Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Effects of an Electronic Medical Records-Linked Diabetes Self-Management System on Treatment Targets in Real Clinical Practice: Retrospective, Observational Cohort Study
- So Jung Yang, Sun-Young Lim, Yoon Hee Choi, Jin Hee Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(2):364-374. Published online March 21, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1878

- 1,025 View
- 14 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study evaluated the effects of a mobile diabetes management program called “iCareD” (College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea) which was integrated into the hospital’s electronic medical records system to minimize the workload of the healthcare team in the real clinical practice setting.
Methods
In this retrospective observational study, we recruited 308 patients. We categorized these patients based on their compliance regarding their use of the iCareD program at home; compliance was determined through self-monitored blood glucose inputs and message subscription rates. We analyzed changes in the ABC (hemoglobin A1c, blood pressure, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol) levels from the baseline to 12 months thereafter, based on the patients’ iCareD usage patterns.
Results
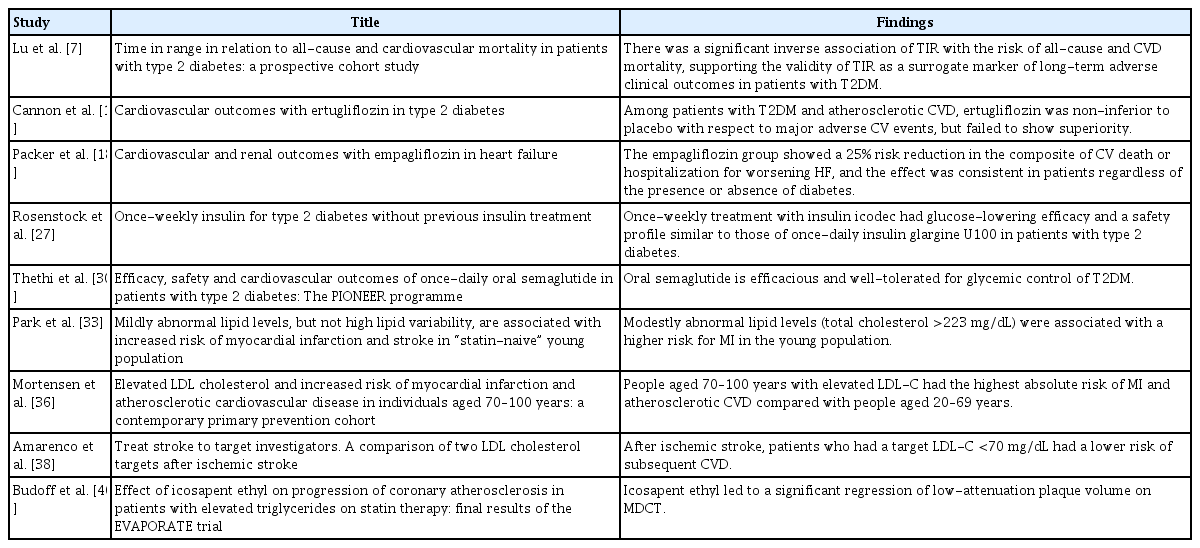
The patients comprised 92 (30%) non-users, 170 (55%) poor-compliance users, and 46 (15%) good-compliance users; the ABC target achievement rate showed prominent changes in good-compliance groups from baseline to 12 months (10.9% vs. 23.9%, P<0.05), whereas no significant changes were observed for poor-compliance users and non-users (13.5% vs. 18.8%, P=0.106; 20.7% vs. 14.1%, P=0.201; respectively).
Conclusion
Implementing the iCareD can improve the ABC levels of patients with diabetes with minimal efforts of the healthcare team in real clinical settings. However, the improvement of patients’ compliance concerning the use of the system without the vigorous intervention of the healthcare team needs to be solved in the future.

Review Articles
- Diabetes
- Best Achievements in Clinical Medicine in Diabetes and Dyslipidemia in 2020
- Eun-Jung Rhee, Mee-Kyung Kim, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):41-50. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.106
- 4,341 View
- 178 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Over the last two decades, our understanding of diabetes and treatment strategies have evolved tremendously, from scientific, mechanistic, and human perspectives. The categories of anti-diabetic medications expanded from a few to numerous, enabling clinicians to personalize diabetes care and treatment. Thanks to rapid growth in the field of science and medical engineering, newer treatment options are coming to the market with various advantages and disadvantages to be aware of. Therefore, clinicians should rapidly adopt new trends based on guidelines and data from many clinical trials in the field of diabetes. In the treatment of dyslipidemia, trends and guidelines are changing every year, and novel therapies are being developed. In this review, we would like to summarize the major achievements in clinical medicine in 2020 in the field of diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin added to metformin plus gemigliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind, randomized, comparator-active study: ENHANCE-D study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Kyung Ah Han, Tae Nyun Kim, Cheol-Young Park, Jung Hwan Park, Sang Yong Kim, Yong Hyun Kim, Kee Ho Song, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Sik Kim, Gwanpyo Koh, Jun Goo Kang, Mi Kyung Kim, Ji Min Han, Nan Hee Kim, Ji Oh Mok, Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Lim, Sang S
Diabetes & Metabolism.2023; 49(4): 101440. CrossRef - Effects of exercise initiation and smoking cessation after new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus on risk of mortality and cardiovascular outcomes
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Jinyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined Effects of Obesity and Dyslipidaemia on the Prevalence of Diabetes Amongst Adults Aged ≥45 Years: Evidence from a Nationally Representative Cross-Sectional Study
Simin Zhang, Donghan Sun, Xiaoyi Qian, Li Li, Wenwen Wu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(13): 8036. CrossRef - Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level, Statin Use and Myocardial Infarction Risk in Young Adults
Heekyoung Jeong, Kyungdo Han, Soon Jib Yoo, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(3): 288. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin added to metformin plus gemigliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind, randomized, comparator-active study: ENHANCE-D study

- Diabetes
- Lessons from Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems in Digital Healthcare
- Hun-Sung Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):541-548. Published online September 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.675
- 6,923 View
- 184 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
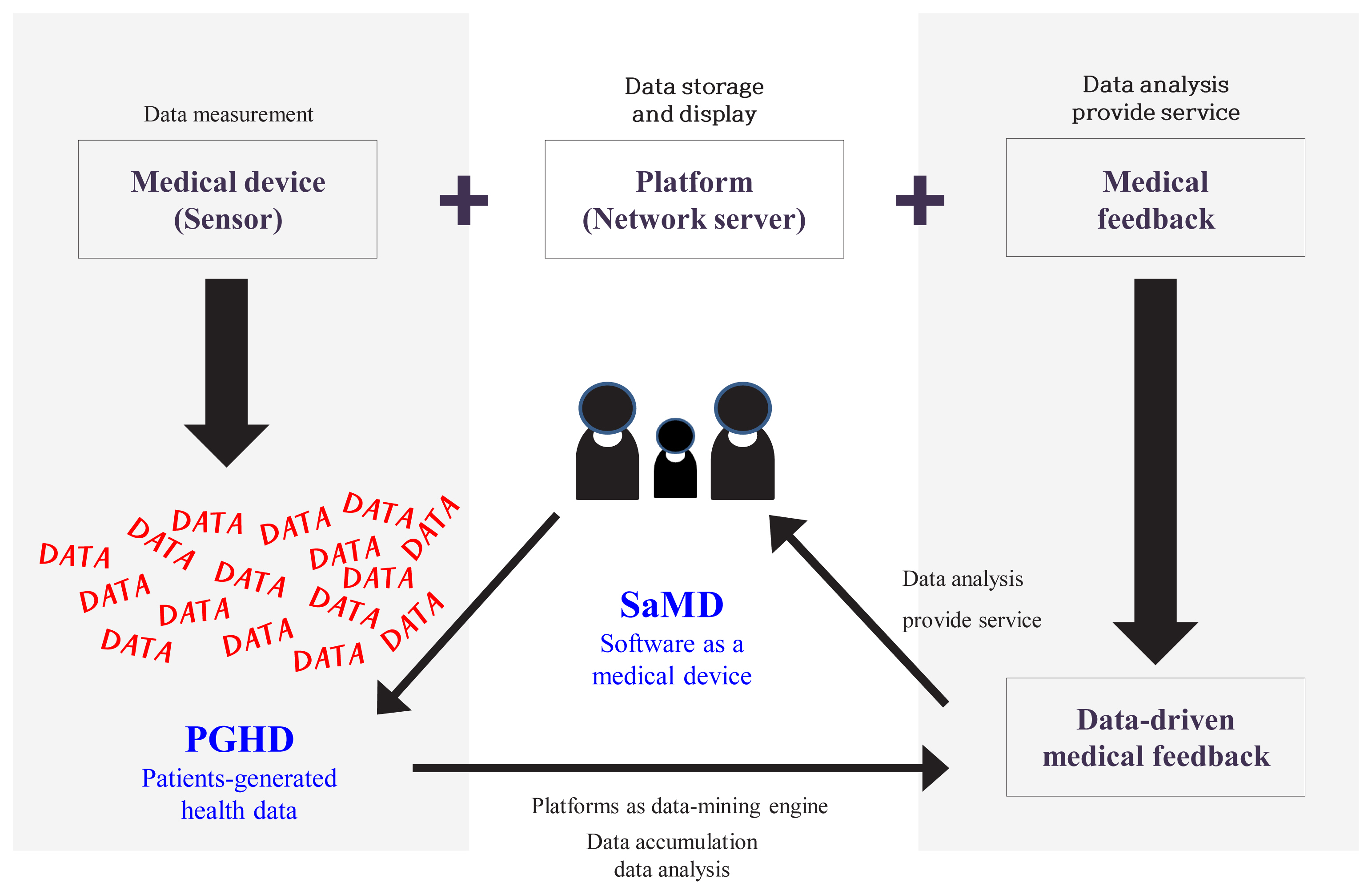
ePub - We live in a digital world where a variety of wearable medical devices are available. These technologies enable us to measure our health in our daily lives. It is increasingly possible to manage our own health directly through data gathered from these wearable devices. Likewise, healthcare professionals have also been able to indirectly monitor patients’ health. Healthcare professionals have accepted that digital technologies will play an increasingly important role in healthcare. Wearable technologies allow better collection of personal medical data, which healthcare professionals can use to improve the quality of healthcare provided to the public. The use of continuous glucose monitoring systems (CGMS) is the most representative and desirable case in the adoption of digital technology in healthcare. Using the case of CGMS and examining its use from the perspective of healthcare professionals, this paper discusses the necessary adjustments required in clinical practices. There is a need for various stakeholders, such as medical staff, patients, industry partners, and policy-makers, to utilize and harness the potential of digital technology.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Managing Talent Among Healthcare Human Resource: Strategies for a New Normal
Divya Aggarwal, Vijit Chaturvedi, Anandhi Ramachandran, Taniya Singh
Journal of Health Management.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Current status of remote collaborative care for hypertension in medically underserved areas
Seo Yeon Baik, Kyoung Min Kim, Hakyoung Park, Jiwon Shinn, Hun-Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2024; 6(1): 33. CrossRef - Using medical big data for clinical research and legal considerations for the protection of personal information: the double-edged sword
Raeun Kim, Jiwon Shinn, Hun-Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2024; 6(1): 8. CrossRef - Diverse perspectives on remote collaborative care for chronic disease management
Seo Yeon Baik, Hakyoung Park, Jiwon Shinn, Hun-Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2024; 6(1): 26. CrossRef - Patent analysis of digital sensors for continuous glucose monitoring
Olena Litvinova, Magdalena Eitenberger, Aylin Bilir, Andy Wai Kan Yeung, Emil D. Parvanov, ArunSundar MohanaSundaram, Jarosław Olav Horbańczuk, Atanas G. Atanasov, Harald Willschke
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Personalized Nutrition 2020: Proceedings from the American Nutrition Association’s 61st Annual Summit
Victoria A. Y. Behm, Corinne L. Bush
Journal of the American College of Nutrition.2021; 40(4): 397. CrossRef - Towards Telemedicine Adoption in Korea: 10 Practical Recommendations for Physicians
Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Perceptron: Basic Principles of Deep Neural Networks
Eung-Hee Kim, Hun-Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2021; 3(3): 64. CrossRef - Lack of Acceptance of Digital Healthcare in the Medical Market: Addressing Old Problems Raised by Various Clinical Professionals and Developing Possible Solutions
Jong Il Park, Hwa Young Lee, Hyunah Kim, Jisan Lee, Jiwon Shinn, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital health and diabetes: experience from India
Jothydev Kesavadev, Gopika Krishnan, Viswanathan Mohan
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 12: 204201882110546. CrossRef
- Managing Talent Among Healthcare Human Resource: Strategies for a New Normal


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



