Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
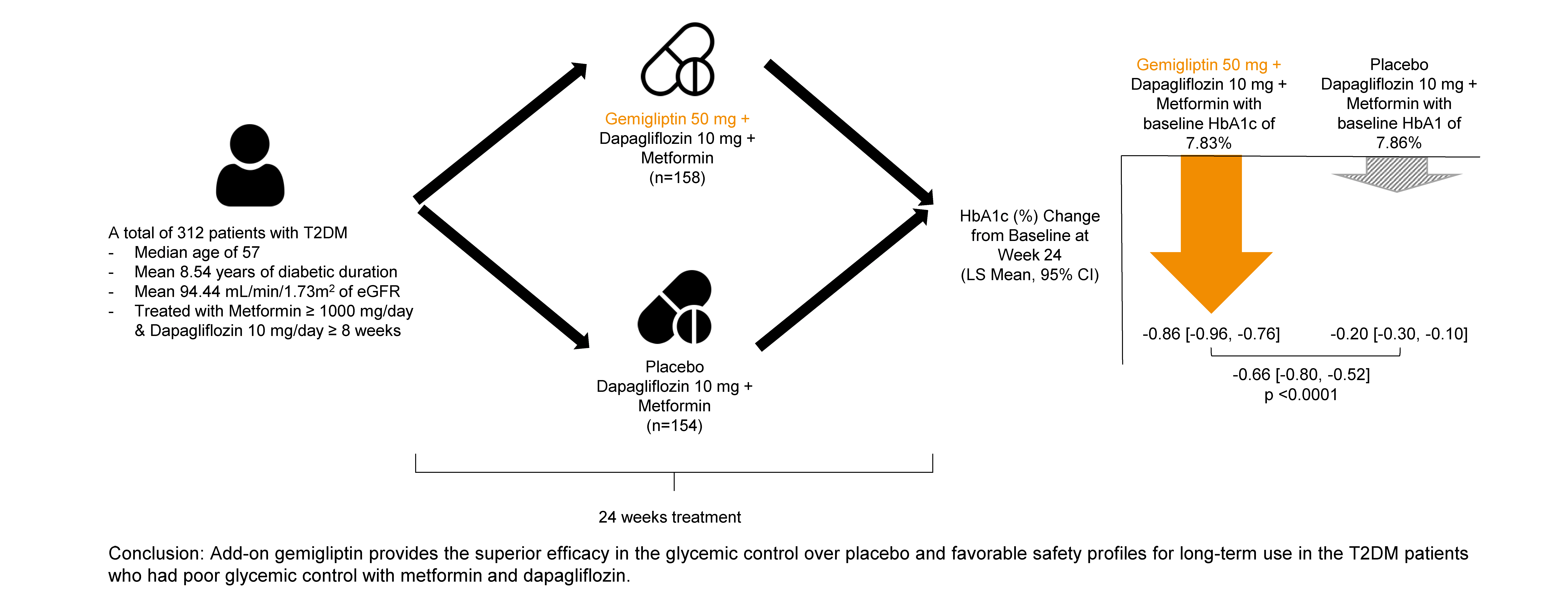
- Efficacy of Gemigliptin Add-on to Dapagliflozin and Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study (SOLUTION)
- Byung Wan Lee, KyungWan Min, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Bon Jeong Ku, Jun Goo Kang, Suk Chon, Won-Young Lee, Mi Kyoung Park, Jae Hyeon Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Keeho Song, Soon Jib Yoo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(3):328-337. Published online June 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1688
- 2,388 View
- 258 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of add-on gemigliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who had inadequate glycemic control with metformin and dapagliflozin.
Methods
In this randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, double-blind, phase III study, 315 patients were randomized to receive either gemigliptin 50 mg (n=159) or placebo (n=156) with metformin and dapagliflozin for 24 weeks. After the 24-week treatment, patients who received the placebo were switched to gemigliptin, and all patients were treated with gemigliptin for an additional 28 weeks.
Results
The baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups, except for body mass index. At week 24, the least squares mean difference (standard error) in hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) changes was –0.66% (0.07) with a 95% confidence interval of –0.80% to –0.52%, demonstrating superior HbA1c reduction in the gemigliptin group. After week 24, the HbA1c level significantly decreased in the placebo group as gemigliptin was administered, whereas the efficacy of HbA1c reduction was maintained up to week 52 in the gemigliptin group. The safety profiles were similar: the incidence rates of treatment-emergent adverse events up to week 24 were 27.67% and 29.22% in the gemigliptin and placebo groups, respectively. The safety profiles after week 24 were similar to those up to week 24 in both groups, and no new safety findings, including hypoglycemia, were noted.
Conclusion
Add-on gemigliptin was well tolerated, providing comparable safety profiles and superior efficacy in glycemic control over placebo for long-term use in patients with T2DM who had poor glycemic control with metformin and dapagliflozin.

- Bone Metabolism
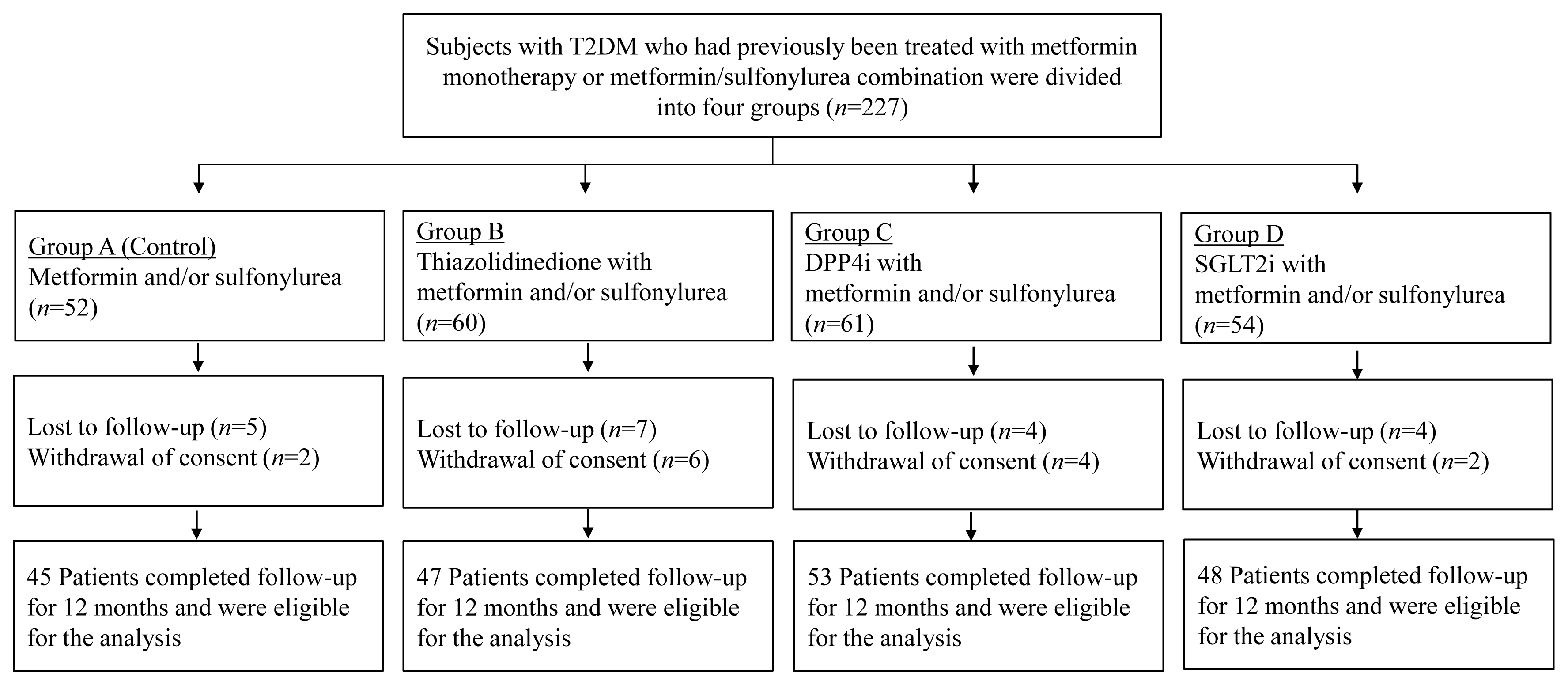
- Comparison of the Effects of Various Antidiabetic Medication on Bone Mineral Density in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Jeonghoon Ha, Yejee Lim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Ki-Ho Song, Seung Hyun Ko, Moo Il Kang, Sung Dae Moon, Ki-Hyun Baek
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):895-903. Published online August 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1026
- 6,081 View
- 229 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Prospective comparative studies on the effects of various antidiabetic agents on bone metabolism are limited. This study aimed to assess changes in bone mass and biochemical bone markers in postmenopausal patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
This prospective, multicenter, open-label, comparative trial included 264 patients with T2DM. Patients who had received a metformin, or sulfonylurea/metformin combination (Group 1); a thiazolidinedione combination (Group 2); a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (gemigliptin) combination (Group 3); or an sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor (empagliflozin) combination (Group 4) were prospectively treated for 12 months; bone mineral density (BMD) and bone turnover marker (BTM) changes were evaluated.
Results
The femoral neck BMD percentage changes were −0.79%±2.86% (Group 1), −2.50%±3.08% (Group 2), −1.05%±2.74% (Group 3), and −1.24%±2.91% (Group 4) (P<0.05). The total hip BMD percentage changes were −0.57%±1.79% (Group 1), −1.74%±1.48% (Group 2), −0.75%±1.87% (Group 3), and −1.27%±1.72% (Group 4) (P<0.05). Mean serum BTM (C-terminal type 1 collagen telopeptide and procollagen type 1 amino-terminal propeptide) levels measured during the study period did not change over time or differ between groups.
Conclusion
Significant bone loss in the femoral neck and total hip was associated with thiazolidinedione combination regimens. However, bone loss was not significantly associated with combination regimens including gemigliptin or empagliflozin. Caution should be exercised during treatment with antidiabetic medications that adversely affect the bone in patients with diabetes at a high risk of bone loss. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Meta-Analysis on the Association Between DPP-4 Inhibitors and Bone Mineral Density and Osteoporosis
Lili Huang, Wei Zhong, Xinghuan Liang, Huijuan Wang, Shi-en Fu, Zuojie Luo
Journal of Clinical Densitometry.2024; 27(1): 101455. CrossRef - A multicentre, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, randomized, parallel comparison, phase 3 trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pioglitazone add‐on therapy in type 2 diabetic patients treated with metformin and dapagliflozin
Soo Lim, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Kyung‐Wan Min, Chang Beom Lee, Sang Yong Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Nan Hee Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim, Seungjoon Oh, Jong Chul Won, Hyuk Sang Kwon, Mi Kyung Kim, Jung Hwan Park, In‐Kyung Jeong, Sungrae Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Bone Turnover Markers with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Microvascular Complications: A Matched Case-Control Study
Yilin Hou, Xiaoyu Hou, Qian Nie, Qiuyang Xia, Rui Hu, Xiaoyue Yang, Guangyao Song, Luping Ren
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 1177. CrossRef - Complementary effects of dapagliflozin and lobeglitazone on metabolism in a diet-induced obese mouse model
Yun Kyung Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Ji In Lee, Bo Yoon Choi, Hyen Chung Cho, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
European Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 957: 175946. CrossRef
- Meta-Analysis on the Association Between DPP-4 Inhibitors and Bone Mineral Density and Osteoporosis

Review Article
- Diabetes
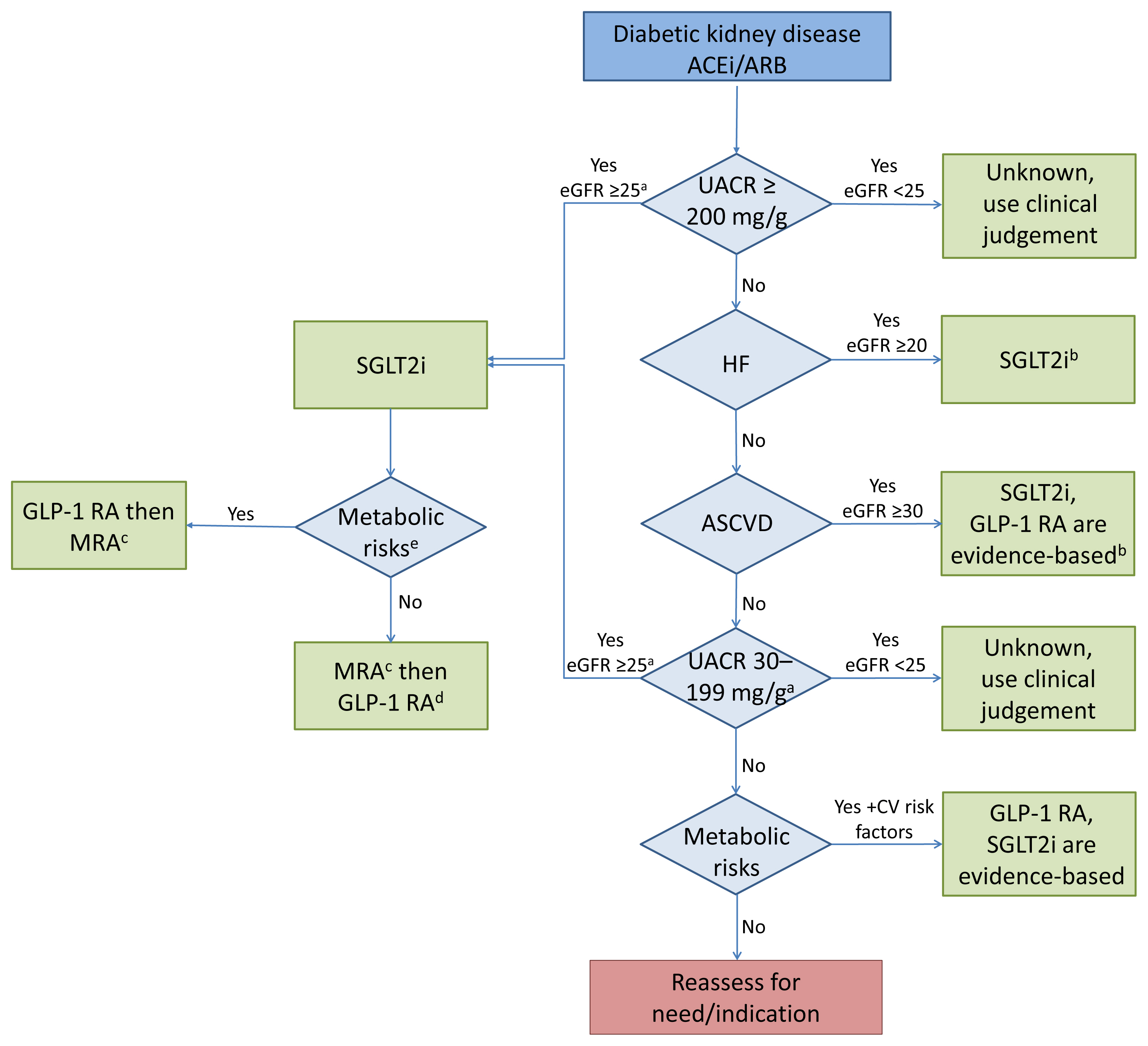
- Cardiorenal Protection in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Jason F. Lee, Ecaterina Berzan, Vikas S. Sridhar, Ayodele Odutayo, David Z.I. Cherney
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(2):256-269. Published online April 19, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.987
- 5,702 View
- 299 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Over the last 5 years there have been many new developments in the management of diabetic kidney disease. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) and sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors were initially used for glycemic control, but more recent studies have now shown that their benefits extend to cardiovascular and kidney outcomes. The recent addition of data on the novel mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) gives us another approach to further decrease the residual risk of diabetic kidney disease progression. In this review we describe the mechanism of action, key studies, and possible adverse effects related to these three classes of medications. The management of type 2 diabetes now includes an increasing number of medications for the management of comorbidities in a patient population at significant risk of cardiovascular disease and progression of chronic kidney disease. It is from this perspective that we seek to outline the rationale for the sequential and/or combined use of SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 RA and MRAs in patients with type 2 diabetes for heart and kidney protection.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relative and Absolute Risks of Adverse Events with Real-World Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in CKD
Ayodele Odutayo, Adeera Levin
Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.2023; 18(5): 557. CrossRef - Renal Protection of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist, Finerenone, in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Dong-Lim Kim, Seung-Eun Lee, Nan Hee Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 43. CrossRef - Intrarenal Mechanisms of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors on Tubuloglomerular Feedback and Natriuresis
Eun Sil Koh, Gheun-Ho Kim, Sungjin Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 359. CrossRef - SGLT2 and DPP4 inhibitors improve Alzheimer’s disease–like pathology and cognitive function through distinct mechanisms in a T2D–AD mouse model
A Young Sim, Da Hyun Choi, Jong Youl Kim, Eun Ran Kim, A-ra Goh, Yong-ho Lee, Jong Eun Lee
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 168: 115755. CrossRef - Narrative review investigating the nephroprotective mechanisms of sodium glucose cotransporter type 2 inhibitors in diabetic and nondiabetic patients with chronic kidney disease
Emma S. Speedtsberg, Martin Tepel
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of CKD
Nimrit Goraya, Jennifer D. Moran
Nephrology Self-Assessment Program.2022; 21(2): 146. CrossRef - Nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonism for cardiovascular and renal disorders − New perspectives for combination therapy
Peter Kolkhof, Amer Joseph, Ulrich Kintscher
Pharmacological Research.2021; 172: 105859. CrossRef - Sodium‐Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors, All‐Cause Mortality, and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Bayesian Meta‐Analysis and Meta‐Regression
Ayodele Odutayo, Bruno R. da Costa, Tiago V. Pereira, Vinay Garg, Samir Iskander, Fatimah Roble, Rahim Lalji, Cesar A. Hincapié, Aquila Akingbade, Myanca Rodrigues, Arnav Agarwal, Bishoy Lawendy, Pakeezah Saadat, Jacob A. Udell, Francesco Cosentino, Peter
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Finerenone: A Potential Treatment for Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Luis D’Marco, María Jesús Puchades, Lorena Gandía, Claudia Forquet, Elena Giménez-Civera, Nayara Panizo, Javier Reque, Isabel Juan-García, Valmore Bermúdez, José Luis Gorriz
touchREVIEWS in Endocrinology.2021; 17(2): 84. CrossRef - Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Mechanisms of Action: A Review
Jorge I. Fonseca-Correa, Ricardo Correa-Rotter
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Relative and Absolute Risks of Adverse Events with Real-World Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors in CKD

Original Article
- Clinical Study
- Comparative Renal Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors on Individual Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- Jae Hyun Bae, Eun-Gee Park, Sunhee Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Seokyung Hahn, Nam Hoon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(2):388-400. Published online March 31, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.912
- 6,335 View
- 360 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To compare the renal effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on individual outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods
We searched electronic databases (MEDLINE, Embase, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials) from inception to June 2019 to identity eligible randomized controlled trials of DPP-4 inhibitors or SGLT2 inhibitors that reported at least one kidney outcome in patients with type 2 diabetes. Outcomes of interest were microalbuminuria, macroalbuminuria, worsening nephropathy, and end-stage kidney disease (ESKD). We performed an arm-based network meta-analysis using Bayesian methods and calculated absolute risks and rank probabilities of each treatment for the outcomes.
Results
Seventeen studies with 87,263 patients were included. SGLT2 inhibitors significantly lowered the risks of individual kidney outcomes, including microalbuminuria (odds ratio [OR], 0.64; 95% credible interval [CrI], 0.41 to 0.93), macroalbuminuria (OR, 0.48; 95% CrI, 0.24 to 0.72), worsening nephropathy (OR, 0.65; 95% CrI, 0.44 to 0.91), and ESKD (OR, 0.65; 95% CrI, 0.46 to 0.98) as compared with placebo. However, DPP-4 inhibitors did not lower the risks. SGLT2 inhibitors were considerably associated with higher absolute risk reductions in all kidney outcomes than DPP-4 inhibitors, although the benefits were statistically insignificant. The rank probabilities showed that SGLT2 inhibitors were better treatments for lowering the risk of albuminuria and ESKD than placebo or DPP-4 inhibitors.
Conclusion
SGLT2 inhibitors were superior to DPP-4 inhibitors in reducing the risk of albuminuria and ESKD in patients with type 2 diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Therapie des Typ-2-Diabetes
Rüdiger Landgraf, Jens Aberle, Andreas L. Birkenfeld, Baptist Gallwitz, Monika Kellerer, Harald H. Klein, Dirk Müller-Wieland, Michael A. Nauck, Tobias Wiesner, Erhard Siegel
Die Diabetologie.2024; 20(2): 212. CrossRef - Ipragliflozin and sitagliptin differentially affect lipid and apolipoprotein profiles in type 2 diabetes: the SUCRE study
Mototsugu Nagao, Jun Sasaki, Kyoko Tanimura-Inagaki, Ichiro Sakuma, Hitoshi Sugihara, Shinichi Oikawa
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Effect of Glucose-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Stroke Prevention: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Ji Soo Kim, Gyeongsil Lee, Kyung-Il Park, Seung-Won Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 312. CrossRef - Therapy of Type 2 Diabetes
Rüdiger Landgraf, Jens Aberle, Andreas L. Birkenfeld, Baptist Gallwitz, Monika Kellerer, Harald H. Klein, Dirk Müller-Wieland, Michael A. Nauck, Tobias Wiesner, Erhard Siegel
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Therapie des Typ-2-Diabetes
Rüdiger Landgraf, Jens Aberle, Andreas L. Birkenfeld, Baptist Gallwitz, Monika Kellerer, Harald H. Klein, Dirk Müller-Wieland, Michael A. Nauck, Tobias Wiesner, Erhard Siegel
Die Diabetologie.2023; 19(5): 658. CrossRef - Renoprotective Effect of Thai Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with SGLT-2 Inhibitors versus DPP-4 Inhibitors: A Real-World Observational Study
Apichaya Chanawong, Suriyon Uitrakul, Supatcha Incomenoy, Natnicha Poonchuay, Rizky Abdulah
Advances in Pharmacological and Pharmaceutical Sciences.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Different nursing interventions on sleep quality among critically ill patients: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Daijin Huang, Yumei Li, Jing Ye, Chang Liu, Dongyan Shen, Yunhui Lv
Medicine.2023; 102(52): e36298. CrossRef - New trends in the approach to the treatment of type 2 diabetes - observations and benefits in the outpatient practice of a diabetologist
Pavel Weber, Hana Meluzínová, Dana Weberová
Klinická farmakologie a farmacie.2022; 35(4): 118. CrossRef - Comparative efficacy of novel antidiabetic drugs on cardiovascular and renal outcomes in patients with diabetic kidney disease: A systematic review and network meta‐analysis
Hongwei Cao, Tao Liu, Li Wang, Qiuhe Ji
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(8): 1448. CrossRef - Therapie des Typ-2-Diabetes
Rüdiger Landgraf, Jens Aberle, Andreas L. Birkenfeld, Baptist Gallwitz, Monika Kellerer, Harald H. Klein, Dirk Müller-Wieland, Michael A. Nauck, Tobias Wiesner, Erhard Siegel
Die Diabetologie.2022; 18(5): 623. CrossRef - Significant reduction in chronic kidney disease progression with sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitors compared to dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors in adults with type 2 diabetes in a UK clinical setting: An observational outcomes study based on inte
Iskandar Idris, Ruiqi Zhang, Jil B. Mamza, Mike Ford, Tamsin Morris, Amitava Banerjee, Kamlesh Khunti
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(11): 2138. CrossRef - Therapy of Type 2 Diabetes
Rüdiger Landgraf, Jens Aberle, Andreas L. Birkenfeld, Baptist Gallwitz, Monika Kellerer, Harald Klein, Dirk Müller-Wieland, Michael A. Nauck, Tobias Wiesner, Erhard Siegel
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2022; 130(S 01): S80. CrossRef - Molecular Mechanistic Pathways Targeted by Natural Compounds in the Prevention and Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Kaixuan Zhou, Xue Zi, Jiayu Song, Qiulu Zhao, Jia Liu, Huiwei Bao, Lijing Li
Molecules.2022; 27(19): 6221. CrossRef - Lower risk of gout in sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors versus dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitors in type-2 diabetes
Jiandong Zhou, Xuejin Liu, Oscar Hou-In Chou, Lifang Li, Sharen Lee, Wing Tak Wong, Qingpeng Zhang, Carlin Chang, Tong Liu, Gary Tse, Fengshi Jing, Bernard Man Yung Cheung
Rheumatology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - New Era for Renal-Protective Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes: Better Renal Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Taking Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors versus Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors
Chan-Hee Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(2): 339. CrossRef - Efficacy / safety balance of DPP-4 inhibitors versus SGLT2 inhibitors in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes
André J. Scheen
Diabetes & Metabolism.2021; 47(6): 101275. CrossRef
- Therapie des Typ-2-Diabetes

Review Article
- Diabetes
- Best Achievements in Clinical Medicine in Diabetes and Dyslipidemia in 2020
- Eun-Jung Rhee, Mee-Kyung Kim, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):41-50. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.106
- 4,284 View
- 177 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Over the last two decades, our understanding of diabetes and treatment strategies have evolved tremendously, from scientific, mechanistic, and human perspectives. The categories of anti-diabetic medications expanded from a few to numerous, enabling clinicians to personalize diabetes care and treatment. Thanks to rapid growth in the field of science and medical engineering, newer treatment options are coming to the market with various advantages and disadvantages to be aware of. Therefore, clinicians should rapidly adopt new trends based on guidelines and data from many clinical trials in the field of diabetes. In the treatment of dyslipidemia, trends and guidelines are changing every year, and novel therapies are being developed. In this review, we would like to summarize the major achievements in clinical medicine in 2020 in the field of diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin added to metformin plus gemigliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind, randomized, comparator-active study: ENHANCE-D study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Kyung Ah Han, Tae Nyun Kim, Cheol-Young Park, Jung Hwan Park, Sang Yong Kim, Yong Hyun Kim, Kee Ho Song, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Sik Kim, Gwanpyo Koh, Jun Goo Kang, Mi Kyung Kim, Ji Min Han, Nan Hee Kim, Ji Oh Mok, Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Lim, Sang S
Diabetes & Metabolism.2023; 49(4): 101440. CrossRef - Effects of exercise initiation and smoking cessation after new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus on risk of mortality and cardiovascular outcomes
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Jinyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined Effects of Obesity and Dyslipidaemia on the Prevalence of Diabetes Amongst Adults Aged ≥45 Years: Evidence from a Nationally Representative Cross-Sectional Study
Simin Zhang, Donghan Sun, Xiaoyi Qian, Li Li, Wenwen Wu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(13): 8036. CrossRef - Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level, Statin Use and Myocardial Infarction Risk in Young Adults
Heekyoung Jeong, Kyungdo Han, Soon Jib Yoo, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(3): 288. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin added to metformin plus gemigliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind, randomized, comparator-active study: ENHANCE-D study

Original Article
- Clinical Study
- Glycemic Efficacy and Metabolic Consequences of an Empagliflozin Add-on versus Conventional Dose-Increasing Strategy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled by Metformin and Sulfonylurea
- Yujin Shin, Ji Hye Moon, Ho Jun Chin, Ele Ferrannini, Soo Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):329-338. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.329
- 6,503 View
- 214 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We assessed the glucose-lowering efficacy of adding empagliflozin versus dose escalating existing medications in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Methods
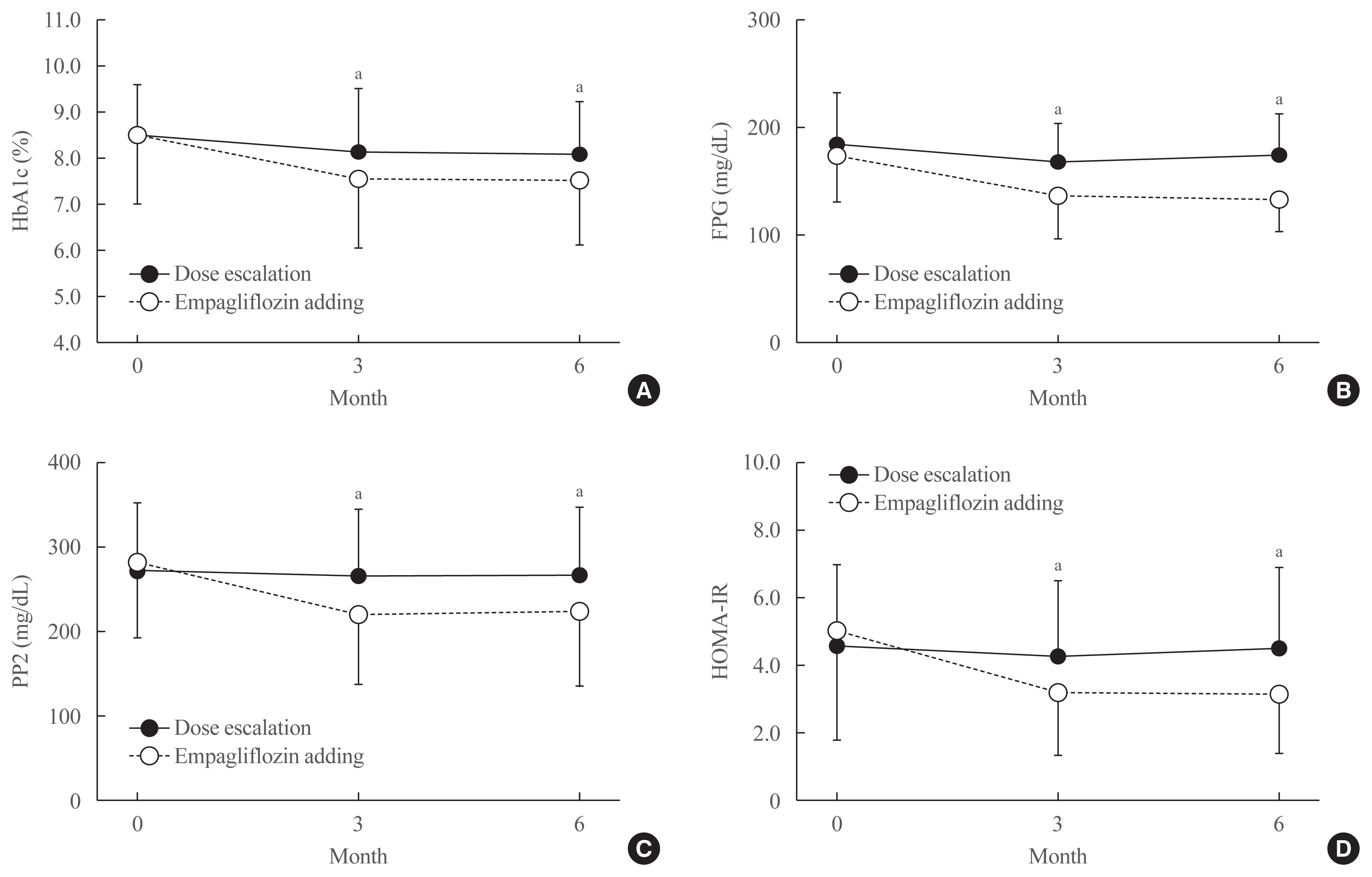
This was a 6-month retrospective case-control study in subjects with uncontrolled T2D (glycated hemoglobin [HbA1c] >7%) on conventional treatment. The study group started add-on therapy with empagliflozin (10 mg once a day) while the control group was up-titrated with existing medication, using either monotherapy or a combination of metformin, sulfonylurea, and a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor. The primary endpoints included changes in HbA1c, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and 2-hour postprandial glucose (PP2) levels. Secondary outcomes included changes in body composition, body mass index (BMI), and serum ketone bodies, and urinary excretion of sodium, potassium, chlorine, calcium, phosphorus, and glucose.
Results
After treatment, the reduction in HbA1c was significantly greater in the empagliflozin group than in controls (from 8.6%±1.6% to 7.6%±1.5% vs. 8.5%±1.1% to 8.1%±1.1%; P<0.01). Similar patterns were found in FPG and PP2 levels. Empagliflozin decreased systolic and diastolic blood pressure, triglycerides, and alanine and aspartate aminotransferase levels. Body weight, BMI, waist circumference, fat mass, and abdominal visceral fat area decreased significantly while lean body mass was maintained. Total ketones, β-hydroxybutyrate, and acetoacetate levels increased significantly after empagliflozin.
Conclusion
In addition to glucose lowering, an empagliflozin add-on regimen decreased blood pressure and body fat, and improved metabolic profiles significantly. Empagliflozin add-on is superior to dose escalation in patients with T2D who have inadequate glycemic control on standard medications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Independent association of thigh muscle fat density with vascular events in Korean adults
Hun Jee Choe, Won Chang, Matthias Blüher, Steven B. Heymsfield, Soo Lim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, Empagliflozin, is associated with significant reduction in weight, body mass index, fasting glucose, and A1c levels in Type 2 diabetic patients with established coronary heart disease: the SUPER GATE study
Satilmis Bilgin, Ozge Kurtkulagi, Tuba Taslamacioglu Duman, Burcin Meryem Atak Tel, Gizem Kahveci, Murat Kiran, Eray Erge, Gulali Aktas
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2022; 191(4): 1647. CrossRef - A randomized clinical trial evaluating the effect of empagliflozin on triglycerides in obese adults: Role of visceral fat
Min Hee Lee, Ian J. Neeland, Natalia de Albuquerque Rocha, Connor Hughes, Craig R. Malloy, Eunsook S. Jin
Metabolism Open.2022; 13: 100161. CrossRef - Initial combination of metformin, sitagliptin, and empagliflozin in drug‐naïve patients with type 2 diabetes: Safety and metabolic effects
Soo Lim, Minji Sohn, Yujin Shin, Ele Ferrannini
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(4): 757. CrossRef - Correlation of dynamic membrane fluctuations in red blood cells with diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular risks
Minji Sohn, Ji Eun Lee, MinGeun Ahn, YongKeun Park, Soo Lim
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison betweeen dapagliflozin add-on therapy and insulin dose escalation in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes treated with insulin: DVI study
Yujin Shin, Haeri Choi, Soo Lim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 175: 108843. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 and Associated Preventive Measures on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in South Korea
Minji Sohn, Bo Kyung Koo, Ho Il Yoon, Kyoung-Ho Song, Eu Suk Kim, Hong Bin Kim, Soo Lim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2021; 30(3): 248. CrossRef
- Independent association of thigh muscle fat density with vascular events in Korean adults


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



