Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
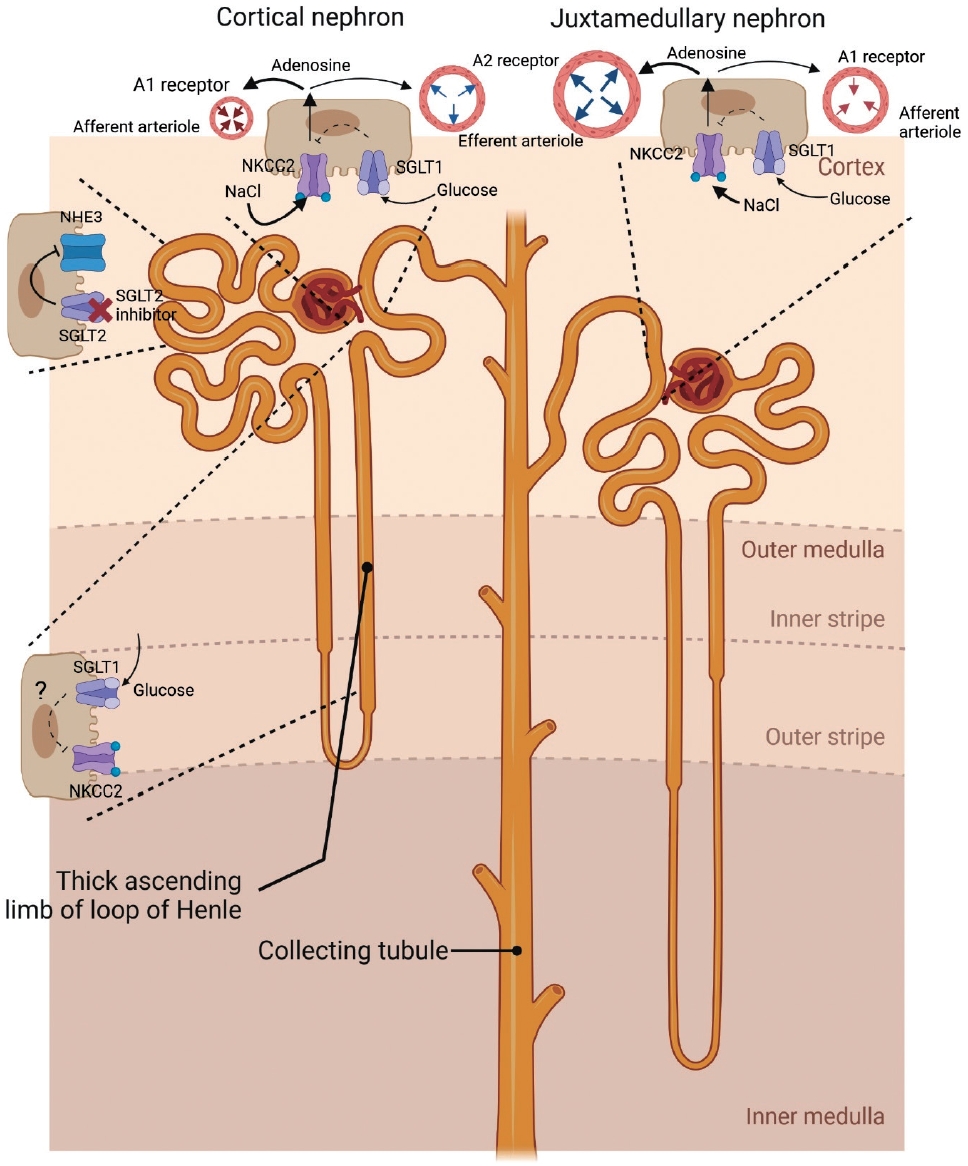
- Intrarenal Mechanisms of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors on Tubuloglomerular Feedback and Natriuresis
- Eun Sil Koh, Gheun-Ho Kim, Sungjin Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):359-372. Published online July 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1764
- 2,755 View
- 444 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - When sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors were first introduced a decade ago, no one expected them to have substantial effects beyond their known glucose-lowering effects, until the emergence of evidence of their robust renal and cardiovascular benefits showing that they could attenuate progression of kidney disease, irrespective of diabetes, as well as prevent the development of acute kidney injury. Still, the precise and elaborate mechanisms underlying the major organ protection of SGLT2 inhibitors remain unclear. SGLT2 inhibitors inhibit the reabsorption of sodium and glucose in the proximal tubule of the kidney and then recovers tubuloglomerular feedback, whereby SGLT2 inhibitors reduce glomerular hyperfiltration. This simple demonstration of their beneficial effects has perplexed experts in seeking more plausible and as yet undisclosed explanations for the whole effects of SGLT2 inhibitors, including metabolism reprogramming and the modulation of hypoxia, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Given that the renal benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with kidney disease but without diabetes were comparable to those seen in patients with diabetes, it may be reasonable to keep the emphasis on their hemodynamic actions. In this context, the aim of the present review is to provide a comprehensive overview of renal hemodynamics in individuals with diabetes who are treated with SGLT2 inhibitors, with a focus on natriuresis associated with the regulation of tubuloglomerular feedback and potential aquaresis. Throughout the discussion of alterations in renal sodium and water transports, particular attention will be given to the potential enhancement of adenosine and its receptors following SGLT2 inhibition.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Results from a cross-specialty consensus on optimal management of patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD): from screening to complications
Mustafa Arici, Samir Helmy Assaad-Khalil, Marcello Casaccia Bertoluci, Jason Choo, Yau-Jiunn Lee, Magdalena Madero, Guillermo Javier Rosa Diez, Vicente Sánchez Polo, Sungjin Chung, Teerawat Thanachayanont, Carol Pollock
BMJ Open.2024; 14(3): e080891. CrossRef - Chronic Kidney Disease and SGLT2 Inhibitors
Eun Sil Koh, Sungjin Chung
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2024; 25(1): 16. CrossRef - Genitourinary Tract Infections in Patients Taking SGLT2 Inhibitors
Veraprapas Kittipibul, Zachary L. Cox, Supavit Chesdachai, Mona Fiuzat, JoAnn Lindenfeld, Robert J. Mentz
Journal of the American College of Cardiology.2024; 83(16): 1568. CrossRef - Synopsis of the Korean Society of Nephrology 2023 Practical Recommendations for the Management of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Sungjin Chung
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2023; 98(6): 270. CrossRef
- Results from a cross-specialty consensus on optimal management of patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD): from screening to complications

Original Article
- Clinical Study
- Glycemic Efficacy and Metabolic Consequences of an Empagliflozin Add-on versus Conventional Dose-Increasing Strategy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled by Metformin and Sulfonylurea
- Yujin Shin, Ji Hye Moon, Ho Jun Chin, Ele Ferrannini, Soo Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):329-338. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.329
- 6,605 View
- 215 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We assessed the glucose-lowering efficacy of adding empagliflozin versus dose escalating existing medications in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Methods
This was a 6-month retrospective case-control study in subjects with uncontrolled T2D (glycated hemoglobin [HbA1c] >7%) on conventional treatment. The study group started add-on therapy with empagliflozin (10 mg once a day) while the control group was up-titrated with existing medication, using either monotherapy or a combination of metformin, sulfonylurea, and a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor. The primary endpoints included changes in HbA1c, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and 2-hour postprandial glucose (PP2) levels. Secondary outcomes included changes in body composition, body mass index (BMI), and serum ketone bodies, and urinary excretion of sodium, potassium, chlorine, calcium, phosphorus, and glucose.
Results
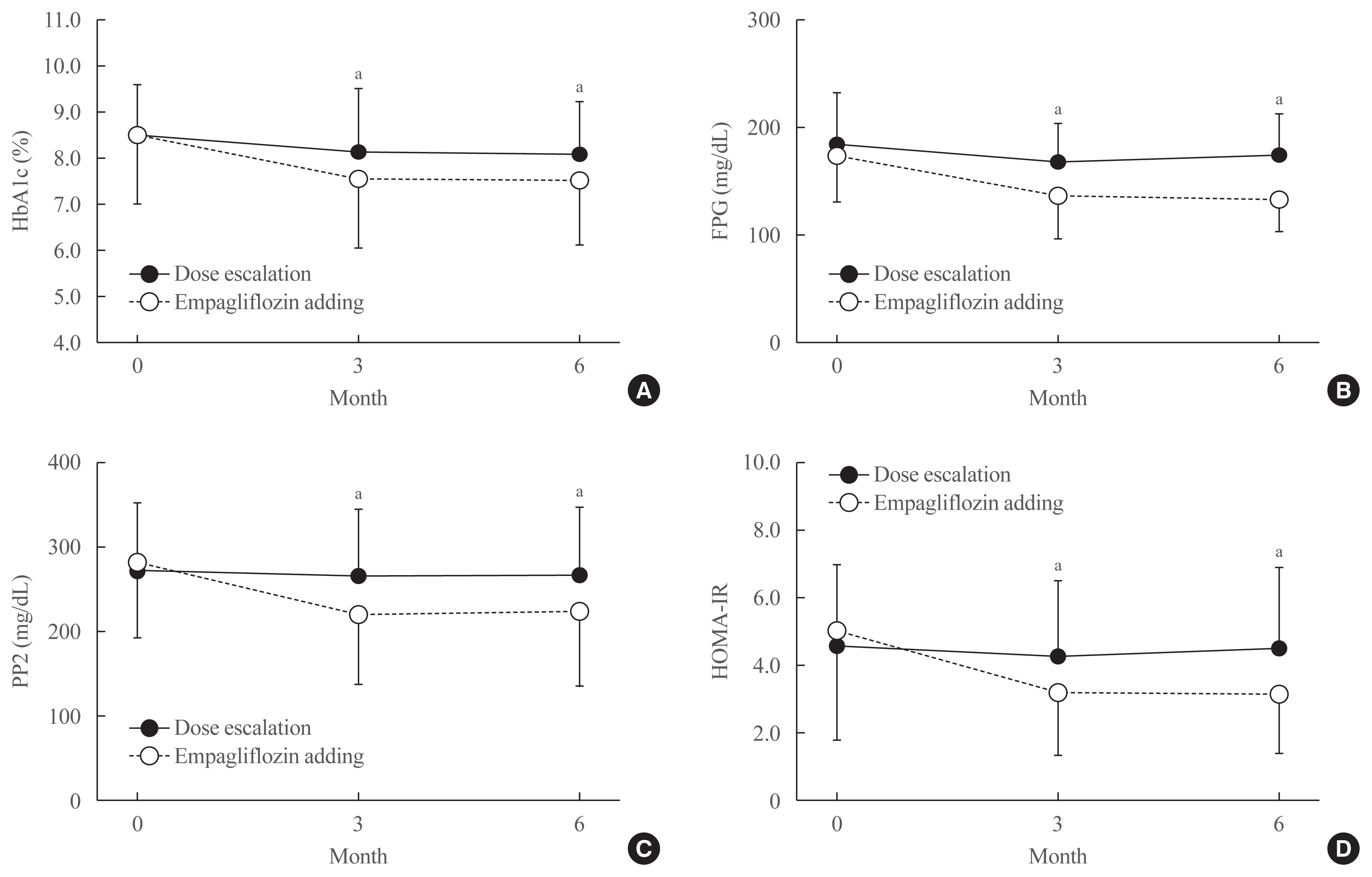
After treatment, the reduction in HbA1c was significantly greater in the empagliflozin group than in controls (from 8.6%±1.6% to 7.6%±1.5% vs. 8.5%±1.1% to 8.1%±1.1%; P<0.01). Similar patterns were found in FPG and PP2 levels. Empagliflozin decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure, triglycerides, and alanine and aspartate aminotransferase levels. Body weight, BMI, waist circumference, fat mass, and abdominal visceral fat area decreased significantly while lean body mass was maintained. Total ketones, β-hydroxybutyrate, and acetoacetate levels increased significantly after empagliflozin.
Conclusion
In addition to glucose lowering, an empagliflozin add-on regimen decreased blood pressure and body fat, and improved metabolic profiles significantly. Empagliflozin add-on is superior to dose escalation in patients with T2D who have inadequate glycemic control on standard medications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Independent association of thigh muscle fat density with vascular events in Korean adults
Hun Jee Choe, Won Chang, Matthias Blüher, Steven B. Heymsfield, Soo Lim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, Empagliflozin, is associated with significant reduction in weight, body mass index, fasting glucose, and A1c levels in Type 2 diabetic patients with established coronary heart disease: the SUPER GATE study
Satilmis Bilgin, Ozge Kurtkulagi, Tuba Taslamacioglu Duman, Burcin Meryem Atak Tel, Gizem Kahveci, Murat Kiran, Eray Erge, Gulali Aktas
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2022; 191(4): 1647. CrossRef - A randomized clinical trial evaluating the effect of empagliflozin on triglycerides in obese adults: Role of visceral fat
Min Hee Lee, Ian J. Neeland, Natalia de Albuquerque Rocha, Connor Hughes, Craig R. Malloy, Eunsook S. Jin
Metabolism Open.2022; 13: 100161. CrossRef - Initial combination of metformin, sitagliptin, and empagliflozin in drug‐naïve patients with type 2 diabetes: Safety and metabolic effects
Soo Lim, Minji Sohn, Yujin Shin, Ele Ferrannini
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(4): 757. CrossRef - Correlation of dynamic membrane fluctuations in red blood cells with diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular risks
Minji Sohn, Ji Eun Lee, MinGeun Ahn, YongKeun Park, Soo Lim
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison betweeen dapagliflozin add-on therapy and insulin dose escalation in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes treated with insulin: DVI study
Yujin Shin, Haeri Choi, Soo Lim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 175: 108843. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 and Associated Preventive Measures on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in South Korea
Minji Sohn, Bo Kyung Koo, Ho Il Yoon, Kyoung-Ho Song, Eu Suk Kim, Hong Bin Kim, Soo Lim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2021; 30(3): 248. CrossRef
- Independent association of thigh muscle fat density with vascular events in Korean adults


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



