Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Metformin and Cervical Cancer Risk in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Study in Korea
- Hyun Min Kim, Min Jin Kang, Sun Ok Song
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):929-937. Published online December 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1613
- Correction in: Endocrinol Metab 2023;38(1):174
- 2,432 View
- 217 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Cervical cancer is a prevalent malignancy that is a major health problem for women worldwide. The cancer-preventive properties of metformin are well-known, but insufficient data have been reported regarding its relationship to cervical cancer. Therefore, in a nationwide population-based study, we investigated the association between metformin use and cervical cancer incidence in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes.
Methods
This retrospective cohort study used the Korean National Health Insurance claims database. Individuals newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes between January 2005 and December 2009 were included. The occurrence of cervical cancer was explored by matching for age, economic status, region of residence, and use of anti-diabetic medication.
Results
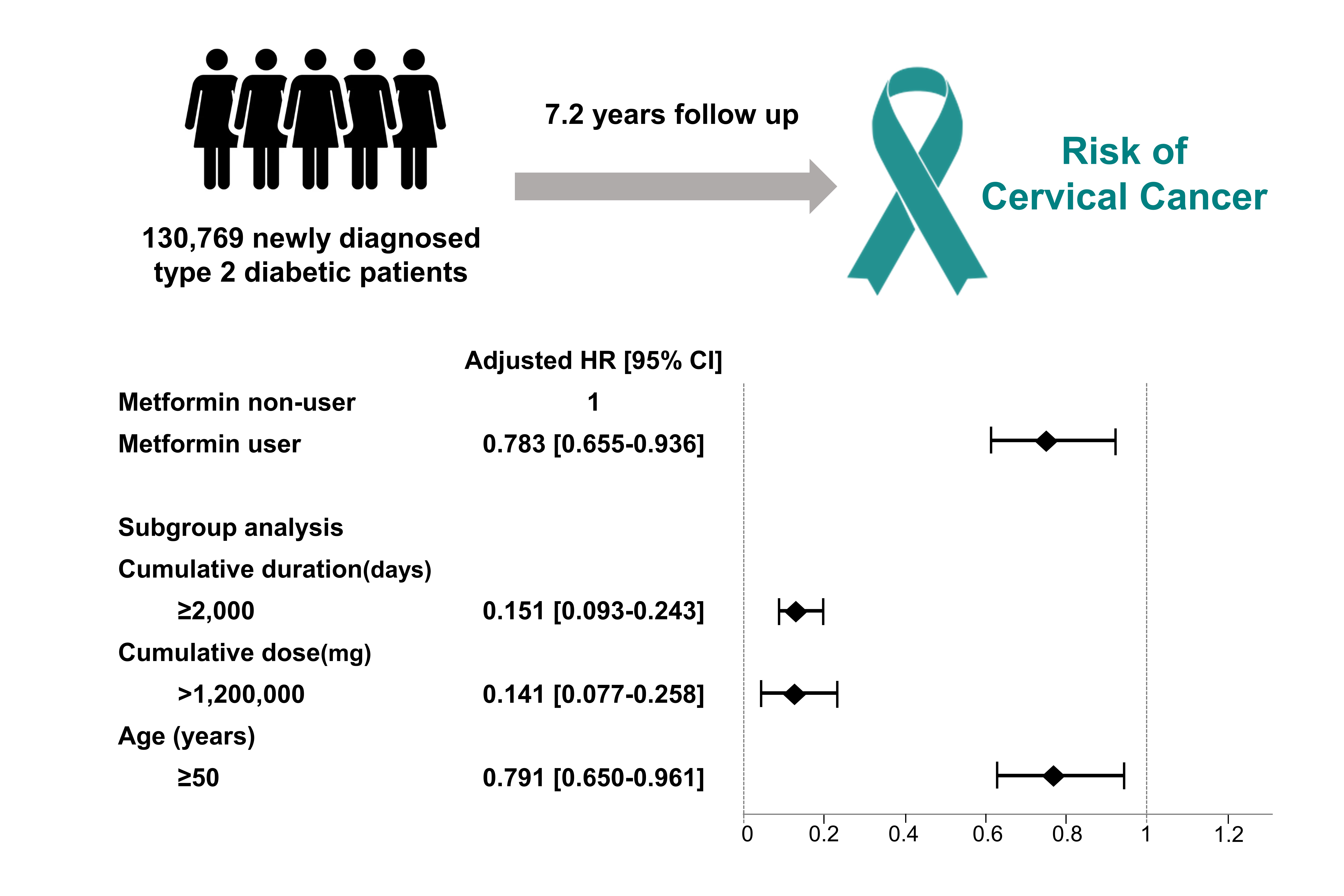
In total, 66,013 metformin users and 64,756 non-users were analyzed. Cervical cancer occurred in 219 metformin users (0.33%) and 274 metformin non-users (0.42%) (hazard ratio [HR], 0.783; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.655 to 0.036; P=0.007). Moreover, cervical cancer risk was considerably reduced in those treated with a high dose (>1,200,000 mg) or for an extended period (≥2,000 days) compared to non-users (HR, 0.151; 95% CI, 0.093 to 0.243; P<0.001; and HR, 0.141; 95% CI, 0.077 to 0.258; P<0.001). The incidence was also significantly lower in metformin users among those over 50 years old (HR, 0.791; 95% CI, 0.650 to 0.961; P<0.001).
Conclusion
Metformin use in patients with newly diagnosed diabetes was associated with a lower risk of cervical cancer in Korea. Furthermore, a significant association was found between the use of metformin and cervical cancer in a dose- and duration-dependent manner and among those over 50 years old. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Repurposing of Chronically Used Drugs in Cancer Therapy: A Chance to Grasp
Mohamad Ali Hijazi, André Gessner, Nahed El-Najjar
Cancers.2023; 15(12): 3199. CrossRef - Network-based drug repurposing for HPV-associated cervical cancer
Faheem Ahmed, Young Jin Yang, Anupama Samantasinghar, Young Woo Kim, Jeong Beom Ko, Kyung Hyun Choi
Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal.2023; 21: 5186. CrossRef - The Use of Metformin and Postoperative Insulin Pump Were Predictive Factors for Outcomes of Diabetic Colorectal Cancer Patients after Surgery
Xu-Rui Liu, Fei Liu, Zi-Wei Li, Quan Lv, Xin-Peng Shu, Lian-Shuo Li, Yue Tong, Wei Zhang, Dong Peng
Nutrition and Cancer.2023; 75(10): 1926. CrossRef
- Repurposing of Chronically Used Drugs in Cancer Therapy: A Chance to Grasp


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



