Clinical and Molecular Characteristics of PRKACA L206R Mutant Cortisol-Producing Adenomas in Korean Patients
Article information
Abstract
Background
An activating mutation (c.617A>C/p.Lys206Arg, L206R) in protein kinase cAMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha (PRKACA) has been reported in 35% to 65% of cases of cortisol-producing adenomas (CPAs). We aimed to compare the clinical characteristics and transcriptome analysis between PRKACA L206R mutants and wild-type CPAs in Korea.
Methods
We included 57 subjects with CPAs who underwent adrenalectomy at Seoul National University Hospital. Sanger sequencing for PRKACA was conducted in 57 CPA tumor tissues. RNA sequencing was performed in 13 fresh-frozen tumor tissues.
Results
The prevalence of the PRKACA L206R mutation was 51% (29/57). The mean age of the study subjects was 42±12 years, and 87.7% (50/57) of the patients were female. Subjects with PRKACA L206R mutant CPAs showed smaller adenoma size (3.3±0.7 cm vs. 3.8±1.2 cm, P=0.059) and lower dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate levels (218±180 ng/mL vs. 1,511±3,307 ng/mL, P=0.001) than those with PRKACA wild-type CPAs. Transcriptome profiling identified 244 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between PRKACA L206R mutant (n=8) and wild-type CPAs (n=5), including five upregulated and 239 downregulated genes in PRKACA L206R mutant CPAs (|fold change| ≥2, P<0.05). Among the upstream regulators of DEGs, CTNNB1 was the most significant transcription regulator. In several pathway analyses, the Wnt signaling pathway was downregulated and the steroid biosynthesis pathway was upregulated in PRKACA mutants. Protein-protein interaction analysis also showed that PRKACA downregulates Wnt signaling and upregulates steroid biosynthesis.
Conclusion
The PRKACA L206R mutation in CPAs causes high hormonal activity with a limited proliferative capacity, as supported by transcriptome profiling.
INTRODUCTION
Cushing syndrome is a critical state of endogenous hypercortisolemia accompanied by metabolic, cardiovascular, and musculoskeletal complications, necessitating surgical or medical treatment. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)-independent Cushing syndrome or primary adrenal Cushing syndrome accounts for 20% to 30% of cases of endogenous Cushing syndrome and encompasses cortisol-producing adenomas (CPAs) and bilateral micronodular or macronodular adrenocortical hyperplasia [1,2].
The cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) signaling pathway plays a major role in ACTH-independent Cushing syndrome. Primary pigmented nodular adrenal diseases, which may be sporadic or part of the Carney complex, is due to germline-inactivating mutations of PRKAR1A (a regulatory unit of PKA) or phosphodiesterase 11A (PDE11A) [3,4]. In addition, an activating germline mutation in guanine nucleotide binding protein, alpha stimulating (GNAS), which encodes a stimulatory G-protein alpha subunit, was found to be related to CPAs in McCune-Albright syndrome [5]. However, the genetic etiology of sporadic CPAs was not established until 2014.
In 2014, four independent groups reported the same recurrent somatic mutation of the protein kinase CAMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha (PRKACA) as a genetic cause of CPAs [6–9]. This somatic (c.617A>C/p.Lys206Arg, L206R) mutation of PRKACA is a common genetic alteration in CPA patients, but its prevalence was highly variable across different case series, occurring in 35% to 65% of patients [10]. The L206R mutation occurs at the interaction site between the regulatory and catalytic subunits of PKA. The L206R gain-of-function mutation is resistant to inhibition of the PKA regulatory subunit [6–9] and renders the mutant catalytic subunits constitutively active [11]. Other somatic mutations in genes such as catenin beta 1 (CTNNB1; 23.1%) and GNAS (5.8%) have also been reported [12,13].
Previous studies have reported that subjects with PRKACA-mutated CPAs tended to have smaller adenomas and more severe hypercortisolism than those with non-PRKACA-mutated CPAs [6,7,9,10,14]. However, the link between this genetic mutation and clinical characteristics remains to be elucidated.
Therefore, we aimed to compare the clinical characteristics between subjects with PRKACA L206R-mutated CPAs and those with wild-type CPAs in Korea. In addition, we investigated whether transcriptome analysis using RNA sequencing could yield insights into the characteristics of PRKACA L206R mutant CPAs.
METHODS
Study subjects
In this clinical study, we enrolled 57 subjects who were diagnosed with overt Cushing syndrome and CPAs and underwent adrenalectomy at Seoul National University Hospital from March 2004 to January 2017. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Hospital (IRB no. 1803-144-934). Consent was obtained from each subject after a full explanation of the purpose and nature of all procedures used.
Forty-four CPAs were sequenced for the PRKACA L206R mutation using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumor tissues. Among them, 20 CPAs (45.4%) harbored the PRKACA L206R mutation. Additionally, we sequenced 13 CPAs for the PRKACA L206R mutation using frozen fresh tumor tissues. Eight of these 13 CPAs revealed the PRKACA L206R mutation. Seven wild-type CPAs, for which frozen tissues were available, were further analyzed through whole-exome sequencing (WES). The removed CPA tissues were immediately snap-frozen over dry ice and stored in plastic tubes at −80°C until analysis. Leukocyte DNA corresponding to seven wild-type CPAs was also processed to WES. WES revealed that one CPA harbored the PRKACA L206R somatic mutation, and another CPA harbored both the K214E (c.A640G) and p.H88Y (c.262T) somatic mutations. Two CPAs had the GNAS R201C mutation. Finally, a total of 56 subjects with confirmed CPAs were included in the analysis of clinical features. Among them, RNA sequencing was only conducted in 13 CPAs with available fresh-frozen tissues.
The diagnosis of CPAs was confirmed by a non-suppressed overnight 1-mg dexamethasone suppression test (>1.8 μg/dL), elevated 24-hour urinary free cortisol (UFC) (>75 μg/day), a low level of plasma ACTH, typical adrenal adenomas, and overt Cushing syndrome symptoms such as moon face, centripetal obesity, bruising, and purple striae. After adrenalectomy, subjects experienced postoperative adrenal insufficiency and the pathology results showed adrenal cortical adenomas. Serum cortisol and 24-hour UFC levels were measured using a radioimmunoassay kit (IMMUNOTEC, Prague, Czech Republic). Morning blood samples for plasma ACTH levels were collected in a prechilled tube containing ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), immediately separated at 4°C, and stored at −80°C until needed. Plasma ACTH levels were measured using an immunoradiometric assay (CIS-Bio International, Saclay, France). The serum dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S) level was gauged using a competitive binding radioimmunoassay kit (Diagnostic Products Corp., Los Angeles, CA, USA), and the reference range was 350 to 4,300 ng/mL.
Sanger sequencing for the PRKACA L206R mutation
We sequenced all 10 exons of the PRKACA gene. Randomly selected variants identified exclusively by WES were further confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Sanger sequencing. The specific primers are shown in Supplemental Table S1. The products were directly sequenced by Macrogen Inc. (Seoul, Korea) using an ABI 3730 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA) with an ABI PRISM terminator cycle sequencing kit v3.1.
Whole-exome sequencing
To find causal variants, we performed WES for seven patients. We generated libraries from genomic DNA derived from patients’ blood and tissues. An exome captured sequencing library was produced from SureSelect Human All Exon V6 (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) with an input of 200 ng of genomic DNA. The exome capture platform method was conducted according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The captured DNA was sequenced using the NextSeq 500 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) platform with paired-end reads.
WES data processing
WES reads from patients’ tumor and blood samples were aligned with the reference human genome GRCh37/hg19 using the Burrows-Wheeler Aligner (BWA) (v0.7.15-r1140). Deduplication and local re-alignment were performed using the Genome Analysis Tool Kit (GATK, v4.0.5.1). Somatic variants were called using GATK MuTect2 and variants were filtered by removing variants with a minor allele frequency ≥0.1% in the dbSNP138, 1,000 genomes, Exome Variant Server, and Exome Aggregate Consortium databases. Exonic and splicing variants were selected for further analysis.
RNA sequencing analysis
For RNA sequencing, the total RNA was isolated using QIAzol lysis reagent (Qiagen, Germantown, MD, USA) including a DNase I (Roche, Mannheim, Germany) digestion step. Total RNA quantity, quality, and purity were determined using a Nanodrop spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies, Rockland, DE, USA) and a 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies). For library preparation for whole-transcriptome analyses, we used the TruSeq Stranded Total RNA with RiboZero Gold Sample Preparation Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Illumina; catalog no. 20020599) starting from 1,000 ng of total RNA. Accurate quantitation of cDNA libraries was performed using the QuantiFluor dsDNA System and a Quantus fluorometer (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). The first-strand cDNA, followed by second-strand cDNA, was synthesized from purified fragmented RNAs with the removal of ribosomal RNA. End repair was performed, followed by adenylation of the 3′ ends. Adapters were ligated, and PCR was conducted to selectively enrich DNA fragments with adapters and to amplify the amount of DNA in the library, respectively. Quality control of generated libraries was conducted using the 2100 Bioanalyzer. The libraries were paired-end sequenced by NextSeq 500 sequencing system (Illumina).
RNA sequencing data processing
RNA sequencing reads were filtered using Trimmomatic (version 0.36) [15]. Filtered reads were aligned to the human genome using Spliced Transcripts Alignment to a Reference (STAR, version 2.5.3a) [16], and gene expression levels were calculated using RNA-Seq by Expectation-Maximization (RSEM, version 1.3.1) [17]. The GRCh37/hg19 FASTA file from the University of California Santa Cruz (UCSC) genome browser and the annotation GTF file from the UCSC refFlat table were used to create the STAR and RSEM genome indexes. Transcript per million (TPM) normalized gene expression values were used for further analysis.
Genes with median TPM >5 in at least one condition (PRKACA L206R or wild-type) were selected for further analysis. Genes with a fold change ≥2 and a t test P<0.05 for the log2-transformed TPM were considered as differentially expressed. Among the differentially expressed genes (DEGs), the number of upregulated genes in PRKACA mutants was small, and further analysis was conducted using downregulated genes in PRKACA mutants. Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis was performed using enrichR [18]. WikiPathways 2019, Panther 2016, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) 2021, and gene set enrichment analyses were applied for an enriched pathway analysis of the downregulated pathways in PRKACA mutants [19]. Upstream regulator analysis was performed using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) [20]. Color-mapped canonical pathways were generated using genes with a median TPM >5 in at least one condition through the use of IPA.
Statistical analysis
Data were shown as mean±standard deviation or number (%). We performed the chi-square test for categorical variables and the Student’s t test for continuous variables. A P<0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
RESULTS
The prevalence of the PRKACA L206R mutation was 53% (30/ 57). No other mutations in the PRKACA gene were found. The mean age of the study subjects was 42±12 years, and 89.5% (51/57) of the patients were female. The clinical and biochemical characteristics of the study subjects according to PRKACA somatic mutation status are shown in Table 1. Subjects with PRKACA L206R mutant CPAs showed smaller adenoma size (3.24±0.72 cm vs. 3.87±1.30 cm, P=0.044) and lower DHEA-S levels (221±176 ng/mL vs. 1,511±3,307 ng/mL, P=0.001) than those with PRKACA wild-type CPAs.
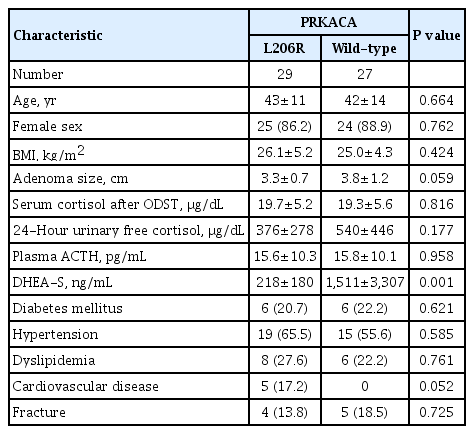
Clinical and Biochemical Characteristics of Study Subjects According to PRKACA Somatic Mutation Status
RNA sequencing was performed in eight PRKACA L206R-mutated and five wild-type CPAs using fresh-frozen tissue samples. The clinical characteristics of the study subjects who underwent RNA sequencing are shown in Supplemental Table S2. In Fig. 1, a volcano plot shows the magnitude (x-axis) and the statistical significance (y-axis) of differences in gene expression in the two groups. There were 244 DEGs between the two groups, including five upregulated and 239 downregulated genes in PRKACA mutants (|fold change| ≥2, P<0.05) (Supplemental Material S1).

Analysis of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between protein kinase cAMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha (PRKACA) L206R mutants and wild-type cortisol-producing adenomas (CPAs). (A) Volcano plot of DEGs, showing the magnitude (x-axis) and the statistical significance (y-axis) of differences in gene expression between PRKACA L206R mutants and wild-type CPAs. (B) A t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (tSNE) plot. FC, fold change.
Table 2 shows the five upregulated and top 15 downregulated genes in the PRKACA mutants. The SNORA21B, CLCN5, ARSG, TMEM217, and SH3BGR genes were significantly upregulated in PRKACA mutants. Due to the small number of upregulated genes in PRKACA mutants, further ontology or pathway analyses only included downregulated genes.
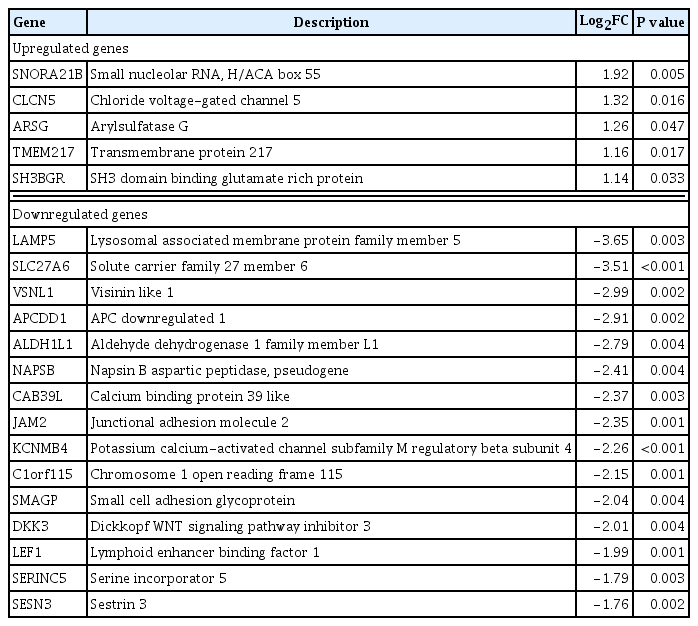
Major Differentially Expressed Genes in PRKACA L206R Mutants Compared with Wild-Type Cortisol-Producing Adenomas (|FC| ≥2, P<0.05)
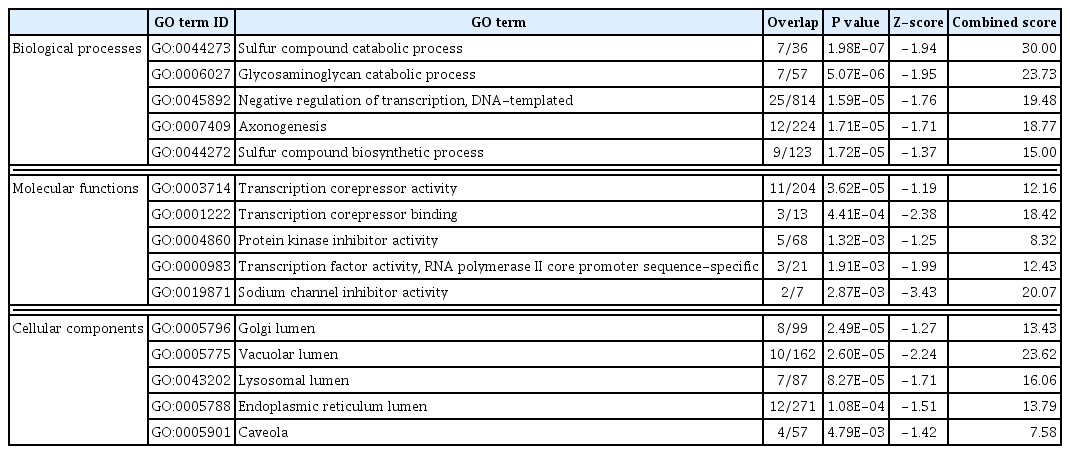
DAVID was used to perform a GO analysis for the downregulated genes in PRKACA mutants. A total of 290 GO terms satisfied the cut-off criterion (P<0.05), and these terms consisted of 237 biological processes, 34 molecular functions, and 19 cellular components. The top five most significantly enriched GO terms in each category are presented in Table 3. The most significant GO terms were “sulfur compound catabolic process,” “transcription corepressor activity,” and “Golgi lumen.” We further assessed the upstream regulators of DEGs using the IPA. CTNNB1 was found to be the most significant transcriptional regulator of the downregulated genes, including BMP4, CCND1, LEF1, PLS3, PTCH1, TOB2, TSC22D1, UDP-glucose ceramide glucosyltransferase (UGCG), and versican (VCAN) (Fig. 2, Supplemental Table S3).

Catenin beta 1 (CTNNB1) as an upstream regulator of downregulated genes such as bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4), cyclin D1 (CCND1), lymphoid enhancer binding factor 1 (LEF1), plastin 3 (PLS3), patched 1 (PTCH1), transducer of ERBB2, 2 (TOB2), TSC22 domain family member 1 (TSC22D1), UDP-glucose ceramide glucosyltransferase (UGCG), and versican (VCAN) in protein kinase cAMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha (PRKACA) L206R mutants. Green, downregulation in PRKACA L206R mutants.
Pathway analyses were performed through WikiPathways 2019 and Panther 2016 using 479 downregulated genes (P<0.05) (Table 4). The Wnt signaling pathway was significantly downregulated in PRKACA mutants in both WikiPathways 2019 and Panther 2016. Using all DEGs regardless of the significance of the P value and fold change, we performed a KEGG pathway analysis of Cushing syndrome (has04934) (Fig. 3). Genes involved in steroid hormone biosynthesis, including steroidogenic acute regulatory (STAR), CYP11A1, CYP17A1, HSD3B2, and CYP21A, were upregulated, but Wnt signaling-related genes, including Wnt, Frizzled, DVL, glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3B), Axin, and T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor (TCF/ LEF), were downregulated in PRKACA mutants (Supplemental Fig. S1).

Enriched Pathway Analysis of the Downregulated Genes in PRKACA Mutants Using WikiPathways 2019, Panther 2016, and KEGG 2021
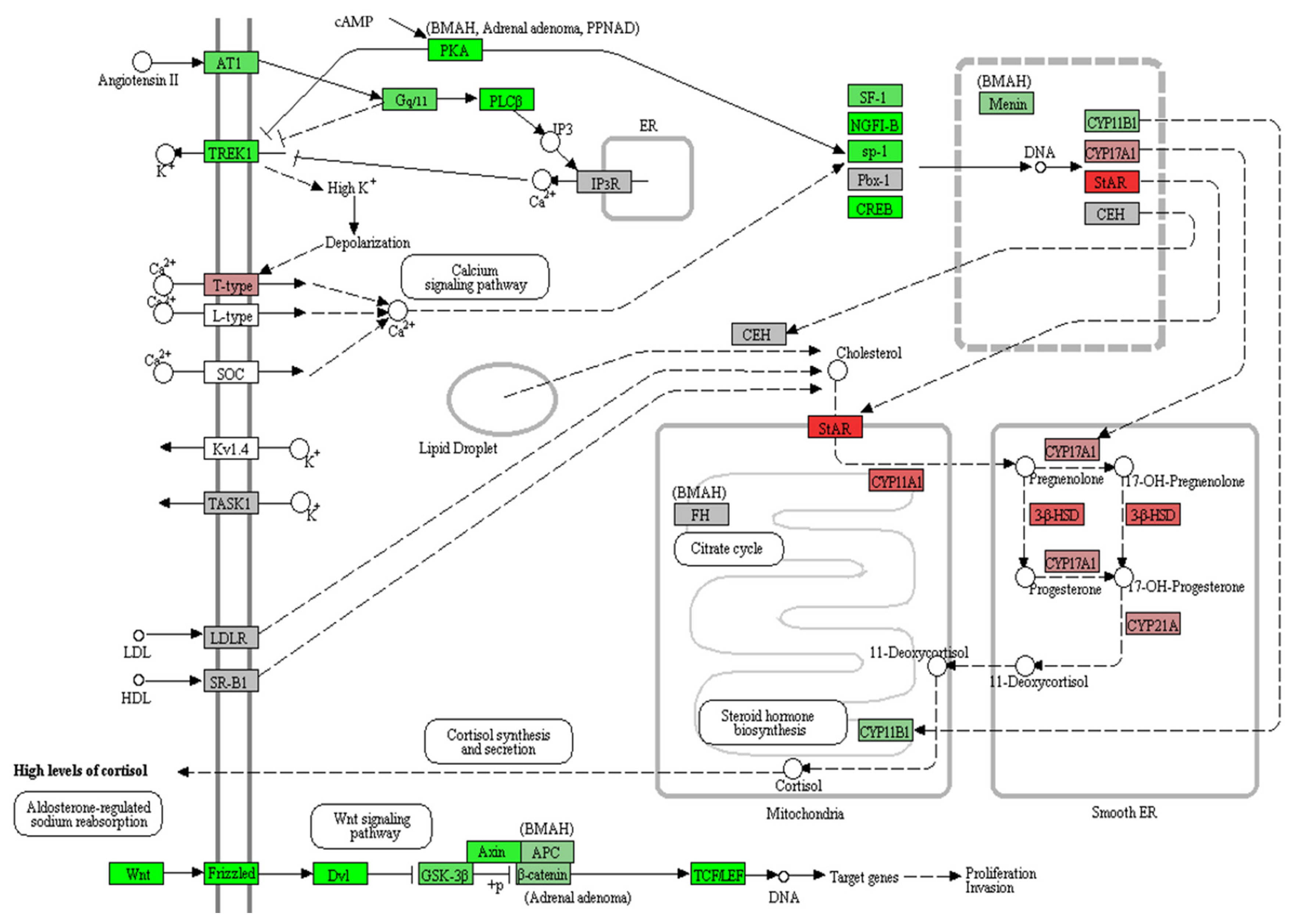
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis of Cushing syndrome (hsa04934). Red, upregulation in protein kinase cAMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha (PRKACA) L206R mutants; green, downregulation in PRKACA L206R mutants. Steroid hormone biosynthesis, including STAR, CYP11A1, CYP17A1, HSD3B2, and CYP21A, was upregulated, but Wnt signaling-related genes, including Wnt, Frizzled, DVL, glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3B), Axin, and TCF/LEF, were downregulated.
DISCUSSION
In this clinical study, we demonstrated that PRKACA mutant CPAs were smaller than nonmutated CPAs, but the degree of hypercortisolism was not different between the PRKACA mutant and wild-type groups. Through a transcriptome analysis, we identified downregulation of the Wnt signaling pathway in PRKACA mutants.
The present study showed that the prevalence of the somatic PRKACA L206R mutation in CPAs was 53% in our cohort, similar to the pooled prevalence previously reported in Asian cohorts. In Asian cohorts, the hotspot somatic L206R mutation in PRKACA was discovered in 59% of patients (overall, 114/195), although in Europe and the USA, the pooled prevalence was reported to be 35% (65/184) [6–10]. The genetic background for this ethnic difference remains to be elucidated, but Asian populations have been found to harbor the PRKACA L206R mutation more frequently than Western populations.
We showed that subjects with the PRKACA L206R mutation had lower DHEA-S levels than those with wild-type PRKACA. However, there were no significant differences in levels of serum cortisol after suppression, ACTH, and 24-hour UFC between the two groups. Previous studies regarding hormone activity have reported contradictory results. Cao et al. [8] reported that there were no significant differences in cortisol production between CPA subjects with and without the PRKACA mutation. However, other groups revealed higher serum cortisol levels after 1 mg of dexamethasone and urinary cortisol levels [6,7]. Although previous studies did not measure DHEA-S, the lower levels of DHEA-S may reflect more strongly suppressed ACTH secretion due to higher autonomous cortisol production [21,22]. An alternative explanation may be that the age at diagnosis was not significantly different between the two groups in the present study, while patients with the PRKACA mutation were found to be younger in other studies [6,7].
High cortisol secretion from CPAs may be related to the activation of steroidogenesis pathways. Cao et al. [8] identified significant enrichment of the GO terms “biosynthesis and metabolism of steroid and cholesterol” and “response to chemical stimulus” in PRKACA mutants, with increased expression of genes including STAR, MC2R, GSTA1, CXCL2, and S100A8/9. Beuschlein et al. [6] also conducted a tissue microarray analysis and showed that MC2R, STAR, CYP11A1, HSD3B2, and CYP21A2 expression was higher in PRKACA mutants (n=11) than in non-mutants (n=8). Goh et al. [9] also discovered a higher steroidogenic enzymatic activity in PRKACA mutants.
Similar to the previous studies, we also demonstrated that steroidogenesis-related genes were upregulated in PRKACA mutants. In KEGG pathway analysis of Cushing syndrome, the STAR, CYP11A1, HSD3B2, CYP21A2, and CYP17A1 genes were upregulated in PRKACA mutants compared with non-mutants. PRKACA phosphorylates and activates cAMP responsive element binding protein 1 (CREB1) and Sp1 transcription factor (SP1). CREB1 induces gene transcription in response to hormonal stimulation of the cAMP pathway. SP1 is a transcription factor that can activate or repress transcription in response to physiological and pathological stimuli. Sequentially, the CREB-SP1 complex activate NR5A1 (steroidogenic factor 1 [SF1]). NR5A1 is an essential transcriptional activator for sexual differentiation and the formation of the primary steroidogenic tissues. SP1 and NR5A1 physically interact and cooperate in the regulation of human steroidogenic acute regulatory (STAR) protein promoter activity [23]. STAR expression correlates with PKA activation in CPAs [24]. NR5A1 activates the glucocorticoid-specific synthesis pathway by suppressing aldosterone synthase (CYP11B2) activity. Thus, the PRKACA mutation constitutively activates STAR and NR5A1, which play a role in the pathogenesis of CPAs.
Our analysis revealed that the somatic PRKACA L206R mutation was related to smaller adenoma size. This finding is consistent with the results of the previous studies [6–9,25]. Smaller adenoma size can be interpreted as indicating that PRKACA mutants are less proliferative than wild-type tumors. Similarly, cAMP-stimulated PKA activity was lower in larger nodules than in smaller ones in bilateral macronodular adrenal hyperplasia [26]. Consistent with this clinical feature, our transcriptomic data pathway analysis presented tumor-related pathways such as metastatic brain tumor and endometrial cancer. Moreover, Wnt signaling pathway-related genes, such as LEF1, APCDD1, DKK3, RSPO3, and DACH1, were downregulated in PRKACA mutants compared with PRKACA wild-type tumors. The downregulated Wnt signaling pathway was corroborated by an upstream regulator analysis using IPA. CTNNB1, the core transcription factor of Wnt signaling, was the top upstream regulator of downregulated genes in PRKACA mutants. In the presence of Wnt ligands, CTNNB1 is not ubiquitinated and accumulates in the nucleus, where it acts as a coactivator for transcription factors of the TCF/LEF family, leading to the activation of Wnt-responsive genes.
However, PKA phosphorylates β-catenin, which is encoded by CTNNB, inhibits the ubiquitination of β-catenin, and activates Wnt signaling in other cells [27,28]. Previous studies have also shown that increased cAMP signaling elevates Wnt/β-catenin signaling [29,30]. These findings are opposite to those of our transcriptome analysis. Nevertheless, Drelon et al. [31] also demonstrated that constitutive PKA activation in the zona fasciculata was a major driver of Wnt inhibition and inhibited β-catenin-induced tumorigenesis. They also identified that PKA inactivation accelerated Wnt-induced tumorigenesis. They clearly showed that in H295R human adrenal cortical cell lines, the Wnt pathway responded negatively to PKA stimulation, whereas in COS7 cells (monkey kidney immortalized cells), the Wnt pathway responded positively to PKA stimulation [31]. They explained that the different role of PKA on Wnt/β-catenin signaling within the adrenal cortex was due to inactive T41/S45 phosphorylation of β-catenin [31]. In The Cancer Genome Atlas cohort of adrenal cortical carcinoma, STAR expression was negatively correlated with Wnt activation signatures such as LEF1, AXIN2, and APCDD1 [31]. PKA may act as a tumor suppressor in the adrenal cortex through the repression of Wnt signaling.
Several limitations of this study need to be mentioned. RNA sequencing was performed in 13 CPAs among 57 subjects because of the limited number of available frozen tissue samples from the CPAs. Thus, a future study with a larger sample size will be needed to clarify the molecular pathogenesis of CPAs through a pathway or network analysis. An ontology and pathway analysis regarding the upregulated genes in PRKACA mutants could not be performed due to the small number of upregulated genes in PRKACA mutants. Due to the lack of tumor tissues, we could not validate the expression of DEGs by methods such as quantitative PCR.
In this study, we reported the prevalence of somatic PRKACA L206R mutations in Koreans for the first time. In addition, we demonstrated that PKA activation driven by the PRKACA L206R somatic mutation in CPAs upregulated the glucocorticoid synthesis pathway and inhibited the Wnt signaling pathway, thereby resulting in smaller adenoma size. We believe that these results will be helpful to further research on the mechanism underlying the development of PRKACA L206R-mutated CPAs.
Supplementary Information
Sequencing Primers Information for PRKACA Mutation
Clinical Characteristics of Patients Undergoing RNA Sequencing
Top Upstream Regulators
Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) identified that the gene set for Wnt protein binding was downregulated in protein kinase cAMP-activated catalytic subunit alpha (PRKACA) mutants (normalized enrichment score=–1.659, nominal P=0.006).
Acknowledgements
Some samples derived from the Seoul National University Hospital Human Biobank, a member of the National Biobank of Korea, were obtained with informed consent under Institutional Review Board-approved protocols. This study was supported by a grant from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (No. 2E26990-17-098, 2E28030-18-033, 2E29290-19-019) and a grant from the National Research Foundation by the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea (Project No. NRF-2020R1C1C1010723). This work was presented as an abstract at the Seventh ESE Young Endocrinologists and Scientists (EYES) Meeting in Athens, Greece.
Notes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conception or design: J.H.K. Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: I.J., S.K., R.Y.S., K.K., S.C., J.S.L., M.K.G., M.W.S., K.E.L., J.H.K. Drafting the work or revising: I.J., S.K., R.Y.S., K.K., S.C., J.S.L., M.K.G., M.W.S., K.E.L., J.H.K. Final approval of the manuscript: I.J., S.K., R.Y.S., K.K., S.C., J.S.L., M.K.G., M.W.S., K.E.L., J.H.K.