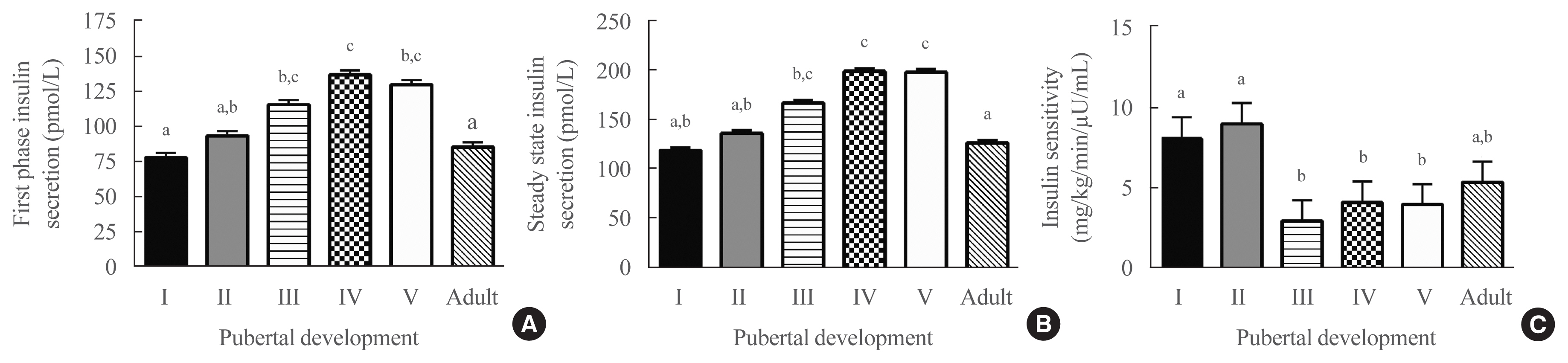
- Cross-Sectional and Longitudinal Examination of Insulin Sensitivity and Secretion across Puberty among Non-Hispanic Black and White Children
- Shannon E. Marwitz, Megan V. Gaines, Sheila M. Brady, Sarah J. Mi, Miranda M. Broadney, Susan Z. Yanovski, Van S. Hubbard, Jack A. Yanovski
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):847-857. Published online November 18, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.771
- 4,092 View
- 86 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Few studies using criterion measures of insulin sensitivity (SI) and insulin secretory capacity (ISC) have been conducted across puberty to adulthood. We examined how SI and ISC change from pre-puberty through adulthood.
Methods
Hyperglycemic clamp studies were performed in a convenience sample of non-Hispanic Black (NHB) and White children evaluated at age 6 to 12 years and at approximately 5-year intervals into adulthood (maximum age 27 years). SI and ISC (first-phase and steady-state insulin secretion) were determined cross-sectionally in 133 unique participants across puberty and in adulthood. Additionally, longitudinal changes in SI and ISC were compared at two timepoints among three groups defined by changes in pubertal development: pre-pubertal at baseline and late-pubertal at follow-up (n=27), early-pubertal at baseline and late-pubertal at follow-up (n=27), and late-pubertal at baseline and adult at follow-up (n=24).
Results
Cross-sectionally, SI was highest in pre-puberty and early puberty and lowest in mid-puberty (analysis of covariance [ANCOVA] P=0.001). Longitudinally, SI decreased from pre-puberty to late puberty (P<0.001), then increased somewhat from late puberty to adulthood. Cross-sectionally, first-phase and steady-state ISC increased during puberty and decreased in adulthood (ANCOVA P<0.02). Longitudinally, steady-state and first-phase ISC increased from pre-puberty to late puberty (P<0.007), and steady-state ISC decreased from late puberty to adulthood. The NHB group had lower SI (P=0.003) and greater first-phase and steady-state ISC (P≤0.001), independent of pubertal development.
Conclusion
This study confirms that SI decreases and ISC increases transiently during puberty and shows that these changes largely resolve in adulthood. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploratory Longitudinal Analysis of the Circulating CHIT1 Activity in Pediatric Patients with Obesity
Ioana Țaranu, Nicoleta Răcătăianu, Cristina Drugan, Cristina-Sorina Cătană, Andreea-Manuela Mirea, Diana Miclea, Sorana D. Bolboacă
Children.2023; 10(1): 124. CrossRef - Insulin Clearance in Health and Disease
Sonia M. Najjar, Sonia Caprio, Amalia Gastaldelli
Annual Review of Physiology.2023; 85(1): 363. CrossRef - Influence of puberty on relationships between body composition and blood pressure: a cross-sectional study
Esther A. Kwarteng, Lisa M. Shank, Loie M. Faulkner, Lucy K. Loch, Syeda Fatima, Suryaa Gupta, Hannah E. Haynes, Kaitlin L. Ballenger, Megan N. Parker, Sheila M. Brady, Anna Zenno, Marian Tanofsky-Kraff, Jack A. Yanovski
Pediatric Research.2023; 94(2): 781. CrossRef - Distribution of OGTT-Related Variables in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis from Puberty to Adulthood: An Italian Multicenter Study
Andrea Foppiani, Fabiana Ciciriello, Arianna Bisogno, Silvia Bricchi, Carla Colombo, Federico Alghisi, Vincenzina Lucidi, Maria Ausilia Catena, Mariacristina Lucanto, Andrea Mari, Giorgio Bedogni, Alberto Battezzati
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(3): 469. CrossRef - Fat-free/lean body mass in children with insulin resistance or metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Diana Paola Córdoba-Rodríguez, Iris Iglesia, Alejandro Gomez-Bruton, Gerardo Rodríguez, José Antonio Casajús, Hernan Morales-Devia, Luis A. Moreno
BMC Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating Triglyceride and Glucose Index as a Simple and Easy-to-Calculate Marker for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of General Internal Medicine.2022; 37(16): 4153. CrossRef - An update of the consensus statement on insulin resistance in children 2010
Veronica Maria Tagi, Sona Samvelyan, Francesco Chiarelli
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietary sugar restriction reduces hepatic de novo lipogenesis in boys with fatty liver disease
Stephanie T. Chung, Sheela N. Magge
Journal of Clinical Investigation.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Exploratory Longitudinal Analysis of the Circulating CHIT1 Activity in Pediatric Patients with Obesity

- Clinical Study
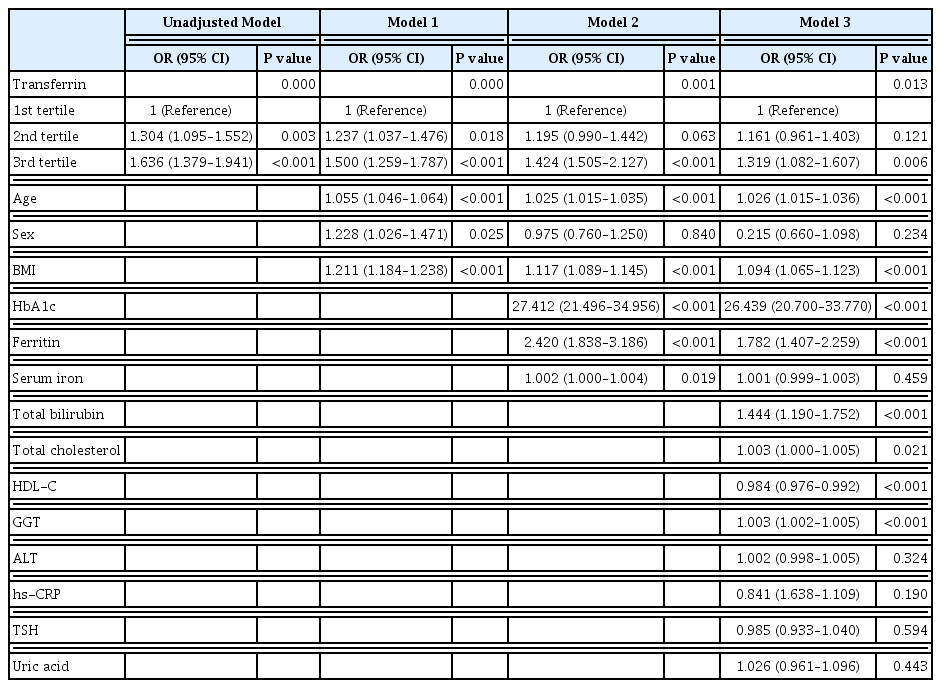
- Serum Transferrin Predicts New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes in Koreans: A 4-Year Retrospective Longitudinal Study
- Jong Dai Kim, Dong-Mee Lim, Keun-Young Park, Se Eun Park, Eun Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki Won Oh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):610-617. Published online September 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.721
- 4,393 View
- 98 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
It is well known that high serum ferritin, a marker of iron storage, predicts incident type 2 diabetes. Limited information is available on the association between transferrin, another marker of iron metabolism, and type 2 diabetes. Thus, we investigated the association between transferrin and incident type 2 diabetes.
Methods
Total 31,717 participants (mean age, 40.4±7.2 years) in a health screening program in 2005 were assessed via cross-sectional analysis. We included 30,699 subjects who underwent medical check-up in 2005 and 2009 and did not have type 2 diabetes at baseline in this retrospective longitudinal analysis.
Results
The serum transferrin level was higher in the type 2 diabetes group than in the non-type 2 diabetes group (58.32±7.74 μmol/L vs. 56.17±7.96 μmol/L, P<0.001). Transferrin correlated with fasting serum glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin in the correlational analysis (r=0.062, P<0.001 and r=0.077, P<0.001, respectively) after full adjustment for covariates. Transferrin was more closely related to homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance than to homeostasis model assessment of β cell function (r=0.042, P<0.001 and r=–0.019, P=0.004, respectively) after full adjustment. Transferrin predicted incident type 2 diabetes in non-type 2 diabetic subjects in a multivariate linear regression analysis; the odds ratio (95% confidence interval [CI]) of the 3rd tertile compared to that in the 1st tertile of transferrin for incident diabetes was 1.319 (95% CI, 1.082 to 1.607) after full adjustment (P=0.006).
Conclusion
Transferrin is positively associated with incident type 2 diabetes in Koreans. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Plasma proteome profiling reveals the therapeutic effects of the PPAR pan-agonist chiglitazar on insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, and inflammation in type 2 diabetes
Xingyue Wang, You Wang, Junjie Hou, Hongyang Liu, Rong Zeng, Xiangyu Li, Mei Han, Qingrun Li, Linong Ji, Desi Pan, Weiping Jia, Wen Zhong, Tao Xu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasma Proteomic Signature of Endometrial Cancer in Patients with Diabetes
Muhammad Mujammami, Mohamed Rafiullah, Khalid Akkour, Assim A. Alfadda, Afshan Masood, Salini Scaria Joy, Hani Alhalal, Maria Arafah, Eman Alshehri, Ibrahim O. Alanazi, Hicham Benabdelkamel
ACS Omega.2024; 9(4): 4721. CrossRef - Association between systemic iron status and β-cell function and insulin sensitivity in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes
Yao Qin, Yiting Huang, Yuxiao Li, Lu Qin, Qianying Wei, Xin Chen, Chuanhui Yang, Mei Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Body Iron Metabolism with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Women of Childbearing Age: Results from the China Adult Chronic Disease and Nutrition Surveillance (2015)
Jie Feng, Xiaoyun Shan, Lijuan Wang, Jiaxi Lu, Yang Cao, Lichen Yang
Nutrients.2023; 15(8): 1935. CrossRef - Serum Level of Ceruloplasmin, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and Transferrin as Markers of Severity in SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Patricia-Andrada Reștea, Ștefan Țigan, Laura Grațiela Vicaș, Luminița Fritea, Eleonora Marian, Tunde Jurca, Annamaria Pallag, Iulius Liviu Mureșan, Corina Moisa, Otilia Micle, Mariana Eugenia Mureșan
Microbiology Research.2023; 14(4): 1670. CrossRef
- Plasma proteome profiling reveals the therapeutic effects of the PPAR pan-agonist chiglitazar on insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, and inflammation in type 2 diabetes

- Obesity and Metabolism
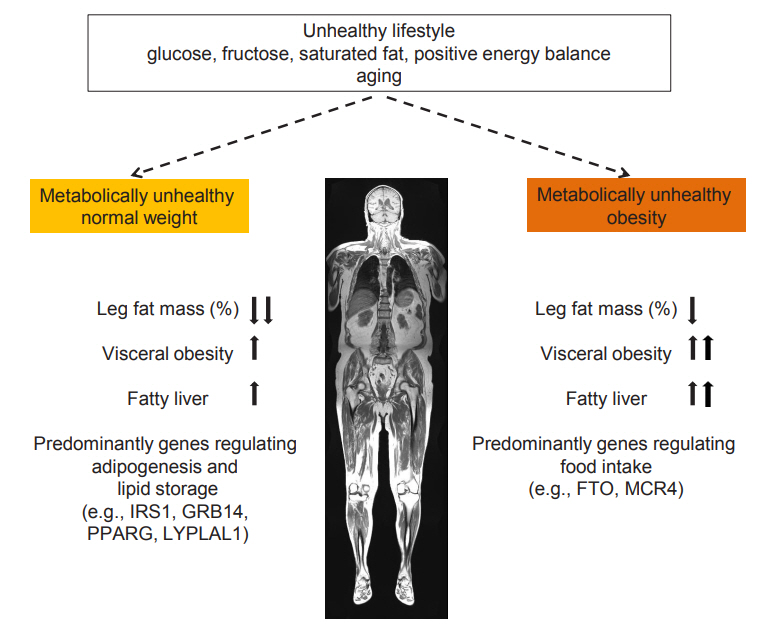
- Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Normal Weight and Obesity
- Norbert Stefan
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):487-493. Published online August 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.301
- 9,089 View
- 437 Download
- 31 Web of Science
- 30 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Increased fat mass is an established risk factor for the cardiometabolic diseases type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (CVD) and is associated with increased risk of all-cause and CVD mortality. However, also very low fat mass associates with such an increased risk. Whether impaired metabolic health, characterized by hypertension, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and subclinical inflammation, may explain part of the elevated risk of cardiometabolic diseases that is found in many subjects with very low fat mass, as it does in many obese subjects, is unknown. An important pathomechanism of impaired metabolic health is disproportionate fat distribution. In this article the risk of cardiometabolic diseases and mortality in subjects with metabolically healthy and unhealthy normal weight and obesity is summarized. Furthermore, the change of metabolic health during a longer period of follow-up and its impact on cardiometabolic diseases is being discussed. Finally, the implementation of the concept of metabolic health in daily clinical practice is being highlighted.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Phenotyping obesity: A focus on metabolically healthy obesity and metabolically unhealthy normal weight
Rachel Agius, Nikolai P. Pace, Stephen Fava
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing verum and sham acupoint catgut embedding for adults with obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Jin-huan Yue, Xiao-ling Li, Yu-ying Zhang, Guan-hu Yang, Jeffrey Zhong-xue Mah, Ang Li, Wei-wei Zhao, Yu-lin Wang, Qin-hong Zhang, Jia-qi Huang
Medicine.2024; 103(4): e36653. CrossRef - Association between Weight Change and Incidence of Dyslipidemia in Young Adults: A Retrospective Cohort Study of Korean Male Soldiers
Joon-Young Yoon, Won Ju Park, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Cheol-Kyu Park, Wonsuk Choi
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2024; 33(1): 36. CrossRef - Metabolically Healthy Obesity: An Eye-opener
Purushothaman Padmanabhan, Nagendram Dinakaran, Somnath Verma, S Keerthana
Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Endoscopy Practice.2023; 3(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of metabolic health and obesity on all-cause death and CVD incidence in Korean adults: a retrospective cohort study
Ye-Seul Kim, Sang-Jun Shin, Yonghwan Kim, Joungyoun Kim, Hee-Taik Kang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Coffee and metabolic phenotypes: A cross-sectional analysis of the Japan multi-institutional collaborative cohort (J-MICC) study
Takeshi Watanabe, Kokichi Arisawa, Tien Van Nguyen, Masashi Ishizu, Sakurako Katsuura-Kamano, Asahi Hishida, Takashi Tamura, Yasufumi Kato, Rieko Okada, Rie Ibusuki, Chihaya Koriyama, Sadao Suzuki, Takahiro Otani, Teruhide Koyama, Satomi Tomida, Kiyonori
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2023; 33(3): 620. CrossRef - Metabolically unhealthy phenotype in adults with normal weight: Is cardiometabolic health worse off when compared to adults with obesity?
Myong-Won Seo, Joon Young Kim
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2023; 17(2): 116. CrossRef - Association between metabolic obesity phenotypes and multiple myeloma hospitalization burden: A national retrospective study
Yue Zhang, Xiude Fan, Chunhui Zhao, Zinuo Yuan, Yiping Cheng, Yafei Wu, Junming Han, Zhongshang Yuan, Yuanfei Zhao, Keke Lu
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolically healthy obesity: Misleading phrase or healthy phenotype?
Cem Tanriover, Sidar Copur, Abduzhappar Gaipov, Batu Ozlusen, Rustu E. Akcan, Masanari Kuwabara, Mads Hornum, Daniel H. Van Raalte, Mehmet Kanbay
European Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 111: 5. CrossRef - Prevalence of combined metabolic health and weight status by various diagnosis criteria and association with cardiometabolic disease in Korean adults
Myong-Won Seo, Jung-Min Lee, Hyun Chul Jung
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2023; 17(2): 137. CrossRef - Precision medicine in complex diseases—Molecular subgrouping for improved prediction and treatment stratification
Åsa Johansson, Ole A. Andreassen, Søren Brunak, Paul W. Franks, Harald Hedman, Ruth J. F. Loos, Benjamin Meder, Erik Melén, Craig E. Wheelock, Bo Jacobsson
Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 294(4): 378. CrossRef - Lipid droplet biogenesis and functions in health and disease
Armella Zadoorian, Ximing Du, Hongyuan Yang
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2023; 19(8): 443. CrossRef - Molecular Mechanisms for the Vicious Cycle between Insulin Resistance and the Inflammatory Response in Obesity
Dariusz Szukiewicz
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(12): 9818. CrossRef - Insulin Resistance Is the Main Characteristic of Metabolically Unhealthy Obesity (MUO) Associated with NASH in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery
Sophia M. Schmitz, Sebastian Storms, Alexander Koch, Christine Stier, Andreas Kroh, Karl P. Rheinwalt, Sandra Schipper, Karim Hamesch, Tom F. Ulmer, Ulf P. Neumann, Patrick H. Alizai
Biomedicines.2023; 11(6): 1595. CrossRef - Hyperleptinemia as a marker of various phenotypes of obesity and overweight in women with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus
L. V. Kondrateva, Yu. N. Gorbunova, T. A. Panafidina, T. V. Popkova
Rheumatology Science and Practice.2023; 61(3): 339. CrossRef - Predictable Representation of Metabolic Synthesis Pathways of Vitamins and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Obese Adults
A. V. Shestopalov, L. A. Ganenko, I. M. Kolesnikova, T. V. Grigoryeva, I. Yu. Vasilyev, Yu. L. Naboka, N. I. Volkova, O. V. Borisenko, S. A. Roumiantsev
Journal of Evolutionary Biochemistry and Physiology.2023; 59(5): 1510. CrossRef - Metabolically unhealthy individuals, either with obesity or not, have a higher risk of critical coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes than metabolically healthy individuals without obesity
Nam Hoon Kim, Kyeong Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim
Metabolism.2022; 128: 154894. CrossRef - Associations between obesity, metabolic syndrome, and endometrial cancer risk in East Asian women
Boyoung Park
Journal of Gynecologic Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin and cancer: a tangled web
Brooks P. Leitner, Stephan Siebel, Ngozi D. Akingbesote, Xinyi Zhang, Rachel J. Perry
Biochemical Journal.2022; 479(5): 583. CrossRef - Relationships Between Metabolic Body Composition Status and Rapid Kidney Function Decline in a Community-Based Population: A Prospective Observational Study
Shao-Chi Chu, Po-Hsi Wang, Kuan-Ying Lu, Chia-Chun Ko, Yun-Hsuan She, Chin-Chan Lee, I-Wen Wu, Chiao-Yin Sun, Heng-Jung Hsu, Heng-Chih Pan
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dissecting the clinical relevance of polygenic risk score for obesity—a cross-sectional, longitudinal analysis
Eun Kyung Choe, Manu Shivakumar, Seung Mi Lee, Anurag Verma, Dokyoon Kim
International Journal of Obesity.2022; 46(9): 1686. CrossRef - Metabolic and Obesity Phenotype Trajectories in Taiwanese Medical Personnel
Hsin-Yun Chang, Jer-Hao Chang, Yin-Fan Chang, Chih-Hsing Wu, Yi-Ching Yang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(13): 8184. CrossRef - Sex Differences in Cardiovascular Impact of Early Metabolic Impairment: Interplay between Dysbiosis and Adipose Inflammation
Haneen S. Dwaib, Ibrahim AlZaim, Ghina Ajouz, Ali H. Eid, Ahmed El-Yazbi
Molecular Pharmacology.2022; 102(1): 60. CrossRef - Reduced leukocyte mitochondrial copy number in metabolic syndrome and metabolically healthy obesity
Rachel Agius, Nikolai Paul Pace, Stephen Fava
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in BMI and physical activity from youth to adulthood distinguish normal-weight, metabolically obese adults from those who remain healthy
A. Viitasalo, K. Pahkala, T. Lehtimäki, JSA. Viikari, TH. Tammelin, O. Raitakari, TO. Kilpeläinen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathogenesis, Murine Models, and Clinical Implications of Metabolically Healthy Obesity
Yun Kyung Cho, Yoo La Lee, Chang Hee Jung
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(17): 9614. CrossRef - Metabolically healthy obesity: it is time to consider its dynamic changes
Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(4): 123. CrossRef - Obesity as a Risk Factor for Breast Cancer—The Role of miRNA
Karolina Hanusek, Jakub Karczmarski, Anna Litwiniuk, Katarzyna Urbańska, Filip Ambrozkiewicz, Andrzej Kwiatkowski, Lidia Martyńska, Anita Domańska, Wojciech Bik, Agnieszka Paziewska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(24): 15683. CrossRef - Propensity Score–Matching Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG) vs. Gastric Bypass (RYGB) in Patients ≥ 60 Years
Omar Thaher, Stefanie Wolf, Martin Hukauf, Christine Stroh
Obesity Surgery.2021; 31(6): 2682. CrossRef - Associations between obesity, metabolic health, and the risk of breast cancer in East Asian women
Boyoung Park, Soyeoun Kim, Hayoung Kim, Chihwan Cha, Min Sung Chung
British Journal of Cancer.2021; 125(12): 1718. CrossRef
- Phenotyping obesity: A focus on metabolically healthy obesity and metabolically unhealthy normal weight

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Diabetes: An Epidemiological Perspective
- Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(3):226-233. Published online September 26, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.3.226
- 10,672 View
- 313 Download
- 66 Web of Science
- 68 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is thought to stem from the body's inability to store excess energy in adipocytes; as such, it is commonly viewed as the hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome. The pathogenesis of NAFLD involves ectopic fat accumulation, which also takes place in the liver, muscle and visceral fat. NAFLD is rapidly becoming more widespread in Korea, with an estimated prevalence of 30% in adults. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and NAFLD share insulin resistance as a common pathophysiological mechanism, and each of these two diseases affects the development of the other. Recent studies have suggested that NAFLD is often present as a comorbidity in T2DM patients. The mutual interrelationship between these conditions is shown by findings suggesting that T2DM can exacerbate NAFLD by promoting progression to nonalcoholic hepatosteatosis or fibrosis, while NAFLD causes the natural course of diabetic complications to worsen in T2DM patients. It remains unknown whether one disease is the cause of the other or vice versa. In this review, I would like to discuss current epidemiological data on the associations between NAFLD and T2DM, and how each disease affects the course of the other.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of exercise intervention on clinical parameters in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Yu Zeng, Xuemei Zhang, Wenling Luo, Yunjian Sheng
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2024; 36(1): 1. CrossRef - Phase 2, open-label, rollover study of cenicriviroc for liver fibrosis associated with metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis
Sven M. Francque, Alexander Hodge, Jerome Boursier, Ziad H. Younes, Gerardo Rodriguez-Araujo, Grace S. Park, Naim Alkhouri, Manal F. Abdelmalek
Hepatology Communications.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Two-Year Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Initial Triple Combination of Metformin, Sitagliptin, and Empagliflozin in Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Young-Hwan Park, Minji Sohn, So Yeon Lee, Soo Lim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 253. CrossRef - Research Progress of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
强江 郭
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(03): 561. CrossRef - Anti-osteoporotic treatments in the era of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: friend or foe
Maria Eleni Chondrogianni, Ioannis Kyrou, Theodoros Androutsakos, Christina-Maria Flessa, Evangelos Menenakos, Kamaljit Kaur Chatha, Yekaterina Aranan, Athanasios G. Papavassiliou, Eva Kassi, Harpal S. Randeva
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Obeticholic Acid and Insulin Sensitivity in Overweight Patients with Prediabetes
H. Amer, M. Nesim, H. Mansour, E. Nasr, N. Ahmed
Obesity and metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Utility of Indices Obtained during Medical Checkups for Predicting Fatty Liver Disease in Non-obese People
Naoya Otsubo, Tatsuya Fukuda, Genhin Cho, Fumiaki Ishibashi, Tetsuya Yamada, Koshiro Monzen
Internal Medicine.2023; 62(16): 2307. CrossRef - Liraglutide on type 2 diabetes mellitus with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 16 RCTs
Yan Zhao, Wenli Zhao, Huaien Bu, Maeda Toshiyoshi, Ye Zhao
Medicine.2023; 102(6): e32892. CrossRef - Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Mortality: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 220. CrossRef - Metabolomics analysis reveals serum biomarkers in patients with diabetic sarcopenia
Yuwei Tan, Xiaosong Liu, Yinping Yang, Baoying Li, Fei Yu, Wenqian Zhao, Chunli Fu, Xin Yu, Zhenxia Han, Mei Cheng
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Antagonizing apolipoprotein J chaperone promotes proteasomal degradation of mTOR and relieves hepatic lipid deposition
Shuangdi Duan, Nong Qin, Jiayi Pi, Pei Sun, Yating Gao, Lamei Liu, Zenghui Li, Ya Li, Liyang Shi, Qiang Gao, Ye Qiu, Songqing Tang, Chun-Hsiang Wang, Tzu-Ying Chen, Sin-Tian Wang, Kung-Chia Young, Hung-Yu Sun
Hepatology.2023; 78(4): 1182. CrossRef - The Influence of Metabolic Factors in Patients with Chronic Viral Hepatitis C Who Received Oral Antiviral Treatment
Oana Irina Gavril, Radu Sebastian Gavril, Florin Mitu, Otilia Gavrilescu, Iolanda Valentina Popa, Diana Tatarciuc, Andrei Drugescu, Andrei Catalin Oprescu, Andreea Gherasim, Laura Mihalache, Irina Mihaela Esanu
Metabolites.2023; 13(4): 571. CrossRef - The bidirectional relationship between NAFLD and type 2 diabetes: A prospective population-based cohort study
Minzhen Wang, Yanan Zhao, Yingqian He, Lulu Zhang, Jing Liu, Shan Zheng, Yana Bai
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2023; 33(8): 1521. CrossRef - Visceral fat: A key mediator of NAFLD development and progression
Savita Bansal, Meenakshi Vachher, Taruna Arora, Bhupender Kumar, Archana Burman
Human Nutrition & Metabolism.2023; 33: 200210. CrossRef - Greater Severity of Steatosis Is Associated with a Higher Risk of Incident Diabetes: A Retrospective Longitudinal Study
Ji Min Han, Jung Hwan Cho, Hye In Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Yu-Ji Lee, Jung Won Lee, Kwang Min Kim, Ji Cheol Bae
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 418. CrossRef - The role of TRIM family in metabolic associated fatty liver disease
Jingyue Zhang, Yingming Zhang, Ze Ren, Dongmei Yan, Guiying Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetic retinopathy: Is there an association?
Mathew Jacob, Mary Joseph, Jyothi Idiculla
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2023; 12(9): 2028. CrossRef - Camel whey protein improves diabetic liver injury by targeting ACMSD and promoting de novo NAD+ synthesis
Zhihua Dou, Huaibin Yao, Yutong Xie, Ying Liu, Yang Gao, Jie Yang
Journal of Functional Foods.2023; 110: 105835. CrossRef - Gut microbiota and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Boyeon Kim, Bukyung Kim
Kosin Medical Journal.2023; 38(3): 169. CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
E.G. Mankieva, E.I. Kukhareva
Dokazatel'naya gastroenterologiya.2023; 12(4): 103. CrossRef - Body Fat Distribution, Glucose Metabolism, and Diabetes Status Among Older Adults: The Multiethnic Cohort Adiposity Phenotype Study
Gertraud Maskarinec, Phyllis Raquinio, Bruce S. Kristal, Adrian A. Franke, Steven D. Buchthal, Thomas M. Ernst, Kristine R. Monroe, John A. Shepherd, Yurii B. Shvetsov, Loïc Le Marchand, Unhee Lim
Journal of Epidemiology.2022; 32(7): 314. CrossRef - Evaluation of the reciprocal interaction between hepatic steatosis and type 2 diabetes: a comparative analysis with respect to anti-diabetic treatment, glycemic control, renal and hepatic function
Teslime Ayaz, Hatice Beyazal Polat, Bilgesah Kilictas
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2022; 42(3): 421. CrossRef - Glycemic control, the unconsidered outcome in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Diego García-Compeán, Emanuela Orsi, Tsutomu Nishida, Ramesh Kumar
Annals of Hepatology.2022; 27(1): 100648. CrossRef - Prevalence of High and Moderate Risk Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Among Adults in the United States, 1999–2016
Pegah Golabi, James M. Paik, Michael Harring, Elena Younossi, Khaled Kabbara, Zobair M. Younossi
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 20(12): 2838. CrossRef - The Influence of Obesity and Metabolic Health on Vascular Health
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 1. CrossRef - Lifestyle as well as metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an umbrella review of evidence from observational studies and randomized controlled trials
Xiaojuan Peng, Juan Li, Hailiang Zhao, Junlong Lai, Junqin Lin, Shaohui Tang
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Insulin Resistance on Hepatic Fibrosis among United States Adults with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: NHANES 2017 to 2018
Ji Cheol Bae, Lauren A. Beste, Kristina M. Utzschneider
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 455. CrossRef - Extra-Glycemic Effects of Anti-Diabetic Medications: Two Birds with One Stone?
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 415. CrossRef - Structurally‐engineered fatty acid 1024 (SEFA‐1024) improves diet‐induced obesity, insulin resistance, and fatty liver disease
Jordon D. Secor, Bennet S. Cho, Lumeng J. Yu, Amy Pan, Victoria H. Ko, Duy T. Dao, Michael Feigh, Lorenzo Anez‐Bustillos, Gillian L. Fell, David A. Fraser, Kathleen M. Gura, Mark Puder
Lipids.2022; 57(4-5): 241. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance in Adults: A before and after Pandemic Lockdown Longitudinal Study
Ángel Arturo López-González, Bárbara Altisench Jané, Luis Masmiquel Comas, Sebastiana Arroyo Bote, Hilda María González San Miguel, José Ignacio Ramírez Manent
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2795. CrossRef - Captopril and Spironolactone can Attenuate Diabetic Nephropathy in Wistar Rats
by Targeting ABCA1 and microRNA-33
Tina Ghaffari, Nariman Moradi, Elham Chamani, Zahra Ebadi, Reza Fadaei, Shahin Alizadeh-Fanalou, Sahar Yarahmadi, Soudabeh Fallah
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2022; 28(16): 1367. CrossRef - Elevated serum γ-glutamyl transferase is associated with low muscle function in adults independent of muscle mass
Seunghyun Lee, Dawon Song, Sungjae Shin, Namki Hong, Yumie Rhee
Nutrition.2022; 103-104: 111813. CrossRef - Cross-sectional association between prolactin levels and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a retrospective analysis of patients from a single hospital in China
Yuanyuan Zhang, Huaizhen Liu
BMJ Open.2022; 12(10): e062252. CrossRef - Non-invasive screening, staging and management of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients : what do we know so far ?
Q Binet, A Loumaye, V Preumont, J-P Thissen, M.P. Hermans, N Lanthier
Acta Gastro Enterologica Belgica.2022; 85(2): 346. CrossRef - Diosgenin Ameliorated Type II Diabetes-Associated Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Inhibiting De Novo Lipogenesis and Improving Fatty Acid Oxidation and Mitochondrial Function in Rats
Yujie Zhong, Zhiman Li, Ruyi Jin, Yanpeng Yao, Silan He, Min Lei, Xin Wang, Chao Shi, Li Gao, Xiaoli Peng
Nutrients.2022; 14(23): 4994. CrossRef - Correlation between Component Factors of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Metabolic Syndrome in Nurses: An Observational and Cross-Sectional Study
Wen-Pei Chang, Yu-Pei Chang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(23): 16294. CrossRef - Recent advances and potentiality of postbiotics in the food industry: Composition, inactivation methods, current applications in metabolic syndrome, and future trends
Yujie Zhong, Tao Wang, Ruilin Luo, Jiayu Liu, Ruyi Jin, Xiaoli Peng
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Holistic analysis of hepatosteatosis literature: a scientometric study of global hepatosteatosis publications between 1980 and 2019
Fatih ESKİN, Engin ŞENEL
Journal of Medicine and Palliative Care.2022; 3(4): 300. CrossRef - Terpenoids: Natural Compounds for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Therapy
Pengyu Yao, Yajuan Liu
Molecules.2022; 28(1): 272. CrossRef - Association of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Dis-ease and Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: a Cross-Sectional Study
Zahra Heidari, Zahra Sharafi
Iranian South Medical Journal.2022; 25(1): 30. CrossRef - Race and Ethnicity in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): A Narrative Review
Kiarash Riazi, Mark G. Swain, Stephen E. Congly, Gilaad G. Kaplan, Abdel-Aziz Shaheen
Nutrients.2022; 14(21): 4556. CrossRef - MAFLD vs. NAFLD: shared features and potential changes in epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and pharmacotherapy
Ying-Xin Xian, Jian-Ping Weng, Fen Xu
Chinese Medical Journal.2021; 134(1): 8. CrossRef - Factors associated with elevated alanine aminotransferase in employees of a German chemical company: results of a large cross-sectional study
Matthias Claus, Christoph Antoni, Bernd Hofmann
BMC Gastroenterology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Treatment potential of LPCN 1144 on liver health and metabolic regulation in a non-genomic, high fat diet induced NASH rabbit model
P. Comeglio, E. Sarchielli, S. Filippi, I. Cellai, G. Guarnieri, A. Morelli, G. Rastrelli, E. Maseroli, S. Cipriani, T. Mello, A. Galli, B. J. Bruno, K. Kim, K. Vangara, K. Papangkorn, N. Chidambaram, M. V. Patel, M. Maggi, L. Vignozzi
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2021; 44(10): 2175. CrossRef - Cellular protein markers, therapeutics, and drug delivery strategies in the treatment of diabetes-associated liver fibrosis
Chien-Yu Lin, Pratik Adhikary, Kun Cheng
Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews.2021; 174: 127. CrossRef - Trend for Clinical Use of Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD)
Hiroshi Bando
Asploro Journal of Biomedical and Clinical Case Reports.2021; 4(2): 99. CrossRef - Prediction of Cardiovascular Risk Using Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Scoring Systems
Ye-Na Kweon, Hae-Jin Ko, A-Sol Kim, Hye-In Choi, Ji-Eun Song, Ji-Yeon Park, Sung-Min Kim, Hee-Eun Hong, Kyung-Jin Min
Healthcare.2021; 9(7): 899. CrossRef - Melatonin ameliorates hepatic steatosis by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome in db/db mice
Yongxiang Yu, Dongru Chen, Yuhua Zhao, Jianjun Zhu, Xiaohui Dong
International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology.2021; 35: 205873842110368. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Its Association With Diabetes Mellitus
Jaskamal Padda, Khizer Khalid, Anwar Khedr, Fahriba Tasnim, Ola A Al-Ewaidat, Ayden Charlene Cooper, Gutteridge Jean-Charles
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and the risk of insulin-requiring gestational diabetes
Sang Youn You, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hawn Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum syndecan‐4 is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Shu Jing Xia, Li Zhong Tang, Wen Hua Li, Zhao Shan Xu, Li Li Zhang, Feng Gan Cheng, Hong Xia Chen, Zi Hua Wang, Yu Cheng Luo, An Na Dai, Jian Gao Fan
Journal of Digestive Diseases.2021; 22(9): 536. CrossRef - Non-Laboratory-Based Simple Screening Model for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Developed Using Multi-Center Cohorts
Jiwon Kim, Minyoung Lee, Soo Yeon Kim, Ji-Hye Kim, Ji Sun Nam, Sung Wan Chun, Se Eun Park, Kwang Joon Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Joo Young Nam, Eun Seok Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 823. CrossRef - Grape pomace reduces the severity of non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis and the development of steatohepatitis by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing ectopic fat deposition in mice
Tehila Daniel, Michaella Ben-Shachar, Elyashiv Drori, Sharleen Hamad, Anna Permyakova, Elad Ben-Cnaan, Joseph Tam, Zohar Kerem, Tovit Rosenzweig
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2021; 98: 108867. CrossRef - The Interplay between Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Base Excision Repair and Metabolic Syndrome in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Sylwia Ziolkowska, Agata Binienda, Maciej Jabłkowski, Janusz Szemraj, Piotr Czarny
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(20): 11128. CrossRef - The Leg Fat to Total Fat Ratio Is Associated with Lower Risks of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Less Severe Hepatic Fibrosis: Results from Nationwide Surveys (KNHANES 2008–2011)
Hyun Min Kim, Yong-ho Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(6): 1232. CrossRef - Tip 2 Diyabet Modeli Ratların Karaciğer Dokularında Kodlanan Genlerin İfade Düzeyleri
Lütfiye ÖZPAK, Ayfer PAZARBAŞI
Ankara Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2021; 10(1): 25. CrossRef - Gut microbiota and human NAFLD: disentangling microbial signatures from metabolic disorders
Judith Aron-Wisnewsky, Chloé Vigliotti, Julia Witjes, Phuong Le, Adriaan G. Holleboom, Joanne Verheij, Max Nieuwdorp, Karine Clément
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2020; 17(5): 279. CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and primary care physicians
Ludovico Abenavoli, Anna C. Procopio, Milica Medić-Stojanoska, Francesco Luzza
Minerva Gastroenterologica e Dietologica.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Insulin Resistance and Diabetes in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Hideki Fujii, Norifumi Kawada
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(11): 3863. CrossRef - Active vitamin D supplementation alleviates initiation and progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by repressing the p53 pathway
Yuanyuan Liu, Mengjie Wang, Wei Xu, Hongman Zhang, Weihe Qian, Xiang Li, Xingbo Cheng
Life Sciences.2020; 241: 117086. CrossRef - Serum lipoprotein(a) levels and insulin resistance have opposite effects on fatty liver disease
Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
Atherosclerosis.2020; 308: 1. CrossRef - The effect of liraglutide on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Xueyang Zhang, Ran Bai, Yong Jia, Junwei Zong, Yongbo Wang, Yanan Dong
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2020; 40(4): 491. CrossRef - Association between Thyroid Function and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Euthyroid Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Bin Huang, Shengju Yang, Shandong Ye
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - The Absence of NLRP3-inflammasome Modulates Hepatic Fibrosis Progression, Lipid Metabolism, and Inflammation in KO NLRP3 Mice during Aging
Paloma Gallego, Beatriz Castejón-Vega, José A. del Campo, Mario D. Cordero
Cells.2020; 9(10): 2148. CrossRef - Prevalence of people at risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus and the involvement of community pharmacies in a national screening campaign: a pioneer action in Brazil
Cassyano J. Correr, Wendel Coura-Vital, Josélia C. Q. P. Frade, Renata C. R. M. Nascimento, Lúbia G. Nascimento, Eliete B. Pinheiro, Wesley M. Ferreira, Janice S. Reis, Karla F. S. Melo, Roberto Pontarolo, Mônica S. A. Lenzi, José V. Almeida, Hermelinda C
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Beneficial effect of anti-diabetic drugs for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung-Soo Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2020; 26(4): 430. CrossRef Elevated TPOAb is a Strong Predictor of Autoimmune Development in Patients of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Case–Control Study
Chenyi Wang, Qianglong Niu, Haihong Lv, Qian Li, Yuping Ma, Jiaojiao Tan, Chunhua Liu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4369. CrossRef- Sarcopoterium spinosum Inhibited the Development of Non-Alcoholic Steatosis and Steatohepatitis in Mice
Ayala Wollman, Tehila Daniel, Tovit Rosenzweig
Nutrients.2019; 11(12): 3044. CrossRef
- Effect of exercise intervention on clinical parameters in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials

- Clinical Study
- Triglyceride Glucose Index Is Superior to the Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance for Predicting Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Korean Adults
- Sang Bae Lee, Min Kyung Kim, Shinae Kang, Kahui Park, Jung Hye Kim, Su Jung Baik, Ji Sun Nam, Chul Woo Ahn, Jong Suk Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(2):179-186. Published online May 20, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.2.179
- 7,370 View
- 143 Download
- 81 Web of Science
- 80 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Recently, the triglyceride glucose (TyG) index has been considered a surrogate marker of insulin resistance which is a well-known pathogenic factor in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). However, few studies have investigated the relationship between the TyG index and NAFLD. Thus, we investigated the relationship between the TyG index and NAFLD and the effectiveness of the TyG index compared with the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) in identifying NAFLD in Korean adults.
Methods Participants of 4,986 who underwent ultrasonography in a health promotion center were enrolled. The TyG index was calculated as ln [fasting triglycerides (mg/dL)×fasting glucose (mg/dL)/2], and HOMA-IR was estimated. NAFLD was diagnosed by ultrasonography.
Results Significant differences were observed in metabolic parameters among the quartiles of the TyG index. The prevalence of NAFLD significantly increased with increment in the TyG index. After adjusting for multiple risk factors, a logistic regression analysis was performed. When the highest and lowest quartiles of the TyG index and HOMA-IR were compared, the odds ratios for the prevalence of NAFLD were 2.94 and 1.93 (95% confidence interval, 2.32 to 3.72 and 1.43 to 2.61; both
P for trend <0.01), respectively. According to the receiver operating characteristic analysis, the TyG index was superior to HOMA-IR in predicting NAFLD.Conclusion The TyG index and prevalence of NAFLD were significantly related and the TyG index was superior to HOMA-IR in predicting NAFLD in Korean adults.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Triglyceride-glucose body mass index predicts prognosis in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction
Ming Liu, Jianyuan Pan, Ke Meng, Yuwei Wang, Xueqing Sun, Likun Ma, Xiaofan Yu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index is capable of identifying metabolically obese, normal-weight older individuals
Bokun Kim, Keisuke Taniguchi, Tomonori Isobe, Sechang Oh
Journal of Physiological Anthropology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of triglyceride/glucose index and related parameters with Indian Diabetes Risk Score assessment in non-diabetic individuals visiting primary healthcare centre—A community-based cross-sectional study
Sivapragasam Ramalingam, Amlan Kumar Kar, Rajini Senthil
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2024; 13(1): 235. CrossRef - Insulin resistance in NSCLC: unraveling the link between development, diagnosis, and treatment
Shizhang Zhan, Liu Wang, Wenping Wang, Ruoran Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between the triglyceride–glucose index and prognosis in postoperative renal cell carcinoma patients: a retrospective cohort study
Guoliang Qin, Zhuang Sun, Yuxiang Jin, Xiangguo Ren, Zhaocun Zhang, Shuo Wang, Guanwen Zhou, Kun Huang, Haifeng Zhao, Xianzhou Jiang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Profiling triglyceride-glucose index in Filipinos with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a single-center study
Chastene Christopher Flake, Madonna Morales-Valenzuela, Raphael Enrique Tiongco, Annalyn Navarro
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic Performance of Insulin Resistance Indices for Identifying Metabolic Dysfunction–Associated Fatty Liver Disease
A. Lum Han, Hee Kyung Lee, Sae Ron Shin
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Triglyceride-Glucose Index is Associated with Vitamin D Status in Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Zhiping Liu, Wensha Zhang, Zhiwei Zhao, Wenhao Li, Jinhua Zhang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 2651. CrossRef - The triglyceride and glucose index and risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A dose–response meta-analysis
Qin Ling, Jiawei Chen, Xiao Liu, Yi Xu, Jianyong Ma, Peng Yu, Kai Zheng, Fuwei Liu, Jun Luo
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride–Glucose Index as a Potential Indicator of Sarcopenic Obesity in Older People
Bokun Kim, Gwonmin Kim, Yongkook Lee, Keisuke Taniguchi, Tomonori Isobe, Sechang Oh
Nutrients.2023; 15(3): 555. CrossRef - Association of insulin resistance with bone mineral density in a nationwide health check-up population in China
Ming Zhuo, Ze Chen, Mao-Lin Zhong, Fang Lei, Juan-Juan Qin, Shuhua Liu, Ye-Mao Liu, Tao Sun, Xiao-Jing Zhang, Lihua Zhu, Jingjing Cai, Jun-Ming Ye, Erping Yang
Bone.2023; 170: 116703. CrossRef - Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Mortality: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 220. CrossRef - Comparison of the prognostic value of a comprehensive set of predictors in identifying risk of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease among employed adults
Ze Yang, Bin Yu, Zihang Wang, Zhitao Li, Bo Yang, Honglian Zeng, Shujuan Yang
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The triglyceride glucose index and CDKAL1 gene rs10946398 SNP are associated with NAFLD in Chinese adults
Jun ZHU, Dujuan XU, Ruihua YANG, Min LIU, Ying LIU
Minerva Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - PNPLA3 rs738409 risk genotype decouples TyG index from HOMA2-IR and intrahepatic lipid content
Ákos Nádasdi, Viktor Gál, Tamás Masszi, Anikó Somogyi, Gábor Firneisz
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Baseline level and change trajectory of the triglyceride-glucose index in relation to the development of NAFLD: a large population-based cohort study
Yaqin Wang, Jiangang Wang, Lei Liu, Pingting Yang, Shuwen Deng, Xuelian Liu, Linlin Zhao, Changfa Wang, Ying Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing temporal differences in the predictive power of baseline TyG-related parameters for future diabetes: an analysis using time-dependent receiver operating characteristics
Maobin Kuang, Ruijuan Yang, Xin Huang, Chao Wang, Guotai Sheng, Guobo Xie, Yang Zou
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance (METS-IR) Predicts Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Ischemic Cardiomyopathy
Xuehe Zhang, Fen Liu, Wenling Li, Jixin Zhang, Tong Zhang, Xiaolin Yu, Junyi Luo, Qian Zhao, Jinyu Zhang, Binbin Fang, Yining Yang, Xiaomei Li
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 1283. CrossRef - Prevalence and Risk Factors of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Among Hospital Staff
Daya Zhang, Lijun Zhang, Shiju Chen, Runxiang Chen, Xiaodong Zhang, Feihu Bai
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 1221. CrossRef - The metabolic score of insulin resistance is positively correlated with bone mineral density in postmenopausal patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Peng Gu, Bin Pu, Qiao Xin, Dan Yue, LieLiang Luo, JiaSheng Tao, HaiShan Li, Ming Chen, MingHua Hu, XiaoRong Hu, XiaoHui Zheng, ZhanPeng Zeng
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence estimates of the insulin resistance and associated prevalence of heart failure among United Status adults
Xiaozhong Li, Jihong Wang, Liyan Niu, Ziqi Tan, Jianyong Ma, Ling He, Peng Yu, Xiao Liu, Juxiang Li
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - From NAFLD to HCC: Advances in noninvasive diagnosis
Qinchen Xu, Maoxiao Feng, Yidan Ren, Xiaoyan Liu, Huiru Gao, Zigan Li, Xin Su, Qin Wang, Yunshan Wang
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 165: 115028. CrossRef - Usefulness of two-dimensional shear wave elastography in the assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents
Jong Seo Yoon, Kyoung Ja Lim, Il Tae Hwang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A non-linear relationship between triglyceride glucose waist circumference and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a Japanese population: a secondary analysis
Xiaojie He, Xinyue Huang, Yafang Qian, Ting Sun
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Neck Circumference as a Predictor of Insulin Resistance in People with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Da-Hye Son, Jee Hye Han, Jun-Hyuk Lee
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(3): 214. CrossRef - Prediction and Validation of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Using Insulin Resistance-Related Indices in the Japanese Population
Kengo Moriyama, Nagamu Inoue, Jin Imai, Yumi Masuda, Chizumi Yamada, Noriaki Kishimoto, Shinji Takashimizu, Akira Kubo, Yasuhiro Nishizaki
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2023; 21(9): 489. CrossRef - Application value of triglyceride-glucose index and triglyceride-glucose body mass index in evaluating the degree of hepatic steatosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Mengyuan Wang, Mingxing Chang, Peipu Shen, Wei Wei, Huayao Li, Guifang Shen
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance as a Potential Screening Test for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Korean Adults without Diabetes
Hyejung Lee, Jae-Ho Lee
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2023; 13(4): 233. CrossRef - Comparison of the Triglyceride Glucose Index and Modified Triglyceride Glucose Indices to Predict Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Youths
Kyungchul Song, Goeun Park, Hye Sun Lee, Myeongseob Lee, Hae In Lee, Han Saem Choi, Junghwan Suh, Ahreum Kwon, Ho-Seong Kim, Hyun Wook Chae
The Journal of Pediatrics.2022; 242: 79. CrossRef - The triglyceride-glucose index as a clinical useful marker for metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD): a population-based study among Iranian adults
Ehsaneh Taheri, Mohammad Amin Pourhoseingholi, Alireza Moslem, Amir Hossein Hassani, Alireza Mousavi Jarrahi, Hamid Asadzadeh Aghdaei, Mohammad Reza Zali, Behzad Hatami
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2022; 21(1): 97. CrossRef - Comparison of triglyceride-glucose index and HOMA-IR for predicting prevalence and incidence of metabolic syndrome
Da-Hye Son, Hye Sun Lee, Yong-Jae Lee, Jun-Hyuk Lee, Jee-Hye Han
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2022; 32(3): 596. CrossRef - Triglycerides/Glucose Index Is Associated with Sperm Parameters and Sperm DNA Fragmentation in Primary Infertile Men: A Cross-Sectional Study
Federico Belladelli, Luca Boeri, Edoardo Pozzi, Giuseppe Fallara, Christian Corsini, Luigi Candela, Walter Cazzaniga, Daniele Cignoli, Luca Pagliardini, Alessia D’Arma, Paolo Capogrosso, Eugenio Ventimiglia, Francesco Montorsi, Andrea Salonia
Metabolites.2022; 12(2): 143. CrossRef - Association of triglyceride-glucose index and stroke recurrence among nondiabetic patients with acute ischemic stroke
Xiaomeng Yang, Guangyao Wang, Jing Jing, Anxin Wang, Xiaoli Zhang, Qian Jia, Xia Meng, Xingquan Zhao, Liping Liu, Hao Li, Yongjun Wang, Yilong Wang
BMC Neurology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The triglycerides and glucose (TyG) index: A new marker associated with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in obese patients
Benjamin Rivière, Audrey Jaussent, Valérie Macioce, Stéphanie Faure, Nicolas Builles, Patrick Lefebvre, Philippe Géraud, Marie-Christine Picot, Sandra Rebuffat, Eric Renard, Valérie Paradis, Marie-Dominique Servais, Nathalie de Preville, David Nocca, Anne
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(4): 101345. CrossRef - Association of triglyceride-glucose with cardiac hemodynamics in type 2 diabetes
Chenxi Wang, Zhicong Zhao, Xia Deng, Zhensheng Cai, Tian Gu, Lian Li, Chang Guo, Dong Wang, Ling Yang, Li Zhao, Guoyue Yuan
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2022; 19(2): 147916412210833. CrossRef - Comparison of the Modified TyG Indices and Other Parameters to Predict Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Youth
Kyungchul Song, Hae Won Lee, Han Saem Choi, Goeun Park, Hye Sun Lee, Su Jin Kim, Myeongseob Lee, Junghwan Suh, Ahreum Kwon, Ho-Seong Kim, Hyun Wook Chae
Biology.2022; 11(5): 685. CrossRef - Triglyceride-Glucose Index for Early Prediction of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis of 121,975 Individuals
Azizullah Beran, Hazem Ayesh, Mohammed Mhanna, Waseem Wahood, Sami Ghazaleh, Ziad Abuhelwa, Wasef Sayeh, Nameer Aladamat, Rami Musallam, Reem Matar, Saif-Eddin Malhas, Ragheb Assaly
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2666. CrossRef - Triglyceride and Glucose Index as a Screening Tool for Nonalcoholic Liver Disease in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
Anca Maria Amzolini, Mircea-Cătălin Forțofoiu, Anca Barău Alhija, Ionela Mihaela Vladu, Diana Clenciu, Adina Mitrea, Maria Forțofoiu, Daniela Matei, Magdalena Diaconu, Marinela Sinziana Tudor, Elena Simona Micu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(11): 3043. CrossRef - Triglyceride glucose index is superior biomarker for predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents
Jong Seo Yoon, Hye Jin Lee, Hwal Rim Jeong, Young Suk Shim, Min Jae Kang, Il Tae Hwang
Endocrine Journal.2022; 69(5): 559. CrossRef - Triglyceride and glucose index is a simple and easy‐to‐calculate marker associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung‐Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong‐Yup Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park
Obesity.2022; 30(6): 1279. CrossRef - Evaluating Triglyceride and Glucose Index as a Simple and Easy-to-Calculate Marker for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of General Internal Medicine.2022; 37(16): 4153. CrossRef - The Role of Insulin Resistance in Fueling NAFLD Pathogenesis: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Implications
Rossella Palma, Annamaria Pronio, Mario Romeo, Flavia Scognamiglio, Lorenzo Ventriglia, Vittorio Maria Ormando, Antonietta Lamazza, Stefano Pontone, Alessandro Federico, Marcello Dallio
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(13): 3649. CrossRef - Comparison of the diagnostic value between triglyceride-glucose index and triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease patients: a retrospective cross-sectional study
Zhi Liu, He He, Yuzhao Dai, Lidan Yang, Shenling Liao, Zhenmei An, Shuangqing Li
Lipids in Health and Disease.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin Resistance Markers to Detect Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Male Hispanic Population
Maritza Pérez-Mayorga, Jose P. Lopez-Lopez, Maria A. Chacon-Manosalva, Maria G Castillo, Johanna Otero, Daniel Martinez-Bello, Diego Gomez-Arbelaez, Daniel D. Cohen, Patricio Lopez-Jaramillo, Federico Ravaioli
Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Risk factors and prediction model for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in northwest China
Danting Li, Meiyu Zhang, Shengli Wu, Huiwen Tan, Nong Li
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The triglyceride glucose index is associated with the cerebral small vessel disease in a memory clinic population
Jiayu Zhang, Ming Hu, Yanqiu Jia, Shicong Zhao, Peiyuan Lv, Mingyue Fan, Yuanyuan Shi, Wei Jin
Journal of Clinical Neuroscience.2022; 104: 126. CrossRef - Integrating experimental model, LC-MS/MS chemical analysis, and systems biology approach to investigate the possible antidiabetic effect and mechanisms of Matricaria aurea (Golden Chamomile) in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yassin Ismail, Dina M. Fahmy, Maivel H. Ghattas, Mai M. Ahmed, Walaa Zehry, Samy M. Saleh, Dina M. Abo-elmatty
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Laboratory data clustering in defining population cohorts: Case study on metabolic indicators
Ivan Pavicevic, Goran Miljus, Olgica Nedic
Journal of the Serbian Chemical Society.2022; 87(9): 1025. CrossRef - Association of triglyceride glucose-body mass index with non-small cell lung cancer risk: A case-control study on Chinese adults
Feifei Wang, Ting He, Guoliang Wang, Tuo Han, Zhongqiang Yao
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Risk of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Cohort Study
Ru Zhang, Qing Guan, Mengting Zhang, Yajie Ding, Zongzhe Tang, Hongliang Wang, Wei Zhang, Yue Chen, Rong Jiang, Yan Cui, Jie Wang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 3167. CrossRef - Association between the triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index and increased blood pressure in normotensive subjects: a population-based study
Dong-Hwa Lee, Jong Eun Park, So Young Kim, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Jong-Hyock Park
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Fructose consumption correlates with triglyceride-glucose index and glycemic status in healthy adults
Eda Keskin, Havvanur Yoldas Ilktac
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2022; 52: 184. CrossRef - Associations Between Type 2 Diabetes Subtypes and Complications: Analysis of the Malaysia National Diabetes Registry
Rasa Kazlauskaite, Nathan Ellermeier, Carrie Ngongo, Arunah Chandran, Pankaja Desai, Ethan Ritz, Rachel Nugent, Feisul Idzwan Mustapha
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Independent and combined effects of triglyceride-glucose index on prehypertension risk: a cross-sectional survey in China
Hong Xie, Jian Song, Liangliang Sun, Xinxin Xie, Yehuan Sun
Journal of Human Hypertension.2021; 35(3): 207. CrossRef - Association of Triglyceride-Glucose Index with Bone Mineral Density in Non-diabetic Koreans: KNHANES 2008–2011
Jee Hee Yoon, A Ram Hong, Wonsuk Choi, Ji Yong Park, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang
Calcified Tissue International.2021; 108(2): 176. CrossRef - Triglyceride‐Glucose Index (TyG) is associated with erectile dysfunction: A cross‐sectional study
Mehmet Yilmaz, Mustafa Karaaslan, Senol Tonyali, Mecit Celik, Tuncay Toprak, Oner Odabas
Andrology.2021; 9(1): 238. CrossRef - Triglyceride Glucose Index and Related Parameters (Triglyceride Glucose-Body Mass Index and Triglyceride Glucose-Waist Circumference) Identify Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver and Liver Fibrosis in Individuals with Overweight/Obesity
Mohammad E. Khamseh, Mojtaba Malek, Rowshanak Abbasi, Hoda Taheri, Maryam Lahouti, Fariba Alaei-Shahmiri
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2021; 19(3): 167. CrossRef - Triglyceride and glucose index and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Jung A Kim, Jinsil Kim, Eun Roh, So-hyeon Hong, You-Bin Lee, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi, Eunjin Noh, Soon Young Hwang, Geum Joon Cho, Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 171: 108533. CrossRef - Association of the triglyceride and glucose index with low muscle mass: KNHANES 2008–2011
Jung A. Kim, Soon Young Hwang, Ji Hee Yu, Eun Roh, So-hyeon Hong, You-Bin Lee, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The triglycerides and glucose index is strongly associated with hepatic steatosis in children with overweight or obesity
Luis E. Simental-Mendía, César Javier Ortega-Pacheco, Elvira García-Guerrero, María Alejandra Sicsik-Aragón, Fernando Guerrero-Romero, Gerardo Martínez-Aguilar
European Journal of Pediatrics.2021; 180(6): 1755. CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index and the risk of stroke and its subtypes in the general population: an 11-year follow-up
Anxin Wang, Guangyao Wang, Qian Liu, Yingting Zuo, Shuohua Chen, Boni Tao, Xue Tian, Penglian Wang, Xia Meng, Shouling Wu, Yongjun Wang, Yilong Wang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Triglyceride Glucose Index and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Risk in Chinese Population
Xin Yan, Yujuan Gao, Jingzhi Tong, Mi Tian, Jinghong Dai, Yi Zhuang
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride Glucose Index Is Associated With Arterial Stiffness and 10-Year Cardiovascular Disease Risk in a Chinese Population
Wen Guo, Wenfang Zhu, Juan Wu, Xiaona Li, Jing Lu, Pei Qin, Cheng Zhu, Nianzhen Xu, Qun Zhang
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - An Analysis of the Potential Relationship of Triglyceride Glucose and Body Mass Index With Stroke Prognosis
Zongyi Hou, Yuesong Pan, Yindong Yang, Xiaofan Yang, Xianglong Xiang, Yilong Wang, Zixiao Li, Xingquan Zhao, Hao Li, Xia Meng, Yongjun Wang
Frontiers in Neurology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals in the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Comprehensive Review
Raquel Cano, José Pérez, Lissé Dávila, Ángel Ortega, Yosselin Gómez, Nereida Valero-Cedeño, Heliana Parra, Alexander Manzano, Teresa Véliz Castro, María Albornoz, Gabriel Cano, Joselyn Rojas-Quintero, Maricarmen Chacín, Valmore Bermúdez
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(9): 4807. CrossRef - Triglyceride glucose (TyG) index and the progression of liver fibrosis: A cross-sectional study
Helda Tutunchi, Fatemeh Naeini, Majid Mobasseri, Alireza Ostadrahimi
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2021; 44: 483. CrossRef - Newly proposed insulin resistance indexes called TyG-NC and TyG-NHtR show efficacy in diagnosing the metabolic syndrome
M. Mirr, D. Skrypnik, P. Bogdański, M. Owecki
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2021; 44(12): 2831. CrossRef - Association Between the Triglyceride–Glucose Index and Outcomes of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Large-Scale Health Management Cohort Study
Jing Liu, Liying Guan, Meng Zhao, Qihang Li, An Song, Ling Gao, Haiyan Lin, Jiajun Zhao
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 2829. CrossRef - Association between triglyceride-glucose index and thyroid function in euthyroid adults: The Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey 2015
Wonsuk Choi, Ji Yong Park, A. Ram Hong, Jee Hee Yoon, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sun Young Lee
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(7): e0254630. CrossRef - Triglyceride glucose-waist to height ratio: a novel and effective marker for identifying hepatic steatosis in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Mojtaba Malek, Mohammad E. Khamseh, Haleh Chehrehgosha, Sohrab Nobarani, Fariba Alaei-Shahmiri
Endocrine.2021; 74(3): 538. CrossRef - The association between triglyceride-glucose index, cardio-cerebrovascular diseases, and death in Korean adults: A retrospective study based on the NHIS-HEALS cohort
Joungyoun Kim, Sang-Jun Shin, Hee-Taik Kang, Claudio Passino
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(11): e0259212. CrossRef - A population-based study of TyG index distribution and its relationship to cardiometabolic risk factors in children and adolescents
Jong Seo Yoon, Young Suk Shim, Hae Sang Lee, Il Tae Hwang, Jin Soon Hwang
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of several blood lipid-related indexes in the screening of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in women: a cross-sectional study in the Pearl River Delta region of southern China
Jingrui Wang, Zhenzhen Su, Yijin Feng, Ruihan Xi, Jiamin Liu, Peixi Wang
BMC Gastroenterology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The value of the triglyceride-glucose index in the diagnosis of insulin resistance in early forms of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
A. A. Shipovskaya, N. A. Larina, I. V. Kurbatova, O. P. Dudanova
Experimental and Clinical Gastroenterology.2021; (10): 43. CrossRef - Triglyceride Glucose-Waist Circumference Is Superior to the Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance in Identifying Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Healthy Subjects
Hwi Seung Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Chang Hee Jung, Joong-Yeol Park, Hong-Kyu Kim, Woo Je Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 11(1): 41. CrossRef - Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance and lobular inflammation in nondiabetic patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: methodological considerations
Denis Monneret, Dominique Bonnefont-Rousselot
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2020; 32(4): 542. CrossRef - Helicobacter pylori infection may increase the severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via promoting liver function damage, glycometabolism, lipid metabolism, inflammatory reaction and metabolic syndrome
Chen Chen, Caiyun Zhang, Xuelin Wang, Feijuan Zhang, Ze Zhang, Pengchai Ma, Shuzhi Feng
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2020; 32(7): 857. CrossRef - Beneficial effect of anti-diabetic drugs for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung-Soo Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2020; 26(4): 430. CrossRef - The triglyceride-glucose index is associated with the severity of hepatic steatosis and the presence of liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a cross-sectional study in Chinese adults
Wen Guo, Jing Lu, Pei Qin, Xiaona Li, Wenfang Zhu, Juan Wu, Nianzhen Xu, Qun Zhang
Lipids in Health and Disease.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between triglyceride glucose-body mass index and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the non-obese Chinese population with normal blood lipid levels: a secondary analysis based on a prospective cohort study
Yaling Li, Rui Zheng, Jie Li, Shuyi Feng, Li Wang, Zhiming Huang
Lipids in Health and Disease.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Triglyceride-glucose body mass index predicts prognosis in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Myths about Insulin Resistance: Tribute to Gerald Reaven
- Sun H. Kim, Fahim Abbasi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(1):47-52. Published online March 21, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.1.47
- 6,722 View
- 143 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Gerald Reaven was often called the “father of insulin resistance.” On the 1-year anniversary of his death in 2018, we challenge three myths associated with insulin resistance: metformin improves insulin resistance; measurement of waist circumference predicts insulin resistance better than body mass index; and insulin resistance causes weight gain. In this review, we highlight Reaven's relevant research that helped to dispel these myths associated with insulin resistance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of Antidiabetic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Carissa carandas Linn Extract: In Vitro and In Vivo Study
Manaschanok Lailerd, Thiri Wai Linn, Narissara Lailerd, Duangporn Amornlerdpison, Arisa Imsumran
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(11): 6454. CrossRef - Association of primary allostatic load mediators and metabolic syndrome (MetS): A systematic review
Francis Osei, Andrea Block, Pia-Maria Wippert
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Anthropometric indices and the risk of incident sudden cardiac death among adults with and without diabetes: over 15 years of follow-up in The Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study
Seyyed Saeed Moazzeni, Seyed Saeed Tamehri Zadeh, Samaneh Asgari, Fereidoun Azizi, Farzad Hadaegh
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome or Insulin Resistance: Evolution, Controversies and Association With Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Arun K. Chopra
Indian Journal of Clinical Cardiology.2020; 1(2): 77. CrossRef
- Assessment of Antidiabetic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Carissa carandas Linn Extract: In Vitro and In Vivo Study

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Implications of Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response and Mitokines: A Perspective on Fatty Liver Diseases
- Hyon-Seung Yi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(1):39-46. Published online March 21, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.1.39
- 5,881 View
- 140 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 25 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub The signaling network of the mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) and mitohormesis is a retrograde signaling pathway through which mitochondria-to-nucleus communication occurs in organisms. Recently, it has been shown that the UPRmt is closely associated with metabolic disorders and conditions involving insulin resistance, such as alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver and fibrotic liver disease. Scientific efforts to understand the UPRmt and mitohormesis, as well as to establish the mitochondrial proteome, have established the importance of mitochondrial quality control in the development and progression of metabolic liver diseases, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). In this review, we integrate and discuss the recent data from the literature on the UPRmt and mitohormesis in metabolic liver diseases, including NAFLD/NASH and fibrosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Aberrant mitochondrial aggregation of TDP-43 activated mitochondrial unfolded protein response and contributed to recovery of acetaminophen induced acute liver injury
Zhaoxiong Liu, Yalong Qiang, Shulin Shan, Shuai Wang, Zhidan Liu, Yiyu Yang, Zhengcheng Huang, Mingxue Song, Xiulan Zhao, Fuyong Song
Toxicology Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Autophagy and the unfolded protein response shape the non-alcoholic fatty liver landscape: decoding the labyrinth
Zahra Dashti, Zeynab Yousefi, Pouria Kiani, Motahareh Taghizadeh, Mohammad Hasan Maleki, Mohammad Borji, Omid Vakili, Sayed Mohammad Shafiee
Metabolism.2024; 154: 155811. CrossRef - Recent progress in understanding mitokines as diagnostic and therapeutic targets in hepatocellular carcinoma
Jiang Wang, Lan-Zhu Luo, Dao-Miao Liang, Chao Guo, Zhi-Hong Huang, Xiao-Hong Jian, Jie Wen
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2023; 11(23): 5416. CrossRef - From Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver to Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Story of (Mal)Adapted Mitochondria
Ricardo Amorim, Carina C. Magalhães, Fernanda Borges, Paulo J. Oliveira, José Teixeira
Biology.2023; 12(4): 595. CrossRef - Natural Drugs: A New Direction for the Prevention and Treatment of Diabetes
Peishan Wu, Xiaolei Wang
Molecules.2023; 28(14): 5525. CrossRef - Mitochondrial Quality Control via Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response (mtUPR) in Ageing and Neurodegenerative Diseases
Paula Cilleros-Holgado, David Gómez-Fernández, Rocío Piñero-Pérez, Jose Manuel Romero-Domínguez, Diana Reche-López, Alejandra López-Cabrera, Mónica Álvarez-Córdoba, Manuel Munuera-Cabeza, Marta Talaverón-Rey, Alejandra Suárez-Carrillo, Ana Romero-González
Biomolecules.2023; 13(12): 1789. CrossRef - Heat Shock Protein 60 Restricts Release of Mitochondrial dsRNA to Suppress Hepatic Inflammation and Ameliorate Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice
Ying-Hsien Huang, Feng-Sheng Wang, Pei-Wen Wang, Hung-Yu Lin, Sheng-Dean Luo, Ya-Ling Yang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(1): 577. CrossRef - UPRmt activation improves pathological alterations in cellular models of mitochondrial diseases
Juan M. Suárez-Rivero, Carmen J. Pastor-Maldonado, Suleva Povea-Cabello, Mónica Álvarez-Córdoba, Irene Villalón-García, Marta Talaverón-Rey, Alejandra Suárez-Carrillo, Manuel Munuera-Cabeza, Diana Reche-López, Paula Cilleros-Holgado, Rocío Piñero-Perez, J
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Umbilical Cord-Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Improves Insulin Resistance in C2C12 Cell
Kyung-Soo Kim, Yeon Kyung Choi, Mi Jin Kim, Jung Wook Hwang, Kyunghoon Min, Sang Youn Jung, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Soo Choi, Yong-Wook Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 260. CrossRef - Mitochondrial unfolded protein response: An emerging pathway in human diseases
Li Zhu, Qionglin Zhou, Lu He, Linxi Chen
Free Radical Biology and Medicine.2021; 163: 125. CrossRef - Mitochondrial dynamics and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): new perspectives for a fairy-tale ending?
Miriam Longo, Marica Meroni, Erika Paolini, Chiara Macchi, Paola Dongiovanni
Metabolism.2021; 117: 154708. CrossRef - Mitochondrial unfolded protein response: A novel pathway in metabolism and immunity
Li Zhu, Xuling Luo, Nian Fu, Linxi Chen
Pharmacological Research.2021; 168: 105603. CrossRef - Mitochondrial Metabolic Signatures in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Ho-Yeop Lee, Ha Thi Nga, Jingwen Tian, Hyon-Seung Yi
Cells.2021; 10(8): 1901. CrossRef - Cnm1 mediates nucleus–mitochondria contact site formation in response to phospholipid levels
Michal Eisenberg-Bord, Naama Zung, Javier Collado, Layla Drwesh, Emma J. Fenech, Amir Fadel, Nili Dezorella, Yury S. Bykov, Doron Rapaport, Ruben Fernandez-Busnadiego, Maya Schuldiner
Journal of Cell Biology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Carnitine Orotate Complex in Fatty Liver
Hyon-Seung Yi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 866. CrossRef - Serum GDF15 Level Is Independent of Sarcopenia in Older Asian Adults
Ha Thi Nga, Il-Young Jang, Da Ae Kim, So Jeong Park, Jin Young Lee, Seungjoo Lee, Jeoung Hee Kim, Eunju Lee, Jin Hoon Park, Young-Ho Lee, Hyon-Seung Yi, Beom-Jun Kim
Gerontology.2021; 67(5): 525. CrossRef - Exogenous Therapeutics of Microrna-29a Attenuates Development of Hepatic Fibrosis in Cholestatic Animal Model through Regulation of Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase p85 Alpha
Ya-Ling Yang, Feng-Sheng Wang, Hung-Yu Lin, Ying-Hsien Huang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(10): 3636. CrossRef - High-altitude chronic hypoxia ameliorates obesity-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice by regulating mitochondrial and AMPK signaling
Kang Song, Yifan Zhang, Qin Ga, Zhenzhong Bai, Ri-Li Ge
Life Sciences.2020; 252: 117633. CrossRef - NRF-2 and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Arturo Solano-Urrusquieta, José A. Morales-González, Graciela E. Castro-Narro, Eira Cerda-Reyes, Perla D. Flores-Rangel, Raul Fierros-Oceguera
Annals of Hepatology.2020; 19(5): 458. CrossRef - Mitochondrial Quality Control in the Heart: New Drug Targets for Cardiovascular Disease
Chang-Myung Oh, Dongryeol Ryu, Sungsoo Cho, Yangsoo Jang
Korean Circulation Journal.2020; 50(5): 395. CrossRef - Growth differentiation factor 15 protects against the aging‐mediated systemic inflammatory response in humans and mice
Ji Sun Moon, Ludger J. E. Goeminne, Jung Tae Kim, Jing Wen Tian, Seok‐Hwan Kim, Ha Thi Nga, Seul Gi Kang, Baeki E. Kang, Jin‐Seok Byun, Young‐Sun Lee, Jae‐Han Jeon, Minho Shong, Johan Auwerx, Dongryeol Ryu, Hyon‐Seung Yi
Aging Cell.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - miR-29a Modulates GSK3β/SIRT1-Linked Mitochondrial Proteostatic Stress to Ameliorate Mouse Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
Ya-Ling Yang, Pei-Wen Wang, Feng-Sheng Wang, Hung-Yu Lin, Ying-Hsien Huang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(18): 6884. CrossRef - Impact of Mitophagy and Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response as New Adaptive Mechanisms Underlying Old Pathologies: Sarcopenia and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Rodrigo Urbina-Varela, Nataly Castillo, Luis A. Videla, Andrea del Campo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(20): 7704. CrossRef - Molecular insights into the role of mitochondria in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Jin Lee, Jeong-Su Park, Yoon Seok Roh
Archives of Pharmacal Research.2019; 42(11): 935. CrossRef - A siRNA mediated hepatic dpp4 knockdown affects lipid, but not glucose metabolism in diabetic mice
Sven Wolfgang Görgens, Kerstin Jahn-Hofmann, Dinesh Bangari, Sheila Cummings, Christiane Metz-Weidmann, Uwe Schwahn, Paulus Wohlfart, Matthias Schäfer, Maximilian Bielohuby, Marcia B. Aguila
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(12): e0225835. CrossRef
- Aberrant mitochondrial aggregation of TDP-43 activated mitochondrial unfolded protein response and contributed to recovery of acetaminophen induced acute liver injury

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Metabolic Syndrome and Insulin Resistance Syndrome among Infertile Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study from Central Vietnam
- Minh Tam Le, Vu Quoc Huy Nguyen, Quang Vinh Truong, Dinh Duong Le, Viet Nguyen Sa Le, Ngoc Thanh Cao
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(4):447-458. Published online November 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.4.447
- 4,352 View
- 78 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common endocrinopathies among reproductive-age women. Its metabolic features often overlap with those associated with metabolic syndrome (MS) and insulin resistance syndrome (IRS). The objective of this study was to determine the prevalence and predictors of MS and IRS in infertile Vietnamese women with PCOS.
Methods A cross-sectional study was conducted at a tertiary fertility centre at Hue University Hospital from June 2016 to November 2017. A total of 441 infertile women diagnosed with PCOS based on the revised 2003 Rotterdam consensus criteria were enrolled. MS and IRS were defined based on the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/American Heart Association Adult Treatment Panel III 2005 and American College of Endocrinology IRS 2003 criteria, respectively. Complete clinical and biochemical measurements of 318 women were available for analysis. Independent predictors of MS and IRS were identified using multivariate logistic regression.
Results The overall prevalence of MS and IRS in women with PCOS was 10.4% and 27.0%, respectively. We identified older age (>30 years) and obesity as independent predictors of MS and IRS. Elevated anti-Müllerian hormone levels increased the risk of IRS, but not that of MS.
Conclusion MS and IRS are prevalent disorders among infertile Vietnamese women with PCOS. PCOS is not solely a reproductive problem. Screening and early intervention for MS and/or IRS based on anthropometric, metabolic, and reproductive hormone risk factors should be an integral part of fertility care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Role of the tripartite motif‐containing (TRIM) family of proteins in insulin resistance and related disorders
Jianrong Chen, Xianjie Feng, Xu Zhou, Yong Li
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(1): 3. CrossRef - Effect of pharmacological interventions on lipid profiles and C‐reactive protein in polycystic ovary syndrome: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Mohammed A. Abdalla, Najeeb Shah, Harshal Deshmukh, Amirhossein Sahebkar, Linda Östlundh, Rami H. Al‐Rifai, Stephen L. Atkin, Thozhukat Sathyapalan
Clinical Endocrinology.2022; 96(4): 443. CrossRef - A Cross-Sectional Study of Serum Ferritin Levels in Vietnamese Adults with Metabolic Syndrome
Thua Nguyen Tran, Huu Dang Tran, Thanh Tung Tran-Huu, Duc Minh Tran, Quang Nhat Tran
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 1517. CrossRef - The effects of metformin on clinical features, endocrine and metabolic profiles of infertile women with polycystic ovary syndrome
Sa Le Viet
Journal of Clinical Medicine- Hue Central Hospital.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Uric acid metabolism in polycystic ovary syndrome
Yan-Nan Liu, Hai Luo, Xuan Che, Hui Peng, Ming Li, Ke-Xuan Liu
Clinica Chimica Acta.2021; 517: 74. CrossRef - PREVALENCE OF METABOLIC SYNDROME AND INSULIN RESISTANCE AMONG PCOS WOMEN ATTENDING TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL IN NORTH INDIAN POPULATION.
Anita R Bhatia, Peyir Bagra, Jyotsna Suri, Rajni Dawar
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2021; : 35. CrossRef - “Obesity and Insulin Resistance” Is the Component of the Metabolic Syndrome Most Strongly Associated with Oxidative Stress
Grzegorz K. Jakubiak, Kamila Osadnik, Mateusz Lejawa, Tadeusz Osadnik, Marcin Goławski, Piotr Lewandowski, Natalia Pawlas
Antioxidants.2021; 11(1): 79. CrossRef - Correlation between serum AMH levels and cardiometabolic indices in PCOS women
Subarna Mitra, GautomK Saharia, SaubhagyaK Jena
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 25(6): 545. CrossRef - Predicting Risk of Insulin Resistance in a Chinese Population with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Designing and Testing a New Predictive Nomogram
Feng Jiang, Ke Wei, Wenjun Lyu, Chuyan Wu
BioMed Research International.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Association of the Genetic Polymorphisms rs6259 and rs727428 of the SHBG Gene with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Risk: A Meta-Analysis
Xihong Liao, Shujun Cao
Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers.2020; 24(8): 492. CrossRef - The relationship between glomerular filtration rate, and metabolic and inflammatory parameters in obese and non-obese patients with polycystic ovary syndrome
Mustafa Can, Cevdet Duran, Ibrahim Guney, Halis Elmas, Mehmet Ayhan, Said Sami Erdem
Clínica e Investigación en Arteriosclerosis.2020; 32(6): 256. CrossRef - Effect of Central Obesity and Hyperandrogenism on Selected Inflammatory Markers in Patients with PCOS: A WHtR-Matched Case-Control Study
Małgorzata Kałużna, Magdalena Człapka-Matyasik, Katarzyna Wachowiak-Ochmańska, Jerzy Moczko, Jolanta Kaczmarek, Adam Janicki, Katarzyna Piątek, Marek Ruchała, Katarzyna Ziemnicka
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(9): 3024. CrossRef - The relationship between glomerular filtration rate, and metabolic and inflammatory parameters in obese and non-obese patients with polycystic ovary syndrome
Mustafa Can, Cevdet Duran, Ibrahim Guney, Halis Elmas, Mehmet Ayhan, Said Sami Erdem
Clínica e Investigación en Arteriosclerosis (English Edition).2020; 32(6): 256. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia involvement in the development of polycystic ovary syndrome
Qi Liu, Yuan-jie Xie, Li-hua Qu, Meng-xia Zhang, Zhong-cheng Mo
Taiwanese Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.2019; 58(4): 447. CrossRef
- Role of the tripartite motif‐containing (TRIM) family of proteins in insulin resistance and related disorders


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



