Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Miscellaneous
- Association between N-Terminal Prohormone Brain Natriuretic Peptide and Decreased Skeletal Muscle Mass in a Healthy Adult Population: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Tae Kyung Yoo, Marie Yung-Chen Wu, Moon Soo Kim, Mi-Yeon Lee, Yong-Taek Lee, Kyung Jae Yoon, Chul-Hyun Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):269-276. Published online March 13, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1588
- 1,875 View
- 77 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Although an inverse association between the N-terminal prohormone brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and obesity exists, only few major studies have assessed the association between NT-proBNP levels and skeletal muscle mass in asymptomatic healthy adults. Therefore, this cross-sectional study was conducted.
Methods
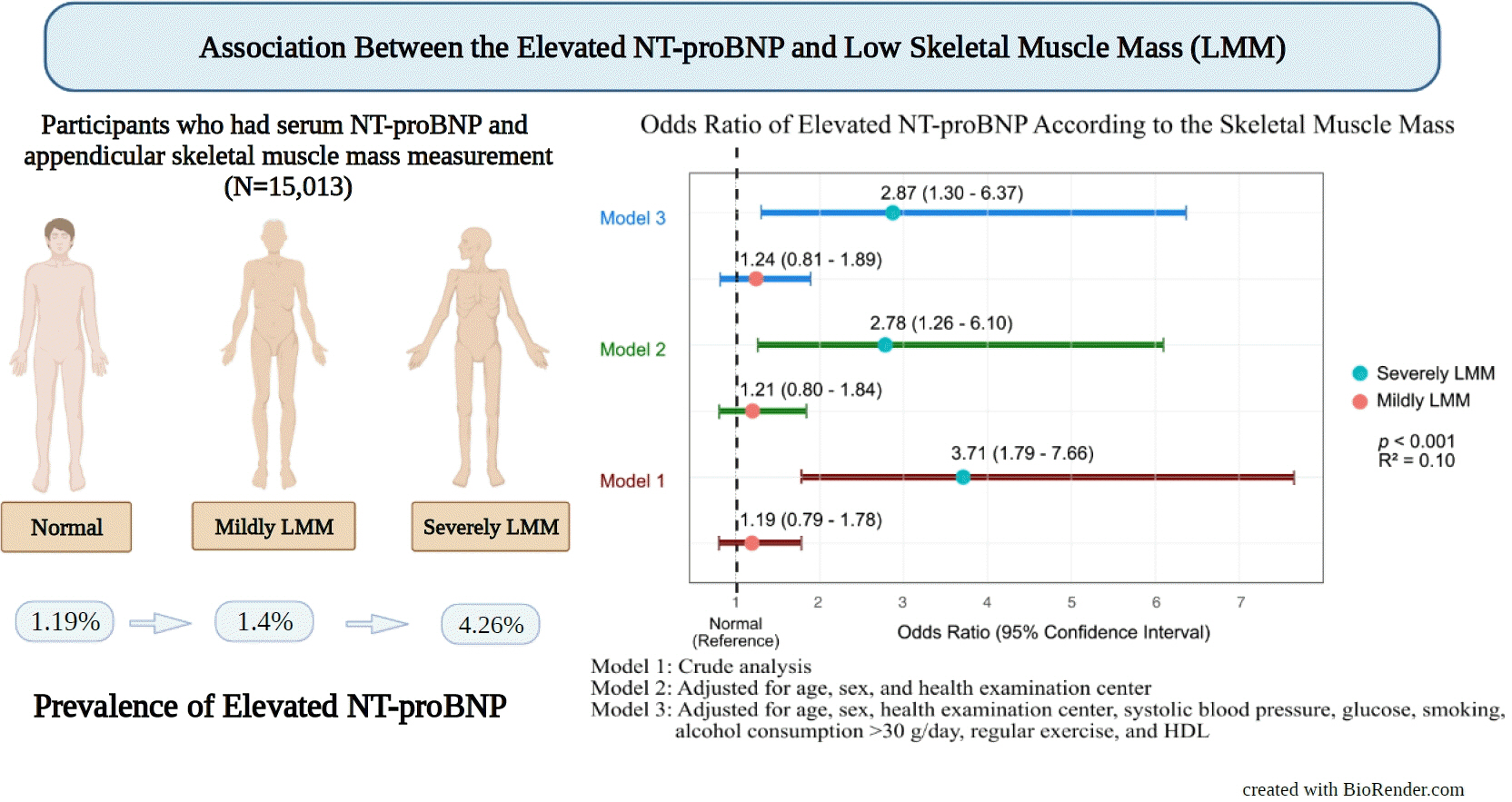
We assessed participants who underwent health examinations at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital in South Korea from January 2012 to December 2019. Appendicular skeletal muscle mass was measured using a bioelectrical impedance analyzer, and the skeletal muscle mass index (SMI) was calculated. Participants were divided into the control, mildly low skeletal muscle mass (LMM) (−2 standard deviation [SD] < SMI ≤−1 [SD]), and severely LMM groups (SD ≤−2) based on their SMI. The association between elevated NT-proBNP level (≥125 pg/mL) and skeletal muscle mass was assessed using multivariable logistic regression analysis with adjustment for confounding factors.
Results
This study enrolled 15,013 participants (mean age, 37.52±9.52; men, 54.24%; control, n=12,827; mildly LMM, n=1,998; severely LMM, n=188). Prevalence of elevated NT-proBNP was higher in mildly and severely LMM groups than in the control group (control, 1.19%; mildly LMM, 1.4%; severely LMM, 4.26%; P=0.001). The adjusted odds ratio (OR) of elevated NT-proBNP was significantly higher in severely LMM (OR, 2.87; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.3 to 6.37) than in control (OR, 1.00; reference) or mildly LMM groups (OR, 1.24; 95% CI, 0.81 to 1.89).
Conclusion
Our results showed that NT-proBNP elevation were more prevalent in participants with LMM. In addition, our study showed an association between skeletal muscle mass and NT-proBNP level in a relatively young and healthy adult population.

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Brain Regulation of Energy Metabolism
- Eun Roh, Min-Seon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(4):519-524. Published online December 20, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.4.519
- 9,908 View
- 182 Download
- 53 Web of Science
- 53 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader In healthy individuals, energy intake is in balance with energy expenditure, which helps to maintain a normal body weight. The brain's inability to control energy homeostasis underlies the pathology of hyperphagia and obesity. The brain detects body energy excess and deficit by sensing the levels of circulating metabolic hormones and nutrients and by receiving metabolic information from the periphery via the autonomic nervous system. A specialized neuronal network coordinates energy intake behavior and the metabolic processes affecting energy expenditure. Here, we briefly review neuronal mechanisms by which our body maintains energy balance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hypothalamic AMP-Activated Protein Kinase as a Whole-Body Energy Sensor and Regulator
Se Hee Min, Do Kyeong Song, Chan Hee Lee, Eun Roh, Min-Seon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 1. CrossRef - Central inhibition of stearoyl-CoA desaturase has minimal effects on the peripheral metabolic symptoms of the 3xTg Alzheimer’s disease mouse model
Laura K. Hamilton, Paule E. H. M’Bra, Sophia Mailloux, Manon Galoppin, Anne Aumont, Karl J. L. Fernandes
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Adipokines from white adipose tissue in regulation of whole body energy homeostasis
Bijayashree Sahu, Naresh C. Bal
Biochimie.2023; 204: 92. CrossRef - Growth hormone receptor (GHR) in AgRP neurons regulates thermogenesis in a sex-specific manner
Lukas Stilgenbauer, Juliana Bezerra Medeiros de Lima, Lucas Kniess Debarba, Manal Khan, Lisa Koshko, John J. Kopchick, Andrzej Bartke, Augusto Schneider, Marianna Sadagurski
GeroScience.2023; 45(3): 1745. CrossRef - Living high - training low model applied to C57BL/6J mice: Effects on physiological parameters related to aerobic fitness and acid-base balance
Pedro Paulo Menezes Scariot, Marcelo Papoti, Emanuel Elias Camolese Polisel, Juan Bordon Orsi, Paul R. Van Ginkel, Tomas A. Prolla, Fúlvia Barros Manchado-Gobatto, Claudio Alexandre Gobatto
Life Sciences.2023; 317: 121443. CrossRef - Whole Transcriptome Analysis of Hypothalamus in Mice during Short-Term Starvation
Eun-Young Oh, Byong Seo Park, Hye Rim Yang, Ho Gyun Lee, Thai Hien Tu, Sunggu Yang, Mi-Ryung Han, Jae Geun Kim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3204. CrossRef - Hormonal Gut–Brain Signaling for the Treatment of Obesity
Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3384. CrossRef - Neuronal Blockade of Thyroid Hormone Signaling Increases Sensitivity to Diet-Induced Obesity in Adult Male Mice
Eva Rial-Pensado, Laurence Canaple, Romain Guyot, Christoffer Clemmensen, Joëlle Wiersema, Shijia Wu, Sabine Richard, Anita Boelen, Timo D Müller, Miguel López, Frédéric Flamant, Karine Gauthier
Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Genetic Contributors to Obesity
Ramya Sivasubramanian, Sonali Malhotra
Gastroenterology Clinics of North America.2023; 52(2): 323. CrossRef - Neurocomputational mechanisms of food and physical activity decision-making in male adolescents
Seung-Lark Lim, Amanda S. Bruce, Robin P. Shook
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Induction of a torpor-like hypothermic and hypometabolic state in rodents by ultrasound
Yaoheng Yang, Jinyun Yuan, Rachael L. Field, Dezhuang Ye, Zhongtao Hu, Kevin Xu, Lu Xu, Yan Gong, Yimei Yue, Alexxai V. Kravitz, Michael R. Bruchas, Jianmin Cui, Jonathan R. Brestoff, Hong Chen
Nature Metabolism.2023; 5(5): 789. CrossRef - Changes in hypothalamic mu-opioid receptor expression following acute olanzapine treatment in female rats: Implications for feeding behavior
Maiken Krogsbaek, Nick Yao Larsen, Anne M. Landau, Connie Sanchez, Jens Randel Nyengaard
Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy.2023; 132: 102324. CrossRef - Insulin Resistance and Glucose Metabolism during Infection
Borros Arneth
Endocrines.2023; 4(4): 685. CrossRef - The PACAP Paradox: Dynamic and Surprisingly Pleiotropic Actions in the Central Regulation of Energy Homeostasis
Nikki Le, Sarah Sayers, Veronica Mata-Pacheco, Edward J. Wagner
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Link Between Energy-Related Sensations and Metabolism: Implications for Treating Fatigue
Marco Filippi, Rainer Krähenmann, Patrick Fissler
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Unaltered Tonic Inhibition in the Arcuate Nucleus of Diet-induced Obese Mice
Moonsun Sa, Jung Moo Lee, Mingu Gordon Park, Jiwoon Lim, Jong Min Joseph Kim, Wuhyun Koh, Bo-Eun Yoon, C. Justin Lee
Experimental Neurobiology.2022; 31(3): 147. CrossRef - Hypothalamus–Muscle Parallel Induction of Metabolic Pathways Following Physical Exercise
Almog Katz, Meital Gonen, Yael Shahar, Asael Roichman, Batia Lerrer, Haim Yosef Cohen
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Monocarboxylate transporters (MCTs) in skeletal muscle and hypothalamus of less or more physically active mice exposed to aerobic training
P.P.M. Scariot, F.B. Manchado-Gobatto, W.R. Beck, M. Papoti, P.R. Van Ginkel, C.A. Gobatto
Life Sciences.2022; 307: 120872. CrossRef - Obesity-Related Genes Expression in Testes and Sperm Parameters Respond to GLP-1 and Caloric Restriction
Ana S. Correia, Sara C. Pereira, Tiago Morais, Ana D. Martins, Mariana P. Monteiro, Marco G. Alves, Pedro F. Oliveira
Biomedicines.2022; 10(10): 2609. CrossRef - A pilot study of contrast-enhanced electrical impedance tomography for real-time imaging of cerebral perfusion
Yuyan Zhang, Jian’an Ye, Yang Jiao, Weirui Zhang, Tao Zhang, Xiang Tian, Xuetao Shi, Feng Fu, Liang Wang, Canhua Xu
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Repercussions of maternal exposure to high-fat diet on offspring feeding behavior and body composition: a systematic review
Wenicios Ferreira Chaves, Isabeli Lins Pinheiro, Jacqueline Maria da Silva, Raul Manhães-de-Castro, Raquel da Silva Aragão
Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease.2021; 12(2): 220. CrossRef - Obesity-associated Pathways of Anthocyanins
Elif YILDIZ, Metin GULDAS, Pinar ELLERGEZEN, Asli Gul ACAR, Ozan GURBUZ
Food Science and Technology.2021; 41( suppl 1): 1. CrossRef - Prostaglandin in the ventromedial hypothalamus regulates peripheral glucose metabolism
Ming-Liang Lee, Hirokazu Matsunaga, Yuki Sugiura, Takahiro Hayasaka, Izumi Yamamoto, Taiga Ishimoto, Daigo Imoto, Makoto Suematsu, Norifumi Iijima, Kazuhiro Kimura, Sabrina Diano, Chitoku Toda
Nature Communications.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Sleep and Cardiovascular Risk
Lyudmila Korostovtseva, Mikhail Bochkarev, Yurii Sviryaev
Sleep Medicine Clinics.2021; 16(3): 485. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Early Onset Genetic Obesity in Childhood
Sonali Malhotra, Ramya Sivasubramanian, Gitanjali Srivastava
Journal of Pediatric Genetics.2021; 10(03): 194. CrossRef - Gene expression atlas of energy balance brain regions
Maria Caterina De Rosa, Hannah J. Glover, George Stratigopoulos, Charles A. LeDuc, Qi Su, Yufeng Shen, Mark W. Sleeman, Wendy K. Chung, Rudolph L. Leibel, Judith Y. Altarejos, Claudia A. Doege
JCI Insight.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - New Peptides as Potential Players in the Crosstalk Between the Brain and Obesity, Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases
Magdalena Czerwińska, Katarzyna Czarzasta, Agnieszka Cudnoch-Jędrzejewska
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A putative role for lncRNAs in epigenetic regulation of memory
Ashleigh B. Irwin, Rudhab Bahabry, Farah D. Lubin
Neurochemistry International.2021; 150: 105184. CrossRef - Alteration of Relative Rates of Biodegradation and Regeneration of Cervical Spine Cartilage through the Restoration of Arterial Blood Flow Access to Rhomboid Fossa: A Hypothesis
Kirill V. Zhukov, Alexandre A. Vetcher, Bagrat A. Gasparuan, Alexander Y. Shishonin
Polymers.2021; 13(23): 4248. CrossRef - Placental NEGR1 DNA methylation is associated with BMI and neurodevelopment in preschool-age children
E Breton, V Gagné-Ouellet, K Thibeault, R Guérin, Rj Van Lieshout, P Perron, Mf Hivert, L Bouchard
Epigenetics.2020; 15(3): 323. CrossRef - The dorsomedial hypothalamus and nucleus of the solitary tract as key regulators in a rat model of chronic obesity
Chen Zhang, Pernille Barkholt, Jens Christian Nielsen, Ditte Dencker Thorbek, Kristoffer Rigbolt, Niels Vrang, David Paul Drucker Woldbye, Jacob Jelsing
Brain Research.2020; 1727: 146538. CrossRef - Hypothalamic NAD+-Sirtuin Axis: Function and Regulation
Eun Roh, Min-Seon Kim
Biomolecules.2020; 10(3): 396. CrossRef - The Rho/Rac Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor Vav1 Regulates Hif-1α and Glut-1 Expression and Glucose Uptake in the Brain
Jaewoo Hong, Yurim Kim, Sudhirkumar Yanpallewar, P. Charles Lin
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(4): 1341. CrossRef - Sirtuin (SIRT)-1: At the crossroads of puberty and metabolism
Carlos F. Aylwin, Alejandro Lomniczi
Current Opinion in Endocrine and Metabolic Research.2020; 14: 65. CrossRef - Metabolomics Reveals the Alteration of Metabolic Pathway by Alpha-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone in B16F10 Melanoma Cells
Seung-Ho Seo, Jae Kwon Jo, Eun-Ju Kim, Seong-Eun Park, Seo Yeon Shin, Kyung Mok Park, Hong-Seok Son
Molecules.2020; 25(15): 3384. CrossRef - Noninvasive real-time detection of cerebral blood perfusion in hemorrhagic shock rabbits based on whole-brain magnetic induction phase shift: an experimental study
Wencai Pan, Wei Zhuang, Yinbao Chong, Mingxin Qin, Yang Li, Jingjing Xiao, Qing Wang, Shihui Zhang, Shuanglin Zhao, Peng Zhao
Physiological Measurement.2020; 41(9): 095004. CrossRef - Neurochemical regulators of food behavior for pharmacological treatment of obesity: current status and future prospects
Gayane Sargis Vardanyan, Hasmik Samvel Harutyunyan, Michail Iosif Aghajanov, Ruben Sargis Vardanyan
Future Medicinal Chemistry.2020; 12(20): 1865. CrossRef - The Co-occurrence of Pediatric Obesity and ADHD: an Understanding of Shared Pathophysiology and Implications for Collaborative Management
Valerie M. O’Hara, Jennifer L. Curran, Nancy T. Browne
Current Obesity Reports.2020; 9(4): 451. CrossRef - Constitutive Androstane Receptor: A Peripheral and a Neurovascular Stress or Environmental Sensor
Fabiana Oliviero, Céline Lukowicz, Badreddine Boussadia, Isabel Forner-Piquer, Jean-Marc Pascussi, Nicola Marchi, Laila Mselli-Lakhal
Cells.2020; 9(11): 2426. CrossRef - Automated diffusion-based parcellation of the hypothalamus reveals subunit-specific associations with obesity
Melanie Spindler, Jale Özyurt, Christiane M. Thiel
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - SIRT1 in Astrocytes Regulates Glucose Metabolism and Reproductive Function
Irene Choi, Emily Rickert, Marina Fernandez, Nicholas J G Webster
Endocrinology.2019; 160(6): 1547. CrossRef - Hypothalamic mechanisms associated with corticotropin-releasing factor-induced anorexia in chicks
Jinxin Wang, Justin Matias, Elizabeth R. Gilbert, Tetsuya Tachibana, Mark A. Cline
Neuropeptides.2019; 74: 95. CrossRef - HMG-CoA synthase 2 drives brain metabolic reprogramming in cocaine exposure
Xue Shao, Yunxuan Tang, Hailei Long, Hui Gu, Jie Zhang, Pengchi Deng, Yinglan Zhao, Xiaobo Cen
Neuropharmacology.2019; 148: 377. CrossRef - The Effect of Feeding Behavior on Hypothalamus in Obese Type 2 Diabetic Rats with Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Intervention
Ke Lu, Xiaoyan Chen, Jianhua Yan, Xinchun Li, Chen Huang, Qi Wan, Xuelian Deng, Qiao Zou
Obesity Facts.2018; 11(3): 181. CrossRef - The Long-Term Impact of High Levels of Alpha-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone in Energy Balance Among Obese Adolescents
Ana Claudia Pelissari Kravchychyn, Raquel Munhoz da Silveira Campos, Flávia Campos Corgosinho, Deborah Cristina Landi Masquio, Sofia Emanuelle de Castro Ferreira Vicente, Yasmin Alaby Martins Ferreira, Patrícia Leão Silva, Aline de Piano Ganen, Lila Missa
Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism.2018; 72(4): 279. CrossRef - Psychopharmacological advances in eating disorders
Hubertus Himmerich, Janet Treasure
Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology.2018; 11(1): 95. CrossRef - Food engineering into the XXI century
José Miguel Aguilera
AIChE Journal.2018; 64(1): 2. CrossRef - The Role of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 (GLP1) in Type 3 Diabetes: GLP-1 Controls Insulin Resistance, Neuroinflammation and Neurogenesis in the Brain
Choon Bae, Juhyun Song
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2017; 18(11): 2493. CrossRef - “I Am I and My Bacterial Circumstances”: Linking Gut Microbiome, Neurodevelopment, and Depression
Juan M. Lima-Ojeda, Rainer Rupprecht, Thomas C. Baghai
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Hypothalamic circuits regulating appetite and energy homeostasis: pathways to obesity
Katharina Timper, Jens C. Brüning
Disease Models & Mechanisms.2017; 10(6): 679. CrossRef - Brain glucose metabolism: Role of Wnt signaling in the metabolic impairment in Alzheimer’s disease
Pedro Cisternas, Nibaldo C. Inestrosa
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews.2017; 80: 316. CrossRef - Astrocyte-Specific Deletion of Peroxisome-Proliferator Activated Receptor-γ Impairs Glucose Metabolism and Estrous Cycling in Female Mice
Marina O Fernandez, Katherine Hsueh, Hyun Tae Park, Consuelo Sauceda, Vicky Hwang, Deepak Kumar, Sun Kim, Emily Rickert, Sumana Mahata, Nicholas J G Webster
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2017; 1(11): 1332. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef
- Hypothalamic AMP-Activated Protein Kinase as a Whole-Body Energy Sensor and Regulator

- Adrenal gland
- Herpes Virus Entry Mediator Signaling in the Brain Is Imperative in Acute Inflammation-Induced Anorexia and Body Weight Loss
- Kwang Kon Kim, Sung Ho Jin, Byung Ju Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2013;28(3):214-220. Published online September 13, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2013.28.3.214
- 3,052 View
- 30 Download
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Reduced appetite and body weight loss are typical symptoms of inflammatory diseases. A number of inflammatory stimuli are responsible for the imbalance in energy homeostasis, leading to metabolic disorders. The herpes virus entry mediator (HVEM) protein plays an important role in the development of various inflammatory diseases, such as intestinal inflammation and diet-induced obesity. However, the role of HVEM in the brain is largely unknown. This study aims to investigate whether HVEM signaling in the brain is involved in inflammation-induced anorexia and body weight loss.
Methods Food intake and body weight were measured at 24 hours after intraperitoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or intracerebroventricular injection of recombinant mouse LIGHT (also called tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily 14, TNFSF14), an HVEM ligand, into 8- to 10-week-old male C57BL/6 mice and mice lacking HVEM expression (HVEM-/-). We also assessed LPS-induced change in hypothalamic expression of HVEM using immunohistochemistry.
Results Administration of LPS significantly reduced food intake and body weight, and moreover, increased expression of HVEM in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus. However, LPS induced only minor decreases in food intake and body weight in HVEM-/- mice. Administration of LIGHT into the brain was very effective at decreasing food intake and body weight in wild-type mice, but was less effective in HVEM-/- mice.
Conclusion Activation of brain HVEM signaling is responsible for inflammation-induced anorexia and body weight loss.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pediatric traumatic brain injury and a subsequent transient immune challenge independently influenced chronic outcomes in male mice
Rishabh Sharma, Pablo M. Casillas-Espinosa, Larissa K. Dill, Sarah S.J. Rewell, Matthew R. Hudson, Terence J. O'Brien, Sandy R. Shultz, Bridgette D. Semple
Brain, Behavior, and Immunity.2022; 100: 29. CrossRef - Bodyweight, locomotion, and behavioral responses of the naked mole rat (Heterocephalus glaber) to lipopolysaccharide administration
Mosiany Letura Kisipan, Rodi Omondi Ojoo, Titus Ikusya Kanui, Klas S. P. Abelson
Journal of Comparative Physiology A.2022; 208(4): 493. CrossRef - Intestinal Epithelial Toll-like Receptor 4 Deficiency Modifies the Response to the Activity-Based Anorexia Model in a Sex-Dependent Manner: A Preliminary Study
Pauline Tirelle, Colin Salaün, Alexandre Kauffmann, Christine Bôle-Feysot, Charlène Guérin, Marion Huré, Alexis Goichon, Asma Amamou, Jonathan Breton, Jean-Luc do Rego, Pierre Déchelotte, Najate Achamrah, Moïse Coëffier
Nutrients.2022; 14(17): 3607. CrossRef - A systemic immune challenge to model hospital-acquired infections independently regulates immune responses after pediatric traumatic brain injury
Rishabh Sharma, Akram Zamani, Larissa K. Dill, Mujun Sun, Erskine Chu, Marcus J. Robinson, Terence J. O’Brien, Sandy R. Shultz, Bridgette D. Semple
Journal of Neuroinflammation.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Inflammation-induced alterations in maternal-fetal Heme Oxygenase (HO) are associated with sustained innate immune cell dysregulation in mouse offspring
Maide Ozen, Hui Zhao, Flora Kalish, Yang Yang, Lauren L. Jantzie, Ronald J. Wong, David K. Stevenson, Leticia Reyes
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(6): e0252642. CrossRef - Treatment With Lipopolysaccharide Induces Distinct Changes in Metabolite Profile and Body Weight in 129Sv and Bl6 Mouse Strains
Maria Piirsalu, Egon Taalberg, Kersti Lilleväli, Li Tian, Mihkel Zilmer, Eero Vasar
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Systemic effects in naïve mice injected with immunomodulatory lectin ArtinM
Patrícia Kellen Martins Oliveira Brito, Thiago Eleutério Gonçalves, Fabrício Freitas Fernandes, Camila Botelho Miguel, Wellington Francisco Rodrigues, Javier Emílio Lazo Chica, Maria Cristina Roque-Barreira, Thiago Aparecido da Silva, Sujit Kumar Bhutia
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(10): e0187151. CrossRef - Corosolic acid ameliorates acute inflammation through inhibition of IRAK-1 phosphorylation in macrophages
Seung-Jae Kim, Ji-Young Cha, Hye Suk Kang, Jae-Ho Lee, Ji Yoon Lee, Jae-Hyung Park, Jae-Hoon Bae, Dae-Kyu Song, Seung-Soon Im
BMB Reports.2016; 49(5): 276. CrossRef - Patent Highlights April–May 2016
Hermann AM Mucke
Pharmaceutical Patent Analyst.2016; 5(5): 301. CrossRef - Brief Review of Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2013
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(3): 251. CrossRef - Overexpression of CCN3 Inhibits Inflammation and Progression of Atherosclerosis in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice
Jun Liu, Yingang Ren, Li Kang, Lihua Zhang, Philip Michael Bauer
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(4): e94912. CrossRef
- Pediatric traumatic brain injury and a subsequent transient immune challenge independently influenced chronic outcomes in male mice

- Effects of Dopamine on the Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone(GnRH) Neurons.
- Han Seong Kyu
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2005;20(5):488-495. Published online October 1, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2005.20.5.488
- 1,590 View
- 42 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) neurons represent the final output cells of the neural network that controls fertility. Dopamine (DA) has been shown to control gonadotropin release in many species. However, the direct membrane effects of DA and the related receptors on GnRH neurons remain poorly understood. The purpose of this study was to investigate the direct actions of DA on GnRH neurons and the related receptors using brain slice electrophysiology. METHODS: Gramicidin-perforated patch clamp recordings were made from the GnRH neurons to examine the direct membrane effects of DA in GnRH-EGFP mut5 mice. RESULTS: DA induced hyperpolarization of the GnRH neurons, which was maintained in the presence of tetrodotoxin (TTX), a Na+ channel blocker, suggesting a direct, rather than indirect, action of DA on GnRH neurons. DA-induced hyperpolarizing effects were blocked by prazosin, an alpah1-adrenergic antagonist, and mimicked by phenylephrine (PE), an alpha1-adrenergic agonist. CONCLUSIONS: These data indicate that DA exerts a direct inhibitory effect on GnRH neurons via the alpha1- adrenergic receptors. These results support the general concept that dopaminergic afference represents a predominantly inhibitory component of the GnRH neuronal network. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Carving the senescent phenotype by the chemical reactivity of catecholamines: An integrative review
Aleksei G. Golubev
Ageing Research Reviews.2022; 75: 101570. CrossRef - The adverse effects of psychotropic drugs as an endocrine disrupting chemicals on the hypothalamic-pituitary regulation in male
Sinem Ilgin
Life Sciences.2020; 253: 117704. CrossRef
- Carving the senescent phenotype by the chemical reactivity of catecholamines: An integrative review

- Brain Metastasis from Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Report of 2 Cases.
- Jung Gu Lee, Ki Young Lee, Yon Sil Jung, Hong Kyu Kim, Hye Young Park, Jong Ho Kim, Moon Ho Kang
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1999;14(4):745-751. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,084 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Papillary carcinoma, the commonest thyroid malignancy, has an indolent clinical course and carries a good prognosis. Metastasis usually occurs to regional lymph nodes, including cervical and upper mediastinal nodes. Distant metastasis is uncommon, lung and bone being the commonest sites. Brain metastasis from papillary thyroid cancer is rare, with a frequency of less than 1% in several reported series and an extremely poor prognosis. The first case was a 74-year-old female patient with papillary cancer who took total thyroidectomy followed by 131I therapy 1 month later. Two days after 131I therapy, she developed headache, vomiting and left hemiplegia. Brain MRI and 131I whole body scan showed solitary brain metastasis in right parietal lobe. After a few weeks her condition improved enough to maintain her usual daily activity despite mild motor weakness. The second one, a 64-year-old female patient presented with headache and vomiting. Two years previously, she had taken total thyroidectomy and 131I ablation therapy after diagnosis of thyroid papillary cancer. Eight months before, she had undergone radical neck dissection because of relapse in cervical lymph nodes. Brain MRI revealed multple metastatic lesions including cerebellum. This patient did not report for follow-up after 2 months of discharge.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



