Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
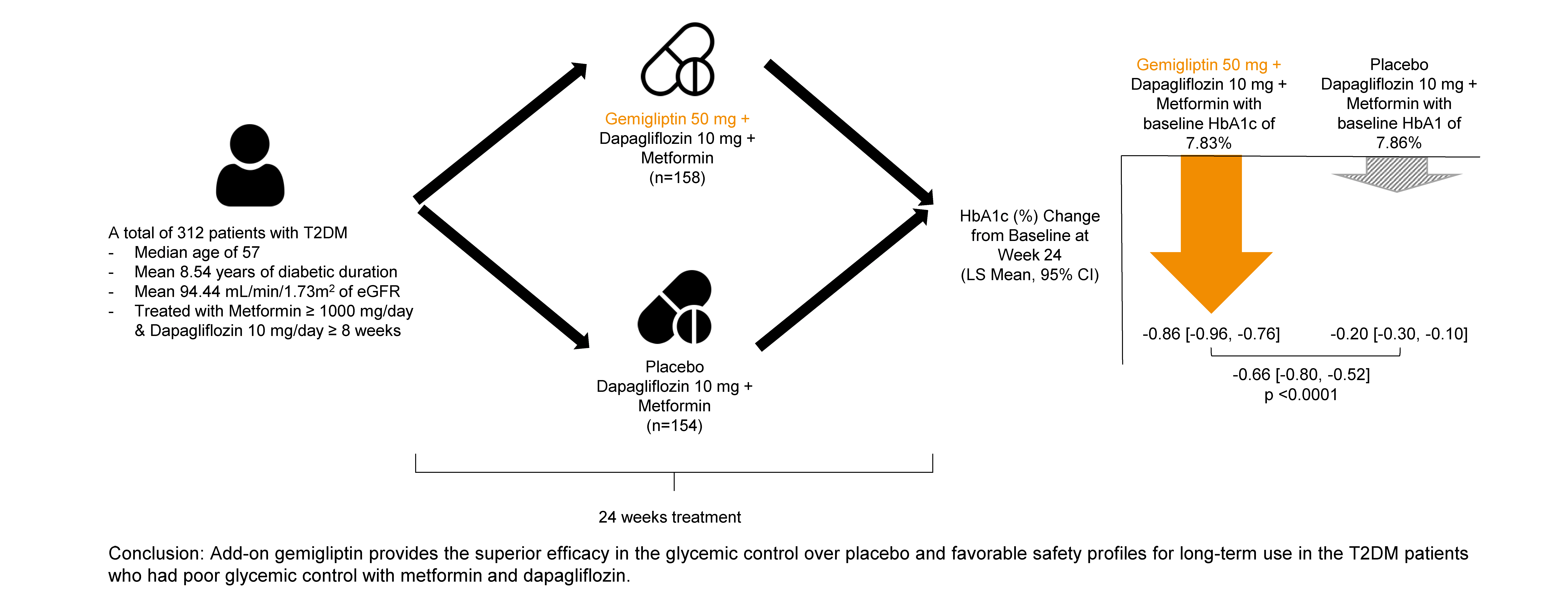
- Efficacy of Gemigliptin Add-on to Dapagliflozin and Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study (SOLUTION)
- Byung Wan Lee, KyungWan Min, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Bon Jeong Ku, Jun Goo Kang, Suk Chon, Won-Young Lee, Mi Kyoung Park, Jae Hyeon Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Keeho Song, Soon Jib Yoo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(3):328-337. Published online June 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1688
- 2,422 View
- 264 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of add-on gemigliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who had inadequate glycemic control with metformin and dapagliflozin.
Methods
In this randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, double-blind, phase III study, 315 patients were randomized to receive either gemigliptin 50 mg (n=159) or placebo (n=156) with metformin and dapagliflozin for 24 weeks. After the 24-week treatment, patients who received the placebo were switched to gemigliptin, and all patients were treated with gemigliptin for an additional 28 weeks.
Results
The baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups, except for body mass index. At week 24, the least squares mean difference (standard error) in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) changes was –0.66% (0.07) with a 95% confidence interval of –0.80% to –0.52%, demonstrating superior HbA1c reduction in the gemigliptin group. After week 24, the HbA1c level significantly decreased in the placebo group as gemigliptin was administered, whereas the efficacy of HbA1c reduction was maintained up to week 52 in the gemigliptin group. The safety profiles were similar: the incidence rates of treatment-emergent adverse events up to week 24 were 27.67% and 29.22% in the gemigliptin and placebo groups, respectively. The safety profiles after week 24 were similar to those up to week 24 in both groups, and no new safety findings, including hypoglycemia, were noted.
Conclusion
Add-on gemigliptin was well tolerated, providing comparable safety profiles and superior efficacy in glycemic control over placebo for long-term use in patients with T2DM who had poor glycemic control with metformin and dapagliflozin.

- Diabetes
- Retrospective Analysis of the Efficacy of Dapagliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in a Primary Clinic in Korea
- Sang Hyun Park, Young Ju Choi, Eun-Jung Rhee, Kab Bum Huh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(1):70-79. Published online March 21, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.1.70
- 5,754 View
- 95 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background We aimed to retrospectively analyze the efficacy of 10 mg dapagliflozin (DAPA), which is a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor, in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes who visited a primary diabetes clinic.
Methods In total, 83 patients with type 2 diabetes, who received treatment with DAPA for the first time in a primary diabetes clinic between January 2015 and October 2015, were included in the study. The effect of DAPA in lowering glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels was evaluated via chart review at 6 months follow-up. The patients were categorized into five groups according to add-on to or switched from other glucose-lowering agents: add-on to metformin (MET,
n =10), add-on to MET+dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor (DPP4i,n =12), switched from sulfonylurea (SU,n =13), switched from DPP4i (n =11), and switched from thiazolidinedione (TZD,n =37). All the participants had already used MET for their regimen.Results Treatment with DAPA reduced HbA1c level by 1.2%±0.8%. Moreover, a significant decrease was observed in all subgroups: add-on to MET, −1.2%±0.7%; add-on to MET+DPP4i, −1.4%±0.8%; switched from SU, −1.4%±0.7%; switched from DPP4i, −0.5%±0.7%; and switched from TZD, −1.2%±0.9% (
P <0.01). A significant decrease in body weight (−3.1±2.6 kg,P <0.001) was observed after DAPA administration. Estimated glomerular filtration rate and urine microalbumin were significantly decreased after 6 months of treatment with DAPA (−4.0±13.5 mL/min/1.73 m2,P =0.03; −23.6±45.9 mg/L,P <0.001).Conclusion Treatment with DAPA, whether added to or switched from other glucose-lowering agents, significantly decreased HbA1c levels in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes who visited a single primary diabetes clinic. DAPA can be considered as an optimal second-line treatment for patients with type 2 diabetes, as supported by real-world evidence studies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin ameliorates the fluid-retaining effect of the endothelin A receptor antagonist zibotentan
Vandana Veenit, Hiddo J L Heerspink, Christine Ahlström, Peter J Greasley, Stanko Skritic, Natalie van Zuydam, Donald E Kohan, Pernille B L Hansen, Robert I Menzies
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation.2023; 38(10): 2289. CrossRef
- The sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin ameliorates the fluid-retaining effect of the endothelin A receptor antagonist zibotentan


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



