Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Clinical Study
- Relationship of Sarcopenia with Microcirculation Measured by Skin Perfusion Pressure in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Chan-Hee Jung, Yoon Young Cho, Dughyun Choi, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chul-Hee Kim, Ji-Oh Mok
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):578-586. Published online September 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.679
- 5,345 View
- 122 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Few studies have examined the relationship of sarcopenia with the microcirculation. The current study investigated the relationship of sarcopenia with microcirculatory function, as assessed by skin perfusion pressure (SPP), in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients.
Methods
In total, 102 T2DM patients who underwent SPP measurements and bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) were enrolled in this cross-sectional study. SPP was assessed using the laser Doppler technique. Sarcopenia was defined as low height-adjusted appendicular muscle mass (men, <7 kg/m2; women, <5.7 kg/m2) using BIA. We divided the participants into two groups based on SPP (≤50 and >50 mm Hg), and an SPP below 50 mm Hg was considered to reflect impaired microcirculation.
Results
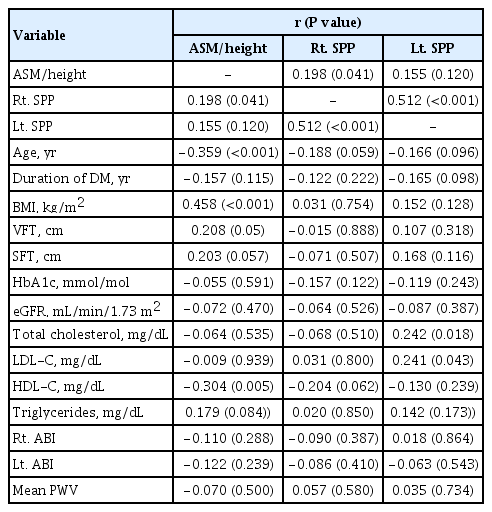
Fourteen patients (13.7%) were diagnosed with impaired microcirculatory function of the lower limb based on SPP. The prevalence of sarcopenia in all subjects was 11.8%, but the percentage of patients with an SPP ≤50 mm Hg who had sarcopenia was more than triple that of patients with an SPP >50 mm Hg (28.6% vs. 9.1%, P=0.036). A significant positive correlation was found between SPP and appendicular muscle mass adjusted for height (P=0.041 for right-sided SPP). Multiple logistic regression analysis showed that patients with sarcopenia had an odds ratio of 4.1 (95% confidence interval, 1.01 to 24.9) for having an SPP ≤50 mm Hg even after adjustment for confounding factors.
Conclusion
These results suggest that sarcopenia may be significantly associated with impaired microcirculation in patients with T2DM. Nonetheless, the small number of patients and wide CI require cautious interpretation of the results. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preclinical study of diabetic foot ulcers: From pathogenesis to vivo/vitro models and clinical therapeutic transformation
Yuqing Du, Jie Wang, Weijing Fan, Renyan Huang, Hongfei Wang, Guobin Liu
International Wound Journal.2023; 20(10): 4394. CrossRef - Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis for the Assessment of Body Composition in Sarcopenia and Type 2 Diabetes
Stefano Sbrignadello, Christian Göbl, Andrea Tura
Nutrients.2022; 14(9): 1864. CrossRef - Discrimination between possible sarcopenia and metabolic syndrome using the arterial pulse spectrum and machine-learning analysis
Li-Wei Wu, Te OuYoung, Yu-Chih Chiu, Ho-Feng Hsieh, Hsin Hsiu
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The prevalence and risk factors of sarcopenia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yaqin Ai, Ruoxin Xu, Lingping Liu
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Preclinical study of diabetic foot ulcers: From pathogenesis to vivo/vitro models and clinical therapeutic transformation

- Thyroid
- Solitary Skin Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Hyemi Kwon, Hyojung Kim, Sojung Park, Dong Eun Song, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(4):579-583. Published online December 29, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.4.579
- 3,991 View
- 41 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader A solitary skin metastasis is a rare manifestation of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). A 55-year-old woman presented with a movable subcutaneous nodule in her anterior neck for several months. Three years ago, she underwent total thyroidectomy and remnant ablation for classical PTC (pT3N0M0) and was under thyroxine suppression therapy without any evidence of recurrent disease. The subcutaneous nodule was 0.4 cm in size, firm, and movable without any change in the overlying skin. Recurrent PTC was confirmed after excision biopsy. Eight months after, she got a new nodule along the previous excision site. After punch biopsy, metastatic PTC was confirmed in the deep dermis and was re-excised with a clear resection margin. This is the first report of a case of solitary skin metastasis of PTC in Korea. Although solitary skin metastasis of PTC is rare, it should be considered in patients with a skin nodule.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Skin Metastasis Occurring 30 Years After Thyroidectomy for Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Mohammed S Alwhaid, Olaa Mhish, Mutahir A Tunio, Salman AlMalki, Mushabbab Al Asiri, Khalid Al-Qahtani
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Solitary Nasopharyngeal Metastasis From Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Shown on FDG PET/CT
Anqi Xu, Xiao Jie, Yan Xiu, Hongcheng Shi
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2022; 47(5): e425. CrossRef - PD-L1-positive Anaplastic Transformation in a BRAF V600E Expressing Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma with Cutaneous Metastasis: An Unusual Case Report
Pooja Ramakant, Anand Mishra, Chanchal Rana, Kulranjan Singh
Indian Journal of Endocrine Surgery and Research.2022; 17(1): 21. CrossRef - Unusual Thyroid Carcinoma Metastases: a Case Series and Literature Review
Eleonora Farina, Fabio Monari, Giovanni Tallini, Andrea Repaci, Renzo Mazzarotto, Francesca Giunchi, Riccardo Panzacchi, Silvia Cammelli, Gilbert D. A. Padula, Francesco Deodato, Renato Pasquali, Stefano Fanti, Michelangelo Fiorentino, Alessio G. Morganti
Endocrine Pathology.2016; 27(1): 55. CrossRef - Skin manifestations of endocrine and neuroendocrine tumors
Jonathan S. Leventhal, Irwin M. Braverman
Seminars in Oncology.2016; 43(3): 335. CrossRef - Isolated Metastasis in Male Breast from Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma – Oncological Curiosity. A Case Report and Review of Literature
Lakshminarasimman Parasuraman, Shubhada V. Kane, Prathamesh S. Pai, Kintan Shanghvi
Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology.2016; 7(1): 91. CrossRef - A Closer Look at Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
Won Bae Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 1. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef
- Skin Metastasis Occurring 30 Years After Thyroidectomy for Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma

- Clinical Applicability of Ultrasonometric Skin Thickness Measurement in the Diagnosis of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: Comparison with DXA.
- Young Seol Kim, In Kwon Han, Duk Ju Lee, Kwang Min Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1998;13(1):60-66. Published online January 1, 2001
- 885 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Osteoporosis is developed by progressive decrease of bone rnass from decreased collagen content of bone. Accurate measurement of bone collagen is necessary for the diagnosis of osteoporosis and it is possible by bone biopsy, however bone biopsy is not easy in clinical practice. Skin collagen is consist with type I collagen which is same type of bone collagen and progressive decrease of bone collagen is reflected by decrease of skin collagen. Since skin thickness reflect skin collagen amount, skin thickness measurement may be a useful method for the evaluation of osteoporosis. So ultrasonic skin thickness measurement was developed for the evaluation of osteoporosis. METHODS: A randomly selected 200 women aged fram 30 to 71 years old were asked to have their skin thickness measured as well as lumbar vertebral DXA(Norland, USA) bone densitometry. Except for the two women who failed to complete the study, 45(22.7%) of these women were diagnosed as normal, 74(37.4%) were osteopenic and 79(39.9%) were diagnosed as osteoporosis patients using the WHO criteria. Skin thickness was measured using 20MHz Osteoson DCIII (Minhorst, Germany) at the medial side of the upper arm. A minimal of Two scans were measured and the mean value was cakulated automatically. RESULTS: The correlation coefficient of skin thickness and age was -0.121(ns), DXA BMD(bone mineral density) and age was -0.420(P<0.01), skin thickness and DXA BMD L2-L4 was 0.181(P<0.05). Skin thickness was significantly correlated with body weight(correlation coefficient 0.254, P<0.01) and BMI(correlation coefficient 0.195, P<0.01). Furthermore, the mean and standard deviation of skin thickness in normal BMD group was 0.94+-0.021mm, osteopenic group was 0.92+-0.006mm, and osteoporotic group was 0.89+-0.018mm. There was statistically significant difference in the mean values of skin thickness between the three groups even adjusted with age and BMI(P<0.05). The mean and standard deviation of skin tbickness of healthy 20-40 year old women was 1.11+-0,023mm and their mean and standard deviation of L2-L4 mean BMD was 1.17+-0.145mg/cm2. The diagnostic predictability of skin thickness less than 1mm as the risk of osteoporosis(BMD T score less than -1.0) was evaluated. The sensitivity and the specificity of skin thickness less than 1mm being osteoporotic were 78,2% and 57.8% respectively. The positive and negative predictive value of the skin thickness less than 1mm being osteoporotic were 82.2% and 36.5% respectively. CONCLUSION: This study indicate that the skin thickaess measured with the ultrasound method show good correlatian with the bone density measured with conventional DXA at the lumbar vertebra and the skin thickness less than 1mm on the medial side of the opper arm is relatively sensitive in diagnosing osteoporosis risk in Korean women. The authors suggested that a large randomized control study to define the relationship between the skin thickness and the other determinants of bone turnover in the near future.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



