Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Calcium & bone metabolism
- Higher Plasma Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1 Is Associated with Lower Risk for Sarcopenia in Older Asian Adults
- Sunghwan Ji, Kyunggon Kim, So Jeong Park, Jin Young Lee, Hee-Won Jung, Hyun Ju Yoo, Il-Young Jang, Eunju Lee, Ji Yeon Baek, Beom-Jun Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):701-708. Published online October 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1783

- 1,684 View
- 77 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Despite the protective effects of stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1) in stimulating muscle regeneration shown in experimental research, there is a lack of clinical studies linking circulating SDF-1 concentrations with muscle phenotypes. In order to elucidate the role of SDF-1 as a potential biomarker reflecting human muscle health, we investigated the association of plasma SDF-1 levels with sarcopenia in older adults.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 97 community-dwelling participants who underwent a comprehensive geriatric assessment at a tertiary hospital in South Korea. Sarcopenia was defined by specific cutoff values applicable to the Asian population, whereas plasma SDF-1 levels were determined using an enzyme immunoassay.
Results
After accounting for sex, age, and body mass index, participants with sarcopenia and low muscle mass exhibited plasma SDF-1 levels that were 21.8% and 18.3% lower than those without these conditions, respectively (P=0.008 and P=0.009, respectively). Consistently, higher plasma SDF-1 levels exhibited a significant correlation with higher skeletal muscle mass index (SMI) and gait speed (both P=0.043), and the risk of sarcopenia and low muscle mass decreased by 58% and 55% per standard deviation increase in plasma SDF-1 levels, respectively (P=0.045 and P=0.030, respectively). Furthermore, participants in the highest SDF-1 tertile exhibited significantly higher SMI compared to those in the lowest tertile (P=0.012).
Conclusion
These findings clinically corroborate earlier experimental discoveries highlighting the muscle anabolic effects of SDF- 1 and support the potential role of circulating SDF-1 as a biomarker reflecting human muscle health in older adults.

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Human Leukocyte Antigens and Biomarkers in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Induced by Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors
- Hidefumi Inaba, Yosuke Kaido, Saya Ito, Tomonao Hirobata, Gen Inoue, Takakazu Sugita, Yuki Yamamoto, Masatoshi Jinnin, Hiroaki Kimura, Tomoko Kobayashi, Shintaro Iwama, Hiroshi Arima, Takaaki Matsuoka
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):84-95. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1282
- 4,214 View
- 159 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Type 1 diabetes mellitus induced by immune-checkpoint inhibitors (ICI-T1DM) is a rare critical entity. However, the etiology of ICI-T1DM remains unclear.
Methods
In order to elucidate risk factors for ICI-T1DM, we evaluated the clinical course and immunological status of patients with ICI-T1DM who had been diagnosed during 2016 to 2021.
Results
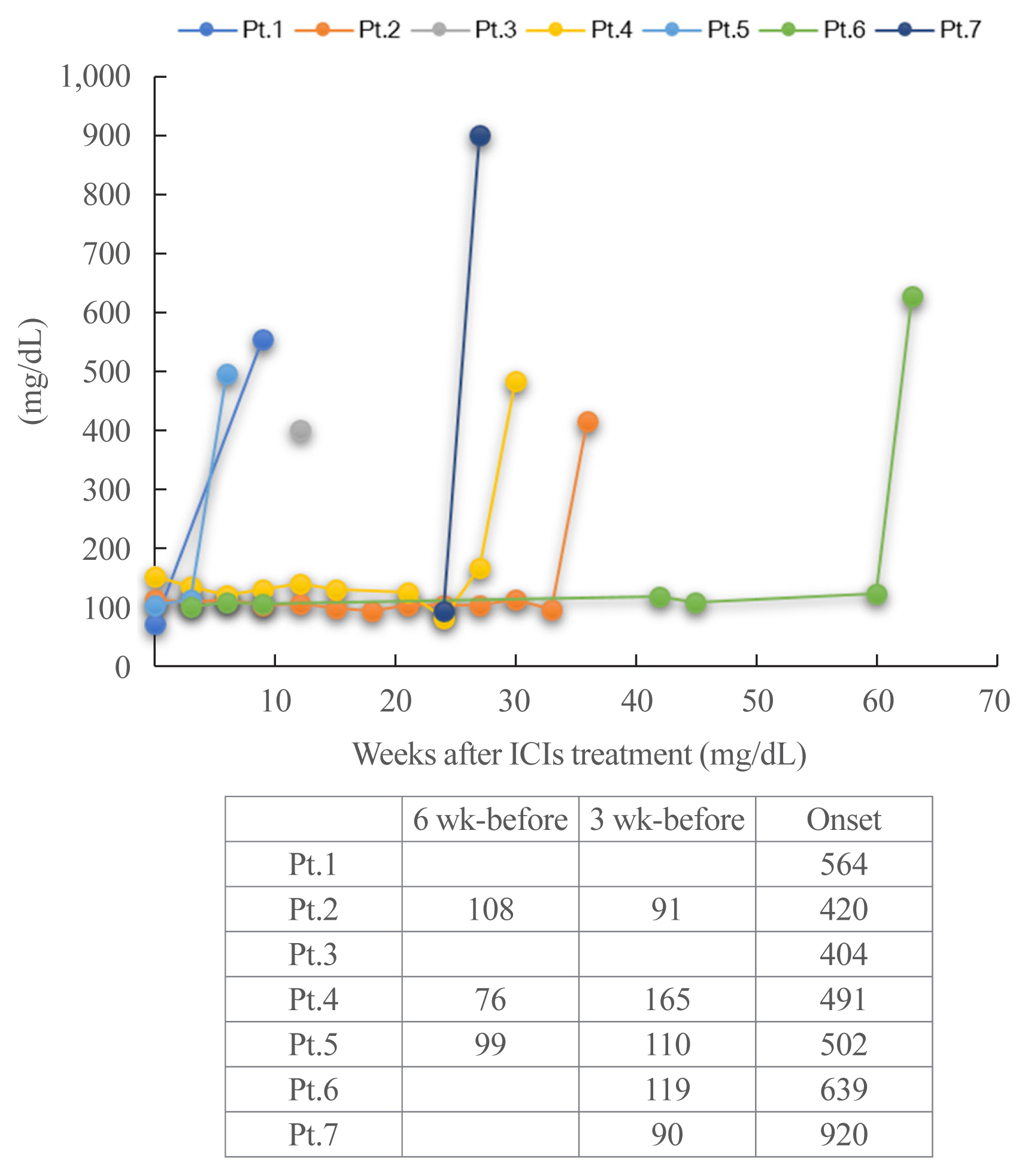
Seven of 871 (0.8%, six men and one woman) patients developed ICI-T1DM. We revealed that the allele frequencies of human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DPA1*02:02 and DPB1*05:01 were significantly higher in the patients with ICI-T1DM In comparison to the controls who received ICI (11/14 vs. 10/26, P=0.022; 11/14 vs. 7/26, P=0.0027, respectively). HLA-DRB1*04:05, which has been found to be a T1DM susceptibility allele in Asians, was also observed as a high-risk allele for ICI-T1DM. The significance of the HLA-DPB1*05:01 and DRB1*04:05 alleles was confirmed by an analysis of four additional patients. The absolute/relative neutrophil count, neutrophils-lymphocyte ratio, and neutrophil-eosinophil ratio increased, and the absolute lymphocyte count and absolute/relative eosinophil count decreased at the onset as compared with 6 weeks before. In two patients, alterations in cytokines and chemokines were found at the onset.
Conclusion
Novel high-risk HLA alleles and haplotypes were identified in ICI-T1DM, and peripheral blood factors may be utilized as biomarkers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Type 1 diabetes mellitus affected by potential toxicity from long-term use of nivolumab
Yuma Motomura, Shin Urai, Yushi Hirota, Naoki Takegawa, Hironori Bando, Masaaki Yamamoto, Hidenori Fukuoka, Masahiro Tsuda, Wataru Ogawa
Diabetology International.2024; 15(1): 130. CrossRef - Review – The impact of pharmacogenetics on the outcome of immune checkpoint inhibitors
Karlijn de Joode, Niels Heersche, Edwin A. Basak, Sander Bins, Astrid A.M. van der Veldt, Ron H.N. van Schaik, Ron H.J. Mathijssen
Cancer Treatment Reviews.2024; 122: 102662. CrossRef - Reaching the Diagnosis of Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Different Clinical Scenarios: A Real-World Application of Updated Diagnostic Criteria
Anna Angelousi, Dimitrios C. Ziogas, Vasiliki Siampanopoulou, Chrysoula Mytareli, Amalia Anastasopoulou, George Lyrarakis, Helen Gogas
Diseases.2024; 12(2): 40. CrossRef - Non-Invasive Predictive Biomarkers for Immune-Related Adverse Events Due to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Ben Ponvilawan, Abdul Wali Khan, Janakiraman Subramanian, Dhruv Bansal
Cancers.2024; 16(6): 1225. CrossRef - A case of rapidly progressive insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus without islet autoantibodies developed over two years after the first dose of nivolumab
Kota Nishihama, Yuko Okano, Chisa Inoue, Kanako Maki, Kazuhito Eguchi, Soichiro Tanaka, Atsuro Takeshita, Mei Uemura, Taro Yasuma, Toshinari Suzuki, Esteban C. Gabazza, Yutaka Yano
Diabetology International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A single center case series of immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus, patterns of disease onset and long-term clinical outcome
John Marsiglio, Jordan P. McPherson, Magdalena Kovacsovics-Bankowski, Joanne Jeter, Christos Vaklavas, Umang Swami, Douglas Grossmann, Alyssa Erickson-Wayman, Heloisa P. Soares, Katie Kerrigan, Berit Gibson, Jennifer Anne Doherty, John Hyngstrom, Sheetal
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive Biomarkers for Immune-Related Endocrinopathies following Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Treatment
Almog Shalit, Panagiotis Sarantis, Evangelos Koustas, Eleni-Myrto Trifylli, Dimitris Matthaios, Michalis V. Karamouzis
Cancers.2023; 15(2): 375. CrossRef - Predictive Biomarkers for Checkpoint Inhibitor Immune-Related Adverse Events
Iñigo Les, Mireia Martínez, Inés Pérez-Francisco, María Cabero, Lucía Teijeira, Virginia Arrazubi, Nuria Torrego, Ana Campillo-Calatayud, Iñaki Elejalde, Grazyna Kochan, David Escors
Cancers.2023; 15(5): 1629. CrossRef - Amino acid polymorphisms in human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen class II and proinsulin epitope have impacts on type 1 diabetes mellitus induced by immune-checkpoint inhibitors
Hidefumi Inaba, Shuhei Morita, Daisuke Kosugi, Yuki Asai, Yosuke Kaido, Saya Ito, Tomonao Hirobata, Gen Inoue, Yuki Yamamoto, Masatoshi Jinnin, Hiroaki Kimura, Masao Ota, Yuko Okudaira, Hiroyasu Nakatani, Tomoko Kobayashi, Shintaro Iwama, Hiroshi Arima, T
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical characteristics and human leukocyte antigens in patients with immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced type 1 diabetes and pituitary dysfunction: a single center prospective study
Natsuko Hara, Hirotsugu Suwanai, Fumiyoshi Yakou, Keitaro Ishii, Hajime Iwasaki, Hironori Abe, Jumpei Shikuma, Hiroyuki Sakai, Takashi Miwa, Ryo Suzuki
Endocrine.2023; 81(3): 477. CrossRef - Autoimmunity in immune checkpoint inhibitor‐induced immune‐related adverse events: A focus on autoimmune skin toxicity and pneumonitis
Fiamma Berner, Lukas Flatz
Immunological Reviews.2023; 318(1): 37. CrossRef - Prediction-based prompt levothyroxine replacement to prevent a hypothyroid state after immune-related adverse events involving the thyroid gland
Ichiro Yamauchi, Takuro Hakata, Taku Sugawa, Daisuke Kosugi, Haruka Fujita, Kentaro Okamoto, Yohei Ueda, Toshihito Fujii, Daisuke Taura, Norio Harada, Nobuya Inagaki
Endocrine Journal.2023; 70(10): 987. CrossRef - Key Determinants of Immune-Mediated Adverse Reactions to Oncology Drugs
Yihan Zhou, Shan Ding
Cancers.2023; 15(23): 5622. CrossRef - Risk factors and predictors of immune-related adverse events: implications for patients with non-small cell lung cancer
Majd Issa, Joy Tang, Yizhen Guo, Chris Coss, Thomas A. Mace, Jason Bischof, Mitch Phelps, Carolyn J Presley, Dwight H Owen
Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy.2022; 22(8): 861. CrossRef - Risk Factors and Biomarkers for Immune-Related Adverse Events: A Practical Guide to Identifying High-Risk Patients and Rechallenging Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Adithya Chennamadhavuni, Laith Abushahin, Ning Jin, Carolyn J. Presley, Ashish Manne
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Flash Glucose Monitoring and Diabetes Mellitus Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: An Approach to Clinical Practice
Pablo Rodríguez de Vera-Gómez, Ana Piñar-Gutiérrez, Raquel Guerrero-Vázquez, Virginia Bellido, Cristóbal Morales-Portillo, María Pilar Sancho-Márquez, Pablo Espejo-García, Noelia Gros-Herguido, Gema López-Gallardo, María Asunción Martínez-Brocca, Alfonso
Journal of Diabetes Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus affected by potential toxicity from long-term use of nivolumab

- Gene Expression Regulation by Agonist-Independent Constitutive Signaling of Melanocortin-1 Receptor
- Ikjoo Seong, Jaesang Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(2):179-184. Published online June 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.2.179
- 3,374 View
- 33 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Melanocortin-1 receptor (Mc1r), a key signaling receptor for melanogenesis, has been reported to mediate migration of B16F10 melanoma cells. Interestingly, this activity appears to be a part of the constitutive signaling of Mc1r.
Methods We carried out small interfering RNA-mediated knock-down of Mc1r on murine melanoma B16F10 cells and performed microarray analysis to characterize changes in the gene expression profile.
Results We isolated 22 and four genes whose expression decreased and increased, respectively, by 2.5-fold or higher as the result of Mc1r knock-down. Several down-regulated genes have been proposed to be involved in cell migration. Among these genes are several members of the chemokine gene family.
Conclusion We provide a gene set for further functional analyses of Mc1r. The Mc1r target genes we present may be particularly relevant for understanding the ligand-independent activity of Mc1r. Further examination of the mode of action may lead to novel strategies in regulating the migration and metastasis of melanoma cells.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- NRF2 and Key Transcriptional Targets in Melanoma Redox Manipulation
Evan L. Carpenter, Alyssa L. Becker, Arup K. Indra
Cancers.2022; 14(6): 1531. CrossRef - Hormonal Regulation of the Repair of UV Photoproducts in Melanocytes by the Melanocortin Signaling Axis
Stuart G. Jarrett, John A. D'Orazio
Photochemistry and Photobiology.2017; 93(1): 245. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- NRF2 and Key Transcriptional Targets in Melanoma Redox Manipulation


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



