Article type
- Page Path
- HOME > BROWSE ARTICLES > Article type
Original Articles
- Miscellaneous
- Association between N-Terminal Prohormone Brain Natriuretic Peptide and Decreased Skeletal Muscle Mass in a Healthy Adult Population: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Tae Kyung Yoo, Marie Yung-Chen Wu, Moon Soo Kim, Mi-Yeon Lee, Yong-Taek Lee, Kyung Jae Yoon, Chul-Hyun Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):269-276. Published online March 13, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1588
- 1,751 View
- 75 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Although an inverse association between the N-terminal prohormone brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and obesity exists, only few major studies have assessed the association between NT-proBNP levels and skeletal muscle mass in asymptomatic healthy adults. Therefore, this cross-sectional study was conducted.
Methods
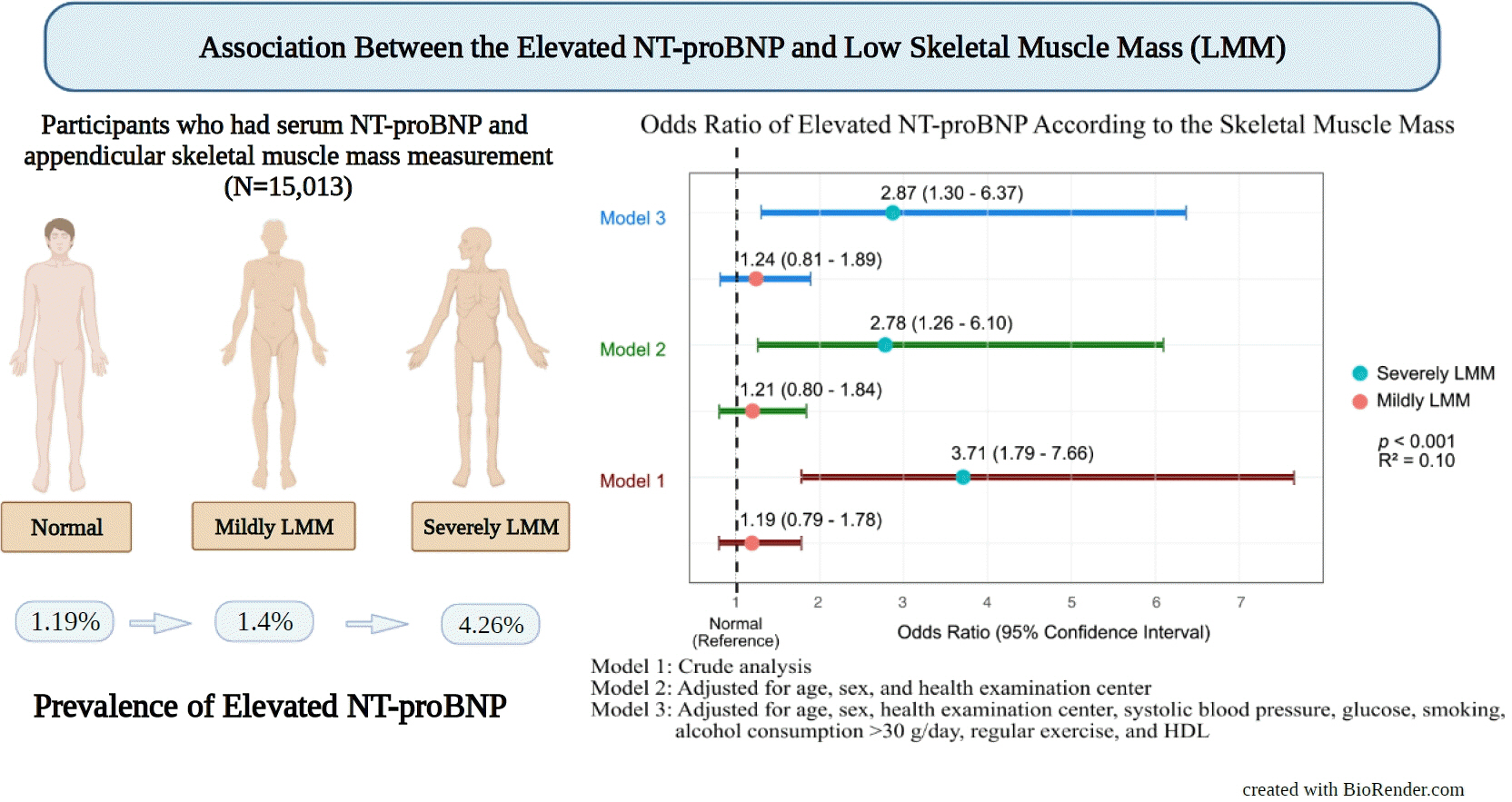
We assessed participants who underwent health examinations at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital in South Korea from January 2012 to December 2019. Appendicular skeletal muscle mass was measured using a bioelectrical impedance analyzer, and the skeletal muscle mass index (SMI) was calculated. Participants were divided into the control, mildly low skeletal muscle mass (LMM) (−2 standard deviation [SD] < SMI ≤−1 [SD]), and severely LMM groups (SD ≤−2) based on their SMI. The association between elevated NT-proBNP level (≥125 pg/mL) and skeletal muscle mass was assessed using multivariable logistic regression analysis with adjustment for confounding factors.
Results
This study enrolled 15,013 participants (mean age, 37.52±9.52; men, 54.24%; control, n=12,827; mildly LMM, n=1,998; severely LMM, n=188). Prevalence of elevated NT-proBNP was higher in mildly and severely LMM groups than in the control group (control, 1.19%; mildly LMM, 1.4%; severely LMM, 4.26%; P=0.001). The adjusted odds ratio (OR) of elevated NT-proBNP was significantly higher in severely LMM (OR, 2.87; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.3 to 6.37) than in control (OR, 1.00; reference) or mildly LMM groups (OR, 1.24; 95% CI, 0.81 to 1.89).
Conclusion
Our results showed that NT-proBNP elevation were more prevalent in participants with LMM. In addition, our study showed an association between skeletal muscle mass and NT-proBNP level in a relatively young and healthy adult population.

- Calcium & bone metabolism
- Persistence with Denosumab in Male Osteoporosis Patients: A Real-World, Non-Interventional Multicenter Study
- Chaiho Jeong, Jeongmin Lee, Jinyoung Kim, Jeonghoon Ha, Kwanhoon Jo, Yejee Lim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Tae-Seo Sohn, Ki-Ho Song, Moo Il Kang, Ki-Hyun Baek
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):260-268. Published online April 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1663
- 1,716 View
- 106 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Persistence with denosumab in male patients has not been adequately investigated, although poor denosumab persistence is associated with a significant risk of rebound vertebral fractures.
Methods
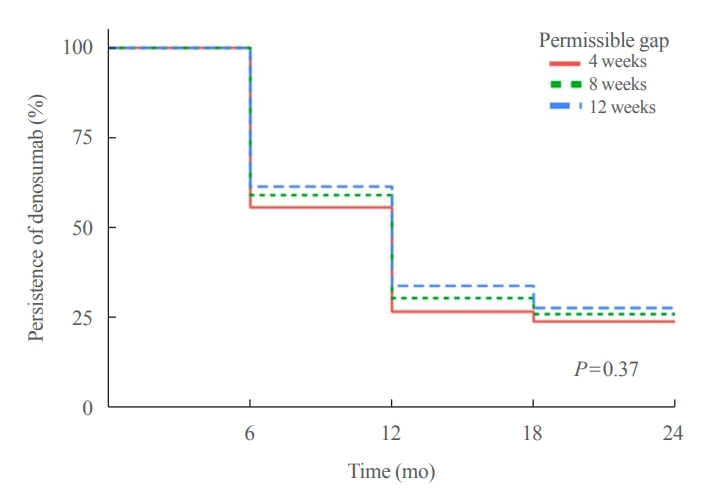
We retrospectively evaluated 294 Korean male osteoporosis patients treated with denosumab at three medical centers and examined their persistence with four doses of denosumab injection over 24 months of treatment. Persistence was defined as the extent to which a patient adhered to denosumab treatment in terms of the prescribed interval and dose, with a permissible gap of 8 weeks. For patients who missed their scheduled treatment appointment(s) during the follow-up period (i.e., no-shows), Cox proportional regression analysis was conducted to explore the factors associated with poor adherence. Several factors were considered, such as age, prior anti-osteoporotic drug use, the treatment provider’s medical specialty, the proximity to the medical center, and financial burdens of treatment.
Results
Out of 294 male patients, 77 (26.2%) completed all four sequential rounds of the denosumab treatment. Out of 217 patients who did not complete the denosumab treatment, 138 (63.6%) missed the scheduled treatment(s). Missing treatment was significantly associated with age (odds ratio [OR], 1.03), prior bisphosphonate use (OR, 0.76), and prescription by non-endocrinologists (OR, 2.24). Denosumab was stopped in 44 (20.3%) patients due to medical errors, in 24 (11.1%) patients due to a T-score improvement over –2.5, and in five (2.3%) patients due to expected dental procedures.
Conclusion
Our study showed that only one-fourth of Korean male osteoporosis patients were fully adherent to 24 months of denosumab treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Denosumab
Reactions Weekly.2023; 1963(1): 206. CrossRef
- Denosumab

- Adrenal gland
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Mortality and Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Patients with Long-Term Glucocorticoid Therapy: A Korean Nationwide Cohort Study
- Eu Jeong Ku, Keeho Song, Kyoung Min Kim, Gi Hyeon Seo, Soon Jib Yoo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):253-259. Published online March 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1607
- 2,520 View
- 101 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) among patients with long-term glucocorticoid treatment (LTGT) has not been established. We aimed to evaluate the association between LTGT and COVID-19 prognosis.
Methods
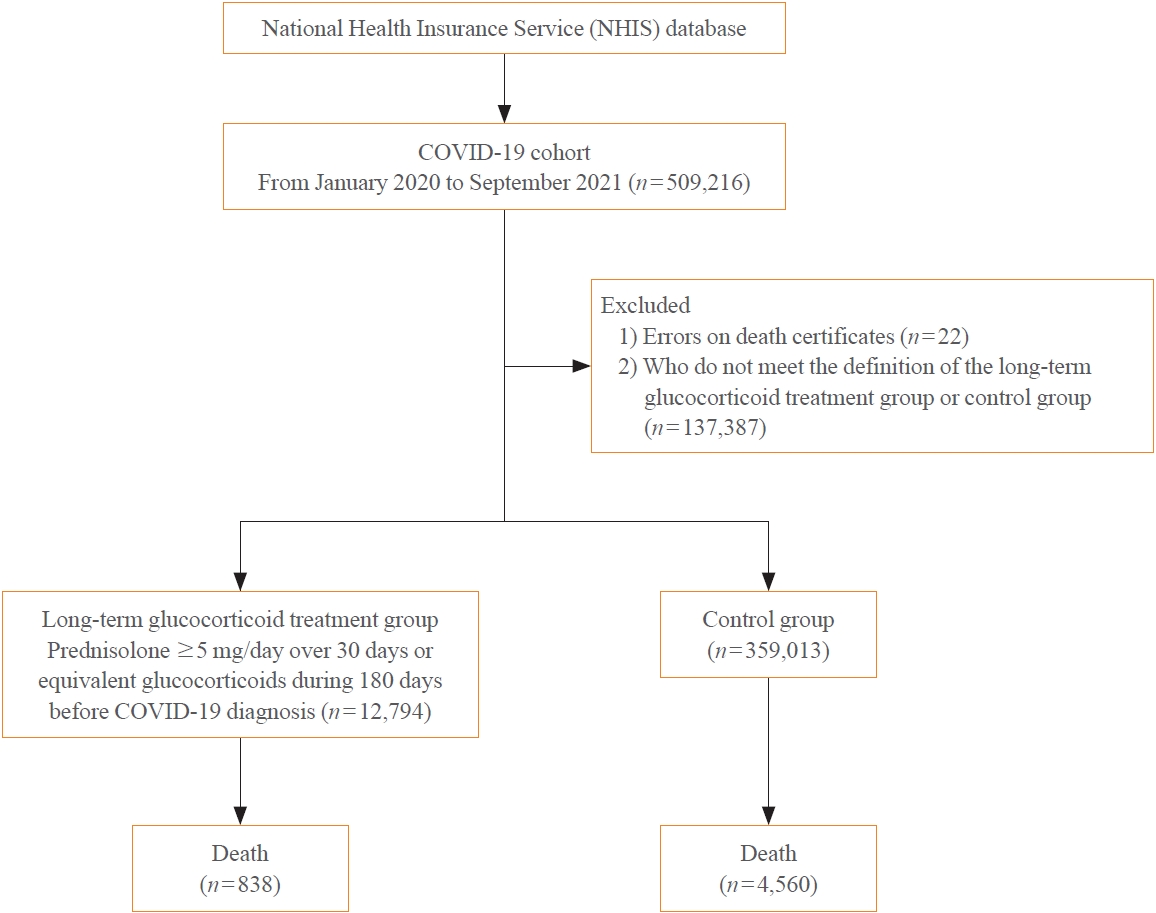
A Korean nationwide cohort database of COVID-19 patients between January 2019 and September 2021 was used. LTGT was defined as exposure to at least 150 mg of prednisolone (≥5 mg/day and ≥30 days) or equivalent glucocorticoids 180 days before COVID-19 infection. The outcome measurements were mortality, hospitalization, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, length of stay, and mechanical ventilation.
Results
Among confirmed patients with COVID-19, the LTGT group (n=12,794) was older and had a higher proportion of comorbidities than the control (n=359,013). The LTGT group showed higher in-hospital, 30-day, and 90-day mortality rates than the control (14.0% vs. 2.3%, 5.9% vs. 1.1%, and 9.9% vs. 1.8%, respectively; all P<0.001). Except for the hospitalization rate, the length of stay, ICU admission, and mechanical ventilation proportions were significantly higher in the LTGT group than in the control (all P<0.001). Overall mortality was higher in the LTGT group than in the control group, and the significance remained in the fully adjusted model (odds ratio [OR], 5.75; 95% confidence interval [CI], 5.31 to 6.23) (adjusted OR, 1.82; 95% CI, 1.67 to 2.00). The LTGT group showed a higher mortality rate than the control within the same comorbidity score category.
Conclusion
Long-term exposure to glucocorticoids increased the mortality and severity of COVID-19. Prevention and early proactive measures are inevitable in the high-risk LTGT group with many comorbidities. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glucocorticoids as a Double-Edged Sword in the Treatment of COVID-19: Mortality and Severity of COVID-19 in Patients Receiving Long-Term Glucocorticoid Therapy
Eun-Hee Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 223. CrossRef - Pituitary Diseases and COVID-19 Outcomes in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Jeonghoon Ha, Kyoung Min Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(14): 4799. CrossRef
- Glucocorticoids as a Double-Edged Sword in the Treatment of COVID-19: Mortality and Severity of COVID-19 in Patients Receiving Long-Term Glucocorticoid Therapy

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Risk for Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus after COVID-19 among Korean Adults: A Nationwide Matched Cohort Study
- Jong Han Choi, Kyoung Min Kim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):245-252. Published online April 5, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1662
- 2,191 View
- 118 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) can cause various extrapulmonary sequelae, including diabetes. However, it is unclear whether these effects persist 30 days after diagnosis. Hence, we investigated the incidence of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in the post-acute phase of COVID-19.
Methods
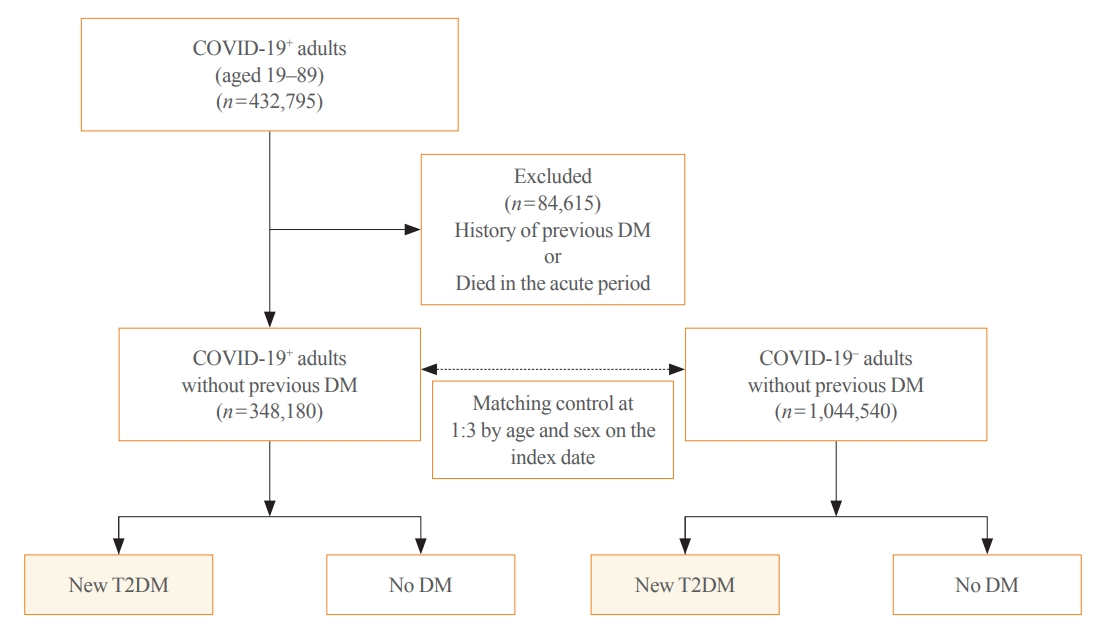
This cohort study used data from the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service, a representative national healthcare database in Korea. We established a cohort of 348,180 individuals diagnosed with COVID-19 without a history of diabetes between January 2020 and September 2021. The control group consisted of sex- and age-matched individuals with neither a history of diabetes nor COVID-19. We assessed the hazard ratios (HR) of newly diagnosed T2DM patients with COVID-19 compared to controls, adjusted for age, sex, and the presence of hypertension and dyslipidemia.
Results
In the post-acute phase, patients with COVID-19 had an increased risk of newly diagnosed T2DM compared to those without COVID-19 (adjusted HR, 1.30; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.27 to 1.33). The adjusted HRs of non-hospitalized, hospitalized, and intensive care unit-admitted patients were 1.14 (95% CI, 1.08 to 1.19), 1.34 (95% CI, 1.30 to 1.38), and 1.78 (95% CI, 1.59 to 1.99), respectively. The risk of T2DM in patients who were not administered glucocorticoids also increased (adjusted HR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.25 to 1.32).
Conclusion
COVID-19 may increase the risk of developing T2DM beyond the acute period. The higher the severity of COVID-19 in the acute phase, the higher the risk of newly diagnosed T2DM. Therefore, T2DM should be included as a component of managing long-term COVID-19. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus in COVID-19: A Scoping Review
Anca Pantea Stoian, Ioana-Cristina Bica, Teodor Salmen, Wael Al Mahmeed, Khalid Al-Rasadi, Kamila Al-Alawi, Maciej Banach, Yajnavalka Banerjee, Antonio Ceriello, Mustafa Cesur, Francesco Cosentino, Alberto Firenze, Massimo Galia, Su-Yen Goh, Andrej Janez,
Diabetes Therapy.2024; 15(1): 33. CrossRef - Pituitary Diseases and COVID-19 Outcomes in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Jeonghoon Ha, Kyoung Min Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(14): 4799. CrossRef
- New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus in COVID-19: A Scoping Review

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
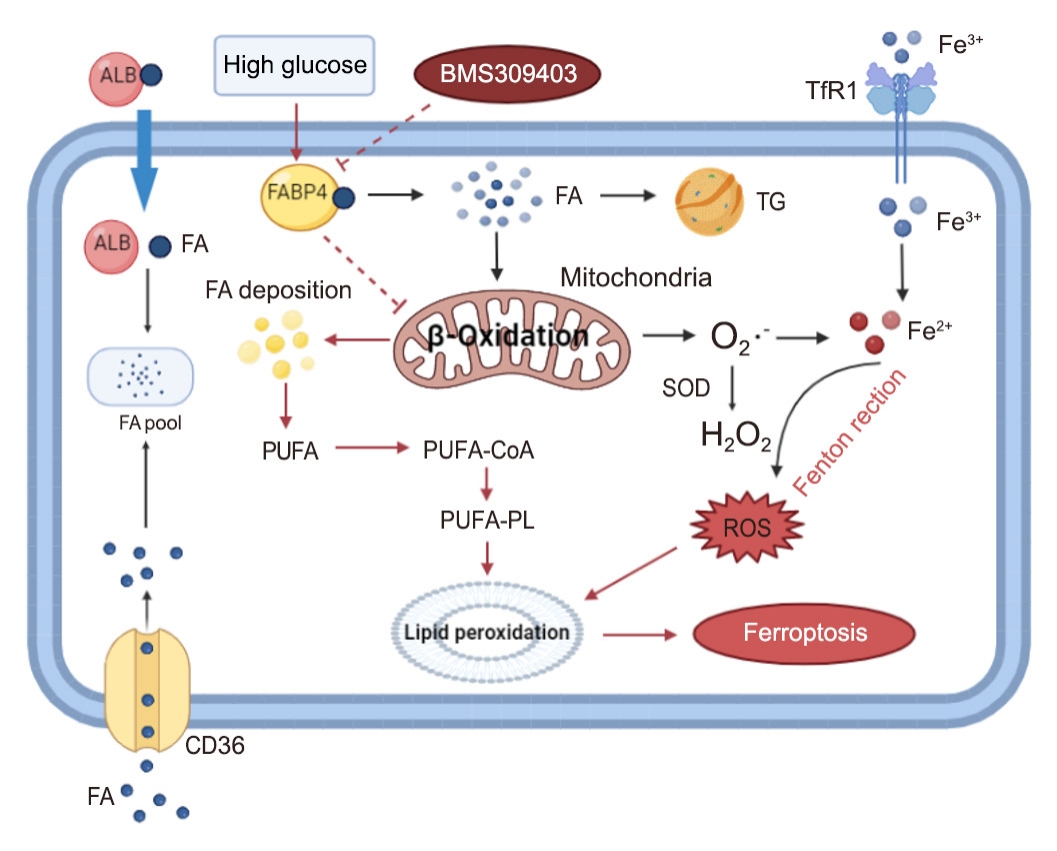
- Inhibition of Fatty Acid β-Oxidation by Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 Induces Ferroptosis in HK2 Cells Under High Glucose Conditions
- Jiasi Chen, Keping Wu, Yan Lei, Mingcheng Huang, Lokyu Cheng, Hui Guan, Jiawen Lin, Ming Zhong, Xiaohua Wang, Zhihua Zheng
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):226-244. Published online April 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1604
- 3,486 View
- 174 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Ferroptosis, which is caused by an iron-dependent accumulation of lipid hydroperoxides, is a type of cell death linked to diabetic kidney disease (DKD). Previous research has shown that fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4) is involved in the regulation of ferroptosis in diabetic retinopathy. The present study was constructed to explore the role of FABP4 in the regulation of ferroptosis in DKD.
Methods
We first detected the expression of FABP4 and proteins related to ferroptosis in renal biopsies of patients with DKD. Then, we used a FABP4 inhibitor and small interfering RNA to investigate the role of FABP4 in ferroptosis induced by high glucose in human renal proximal tubular epithelial (HG-HK2) cells.
Results
In kidney biopsies of DKD patients, the expression of FABP4 was elevated, whereas carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1A (CP-T1A), glutathione peroxidase 4, ferritin heavy chain, and ferritin light chain showed reduced expression. In HG-HK2 cells, the induction of ferroptosis was accompanied by an increase in FABP4. Inhibition of FABP4 in HG-HK2 cells changed the redox state, sup-pressing the production of reactive oxygen species, ferrous iron (Fe2+), and malondialdehyde, increasing superoxide dismutase, and reversing ferroptosis-associated mitochondrial damage. The inhibition of FABP4 also increased the expression of CPT1A, reversed lipid deposition, and restored impaired fatty acid β-oxidation. In addition, the inhibition of CPT1A could induce ferroptosis in HK2 cells.
Conclusion
Our results suggest that FABP4 mediates ferroptosis in HG-HK2 cells by inhibiting fatty acid β-oxidation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fatty Acid Binding Protein-4 Silencing Inhibits Ferroptosis to Alleviate Lipopolysaccharide-induced Injury of Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells by Blocking Janus Kinase 2/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Signaling
Suo Xu, Jiye Luo, Yanli Wang, Xiaobing Chen
Chinese Journal of Physiology.2024; 67(1): 47. CrossRef - Ferroptosis in Liver Disease: Natural Active Compounds and Therapeutic Implications
Zhili Wu, Yanru Zhu, Wenchao Liu, Balamuralikrishnan Balasubramanian, Xiao Xu, Junhu Yao, Xinjian Lei
Antioxidants.2024; 13(3): 352. CrossRef - Mechanisms and regulations of ferroptosis
Xu-Dong Zhang, Zhong-Yuan Liu, Mao-Sen Wang, Yu-Xiang Guo, Xiang-Kun Wang, Kai Luo, Shuai Huang, Ren-Feng Li
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting epigenetic and posttranslational modifications regulating ferroptosis for the treatment of diseases
Yumin Wang, Jing Hu, Shuang Wu, Joshua S. Fleishman, Yulin Li, Yinshi Xu, Wailong Zou, Jinhua Wang, Yukuan Feng, Jichao Chen, Hongquan Wang
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Fatty Acid Binding Protein-4 Silencing Inhibits Ferroptosis to Alleviate Lipopolysaccharide-induced Injury of Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells by Blocking Janus Kinase 2/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Signaling

Editorial
- Adrenal gland
- Glucocorticoids as a Double-Edged Sword in the Treatment of COVID-19: Mortality and Severity of COVID-19 in Patients Receiving Long-Term Glucocorticoid Therapy
- Eun-Hee Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):223-225. Published online April 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.201
- 1,152 View
- 67 Download

Review Articles
- Miscellaneous
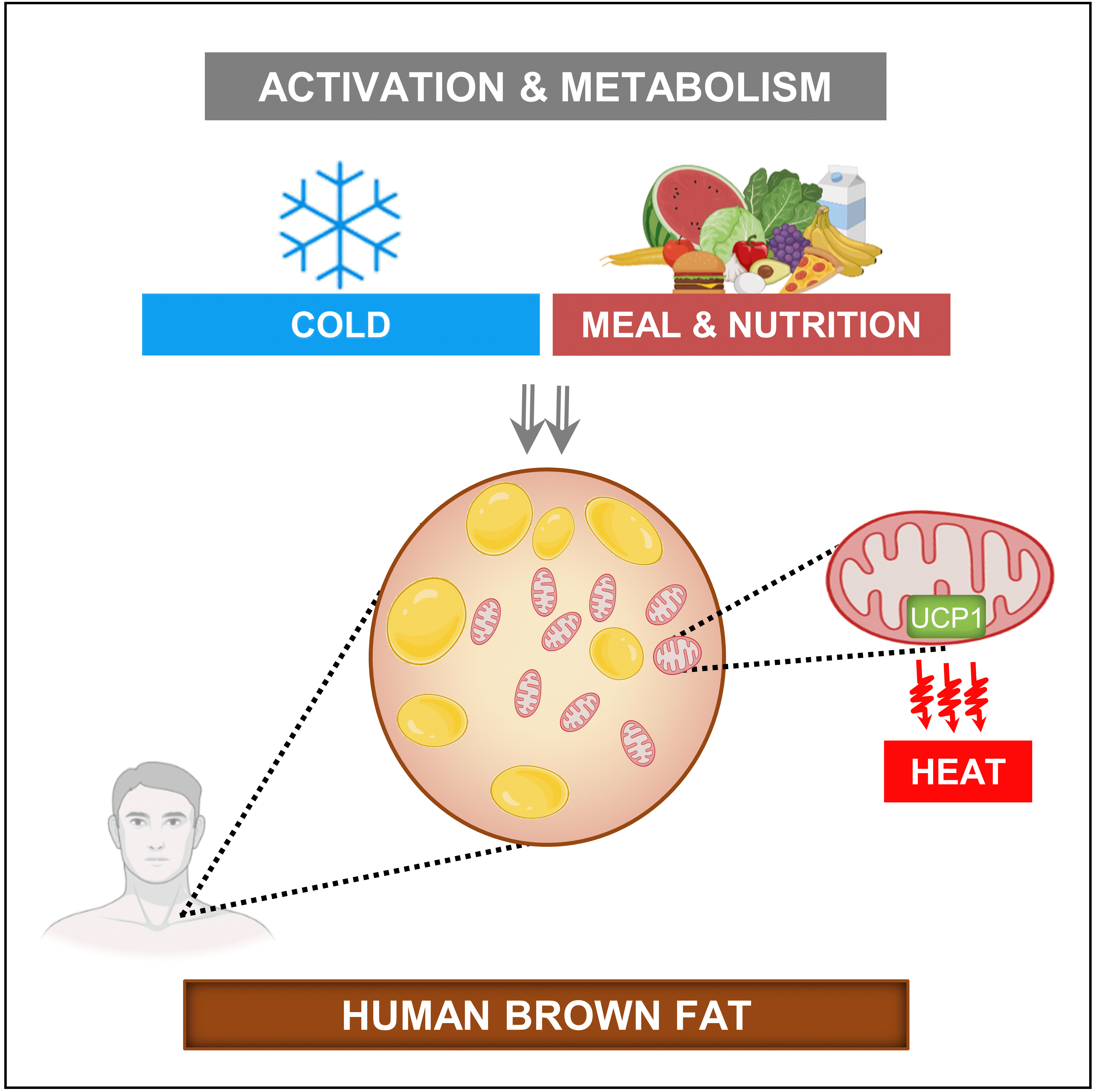
- Brown Adipose Tissue: Activation and Metabolism in Humans
- Imane Hachemi, Mueez U-Din
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):214-222. Published online March 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1659
- 5,828 View
- 434 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Brown adipose tissue (BAT) is a thermogenic organ contributing to non-shivering thermogenesis. BAT becomes active under cold stress via sympathetic nervous system activation. However, recent evidence has suggested that BAT may also be active at thermoneutrality and in a postprandial state. BAT has superior energy dissipation capacity compared to white adipose tissue (WAT) and muscles. Thus, it has been proposed that the recruitment and activation of additional BAT may increase the overall energy-expending capacity in humans, potentially improving current whole-body weight management strategies. Nutrition plays a central role in obesity and weight management. Thus, this review discusses human studies describing BAT hyper-metabolism after dietary interventions. Nutritional agents that can potentially recruit brown adipocytes via the process of BAT-WAT transdifferentiation are also discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Spermidine activates adipose tissue thermogenesis through autophagy and fibroblast growth factor 21
Yinhua Ni, Liujie Zheng, Liqian Zhang, Jiamin Li, Yuxiang Pan, Haimei Du, Zhaorong Wang, Zhengwei Fu
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2024; 125: 109569. CrossRef - A natural sustained-intestinal release formulation of red chili pepper extracted capsaicinoids (Capsifen®) safely modulates energy balance and endurance performance: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
N. Roopashree, Das S. Syam, I. M. Krishnakumar, K. N. Mala, Bradley S. Fleenor, Jestin Thomas
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - MRI Methods to Visualize and Quantify Adipose Tissue in Health and Disease
Katerina Nikiforaki, Kostas Marias
Biomedicines.2023; 11(12): 3179. CrossRef
- Spermidine activates adipose tissue thermogenesis through autophagy and fibroblast growth factor 21

- Calcium & bone metabolism
- New Insights into Calorie Restriction Induced Bone Loss
- Linyi Liu, Clifford J. Rosen
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):203-213. Published online April 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1673

- 3,215 View
- 174 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Caloric restriction (CR) is now a popular lifestyle choice due to its ability in experimental animals to improve lifespan, reduce body weight, and lessen oxidative stress. However, more and more emerging evidence suggests this treatment requires careful consideration because of its detrimental effects on the skeletal system. Experimental and clinical studies show that CR can suppress bone growth and raise the risk of fracture, but the specific mechanisms are poorly understood. Reduced mechanical loading has long been thought to be the primary cause of weight loss-induced bone loss from calorie restriction. Despite fat loss in peripheral depots with calorie restriction, bone marrow adipose tissue (BMAT) increases, and this may play a significant role in this pathological process. Here, we update recent advances in our understanding of the effects of CR on the skeleton, the possible pathogenic role of BMAT in CR-induced bone loss, and some strategies to mitigate any potential side effects on the skeletal system.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Obesity, diabetes and risk of bone fragility: How BMAT behavior is affected by metabolic disturbances and its influence on bone health
Gregório Corrêa Guimarães, João Bosco Costa Coelho, João Gabriel Oliveira Silva, Ana Carolina Chalfun de Sant’Ana, Cássia Alves Carrilho de Sá, Júlia Marques Moreno, Lívia Marçal Reis, Camila Souza de Oliveira Guimarães
Osteoporosis International.2024; 35(4): 575. CrossRef - Bone Marrow Adipose Tissue Is Not Required for Reconstitution of the Immune System Following Irradiation in Male Mice
Jessica A. Keune, Carmen P. Wong, Adam J. Branscum, Scott A. Menn, Urszula T. Iwaniec, Russell T. Turner
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(4): 1980. CrossRef - Dietary restriction plus exercise change gene expression of Cxcl12 abundant reticular cells in female mice
Aoi Ikedo, Yuuki Imai
Journal of Bone and Mineral Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Obesity, diabetes and risk of bone fragility: How BMAT behavior is affected by metabolic disturbances and its influence on bone health

- Thyroid
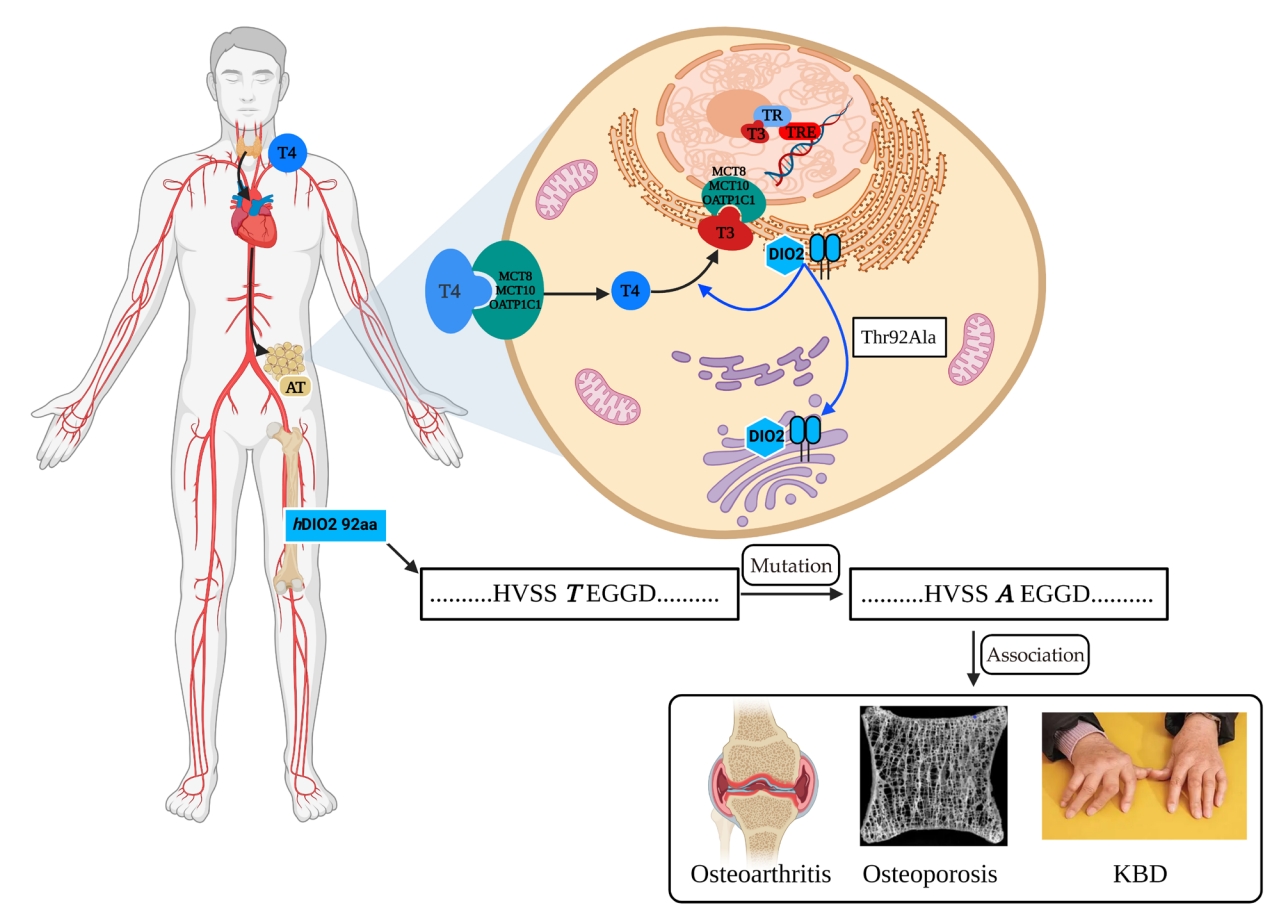
- The Physiological Functions and Polymorphisms of Type II Deiodinase
- Yan Deng, Yi Han, Sheng Gao, Wei Dong, Yang Yu
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):190-202. Published online April 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1599
- 4,221 View
- 172 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Type II deiodinase (DIO2) is thought to provide triiodothyronine (T3) to the nucleus to meet intracellular needs by deiodinating the prohormone thyroxine. DIO2 is expressed widely in many tissues and plays an important role in a variety of physiological processes, such as controlling T3 content in developing tissues (e.g., bone, muscles, and skin) and the adult brain, and regulating adaptive thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue (BAT). However, the identification and cloning of DIO2 have been challenging. In recent years, several clinical investigations have focused on the Thr92Ala polymorphism, which is closely correlated with clinical syndromes such as type 2 diabetes, obesity, hypertension, and osteoarthritis. Thr92Ala-DIO2 was also found to be related to bone and neurodegenerative diseases and tumors. However, relatively few reviews have synthesized research on individual deiodinases, especially DIO2, in the past 5 years. This review summarizes current knowledge regarding the physiological functions of DIO2 in thyroid hormone signaling and adaptive thermogenesis in BAT and the brain, as well as the associations between Thr92Ala-DIO2 and bone and neurodegenerative diseases and tumors. This discussion is expected to provide insights into the physiological functions of DIO2 and the clinical syndromes associated with Thr92Ala-DIO2.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Noncatalytic Reductive Deiodination of Thyroid Hormones. Electrochemistry and Quantum Chemical Calculations
Piotr P. Romańczyk, Stefan S. Kurek
ChemElectroChem.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Noncatalytic Reductive Deiodination of Thyroid Hormones. Electrochemistry and Quantum Chemical Calculations

- Thyroid
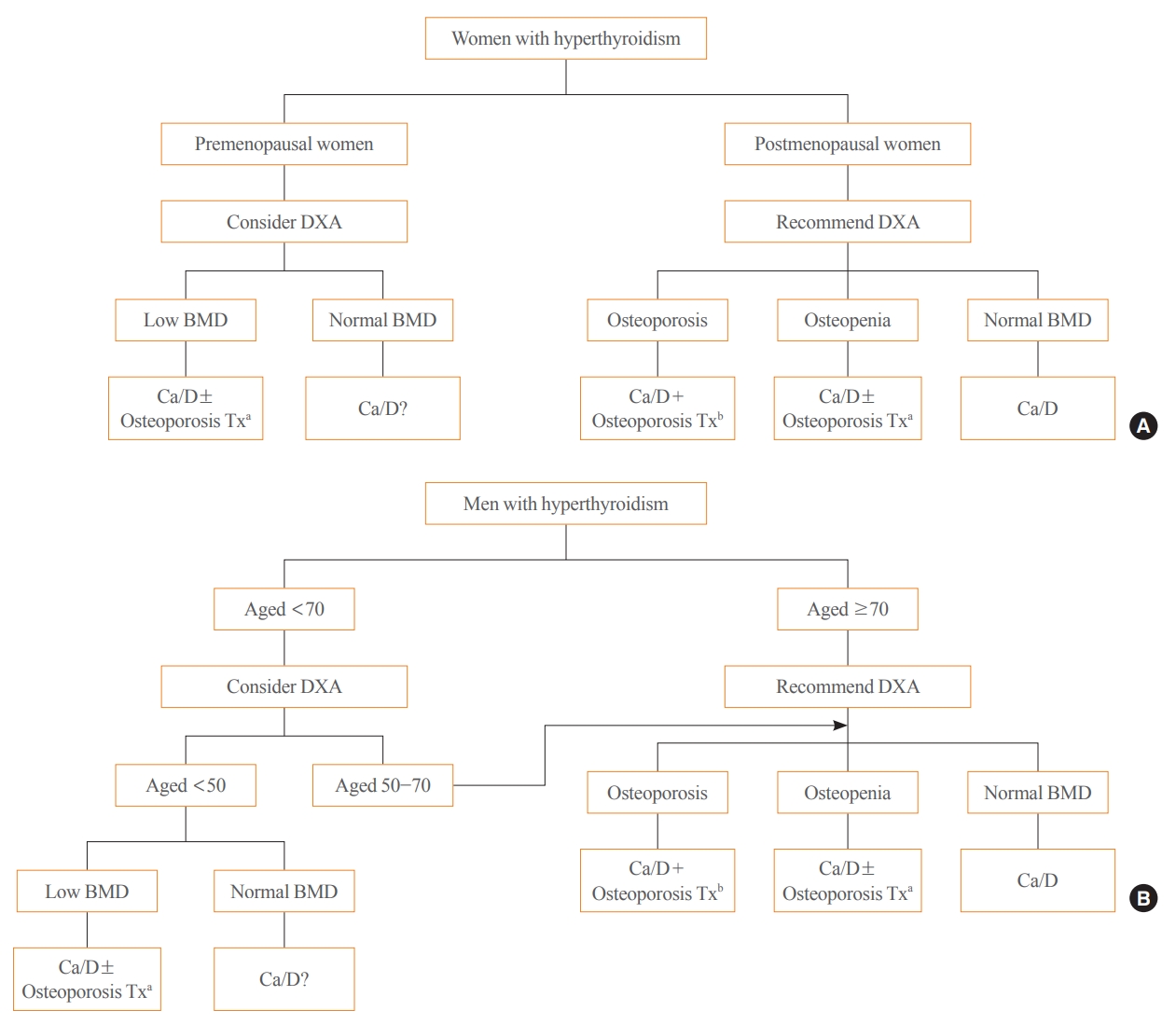
- Evaluation and Management of Bone Health in Patients with Thyroid Diseases: A Position Statement of the Korean Thyroid Association
- A Ram Hong, Ho-Cheol Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):175-189. Published online April 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1701
- 3,713 View
- 243 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Thyroid hormones play an important physiological role in maintaining adult bone structure and strength. Consequently, thyroid dysfunction is related to skeletal outcomes. Overt hyperthyroidism is an established cause of high bone turnover with accelerated bone loss, leading to osteoporosis and increased fracture risk. Hyperthyroidism induced by thyroid-stimulating hormone-suppressive therapy in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer is a cause of secondary osteoporosis. In contrast, there is a lack of evidence on the negative impact of hypothyroidism on bone health. Considering the clinical updates on the importance of bone health in thyroid dysfunction, the Task Force from the Clinical Practice Guidelines Development Committee of the Korean Thyroid Association recently developed a position statement on the evaluation and management of bone health of patients with thyroid diseases, particularly focused on endogenous hyperthyroidism and thyroid-stimulating hormone-suppressive therapy-associated hyperthyroidism in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Herein, we review the Korean Thyroid Association’s position statement on the evaluation and management of bone health associated with thyroid diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnosis and therapeutic approach to bone health in patients with hypopituitarism
Justyna Kuliczkowska-Płaksej, Aleksandra Zdrojowy-Wełna, Aleksandra Jawiarczyk-Przybyłowska, Łukasz Gojny, Marek Bolanowski
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Review on the protective activity of osthole against the pathogenesis of osteoporosis
Jincai Chen, Xiaofei Liao, Juwen Gan
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Diagnosis and therapeutic approach to bone health in patients with hypopituitarism

Corrigendum
- Miscellaneous
- Corrigendum: Correction of Acknowledgments. Metformin and Cervical Cancer Risk in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Study in Korea
- Hyun Min Kim, Min Jin Kang, Sun Ok Song
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):174. Published online January 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.101
- Corrects: Endocrinol Metab 2022;37(6):929
- 1,086 View
- 100 Download

Original Articles
- Calcium & bone metabolism
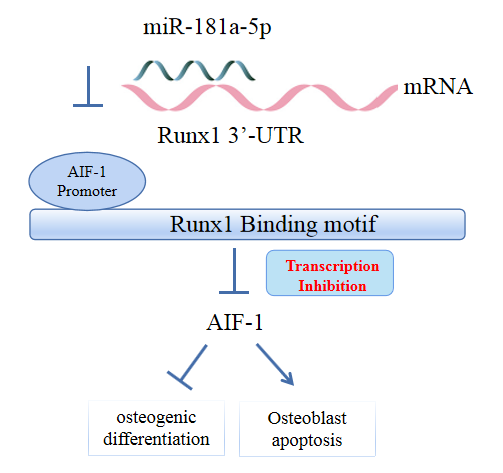
- MicroRNA-181a-5p Curbs Osteogenic Differentiation and Bone Formation Partially Through Impairing Runx1-Dependent Inhibition of AIF-1 Transcription
- Jingwei Liu, Xueying Chang, Daming Dong
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):156-173. Published online January 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1516
- 1,540 View
- 99 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Evidence has revealed the involvement of microRNAs (miRNAs) in modulating osteogenic differentiation, implying the promise of miRNA-based therapies for treating osteoporosis. This study investigated whether miR-181a-5p influences osteogenic differentiation and bone formation and aimed to establish the mechanisms in depth.
Methods
Clinical serum samples were obtained from osteoporosis patients, and MC3T3-E1 cells were treated with osteogenic induction medium (OIM) to induce osteogenic differentiation. miR-181a-5p-, Runt-related transcription factor 1 (Runx1)-, and/or allograft inflammatory factor-1 (AIF-1)-associated oligonucleotides or vectors were transfected into MC3T3-E1 cells to explore their function in relation to the number of calcified nodules, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining and activity, expression levels of osteogenesis-related proteins, and apoptosis. Luciferase activity, RNA immunoprecipitation, and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays were employed to validate the binding relationship between miR-181a-5p and Runx1, and the transcriptional regulatory relationship between Runx1 and AIF-1. Ovariectomy (OVX)-induced mice were injected with a miR-181a-5p antagonist for in vivo verification.
Results
miR-181a-5p was highly expressed in the serum of osteoporosis patients. OIM treatment decreased miR-181a-5p and AIF-1 expression, but promoted Runx1 expression in MC3T-E1 cells. Meanwhile, upregulated miR-181a-5p suppressed OIM-induced increases in calcified nodules, ALP content, and osteogenesis-related protein expression. Mechanically, miR-181a-5p targeted Runx1, which acted as a transcription factor to negatively modulate AIF-1 expression. Downregulated Runx1 suppressed the miR-181a-5p inhibitor-mediated promotion of osteogenic differentiation, and downregulated AIF-1 reversed the miR-181a-5p mimic-induced inhibition of osteogenic differentiation. Tail vein injection of a miR-181a-5p antagonist induced bone formation in OVX-induced osteoporotic mice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, miR-181a-5p affects osteogenic differentiation and bone formation partially via the modulation of the Runx1/AIF-1 axis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Scopolamine regulates the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells through lactylation modification of RUNX2 protein
Ying Wu, Pan Gong
Pharmacology Research & Perspectives.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Scopolamine regulates the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells through lactylation modification of RUNX2 protein

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
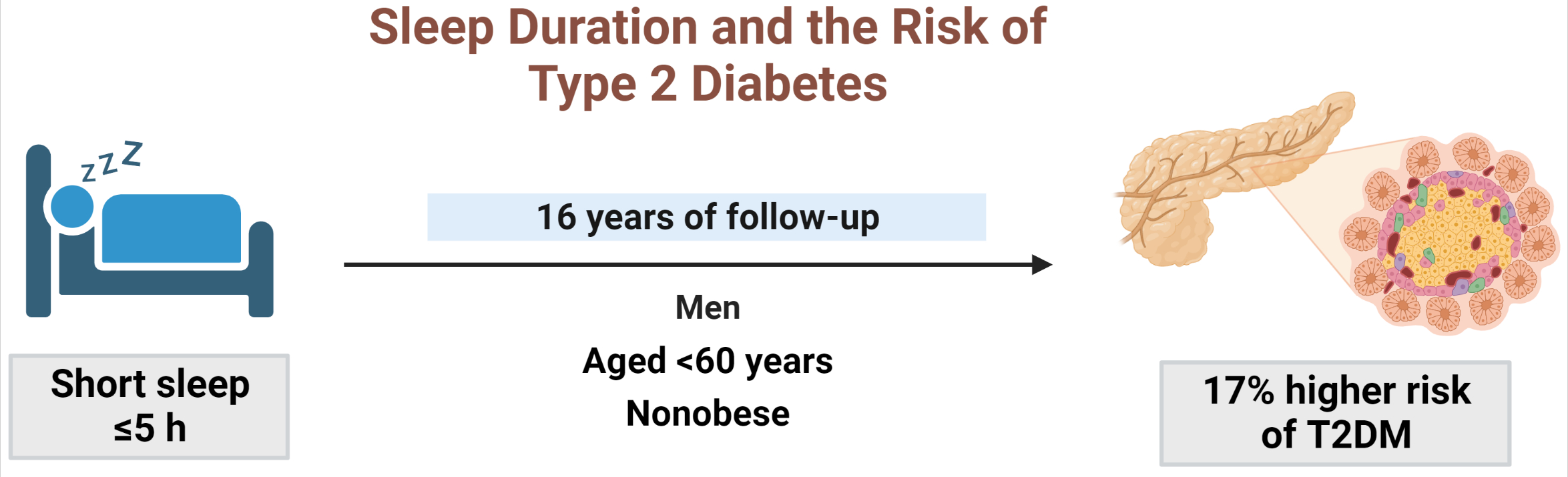
- Sleep Duration and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: A Community-Based Cohort Study with a 16-Year Follow-up
- Da Young Lee, Inha Jung, So Young Park, Ji Hee Yu, Ji A Seo, Kyeong Jin Kim, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Seung Ku Lee, Chol Shin, Nan Hee Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):146-155. Published online February 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1582
- 2,533 View
- 156 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We aimed to investigate the moderating effects of obesity, age, and sex on the association between sleep duration and the development of diabetes in Asians.
Methods
We analyzed data from a cohort of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study conducted from 2001 to 2020. After excluding shift workers and those with diabetes at baseline, 7,407 participants were stratified into three groups according to sleep duration: ≤5 hours/night, >5 to 7 hours/night (reference), and >7 hours/night. The Cox proportional hazards analyses were used to calculate the hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for incident type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Subgroup analyses were performed according to obesity, age, and sex.
Results
During 16 years of follow-up, 2,024 cases of T2DM were identified. Individuals who slept ≤5 h/night had a higher risk of incident diabetes than the reference group (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.02 to 1.33). The subgroup analysis observed a valid interaction with sleep duration only for obesity. A higher risk of T2DM was observed in the ≤5 hours/night group in non-obese individuals, men, and those aged <60 years, and in the >7 hours/night group in obese individuals (HRs were 1.34 [95% CI, 1.11 to 1.61], 1.22 [95% CI, 1 to 1.49], and 1.18 [95% CI, 1.01 to 1.39], respectively).
Conclusion
This study confirmed the effect of sleep deprivation on the risk of T2DM throughout the 16-year follow-up period. This impact was confined to non-obese or young individuals and men. We observed a significant interaction between sleep duration and obesity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Attention to Innate Circadian Rhythm and the Impact of Its Disruption on Diabetes
Da Young Lee, Inha Jung, So Young Park, Ji Hee Yu, Ji A Seo, Kyeong Jin Kim, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 37. CrossRef - Role of Sleep and Sleep Disorders in Cardiometabolic Risk: a Review and Update
Shaden O. Qasrawi, Ahmed S. BaHammam
Current Sleep Medicine Reports.2024; 10(1): 34. CrossRef - Evaluating reliability in wearable devices for sleep staging
Vera Birrer, Mohamed Elgendi, Olivier Lambercy, Carlo Menon
npj Digital Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - All That Glitters Is Not Gold: The Same Sleep Time, but Different Diabetogenic Outcomes
Bohye Kim, Obin Kwon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 78. CrossRef - The Link Between Sleeping and Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review
Ali Darraj
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Attention to Innate Circadian Rhythm and the Impact of Its Disruption on Diabetes

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Impact of Post-Transplant Diabetes Mellitus on Survival and Cardiovascular Events in Kidney Transplant Recipients
- Ja Young Jeon, Shin Han-Bit, Bum Hee Park, Nami Lee, Hae Jin Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Kwan-Woo Lee, Seung Jin Han
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):139-145. Published online February 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1594

- 1,613 View
- 118 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Post-transplant diabetes mellitus (PTDM) is a risk factor for poor outcomes after kidney transplantation (KT). However, the outcomes of KT have improved recently. Therefore, we investigated whether PTDM is still a risk factor for mortality, major atherosclerotic cardiovascular events (MACEs), and graft failure in KT recipients.
Methods
We studied a retrospective cohort of KT recipients (between 1994 and 2017) at a single tertiary center, and compared the rates of death, MACEs, overall graft failure, and death-censored graft failure after KT between patients with and without PTDM using Kaplan-Meier analysis and a Cox proportional hazard model.
Results
Of 571 KT recipients, 153 (26.8%) were diagnosed with PTDM. The mean follow-up duration was 9.6 years. In the Kaplan- Meier analysis, the PTDM group did not have a significantly increased risk of death or four-point MACE compared with the non-diabetes mellitus group (log-rank test, P=0.957 and P=0.079, respectively). Multivariate Cox proportional hazard models showed that PTDM did not have a negative impact on death or four-point MACE (P=0.137 and P=0.181, respectively). In addition, PTDM was not significantly associated with overall or death-censored graft failure. However, patients with a long duration of PTDM had a higher incidence of four-point MACE.
Conclusion
Patient survival and MACEs were comparable between groups with and without PTDM. However, PTDM patients with long duration diabetes were at higher risk of cardiovascular disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of post-transplant diabetes mellitus on cardiovascular events and mortality: a single‐center retrospective cohort study
Uğur Ünlütürk, Tolga Yıldırım, Merve Savaş, Seda Hanife Oğuz, Büşra Fırlatan, Deniz Yüce, Nesrin Damla Karakaplan, Cemile Selimova, Rahmi Yılmaz, Yunus Erdem, Miyase Bayraktar
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of new-onset diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Qiufeng Du, Tao Li, Xiaodong Yi, Shuang Song, Jing Kang, Yunlan Jiang
Acta Diabetologica.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Safety and efficacy of semaglutide in post kidney transplant patients with type 2 diabetes or Post-Transplant diabetes
Moeber Mohammed Mahzari, Omar Buraykan Alluhayyan, Mahdi Hamad Almutairi, Mohammed Abdullah Bayounis, Yazeed Hasan Alrayani, Amir A. Omair, Awad Saad Alshahrani
Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology.2024; 36: 100343. CrossRef
- Effect of post-transplant diabetes mellitus on cardiovascular events and mortality: a single‐center retrospective cohort study

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Predicting the Risk of Insulin-Requiring Gestational Diabetes before Pregnancy: A Model Generated from a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
- Seung-Hwan Lee, Jin Yu, Kyungdo Han, Seung Woo Lee, Sang Youn You, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(1):129-138. Published online January 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1609

- 2,084 View
- 152 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The severity of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes. We aimed to generate a risk model for predicting insulin-requiring GDM before pregnancy in Korean women.
Methods
A total of 417,210 women who received a health examination within 52 weeks before pregnancy and delivered between 2011 and 2015 were recruited from the Korean National Health Insurance database. The risk prediction model was created using a sample of 70% of the participants, while the remaining 30% were used for internal validation. Risk scores were assigned based on the hazard ratios for each risk factor in the multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression model. Six risk variables were selected, and a risk nomogram was created to estimate the risk of insulin-requiring GDM.
Results
A total of 2,891 (0.69%) women developed insulin-requiring GDM. Age, body mass index (BMI), current smoking, fasting blood glucose (FBG), total cholesterol, and γ-glutamyl transferase were significant risk factors for insulin-requiring GDM and were incorporated into the risk model. Among the variables, old age, high BMI, and high FBG level were the main contributors to an increased risk of insulin-requiring GDM. The concordance index of the risk model for predicting insulin-requiring GDM was 0.783 (95% confidence interval, 0.766 to 0.799). The validation cohort’s incidence rates for insulin-requiring GDM were consistent with the risk model’s predictions.
Conclusion
A novel risk engine was generated to predict insulin-requiring GDM among Korean women. This model may provide helpful information for identifying high-risk women and enhancing prepregnancy care. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Establishment and validation of a nomogram to predict the neck contracture after skin grafting in burn patients: A multicentre cohort study
Rui Li, Yangyang Zheng, Xijuan Fan, Zilong Cao, Qiang Yue, Jincai Fan, Cheng Gan, Hu Jiao, Liqiang Liu
International Wound Journal.2023; 20(9): 3648. CrossRef - Predicting the Need for Insulin Treatment: A Risk-Based Approach to the Management of Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Anna S. Koefoed, H. David McIntyre, Kristen S. Gibbons, Charlotte W. Poulsen, Jens Fuglsang, Per G. Ovesen
Reproductive Medicine.2023; 4(3): 133. CrossRef - Prepregnancy Glucose Levels Within Normal Range and Its Impact on Obstetric Complications in Subsequent Pregnancy: A Population Cohort Study
Ho Yeon Kim, Ki Hoon Ahn, Geum Joon Cho, Soon-Cheol Hong, Min-Jeong Oh, Hai-Joong Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 525. CrossRef - The CHANGED Score—A New Tool for the Prediction of Insulin Dependency in Gestational Diabetes
Paul Rostin, Selina Balke, Dorota Sroka, Laura Fangmann, Petra Weid, Wolfgang Henrich, Josefine Theresia Königbauer
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(22): 7169. CrossRef
- Establishment and validation of a nomogram to predict the neck contracture after skin grafting in burn patients: A multicentre cohort study


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



