Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Thyroid
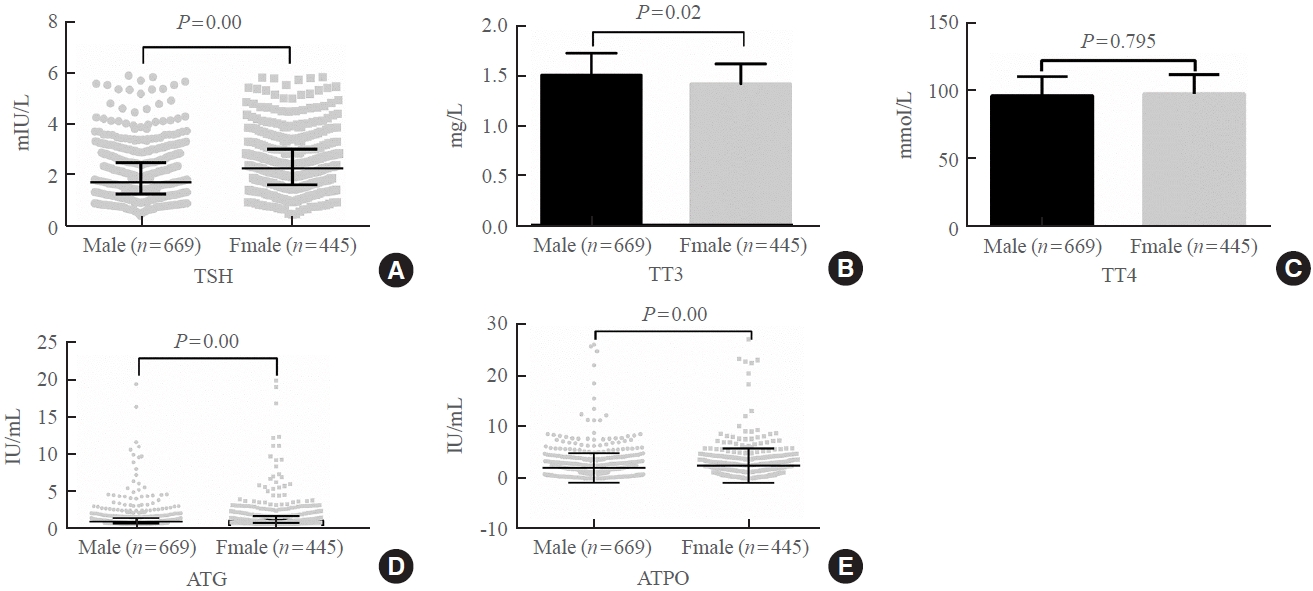
- Thyroid Hormone Reference Intervals among Healthy Individuals In Lanzhou, China
- Yan Lu, Wen-Xia Zhang, De-Hong Li, Lian-Hua Wei, Yu-Jun Zhang, Fu-Na Shi, Shen Zhou
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(3):347-356. Published online June 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1638
- 2,131 View
- 125 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The common reference intervals (RIs) for thyroid hormones currently used in China are provided by equipment manufacturers. This study aimed to establish thyroid hormone RIs in the population of Lanzhou, a city in the subplateau region of northwest China, and compare them with previous reports and manufacturer-provided values.
Methods
In total, 3,123 individuals (1,680 men, 1,443 women) from Lanzhou, an iodine-adequate area of China, perceived as healthy were selected. The Abbott Architect analyzer was used to determine the serum concentration of thyroid hormones. The 95% RI was estimated using the 2.5th and 97.5th percentiles as the lower and upper reference limits, respectively.
Results
The serum levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), total triiodothyronine (TT3), antithyroglobulin (ATG) antibody, and antithyroid peroxidase (ATPO) antibody levels were significantly correlated with sex (P<0.05). TSH, total thyroxine (TT4), and ATPO levels were significantly correlated with age (P<0.05). The serum levels of TSH, ATG, and ATPO in men were significantly lower than in women; in contrast, the serum TT3 level was significantly higher in men than in women (P<0.05). Serum TSH, TT3, TT4, and ATG levels differed across age groups (P<0.05), but no such variation was observed for ATG levels (P>0.05). The established RIs of TSH, ATG, and ATPO in this study differed between sexes (P<0.05). The thyroid hormone RIs established herein were inconsistent with the manufacturer-provided values.
Conclusion
The RIs of thyroid hormones in the healthy population of Lanzhou were inconsistent with those in the manufacturer’s manual. Validated sex-specific values are required for diagnosing thyroid diseases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Burden of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in subclinical hypothyroidism
Mahmood Dhahir Al-Mendalawi
Journal of Clinical and Scientific Research.2024; 13(1): 68. CrossRef
- Burden of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in subclinical hypothyroidism

- Endocrine Research
- Comparison of Thyroglobulin Measurements Using Three Different Immunoassay Kits: A BRAMHS Tg-Plus RIA Kit, a BRAMHS hTg Sensitive Kryptor Kit, and a Beckman Coulter ACCESS Immunoassay Kit
- Mijin Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Jong Jin Lee, Jin-Sook Ryu, Eun-Jung Cho, Dae-Hyun Ko, Woochang Lee, Sail Chun, Won-Ki Min, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(3):462-468. Published online August 2, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.3.462
- 5,153 View
- 49 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Second-generation thyroglobulin immunometric assays (Tg-IMAs) have been developed with improved sensitivity. Our aim was to compare the diagnostic value of Tg-IMA measurements using a Kryptor (BRAHMS AG) kit (Tg-K) and an ACCESS (Beckman Coulter) kit (Tg-A) with that of the first-generation Tg measurement using a Tg-plus (BRAHMS AG) kit (Tg+).
Methods We enrolled 82 differentiated thyroid cancer patients who underwent total thyroidectomy with radioactive iodine remnant ablation and who underwent diagnostic whole body scan using recombinant human thyroid stimulating hormone (rhTSH). The Tg+, Tg-K, and Tg-A were measured before rhTSH administration during levothyroxine treatment (suppressed Tg) from the same sample. Serum Tg+ was measured after rhTSH stimulation (stimulated Tg).
Results Suppressed Tg+ was more significantly correlated with suppressed Tg-K (
R 2=0.919,P <0.001) than with suppressed Tg-A (R 2=0.536,P <0.001). The optimal cut-off values of suppressed Tg+, Tg-K, and Tg-A for predicting stimulated Tg+ of 1 ng/mL were 0.3, 0.2, and 0.2 ng/mL, respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of suppressed Tg+ were 67%, 100%, and 90%, respectively; those of suppressed Tg-K were 83%, 90%, and 88%; those of suppressed Tg-A were 96%, 82%, and 87%, respectively. The positive predictive and negative predictive values of Tg+ were 100% and 87%, respectively; those of Tg-K were 79% and 92%; and those of Tg-A were 73% and 98%.Conclusion We could not clearly demonstrate which kit had better diagnostic performance after comparison of first-generation Tg measurements with Tg-IMA measurements. Also, there were kit-to-kit variations between Tg-IMA kits. Suppressed Tg measured by Tg-IMA was insufficient to completely substitute for a stimulated Tg measurement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of the diagnostic performances of US-guided fine needle aspiration cytology and thyroglobulin measurement for lymph node metastases in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma: a meta-analysis
Rong-Bin Liu, Da-Lei Zhou, Bo-Heng Xu, Xin-Hua Yang, Qing Liu, Xiao Zhang, Tao Tang, Zu-Lu Ye, Yue Li
European Radiology.2021; 31(5): 2903. CrossRef - Preoperative Serum Thyroglobulin and Its Correlation with the Burden and Extent of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Hosu Kim, So Young Park, Jun-Ho Choe, Jee Soo Kim, Soo Yeon Hahn, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Jaehoon Jung, Tae Hyuk Kim
Cancers.2020; 12(3): 625. CrossRef - Estimating the Growth Rate of Lung Metastases in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors or Doubling Time?
Eyun Song, Jonghwa Ahn, Min Ji Jeon, Sang Min Lee, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Jung Hwan Baek, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
Thyroid.2020; 30(3): 418. CrossRef - Impact of delayed radioiodine therapy in intermediate‐/high‐risk papillary thyroid carcinoma
Mijin Kim, Minkyu Han, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, In Joo Kim, Jin‐Sook Ryu, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Tae Yong Kim, Bo Hyun Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2019; 91(3): 449. CrossRef - Tertiary Care Experience of Sorafenib in the Treatment of Progressive Radioiodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: A Korean Multicenter Study
Mijin Kim, Tae Hyuk Kim, Dong Yeob Shin, Dong Jun Lim, Eui Young Kim, Won Bae Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Young Kee Shong, Bo Hyun Kim, Won Gu Kim
Thyroid.2018; 28(3): 340. CrossRef - A Follow-Up Strategy for Patients with an Excellent Response to Initial Therapy for Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: Less Is Better
Min Ji Jeon, Mijin Kim, Suyeon Park, Hye-Seon Oh, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
Thyroid.2018; 28(2): 187. CrossRef - Preoperative serum thyroglobulin predicts initial distant metastasis in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer
Hosu Kim, Young Nam Kim, Hye In Kim, So Young Park, Jun-Ho Choe, Jung-Han Kim, Jee Soo Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Tae Hyuk Kim, Sun Wook Kim
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparison of the diagnostic performances of US-guided fine needle aspiration cytology and thyroglobulin measurement for lymph node metastases in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma: a meta-analysis

- Influence of Anti-thyroglobulin Antibody on the Measurement of Thyroglobulin using the Immunoradiometric Assay.
- Byeong Cheol Ahn, Jin Ho Bae, Shin Young Jeong, Ho Yong Park, Jung Guk Kim, Sung Woo Ha, Jaetae Lee, Bo Wan Kim, Kyu Bo Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2004;19(1):42-47. Published online February 1, 2004
- 1,306 View
- 24 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Serum thyroglobulin(Tg) is a valuable and sensitive tool needed in the follow-up of patients with differentiated thyroid cancer(DTC), but antithyroglobulin antibody(Anti-Tg), common in patients with DTC, can interfere with the assay for Tg. In this study, we evaluated the influence of Anti-Tg on the measurement of Tg using the immunoradiometric assay(IRMA). METHODS: In using ELSA-hTg in vivo test(CIS international, Schering, France), a solid phase two-site IRMA was used to measure Tg(23.5ng/mL, 62.5ng/mL) under the absence or presence of three concentrations of Anti-Tg(25U/mL, 50U/mL, 100U/mL). We also performed Tg measurement using patients serum that was mixed with patients serum containing high Anti-Tg. ANOVA and Scheffe tests were performed to evaluate the effect of Anti-Tg on Tg IRMA, and an inverse regression was made to calculate the level of Tg from measured Tg and used Anti-Tg levels and also to assess the degree of effect of anti-Tg on Tg IRMA. RESULTS: In measuring Tg using the standard solution, the presence of Anti-Tg resulted in a falsely suppressed Tg value. The IRMAs for 23.5ng/mL of the standard Tg solution resulted in 24.5+/-.1 ng/mL under no Anti-Tg, 11.8+/-.4ng/mL under 25U/mL of Anti-Tg, 7.7+/-.1ng/mL under 50U/mL of Anti-Tg, and 4.5+/-.4ng/mL under 100U/mL of Anti-Tg. IRMAs 62.5ng/mL of the standard Tg solution resulted in 65.9+/-.7ng/mL under no Anti-Tg, 36.3+/-.2ng/mL under 25U/mL of Anti-Tg, 23.7+/-.7ng/mL under 50U/mL of Anti-Tg, and 14.0+/-.0ng/mL under 100U/mL of Anti-Tg. (ANOVA test, p=0.000). The degree of suppression of the measured Tg value was positively correlated with the Anti-Tg level (Quadratic model regression, Sig T=0.000). The presence of Anti-Tg also resulted in a falsely suppressed Tg value for the Tg measurement using patient's serum. CONCLUSION: The presence of Anti-Tg could consist of the use of Tg as a tumor, therefore Anti-Tg should be measured in all patients diagnosed with DTC. The interpretation of the Tg level must be performed with extreme caution in patients with Anti-Tg.

- The Incidence of Postpartum Thyroiditis and Effect of High Iodine Intake on it in Korean Women.
- Won Bae Kim, Chang Hoon Yim, Kyung Soo Park, Byoung Sool Moon, Jae Hoon Lee, Hye Won Jun, Ho Jun Jin, Sung Yeon Kim, Bo Yeon Cho, Hong Gyu Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1998;13(3):339-350. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,089 View
- 28 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Postpartum thyroiditis(PPT) is one of syndromes of thyroid dysfunction that occurs in the first year after parturition. Reported incidence of PPT is 3.9-8.2% of postpartum women in several studies from different countries. The fact that 52-100% of patients with PPT have thyroid autoantibodies, and that lymphocytic infiltration of thyroid gland is the characteristic pathological feature of PPT suggest that PPT is an autoimmune disease. High iodine intake in short term period is known to aggrevate the experimental autoimmune thyroiditis. This study was performed to investigate the incidence and clinical features of PPT in Korean postpartum women who usually ingest excessive amount of idine in immediate postpartum period and to investigate the predictive value of thyroid autoantibodies in the development of PPT in them. METHOD: Between March 1996 and February 1997, 99 women without previous history of any thyroid disease who delivered babies at Boramae hospital were enrolled. Thyroid function parameters(T3, T4, free T4, TSH), thyroid autoantibodies(anti-microsomal antibody, anti-thyroglobulin antibody) and urinary iodine excretion were measured prospectively before and 1, 3 months after delivery. Dietary iodine intake during postpartum period was evaluated by questionnaire, and clinical parameters were followed up. RESULTS: During 3 months of observation, PPT developed in 8.1%(8/99) of postpartum women. Five cases had typical course having thyrotoxic phase and the other 3 cases had hypothyroid phase without toxic phase. However, only one of those required thyroid hormone replacement therapy in the latter group. There were no differences in age, baseline thyroid function parameters, parity, percent cases with family history of thyroid disease between those developed PPT (n=8) and those did not develop PPT(n=91). Duration of high iodine intake(3.8 +- 0.5 wk. vs. 3.7 +- 0.8 wk., p>0.05), total ingested amount of high iodine diet(77 +- 28 vs. 79 +- 24 bowels of miyokguk, p)0.05), and the urinary iodine excretion(1.9 +- 1.4 mg/g creatinine vs. 3.7 +- 3.7mg/g creatinine, p0.05) at 1 month postpartum were not different between two groups. Of 99 total subjects, anti-microsomal antibody(AMA) was present in 13.1%(13/99) before delivery in their sera. Positive predictive value of the presence of AMA before delivery in predicting the development of PPT was 30.8%. CONCLUSION: The fact that incidence of PPT in normal Korean postpartum women who usually have high iodine intake in immediate postpartum period is not higher than those of other countries, and that there was no difference in the amount of iodine intake between those developed PPT and those did not suggest that high iodine intake in immediate postpartum period do not influence on the incidence of PPT. The presence of AMA before delivery had low specificity in prediction of development of PPT, so the measurement of AMA seems not to be a useful screening test.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



