Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Clinicopathological Features and Molecular Signatures of Lateral Neck Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
- Jinsun Lim, Han Sai Lee, Jin-Hyung Heo, Young Shin Song
- Received November 19, 2023 Accepted January 25, 2024 Published online April 4, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1885 [Epub ahead of print]
- 234 View
- 12 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The predictive factors for lateral neck lymph node metastasis (LLNM) in papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC) remain undetermined. This study investigated the clinicopathological characteristics, transcriptomes, and tumor microenvironment in PTMC according to the LLNM status. We aimed to identify the biomarkers associated with LLNM development.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of patients with PTMC from two independent institutions between 2018 and 2022 (n=597 and n=467). We compared clinicopathological features between patients without lymph node metastasis (N0) and those with LLNM (N1b). Additionally, laser capture microdissection and RNA sequencing were performed on primary tumors from both groups, including metastatic lymph nodes from the N1b group (n=30; 20 primary tumors and 10 paired LLNMs). We corroborated the findings using RNA sequencing data from 16 BRAF-like PTMCs from The Cancer Genome Atlas. Transcriptomic analyses were validated by immunohistochemical staining.
Results
Clinicopathological characteristics, such as male sex, multifocality, extrathyroidal extension, lymphatic invasion, and central node metastasis showed associations with LLNM in PTMCs. Transcriptomic profiles between the N0 and N1b PTMC groups were similar. However, tumor microenvironment deconvolution from RNA sequencing and immunohistochemistry revealed an increased abundance of tumor-associated macrophages, particularly M2 macrophages, in the N1b group.
Conclusion
Patients with PTMC who have a male sex, multifocality, extrathyroidal extension, lymphatic invasion, and central node metastasis exhibited an elevated risk for LLNM. Furthermore, infiltration of M2 macrophages in the tumor microenvironment potentially supports tumor progression and LLNM in PTMCs.

Review Article
- Thyroid
- Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Thyroid Cancers: A Review of Current Practice Guidelines
- Min Joo Kim, Jae Hoon Moon, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Kyong Yeun Jung, Ji Ye Lee, Ji-hoon Kim, Kyungsik Kim, Sue K. Park, Young Joo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):47-60. Published online February 15, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2024.1937

- 1,633 View
- 151 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The indolent nature and favorable outcomes associated with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma have prompted numerous prospective studies on active surveillance (AS) and its adoption as an alternative to immediate surgery in managing low-risk thyroid cancer. This article reviews the current status of AS, as outlined in various international practice guidelines. AS is typically recommended for tumors that measure 1 cm or less in diameter and do not exhibit aggressive subtypes on cytology, extrathyroidal extension, lymph node metastasis, or distant metastasis. To determine the most appropriate candidates for AS, factors such as tumor size, location, multiplicity, and ultrasound findings are considered, along with patient characteristics like medical condition, age, and family history. Moreover, shared decision-making, which includes patient-reported outcomes such as quality of life and cost-effectiveness, is essential. During AS, patients undergo regular ultrasound examinations to monitor for signs of disease progression, including tumor growth, extrathyroidal extension, or lymph node metastasis. In conclusion, while AS is a feasible and reliable approach for managing lowrisk thyroid cancer, it requires careful patient selection, effective communication for shared decision-making, standardized follow-up protocols, and a clear definition of disease progression.

Original Articles
- Thyroid
- Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma as an Acceptable Management Option with Additional Benefits: A Comprehensive Systematic Review
- Jee Hee Yoon, Wonsuk Choi, Ji Yong Park, A Ram Hong, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):152-163. Published online January 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1794
- 1,052 View
- 38 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
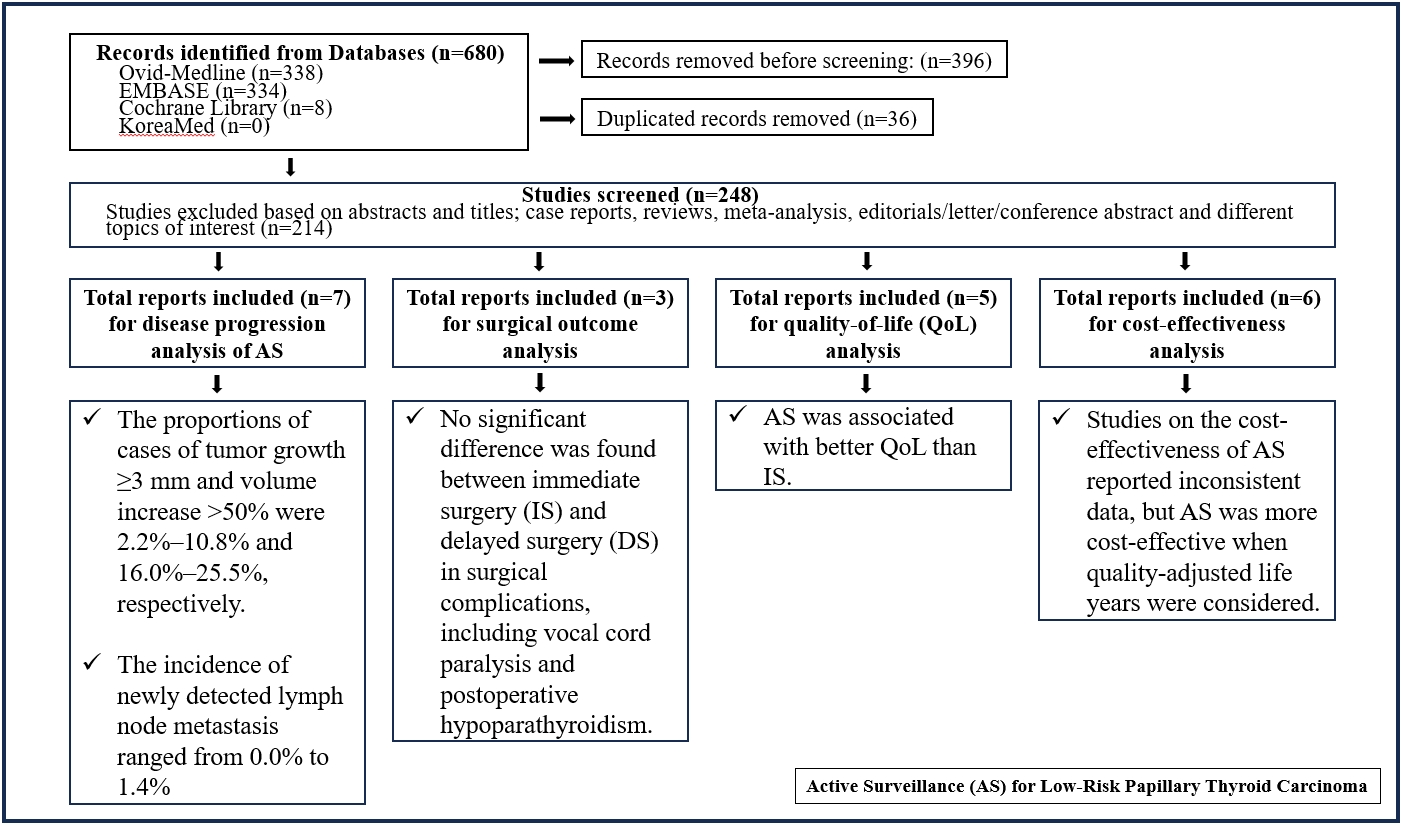
Active surveillance (AS) has been introduced as a management strategy for low-risk papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) due to its typically indolent nature. Despite this, the widespread adoption of AS has encountered several challenges. The aim of this systematic review was to evaluate the safety of AS related to disease progression and its benefits compared with immediate surgery (IS).
Methods
Studies related to AS in patients with low-risk PTC were searched through the Ovid MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane Library, and KoreaMed databases. Studies on disease progression, surgical complication, quality of life (QoL), and cost-effectiveness were separately analyzed and narratively synthesized.
Results
In the evaluation of disease progression, the proportions of cases with tumor growth ≥3 mm and a volume increase >50% were 2.2%–10.8% and 16.0%–25.5%, respectively. Newly detected lymph node metastasis was identified in 0.0%–1.4% of patients. No significant difference was found between IS and delayed surgery in surgical complications, including vocal cord paralysis and postoperative hypoparathyroidism. AS was associated with better QoL than IS. Studies on the cost-effectiveness of AS reported inconsistent data, but AS was more cost-effective when quality-adjusted life years were considered.
Conclusion
AS is an acceptable management option for patients with low-risk PTC based on the low rate of disease progression and the absence of an increased mortality risk. AS has additional benefits, including improved QoL and greater QoL-based cost-effectiveness. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- It Is Time to Understand the Additional Benefits of Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Kyeong Jin Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 95. CrossRef
- It Is Time to Understand the Additional Benefits of Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma

- Thyroid
- Comparative Analysis of Driver Mutations and Transcriptomes in Papillary Thyroid Cancer by Region of Residence in South Korea
- Jandee Lee, Seonhyang Jeong, Hwa Young Lee, Sunmi Park, Meesson Jeong, Young Suk Jo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):720-729. Published online November 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1758

- 928 View
- 42 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Radiation exposure is a well-known risk factor for papillary thyroid cancer (PTC). South Korea has 24 nuclear reactors in operation; however, no molecular biological analysis has been performed on patients with PTC living near nuclear power plants.
Methods
We retrospectively included patients with PTC (n=512) divided into three groups according to their place of residence at the time of operation: inland areas (n=300), coastal areas far from nuclear power plants (n=134), and nuclear power plant areas (n=78). After propensity score matching (1:1:1) by age, sex, and surgical procedure, the frequency of representative driver mutations and gene expression profiles were compared (n=50 per group). Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), BRAF, thyroid differentiation, and radiation scores were calculated and compared.
Results
No significant difference was observed in clinicopathological characteristics, including radiation exposure history and the frequency of incidentally discovered thyroid cancer, among the three groups. BRAFV600E mutation was most frequently detected in the groups, with no difference among the three groups. Furthermore, gene expression profiles showed no statistically significant difference. EMT and BRAF scores were higher in our cohort than in cohorts from Chernobyl tissue bank and The Cancer Genome Atlas Thyroid Cancer; however, there was no difference according to the place of residence. Radiation scores were highest in the Chernobyl tissue bank but exhibited no difference according to the place of residence.
Conclusion
Differences in clinicopathological characteristics, frequency of representative driver mutations, and gene expression profiles were not observed according to patients’ region of residence in South Korea.

- Thyroid
- Different Molecular Phenotypes of Progression in BRAF- and RAS-Like Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Jinsun Lim, Han Sai Lee, Jiyun Park, Kyung-Soo Kim, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Wook Cho, Young Shin Song
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(4):445-454. Published online July 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1702
- 1,565 View
- 98 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
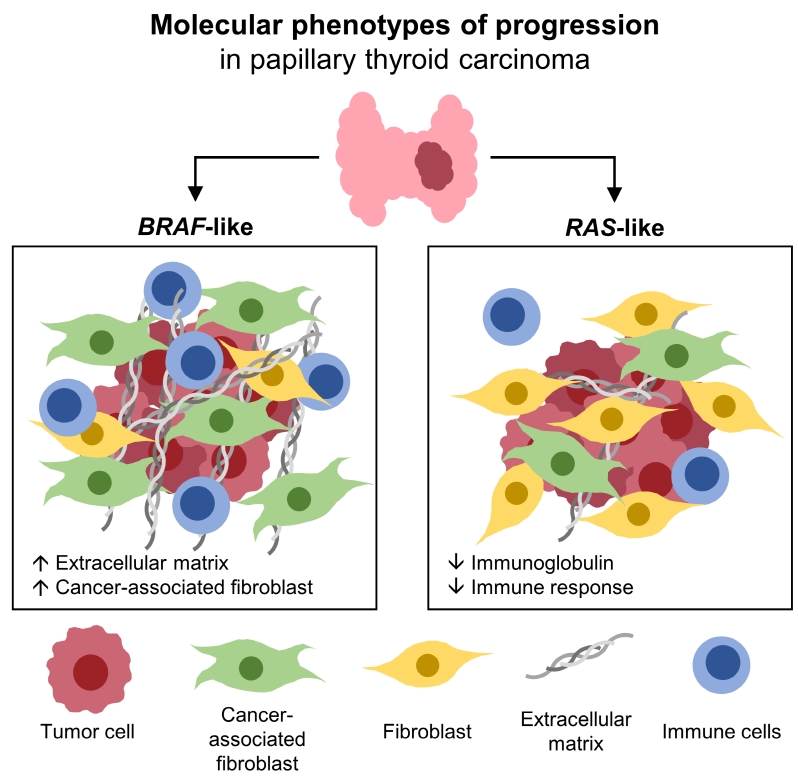
Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) can be classified into two distinct molecular subtypes, BRAF-like (BL) and RASlike (RL). However, the molecular characteristics of each subtype according to clinicopathological factors have not yet been determined. We aimed to investigate the gene signatures and tumor microenvironment according to clinicopathological factors, and to identify the mechanism of progression in BL-PTCs and RL-PTCs.
Methods
We analyzed RNA sequencing data and corresponding clinicopathological information of 503 patients with PTC from The Cancer Genome Atlas database. We performed differentially expressed gene (DEG), Gene Ontology, and molecular pathway enrichment analyses according to clinicopathological factors in each molecular subtype. EcoTyper and CIBERSORTx were used to deconvolve the tumor cell types and their surrounding microenvironment.
Results
Even for the same clinicopathological factors, overlapping DEGs between the two molecular subtypes were uncommon, indicating that BL-PTCs and RL-PTCs have different progression mechanisms. Genes related to the extracellular matrix were commonly upregulated in BL-PTCs with aggressive clinicopathological factors, such as old age (≥55 years), presence of extrathyroidal extension, lymph node metastasis, advanced tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage, and high metastasis-age-completeness of resection- invasion-size (MACIS) scores (≥6). Furthermore, in the deconvolution analysis of tumor microenvironment, cancer-associated fibroblasts were significantly enriched. In contrast, in RL-PTCs, downregulation of immune response and immunoglobulin-related genes was significantly associated with aggressive characteristics, even after adjusting for thyroiditis status.
Conclusion
The molecular phenotypes of cancer progression differed between BL-PTC and RL-PTC. In particular, extracellular matrix and cancer-associated fibroblasts, which constitute the tumor microenvironment, would play an important role in the progression of BL-PTC that accounts for the majority of advanced PTCs.

- Thyroid
- Diagnostic Performance of Thyroid Core Needle Biopsy Using the Revised Reporting System: Comparison with Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
- Kwangsoon Kim, Ja Seong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim, So Lyung Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):159-169. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1299
- 3,778 View
- 161 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
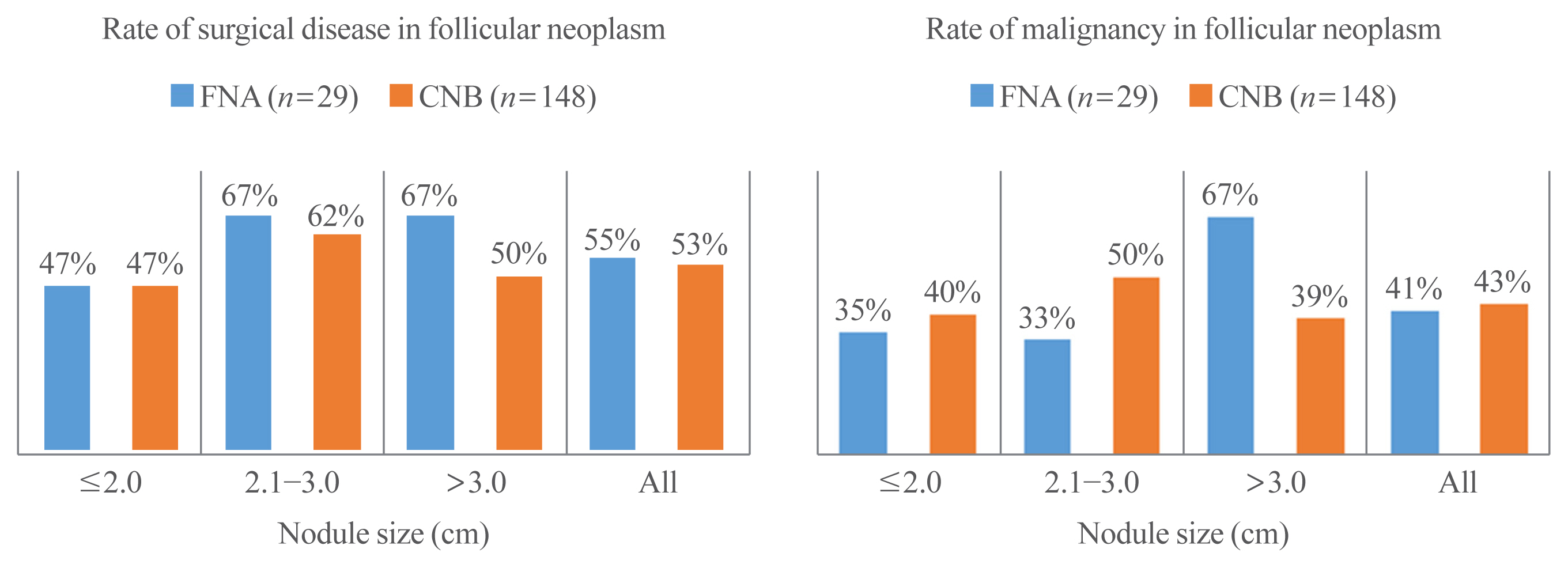
We aim to validate the diagnostic performance of thyroid core needle biopsy (CNB) for diagnosing malignancy in clinical settings to align with the changes made in recently updated thyroid CNB guidelines.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 1,381 thyroid CNB and 2,223 fine needle aspiration (FNA) samples. The FNA and CNB slides were interpreted according to the Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology and updated practice guidelines for thyroid CNB, respectively.
Results
Compared to FNA, CNB showed lower rates of inconclusive results: categories I (2.8% vs. 11.2%) and III (1.2% vs. 6.2%), and higher rates of categories II (60.9% vs. 50.4%) and IV (17.5% vs. 2.0%). The upper and lower bounds of the risk of malignancy (ROM) for category IV of CNB were 43.2% and 26.6%, respectively. The CNB subcategory IVb with nuclear atypia had a higher ROM than the subcategory without nuclear atypia (40%–62% vs. 23%–36%). In histologically confirmed cases, there was no significant difference in the diagnostic performance between CNB and FNA for malignancy. However, neoplastic diseases were more frequently detected by CNB than by FNA (88.8% vs. 77.6%, P=0.046). In category IV, there was no difference in unnecessary surgery rate between CNB and FNA (4.7% vs. 6.9%, P=0.6361).
Conclusion
Thyroid CNB decreased the rate of inconclusive results and showed a higher category IV diagnostic rate than FNA. The revised guidelines for thyroid CNB proved to be an excellent reporting system for assessing thyroid nodules. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Examining the impact of several factors including COVID‐19 on thyroid fine‐needle aspiration biopsy
Muzaffer Serdar Deniz, Merve Dindar
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2024; 52(1): 42. CrossRef - Consensus SFE-AFCE-SFMN 2022 sur la prise en charge des nodules thyroïdiens : intérêt et place de la cytologie thyroïdienne
Myriam Decaussin-Petrucci, Beatrix Cochand Priollet, Emannuelle Leteurtre, Frédérique Albarel, Françoise Borson-Chazot
Annales de Pathologie.2024; 44(1): 20. CrossRef - A comparative analysis of core needle biopsy and repeat fine needle aspiration in patients with inconclusive initial cytology of thyroid nodules
Xuejiao Su, Can Yue, Wanting Yang, Buyun Ma
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Preoperative Risk Stratification of Follicular-patterned Thyroid Lesions on Core Needle Biopsy by Histologic Subtyping and RAS Variant-specific Immunohistochemistry
Meejeong Kim, Sora Jeon, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(2): 247. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Patients with Thyroid Nodules
Young Joo Park, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Soo Hwan Kang, Bon Seok Koo, Sun Wook Kim, Dong Gyu Na, Seung-Kuk Baek, So Won Oh, Min Kyoung Lee, Sang-Woo Lee, Young Ah Lee, Yong Sang Lee, Ji Ye Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Leehi Joo, Yuh-Seog Jung, Chan Kwon Jung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2023; 16(1): 1. CrossRef - Reevaluating diagnostic categories and associated malignancy risks in thyroid core needle biopsy
Chan Kwon Jung
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(4): 208. CrossRef - A Matched-Pair Analysis of Nuclear Morphologic Features Between Core Needle Biopsy and Surgical Specimen in Thyroid Tumors Using a Deep Learning Model
Faridul Haq, Andrey Bychkov, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2022; 33(4): 472. CrossRef
- Examining the impact of several factors including COVID‐19 on thyroid fine‐needle aspiration biopsy

- Thyroid
- Clinicopathological Characteristics and Disease-Free Survival in Patients with Hürthle Cell Carcinoma: A Multicenter Cohort Study in South Korea
- Meihua Jin, Eun Sook Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Hee Kyung Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Mijin Kim, Won Gu Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1078-1085. Published online October 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1151

- 3,822 View
- 110 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Hürthle cell carcinoma (HCC), a type of thyroid carcinoma, is rare in South Korea, and few studies have investigated its prognosis.
Methods
This long-term multicenter retrospective cohort study evaluated the clinicopathological features and clinical outcomes in patients with HCC who underwent thyroid surgery between 1996 and 2009.
Results
The mean age of the 97 patients included in the study was 50.3 years, and 26.8% were male. The mean size of the primary tumor was 3.2±1.8 cm, and three (3.1%) patients had distant metastasis at initial diagnosis. Ultrasonographic findings were available for 73 patients; the number of nodules with low-, intermediate-, and high suspicion was 28 (38.4%), 27 (37.0%), and 18 (24.7%), respectively, based on the Korean-Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System. Preoperatively, follicular neoplasm (FN) or suspicion for FN accounted for 65.2% of the cases according to the Bethesda category, and 13% had malignancy or suspicious for malignancy. During a median follow-up of 8.5 years, eight (8.2%) patients had persistent/recurrent disease, and none died of HCC. Older age, gross extrathyroidal extension (ETE), and widely invasive types of tumors were significantly associated with distant metastasis (all P<0.01). Gross ETE (hazard ratio [HR], 27.7; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.2 to 346.4; P=0.01) and widely invasive classification (HR, 6.5; 95% CI, 1.1 to 39.4; P=0.04) were independent risk factors for poor disease-free survival (DFS).
Conclusion
The long-term prognosis of HCC is relatively favorable in South Korea from this study, although this is not a nation-wide data, and gross ETE and widely invasive cancer are significant prognostic factors for DFS. The diagnosis of HCC by ultrasonography and cytopathology remains challenging. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Molecular Alterations and Comprehensive Clinical Management of Oncocytic Thyroid Carcinoma
Lindsay A. Bischoff, Ian Ganly, Laura Fugazzola, Erin Buczek, William C. Faquin, Bryan R. Haugen, Bryan McIver, Caitlin P. McMullen, Kate Newbold, Daniel J. Rocke, Marika D. Russell, Mabel Ryder, Peter M. Sadow, Eric Sherman, Maisie Shindo, David C. Shonk
JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery.2024; 150(3): 265. CrossRef - Oncocytic carcinoma of the thyroid: Conclusions from a 20‐year patient cohort
Nelson R. Gruszczynski, Shahzeb S. Hasan, Ana G. Brennan, Julian De La Chapa, Adithya S. Reddy, David N. Martin, Prem P. Batchala, Edward B. Stelow, Eric M. Dowling, Katherine L. Fedder, Jonathan C. Garneau, David C. Shonka
Head & Neck.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hurthle cell carcinoma: a rare variant of thyroid malignancy – a case report
Yuvraj Adhikari, Anupama Marasini, Nawaraj Adhikari, Laxman D. Paneru, Binit Upadhaya Regmi, Manita Raut
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2023; 85(5): 1940. CrossRef - Hürthle Cell Carcinoma: Single Center Analysis and Considerations for Surgical Management Based on the Recent Literature
Costanza Chiapponi, Milan J.M. Hartmann, Matthias Schmidt, Michael Faust, Christiane J. Bruns, Anne M. Schultheis, Hakan Alakus
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Molecular Alterations and Comprehensive Clinical Management of Oncocytic Thyroid Carcinoma

- Thyroid
- Lobeglitazone, A Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-Gamma Agonist, Inhibits Papillary Thyroid Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion by Suppressing p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway
- Jun-Qing Jin, Jeong-Sun Han, Jeonghoon Ha, Han-Sang Baek, Dong-Jun Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1095-1110. Published online October 14, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1155
- 4,649 View
- 159 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-γ) ligands have been widely shown to correlate with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and cancer progression. Lobeglitazone (LGZ) is a novel ligand of PPAR-γ; and its role in EMT and metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) is poorly understood. We aimed to investigate the role of LGZ in metastatic behavior of PTC cells.
Methods
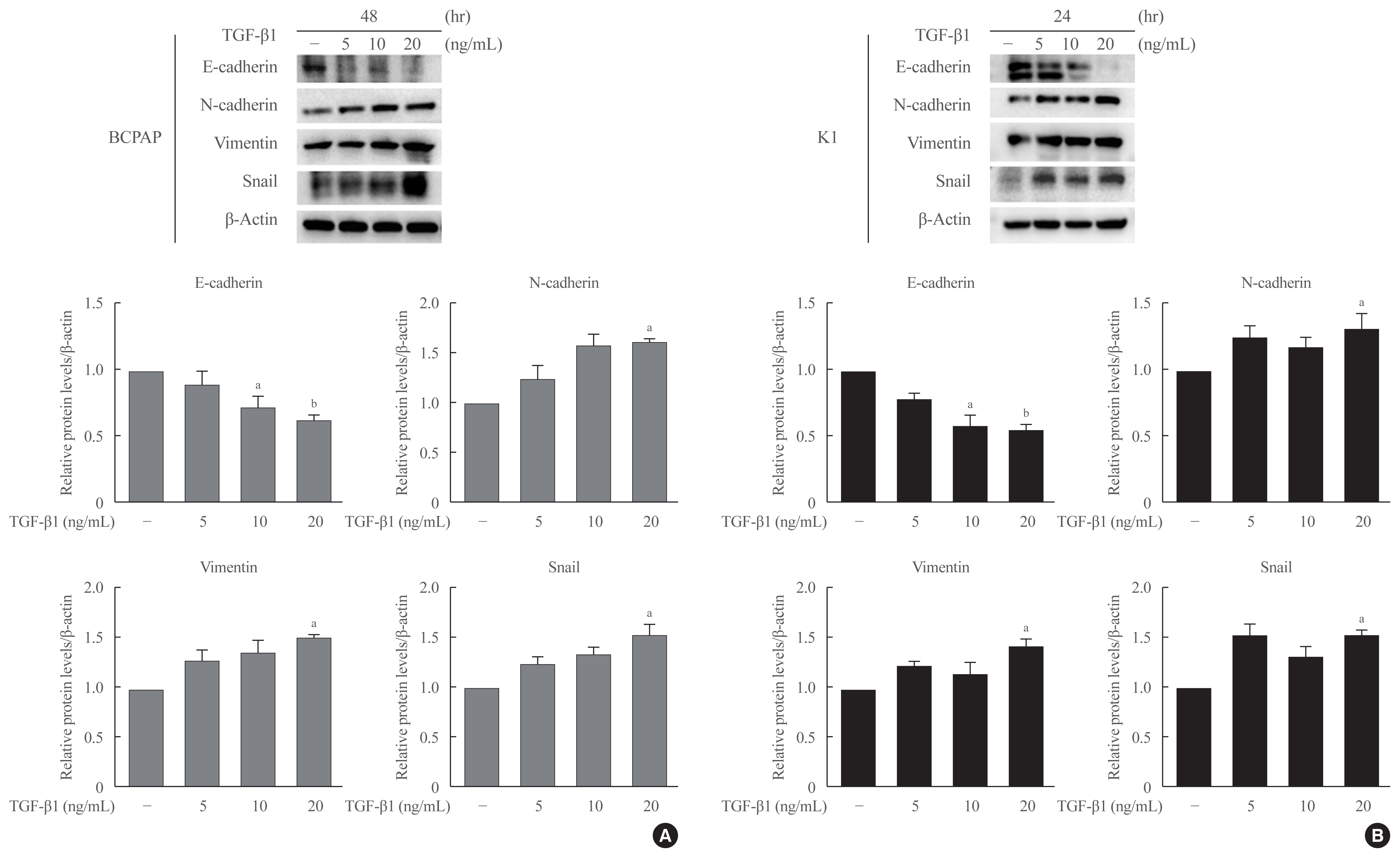
Half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of LGZ in BRAF-mutated PTC cell lines (BCPAP and K1) were determined using MTT assay. Rosiglitazone (RGZ), the PPAR-γ ligand was used as a positive control. The protein expression of PPAR-γ, cell-surface proteins (E-cadherin, N-cadherin), cytoskeletal protein (Vimentin), transcription factor (Snail), p38 mitogenactivated protein kinase (MAPK), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 pathway, and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 expression were measured using Western blotting. Changes in E-cadherin expression were also determined using immunocytochemistry. Cell migration and invasion were analyzed using wound healing and Matrigel invasion assays.
Results
Treatment with LGZ or RGZ significantly inhibited transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-β1)-induced EMT-associated processes such as fibroblast-like morphological changes, EMT-related protein expression, and increased cell migration and invasion in BCPAP and K1 cells. LGZ restored TGF-β1-induced loss of E-cadherin, as observed using immunocytochemistry. Furthermore, LGZ and RGZ suppressed TGF-β1-induced MMP-2 expression and phosphorylation of p38 MAPK, but not ERK1/2. Although there was no change in PPAR-γ expression after treatment with LGZ or RGZ, the effect of downstream processes mediated by LGZ was hampered by GW9662, a PPAR-γ antagonist.
Conclusion
LGZ inhibits TGF-β1-induced EMT, migration, and invasion through the p38 MAPK signaling pathway in a PPAR-γ-dependent manner in PTC cells. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetes Mellitus and Thyroid Cancers: Risky Correlation, Underlying Mechanisms and Clinical Prevention
Rongqian Wu, Junping Zhang, Guilin Zou, Shanshan Li, Jinying Wang, Xiaoxinlei Li, Jixiong Xu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2024; Volume 17: 809. CrossRef - Clinicopathological Evaluation of Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Ando Takahito, Kimihito Fujii, Hirona Banno, Masayuki Saito, Yukie Ito, Mirai Ido, Manami Goto, Yukako Mouri, Junko Kousaka, Tsuneo Imai, Shogo Nakano
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Pioglitazone, a peroxisome proliferator‑activated receptor γ agonist, induces cell death and inhibits the proliferation of hypoxic HepG2 cells by promoting excessive production of reactive oxygen species
Guohao Huang, Mengfan Zhang, Manzhou Wang, Wenze Xu, Xuhua Duan, Xinwei Han, Jianzhuang Ren
Oncology Letters.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Activation of PPARγ by (2Z,4E,6E)-2-methoxyocta-2,4,6-trienoic Acid Counteracts the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Process in Skin Carcinogenesis
Enrica Flori, Sarah Mosca, Giorgia Cardinali, Stefania Briganti, Monica Ottaviani, Daniela Kovacs, Isabella Manni, Mauro Truglio, Arianna Mastrofrancesco, Marco Zaccarini, Carlo Cota, Giulia Piaggio, Mauro Picardo
Cells.2023; 12(7): 1007. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to metabolic syndrome increases thyroid cancer risk in young adults: a population-based cohort study
Jinyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(4): 526. CrossRef - Drug repositioning in thyroid cancer treatment: the intriguing case of anti-diabetic drugs
Alessia Greco, Francesca Coperchini, Laura Croce, Flavia Magri, Marsida Teliti, Mario Rotondi
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Fish and the Thyroid: A Janus Bifrons Relationship Caused by Pollutants and the Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
Salvatore Benvenga, Fausto Famà, Laura Giovanna Perdichizzi, Alessandro Antonelli, Gabriela Brenta, Francesco Vermiglio, Mariacarla Moleti
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Identifying and categorizing compounds that reduce corneal transforming growth factor beta induced protein levels: a scoping review
Gabriella Guo Sciriha, Janet Sultana, Joseph Borg
Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology.2022; 15(12): 1423. CrossRef
- Diabetes Mellitus and Thyroid Cancers: Risky Correlation, Underlying Mechanisms and Clinical Prevention

- Thyroid
- Association between Iodine Intake, Thyroid Function, and Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Case-Control Study
- Kyungsik Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Young Joo Park, Kyu Eun Lee, Dong-Wook Lee, Sue K. Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):790-799. Published online August 11, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1034
- 4,675 View
- 234 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
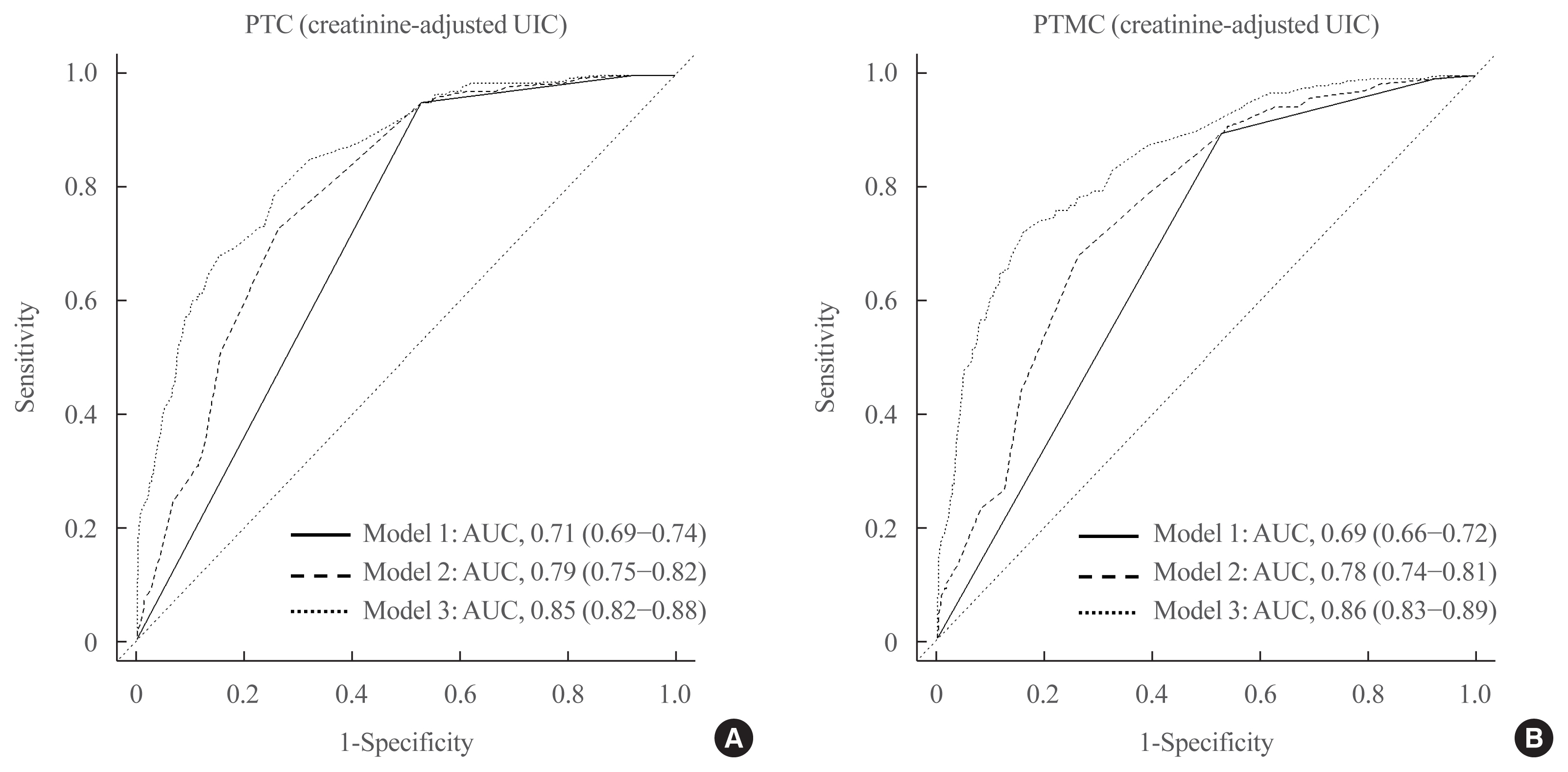
This study aimed to assess the effects of iodine intake, thyroid function, and their combined effect on the risk of papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) and papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (PTMC).
Methods
A case-control study was conducted including 500 community-based controls who had undergone a health check-up, and 446 overall PTC cases (209 PTC and 237 PTMC) from the Thyroid Cancer Longitudinal Study. Urinary iodine concentration (UIC), was used as an indicator of iodine intake, and serum for thyroid function. The risk of PTC and PTMC was estimated using unconditional logistic regression.
Results
Excessive iodine intake (UIC ≥220 μg/gCr) was associated with both PTC (odds ratio [OR], 18.13 95% confidence interval [CI], 8.87 to 37.04) and PTMC (OR, 8.02; 95% CI, 4.64 to 13.87), compared to adequate iodine intake (UIC, 85 to 219 μg/gCr). Free thyroxine (T4) levels ≥1.25 ng/dL were associated with PTC (OR, 1.97; 95% CI, 1.36 to 2.87) and PTMC (OR, 2.98; 95% CI, 2.01 to 4.41), compared to free T4 levels of 0.7 to 1.24 ng/dL. Individuals with excessive iodine intake and high free T4 levels had a greatly increased OR of PTC (OR, 43.48; 95% CI, 12.63 to 149.62), and PTMC (OR, 26.96; 95% CI, 10.26 to 70.89), compared to individuals with adequate iodine intake and low free T4 levels.
Conclusion
Excessive iodine intake using creatinine-adjusted UIC and high free T4 levels may have a synergistic effect on PTC and PTMC. Considering both iodine intake and thyroid function is important to assess PTC and PTMC risk. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between urinary iodine concentration and the risk of papillary thyroid cancer by sex and age: a case–control study
Yerin Hwang, Hyun-Kyung Oh, Jae Hoon Chung, Sun Wook Kim, Jung-Han Kim, Jee Soo Kim, Myung-Hee Shin
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between iodine nutrition and cervical lymph node metastasis of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
Hengqiang Zhao, Jin Hu, Le Cui, Yiping Gong, Tao Huang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sex-specific Associations between Body Mass Index and Thyroid Cancer Incidence among Korean Adults
Kyoung-Nam Kim, Kyungsik Kim, Sangjun Lee, Sue K. Park
Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.2023; 32(9): 1227. CrossRef - Nomogram Model Based on Iodine Nutrition and Clinical Characteristics of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma to Predict Lateral Lymph Node Metastasis
Junrong Wang, Yuzhang Gao, Yuxuan Zong, Weitong Gao, Xueying Wang, Ji Sun, Susheng Miao
Cancer Control.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Content of Copper, Iron, Iodine, Rubidium, Strontium and Zinc in Thyroid Malignant Nodules and Thyroid Tissue adjacent to Nodules
Vladimir Zaichick, Qiping Dong
Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Pathology.2022; 1(4): 7. CrossRef - Distinguish Thyroid Malignant from Benign Alterations using Trace Element Contents in Nodular Tissue determined by Neutron Activation and Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
Vladimir Zaichick
Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Pathology.2022; 1(4): 18. CrossRef - Seaweed and Iodine Intakes and SLC5A5 rs77277498 in Relation to Thyroid Cancer
Tung Hoang, Eun Kyung Lee, Jeonghee Lee, Yul Hwangbo, Jeongseon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 513. CrossRef - Iodine nutrition and papillary thyroid cancer
Xueqi Zhang, Fan Zhang, Qiuxian Li, Chuyao Feng, Weiping Teng
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between urinary iodine concentration and papillary thyroid cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Xueqi Zhang, Fan Zhang, Qiuxian Li, Renaguli Aihaiti, Chuyao Feng, Deshi Chen, Xu Zhao, Weiping Teng
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Screening and validation of lymph node metastasis risk-factor genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Qiaoyue Zhang, Jing Li, Hengyan Shen, Xinyu Bai, Tao Zhang, Ping Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnosis of Thyroid Malignancy using Levels of Chemical Element Contents in Nodular Tissue
Vladimir Zaichick
Journal of Health Care and Research.2022; 3(1): 16. CrossRef - Associations of Habitual Mineral Intake with New-Onset Prediabetes/Diabetes after Acute Pancreatitis
Claire F. Norbitt, Wandia Kimita, Juyeon Ko, Sakina H. Bharmal, Maxim S. Petrov
Nutrients.2021; 13(11): 3978. CrossRef
- Association between urinary iodine concentration and the risk of papillary thyroid cancer by sex and age: a case–control study

Review Article
- Thyroid
- Current Guidelines for Management of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):514-524. Published online June 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1082

- 17,762 View
- 1,694 Download
- 28 Web of Science
- 30 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) is a rare neuroendocrine tumor originating from the parafollicular cells. The diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for the condition are different from those used for well-differentiated thyroid cancer. Since the 2015 American Thyroid Association guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of MTC, the latest, including the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and European Association for Medical Oncology guidelines have been updated to reflect several recent advances in the management of MTC. Advances in molecular diagnosis and postoperative risk stratification systems have led to individualized treatment and follow-up strategies. Multi-kinase inhibitors, such as vandetanib and cabozantinib, can prolong disease progression-free survival with favorable adverse effects. In addition, potent selective rearranged during transfection (RET) inhibitors (selpercatinib and pralsetinib) have shown a promising efficacy in recent clinical trials. This review summarizes the management of MTC in recent guidelines focused on sporadic MTC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Molecular imaging and related therapeutic options for medullary thyroid carcinoma: state of the art and future opportunities
Alessio Imperiale, Valentina Berti, Mickaël Burgy, Roberto Luigi Cazzato, Arnoldo Piccardo, Giorgio Treglia
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2024; 25(1): 187. CrossRef - Diffuse C-Cells Hyperplasia Is the Source of False Positive Calcitonin Measurement in FNA Washout Fluids of Thyroid Nodules: A Rational Clinical Approach to Avoiding Unnecessary Surgery
Chiara Mura, Rossella Rodia, Silvia Corrias, Antonello Cappai, Maria Letizia Lai, Gian Luigi Canu, Fabio Medas, Pietro Giorgio Calò, Stefano Mariotti, Francesco Boi
Cancers.2024; 16(1): 210. CrossRef - Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy and Safety Evaluation of Vandetanib in
the Treatment of Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Tong-cheng Xian, Min-ye Yang, Xue-lin Zhang, Jie Wang, Yi Luo
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Successful localisation of recurrent thyroid cancer using preoperative patent blue dye injection
B. O. Evranos, N. Ince, H. Ataş, S. B. Polat, H. Ahsen, N. N. Imga, A. Dirikoc, O. Topaloglu, T. Tutuncu, R. Ersoy, B. Cakir
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Current and future of immunotherapy for thyroid cancer based on bibliometrics and clinical trials
Ke Wang, Ying Zhang, Yang Xing, Hong Wang, Minghua He, Rui Guo
Discover Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Combining radiomics with thyroid imaging reporting and data system to predict lateral cervical lymph node metastases in medullary thyroid cancer
Zhiqiang Liu, Xiwei Zhang, Xiaohui Zhao, Qianqian Guo, Zhengjiang Li, Minghui Wei, Lijuan Niu, Changming An
BMC Medical Imaging.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Update on Management of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: Focus on Nuclear Medicine
Giorgio Treglia, Vittoria Rufini, Arnoldo Piccardo, Alessio Imperiale
Seminars in Nuclear Medicine.2023; 53(4): 481. CrossRef - Cabozantinib, Vandetanib, Pralsetinib and Selpercatinib as Treatment for Progressed Medullary Thyroid Cancer with a Main Focus on Hypertension as Adverse Effect
Linnea Højer Wang, Markus Wehland, Petra M. Wise, Manfred Infanger, Daniela Grimm, Michael C. Kreissl
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(3): 2312. CrossRef - A proposed grading scheme for predicting recurrence in medullary thyroid cancer based on the Ki67 index and metastatic lymph node ratio
Pengfei Xu, Di Wu, Xuekui Liu
Endocrine.2023; 81(1): 107. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE in Adults with Inoperable or Metastatic Somatostatin Receptor-Positive Pheochromocytomas/Paragangliomas, Bronchial and Unknown Origin Neuroendocrine Tumors, and Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Systematic Literatur
Marianna Hertelendi, Oulaya Belguenani, Azzeddine Cherfi, Ilya Folitar, Gabor Kollar, Berna Degirmenci Polack
Biomedicines.2023; 11(4): 1024. CrossRef - PET/CT with various radiopharmaceuticals in the complex diagnosis of medullary thyroid carcinoma: a review
N. V. Tsentr, A. E. Ertman, D. V. Ryzhkova
Diagnostic radiology and radiotherapy.2023; 14(2): 31. CrossRef - Physical activity and reduced risk of fracture in thyroid cancer patients after thyroidectomy — a nationwide cohort study
Jinyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Jin-Hyung Jung, Jeonghoon Ha, Chaiho Jeong, Jun-Young Heu, Se-Won Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Yejee Lim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Hyun Baek
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Different RONS Generation in MTC-SK and NSCL Cells Lead to Varying Antitumoral Effects of Alpha-Ketoglutarate + 5-HMF
Joachim Greilberger, Katharina Erlbacher, Philipp Stiegler, Reinhold Wintersteiger, Ralf Herwig
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2023; 45(8): 6503. CrossRef - Medullary thyroid carcinoma
Maria Rosa Pelizzo, Esmeralda Isabella Mazza, Caterina Mian, Isabella Merante Boschin
Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy.2023; 23(9): 943. CrossRef - Mixed medullary‑follicular thyroid carcinoma: A case report and literature review
Yonghui Wang, Dandan Yin, Guifang Ren, Zhengjiang Wang, Fanhua Kong
Oncology Letters.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) in patients with medullary thyroid carcinoma is characterized by specific fragmentation and methylation changes with diagnostic value
Anna Citarella, Zein Mersini Besharat, Sofia Trocchianesi, Tanja Milena Autilio, Antonella Verrienti, Giuseppina Catanzaro, Elena Splendiani, Zaira Spinello, Silvia Cantara, Patrizia Zavattari, Eleonora Loi, Cristina Romei, Raffaele Ciampi, Luciano Pezzul
Biomarker Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in Diagnostics and Therapy of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma (MTC)– A Mini-Review
Michał Miciak, Krzysztof Jurkiewicz
Clinical Cancer Investigation Journal.2023; 12(5): 1. CrossRef - The Evolving Treatment Landscape of Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Marta Laganà, Valentina Cremaschi, Andrea Alberti, Danica M. Vodopivec Kuri, Deborah Cosentini, Alfredo Berruti
Current Treatment Options in Oncology.2023; 24(12): 1815. CrossRef - Pralsetinib: chemical and therapeutic development with FDA authorization for the management of RET fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancers
Faraat Ali, Kumari Neha, Garima Chauhan
Archives of Pharmacal Research.2022; 45(5): 309. CrossRef - Psychosocial Characteristics and Experiences in Patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2 (MEN2) and Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma (MTC)
Robin Lockridge, Sima Bedoya, Taryn Allen, Brigitte Widemann, Srivandana Akshintala, John Glod, Lori Wiener
Children.2022; 9(6): 774. CrossRef - Aggressive clinical course of medullary thyroid microcarcinoma
Tamara Janić, Mirjana Stojković, Sanja Klet, Bojan Marković, Beleslin Nedeljković, Jasmina Ćirić, Miloš Žarković
Medicinski glasnik Specijalne bolnice za bolesti štitaste žlezde i bolesti metabolizma.2022; 27(85): 63. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of somatostatin and CXCR4 receptor expression in different types of thyroid carcinoma using well-characterised monoclonal antibodies
Max Czajkowski, Daniel Kaemmerer, Jörg Sänger, Guido Sauter, Ralph M. Wirtz, Stefan Schulz, Amelie Lupp
BMC Cancer.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metastatic Risk Stratification of 2526 Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Patients: A Study Based on Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Database
Minh-Khang Le, Masataka Kawai, Toru Odate, Huy Gia Vuong, Naoki Oishi, Tetsuo Kondo
Endocrine Pathology.2022; 33(3): 348. CrossRef - Update on the Diagnosis and Management of Medullary Thyroid Cancer: What Has Changed in Recent Years?
Krzysztof Kaliszewski, Maksymilian Ludwig, Bartłomiej Ludwig, Agnieszka Mikuła, Maria Greniuk, Jerzy Rudnicki
Cancers.2022; 14(15): 3643. CrossRef - Immunotherapy of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Any Role for the Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells?
Giuseppe Fanciulli, Roberta Modica, Anna La Salvia, Federica Campolo, Tullio Florio, Nevena Mikovic, Alice Plebani, Valentina Di Vito, Annamaria Colao, Antongiulio Faggiano
Cancers.2022; 14(16): 3991. CrossRef - Preclinical Evaluation of Novel Tyrosine-Kinase Inhibitors in Medullary Thyroid Cancer
Davide Saronni, Germano Gaudenzi, Alessandra Dicitore, Silvia Carra, Maria Celeste Cantone, Maria Orietta Borghi, Andrea Barbieri, Luca Mignani, Leo J. Hofland, Luca Persani, Giovanni Vitale
Cancers.2022; 14(18): 4442. CrossRef - Rapid and long-lasting response to selpercatinib of paraneoplastic Cushing’s syndrome in medullary thyroid carcinoma
Marine Sitbon, Porhuoy Chou, Seydou Bengaly, Brigitte Poirot, Marie Laloi-Michelin, Laure Deville, Atanas Pachev, Ahouefa Kowo-Bille, Clement Dumont, Cécile N Chougnet
European Thyroid Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Ginsenoside Rg3 Alleviates Antithyroid Cancer Drug Vandetanib-Induced QT Interval Prolongation
Juan Zhang, Dan Luo, Fang Li, Zhiyi Li, Xiaoli Gao, Jie Qiao, Lin Wu, Miaoling Li, Shao Liang
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - THE ROLE OF CALCITONIN IN THE PREOPERATIVE STAGE AS THE PREDICTOR OF MEDULLARY THYROID CANCER METASTASES
Volodymyr Palamarchuk , Viktor Smolyar , Oleksandr Tovkay, Oleksandr Nechay, Volodymyr Kuts , Revaz Sichinava , Oleh Mazur
Ukrainian Scientific Medical Youth Journal.2021; 127(4): 68. CrossRef - THE ROLE OF CALCITONIN IN THE PREOPERATIVE STAGE AS THE PREDICTOR OF MEDULLARY THYROID CANCER METASTASES
Volodymyr Palamarchuk , Viktor Smolyar , Oleksandr Tovkay , Oleksandr Nechay , Volodymyr Kuts , Revaz Sichinava , Oleh Mazur
The Ukrainian Scientific Medical Youth Journal.2021; 4(127): 68. CrossRef
- Molecular imaging and related therapeutic options for medullary thyroid carcinoma: state of the art and future opportunities

Original Articles
- Thyroid
- Evaluation of Iodine Status among Korean Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer Using Dietary and Urinary Iodine
- Ji Yeon Choi, Joon-Hyop Lee, YoonJu Song
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):607-618. Published online June 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1005
- 3,853 View
- 119 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Concerns have been raised regarding thyroid disorders caused by excessive iodine in Koreans, who have iodine-rich diets. This study evaluated iodine status using dietary iodine intake and urinary iodine in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) patients.
Methods
Dietary data of PTC patients were assessed using a 24-hour recall and food frequency questionnaire (FFQ), and urinary iodine concentrations (UICs) were also obtained. To compare the iodine status of PTC patients, Korean adults with or without thyroid disease from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, which had 24-hour recall data and urinary iodine measurements, were analyzed.
Results
The median daily iodine intake by 24-hour recall was 341.7 μg/day in PTC patients, similar to the levels of other Korean adults. Based on UICs, the prevalence of excessive iodine was 54.4% in PTC patients, which was similar to the prevalence among subjects with thyroid disease (55.4%) but slightly higher than that in subjects without thyroid disease (47.7%). Based on dietary iodine by 24-hour recall, the prevalence of excessive iodine intake was 7.2%, which was higher than that among subjects with (4.4%) or without (3.9%) thyroid disease. The dietary iodine intake based on 24-hour recall was closely correlated with the UIC (r=0.4826) in PTC patients, but dietary iodine by FFQ was not significantly correlated with either 24-hour recall or UIC-based dietary iodine.
Conclusion
Excessive iodine intake was more common in PTC patients than in subjects without thyroid disease. Further longitudinal research is necessary to elucidate the role of dietary iodine in PTC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between iodine nutrition and cervical lymph node metastasis of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma
Hengqiang Zhao, Jin Hu, Le Cui, Yiping Gong, Tao Huang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of iodine restriction on short-term changes in thyroid function in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism
Obin Kwon, Dong Yeob Shin, Eun Jig Lee
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2022; 55(2): 250. CrossRef - Iodine nutrition and papillary thyroid cancer
Xueqi Zhang, Fan Zhang, Qiuxian Li, Chuyao Feng, Weiping Teng
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between iodine nutrition and cervical lymph node metastasis of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma

- Clinical Study
- Protocol for a Korean Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study of Active Surveillance or Surgery (KoMPASS) in Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
- Min Ji Jeon, Yea Eun Kang, Jae Hoon Moon, Dong Jun Lim, Chang Yoon Lee, Yong Sang Lee, Sun Wook Kim, Min-Hee Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Minho Shong, Sun Wook Cho, Won Bae Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(2):359-364. Published online March 23, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.890
- Correction in: Endocrinol Metab 2022;37(1):181
- 5,736 View
- 199 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
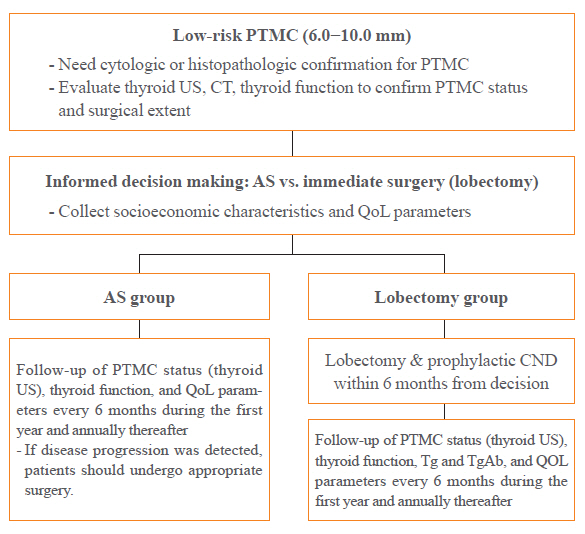
ePub - Background
A Korean Multicenter Prospective cohort study of Active Surveillance or Surgery (KoMPASS) for papillary thyroid microcarcinomas (PTMCs) has been initiated. The aim is to compare clinical outcomes between active surveillance (AS) and an immediate lobectomy for low-risk PTMCs. We here outline the detailed protocol for this study.
Methods
Adult patients with a cytopathologically confirmed PTMC sized 6.0 to 10.0 mm by ultrasound (US) will be included. Patients will be excluded if they have a suspicious extra-thyroidal extension or metastasis of a PTMC or multiple thyroid nodules or other thyroid diseases which require a total thyroidectomy. Printed material describing the prognosis of PTMCs, and the pros and cons of each management option, will be provided to eligible patients to select their preferred intervention. For the AS group, thyroid US, thyroid function, and quality of life (QoL) parameters will be monitored every 6 months during the first year, and then annually thereafter. Disease progression will be defined as a ≥3 mm increase in maximal diameter of a PTMC, or the development of new thyroid cancers or metastases. If progression is detected, patients should undergo appropriate surgery. For the lobectomy group, a lobectomy with prophylactic central neck dissection will be done within 6 months. After initial surgery, thyroid US, thyroid function, serum thyroglobulin (Tg), anti-Tg antibody, and QoL parameters will be monitored every 6 months during the first year and annually thereafter. Disease progression will be defined in these cases as the development of new thyroid cancers or metastases.
Conclusion
KoMPASS findings will help to confirm the role of AS, and develop individualized management strategies, for low-risk PTMCs. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Thyroid Cancers: A Review of Current Practice Guidelines
Min Joo Kim, Jae Hoon Moon, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Shin Song, Kyong Yeun Jung, Ji Ye Lee, Ji-hoon Kim, Kyungsik Kim, Sue K. Park, Young Joo Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 47. CrossRef - It Is Time to Understand the Additional Benefits of Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Kyeong Jin Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 95. CrossRef - Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma as an Acceptable Management Option with Additional Benefits: A Comprehensive Systematic Review
Jee Hee Yoon, Wonsuk Choi, Ji Yong Park, A Ram Hong, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 152. CrossRef - Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma as an Acceptable Management Option with Additional Benefits: A Comprehensive Systematic Review
Jee Hee Yoon, Wonsuk Choi, Ji Yong Park, A Ram Hong, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 152. CrossRef - Thyroid‐Stimulating Hormone, Age, and Tumor Size are Risk Factors for Progression During Active Surveillance of Low‐Risk Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma in Adults
Yasuhiro Ito, Akira Miyauchi, Makoto Fujishima, Takuya Noda, Tsutomu Sano, Takahiro Sasaki, Taketoshi Kishi, Tomohiko Nakamura
World Journal of Surgery.2023; 47(2): 392. CrossRef - Thyroid FNA cytology: The Eastern versus Western perspectives
Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Manon Auger, Chan Kwon Jung, Fabiano Mesquita Callegari
Cancer Cytopathology.2023; 131(7): 415. CrossRef - To Screen or Not to Screen?
Do Joon Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 69. CrossRef - Lower Thyroid Cancer Mortality in Patients Detected by Screening: A Meta-Analysis
Shinje Moon, Young Shin Song, Kyong Yeun Jung, Eun Kyung Lee, Young Joo Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 93. CrossRef - Long-Term Outcomes of Active Surveillance and Immediate Surgery for Adult Patients with Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: 30-Year Experience
Akira Miyauchi, Yasuhiro Ito, Makoto Fujishima, Akihiro Miya, Naoyoshi Onoda, Minoru Kihara, Takuya Higashiyama, Hiroo Masuoka, Shiori Kawano, Takahiro Sasaki, Mitsushige Nishikawa, Shuji Fukata, Takashi Akamizu, Mitsuru Ito, Eijun Nishihara, Mako Hisakad
Thyroid®.2023; 33(7): 817. CrossRef - Active Surveillance Outcomes of Patients with Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma According to Levothyroxine Treatment Status
Masashi Yamamoto, Akira Miyauchi, Yasuhiro Ito, Makoto Fujishima, Takahiro Sasaki, Takumi Kudo
Thyroid®.2023; 33(10): 1182. CrossRef - Cost-Effectiveness of Active Surveillance Compared to Early Surgery of Small Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Retrospective Study on a Korean Population
Han-Sang Baek, Jeonghoon Ha, Kwangsoon Kim, Jaseong Bae, Jeong Soo Kim, Sungju Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Chulmin Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimal Cutoff Values of the Contact Angle of Tumor on Sonography System for Predicting Extrathyroidal Extension of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma by Tumor Location
Ik Beom Shin, Do Hoon Koo, Dong Sik Bae
Clinical Medicine Insights: Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermal ablation for papillary thyroid microcarcinoma located in the isthmus: a study with 3 years of follow-up
Lin Zheng, Fang-yi Liu, Jie Yu, Zhi-gang Cheng, Xiao-ling Yu, Xiao-cong Dong, Zhi-yu Han, Ping Liang
Future Oncology.2022; 18(4): 471. CrossRef - Trends in the Management of Localized Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma in the United States (2000–2018)
Elisa Pasqual, Julie Ann Sosa, Yingxi Chen, Sara J. Schonfeld, Amy Berrington de González, Cari M. Kitahara
Thyroid.2022; 32(4): 397. CrossRef - Management of Low-Risk Thyroid Cancers: Is Active Surveillance a Valid Option? A Systematic Review of the Literature
Renato Patrone, Nunzio Velotti, Stefania Masone, Alessandra Conzo, Luigi Flagiello, Chiara Cacciatore, Marco Filardo, Vincenza Granata, Francesco Izzo, Domenico Testa, Stefano Avenia, Alessandro Sanguinetti, Andrea Polistena, Giovanni Conzo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(16): 3569. CrossRef - Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Active Surveillance Compared to Early Surgery in Small Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Systemic Review
Han-sang Baek, Chai-ho Jeong, Jeonghoon Ha, Ja-Seong Bae, Jeong-soo Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Chul-Min Kim
Cancer Management and Research.2021; Volume 13: 6721. CrossRef - Active Surveillance as an Effective Management Option for Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma
Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 717. CrossRef
- Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Thyroid Cancers: A Review of Current Practice Guidelines

- Clinical Study
- Molecular Correlates and Nuclear Features of Encapsulated Follicular-Patterned Thyroid Neoplasms
- Chan Kwon Jung, Andrey Bychkov, Dong Eun Song, Jang-Hee Kim, Yun Zhu, Zhiyan Liu, Somboon Keelawat, Chiung-Ru Lai, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Kaori Kameyama, Kennichi Kakudo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):123-133. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.860

- 5,006 View
- 147 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Assessing nuclear features is diagnostically challenging in the aspect of thyroid pathology. The aim of this study was to determine whether pathologists could distinguish BRAF-like and RAS-like nuclear features morphologically and identify morphological features to differentiate thyroid tumors with RAS-like mutations from encapsulated papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) with predominant follicular growth and BRAFV600E mutation.
Methods
Representative whole slide images of 16 encapsulated thyroid tumors with predominant follicular growth were reviewed by 12 thyroid pathologists using a web browser-based image viewer. Total nuclear score was calculated from semi-quantitatively scored eight nuclear features. The molecular profile of RAS and BRAF genes was determined by Sanger sequencing.
Results
Total nuclear score ranging 0 to 24 could differentiate BRAF-like tumors from RAS-like tumors with a cut-off value of score 14. The interobserver agreement was the highest for the assessment of nuclear pseudoinclusions (NPIs) but the lowest for nuclear elongation and sickle-shaped nuclei. NPIs were found in tumors with BRAFV600E mutation, but not in tumors with RAS-like mutations. Total nuclear scores were significantly higher for tumors with BRAFV600E than for those with RAS-like mutations (P<0.001).
Conclusion
Our results suggest that NPIs and high nuclear scores have diagnostic utility as rule-in markers for differentiating PTC with BRAFV600E mutation from benign or borderline follicular tumors with RAS-like mutations. Relaxation of rigid criteria for nuclear features resulted in an overdiagnosis of PTC. Immunostaining or molecular testing for BRAFV600E mutation is a useful adjunct for cases with high nuclear scores to identify true PTC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differentiating BRAF V600E- and RAS-like alterations in encapsulated follicular patterned tumors through histologic features: a validation study
Chankyung Kim, Shipra Agarwal, Andrey Bychkov, Jen-Fan Hang, Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Kennichi Kakudo, Somboon Keelawat, Chih-Yi Liu, Zhiyan Liu, Truong Phan-Xuan Nguyen, Chanchal Rana, Huy Gia Vuong, Yun Zhu, Chan Kwon Jung
Virchows Archiv.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Presence of Typical “BRAFV600E-Like” Atypia in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma is Highly Specific for the Presence of the BRAFV600E Mutation
John Turchini, Loretta Sioson, Adele Clarkson, Amy Sheen, Leigh Delbridge, Anthony Glover, Mark Sywak, Stan Sidhu, Anthony J. Gill
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(1): 112. CrossRef - Could Oxidative Stress Play a Role in the Development and Clinical Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer?
Maria Kościuszko, Angelika Buczyńska, Adam Jacek Krętowski, Anna Popławska-Kita
Cancers.2023; 15(12): 3182. CrossRef - Pitfalls in thyroid pathology and the medicolegal aspects of error
David N Poller
Diagnostic Histopathology.2023; 29(11): 495. CrossRef - Developing Models to Predict BRAFV600E and RAS Mutational Status in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Using Clinicopathological Features and pERK1/2 Immunohistochemistry Expression
Agnes Stephanie Harahap, Imam Subekti, Sonar Soni Panigoro, Asmarinah, Lisnawati, Retno Asti Werdhani, Hasrayati Agustina, Dina Khoirunnisa, Mutiah Mutmainnah, Fajar Lamhot Gultom, Abdillah Hasbi Assadyk, Maria Francisca Ham
Biomedicines.2023; 11(10): 2803. CrossRef - The Asian Thyroid Working Group, from 2017 to 2023
Kennichi Kakudo, Chan Kwon Jung, Zhiyan Liu, Mitsuyoshi Hirokawa, Andrey Bychkov, Huy Gia Vuong, Somboon Keelawat, Radhika Srinivasan, Jen-Fan Hang, Chiung-Ru Lai
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine.2023; 57(6): 289. CrossRef - Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclear Features (NIFTP): Tumour Entity with a Short History. A Review on Challenges in Our Microscopes, Molecular and Ultrasonographic Profile
Ivana Kholová, Elina Haaga, Jaroslav Ludvik, David Kalfert, Marie Ludvikova
Diagnostics.2022; 12(2): 250. CrossRef - Update from the 2022 World Health Organization Classification of Thyroid Tumors: A Standardized Diagnostic Approach
Chan Kwon Jung, Andrey Bychkov, Kennichi Kakudo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(5): 703. CrossRef - Different Threshold of Malignancy for RAS-like Thyroid Tumors Causes Significant Differences in Thyroid Nodule Practice
Kennichi Kakudo
Cancers.2022; 14(3): 812. CrossRef - The Incidence of Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features: A Meta-Analysis Assessing Worldwide Impact of the Reclassification
Chanchal Rana, Huy Gia Vuong, Thu Quynh Nguyen, Hoang Cong Nguyen, Chan Kwon Jung, Kennichi Kakudo, Andrey Bychkov
Thyroid.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Differentiating BRAF V600E- and RAS-like alterations in encapsulated follicular patterned tumors through histologic features: a validation study

- Clinical Study
- Lactate Dehydrogenase A as a Potential New Biomarker for Thyroid Cancer
- Eun Jeong Ban, Daham Kim, Jin Kyong Kim, Sang-Wook Kang, Jandee Lee, Jong Ju Jeong, Kee-Hyun Nam, Woong Youn Chung, Kunhong Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):96-105. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.819

- 5,733 View
- 185 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Several cancers show increased levels of lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA), which are associated with cancer progression. However, it remains unclear whether LDHA levels are associated with papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) aggressiveness or with the presence of the PTC prognostic marker, the BRAFV600E mutation. This study aimed to evaluate the potential of LDHA as a PTC prognostic marker.
Methods
LDHA expression was examined in 83 PTC tissue specimens by immunohistochemistry. Human thyroid cell lines were genetically manipulated to overexpress BRAFV600E or were treated with a BRAF-specific short hairpin RNA (shBRAF), whose effects on LDHA expression were evaluated by Western blotting. Data from 465 PTC patients were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and analyzed to validate the in vitro results.
Results
LDHA was aberrantly overexpressed in PTC. Intense immunostaining for LDHA was observed in PTC specimens carrying mutated BRAF, whereas the intensity was less in wild-type BRAF samples. Overexpression of BRAFV600E resulted in LDHA upregulation, whereas treatment with shBRAF downregulated LDHA in human thyroid cell lines. Furthermore, LDHA mRNA expression was significantly elevated and associated with BRAFV600E expression in thyroid cancer tissues from TCGA database. Additionally, LDHA overexpression was found to be correlated with aggressive clinical features of PTC, such as lymph node metastases and advanced tumor stages.
Conclusion
LDHA overexpression is associated with the BRAFV600E mutation and an aggressive PTC behavior. Therefore, LDHA may serve as a biomarker and therapeutic target in PTC. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integrated proteogenomic and metabolomic characterization of papillary thyroid cancer with different recurrence risks
Ning Qu, Di Chen, Ben Ma, Lijun Zhang, Qiuping Wang, Yuting Wang, Hongping Wang, Zhaoxian Ni, Wen Wang, Tian Liao, Jun Xiang, Yulong Wang, Shi Jin, Dixin Xue, Weili Wu, Yu Wang, Qinghai Ji, Hui He, Hai-long Piao, Rongliang Shi
Nature Communications.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Peripheral lymphocytes and lactate dehydrogenase correlate with response and survival in head and neck cancers treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors
Cassie Pan, Qian Vicky Wu, Jenna Voutsinas, Jeffrey J. Houlton, Brittany Barber, Zain H. Rizvi, Emily Marchiano, Neal Futran, George E. Laramore, Jay J. Liao, Upendra Parvathaneni, Renato G. Martins, Jonathan R. Fromm, Cristina P. Rodriguez
Cancer Medicine.2023; 12(8): 9384. CrossRef - LncRNA GLTC targets LDHA for succinylation and enzymatic activity to promote progression and radioiodine resistance in papillary thyroid cancer
Liang Shi, Rui Duan, Zhenhua Sun, Qiong Jia, Wenyu Wu, Feng Wang, Jianjun Liu, Hao Zhang, Xue Xue
Cell Death & Differentiation.2023; 30(6): 1517. CrossRef - Integrated analysis of circulating and tissue proteomes reveals that fibronectin 1 is a potential biomarker in papillary thyroid cancer
Guochao Ye, Xiaomei Zhang, Mansheng Li, Zixiang Lin, Yongcan Xu, Haoru Dong, Jie Zhou, Jiaqi Zhang, Sheng Wang, Yunping Zhu, Xiaobo Yu, Xu Qian
BMC Cancer.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting metabolism by B-raf inhibitors and diclofenac restrains the viability of BRAF-mutated thyroid carcinomas with Hif-1α-mediated glycolytic phenotype
Marianna Aprile, Simona Cataldi, Caterina Perfetto, Antonio Federico, Alfredo Ciccodicola, Valerio Costa
British Journal of Cancer.2023; 129(2): 249. CrossRef - circNFATC3 facilitated the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via the miR-520h/LDHA axis
Hongguo Xie, Xiaopeng Lu
Open Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The potential role of reprogrammed glucose metabolism: an emerging actionable codependent target in thyroid cancer
Sai-li Duan, Min Wu, Zhe-Jia Zhang, Shi Chang
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - CENPE and LDHA were potential prognostic biomarkers of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma
Hui-feng Wu, Hao Liu, Zhe-wei Zhang, Ji-min Chen
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Classification for Staging and Managing Patients with Biopolymer-induced Human Adjuvant Disease
Jaime Eduardo Pachón Suárez, Marcela C. Salazar, Victor Z. Rizo
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery - Global Open.2022; 10(2): e4137. CrossRef - Development of Metabolic Synthetic Lethality and Its Implications for Thyroid Cancer
Sang-Hyeon Ju, Seong Eun Lee, Yea Eun Kang, Minho Shong
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 53. CrossRef - Drug delivery for metabolism targeted cancer immunotherapy
Taravat Khodaei, Sahil Inamdar, Abhirami P. Suresh, Abhinav P. Acharya
Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews.2022; 184: 114242. CrossRef - Sulfur quantum dot based fluorescence assay for lactate dehydrogenase activity detection
Shengnan Fan, Xiaoqing Li, Fanghui Ma, Minghui Yang, Juan Su, Xiang Chen
Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry.2022; 430: 113989. CrossRef - STAT3/LINC00671 axis regulates papillary thyroid tumor growth and metastasis via LDHA-mediated glycolysis
Nan Huo, Rui Cong, Zhi-jia Sun, Wen-chao Li, Xiang Zhu, Chun-yuan Xue, Zhao Chen, Lu-yuan Ma, Zhong Chu, Yu-chen Han, Xiao-feng Kang, Song-hao Jia, Nan Du, Lei Kang, Xiao-jie Xu
Cell Death & Disease.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Integrated proteogenomic and metabolomic characterization of papillary thyroid cancer with different recurrence risks

- Clinical Study
- Association of Hyperparathyroidism and Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
- Chaiho Jeong, Hye In Kwon, Hansang Baek, Hun-Sung Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Jeonghoon Ha, Moo Il Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):925-932. Published online December 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.725

- 5,245 View
- 181 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Concomitant papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) and hyperparathyroidism (HPT) have been reported in several studies. Our study aimed to investigate the incidence of concomitant PTC in HPT patients upon preoperative diagnosis and present a clinical opinion on detecting thyroid malignancy in case of parathyroidectomy.
Methods
Patients who underwent parathyroidectomy between January 2009 and December 2019 in two medical centers were included. Of the 279 participants 154 were diagnosed as primary hyperparathyroidism (pHPT) and 125 as secondary hyperparathyroidism (sHPT). The incidence of concomitant PTC and its clinical characteristics were compared with 98 patients who underwent thyroidectomy and were diagnosed with classical PTC during the same period.
Results
Concurrent PTC was detected in 14 patients (9.1%) with pHPT and in nine patients (7.2%) with sHPT. Ten (71.4%) and seven (77.8%) PTCs were microcarcinomas in the pHPT and sHPT cases respectively. In the pHPT patients, vitamin D was lower in the pHPT+PTC group (13.0±3.7 ng/mL) than in the pHPT-only group (18.5±10.4 ng/mL; P=0.01). Vitamin D levels were also lower in the sHPT+PTC group (12.3±5.6 ng/mL) than in the sHPT-only group (18.0±10.2 ng/mL; P=0.12). In the concomitant PTC group, lymph node ratio was higher than in the classical PTC group (P=0.00).
Conclusion
A high prevalence of concomitant PTC was seen in patients with pHPT and sHPT. Those concomitant PTCs were mostly microcarcinomas and had more aggressive features, suggesting that efforts should be made to detect concomitant malignancies in the preoperative parathyroidectomy evaluation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The unexpected effect of parathyroid adenoma on inflammation
Ahmet Tarik Harmantepe, Belma Kocer, Zulfu Bayhan, Emre Gonullu, Ugur Can Dulger
Updates in Surgery.2024; 76(2): 589. CrossRef - Evaluation of Nodular Goiter and Papillary Thyroid Cancer Coincidence in Patients with Primary Hyperparathyroidism
Mustafa ÇALIŞKAN, Hasret CENGİZ, Taner DEMİRCİ
Düzce Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi.2023; 25(2): 200. CrossRef - Papillary thyroid carcinoma coexisting with benign thyroid and parathyroid pathology: clinical and pathomorphological features
A. Dinets, M. Gorobeiko, V. Hoperia, A. Lovin, S. Tarasenko
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2023; 19(4): 274. CrossRef - The Nexus of Hyperparathyroidism and Thyroid Carcinoma: Insights into Pathogenesis and Diagnostic Challenges—A Narrative Review
Gregorio Scerrino, Nunzia Cinzia Paladino, Giuseppina Orlando, Giuseppe Salamone, Pierina Richiusa, Stefano Radellini, Giuseppina Melfa, Giuseppa Graceffa
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(1): 147. CrossRef - Is preoperative parathyroid localization necessary for tertiary hyperparathyroidism?
Rongzhi Wang, Peter Abraham, Brenessa Lindeman, Herbert Chen, Jessica Fazendin
The American Journal of Surgery.2022; 224(3): 918. CrossRef - Papillary thyroid carcinoma prevalence and its predictors in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism
Elif Tutku DURMUŞ, Ayşegül ATMACA, Mehmet KEFELİ, Ramis ÇOLAK, Buğra DURMUŞ, Cafer POLAT
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2022; 5(5): 1499. CrossRef - Association of Hyperparathyroidism and Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Multicenter Retrospective Study (Endocrinol Metab 2020;35:925-32, Chaiho Jeong et al.)
Chaiho Jeong, Jeonghoon Ha, Moo Il Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(1): 205. CrossRef - Association of Hyperparathyroidism and Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Multicenter Retrospective Study (Endocrinol Metab 2020;35:925-32, Chaiho Jeong et al.)
Burcu Candemir, Coşkun Meriç
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(1): 203. CrossRef
- The unexpected effect of parathyroid adenoma on inflammation


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



