Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Calcium & bone metabolism
- Acromegaly and Bone: An Update
- Andrea Giustina
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):655-666. Published online December 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.601

- 1,378 View
- 116 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Since our discovery in 2006 that acromegaly is associated with an increased risk of vertebral fractures, many authors have confirmed this finding in both cross-sectional and prospective studies. Due to the high epidemiological and clinical impact of this newly discovered comorbidity of acromegaly, this topic has progressively become more important and prominent over the years, and the pertinent literature has been enriched by new findings on the pathophysiology and treatment. The aim of this narrative review was to discuss these novel findings, integrating them with the seminal observations, in order to give the reader an updated view of how the field of acromegaly and bone is developing, from strong clinical observations to a mechanistic understanding and possible prevention and treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- New insights into the vitamin D/PTH axis in endocrine-driven metabolic bone diseases
Luigi di Filippo, John P. Bilezikian, Ernesto Canalis, Umberto Terenzi, Andrea Giustina
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- New insights into the vitamin D/PTH axis in endocrine-driven metabolic bone diseases

- Calcium & bone metabolism
- Characteristics Associated with Bone Loss after Spinal Cord Injury: Implications for Hip Region Vulnerability
- Sora Han, Sungjae Shin, Onyoo Kim, Namki Hong
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):578-587. Published online October 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1795
- 1,348 View
- 53 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
In individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI), bone loss progresses rapidly to the area below the level of injury, leading to an increased risk of fracture. However, there are limited data regarding SCI-relevant characteristics for bone loss and the degree of bone loss in individuals with SCI compared with that in non-SCI community-dwelling adults.
Methods
Data from men with SCI who underwent dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry at the National Rehabilitation Center (2008 to 2020) between 12 and 36 months after injury were collected and analyzed. Community-dwelling men were matched 1:1 for age, height, and weight as the control group, using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES, 2008 to 2011).
Results
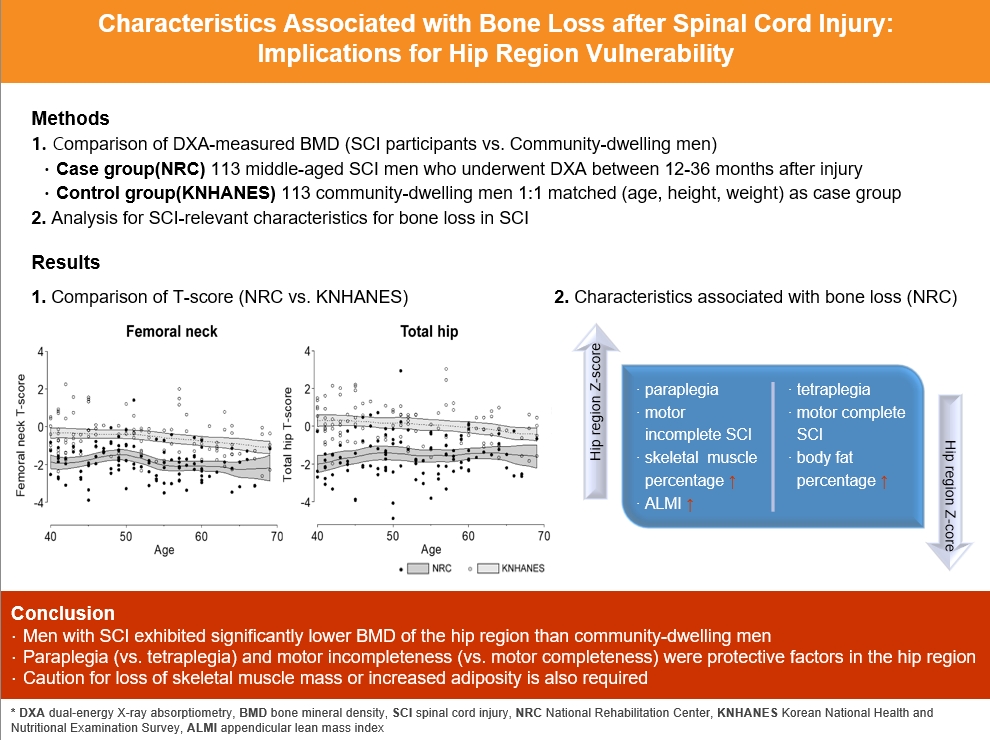
A comparison of the SCI and the matched control group revealed significantly lower hip region T-scores in the SCI group, whereas the lumbar spine T-score did not differ between groups. Among the 113 men with SCI, the paraplegia group exhibited significantly higher Z-scores of the hip region than the tetraplegia group. Participants with motor-incomplete SCI showed relatively preserved Z-scores of the hip region compared to those of the lumbar region. Moreover, in participants with SCI, the percentage of skeletal muscle displayed a moderate positive correlation with femoral neck Z-scores.
Conclusion
Men with SCI exhibited significantly lower bone mineral density of the hip region than community-dwelling men. Paraplegia rather than tetraplegia, and motor incompleteness rather than motor completeness were protective factors in the hip region. Caution for loss of skeletal muscle mass or increased adiposity is also required.

- Thyroid
- Evaluation and Management of Bone Health in Patients with Thyroid Diseases: A Position Statement of the Korean Thyroid Association
- A Ram Hong, Ho-Cheol Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):175-189. Published online April 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1701
- 3,971 View
- 248 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
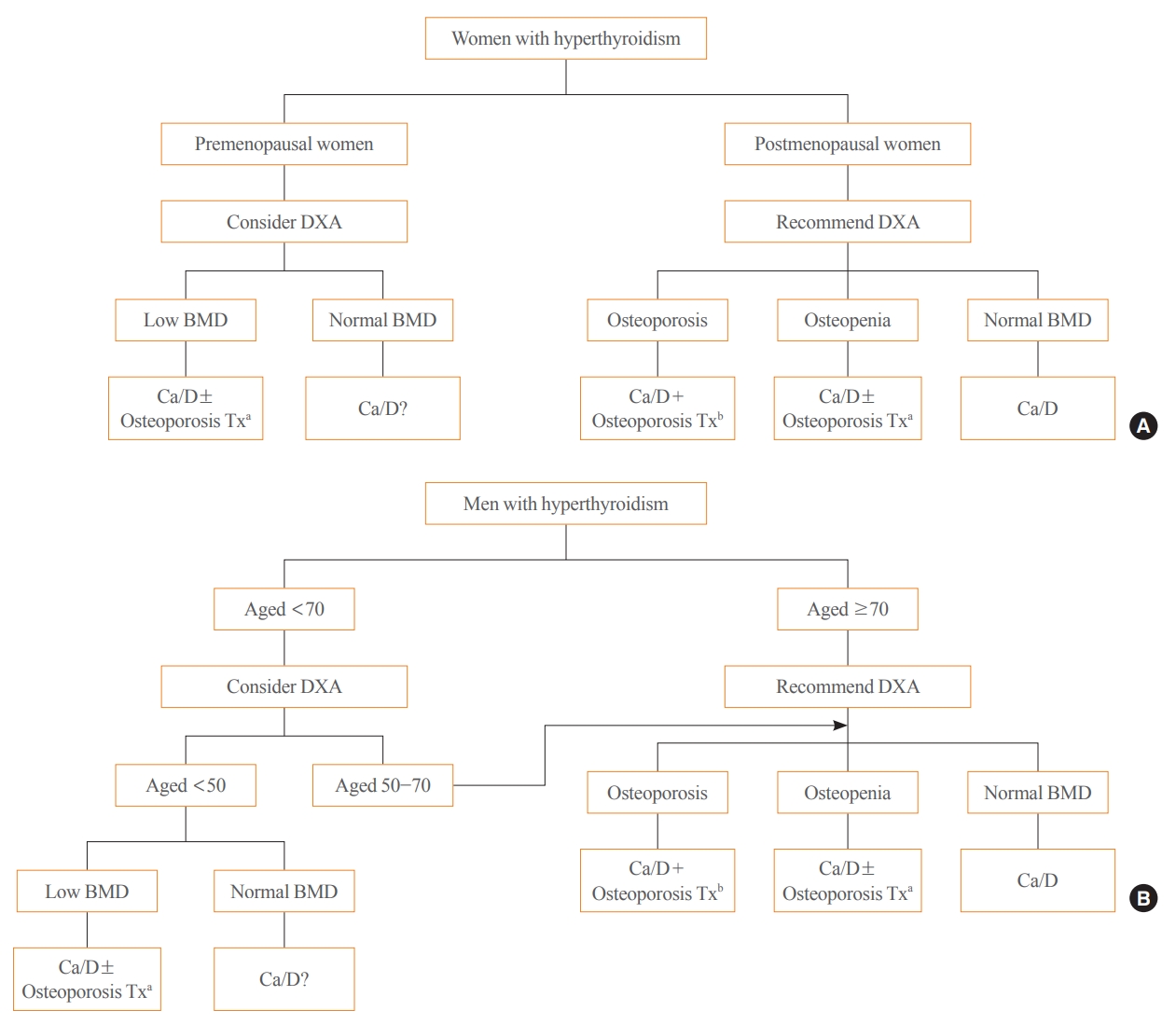
ePub - Thyroid hormones play an important physiological role in maintaining adult bone structure and strength. Consequently, thyroid dysfunction is related to skeletal outcomes. Overt hyperthyroidism is an established cause of high bone turnover with accelerated bone loss, leading to osteoporosis and increased fracture risk. Hyperthyroidism induced by thyroid-stimulating hormone-suppressive therapy in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer is a cause of secondary osteoporosis. In contrast, there is a lack of evidence on the negative impact of hypothyroidism on bone health. Considering the clinical updates on the importance of bone health in thyroid dysfunction, the Task Force from the Clinical Practice Guidelines Development Committee of the Korean Thyroid Association recently developed a position statement on the evaluation and management of bone health of patients with thyroid diseases, particularly focused on endogenous hyperthyroidism and thyroid-stimulating hormone-suppressive therapy-associated hyperthyroidism in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Herein, we review the Korean Thyroid Association’s position statement on the evaluation and management of bone health associated with thyroid diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnosis and therapeutic approach to bone health in patients with hypopituitarism
Justyna Kuliczkowska-Płaksej, Aleksandra Zdrojowy-Wełna, Aleksandra Jawiarczyk-Przybyłowska, Łukasz Gojny, Marek Bolanowski
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis, and Subchondral Insufficiency Fracture: Recent Insights
Shunichi Yokota, Hotaka Ishizu, Takuji Miyazaki, Daisuke Takahashi, Norimasa Iwasaki, Tomohiro Shimizu
Biomedicines.2024; 12(4): 843. CrossRef - Review on the protective activity of osthole against the pathogenesis of osteoporosis
Jincai Chen, Xiaofei Liao, Juwen Gan
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Diagnosis and therapeutic approach to bone health in patients with hypopituitarism

- Calcium & bone metabolism
- Persistence with Denosumab in Male Osteoporosis Patients: A Real-World, Non-Interventional Multicenter Study
- Chaiho Jeong, Jeongmin Lee, Jinyoung Kim, Jeonghoon Ha, Kwanhoon Jo, Yejee Lim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Tae-Seo Sohn, Ki-Ho Song, Moo Il Kang, Ki-Hyun Baek
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):260-268. Published online April 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1663
- 1,788 View
- 111 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Persistence with denosumab in male patients has not been adequately investigated, although poor denosumab persistence is associated with a significant risk of rebound vertebral fractures.
Methods
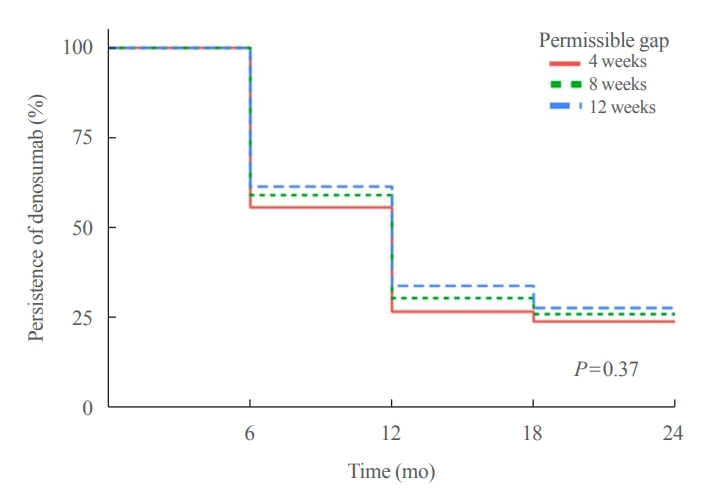
We retrospectively evaluated 294 Korean male osteoporosis patients treated with denosumab at three medical centers and examined their persistence with four doses of denosumab injection over 24 months of treatment. Persistence was defined as the extent to which a patient adhered to denosumab treatment in terms of the prescribed interval and dose, with a permissible gap of 8 weeks. For patients who missed their scheduled treatment appointment(s) during the follow-up period (i.e., no-shows), Cox proportional regression analysis was conducted to explore the factors associated with poor adherence. Several factors were considered, such as age, prior anti-osteoporotic drug use, the treatment provider’s medical specialty, the proximity to the medical center, and financial burdens of treatment.
Results
Out of 294 male patients, 77 (26.2%) completed all four sequential rounds of the denosumab treatment. Out of 217 patients who did not complete the denosumab treatment, 138 (63.6%) missed the scheduled treatment(s). Missing treatment was significantly associated with age (odds ratio [OR], 1.03), prior bisphosphonate use (OR, 0.76), and prescription by non-endocrinologists (OR, 2.24). Denosumab was stopped in 44 (20.3%) patients due to medical errors, in 24 (11.1%) patients due to a T-score improvement over –2.5, and in five (2.3%) patients due to expected dental procedures.
Conclusion
Our study showed that only one-fourth of Korean male osteoporosis patients were fully adherent to 24 months of denosumab treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Denosumab
Reactions Weekly.2023; 1963(1): 206. CrossRef
- Denosumab

- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
- Bone Mineral Density Screening Interval and Transition to Osteoporosis in Asian Women
- Hyunju Park, Heera Yang, Jung Heo, Hye Won Jang, Jae Hoon Chung, Tae Hyuk Kim, Yong-Ki Min, Sun Wook Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):506-512. Published online June 9, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1429

- 3,085 View
- 104 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Bone mineral density (BMD) testing is indicated for women aged 65 years, but screening strategies for osteoporosis are controversial. Currently, there is no study focusing on the BMD testing interval in Asian populations. The current study aimed to evaluate the estimated time interval for screening osteoporosis.
Methods
We conducted a study of 6,385 subjects aged 50 years and older who underwent dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry screening more than twice at Samsung Medical Center as participants in a routine health checkup. Subjects were divided based on baseline T-score into mild osteopenia (T-score, <–1.0 to >–1.5), moderate osteopenia (T-score, ≤–1.5 to >–2.0), and severe osteopenia (T-score, ≤–2.0 to >–2.5). Information about personal medical and social history was collected by a structured questionnaire.
Results
The adjusted estimated BMD testing interval for 10% of the subjects to develop osteoporosis was 13.2 years in mild osteopenia, 5.0 years in moderate osteopenia, and 1.5 years in severe osteopenia.
Conclusion
Our study provides extended information about BMD screening intervals in Asian female population. Baseline T-score was important for predicting BMD screening interval, and repeat BMD testing within 5 years might not be necessary in mild osteopenia subjects. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Bazedoxifene/Vitamin D Combination Therapy on Serum Vitamin D Levels and Bone Turnover Markers in Postmenopausal Women with Osteopenia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Chaiho Jeong, Jeonghoon Ha, Jun-Il Yoo, Young-Kyun Lee, Jung Hee Kim, Yong-Chan Ha, Yong-Ki Min, Dong-Won Byun, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ho Yeon Chung
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2023; 30(2): 189. CrossRef - Bone-modifying agents for non–small-cell lung cancer patients with bone metastases during the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors: A narrative review
Jinyoung Kim, Chaiho Jeong, Jeongmin Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Ki-Hyun Baek, Seohyun Kim, Tai Joon An, Chan Kwon Park, Hyoung Kyu Yoon, Jeong Uk Lim
Seminars in Oncology.2023; 50(3-5): 105. CrossRef
- Effects of Bazedoxifene/Vitamin D Combination Therapy on Serum Vitamin D Levels and Bone Turnover Markers in Postmenopausal Women with Osteopenia: A Randomized Controlled Trial

- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
- Real-World Safety and Effectiveness of Denosumab in Patients with Osteoporosis: A Prospective, Observational Study in South Korea
- Yumie Rhee, Dong-Gune Chang, Jeonghoon Ha, Sooa Kim, Yusun Lee, Euna Jo, Jung-Min Koh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):497-505. Published online June 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1427

- 5,436 View
- 268 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The efficacy and safety of denosumab have been established in a phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial in Korean postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. This postmarketing surveillance study was aimed to investigate the safety and effectiveness of denosumab in Korean real-world clinical practice.
Methods
Patients with osteoporosis who had received denosumab per the Korean approved indications in the postmarketing setting between September 2014 and September 2019 were enrolled. The primary endpoint was the incidence of adverse events (AEs) and adverse drug reactions (ADRs). The secondary endpoint was the percent change from baseline in bone mineral density (BMD) of the lumbar spine, total hip, and femoral neck.
Results
Of the 3,221 patients enrolled, 3,185 were included in the safety analysis set; 2,973 (93.3%) were female, and the mean± standard deviation (SD) age was 68.9±9.9 years. The mean±SD study period was 350.0±71.4 days. AEs, fatal AEs, and ADRs occurred in 19.3%, 0.8%, and 1.6%, respectively. The most frequent AEs, occurring in >0.5% of patients, were dizziness (0.7%), arthralgia (0.7%), back pain (0.6%), and myalgia (0.6%). Hypocalcemia occurred in 0.3% of patients. There were no cases of osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical femoral fracture. Mean±SD percent change from baseline in BMD of the lumbar spine, total hip, and femoral neck was 7.3%±23.6%, 3.6%±31.4%, and 3.2%±10.7%, respectively.
Conclusion
The safety and effectiveness of denosumab in Korean patients with osteoporosis in this study were comparable with those in the Korean randomized controlled trial, with no new safety findings. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of denosumab-induced hypocalcemia: a retrospective observational study of patients routinely monitored with ionized calcium post-injection
Anna Spångeus, Johan Rydetun, Mischa Woisetschläger
Osteoporosis International.2024; 35(1): 173. CrossRef - Cost-consequence analysis of continuous denosumab therapy for osteoporosis treatment in South Korea
Seungju Cha, Minjeong Sohn, Hyowon Yang, Eric J. Yeh, Ki-Hyun Baek, Jeonghoon Ha, Hyemin Ku
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Denosumab and the Risk of Diabetes in Patients Treated for Osteoporosis
Huei-Kai Huang, Albert Tzu-Ming Chuang, Tzu-Chi Liao, Shih-Chieh Shao, Peter Pin-Sung Liu, Yu-Kang Tu, Edward Chia-Cheng Lai
JAMA Network Open.2024; 7(2): e2354734. CrossRef - Adverse Effects of Denosumab in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A 20-Year Retrospective Single-Center Observation Study in Central Taiwan
Tsung-Yin Tsai, Zi-Hong You, Shang-Feng Tsai, Ming-Ju Wu, Tung-Min Yu, Ya-Wen Chuang, Yung-Chieh Lin, Ya-Lian Deng, Chiann-Yi Hsu, Cheng-Hsu Chen
Transplantation Proceedings.2023; 55(4): 837. CrossRef - Persistence with Denosumab in Male Osteoporosis Patients: A Real-World, Non-Interventional Multicenter Study
Chaiho Jeong, Jeongmin Lee, Jinyoung Kim, Jeonghoon Ha, Kwanhoon Jo, Yejee Lim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Tae-Seo Sohn, Ki-Ho Song, Moo Il Kang, Ki-Hyun Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 260. CrossRef - Effect of Denosumab on Bone Density in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: A Comparison with and without Calcium Supplementation in Patients on Standard Diets in Korea
Chaiho Jeong, Jinyoung Kim, Jeongmin Lee, Yejee Lim, Dong-Jun Lim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Jeonghoon Ha
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(21): 6904. CrossRef - Denosumab
Reactions Weekly.2022; 1919(1): 221. CrossRef - Denosumab, an effective osteoporosis treatment option for men
Sung Hye Kong
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2022; 37(5): 947. CrossRef
- Prevalence of denosumab-induced hypocalcemia: a retrospective observational study of patients routinely monitored with ionized calcium post-injection

- Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland
- Metabolic Impacts of Discontinuation and Resumption of Recombinant Human Growth Hormone Treatment during the Transition Period in Patients with Childhood-Onset Growth Hormone Deficiency
- Yun Jeong Lee, Yunha Choi, Han-Wook Yoo, Young Ah Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Han Saem Choi, Ho-Seong Kim, Jae Hyun Kim, Jung Eun Moon, Cheol Woo Ko, Moon Bae Ahn, Byung-Kyu Suh, Jin-Ho Choi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):359-368. Published online April 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1384
- 4,461 View
- 185 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Discontinuing growth hormone (GH) treatment during the transition to adulthood has been associated with adverse health outcomes in patients with childhood-onset growth hormone deficiency (CO-GHD). This study investigated the metabolic changes associated with interrupting GH treatment in adolescents with CO-GHD during the transition period.
Methods
This study included 187 patients with CO-GHD who were confirmed to have adult GHD and were treated at six academic centers in Korea. Data on clinical parameters, including anthropometric measurements, metabolic profiles, and bone mineral density (BMD) at the end of childhood GH treatment, were collected at the time of re-evaluation for GHD and 1 year after treatment resumption.
Results
Most patients (n=182, 97.3%) had organic GHD. The median age at treatment discontinuation and re-evaluation was 15.6 and 18.7 years, respectively. The median duration of treatment interruption was 2.8 years. During treatment discontinuation, body mass index Z-scores and total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein, and non-high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels increased, whereas fasting glucose levels decreased. One year after GH treatment resumption, fasting glucose levels, HDL cholesterol levels, and femoral neck BMD increased significantly. Longer GH interruption (>2 years, 60.4%) resulted in worse lipid profiles at re-evaluation. The duration of interruption was positively correlated with fasting glucose and non-HDL cholesterol levels after adjusting for covariates.
Conclusion
GH treatment interruption during the transition period resulted in worse metabolic parameters, and a longer interruption period was correlated with poorer outcomes. GH treatment should be resumed early in patients with CO-GHD during the transition period. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ghrelin regulating liver activity and its potential effects on liver fibrosis and Echinococcosis
Jiang Zhu, Tanfang Zhou, Meng Menggen, Kalibixiati Aimulajiang, Hao Wen
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Composición de la microbiota en pacientes con déficit de hormona de crecimiento antes y después de recibir tratamiento
Patricia García Navas, María Yolanda Ruíz del Prado, Pablo Villoslada Blanco, Emma Recio Fernández, María Ruíz del Campo, Patricia Pérez Matute
Anales de Pediatría.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between the Stimulated Peak Growth Hormone Level and Metabolic Parameters in Children with Growth Hormone Deficiency
Seong Yong Lee
The Ewha Medical Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dyslipidaemia and growth hormone deficiency – A comprehensive review
Matthias Hepprich, Fahim Ebrahimi, Emanuel Christ
Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 37(6): 101821. CrossRef
- Ghrelin regulating liver activity and its potential effects on liver fibrosis and Echinococcosis

- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
- Discontinuing Denosumab: Can It Be Done Safely? A Review of the Literature
- Wei Lin Tay, Donovan Tay
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):183-194. Published online April 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1369

- 16,283 View
- 901 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Denosumab, which has been approved for the treatment of osteoporosis since 2010, is a fully humanised monoclonal antibody against a cytokine, receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL), involved in bone resorption. Continued use of denosumab results in a potent and sustained decrease in bone turnover, an increase in bone mineral density (BMD), and a reduction in vertebral and hip fractures. The anti-resorptive effects of denosumab are reversible upon cessation, and this reversal is accompanied by a transient marked increase in bone turnover that is associated with bone loss, and of concern, an increased risk of multiple vertebral fractures. In this review, we outline the effects of denosumab withdrawal on bone turnover markers, BMD, histomorphometry, and fracture risk. We provide an update on recent clinical trials that sought to answer how clinicians can transition away from denosumab safely with follow-on therapy to mitigate bone loss and summarise the recommendations of various international guidelines.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Loss of lower extremity bone mineral density 1 year after denosumab is discontinued in persons with subacute spinal cord injury
Christopher M. Cirnigliaro, Michael F. La Fountaine, J. Scott Parrott, Steven C. Kirshblum, Susan J. Sauer, Sue A. Shapses, Isa A. McClure, William A. Bauman
Osteoporosis International.2023; 34(4): 741. CrossRef - Persistence with Denosumab in Male Osteoporosis Patients: A Real-World, Non-Interventional Multicenter Study
Chaiho Jeong, Jeongmin Lee, Jinyoung Kim, Jeonghoon Ha, Kwanhoon Jo, Yejee Lim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Tae-Seo Sohn, Ki-Ho Song, Moo Il Kang, Ki-Hyun Baek
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 260. CrossRef
- Loss of lower extremity bone mineral density 1 year after denosumab is discontinued in persons with subacute spinal cord injury

- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - 10-Year Fracture Risk in Postmenopausal Women with Osteopenia and Osteoporosis in South Korea
- Yeon-Hee Baek, Sun Wook Cho, Han Eol Jeong, Ju Hwan Kim, Yunji Hwang, Jeffrey L. Lange, Ju-Young Shin
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1178-1188. Published online December 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1215
- 5,325 View
- 249 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
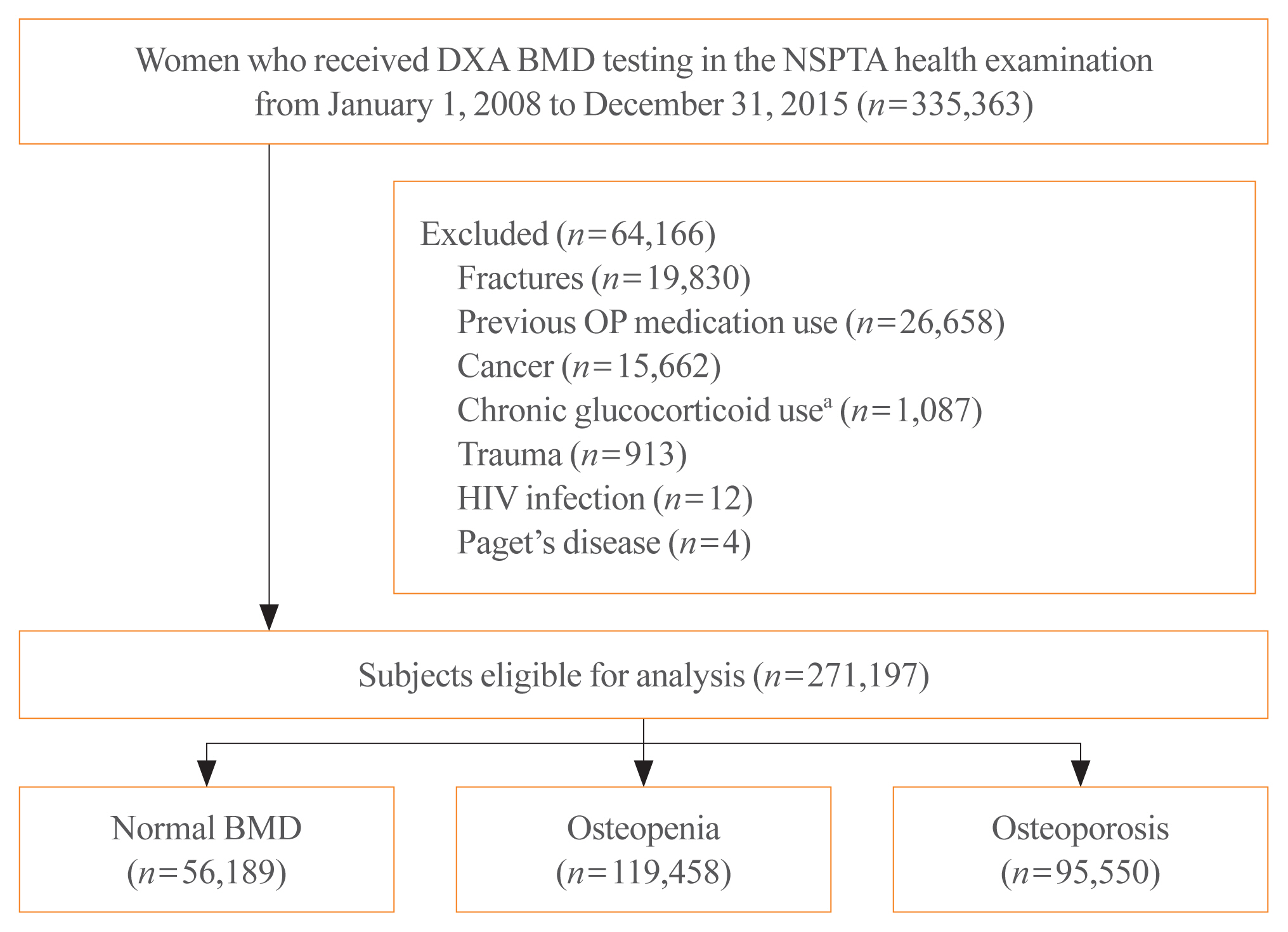
In South Korea, women aged 66 years are eligible for complimentary bone mineral density (BMD) screening via the National Screening Program for Transitional Ages. We aimed to evaluate the 10-year fracture risk in women receiving BMD screening between January 2008 and December 2015.
Methods
BMD was classified as normal (T-score ≥–1.0 standard deviation [SD]), osteopenia (T-score <–1.0 SD and >–2.5 SD), and osteoporosis (T score ≤–2.5 SD) from dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Follow-up continued from the screening date until a diagnosis for clinical fragility fracture (including sites of the vertebrae, hip, pelvis, clavicle, humerus, forearm, wrist, lower leg, and ankle), censored at the earliest date of trauma, death, or December 2017; fracture was ascertained using diagnostic codes from the National Health Insurance Service database. A multivariable Cox proportional hazard model was used to estimate hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the risk of fracture in women with osteopenia or osteoporosis relative to women with normal BMD.
Results
Among the 271,197 women screened, 44.0% had osteopenia and 35.2% had osteoporosis. The 10 year cumulative incidence of fragility fractures was 31.1%, 37.5%, and 44.3% in women with normal BMD, osteopenia, and osteoporosis, respectively. Fracture risk was higher in women with osteopenia (HR, 1.31; 95% CI, 1.28 to 1.34) and osteoporosis (HR, 1.68; 95% CI, 1.64 to 1.72) than in women with normal BMD.
Conclusion
Women with osteopenia and women with osteoporosis, identified by the national BMD screening program, demonstrated a substantially elevated risk of fracture. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Understanding the long-term impact of incident osteoporotic fractures on healthcare utilization and costs in Korean postmenopausal women
S. Han, S. Kim, E.J. Yeh, H.S. Suh
Osteoporosis International.2024; 35(2): 339. CrossRef - Duration of osteoporosis treatment to reduce the risk of subsequent osteoporotic fracture and all-cause mortality in elderly hip fracture patients in a Korean real-world study
Soong Joon Lee, Minjoon Cho, Hojoon Lee, Hyuna Lim, Jae Hyup Lee
Archives of Osteoporosis.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Do Patients with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Have a Higher Prevalence of Osteoporosis? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Chul-Ho Kim, Keunho Kim, Yeonjoo Choi
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2024; 14(3): 303. CrossRef - Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - Chronic airway disease as a major risk factor for fractures in osteopenic women: Nationwide cohort study
Sung Hye Kong, Ae Jeong Jo, Chan Mi Park, Kyun Ik Park, Ji Eun Yun, Jung Hee Kim
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Biomimetic Porous Magnesium Alloy Scaffolds Promote the Repair of Osteoporotic Bone Defects in Rats through Activating the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
Yuanchao Zhu, Gaozhi Jia, Yifei Yang, Jian Weng, Su Liu, Mengwei Zhang, Geng Zhang, Haotian Qin, Yixiao Chen, Qi Yang, Guangyin Yuan, Fei Yu, Hui Zeng
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering.2023; 9(6): 3435. CrossRef - Correlation between bone mineral density and bone metabolic markers in postmenopausal women with osteoporotic fractures at different C-terminal telopeptide of type 1 collagen levels: a retrospective analysis study
Xiaonan Zhu, Lin Chen, Ling Pan, Yuexi Zeng, Qiang Fu, Yanbin Liu, Yongde Peng, Yufan Wang, Li You
Menopause.2023; 30(11): 1139. CrossRef - Age-Dependent Association of Height Loss with Incident Fracture Risk in Postmenopausal Korean Women
Chaewon Lee, Hye-Sun Park, Yumie Rhee, Namki Hong
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 669. CrossRef - A Meaningful Journey to Predict Fractures with Deep Learning
Jeonghoon Ha
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 617. CrossRef - The Efficacy of Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators Monotherapies in Postmenopausal Women with Osteopenia
Kyung Wook Kim, Young Il Kim, Ki-Choul Kim
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2022; 29(3): 185. CrossRef - Correlation of Psoas Muscle Index with Fragility Vertebral Fracture: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study of Middle-Aged and Elderly Women
Yihui Zhang, Yilihamu Dilixiati, Wei Jiang, Xiufeng Cao, Yuanyuan Chen, Hui Guo, Christian-Heinz Anderwald
International Journal of Endocrinology.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef
- Understanding the long-term impact of incident osteoporotic fractures on healthcare utilization and costs in Korean postmenopausal women

- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
- Changes in Serum Dickkopf-1, RANK Ligand, Osteoprotegerin, and Bone Mineral Density after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Treatment
- Eunhee Jang, Jeonghoon Ha, Ki-Hyun Baek, Moo Il Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1211-1218. Published online December 8, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1248
- 3,015 View
- 104 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) regulates bone formation by inhibiting canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway signaling, and indirectly enhances osteoclastic activity by altering the expression ratio of receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL) relative to osteoprotegerin (OPG). However, it is difficult to explain continued bone loss after allogeneic stem cell transplantation (allo-SCT) in terms of changes in only RANKL and OPG. Few studies have evaluated changes in DKK1 after allo-SCT.
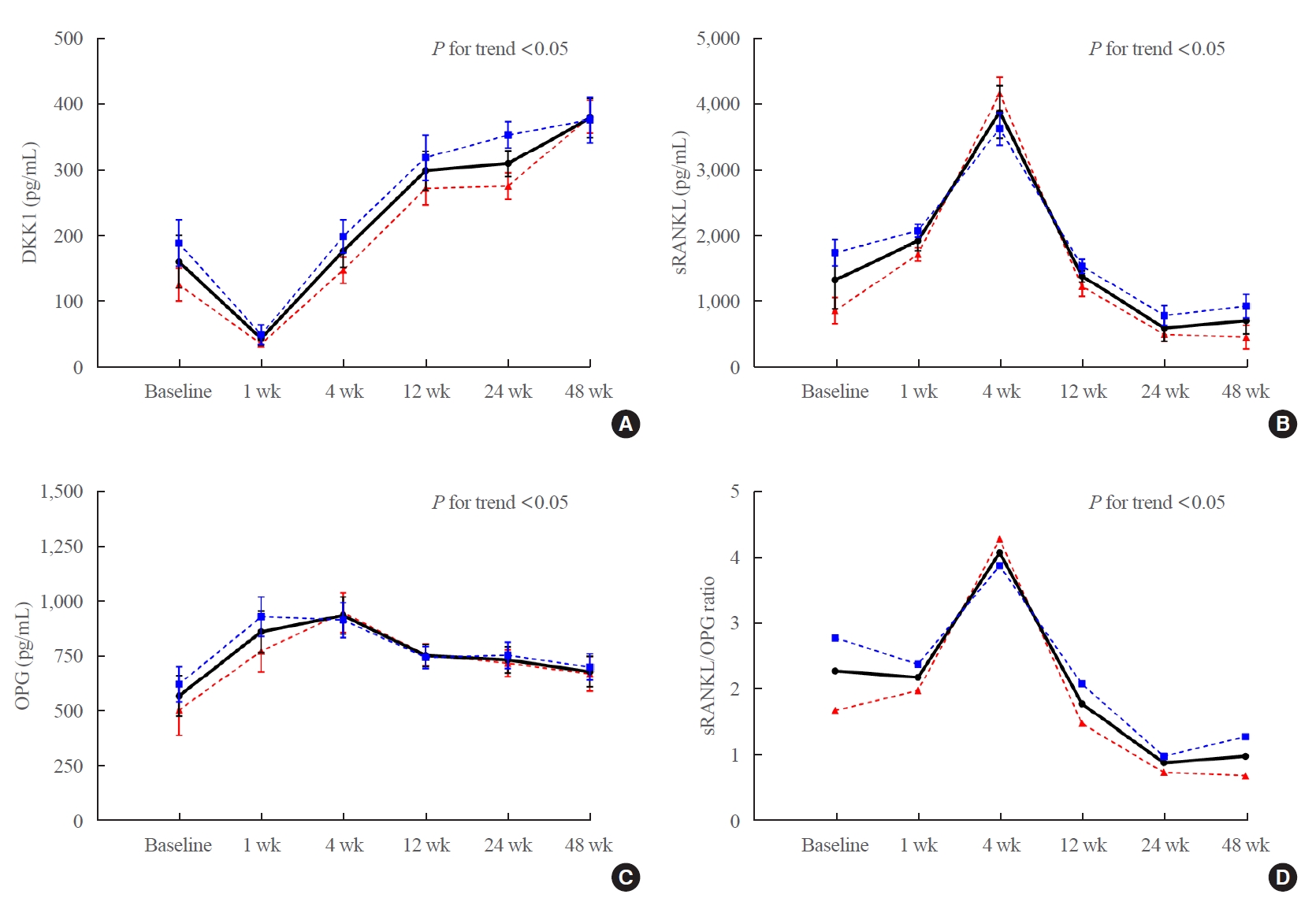
Methods
We prospectively enrolled 36 patients with hematologic malignancies who were scheduled for allo-SCT treatment. Serum DKK1, OPG, and RANKL levels were measured before (baseline), and at 1, 4, 12, 24, and 48 weeks after allo-SCT treatment. Bone mineral density (BMD) was assessed using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry before (baseline) and 24 and 48 weeks after allo-SCT treatment.
Results
After allo-SCT treatment, the DKK1 level decreased rapidly, returned to baseline during the first 4 weeks, and remained elevated for 48 weeks (P<0.0001 for changes observed over time). The serum RANKL/OPG ratio peaked at 4 weeks and then declined (P<0.001 for changes observed over time). BMD decreased relative to the baseline at all timepoints during the study period, and the lumbar spine in female patients had the largest decline (–11.3%±1.6% relative to the baseline at 48 weeks, P<0.05).
Conclusion
Serum DKK1 levels rapidly decreased at 1 week and then continued to increase for 48 weeks; bone mass decreased for 48 weeks following engraftment in patients treated with allo-SCT, suggesting that DKK1-mediated inhibition of osteoblast differentiation plays a role in bone loss in patients undergoing allo-SCT. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fracture risk and assessment in adults with cancer
Carrie Ye, William D. Leslie
Osteoporosis International.2023; 34(3): 449. CrossRef - Short-Term Impact of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Leukemia Patients on Bone Bio Markers, Electrolytes and Blood Profile
Rhythm Joshi, Zehva Khan, Aakriti Garg, Dinesh Bhurani, Nidhi B Agarwal, Ubada Aqeel, Mohd Ashif Khan
OBM Transplantation.2023; 07(02): 1. CrossRef
- Fracture risk and assessment in adults with cancer

- Bone Metabolism
- Comparison of the Effects of Various Antidiabetic Medication on Bone Mineral Density in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Jeonghoon Ha, Yejee Lim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Ki-Ho Song, Seung Hyun Ko, Moo Il Kang, Sung Dae Moon, Ki-Hyun Baek
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):895-903. Published online August 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1026
- 6,163 View
- 230 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Prospective comparative studies on the effects of various antidiabetic agents on bone metabolism are limited. This study aimed to assess changes in bone mass and biochemical bone markers in postmenopausal patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
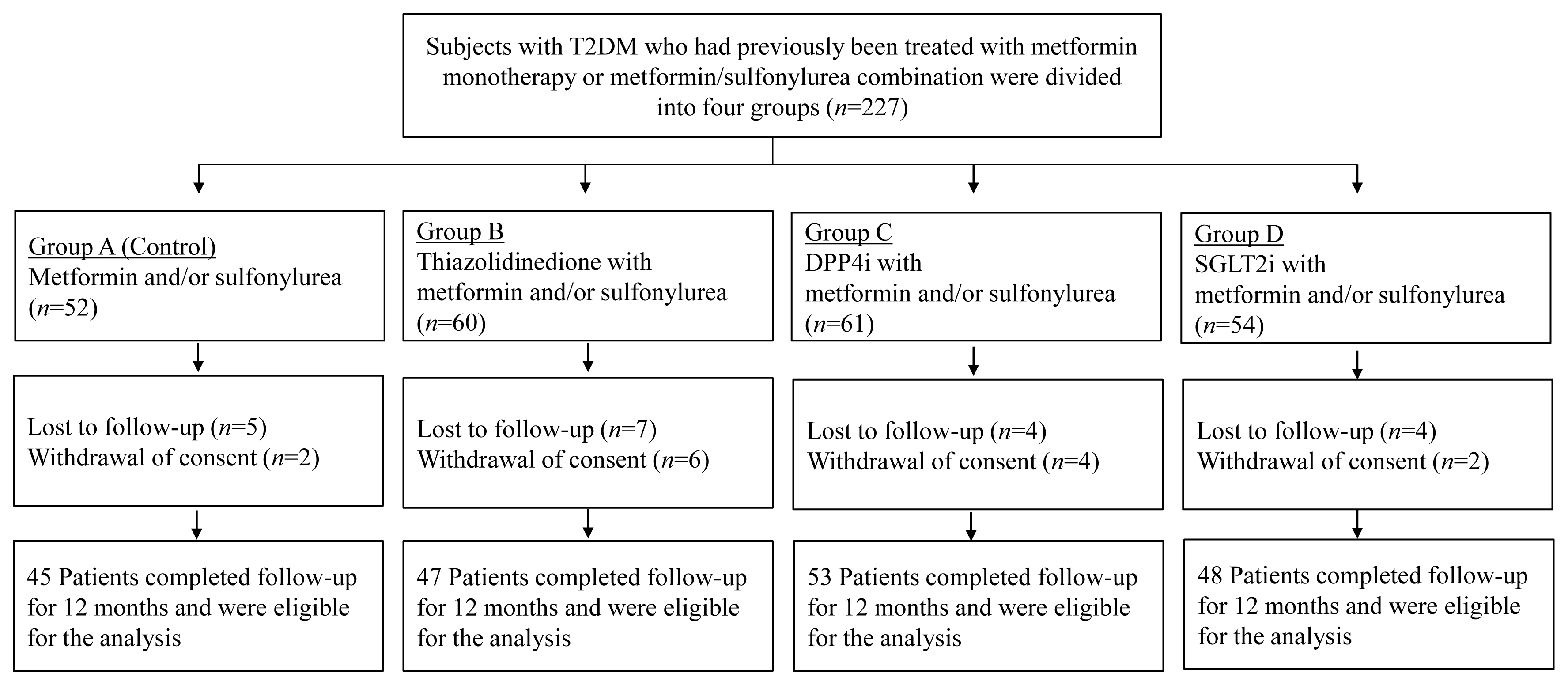
Methods
This prospective, multicenter, open-label, comparative trial included 264 patients with T2DM. Patients who had received a metformin, or sulfonylurea/metformin combination (Group 1); a thiazolidinedione combination (Group 2); a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (gemigliptin) combination (Group 3); or an sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor (empagliflozin) combination (Group 4) were prospectively treated for 12 months; bone mineral density (BMD) and bone turnover marker (BTM) changes were evaluated.
Results
The femoral neck BMD percentage changes were −0.79%±2.86% (Group 1), −2.50%±3.08% (Group 2), −1.05%±2.74% (Group 3), and −1.24%±2.91% (Group 4) (P<0.05). The total hip BMD percentage changes were −0.57%±1.79% (Group 1), −1.74%±1.48% (Group 2), −0.75%±1.87% (Group 3), and −1.27%±1.72% (Group 4) (P<0.05). Mean serum BTM (C-terminal type 1 collagen telopeptide and procollagen type 1 amino-terminal propeptide) levels measured during the study period did not change over time or differ between groups.
Conclusion
Significant bone loss in the femoral neck and total hip was associated with thiazolidinedione combination regimens. However, bone loss was not significantly associated with combination regimens including gemigliptin or empagliflozin. Caution should be exercised during treatment with antidiabetic medications that adversely affect the bone in patients with diabetes at a high risk of bone loss. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Meta-Analysis on the Association Between DPP-4 Inhibitors and Bone Mineral Density and Osteoporosis
Lili Huang, Wei Zhong, Xinghuan Liang, Huijuan Wang, Shi-en Fu, Zuojie Luo
Journal of Clinical Densitometry.2024; 27(1): 101455. CrossRef - A multicentre, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, randomized, parallel comparison, phase 3 trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pioglitazone add‐on therapy in type 2 diabetic patients treated with metformin and dapagliflozin
Soo Lim, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Kyung‐Wan Min, Chang Beom Lee, Sang Yong Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Nan Hee Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim, Seungjoon Oh, Jong Chul Won, Hyuk Sang Kwon, Mi Kyung Kim, Jung Hwan Park, In‐Kyung Jeong, Sungrae Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Bone Turnover Markers with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Microvascular Complications: A Matched Case-Control Study
Yilin Hou, Xiaoyu Hou, Qian Nie, Qiuyang Xia, Rui Hu, Xiaoyue Yang, Guangyao Song, Luping Ren
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 1177. CrossRef - Complementary effects of dapagliflozin and lobeglitazone on metabolism in a diet-induced obese mouse model
Yun Kyung Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Ji In Lee, Bo Yoon Choi, Hyen Chung Cho, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
European Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 957: 175946. CrossRef
- Meta-Analysis on the Association Between DPP-4 Inhibitors and Bone Mineral Density and Osteoporosis

- Clinical Study
- Romosozumab in Postmenopausal Korean Women with Osteoporosis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Efficacy and Safety Study
- Ki-Hyun Baek, Yoon-Sok Chung, Jung-Min Koh, In Joo Kim, Kyoung Min Kim, Yong-Ki Min, Ki Deok Park, Rajani Dinavahi, Judy Maddox, Wenjing Yang, Sooa Kim, Sang Jin Lee, Hyungjin Cho, Sung-Kil Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):60-69. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.848
- 6,859 View
- 390 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This phase 3 study evaluated the efficacy and safety of 6-month treatment with romosozumab in Korean postmenopausal women with osteoporosis.
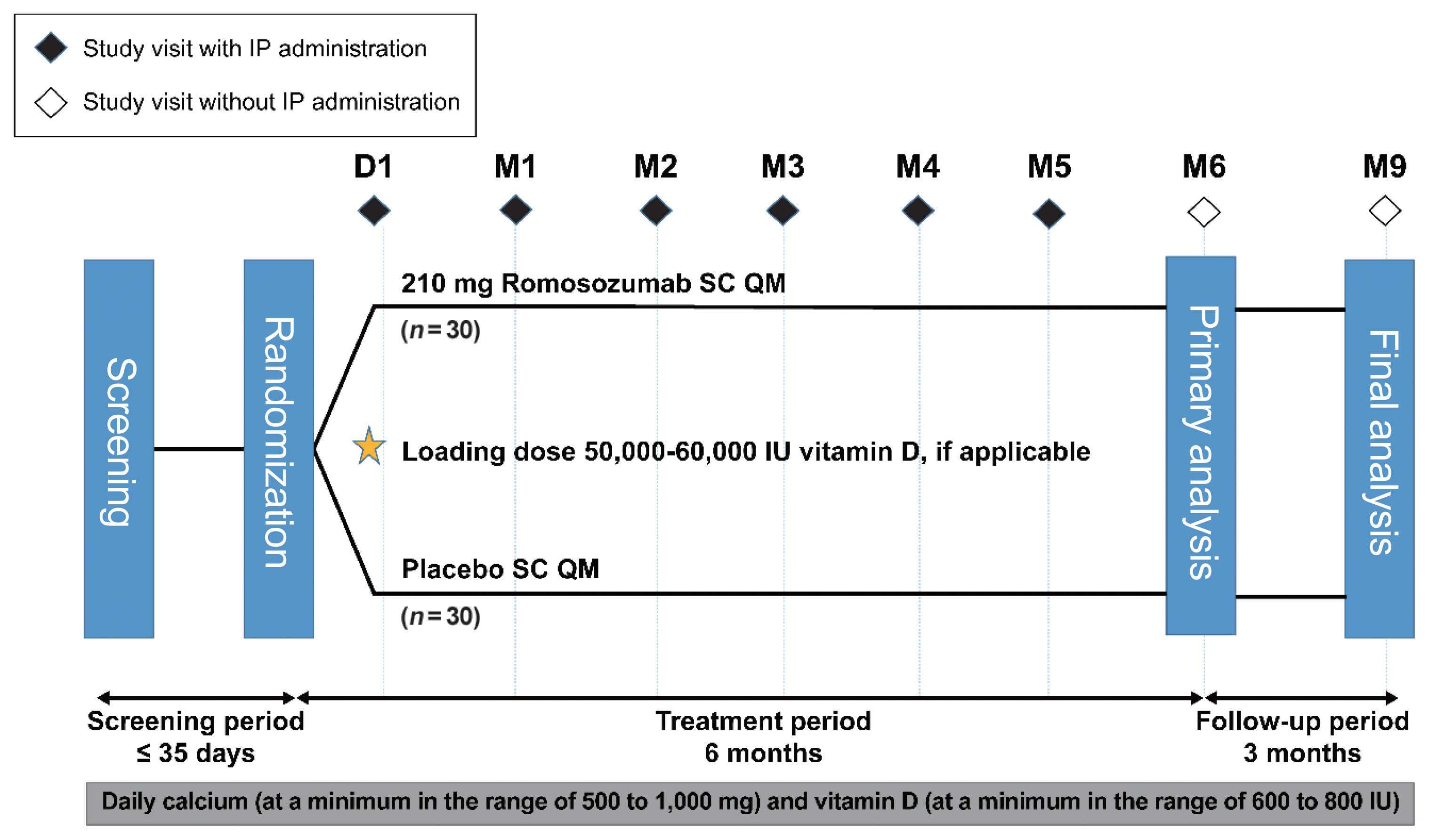
Methods
Sixty-seven postmenopausal women with osteoporosis (bone mineral density [BMD] T-scores ≤–2.5 at the lumbar spine, total hip, or femoral neck) were randomized (1:1) to receive monthly subcutaneous injections of romosozumab (210 mg; n=34) or placebo (n=33) for 6 months.
Results
At month 6, the difference in the least square (LS) mean percent change from baseline in lumbar spine BMD (primary efficacy endpoint) between the romosozumab (9.5%) and placebo (–0.1%) groups was significant (9.6%; 95% confidence interval, 7.6 to 11.5; P<0.001). The difference in the LS mean percent change from baseline was also significant for total hip and femoral neck BMD (secondary efficacy endpoints). After treatment with romosozumab, the percent change from baseline in procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide transiently increased at months 1 and 3, while that in C-terminal telopeptide of type 1 collagen showed a sustained decrease. No events of cancer, hypocalcemia, injection site reaction, positively adjudicated atypical femoral fracture or osteonecrosis of the jaw, or positively adjudicated serious cardiovascular adverse events were observed. At month 9, 17.6% and 2.9% of patients in the romosozumab group developed binding and neutralizing antibodies, respectively.
Conclusion
Treatment with romosozumab for 6 months was well tolerated and significantly increased lumbar spine, total hip, and femoral neck BMD compared with placebo in Korean postmenopausal women with osteoporosis (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT02791516). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A pharmacovigilance analysis of FDA adverse event reporting system events for romosozumab
Zepeng Chen, Ming Li, Shuzhen Li, Yuxi Li, Junyan Wu, Kaifeng Qiu, Xiaoxia Yu, Lin Huang, Guanghui Chen
Expert Opinion on Drug Safety.2023; 22(4): 339. CrossRef - Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of romosozumab (evenity) for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture in postmenopausal women: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials (CDM‐J)
Wenbo Huang, Masashi Nagao, Naohiro Yonemoto, Sen Guo, Takeshi Tanigawa, Yuji Nishizaki
Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety.2023; 32(6): 671. CrossRef - Efficacy and Cardiovascular Safety of Romosozumab: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Review
Seo-Yong Choi, Jeong-Min Kim, Sang-Hyeon Oh, Seunghyun Cheon, Jee-Eun Chung
Korean Journal of Clinical Pharmacy.2023; 33(2): 128. CrossRef - Clinical Studies On Romosozumab: An Alternative For Individuals With A High Risk Of Osteoporotic Fractures: A Current Concepts Review (Part I)
E. Carlos Rodriguez-Merchan, Alonso Moreno-Garcia, Hortensia De la Corte-Rodriguez
SurgiColl.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Romosozumab in osteoporosis: yesterday, today and tomorrow
Dong Wu, Lei Li, Zhun Wen, Guangbin Wang
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of anti-sclerostin antibodies in the treatment of osteoporosis: A meta-analysis and systematic review
Frideriki Poutoglidou, Efthimios Samoladas, Nikolaos Raikos, Dimitrios Kouvelas
Journal of Clinical Densitometry.2022; 25(3): 401. CrossRef - Benefits of lumican on human bone health: clinical evidence using bone marrow aspirates
Yun Sun Lee, So Jeong Park, Jin Young Lee, Eunah Choi, Beom-Jun Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2022; 37(4): 821. CrossRef - What is the risk of cardiovascular events in osteoporotic patients treated with romosozumab?
I. R. Reid
Expert Opinion on Drug Safety.2022; 21(12): 1441. CrossRef - Proxied Therapeutic Inhibition on Wnt Signaling Antagonists and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: Multi-Omics Analyses
Yu Qian, Cheng-Da Yuan, Saber Khederzadeh, Ming-Yu Han, Hai-Xia Liu, Mo-Chang Qiu, Jian-Hua Gao, Wei-Lin Wang, Yun-Piao Hou, Guo-Bo Chen, Ke-Qi Liu, Lin Xu, David Karasik, Shu-Yang Xie, Hou-Feng Zheng
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Multi-Omics Analyses Identify Pleiotropy and Causality Between Circulating Sclerostin and Atrial Fibrillation
Yu Qian, Peng-Lin Guan, Saber Khederzadeh, Ke-Qi Liu, Cheng-Da Yuan, Ming-Yu Han, Hai-Xia Liu, Mo-Chang Qiu, Jian-Hua Gao, Wei-Lin Wang, Yun-Piao Hou, Guo-Bo Chen, Lin Xu, David Karasik, Shu-Yang Xie, sheng zhifeng, Hou-Feng Zheng
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- A pharmacovigilance analysis of FDA adverse event reporting system events for romosozumab

- Clinical Study
- Low Predictive Value of FRAX Adjusted by Trabecular Bone Score for Osteoporotic Fractures in Korean Women: A Community-Based Cohort Study
- Hana Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Min Joo Kim, A Ram Hong, HyungJin Choi, EuJeong Ku, Ji Hyun Lee, Chan Soo Shin, Nam H. Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):359-366. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.359
- 5,986 View
- 132 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The value of the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) and the trabecular bone score (TBS) for assessing osteoporotic fracture risk has not been fully elucidated in Koreans. We conducted this study to clarify the predictive value of FRAX adjusted by TBS for osteoporotic fractures in Korean women.
Methods
After screening 7,192 eligible subjects from the Ansung cohort, 1,165 women aged 45 to 76 years with available bone mineral density (BMD) and TBS data were enrolled in this study. We assessed their clinical risk factors for osteoporotic fractures and evaluated the predictive value of FRAX with or without BMD and TBS.
Results
During the mean follow-up period of 7.5 years, 99 (8.5%) women suffered major osteoporotic fractures (MOFs) and 28 (2.4%) experienced hip fractures. FRAX without BMD, BMD-adjusted FRAX, and TBS-adjusted FRAX were significantly associated with the risk of MOFs (hazard ratio [HR] per percent increase, 1.08; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.03 to 1.14; HR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.03 to 1.15; and HR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.02 to 1.13, respectively). However, BMD-adjusted FRAX and TBS-adjusted FRAX did not predict MOFs better than FRAX without BMD based on the Harrell’s C statistic. FRAX probabilities showed limited value for predicting hip fractures. The cut-off values of FRAX without BMD, FRAX with BMD, and FRAX with BMD adjusted by TBS for predicting MOFs were 7.2%, 5.0%, and 6.7%, respectively.
Conclusion
FRAX with BMD and TBS adjustment did not show better predictive value for osteoporotic fractures in this study than FRAX without adjustment. Moreover, the cut-off values of FRAX probabilities for treatment might be lower in Korean women than in other countries. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Update on the utility of trabecular bone score (TBS) in clinical practice for the management of osteoporosis: a systematic review by the Egyptian Academy of Bone and Muscle Health
Yasser El Miedany, Walaa Elwakil, Mohammed Hassan Abu-Zaid, Safaa Mahran
Egyptian Rheumatology and Rehabilitation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of predictive value of FRAX, trabecular bone score, and bone mineral density for vertebral fractures in systemic sclerosis: A cross-sectional study
Kyung-Ann Lee, Hyun-Joo Kim, Hyun-Sook Kim
Medicine.2023; 102(2): e32580. CrossRef - Screening for the primary prevention of fragility fractures among adults aged 40 years and older in primary care: systematic reviews of the effects and acceptability of screening and treatment, and the accuracy of risk prediction tools
Michelle Gates, Jennifer Pillay, Megan Nuspl, Aireen Wingert, Ben Vandermeer, Lisa Hartling
Systematic Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Chronic airway disease as a major risk factor for fractures in osteopenic women: Nationwide cohort study
Sung Hye Kong, Ae Jeong Jo, Chan Mi Park, Kyun Ik Park, Ji Eun Yun, Jung Hee Kim
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Update on the clinical use of trabecular bone score (TBS) in the management of osteoporosis: results of an expert group meeting organized by the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Disease
Enisa Shevroja, Jean-Yves Reginster, Olivier Lamy, Nasser Al-Daghri, Manju Chandran, Anne-Laurence Demoux-Baiada, Lynn Kohlmeier, Marie-Paule Lecart, Daniel Messina, Bruno Muzzi Camargos, Juraj Payer, Sansin Tuzun, Nicola Veronese, Cyrus Cooper, Eugene V.
Osteoporosis International.2023; 34(9): 1501. CrossRef - Comparison of HU histogram analysis and BMD for proximal femoral fragility fracture assessment: a retrospective single-center case–control study
Sun-Young Park, Hong Il Ha, Injae Lee, Hyun Kyung Lim
European Radiology.2022; 32(3): 1448. CrossRef - Association of Trabecular Bone Score-Adjusted Fracture Risk Assessment Tool with Coronary Artery Calcification in Women
Tzyy-Ling Chuang, Yuh-Feng Wang, Malcolm Koo, Mei-Hua Chuang
Diagnostics.2022; 12(1): 178. CrossRef - Risk of osteoporotic fracture in women using the FRAX tool with and without bone mineral density score in patients followed at a tertiary outpatient clinic ‒ An observational study
Maria Helena Sampaio Favarato, Maria Flora de Almeida, Arnaldo Lichtenstein, Milton de Arruda Martins, Mario Ferreira Junior
Clinics.2022; 77: 100015. CrossRef - Comparison of Trabecular Bone Score–Adjusted Fracture Risk Assessment (TBS-FRAX) and FRAX Tools for Identification of High Fracture Risk among Taiwanese Adults Aged 50 to 90 Years with or without Prediabetes and Diabetes
Tzyy-Ling Chuang, Mei-Hua Chuang, Yuh-Feng Wang, Malcolm Koo
Medicina.2022; 58(12): 1766. CrossRef - Application of the Trabecular Bone Score in Clinical Practice
Sung Hye Kong, Namki Hong, Jin-Woo Kim, Deog Yoon Kim, Jung Hee Kim
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2021; 28(2): 101. CrossRef
- Update on the utility of trabecular bone score (TBS) in clinical practice for the management of osteoporosis: a systematic review by the Egyptian Academy of Bone and Muscle Health

- Bone Metabolism
- Potential Biomarkers to Improve the Prediction of Osteoporotic Fractures
- Beom-Jun Kim, Seung Hun Lee, Jung-Min Koh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):55-63. Published online March 19, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.55

- 4,849 View
- 115 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Osteoporotic fracture (OF) is associated with high disability and morbidity rates. The burden of OF may be reduced by early identification of subjects who are vulnerable to fracture. Although the current fracture risk assessment model includes clinical risk factors (CRFs) and bone mineral density (BMD), its overall ability to identify individuals at high risk for fracture remains suboptimal. Efforts have therefore been made to identify potential biomarkers that can predict the risk of OF, independent of or combined with CRFs and BMD. This review highlights the emerging biomarkers of bone metabolism, including sphongosine-1-phosphate, leucine-rich repeat-containing 17, macrophage migration inhibitory factor, sclerostin, receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand, and periostin, and the importance of biomarker risk score, generated by combining these markers, in enhancing the accuracy of fracture prediction.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ångstrom-scale gold particles loaded with alendronate via alpha-lipoic acid alleviate bone loss in osteoporotic mice
Weihang Gao, Jiao Jiao Li, Jingyu Shi, Hongbing Lan, Yuanyuan Guo, Dehao Fu
Journal of Nanobiotechnology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The administration of bovine hydroxyapatite-alendronate implant accelerates bone defect healing in an osteoporotic rat
Toetik Aryani, Aniek Setiya Budiatin, Samirah, Aulia Maulidina, Aulia Intan Firdaus, Maria Apriliani Gani, Khoirotin Nisak, Junaidi Khotib, Alvi Jauharotus Syukriya
Technology and Health Care.2023; 31(5): 1747. CrossRef - Impact of Intravenous Iron Substitution on Serum Phosphate Levels and Bone Turnover Markers—An Open-Label Pilot Study
Alexandra Struppe, Jakob E. Schanda, Andreas Baierl, Paul Watzl, Christian Muschitz
Nutrients.2023; 15(12): 2693. CrossRef - Dynamics of Bone Disease Biomarkers Dickkopf-1 and Sclerostin in Patients with Multiple Myeloma
Vladimir Gerov, Daniela Gerova, Ilina Micheva, Miglena Nikolova, Galya Mihaylova, Bistra Galunska
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(13): 4440. CrossRef - Impact of vitamin D supplementation on markers of bone turnover: Systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomised controlled trials
Mohammad Hassan Sohouli, Sicong Wang, Faisal Almuqayyid, Mariana Papini Gabiatti, Fateme Mozaffari, Zahra Mohamadian, Nazanin Koushki, Kamar Allayl Alras, Abdullah M. AlHossan, Saud K. Albatati, Aya Alfardous Alazm, Saeed Baradwan, Mihnea‐Alexandru Găman,
European Journal of Clinical Investigation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Night shift work and serum markers of bone turnover in male shift workers
Margherita Martelli, Gianmaria Salvio, Raffaella Lazzarini, Marijana Milinkovic, Alessandro Ciarloni, Giancarlo Balercia, Lory Santarelli, Massimo Bracci
Chronobiology International.2023; 40(9): 1270. CrossRef - Circulating sRANKL, Periostin, and Osteopontin as Biomarkers for the Assessment of Activated Osteoclastogenesis in Myeloma Related Bone Disease
Vladimir Gerov, Daniela Gerova, Ilina Micheva, Miglena Nikolova, Milena Pasheva, Neshe Nazifova, Bistra Galunska
Cancers.2023; 15(23): 5562. CrossRef - Oral Administration of Isovitexin, a Naturally Occurring Apigenin Derivative Showed Osteoanabolic Effect in Ovariectomized Mice: A Comparative Study with Teriparatide
Subhashis Pal, Shivani Sharma, Konica Porwal, Mohammed Riyazuddin, Chirag Kulkarni, Sourav Chattopadhyay, Sabyasachi Sanyal, Jiaur R. Gayen, Naibedya Chattopadhyay
Calcified Tissue International.2022; 111(2): 196. CrossRef - Serum sclerostin levels in osteoporotic fracture patients
Erwin A. Gorter, Casper R. Reinders, Pieta Krijnen, Natasha M. Appelman-Dijkstra, Inger B. Schipper
European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery.2022; 48(6): 4857. CrossRef - Elevated gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase level is associated with an increased risk of hip fracture in postmenopausal women
Kyoung Jin Kim, Namki Hong, Min Heui Yu, Seunghyun Lee, Sungjae Shin, Sin Gon Kim, Yumie Rhee
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of androgen deprivation therapy on serum levels of sclerostin, Dickkopf-1, and osteoprotegerin: a cross-sectional and longitudinal analysis
Alice Wang, Nishi Karunasinghe, Lindsay D. Plank, Shuotun Zhu, Sue Osborne, Charis Brown, Karen Bishop, Tiffany Schwass, Sofian Tijono, Michael Holmes, Jonathan Masters, Roger Huang, Christine Keven, Lynnette R. Ferguson, Ross Lawrenson
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Update on Glucocorticoid Induced Osteoporosis
Soo-Kyung Cho, Yoon-Kyoung Sung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 536. CrossRef - Nobiletin promotes osteogenic differentiation of human osteoblastic cell line (MG-63) through activating the BMP-2/RUNX-2 signaling pathway
Ying Pang, Lili Liu, Hong Mu, Vishnu Priya Veeraraghavan
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2021; 28(9): 4916. CrossRef
- Ångstrom-scale gold particles loaded with alendronate via alpha-lipoic acid alleviate bone loss in osteoporotic mice

- Bone Metabolism
- Effects of Resistance Exercise on Bone Health
- A Ram Hong, Sang Wan Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(4):435-444. Published online November 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.4.435
- 22,686 View
- 375 Download
- 103 Web of Science
- 107 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub The prevalence of chronic diseases including osteoporosis and sarcopenia increases as the population ages. Osteoporosis and sarcopenia are commonly associated with genetics, mechanical factors, and hormonal factors and primarily associated with aging. Many older populations, particularly those with frailty, are likely to have concurrent osteoporosis and sarcopenia, further increasing their risk of disease-related complications. Because bones and muscles are closely interconnected by anatomy, metabolic profile, and chemical components, a diagnosis should be considered for both sarcopenia and osteoporosis, which may be treated with optimal therapeutic interventions eliciting pleiotropic effects on both bones and muscles. Exercise training has been recommended as a promising therapeutic strategy to encounter the loss of bone and muscle mass due to osteosarcopenia. To stimulate the osteogenic effects for bone mass accretion, bone tissues must be exposed to mechanical load exceeding those experienced during daily living activities. Of the several exercise training programs, resistance exercise (RE) is known to be highly beneficial for the preservation of bone and muscle mass. This review summarizes the mechanisms of RE for the preservation of bone and muscle mass and supports the clinical evidences for the use of RE as a therapeutic option in osteosarcopenia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of COVID‐19 pandemic on lifestyle and bone mineral density in young adults
Darina Falbová, Viktória Kovalčíková, Radoslav Beňuš, Simona Sulis, Lenka Vorobeľová
American Journal of Human Biology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity, diabetes and risk of bone fragility: How BMAT behavior is affected by metabolic disturbances and its influence on bone health
Gregório Corrêa Guimarães, João Bosco Costa Coelho, João Gabriel Oliveira Silva, Ana Carolina Chalfun de Sant’Ana, Cássia Alves Carrilho de Sá, Júlia Marques Moreno, Lívia Marçal Reis, Camila Souza de Oliveira Guimarães
Osteoporosis International.2024; 35(4): 575. CrossRef - Bone mineral density after exercise training in patients with chronic kidney disease stages 3 to 5: a sub-study of RENEXC—a randomized controlled trial
Vaida Petrauskiene, Matthias Hellberg, Philippa Svensson, Yunan Zhou, Naomi Clyne
Clinical Kidney Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Atp6v1h Deficiency Blocks Bone Loss in Simulated Microgravity Mice through the Fos-Jun-Src-Integrin Pathway
Zanyan Zhao, Xiangpu Wang, Yu Ma, Xiaohong Duan
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(1): 637. CrossRef - Exercise and Musculoskeletal Health in Men With Low Bone Mineral Density: A Systematic Review
Katherine Hu, Maree Cassimatis, Christian Girgis
Archives of Rehabilitation Research and Clinical Translation.2024; 6(1): 100313. CrossRef - Influence of 8-weeks of supervised static stretching or resistance training of pectoral major muscles on maximal strength, muscle thickness and range of motion
Tim Wohlann, Konstantin Warneke, Vincent Kalder, David G. Behm, Tobias Schmidt, Stephan Schiemann
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - High-Protein Diets during either Resistance or Concurrent Training Have No Detrimental Effect on Bone Parameters in Resistance-Trained Males
Reza Bagheri, Zohreh Karimi, Zeynabalsadat Mousavi, Mahdi Ziaee Bashirzad, Donny M. Camera, Ramin Sadeghi, Vahid Reza Dabbagh, Mehdi Kargarfard, Frederic Dutheil
Nutrients.2024; 16(2): 325. CrossRef - Cafeteria Diet Can Affect Bone Microarchitecture in Sedentary and Trained Male Rats
Marcio Koiti Saito, Beatriz Kawano de Oliveira, Ana Paula Macedo, Caio Sorrentino dos Santos, Ricardo Tadeu Lopes, Jéssica Suzuki Yamanaka, Antonio Carlos Shimano
Journal of Clinical Densitometry.2024; 27(2): 101467. CrossRef - The Relationship Among Probable SARCopenia, Osteoporosis and SuprasPinatus Tendon Tears in Postmenopausal Women: The SARCOSP Study
Murat Kara, Özgür Kara, Mahmut Esad Durmuş, Pelin Analay, Fatıma Edibe Şener, Beyza Nur Çıtır, Gizem Olgu Korkmaz, Zeliha Ünlü, Tülay Tiftik, Eda Gürçay, Cevriye Mülkoğlu, Berkay Yalçınkaya, Fatih Bağcıer, Mahmud Fazıl Aksakal, Kübra Erdoğan, Ahmet Sertçe
Calcified Tissue International.2024; 114(4): 340. CrossRef - Low Bone Mass in Ambulatory Spinal Muscular Atrophy: A Proactive Approach for an Often-Overlooked Impairment
Caitlin Trancho, Bailey Stickney, Stacy Kinirons, David Uher, Cara H. Kanner, Ashwini K. Rao, Michael P. McDermott, Carol Ewing Garber, Darryl C. De Vivo, Jacqueline Montes
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(5): 1336. CrossRef - Predictors of Hand Grip Strength in Adults Without Sarcopenia: Data From the NHANES, 2013–2014
Mansour M Alotaibi
Current Developments in Nutrition.2024; 8(5): 102149. CrossRef - Why don't women engage in muscle strength exercise? An integrative review
A. M. Stimson, C. Anderson, A.‐M. Holt, A. J. Henderson
Health Promotion Journal of Australia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Plant-Based Diets versus the Mediterranean Dietary Pattern and Their Socio-Demographic Determinants in the Spanish Population: Influence on Health and Lifestyle Habits
Elena Sandri, Marco Sguanci, Eva Cantín Larumbe, Germán Cerdá Olmedo, Lisa Ursula Werner, Michela Piredda, Stefano Mancin
Nutrients.2024; 16(9): 1278. CrossRef - From Cells to Environment: Exploring the Interplay between Factors Shaping Bone Health and Disease
Samradhi Singh, Devojit Kumar Sarma, Vinod Verma, Ravinder Nagpal, Manoj Kumar
Medicina.2023; 59(9): 1546. CrossRef - Effect of resistance exercise on bone health of old aged individuals: Review
A. Khanna
Science & Sports.2023; 38(4): 323. CrossRef - Relationship between physical exercise and COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2): systematic review
Robson Chacon Castoldi, Juliana Cristina de Ângelo, Thiago Teixeira Pereira, Rodrigo Martins Dias, Fábio Juliano Negrão
Sport Sciences for Health.2023; 19(1): 55. CrossRef - Impact of Physical Rehabilitation on Bone Biomarkers in Non-Metastatic Breast Cancer Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Alessandro de Sire, Lorenzo Lippi, Nicola Marotta, Arianna Folli, Dario Calafiore, Stefano Moalli, Alessio Turco, Antonio Ammendolia, Nicola Fusco, Marco Invernizzi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(2): 921. CrossRef -
Does wing use and disuse cause behavioural and musculoskeletal changes in domestic fowl (
Gallus gallus domesticus
)?
Renée C. Garant, Bret W. Tobalske, Neila Ben Sassi, Nienke van Staaveren, Dan Tulpan, Tina Widowski, Donald R. Powers, Alexandra Harlander-Matauschek
Royal Society Open Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Increased fat mass negatively influences femoral neck bone mineral density in men but not women
Nipith Charoenngam, Caroline M. Apovian, Chatlert Pongchaiyakul
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Strength Training Variables on Neuromuscular and Morphological Adaptations in Prepubertal Children: A Systematic Review
Alberto Sánchez Pastor, Carlos García-Sánchez, Moisés Marquina Nieto, Alfonso de la Rubia
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(6): 4833. CrossRef - The Role of Oxidative Stress in Multiple Exercise-Regulated Bone Homeostasis
Haoyang Gao, Yilong Zhao, Linlin Zhao, Zhikun Wang, Kai Yan, Bo Gao, Lingli Zhang
Aging and disease.2023; 14(5): 1555. CrossRef - Kadınlarda Fiziksel Aktivite ve Egzersizin Osteoporozu Önleme ve Tedavi Edici Rolü
Sümena HAREKET, İlknur NAZ GÜRŞAN
Cumhuriyet Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Enstitüsü Dergisi.2023; 8(1): 73. CrossRef - Osteosarcopenia as a satellite of aging
B. I. Isaeva, K. M. Alieva-Kharkharova
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2023; 17(9): 130. CrossRef - Examining Physical Wellness as the Fundamental Element for Achieving Holistic Well-Being in Older Persons: Review of Literature and Practical Application in Daily Life
Sheng-Te Hung, Yi-Chen Cheng, Chieh-Chen Wu, Chun-Hsien Su
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2023; Volume 16: 1889. CrossRef - Effects of Exercise, Rehabilitation, and Nutritional Approaches on Body Composition and Bone Density in People with Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Natascia Rinaldo, Alba Pasini, Sofia Straudi, Giovanni Piva, Anna Crepaldi, Andrea Baroni, Lorenzo Caruso, Fabio Manfredini, Nicola Lamberti
Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology.2023; 8(3): 132. CrossRef - Changes in Desk-Based Workers’ Sitting, Standing, and Stepping Time: Short- and Longer-Term Effects on Musculoskeletal Pain
FRANCIS Q. S. DZAKPASU, NEVILLE OWEN, ALISON CARVER, CHRISTIAN J. BRAKENRIDGE, ELIZABETH G. EAKIN, GENEVIEVE N. HEALY, ANTHONY D. LAMONTAGNE, MARJ MOODIE, PIETER COENEN, LEON STRAKER, DAVID W. DUNSTAN
Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise.2023; 55(12): 2241. CrossRef - Shared decision making in sarcopenia treatment
Kang An, Zengxiang Wu, Yu Qiu, Mengjia Pan, Lin Zhang, Zhenmei An, Shuangqing Li
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of combined traditional Chinese medicine therapy in patients of lower limbs injuries with osteoporosis: A retrospective paired cohort study
Yu-Hua Lu, Chi-Hsiang Chung, Chien-Jung Lin, Li-Jen Tsai, Kuang-Chung Shih, Chieh-Hua Lu, Wu-Chien Chien
Medicine.2023; 102(49): e36489. CrossRef - The theory of planned behavior and strength training in college-aged women
Diana Cuy Castellanos, Corinne M. Daprano, Clarissa Blevins, Anne Crecelius
Journal of American College Health.2022; 70(3): 837. CrossRef - The effect of exercise for improving bone health in cancer survivors — A systematic review and meta-analysis
Benjamin Singh, Kellie Toohey
Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport.2022; 25(1): 31. CrossRef - The role of estrogens in osteosarcopenia: from biology to potential dual therapeutic effects
A. Mandelli, E. Tacconi, I. Levinger, G. Duque, A. Hayes
Climacteric.2022; 25(1): 81. CrossRef - Changes in blood bone markers after the first and second bouts of whole‐body eccentric exercises
Tsang‐Hai Huang, Kazunori Nosaka, Trevor C. Chen
Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports.2022; 32(3): 521. CrossRef - Questions Individuals with Cardiac Conditions Engaging in Exercise often Ask Health Fitness Professionals: Research-Based Responses
Kirk D. Hendrickson, Cindy Haskin-Popp, Barry A. Franklin
ACSM'S Health & Fitness Journal.2022; 26(2): 29. CrossRef - Effects of Different Types of Exercise on Kidney Diseases
Hamid Arazi, Majid Mohabbat, Payam Saidie, Akram Falahati, Katsuhiko Suzuki
Sports.2022; 10(3): 42. CrossRef - Sport Activity Load and Skeletomuscular Robustness in Elite Youth Athletes
Irina Kalabiska, Annamaria Zsakai, Dorina Annar, Robert M. Malina, Tamas Szabo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(9): 5083. CrossRef - A pas de deux of osteoporosis and sarcopenia: osteosarcopenia
O. V. Yakushevskaya, S. V. Yureneva, V. I. Komedina
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2022; (6): 116. CrossRef - The Effect of Endurance and Endurance-Strength Training on Bone Health and Body Composition in Centrally Obese Women—A Randomised Pilot Trial
Małgorzata Jamka, Sylwia E. Piotrowska-Brudnicka, Joanna Karolkiewicz, Damian Skrypnik, Paweł Bogdański, Judyta Cielecka-Piontek, Gulnara Sultanova, Jarosław Walkowiak, Edyta Mądry
Healthcare.2022; 10(5): 821. CrossRef - Kinematic and Kinetic Characteristics of Repetitive Countermovement Jumps with Accentuated Eccentric Loading
Micah Gross, Jan Seiler, Bastien Grédy, Fabian Lüthy
Sports.2022; 10(5): 74. CrossRef - Osteosarcopenia: A Narrative Review on Clinical Studies
Angela Polito, Lorenzo Barnaba, Donatella Ciarapica, Elena Azzini
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(10): 5591. CrossRef - Efficacy of Bracing on Thoracic Kyphotic Angle and Functionality in Women with Osteoporosis: A Systematic Review
Beatriz Sánchez-Pinto-Pinto, Carlos Romero-Morales, Daniel López-López, Carmen de-Labra, Guillermo García-Pérez-de-Sevilla
Medicina.2022; 58(6): 693. CrossRef - Are There Any Differences Between the Effect of Resistance and Aerobic Training on Spatial Learning and Memory in the Rat Model of AD?
Khadijeh Ebrahimi, Behrouz Baghaiee
Journal of Clinical Research in Paramedical Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Whole-Body Vibration on Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis and Vascularization in Mice
Takeshi Matsumoto, Akihiro Mukohara
Calcified Tissue International.2022; 111(5): 535. CrossRef - Current Status of the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis
Agustín Aibar-Almazán, Ana Voltes-Martínez, Yolanda Castellote-Caballero, Diego Fernando Afanador-Restrepo, María del Carmen Carcelén-Fraile, Elena López-Ruiz
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(16): 9465. CrossRef - Methodological Proposal for Strength and Power Training in Older Athletes:
A Narrative Review
Emilio Jofré-Saldía, Álvaro Villalobos-Gorigoitía, Gemma Gea-García
Current Aging Science.2022; 15(2): 135. CrossRef - Robotic Walking to Mitigate Bone Mineral Density Decline and Adverse Body Composition in Individuals With Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury
Claire Shackleton, Robert Evans, Sacha West, Wayne Derman, Yumna Albertus
American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation.2022; 101(10): 931. CrossRef - Exploration of Aging-Care Parameters to Predict Mortality of Patients Aged 80-Years and Above with Community-Acquired Pneumonia
Chunxin Lv, Wen Shi, Teng Pan, Houshen Li, Weixiong Peng, Jiayi Xu, Jinhai Deng
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2022; Volume 17: 1379. CrossRef - Pharmacological, Nutritional, and Rehabilitative Interventions to Improve the Complex Management of Osteoporosis in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Narrative Review
Alessandro de Sire, Lorenzo Lippi, Vittorio Aprile, Dario Calafiore, Arianna Folli, Francesco D’Abrosca, Stefano Moalli, Marco Lucchi, Antonio Ammendolia, Marco Invernizzi
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(10): 1626. CrossRef - Resistance circuit training combined with hypoxia stimulates bone system of older adults: A randomized trial
Alba Camacho-Cardenosa, Marta Camacho-Cardenosa, Ismael Martínez-Guardado, Alejo Leal, José María Villa Andrada, Rafael Timón
Experimental Gerontology.2022; 169: 111983. CrossRef - Effects of Strength Training on BDNF in Healthy Young Adults
Miroslaw Babiarz, Radoslaw Laskowski, Tomasz Grzywacz
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(21): 13795. CrossRef - Celecoxib impairs primary human myoblast proliferation and differentiation independent of cyclooxygenase 2 inhibition
Ronald W. Matheny, Alexander L. Kolb, Alyssa V. Geddis, Brandon M. Roberts
Physiological Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects on type 2 diabetes mellitus mouse femoral bone achieved by anti-osteoporosis exercise interventions
Miao Zhang, Yuexuan Li, Lifei Liu, Mei Huang, Miao Wang, Jun Zou
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical Activity and Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Aging Decay: Modulation of Pathways in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
Federica Vita, Sebastiano Gangemi, Giovanni Pioggia, Fabio Trimarchi, Debora Di Mauro
Medicina.2022; 58(6): 767. CrossRef - Sclerostin as a biomarker of physical exercise in osteoporosis: A narrative review
Anna Oniszczuk, Agnieszka Kaczmarek, Mateusz Kaczmarek, Maria Ciałowicz, Ersan Arslan, Ana Filipa Silva, Filipe Manuel Clemente, Eugenia Murawska-Ciałowicz
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise and Bone Health in Cancer: Enemy or Ally?
Alice Avancini, Giulia Benato, Anita Borsati, Luca Oliviero, Lorenzo Belluomini, Marco Sposito, Daniela Tregnago, Ilaria Trestini, Jessica Insolda, Francesca Zacchi, Elena Fiorio, Federico Schena, Michele Milella, Sara Pilotto
Cancers.2022; 14(24): 6078. CrossRef - Composite Indices of Femoral Neck Strength in Middle-Aged Inactive Subjects Vs Former Football Players
Boutros Finianos, Gautier Zunquin, Rawad El Hage
Journal of Clinical Densitometry.2021; 24(2): 214. CrossRef - Relationship between bone strength index of the hemiparetic tibial diaphysis and muscle strength in people with chronic stroke: influence of muscle contraction type and speed
Z. Yang, T. Miller, M. Y. C. Pang
Osteoporosis International.2021; 32(5): 951. CrossRef - Effect of 12 months of creatine supplementation and whole-body resistance training on measures of bone, muscle and strength in older males
Darren G Candow, Philip D Chilibeck, Julianne Gordon, Emelie Vogt, Tim Landeryou, Mojtaba Kaviani, Lisa Paus-Jensen
Nutrition and Health.2021; 27(2): 151. CrossRef - Effects of 6-Month Multimodal Physical Exercise Program on Bone Mineral Density, Fall Risk, Balance, and Gait in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease: A Controlled Clinical Trial
A. Silvia Puente-González, M. Carmen Sánchez-Sánchez, Eduardo J. Fernández-Rodríguez, J. Elicio Hernández-Xumet, Fausto J. Barbero-Iglesias, Roberto Méndez-Sánchez
Brain Sciences.2021; 11(1): 63. CrossRef - Resistance Training Modulates the Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Activity in Different Trabecular Bones in Aged Rats
Ivo Vieira de Sousa Neto, João Luiz Quaglioti Durigan, Gonçalo Carreiro de Farias Junior, Fabio Henrique Bogni, Amanda Lima Ruivo, Juliana Oliveira de Araújo, Keico Okino Nonaka, Heloísa Selistre-de-Araújo, Rita de Cássia Marqueti
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2021; Volume 16: 71. CrossRef - Resistance Exercise in Prostate Cancer Patients: a Short Review
Andrej Zdravkovic, Timothy Hasenoehrl, Richard Crevenna
Current Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Reports.2021; 9(1): 32. CrossRef - Sturz, Sarkopenie und Osteoporose
Marcus Köller
Journal für Mineralstoffwechsel & Muskuloskelettale Erkrankungen.2021; 28(1): 19. CrossRef - Effects of marathon race on selected myokines and sclerostin in middle-aged male amateur runners
Ewa Śliwicka, Tomasz Cisoń, Łucja Pilaczyńska-Szcześniak, Andrzej Ziemba, Anna Straburzyńska-Lupa
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Lower extremity joint loading during Bounce rope skip in comparison to run and walk
Rajani Mullerpatan, Triveni Shetty, Yuvraj Singh, Bela Agarwal
Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies.2021; 26: 1. CrossRef - Powerlifting exercise performance and muscle mass indices and their relationship with bone mineral density
Daniel A. Hackett, Angelo Sabag
Sport Sciences for Health.2021; 17(3): 735. CrossRef - Physical Activity and Bone Health in Men: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Maureen C. Ashe, Isis Kelly dos Santos, Nicola Y. Edward, Laura A. Burnett, Rosanne Barnes, Lena Fleig, Joseph H. Puyat, Joanna E. M. Sale, Heather A. McKay, Lora M Giangregorio
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2021; 28(1): 27. CrossRef - Pathophysiology and treatment of osteoporosis: challenges for clinical practice in older people
J. Barnsley, G. Buckland, P. E. Chan, A. Ong, A. S. Ramos, M. Baxter, F. Laskou, E. M. Dennison, C. Cooper, Harnish P. Patel
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research.2021; 33(4): 759. CrossRef - Sarcopenia and Bone Mass Loss as Risks during Aging on Female Elderly with Light Activity
Yoni Astuti, Zulkhah Noor, Rahmah Rahmah
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 9(T4): 168. CrossRef - Effect of intradialytic exercise on bone profile in hemodialysis patients
Howaida Abdelhameed Elshinnawy, Ahmed Mohamed Bakr Bakr Mohamed, Dina Abou Bakr Farrag, Moustafa Abd Elnassier AbdElgawad
Egyptian Rheumatology and Rehabilitation.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Osteoporosis guidelines from a rehabilitation perspective: systematic analysis and quality appraisal using AGREE II
Giovanni IOLASCON, Alessandro de SIRE, Claudio CURCI, Marco PAOLETTA, Sara LIGUORI, Dario CALAFIORE, Francesca GIMIGLIANO, Antimo MORETTI
European Journal of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Case Study of an 87-Year-Old Male Bodybuilder with Complex Health Conditions
Daniel A. Hackett, Lachlan Mitchell, Guy C. Wilson, Trinidad Valenzuela, Matthew Hollings, Maria Fiatarone Singh
Medicina.2021; 57(7): 664. CrossRef - Frailty Pathogenesis, Assessment, and Management in Older Adults With COVID-19
Quan She, Bo Chen, Wen Liu, Min Li, Weihong Zhao, Jianqing Wu
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimization of transdisciplinary management of elderly with femur proximal extremity fracture: A patient-tailored plan from orthopaedics to rehabilitation
Alessandro de Sire, Marco Invernizzi, Alessio Baricich, Lorenzo Lippi, Antonio Ammendolia, Federico Alberto Grassi, Massimiliano Leigheb
World Journal of Orthopedics.2021; 12(7): 456. CrossRef - International Exercise Recommendations in Older Adults (ICFSR): Expert Consensus Guidelines
Mikel Izquierdo, R.A. Merchant, J.E. Morley, S.D. Anker, I. Aprahamian, H. Arai, M. Aubertin-Leheudre, R. Bernabei, E.L. Cadore, M. Cesari, L.-K. Chen, P. de Souto Barreto, G. Duque, L. Ferrucci, R.A. Fielding, A. García-Hermoso, L.M. Gutiérrez-Robledo, S
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2021; 25(7): 824. CrossRef - Intra-bone nuclear DNA variability and STR typing success in Second World War first ribs
Laura Božič, Tajda Benedik Bevc, Eva Podovšovnik, Tomaž Zupanc, Irena Zupanič Pajnič
International Journal of Legal Medicine.2021; 135(6): 2199. CrossRef - Can Resistance Exercise Be a Tool for Healthy Aging in Post-Menopausal Women with Type 1 Diabetes?
Zeinab Momeni, Jessica E. Logan, Ronald J. Sigal, Jane E. Yardley
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(16): 8716. CrossRef - Role of the Myokine Irisin on Bone Homeostasis: Review of the Current Evidence
Amanda Kornel, Danja J. Den Hartogh, Panagiota Klentrou, Evangelia Tsiani
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(17): 9136. CrossRef - Prevalence and Correlates of Muscle-Strengthening Activity Participation in Croatia: A Cross-Sectional Study in a National Representative Sample of 4561 Adults
Hrvoje Radašević, Jelena Čvrljak, Željko Pedišić, Danijel Jurakić
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(17): 8905. CrossRef - Intra-bone nuclear DNA variability and STR typing success in Second World War 12th thoracic vertebrae
Tajda Benedik Bevc, Laura Božič, Eva Podovšovnik, Tomaž Zupanc, Irena Zupanič Pajnič
Forensic Science International: Genetics.2021; 55: 102587. CrossRef - Vascular Ageing and Aerobic Exercise
Michaela Kozakova, Carlo Palombo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(20): 10666. CrossRef - Efficacy of Creatine Supplementation and Resistance Training on Area and Density of Bone and Muscle in Older Adults
DARREN G. CANDOW, PHILIP D. CHILIBECK, JULIANNE J. GORDON, SAIJA KONTULAINEN
Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise.2021; 53(11): 2388. CrossRef - Perspectives of personalized approach to prevention and treatment of anticonvulsant-induced osteoporosis via action on vitamin D exchange and VDR expression
E. A. Dontseva, V. V. Trefilova, T. E. Popova, M. M. Petrova, M. Al-Zamil
Personalized Psychiatry and Neurology.2021; 1(2): 46. CrossRef - Bone health in adolescence
Maria R. AMBROSIO, Ludovica ALIBERTI, Irene GAGLIARDI, Paola FRANCESCHETTI, Maria C. ZATELLI
Minerva Obstetrics and Gynecology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - To Evaluate the Awareness and Prevention of Osteoporosis in Patients Attending Orthopaedics Outdoor Clinics in a Tertiary Level Hospital
Annie Sandhu, Dharminder Singh, Akashdeep Singh, Kuldip Singh Sand
Trends in Medical Research.2021; 16(2): 73. CrossRef - Novel Insights into the Pathogenesis of Spinal Sarcopenia and Related Therapeutic Approaches: A Narrative Review
Yu-Kai Kuo, Yu-Ching Lin, Ching-Yu Lee, Chih-Yu Chen, Jowy Tani, Tsung-Jen Huang, Hsi Chang, Meng-Huang Wu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(8): 3010. CrossRef - Multifactorial effects of hyperglycaemia, hyperinsulinemia and inflammation on bone remodelling in type 2 diabetes mellitus
V.A. Shahen, M. Gerbaix, S. Koeppenkastrop, S.F. Lim, K.E. McFarlane, Amanda N.L. Nguyen, X.Y. Peng, N.B. Weiss, T.C. Brennan-Speranza
Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews.2020; 55: 109. CrossRef - Effect of pre-treatment of strength training and raloxifene in periestropause on bone healing
Melise Jacon Peres-Ueno, Fernanda Fernandes, Victor Gustavo Balera Brito, Ângela Cristina Nicola, Camila Tami Stringhetta-Garcia, Robson Chacon Castoldi, Amanda Pinatti Menezes, Paulo Cézar Ciarlini, Mário Jeferson Quirino Louzada, Sandra Helena Penha Oli
Bone.2020; 134: 115285. CrossRef - Physical rehabilitation of patients with osteoporosis
E.D. Yehudina, O.S. Kalashnikova
Voprosy kurortologii, fizioterapii i lechebnoi fizicheskoi kul'tury.2020; 97(2): 78. CrossRef - RANKL/RANK/OPG Pathway: A Mechanism Involved in Exercise-Induced Bone Remodeling
Mohammad Tobeiha, Mohammed H. Moghadasian, Negin Amin, Sadegh Jafarnejad
BioMed Research International.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Effects of muscular strength training and growth hormone (GH) supplementation on femoral bone tissue: analysis by Raman spectroscopy, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, and mechanical resistance
Robson Chacon Castoldi, Guilherme Akio Tamura Ozaki, Thiago Alves Garcia, Ines Cristina Giometti, Tatiana Emy Koike, Regina Celi Trindade Camargo, João Domingos Augusto dos Santos Pereira, Carlos José Leopoldo Constantino, Mário Jefferson Quirino Louzada,
Lasers in Medical Science.2020; 35(2): 345. CrossRef - Approaches to the diagnosis and prevention of frailty
S. J. Woolford, O. Sohan, E. M. Dennison, C. Cooper, H. P. Patel
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research.2020; 32(9): 1629. CrossRef - The Impact of Exercise on Bone Health in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—a Systematic Review
R. Viggers, Z. Al-Mashhadi, R. Fuglsang-Nielsen, S. Gregersen, J. Starup-Linde
Current Osteoporosis Reports.2020; 18(4): 357. CrossRef - Transformation of Mature Osteoblasts into Bone Lining Cells and RNA Sequencing-Based Transcriptome Profiling of Mouse Bone during Mechanical Unloading
A Ram Hong, Kwangsoo Kim, Ji Yeon Lee, Jae-Yeon Yang, Jung Hee Kim, Chan Soo Shin, Sang Wan Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 456. CrossRef - Physical Exercise Potentials Against Viral Diseases Like COVID-19 in the Elderly
Sandra Amatriain-Fernández, Thomas Gronwald, Eric Murillo-Rodríguez, Claudio Imperatori, Alexandre Francisco Solano, Alexandra Latini, Henning Budde
Frontiers in Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Osteosarcopenia: beyond age-related muscle and bone loss
Gabriela Fagundes Belchior, Ben Kirk, Evela Aparecida Pereira da Silva, Gustavo Duque
European Geriatric Medicine.2020; 11(5): 715. CrossRef - Mediating role of physical fitness and fat mass on the associations between physical activity and bone health in youth
Duarte Henriques-Neto, João Pedro Magalhães, Pedro Júdice, Megan Hetherington-Rauth, Miguel Peralta, Adilson Marques, Luís B. Sardinha
Journal of Sports Sciences.2020; 38(24): 2811. CrossRef - Impact of physical activity and exercise on bone health in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review of observational and experimental studies
Daniela F. Cardoso, Elisa A. Marques, Diogo V. Leal, Aníbal Ferreira, Luke A. Baker, Alice C. Smith, João L. Viana
BMC Nephrology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Short and medium-term effects of a multicomponent physical exercise program with a Mediterranean diet on bone mineral density, gait, balance, and fall risk for patients with Alzheimer disease
Ana Silvia Puente-González, Felipe Sánchez-González, Juan Elicio Hernández-Xumet, María Carmen Sánchez-Sánchez, Fausto José Barbero-Iglesias, Roberto Méndez-Sánchez
Medicine.2020; 99(38): e22385. CrossRef - Sarcopenia during COVID-19 lockdown restrictions: long-term health effects of short-term muscle loss
Richard Kirwan, Deaglan McCullough, Tom Butler, Fatima Perez de Heredia, Ian G. Davies, Claire Stewart
GeroScience.2020; 42(6): 1547. CrossRef - Acute Effects of Two Types of Dumbbell Exercise on Oxygenated Hemodynamic Concentration of Cerebral Activation in Healthy Young Male Adults: A Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Study
Yana Wang, Jiaojiao Lü, Jifeng Rong, Linjie Song, Wei Wang, Yifan Jiang, Yu Liu, Lingyan Huang
Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Muscle-Derived Lumican Stimulates Bone Formation via Integrin α2β1 and the Downstream ERK Signal
Jin Young Lee, So Jeong Park, Da Ae Kim, Seung Hun Lee, Jung-Min Koh, Beom-Jun Kim
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Age-Based Bone Mineral Density in the Korean Adult Population Using Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry
Jung Chul Lee, Chong Hoon Lee, Dong Wha Chung, Hee Joo Lee, Jae Yong Park
Applied Sciences.2020; 10(23): 8469. CrossRef - Preventive Moderate Continuous Running-Exercise Conditioning Improves the Healing of Non-Critical Size Bone Defects in Male Wistar Rats: A Pilot Study Using µCT
Céline Bourzac, Morad Bensidhoum, Mathieu Manassero, Christine Chappard, Nicolas Michoux, Stéphane Pallu, Hugues Portier
Life.2020; 10(12): 308. CrossRef - BONE MINERAL DENSITY: AN ANALYSIS OF WEIGHT BEARING, RESISTANCE AND IMPACT PHYSICAL ACTIVITIES
Arvind Malik, Sonia Malik, Vishal Dahiya
PARIPEX INDIAN JOURNAL OF RESEARCH.2020; : 1. CrossRef - Effects of ursolic acid on muscle mass and bone microstructure in rats with casting-induced muscle atrophy
Yun Seok Kang, Eun Bi Noh, Sang Hyun Kim
Journal of Exercise Nutrition & Biochemistry.2019; 23(3): 45. CrossRef - Osteoporosis and Sarcopenia Increase Frailty Syndrome in the Elderly
Emanuela A. Greco, Peter Pietschmann, Silvia Migliaccio
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of Health-Related Quality of Life, Fear of Falling and Objective Measures of Physical Function with Bone Health in Postmenopausal Women with Low Bone Mass
Gandham, McMillan, Ng, Humbert, Bonham, Zengin, Ebeling, Scott
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(9): 1370. CrossRef - Osteoblasts are “educated” by crosstalk with metastatic breast cancer cells in the bone tumor microenvironment
Alexus D. Kolb, Alison B. Shupp, Dimpi Mukhopadhyay, Frank C. Marini, Karen M. Bussard
Breast Cancer Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of COVID‐19 pandemic on lifestyle and bone mineral density in young adults


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



