Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Based Therapies: A New Horizon in Obesity Management
- Jang Won Son, Soo Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(2):206-221. Published online April 16, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2024.1940
- 449 View
- 58 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
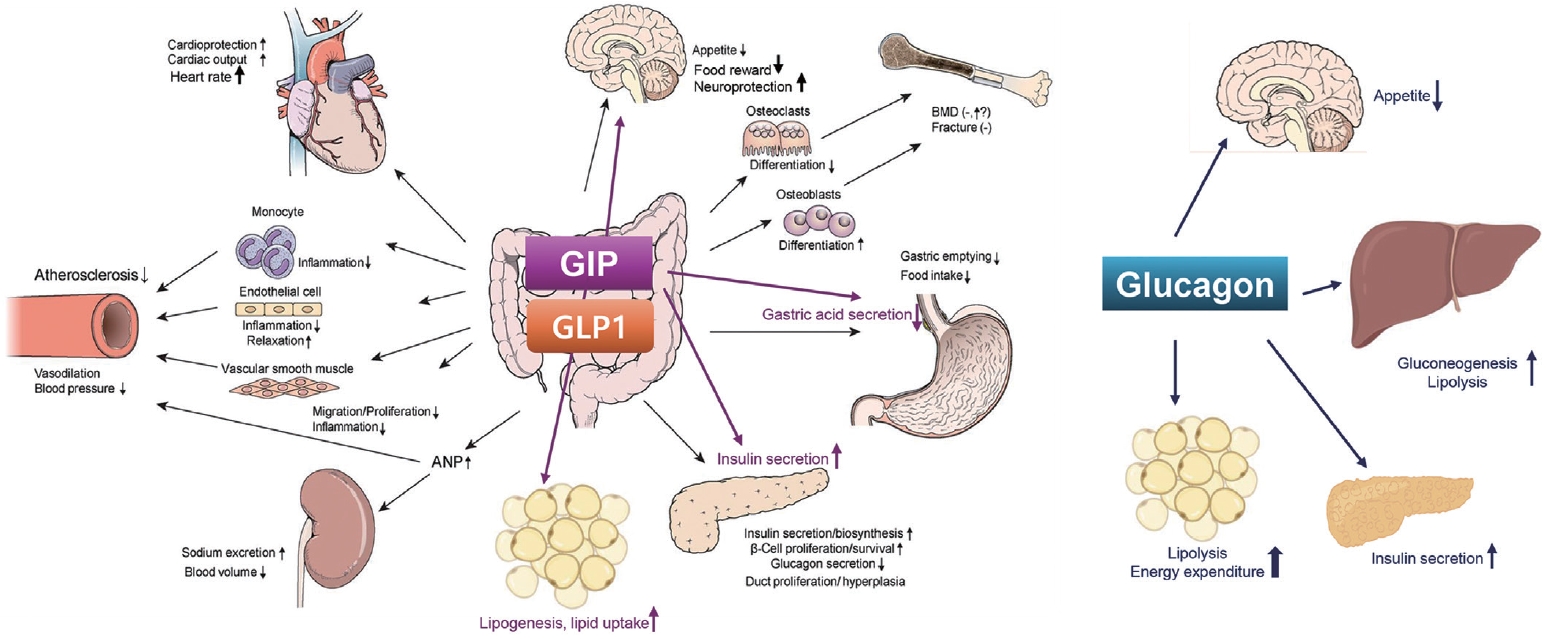
ePub - Obesity is a significant risk factor for health issues like type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. It often proves resistant to traditional lifestyle interventions, prompting a need for more precise therapeutic strategies. This has led to a focus on signaling pathways and neuroendocrine mechanisms to develop targeted obesity treatments. Recent developments in obesity management have been revolutionized by introducing novel glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) based drugs, such as semaglutide and tirzepatide. These drugs are part of an emerging class of nutrient-stimulated hormone-based therapeutics, acting as incretin mimetics to target G-protein–coupled receptors like GLP-1, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), and glucagon. These receptors are vital in regulating body fat and energy balance. The development of multiagonists, including GLP-1–glucagon and GIP–GLP-1–glucagon receptor agonists, especially with the potential for glucagon receptor activation, marks a significant advancement in the field. This review covers the development and clinical efficacy of various GLP-1-based therapeutics, exploring the challenges and future directions in obesity management.

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Dulaglutide Ameliorates Palmitic Acid-Induced Hepatic Steatosis by Activating FAM3A Signaling Pathway
- Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Min-Jeong Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):74-83. Published online February 9, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1293
- 4,881 View
- 235 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
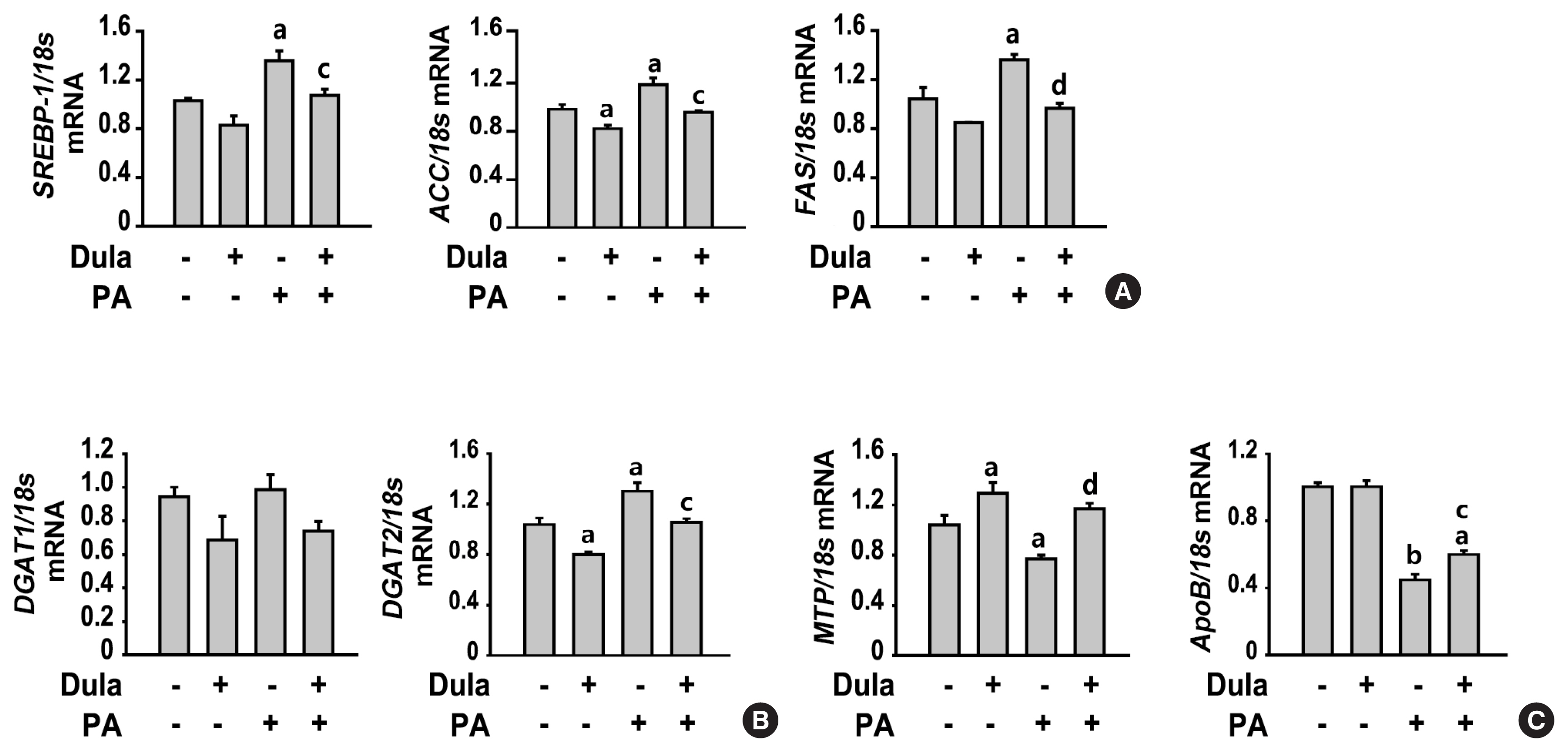
Dulaglutide, a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA), has been shown to reduce body weight and liver fat content in patients with type 2 diabetes. Family with sequence similarity 3 member A (FAM3A) plays a vital role in regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. The aim of this study was to determine the mechanisms by which dulaglutide protects against hepatic steatosis in HepG2 cells treated with palmitic acid (PA).
Methods
HepG2 cells were pretreated with 400 μM PA for 24 hours, followed by treatment with or without 100 nM dulaglutide for 24 hours. Hepatic lipid accumulation was determined using Oil red O staining and triglyceride (TG) assay, and the expression of lipid metabolism-associated factor was analyzed using quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting.
Results
Dulaglutide significantly decreased hepatic lipid accumulation and reduced the expression of genes associated with lipid droplet binding proteins, de novo lipogenesis, and TG synthesis in PA-treated HepG2 cells. Dulaglutide also increased the expression of proteins associated with lipolysis and fatty acid oxidation and FAM3A in PA-treated cells. However, exendin-(9-39), a GLP-1R antagonist, reversed the expression of FAM3A, and fatty acid oxidation-associated factors increased due to dulaglutide. In addition, inhibition of FAM3A by siRNA attenuated the reducing effect of dulaglutide on TG content and its increasing effect on regulation of fatty acid oxidation.
Conclusion
These results suggest that dulaglutide could be used therapeutically for improving nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and its effect could be mediated in part via upregulation of FAM3A expression through a GLP-1R-dependent pathway. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- GLP-1/GLP-1RAs: New Options for the Drug Treatment of NAFLD
Haoran Jiang, Linquan Zang
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2024; 30(2): 100. CrossRef - GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives
Riccardo Nevola, Raffaella Epifani, Simona Imbriani, Giovanni Tortorella, Concetta Aprea, Raffaele Galiero, Luca Rinaldi, Raffaele Marfella, Ferdinando Carlo Sasso
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(2): 1703. CrossRef - FAM3A mediates the phenotypic switch of human aortic smooth muscle cells stimulated with oxidised low-density lipoprotein by influencing the PI3K-AKT pathway
Lei Yang, Baoshun Du, Shitao Zhang, Maode Wang
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal.2023; 59(6): 431. CrossRef - ATP Secretion and Metabolism in Regulating Pancreatic Beta Cell Functions and Hepatic Glycolipid Metabolism
Jing Li, Han Yan, Rui Xiang, Weili Yang, Jingjing Ye, Ruili Yin, Jichun Yang, Yujing Chi
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeted therapeutics and novel signaling pathways in non-alcohol-associated fatty liver/steatohepatitis (NAFL/NASH)
Xiaohan Xu, Kyle L. Poulsen, Lijuan Wu, Shan Liu, Tatsunori Miyata, Qiaoling Song, Qingda Wei, Chenyang Zhao, Chunhua Lin, Jinbo Yang
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- GLP-1/GLP-1RAs: New Options for the Drug Treatment of NAFLD

- Diabetes
- Cardiorenal Protection in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Jason F. Lee, Ecaterina Berzan, Vikas S. Sridhar, Ayodele Odutayo, David Z.I. Cherney
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(2):256-269. Published online April 19, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.987
- 5,721 View
- 300 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
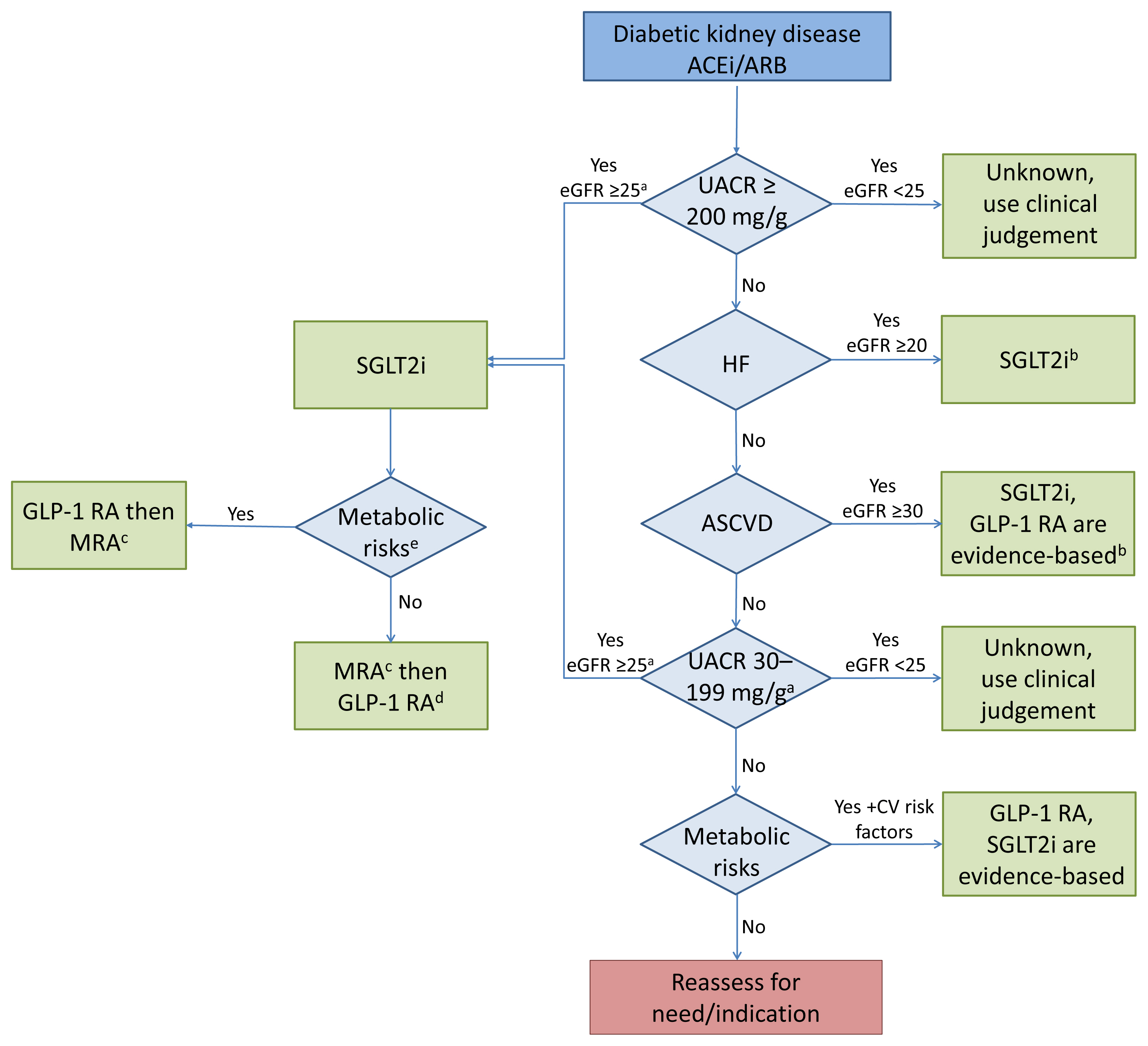
ePub - Over the last 5 years there have been many new developments in the management of diabetic kidney disease. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors were initially used for glycemic control, but more recent studies have now shown that their benefits extend to cardiovascular and kidney outcomes. The recent addition of data on the novel mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) gives us another approach to further decrease the residual risk of diabetic kidney disease progression. In this review we describe the mechanism of action, key studies, and possible adverse effects related to these three classes of medications. The management of type 2 diabetes now includes an increasing number of medications for the management of comorbidities in a patient population at significant risk of cardiovascular disease and progression of chronic kidney disease. It is from this perspective that we seek to outline the rationale for the sequential and/or combined use of SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 RA and MRAs in patients with type 2 diabetes for heart and kidney protection.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relative and Absolute Risks of Adverse Events with Real-World Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in CKD
Ayodele Odutayo, Adeera Levin
Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.2023; 18(5): 557. CrossRef - Renal Protection of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist, Finerenone, in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Dong-Lim Kim, Seung-Eun Lee, Nan Hee Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 43. CrossRef - Intrarenal Mechanisms of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors on Tubuloglomerular Feedback and Natriuresis
Eun Sil Koh, Gheun-Ho Kim, Sungjin Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 359. CrossRef - SGLT2 and DPP4 inhibitors improve Alzheimer’s disease–like pathology and cognitive function through distinct mechanisms in a T2D–AD mouse model
A Young Sim, Da Hyun Choi, Jong Youl Kim, Eun Ran Kim, A-ra Goh, Yong-ho Lee, Jong Eun Lee
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 168: 115755. CrossRef - Narrative review investigating the nephroprotective mechanisms of sodium glucose cotransporter type 2 inhibitors in diabetic and nondiabetic patients with chronic kidney disease
Emma S. Speedtsberg, Martin Tepel
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of CKD
Nimrit Goraya, Jennifer D. Moran
Nephrology Self-Assessment Program.2022; 21(2): 146. CrossRef - Nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonism for cardiovascular and renal disorders − New perspectives for combination therapy
Peter Kolkhof, Amer Joseph, Ulrich Kintscher
Pharmacological Research.2021; 172: 105859. CrossRef - Sodium‐Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors, All‐Cause Mortality, and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Bayesian Meta‐Analysis and Meta‐Regression
Ayodele Odutayo, Bruno R. da Costa, Tiago V. Pereira, Vinay Garg, Samir Iskander, Fatimah Roble, Rahim Lalji, Cesar A. Hincapié, Aquila Akingbade, Myanca Rodrigues, Arnav Agarwal, Bishoy Lawendy, Pakeezah Saadat, Jacob A. Udell, Francesco Cosentino, Peter
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Finerenone: A Potential Treatment for Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Luis D’Marco, María Jesús Puchades, Lorena Gandía, Claudia Forquet, Elena Giménez-Civera, Nayara Panizo, Javier Reque, Isabel Juan-García, Valmore Bermúdez, José Luis Gorriz
touchREVIEWS in Endocrinology.2021; 17(2): 84. CrossRef - Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Mechanisms of Action: A Review
Jorge I. Fonseca-Correa, Ricardo Correa-Rotter
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Relative and Absolute Risks of Adverse Events with Real-World Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in CKD

- Diabetes
- Best Achievements in Clinical Medicine in Diabetes and Dyslipidemia in 2020
- Eun-Jung Rhee, Mee-Kyung Kim, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):41-50. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.106
- 4,302 View
- 178 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Over the last two decades, our understanding of diabetes and treatment strategies have evolved tremendously, from scientific, mechanistic, and human perspectives. The categories of anti-diabetic medications expanded from a few to numerous, enabling clinicians to personalize diabetes care and treatment. Thanks to rapid growth in the field of science and medical engineering, newer treatment options are coming to the market with various advantages and disadvantages to be aware of. Therefore, clinicians should rapidly adopt new trends based on guidelines and data from many clinical trials in the field of diabetes. In the treatment of dyslipidemia, trends and guidelines are changing every year, and novel therapies are being developed. In this review, we would like to summarize the major achievements in clinical medicine in 2020 in the field of diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin added to metformin plus gemigliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind, randomized, comparator-active study: ENHANCE-D study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Kyung Ah Han, Tae Nyun Kim, Cheol-Young Park, Jung Hwan Park, Sang Yong Kim, Yong Hyun Kim, Kee Ho Song, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Sik Kim, Gwanpyo Koh, Jun Goo Kang, Mi Kyung Kim, Ji Min Han, Nan Hee Kim, Ji Oh Mok, Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Lim, Sang S
Diabetes & Metabolism.2023; 49(4): 101440. CrossRef - Effects of exercise initiation and smoking cessation after new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus on risk of mortality and cardiovascular outcomes
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Jinyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined Effects of Obesity and Dyslipidaemia on the Prevalence of Diabetes Amongst Adults Aged ≥45 Years: Evidence from a Nationally Representative Cross-Sectional Study
Simin Zhang, Donghan Sun, Xiaoyi Qian, Li Li, Wenwen Wu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(13): 8036. CrossRef - Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level, Statin Use and Myocardial Infarction Risk in Young Adults
Heekyoung Jeong, Kyungdo Han, Soon Jib Yoo, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(3): 288. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin added to metformin plus gemigliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind, randomized, comparator-active study: ENHANCE-D study

- Diabetes
- A Review of the Effects of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Lean Body Mass in Humans
- Jack Alistair Sargeant, Joseph Henson, James Adam King, Thomas Yates, Kamlesh Khunti, Melanie Jane Davies
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(3):247-262. Published online September 26, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.3.247
- 11,409 View
- 419 Download
- 57 Web of Science
- 59 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Weight loss is an important goal in the management of several chronic conditions, including type 2 diabetes mellitus, and pharmacological therapies that aid weight loss are appealing. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2is) are novel glucose-lowering therapies that have been shown to induce clinically significant reductions in body weight. However, this weight loss may not be attributed solely to fat mass (FM). Given the importance of skeletal muscle and lean body mass (LBM) on cardio-metabolic health and physical function, we reviewed the available literature reporting the effects of GLP-1RAs and SGLT2is on body composition. Results demonstrate that, in most circumstances, the weight loss associated with both therapies predominantly comprises a reduction in FM, although significant heterogeneity exists between studies. In over half of the studies identified, the proportion of LBM reduction ranged between 20% and 50% of total weight lost, which is consistent with diet-induced weight loss and bariatric surgery. No clear differences existed between GLP-1RAs and SGLT2is. Consequently, the loss of LBM and skeletal muscle associated with weight loss induced by GLP-1RAs and SGLT2is warrants attention. Strategies to preserve skeletal muscle and improve physical function, for example through structured exercise, are of great importance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Drug‐related sarcopenia as a secondary sarcopenia
Masafumi Kuzuya
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2024; 24(2): 195. CrossRef - Exercise induces tissue-specific adaptations to enhance cardiometabolic health
Stephen P. Ashcroft, Ben Stocks, Brendan Egan, Juleen R. Zierath
Cell Metabolism.2024; 36(2): 278. CrossRef - Once-weekly semaglutide administered after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: Effects on body weight, glycemic control, and measured nutritional metrics in Japanese patients having both obesity and type 2 diabetes
Rieko Kanai, Sachiho Kinoshita, Izumi Kanbe, Mariko Sameda, Shuhei Yamaoka, Osamu Horikawa, Yasuhiro Watanabe, Ichiro Tatsuno, Kohji Shirai, Takashi Oshiro, Atsuhito Saiki
Obesity Pillars.2024; 9: 100098. CrossRef - Twenty‐four‐hour physical behaviour profiles across type 2 diabetes mellitus subtypes
Joseph Henson, Aikaterina Tziannou, Alex V. Rowlands, Charlotte L. Edwardson, Andrew P. Hall, Melanie J. Davies, Thomas Yates
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(4): 1355. CrossRef - The Current Landscape of Pharmacotherapies for Sarcopenia
Gulistan Bahat, Serdar Ozkok
Drugs & Aging.2024; 41(2): 83. CrossRef - Malnutrition and Sarcopenia as Reasons for Caution with GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Use in HFpEF
ELISSA DRIGGIN, PARAG GOYAL
Journal of Cardiac Failure.2024; 30(4): 610. CrossRef - Is the GLP-1 receptor agonist, semaglutide, a good option for weight loss in persons with HIV?
Daniel Lee, Jacqueline Capeau
AIDS.2024; 38(4): 603. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of tirzepatide, GLP‐1 receptor agonists, and other weight loss drugs in overweight and obesity: a network meta‐analysis
Xin‐Hui Pan, Bryan Tan, Yip Han Chin, Ethan Cheng Zhe Lee, Gwyneth Kong, Bryan Chong, Martin Kueh, Chin Meng Khoo, Anurag Mehta, Priyanka Majety, Gowtham R. Grandhi, Georgios K. Dimitriadis, Roger Foo, Nicholas W. S. Chew, Carel W. Le Roux, Mamas A. Mamas
Obesity.2024; 32(5): 840. CrossRef - Dual and Triple Incretin-Based Co-agonists: Novel Therapeutics for Obesity and Diabetes
Robert M. Gutgesell, Rubén Nogueiras, Matthias H. Tschöp, Timo D. Müller
Diabetes Therapy.2024; 15(5): 1069. CrossRef - Malnutrition in real-world patients hospitalized for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and its potential impact on generalizability of EMPEROR-Preserved trial
Shinsuke Takeuchi, Takashi Kohno, Ayumi Goda, Yasuyuki Shiraishi, Mike Saji, Yuji Nagatomo, Toshikazu D. Tanaka, Makoto Takei, Shintaro Nakano, Kyoko Soejima, Shun Kohsaka, Tsutomu Yoshikawa
International Journal of Cardiology.2023; 370: 263. CrossRef - Marked weight loss on liraglutide 3.0 mg: Real‐life experience of a Swiss cohort with obesity
Sara Santini, Nathalie Vionnet, Jérôme Pasquier, Elena Gonzalez‐Rodriguez, Montserrat Fraga, Nelly Pitteloud, Lucie Favre
Obesity.2023; 31(1): 74. CrossRef - Early type 2 diabetes treatment intensification with glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor agonists in primary care: An Australian perspective on guidelines and the global evidence
Roy Rasalam, Sarah Abdo, Gary Deed, Richard O'Brien, Jane Overland
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(4): 901. CrossRef - The effects of weight‐lowering pharmacotherapies on physical activity, function and fitness: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials
Rishi Jobanputra, Jack A. Sargeant, Abdullah Almaqhawi, Ehtasham Ahmad, Franciskos Arsenyadis, David R. Webb, Louisa Y. Herring, Kamlesh Khunti, Melanie J. Davies, Thomas Yates
Obesity Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Combination of exercise and GLP-1 receptor agonist treatment reduces severity of metabolic syndrome, abdominal obesity, and inflammation: a randomized controlled trial
Rasmus M. Sandsdal, Christian R. Juhl, Simon B. K. Jensen, Julie R. Lundgren, Charlotte Janus, Martin B. Blond, Mads Rosenkilde, Adrian F. Bogh, Lasse Gliemann, Jens-Erik B. Jensen, Charalambos Antoniades, Bente M. Stallknecht, Jens J. Holst, Sten Madsbad
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of novel glucose‐lowering therapies on physical function in people with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomised placebo‐controlled trials
Ehtasham Ahmad, Franciskos Arsenyadis, Abdullah Almaqhawi, Mary Barker, Rishi Jobanputra, Jack A. Sargeant, David R. Webb, Thomas Yates, Melanie J. Davies
Diabetic Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer cachexia as a blueprint for treating obesity
Nikolai P. Jaschke, Tilman D. Rachner
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 34(7): 395. CrossRef - The sun is rising on a new era of pharmacotherapy for obesity: some words of caution
Peter N. Benotti, Bruce R. Bistrian
Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases.2023; 19(9): 1075. CrossRef - Liraglutide Protects Against Diastolic Dysfunction and Improves Ventricular Protein Translation
Cody Rutledge, Angela Enriquez, Kevin Redding, Mabel Lopez, Steven Mullett, Stacy L. Gelhaus, Michael Jurczak, Eric Goetzman, Brett A. Kaufman
Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors on sarcopenia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Sha Zhang, Zhan Qi, Yidong Wang, Danfei Song, Deqiu Zhu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cysteine‐lowering treatment with mesna against obesity: Proof of concept and results from a human phase I, dose‐finding study
Kathrine J. Vinknes, Thomas Olsen, Hasse Khiabani Zaré, Nasser E. Bastani, Emma Stolt, Anja F. Dahl, Roger D. Cox, Helga Refsum, Kjetil Retterstøl, Anders Åsberg, Amany Elshorbagy
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(11): 3161. CrossRef - Repurposing Drugs for Diabetes Mellitus as Potential Pharmacological Treatments for Sarcopenia – A Narrative Review
Miles D. Witham, Antoneta Granic, Ewan Pearson, Sian M. Robinson, Avan A. Sayer
Drugs & Aging.2023; 40(8): 703. CrossRef - Introduction to the dietary management of obesity in adults
Vivian Lee
Clinical Medicine.2023; 23(4): 304. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of the sodium‐glucose co‐transporter‐2 inhibitor empagliflozin in elderly Japanese adults (≥65 years) with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, 52‐week clinical trial (EMPA‐ELDERLY)
Daisuke Yabe, Kosuke Shiki, Gosuke Homma, Thomas Meinicke, Yuji Ogura, Yutaka Seino
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(12): 3538. CrossRef - Independent Link Between Use of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists and Muscle Wasting in Heart Failure Patients Not Receiving Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors
Ryo Numazawa, Satoshi Katano, Toshiyuki Yano, Ryohei Nagaoka, Katsuhiko Ohori, Hidemichi Kouzu, Suguru Honma, Yusuke Fujisawa, Kotaro Yamano, Arata Osanami, Masayuki Koyama, Akiyoshi Hashimoto, Masato Furuhashi
Circulation Journal.2023; 88(1): 10. CrossRef - Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors and Sarcopenia: A controversy that must be solved
Baris Afsar, Rengin Elsurer Afsar
Clinical Nutrition.2023; 42(12): 2338. CrossRef - Oral semaglutide improves body composition and preserves lean mass in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 26-week prospective real-life study
Sara Volpe, Giuseppe Lisco, Margherita Fanelli, Davide Racaniello, Valentina Colaianni, Valentina Lavarra, Domenico Triggiani, Lucilla Crudele, Vincenzo Triggiani, Carlo Sabbà, Giovanni De Pergola, Giuseppina Piazzolla
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Body Composition in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Narrative Review
Soodeh Jahangiri, Mojtaba Malek, Sanjay Kalra, Mohammad E. Khamseh
Diabetes Therapy.2023; 14(12): 2015. CrossRef - Relationship between sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and muscle atrophy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Chengdong Xia, Yufeng Han, Chunhui Yin, Ruyue Geng, Zhenfei Liu, Yongle Du, Mingkun Yu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Lifestyle Modification with Second-Generation Anti-obesity Medications: Comparisons, Questions, and Clinical Opportunities
Thomas A. Wadden, Ariana M. Chao, Molly Moore, Jena S. Tronieri, Adam Gilden, Anastassia Amaro, Sharon Leonard, John M. Jakicic
Current Obesity Reports.2023; 12(4): 453. CrossRef - Sarcopenia and Diabetes: A Detrimental Liaison of Advancing Age
Giuseppe Lisco, Olga Eugenia Disoteo, Anna De Tullio, Vincenzo De Geronimo, Vito Angelo Giagulli, Fabio Monzani, Emilio Jirillo, Renato Cozzi, Edoardo Guastamacchia, Giovanni De Pergola, Vincenzo Triggiani
Nutrients.2023; 16(1): 63. CrossRef - Novel Antidiabetic Strategies and Diabetologists' Views in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
Sabine Kahl, Jennifer Pützer, Michael Roden
Seminars in Liver Disease.2022; 42(01): 048. CrossRef - Effect of Empagliflozin Versus Placebo on Body Fluid Balance in Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Subgroup Analysis of the EMBODY Trial
Yu Hoshika, Yoshiaki Kubota, Kosuke Mozawa, Shuhei Tara, Yukichi Tokita, Kenji Yodogawa, Yu-Ki Iwasaki, Takeshi Yamamoto, Hitoshi Takano, Yayoi Tsukada, Kuniya Asai, Masaaki Miyamoto, Yasushi Miyauchi, Eitaro Kodani, Mitsunori Maruyama, Jun Tanabe, Wataru
Journal of Cardiac Failure.2022; 28(1): 56. CrossRef - Effect of GLP-1 receptor agonist, liraglutide, on muscle in spontaneously diabetic torii fatty rats
Shohei Yamada, Yuji Ogura, Kazuho Inoue, Jun Tanabe, Takeshi Sugaya, Keiichi Ohata, Yoshio Nagai, Yasunori Natsuki, Seiko Hoshino, Shiika Watanabe, Daisuke Ichikawa, Kenjiro Kimura, Yugo Shibagaki, Atsuko Kamijo-Ikemori
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2022; 539: 111472. CrossRef - Exendin-4 alleviates steatosis in an in vitro cell model by lowering FABP1 and FOXA1 expression via the Wnt/-catenin signaling pathway
Olfa Khalifa, Neyla S. AL-Akl, Khaoula Errafii, Abdelilah Arredouani
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Body composition changes at 12 months following different surgical weight loss interventions in adults with obesity: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized control trials
Amy Sylivris, Jakub Mesinovic, David Scott, Paul Jansons
Obesity Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Safety and effectiveness of empagliflozin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: final results of a 3-year post-marketing surveillance study
Kohei Kaku, Kazuhiro Yamamoto, Yumiko Fukushima, Hristo Lliev, Atsutaka Yasui
Expert Opinion on Drug Safety.2022; 21(10): 1315. CrossRef - Safety and effectiveness of empagliflozin according to body mass index in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a subgroup analysis of a 3-year post-marketing surveillance study
Kohei Kaku, Kazuhiro Yamamoto, Yumiko Fukushima, Seiko Mizuno, Daisuke Nitta
Expert Opinion on Drug Safety.2022; 21(11): 1411. CrossRef - Le risque de dénutrition chez le sujet âgé diabétique : une limite à l’utilisation des « nouvelles » classes thérapeutiques ?
Lyse Bordier, Jean Doucet, Bernard Bauduceau
Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques.2022; 16(5): 422. CrossRef - Emerging evidence of the relationship between fat-free mass and ghrelin, glucagon-like peptide-1, and peptide-YY
Austin J. Graybeal, Jada L. Willis, Elisa Morales-Marroquin, Grant M. Tinsley, Sarah E. Messiah, Meena Shah
Nutrition.2022; 103-104: 111815. CrossRef - The Effectiveness of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Semaglutide on Body Composition in Elderly Obese Diabetic Patients: A Pilot Study
Yoshinori Ozeki, Takayuki Masaki, Akari Kamata, Shotaro Miyamoto, Yuichi Yoshida, Mitsuhiro Okamoto, Koro Gotoh, Hirotaka Shibata
Medicines.2022; 9(9): 47. CrossRef - Distribution of lean mass and mortality risk in patients with type 2 diabetes
Li Ding, Yuxin Fan, Jingting Qiao, Jing He, Ruodan Wang, Qing He, Jingqiu Cui, Zhongshu Ma, Fangqiu Zheng, Hua Gao, Chenlin Dai, Hongyan Wei, Jun Li, Yuming Cao, Gang Hu, Ming Liu
Primary Care Diabetes.2022; 16(6): 824. CrossRef - Cardio-sarcopenia: A syndrome of concern in aging
De Rong Loh, Ru-San Tan, Wee Shiong Lim, Angela S. Koh
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Type 2 diabetes
Ehtasham Ahmad, Soo Lim, Roberta Lamptey, David R Webb, Melanie J Davies
The Lancet.2022; 400(10365): 1803. CrossRef - Elevated circulating level of β-aminoisobutyric acid (BAIBA) in heart failure patients with type 2 diabetes receiving sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors
Satoshi Katano, Toshiyuki Yano, Hidemichi Kouzu, Ryohei Nagaoka, Ryo Numazawa, Kotaro Yamano, Yusuke Fujisawa, Katsuhiko Ohori, Nobutaka Nagano, Takefumi Fujito, Ryo Nishikawa, Wataru Ohwada, Masaki Katayose, Tatsuya Sato, Atsushi Kuno, Masato Furuhashi
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - An overview of anamorelin as a treatment option for cancer-associated anorexia and cachexia
Guilherme Wesley Peixoto Da Fonseca, Stephan von Haehling
Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy.2021; 22(7): 889. CrossRef - Liraglutide Does Not Adversely Impact Fat‐Free Mass Loss
Andrew Grannell, William P. Martin, Babak Dehestani, Werd Al‐Najim, John C. Murphy, Carel W. le Roux
Obesity.2021; 29(3): 529. CrossRef - Rationale and design of the EMPA-ELDERLY trial: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 52-week clinical trial of the efficacy and safety of the sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor empagliflozin in elderly Japanese patients with type 2 diabet
Daisuke Yabe, Kosuke Shiki, Keiko Suzaki, Thomas Meinicke, Yutaro Kotobuki, Kenichiro Nishida, Douglas Clark, Atsutaka Yasui, Yutaka Seino
BMJ Open.2021; 11(4): e045844. CrossRef - Cancer Risk in Normal Weight Individuals with Metabolic Obesity: A Narrative Review
Bethina Liu, Hugh E. Giffney, Rhonda S. Arthur, Thomas E. Rohan, Andrew J. Dannenberg
Cancer Prevention Research.2021; 14(5): 509. CrossRef - Comprehensive analysis of LncRNAs expression profiles in an in vitro model of steatosis treated with Exendin-4
Khaoula Errafii, Neyla S. Al-Akl, Olfa Khalifa, Abdelilah Arredouani
Journal of Translational Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Dapagliflozin increases the lean-to total mass ratio in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Vaneza Lira W. Wolf, Ikaro Breder, Luiz Sérgio F. de Carvalho, Alexandre A. S. Soares, Riobaldo M. Cintra, Joaquim Barreto, Daniel B. Munhoz, Sheila T. Kimura-Medorima, Wilson Nadruz, Gil Guerra-Júnior, Thiago Quinaglia, Elza Muscelli, Andrei C. Sposito
Nutrition & Diabetes.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimising the Heart Failure Treatment Pathway: The Role of SGLT2 Inhibitors
Marc Evans, Angharad R. Morgan, Zaheer Yousef, Gethin Ellis, Umesh Dashora, Dipesh C. Patel, Pam Brown, Wasim Hanif, Johnathan N. Townend, Naresh Kanumilli, Jim Moore, John P. H. Wilding, Stephen C. Bain
Drugs.2021; 81(11): 1243. CrossRef - Glucose-lowering Drugs and Hospitalization for Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Additive-effects Network Meta-analysis With More Than 500 000 Patient-years
Riobaldo M Cintra, Ana Claudia Nogueira, Isabella Bonilha, Beatriz M Luchiari, Otavio R Coelho-Filho, Otavio R Coelho, Pedro Schwartzmann, Elza Muscellie, Wilson Nadruz, Luiz Sergio F Carvalho, Andrei C Sposito
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 106(10): 3060. CrossRef - Physical activity and exercise in the management of type 2 diabetes: where to start?
Deirdre Harrington, Joe Henson
Practical Diabetes.2021; 38(5): 35. CrossRef - Efpeglenatide and Heart and Kidney Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes
New England Journal of Medicine.2021; 385(22): 2105. CrossRef - Effects of Antidiabetic Drugs on Muscle Mass in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Satoshi Ida, Ryutaro Kaneko, Kanako Imataka, Kaoru Okubo, Yoshitaka Shirakura, Kentaro Azuma, Ryoko Fujiwara, Kazuya Murata
Current Diabetes Reviews.2021; 17(3): 293. CrossRef - Effects of liraglutide and empagliflozin added to insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled study
Hirotatsu Nakaguchi, Yoshinobu Kondo, Mayu Kyohara, Hiromi Konishi, Koji Oiwa, Yasuo Terauchi
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2020; 11(6): 1542. CrossRef - Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibition Does Not Favorably Modify the Physiological Responses to Dietary Counselling in Diabetes-Free, Sedentary Overweight and Obese Adult Humans
Shane P.P. Ryan, Alissa A. Newman, Jessie R. Wilburn, Lauren D. Rhoades, S. Raj J. Trikha, Ellen C. Godwin, Hayden M. Schoenberg, Micah L. Battson, Taylor R. Ewell, Gary J. Luckasen, Laurie M. Biela, Christopher L. Melby, Christopher Bell
Nutrients.2020; 12(2): 510. CrossRef - GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Treatment in Morbid Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Due to Pathogenic Homozygous Melanocortin-4 Receptor Mutation: A Case Report
Eva W. Iepsen, Christian T. Have, Simon Veedfald, Sten Madsbad, Jens J. Holst, Niels Grarup, Oluf Pedersen, Ivan Brandslund, Jens-Christian Holm, Torben Hansen, Signe S. Torekov
Cell Reports Medicine.2020; 1(1): 100006. CrossRef - Glucagon‐like peptide 1 infusions overcome anabolic resistance to feeding in older human muscle
Haitham Abdulla, Bethan E. Phillips, Daniel J. Wilkinson, Marie Limb, Tereza Jandova, Joseph J. Bass, Debbie Rankin, Jessica Cegielski, Mariwan Sayda, Hannah Crossland, John P. Williams, Kenneth Smith, Iskandar Idris, Philip J. Atherton
Aging Cell.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Drug‐related sarcopenia as a secondary sarcopenia

- New Potential Targets of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists in Pancreatic β-Cells and Hepatocytes
- Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(1):1-5. Published online February 6, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.1.1
- 4,192 View
- 43 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader It is well known that both insulin resistance and decreased insulin secretory capacity are important factors in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). In addition to genetic factors, obesity and lipotoxicity can increase the risk of T2DM. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are novel antidiabetic drugs with multiple effects. They can stimulate glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibit postprandial glucagon release, delay gastric emptying, and induce pancreatic β-cell proliferation. They can also reduce the weight of patients with T2DM and relieve lipotoxicity at the cellular level. Many intracellular targets of GLP-1 have been found, but more remain to be identified. Elucidating these targets could be a basis for developing new potential drugs. My colleagues and I have investigated new targets of GLP-1, with a particular focus on pancreatic β-cell lines and hepatic cell lines. Herein, I summarize the recent work from my laboratory, with profound gratitude for receiving the prestigious 2016 Namgok Award.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Venom Peptides, Polyphenols and Alkaloids: Are They the Next Antidiabetics That Will Preserve β-Cell Mass and Function in Type 2 Diabetes?
Michele Lodato, Valérie Plaisance, Valérie Pawlowski, Maxime Kwapich, Alexandre Barras, Emeline Buissart, Stéphane Dalle, Sabine Szunerits, Jérôme Vicogne, Rabah Boukherroub, Amar Abderrahmani
Cells.2023; 12(6): 940. CrossRef - Diabetes, Incretin Therapy and Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm – What Does the Evidence Show?
Camilla Krizhanovskii , Anders Franco-Cereceda
Current Vascular Pharmacology.2019; 17(5): 432. CrossRef - Toll-like receptor 4 is necessary for glucose-dependent glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion in male mice
Lijuan Wang, Xiandong Zhan, Zhenhui Wang, Jing Ma, Xiaotong Chang, Xiaobo Zhu
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2019; 510(1): 104. CrossRef
- Venom Peptides, Polyphenols and Alkaloids: Are They the Next Antidiabetics That Will Preserve β-Cell Mass and Function in Type 2 Diabetes?

- Thyroid
- Expression of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Its Clinicopathologic Significance
- Min Jung Jung, Su Kyoung Kwon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(4):536-544. Published online December 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.536
- 3,725 View
- 43 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Incretin-based therapies are rapidly becoming one of the main glycemic control strategies in diabetes. Considering the large numbers of papillary thyroid carcinomas (PTCs) and possible effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) on cell proliferation, the expression of GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R) in PTC is likely to have clinical significance. We performed this study to evaluate the expression of GLP-1R in PTC and the clinical meaning of GLP-1R expression in PTC.
Methods Fifty-six cases of PTC, four cases of medullary thyroid cancer (MTC), seven cases of nodular hyperplasia and 56 normal thyroid tissue samples were selected for immunostaining for GLP-1R. Clinical parameters were obtained by retrospective review of medical records.
Results Immunohistochemical staining for GLP-1R showed immunoreactivity in 18 of 56 cases of PTC (32.1%). All four cases of MTC exhibited cytoplasmic GLP-1R expression. Nodular hyperplasia exhibited immunoreactivity in two of seven cases (28.6%). All normal thyroid follicular cells showed negative immunoreactivity. In univariable and multivariable analyses, tumor multifocality was negatively correlated with GLP-1R expression. Extrathyroidal extension showed positive association with GLP-1R expression that was almost significant. Sex, age, tumor size, and lymph node metastasis were not significantly associated with GLP-1R expression.
Conclusion Some parts of PTC tissues express GLP-1R, and GLP-1R expression in PTC was negatively correlated with tumor multifocality. The long-term influence of pharmacologically increased GLP-1 on thyroid follicular cells and development and progression of tumors originating from thyroid follicular cells should be investigated.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of thyroid cancer associated with glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes: A population‐based cohort study
Sungho Bea, Heejun Son, Jae Hyun Bae, Sun Wook Cho, Ju‐Young Shin, Young Min Cho
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(1): 108. CrossRef - Glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor agonists and risk of thyroid cancer: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials
Giovanni Antonio Silverii, Matteo Monami, Marco Gallo, Alberto Ragni, Francesco Prattichizzo, Valerio Renzelli, Antonio Ceriello, Edoardo Mannucci
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(3): 891. CrossRef - Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Thyroid Cancer: A Narrative Review
Ana E. Espinosa De Ycaza, Juan P. Brito, Rozalina G. McCoy, Hui Shao, Naykky Singh Ospina
Thyroid®.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation the impact of liraglutide on the thyroid function tests
Emre URHAN
Turkish Journal of Clinics and Laboratory.2023; 14(2): 339. CrossRef - GLP-1R polymorphism (rs1042044) and expression are associated with the risk of papillary thyroid cancer among the Egyptian population
Rehab S. Abdul-Maksoud, Walid S.H. Elsayed, Nearmeen M. Rashad, Rasha S. Elsayed, Shereen Elshorbagy, Mohamed G. Hamed
Gene.2022; 834: 146597. CrossRef - Use of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Occurrence of Thyroid Disorders: a Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Weiting Hu, Rui Song, Rui Cheng, Caihong Liu, Rui Guo, Wei Tang, Jie Zhang, Qian Zhao, Xing Li, Jing Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - GLP-1 receptor agonist-associated tumor adverse events: A real-world study from 2004 to 2021 based on FAERS
Zheng Yang, Yuhuan Lv, Meng Yu, Mei Mei, Linyu Xiang, Subei Zhao, Rong Li
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Exenatide on Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone and Thyroid Volume
Muhammed Erkam Sencar, Davut Sakiz, Murat Calapkulu, Sema Hepsen, Muhammed Kizilgul, Ilknur Unsal Ozturk, Bekir Ucan, Murat Bayram, Busra Betul Cagir, Safak Akin, Mustafa Ozbek, Erman Cakal
European Thyroid Journal.2019; 8(6): 307. CrossRef - Expression of GLP-1 receptor and CD26 in human thyroid C-cells: The association of thyroid C-cell tumorigenesis with incretin-based medicine
Yuejia Song, Min Zhou, Yang Cao, Jiping Qi, Jingshu Geng, Xiaomin Liu
Oncology Letters.2017; 13(4): 2684. CrossRef - Exendin-4 does not modify growth or apoptosis of human colon cancer cells
He Wenjing, Yu Shuang, Li Weisong, Xiao Haipeng
Endocrine Research.2017; : 1. CrossRef - GLP-1 receptor agonist as treatment for cancer as well as diabetes: beyond blood glucose control
Takashi Nomiyama, Toshihiko Yanase
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2016; : 1. CrossRef - Exendin-4 inhibits growth and augments apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells
Wenjing He, Shuang Yu, Liantang Wang, Mian He, Xiaopei Cao, Yanbing Li, Haipeng Xiao
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2016; 436: 240. CrossRef - Expression of PACAP and PAC1 Receptor in Normal Human Thyroid Gland and in Thyroid Papillary Carcinoma
Sebastian Bardosi, Attila Bardosi, Zsuzsanna Nagy, Dora Reglodi
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience.2016; 60(2): 171. CrossRef - Sitagliptin use and thyroid cancer risk in patients with type 2 diabetes
Chin-Hsiao Tseng
Oncotarget.2016; 7(17): 24871. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef - Response: Expression of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Its Clinicopathologic Significance (Endocrinol Metab2014;29:536-44, Min Jung Jung et al.)
Min Jung Jung, Su Kyoung Kwon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(2): 233. CrossRef - Letter: Expression of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Its Clinicopathologic Significance (Endocrinol Metab2014;29:536-44, Min Jung Jung et al.)
Daeyoon Park, Eun Kyung Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(2): 231. CrossRef
- Risk of thyroid cancer associated with glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes: A population‐based cohort study


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



