Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Thyroid
- Clinical Characteristics and Prognosis of Coexisting Thyroid Cancer in Patients with Graves’ Disease: A Retrospective Multicenter Study
- Jee Hee Yoon, Meihua Jin, Mijin Kim, A Ram Hong, Hee Kyung Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Min Ji Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1268-1276. Published online November 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1227

- 4,769 View
- 184 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The association between Graves’ disease (GD) and co-existing thyroid cancer is still controversial and most of the previously reported data have been based on surgically treated GD patients. This study investigated the clinicopathological findings and prognosis of concomitant thyroid cancer in GD patients in the era of widespread application of ultrasonography.
Methods
Data of GD patients who underwent thyroidectomy for thyroid cancer between 2010 and 2019 in three tertiary hospitals in South Korea (Asan Medical Center, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, and Pusan National University Hospital) were collected and analyzed retrospectively. In the subgroup analysis, aggressiveness and clinical outcomes of thyroid cancer were compared nodular GD and non-nodular GD groups according to the presence or absence of the thyroid nodules other than thyroid cancer (index nodules).
Results
Of the 15,159 GD patients treated at the hospitals during the study period, 262 (1.7%) underwent thyroidectomy for coexisting thyroid cancer. Eleven patients (4.2%) were diagnosed with occult thyroid cancer and 182 patients (69.5%) had microcarcinomas. No differences in thyroid cancer aggressiveness, ultrasonographic findings, or prognosis were observed between the nodular GD and non-nodular GD groups except the cancer subtype. In the multivariate analysis, only lymph node (LN) metastasis was an independent prognostic factor for recurrent/persistent disease of thyroid cancer arising in GD (P=0.020).
Conclusion
The prevalence of concomitant thyroid cancer in GD patients was considerably lower than in previous reports. The clinical outcomes of thyroid cancer in GD patients were also excellent but, more cautious follow-up is necessary for patients with LN metastasis in the same way as for thyroid cancer in non-GD patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Surgical Outcomes of Transoral Versus Open Thyroidectomy for Graves Disease
Suo-Hsien Wang, Wu-Po Chao, Ta-You Lo, Soh-Ching Ng, Yu-Hsien Chen
Surgical Laparoscopy, Endoscopy & Percutaneous Techniques.2024; 34(2): 150. CrossRef - Outcomes of Surgical Treatment for Graves’ Disease: A Single-Center Experience of 216 Cases
Hanxing Sun, Hui Tong, Xiaohui Shen, Haoji Gao, Jie Kuang, Xi Chen, Qinyu Li, Weihua Qiu, Zhuoran Liu, Jiqi Yan
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(4): 1308. CrossRef - Cancer and Mortality Risks of Graves’ Disease in South Korea Based on National Data from 2010 to 2019
Young Ju Choi, Kyungdo Han, Won Kyoung Cho, Min Ho Jung, Byung-Kyu Suh
Clinical Epidemiology.2023; Volume 15: 535. CrossRef - Risk and Prognosis of Thyroid Cancer in Patients with Graves’ Disease: An Umbrella Review
Marco Palella, Francesca Maria Giustolisi, Adriana Modica Fiascaro, Martina Fichera, Antonella Palmieri, Rossella Cannarella, Aldo E. Calogero, Margherita Ferrante, Maria Fiore
Cancers.2023; 15(10): 2724. CrossRef - Characteristics, staging and outcomes of differentiated thyroid cancer in patients with and without Graves’ disease
Chaitra Gopinath, Hanna Crow, Sujata Panthi, Leonidas Bantis, Kenneth D. Burman, Chitra Choudhary
Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology.2023; 33: 100321. CrossRef - Prevalence, Treatment Status, and Comorbidities of Hyperthyroidism in Korea from 2003 to 2018: A Nationwide Population Study
Hwa Young Ahn, Sun Wook Cho, Mi Young Lee, Young Joo Park, Bon Seok Koo, Hang-Seok Chang, Ka Hee Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 436. CrossRef - Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis and Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Follow-Up Study in Patients with Absence of Aggressive Risk Factors at the Surgery of the Primary Tumor
Andrea Marongiu, Susanna Nuvoli, Andrea De Vito, Sonia Vargiu, Angela Spanu, Giuseppe Madeddu
Diagnostics.2023; 13(19): 3068. CrossRef - Table of Contents
Clinical Thyroidology.2022; 34(2): 48. CrossRef - Predisposition to and Prognosis of Thyroid Cancer May Not Be Affected by Graves’ Disease, But Some Questions Still Remain
Yanrui Huang, Haixia Guan
Clinical Thyroidology.2022; 34(2): 59. CrossRef - A Comparative Follow-Up Study of Patients with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Associated or Not with Graves’ Disease
Andrea Marongiu, Susanna Nuvoli, Andrea De Vito, Maria Rondini, Angela Spanu, Giuseppe Madeddu
Diagnostics.2022; 12(11): 2801. CrossRef - An unusual case of papillary thyroid carcinoma presenting as Graves’ disease
Pooja Tiwari, Uma Kaimal Saikia, Abhamoni Baro, Ashok Krishna Bhuyan
Thyroid Research and Practice.2022; 19(1): 47. CrossRef
- Comparison of Surgical Outcomes of Transoral Versus Open Thyroidectomy for Graves Disease

- Thyroid
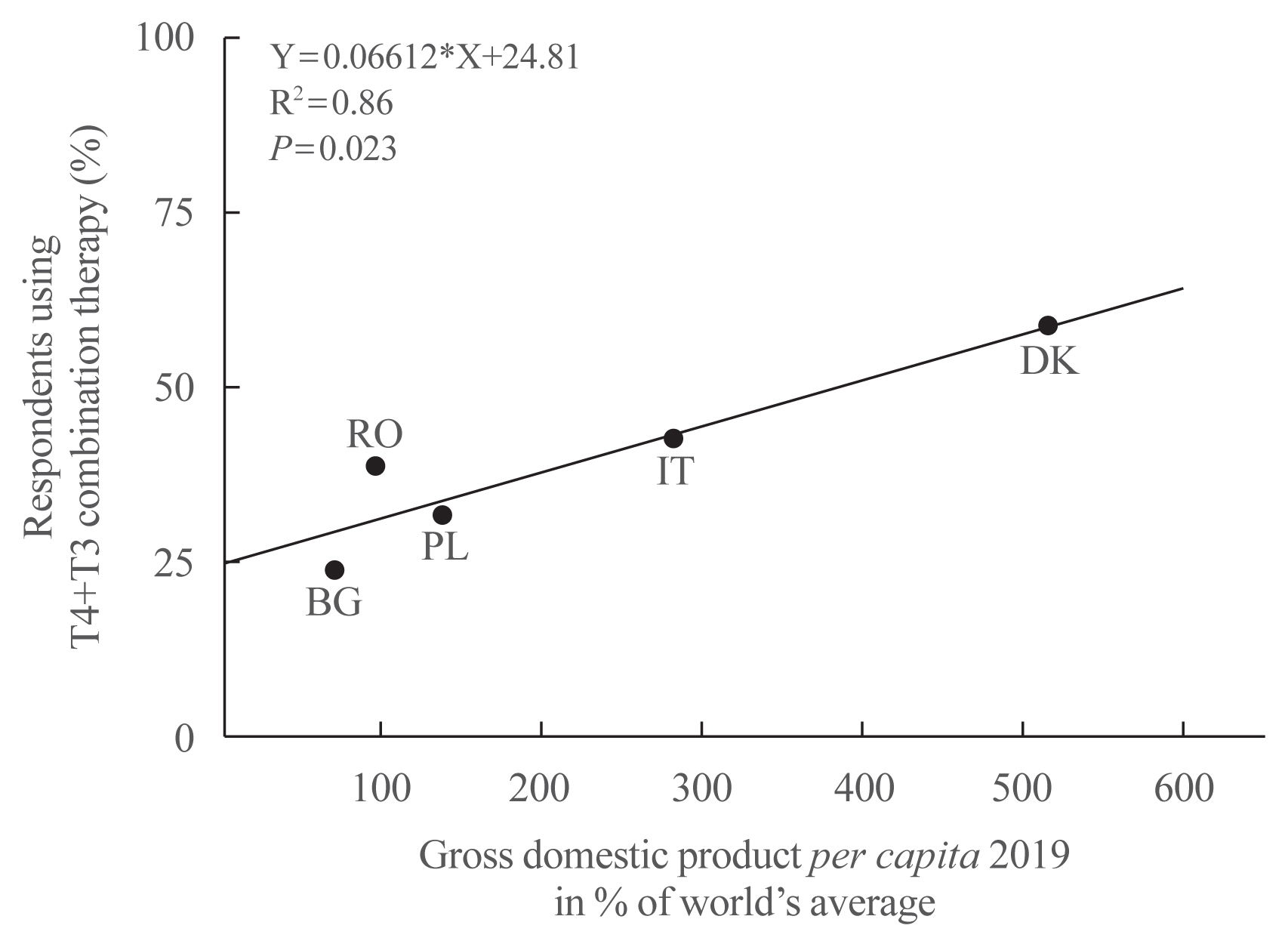
- T4+T3 Combination Therapy: An Unsolved Problem of Increasing Magnitude and Complexity
- Wilmar M. Wiersinga
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):938-951. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.501
- 8,815 View
- 332 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Thyroxine (T4)+triiodothyronine (T3) combination therapy can be considered in case of persistent symptoms despite normal serum thyroid stimulating hormone in levothyroxine (LT4)-treated hypothyroid patients. Combination therapy has gained popularity in the last two decades, especially in countries with a relatively high gross domestic product. The prevalence of persistent symptoms has also increased; most frequent are complaints about energy levels and fatigue (80% to 90%), weight management (70% to 75%), memory (60% to 80%), and mood (40% to 50%). Pathophysiological explanations for persistent problems are unrealistic patient expectations, comorbidities, somatic symptoms, related disorders (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders [DSM-5]), autoimmune neuroinflammation, and low tissue T3. There is fair circumstantial evidence for the latter cause (tissue and specifically brain T3 content is normalized by T4+T3, not by T4 alone), but the other causes are viewed as more relevant in current practice. This might be related to the ‘hype’ that has emerged surrounding T4+T3 therapy. Although more and better-designed trials are needed to validate the efficacy of T4+T3 combination, the management of persistent symptoms should also be directed towards alternative causes. Improving the doctor-patient relationship and including more and better information is crucial. For example, dissatisfaction with the outcomes of T4 treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism can be anticipated as recent trials have demonstrated that LT4 is hardly effective in improving symptoms associated with subclinical hypothyroidism.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of DIO2 and MCT10 Polymorphisms With Persistent Symptoms in LT4-Treated Patients in the UK Biobank
Christian Zinck Jensen, Jonas Lynggaard Isaksen, Gustav Ahlberg, Morten Salling Olesen, Birte Nygaard, Christina Ellervik, Jørgen Kim Kanters
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(2): e613. CrossRef - Quality of life, daily functioning, and symptoms in hypothyroid patients on thyroid replacement therapy: A Dutch survey
Ellen Molewijk, Eric Fliers, Koen Dreijerink, Ad van Dooren, Rob Heerdink
Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology.2024; 35: 100330. CrossRef - Use of thyroid hormones in hypothyroid and euthyroid patients: A survey of members of the Endocrine Society of Australia
Nicole Lafontaine, Suzanne J. Brown, Petros Perros, Enrico Papini, Endre V. Nagy, Roberto Attanasio, Laszlo Hegedüs, John P. Walsh
Clinical Endocrinology.2024; 100(5): 477. CrossRef - Use of Thyroid Hormones in Hypothyroid and Euthyroid Patients: A THESIS questionnaire survey of members of the Irish Endocrine Society
Mohamad Mustafa, Elsheikh Ali, Anne McGowan, Laura McCabe, Laszlo Hegedüs, Roberto Attanasio, Endre V. Nagy, Enrico Papini, Petros Perros, Carla Moran
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2023; 192(5): 2179. CrossRef - Levothyroxine: Conventional and Novel Drug Delivery Formulations
Hanqing Liu, Wei Li, Wen Zhang, Shengrong Sun, Chuang Chen
Endocrine Reviews.2023; 44(3): 393. CrossRef - Re: “Exploring the Genetic Link Between Thyroid Dysfunction and Common Psychiatric Disorders: A Specific Hormonal or a General Autoimmune Comorbidity” by Soheili-Nezhad et al.
Christiaan F. Mooij, A.S. Paul van Trotsenburg
Thyroid®.2023; 33(8): 999. CrossRef - Circulating thyroid hormones and clinical parameters of heart failure in men
Iva Turić, Ivan Velat, Željko Bušić, Viktor Čulić
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of cortical and trabecular bone structure of the mandible in patients using L-Thyroxine
Melike Gulec, Melek Tassoker, Mediha Erturk
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Hypothyroidism on Satisfaction with Care and Treatment and Everyday Living: Results from E-Mode Patient Self-Assessment of Thyroid Therapy, a Cross-Sectional, International Online Patient Survey
Petros Perros, Laszlo Hegedüs, Endre Vezekenyi Nagy, Enrico Papini, Harriet Alexandra Hay, Juan Abad-Madroñero, Amy Johanna Tallett, Megan Bilas, Peter Lakwijk, Alan J. Poots
Thyroid.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association of DIO2 and MCT10 Polymorphisms With Persistent Symptoms in LT4-Treated Patients in the UK Biobank

- Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland
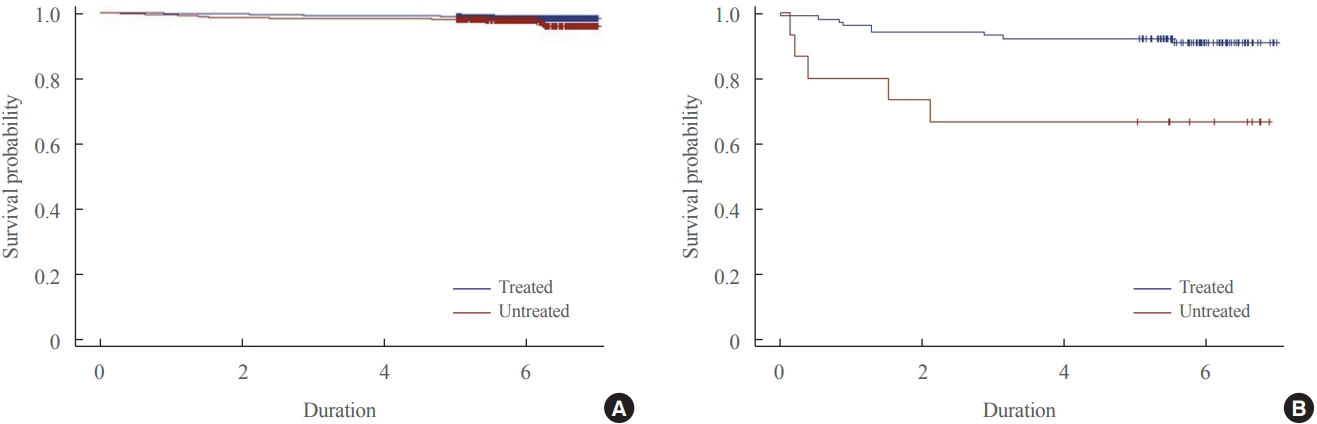
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Descriptive Epidemiology and Survival Analysis of Prolactinomas and Cushing’s Disease in Korea
- Jin Sun Park, Soo Jin Yun, Jung Kuk Lee, So Young Park, Sang Ouk Chin
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):688-696. Published online June 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1000
- 4,692 View
- 132 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Only a few studies have established the epidemiology of prolactinoma and Cushing’s disease in Korea. Furthermore, the incidence of these disease are increasing than before associated with the development of technologies. This study was designed to evaluate the epidemiology of prolactinoma and Cushing’s disease and their survival analysis according to treatment.
Methods
The nationwide, population-based study evaluated incidence and prevalence of prolactinoma and Cushing’s disease using de-identified claims data in The Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service database between 2013 and 2017. The survival analysis investigated regarding treatment over a period of 6 years. A log-rank test and Cox proportional hazard regression analysis were used.
Results
The 6,056 patients with newly diagnosed prolactinoma and 584 patients with Cushing’s disease were recorded between 2013 and 2017. The annual incidence of prolactinoma was 23.5 cases per million, and its prevalence was 82.5 cases per million, and 2.3 cases per million/year and 9.8 cases per million for Cushing’s disease. The survival benefit was insignificant in prolactinoma according to treatment, but treatment of Cushing’s disease ameliorated the survival rate significantly.
Conclusion
Overall, the incidence of prolactinoma and Cushing’s disease was similar with those found previously, but the prevalence of two diseases were inconsistent when compared with the early studies. The present study also proposed necessity of treatment in Cushing’s disease for improving the survival rate. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - Cushing Syndrome
Martin Reincke, Maria Fleseriu
JAMA.2023; 330(2): 170. CrossRef - Clinical Biology of the Pituitary Adenoma
Shlomo Melmed, Ursula B Kaiser, M Beatriz Lopes, Jerome Bertherat, Luis V Syro, Gerald Raverot, Martin Reincke, Gudmundur Johannsson, Albert Beckers, Maria Fleseriu, Andrea Giustina, John A H Wass, Ken K Y Ho
Endocrine Reviews.2022; 43(6): 1003. CrossRef
- Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database

- Thyroid
- Subclinical Hypothyroidism: Prevalence, Health Impact, and Treatment Landscape
- Won Sang Yoo, Hyun Kyung Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):500-513. Published online June 18, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1066

- 9,027 View
- 544 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Subclinical hypothyroidism (sHypo) is defined as normal serum free thyroid hormone levels coexisting with elevated serum thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels. sHypo is a common condition observed in clinical practice with several unique features. Its diagnosis should be based on an understanding of geographic and demographic differences in biochemical criteria versus a global reference range for TSH that is based on the 95% confidence interval of a healthy population. During the differential diagnosis, it is important to remember that a considerable proportion of sHypo cases are transient and reversible in nature; the focus is better placed on persistent or progressive forms, which mainly result from chronic autoimmune thyroiditis. Despite significant evidence documenting the health impacts of sHypo, the effects of levothyroxine treatment (LT4-Tx) in patients with sHypo remains controversial, especially in patients with grade 1 sHypo and older adults. Existing evidence suggests that it is reasonable to refrain from immediate LT4-Tx in most patients if they are closely monitored, except in women who are pregnant or in progressive cases. Future research is needed to further characterize the risks and benefits of LT4-Tx in different patient cohorts.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- THYROID FUNCTION ABNORMALITIES IN PATIENTS WITH CHOLELITHIASIS: A HOSPITAL-BASED CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY
AVANISH KUMAR SAXENA, ANAM FATIMA, KUNDRAPU VEERA VENKATA SIVA, ANUSHKA PARIYA, VAYALAPALLI SYAMA CHINMAYI
Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research.2024; : 138. CrossRef - Subclinical hypothyroidism and clinical outcomes after cardiac surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Michele Dell’Aquila, Camilla S. Rossi, Tulio Caldonazo, Gianmarco Cancelli, Lamia Harik, Giovanni J. Soletti, Kevin R. An, Jordan Leith, Hristo Kirov, Mudathir Ibrahim, Michelle Demetres, Arnaldo Dimagli, Mohamed Rahouma, Mario Gaudino
JTCVS Open.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Relationship between Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness as a Potential Marker of Cardiovascular Risk: A Systematic Review and a Meta-Analysis
Oana-Maria Isailă, Victor Eduard Stoian, Iuliu Fulga, Alin-Ionut Piraianu, Sorin Hostiuc
Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease.2024; 11(4): 98. CrossRef - Subclinical hypothyroidism, outcomes and management guidelines: a narrative review and update of recent literature
Bogumila Urgatz, Salman Razvi
Current Medical Research and Opinion.2023; 39(3): 351. CrossRef - Indicator of thyroid hormones in newborns from mothers with diffuse-endemic goiter
G. T. Makhkamova, Sh. T. Turdieva
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2023; (1): 212. CrossRef - Diagnóstico y tratamiento del hipotiroidismo subclínico en adultos mayores
Debbie Noelia Tebanta Albán, Gabriel Aníbal Hugo Merino, María Valentina Muñoz Arteaga, Ariana Lisseth Vázquez López
Ciencia Digital.2023; 7(1): 6. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Patients with Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Hyun Kyung Chung, Eu Jeong Ku, Won Sang Yoo, Yea Eun Kang, Kyeong Jin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Tae-Yong Kim, Young Joo Park, Chang Ho Ahn, Jee Hee Yoon, Eun Kyung Lee, Jong Min Lee, Eui Dal Jung, Jae Hoon Chung, Yun Jae Chung, Won Bae Kim, Ka Hee Yi, Ho-Cheol Ka
International Journal of Thyroidology.2023; 16(1): 32. CrossRef - Gut microbiota short-chain fatty acids and their impact on the host thyroid function and diseases
María José Mendoza-León, Ashutosh K. Mangalam, Alejandro Regaldiz, Enrique González-Madrid, Ma. Andreina Rangel-Ramírez, Oscar Álvarez-Mardonez, Omar P. Vallejos, Constanza Méndez, Susan M. Bueno, Felipe Melo-González, Yorley Duarte, Ma. Cecilia Opazo, Al
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Human amnion-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve subclinical hypothyroidism by immunocompetence mediating apoptosis inhibition on thyroid cells in aged mice
Chuyu Li, Qiang Rui, Xiaohan Dong, Song Ning, Jing Zhou, Huimin Wu, Chunyan Jiang, Yugui Cui, Jiayin Liu, Jun Jiang, Lianju Qin
Cell and Tissue Research.2023; 394(2): 309. CrossRef - Is Thyroid Dysfunction Associated with Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms? A Population-Based, Nested Case–Control Study from Korea
Hyeree Park, Sun Wook Cho, Sung Ho Lee, Kangmin Kim, Hyun-Seung Kang, Jeong Eun Kim, Aesun Shin, Won-Sang Cho
Thyroid®.2023; 33(12): 1483. CrossRef - The Role of Global Longitudinal Strain in Subclinical Hypothyroid Patients With Heart Failure
Nismat Javed, Vibha Hayagreev, Angel DeLaCruz, Muhammad Saad, Amandeep Singh, Timothy Vittorio
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between shift work and the risk of hypothyroidism in adult male workers in Korea: a cohort study
Seonghyeon Kwon, Yesung Lee, Eunhye Seo, Daehoon Kim, Jaehong Lee, Youshik Jeong, Jihoon Kim, Jinsook Jeong, Woncheol Lee
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Estimation of left ventricular functions in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism: a meta-analysis
Binyi Li, Yong Huang, Zheng Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Five Different Criteria for Diagnosis of Subclinical Hypothyroidism in a Large-Scale Chinese Population
Yan-song Zheng, Sheng-yong Dong, Yan Gong, Jia-hong Wang, Fei Wang, Qiang Zeng
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Cognitive Impairment
Jung-Min Pyun, Young Ho Park, SangYun Kim
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2022; 88(2): 757. CrossRef - Effect of Levothyroxine Supplementation on the Cardiac Morphology and Function in Patients With Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Xichang Wang, Haoyu Wang, Qiuxian Li, Ping Wang, Yumin Xing, Fan Zhang, Jiashu Li, Zhongyan Shan
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(9): 2674. CrossRef - Natural history of subclinical hypothyroidism and prognostic factors for the development of overt hypothyroidism: Tehran Thyroid Study (TTS)
A. Amouzegar, M. Dehghani, H. Abdi, L. Mehran, S. Masoumi, F. Azizi
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2022; 45(12): 2353. CrossRef - Retrospective cohort analysis comparing changes in blood glucose level and body composition according to changes in thyroid‐stimulating hormone level
Hyunah Kim, Da Young Jung, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Jae‐Hyoung Cho, Hyeon Woo Yim, Hun‐Sung Kim
Journal of Diabetes.2022; 14(9): 620. CrossRef - Long working hours and the risk of hypothyroidism in healthy Korean workers: a cohort study
Yesung Lee, Woncheol Lee, Hyoung-Ryoul Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022104. CrossRef
- THYROID FUNCTION ABNORMALITIES IN PATIENTS WITH CHOLELITHIASIS: A HOSPITAL-BASED CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY

- Thyroid
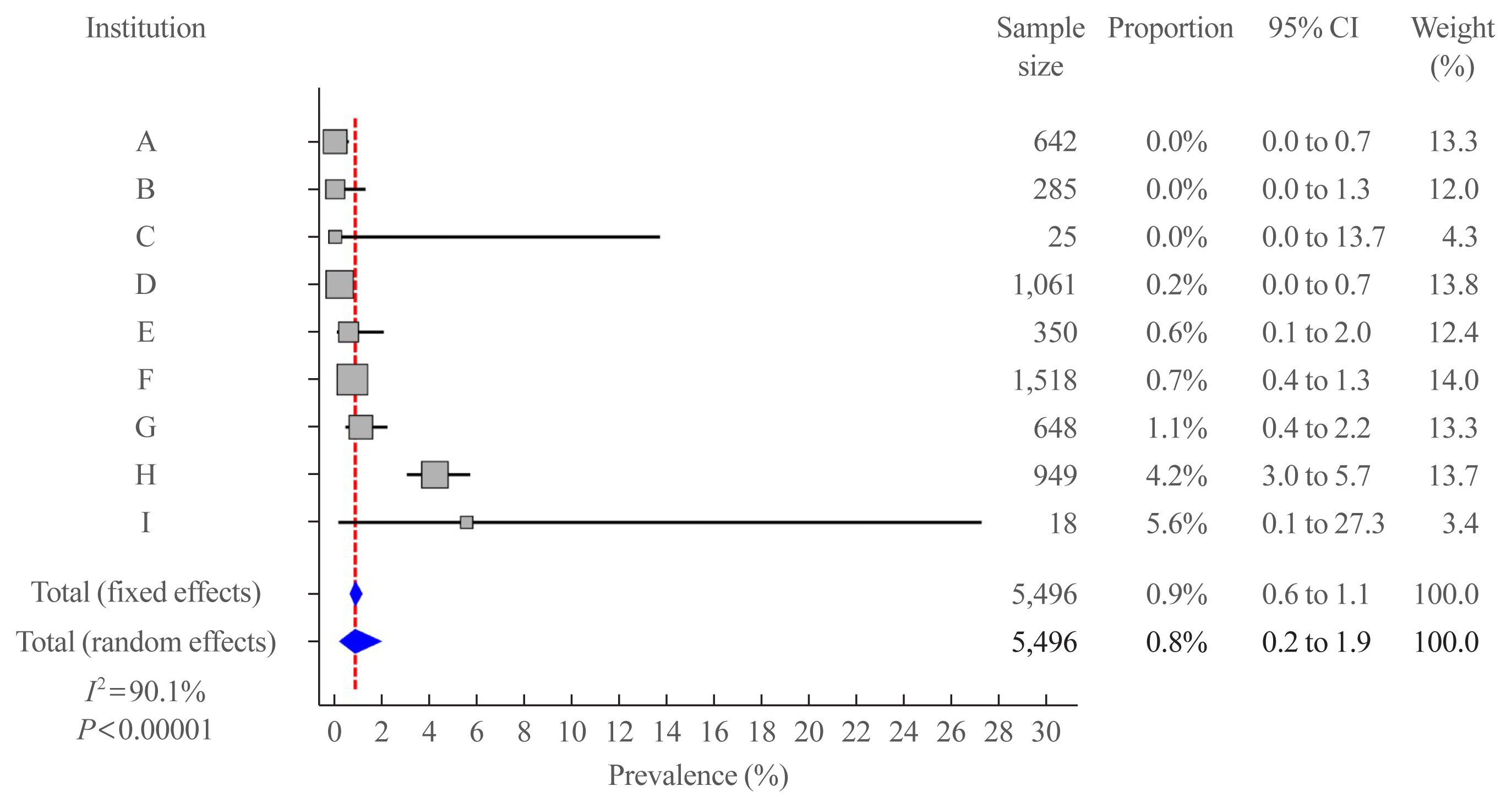
- Clinicopathological Characteristics and Recurrence-Free Survival of Rare Variants of Papillary Thyroid Carcinomas in Korea: A Retrospective Study
- Mijin Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Young Joo Park, Hwa Young Ahn, Hee Sung Kim, Yong Joon Suh, Dughyun Choi, Bu Kyung Kim, Go Eun Yang, Il-Seok Park, Ka Hee Yi, Chan Kwon Jung, Bo Hyun Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):619-627. Published online June 10, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.974
- 4,624 View
- 178 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We aimed to evaluate the clinicopathological features and biological behaviors of Korean thyroid cancer patients with rare variants of papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) to address the ambiguity regarding the prognostic consequences of these variants.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 5,496 patients who underwent thyroid surgery for PTC, between January and December 2012, in nine tertiary hospitals. Rare PTC variants included tall cell (TCV), columnar cell (CCV), diffuse sclerosing (DSV), cribriform-morular (CMV), solid (SV), hobnail, and Warthin-like variants. Recurrence-free survival (RFS) was defined as the time from the date of thyroidectomy until recurrence.
Results
Rare variants accounted for 1.1% (n=63) of the PTC patients; with 0.9% TCV, 0.02% CCV, 0.1% DSV, 0.1% CMV, and 0.1% SV. The mean age of patients and primary tumor size were 42.1±13.1 years and 1.3±0.9 cm, respectively. Extrathyroidal extension and cervical lymph node metastasis were observed in 38 (60.3%) and 37 (58.7%) patients, respectively. Ultrasonographic findings revealed typical malignant features in most cases. During a median follow-up of 7 years, 6.3% of patients experienced a locoregional recurrence. The 5-year RFS rates were 71.4% in patients with DSV or SV, 95.9% for TCV, or CCV, and 100% for other variants. DSV emerged an independent risk factor associated with shorter RFS.
Conclusion
In this multicenter Korean cohort, rare variants accounted for 1.1% of all PTC cases, with TCV being the most frequent subtype. DSV emerged as a significant prognostic factor for RFS. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Serum thyroglobulin testing after thyroid lobectomy in patients with 1–4 cm papillary thyroid carcinoma
Ahreum Jang, Meihua Jin, Chae A Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Yu-Mi Lee, Tae-Yon Sung, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
Endocrine.2023; 81(2): 290. CrossRef - Do Histologically Aggressive Subtypes of Papillary Thyroid
Microcarcinoma have Worse Clinical Outcome than Non-Aggressive Papillary Thyroid
Microcarcinoma Subtypes? A Multicenter Cohort Study
Sayid Shafi Zuhur, Hunkar Aggul, Ugur Avci, Selvinaz Erol, Mazhar Müslüm Tuna, Serhat Uysal, Gulhan Akbaba, Faruk Kilinç, Merve Catak, Sakin Tekin, Ogun Irem Bilen, Beyza Olcay Öztürk, Ecem Bilgehan Erden, Gulsah Elbuken, Halise Cinar Yavuz, Pinar Kadiogl
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2023; 55(05): 323. CrossRef - The Warthin-like variant of papillary thyroid carcinomas: a clinicopathologic analysis report of two cases
Xing Zhao, Yijia Zhang, Pengyu Hao, Mingzhen Zhao, Xingbin Shen
Oncologie.2023; 25(5): 581. CrossRef - A Retrospective Cohort Study with Validation of Predictors of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Outcomes
Ayanthi Wijewardene, Anthony J. Gill, Matti Gild, Diana L. Learoyd, Anthony Robert Glover, Mark Sywak, Stan Sidhu, Paul Roach, Geoffrey Schembri, Jeremy Hoang, Bruce Robinson, Lyndal Tacon, Roderick Clifton-Bligh
Thyroid.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinicopathological Implications of the BRAFV600E Mutation in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma of Ukrainian Patients Exposed to the Chernobyl Radiation in Childhood: A Study for 30 Years After the Accident
Liudmyla Zurnadzhy, Tetiana Bogdanova, Tatiana I. Rogounovitch, Masahiro Ito, Mykola Tronko, Shunichi Yamashita, Norisato Mitsutake, Michael Bolgov, Serhii Chernyshov, Sergii Masiuk, Vladimir A. Saenko
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Serum thyroglobulin testing after thyroid lobectomy in patients with 1–4 cm papillary thyroid carcinoma

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
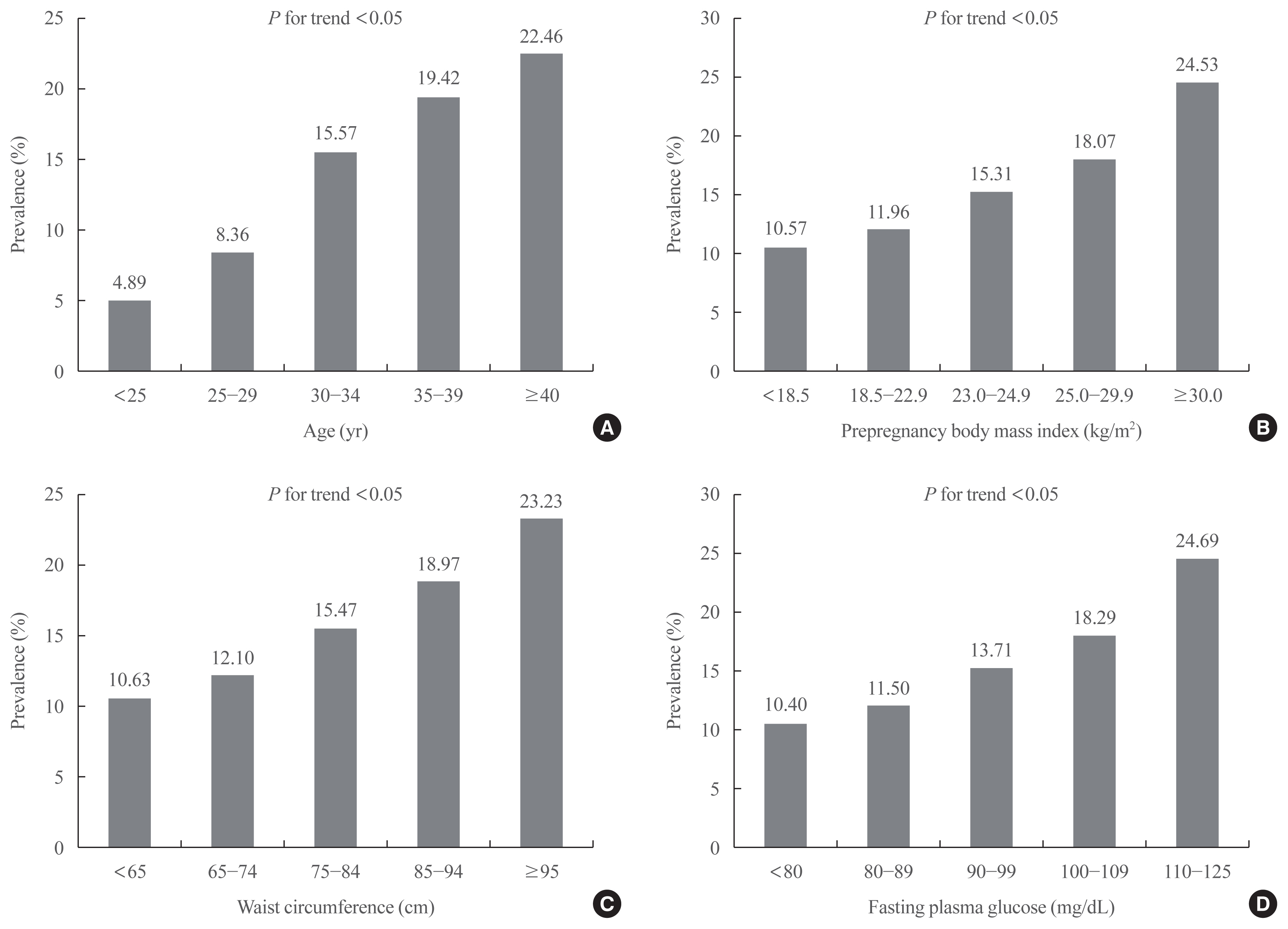
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - The Clinical Characteristics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A National Health Information Database Study
- Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):628-636. Published online May 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.948
- 5,741 View
- 166 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To investigate the clinical characteristics of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in Korea, using a nationwide database.
Methods
We analyzed 417,139 women who gave birth between 2011 and 2015 using the Korean National Health Information Database. They underwent the Korean National Health Screening Program within one year before pregnancy and were not prescribed drugs for diabetes nor diagnosed with diabetes mellitus before 280 days antepartum. Patients with GDM were defined as those who visited the outpatient clinic more than twice with GDM codes.
Results
The prevalence of GDM was 12.70% and increased with increasing maternal age, prepregnancy body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) (P for trend <0.05). As compared with those aged <25 years, the odds ratio for women with GDM aged ≥40 years were 4.804 (95% confidence interval [CI], 4.436 to 5.203) after adjustment for covariates. Women with prepregnancy BMI ≥30 kg/m2 were at 1.898 times (95% CI, 1.736 to 2.075) greater risk for GDM than those with prepregnancy BMI <18.5 kg/m2. Women with WC of ≥95 cm were at 1.158 times (95% CI, 1.029 to 1.191) greater risk for GDM than women with WC of less than 65 cm. High FPG, high income, smoking, and drinking were associated with an elevated risk of GDM.
Conclusion
The prevalence of GDM in Korean women increased up to 12.70% during 2011 to 2015. These data suggest the importance of GDM screening and prevention in high-risk groups in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationships between triglyceride-glucose index and incident gestational diabetes mellitus: a prospective cohort study of a Korean population using publicly available data
Zihe Mo, Changchun Cao, Yong Han, Haofei Hu, Yongcheng He, Xin Zuo
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glucose tolerance test with a single abnormal value as a predictor of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a multicenter retrospective study
Seon Ui Lee, Subeen Hong, Sae Kyung Choi, Su Mi Kim, Jae Eun Shin, Ki Cheol Kil, Yeon Hee Kim, Jeong Ha Wie, Yun Sung Jo, Hyun Sun Ko
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the influence of microbiota on gestational diabetes and its potential as a biomarker
Suresh Bokoliya, Stephanie McClellan, Yanjiao Zhou, Nini Fan
Frontiers in Bacteriology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum afamin levels in predicting gestational diabetes mellitus and preeclampsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Ying Yuan, Wenyin He, Xuejiao Fan, Junyu Liang, Zhen Cao, Lei Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Smoking during pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Kleoniki I. Athanasiadou, Stavroula A. Paschou, Evgenia Papakonstantinou, Vasiliki Vasileiou, Fotini Kanouta, Paraskevi Kazakou, Katerina Stefanaki, Georgia N. Kassi, Theodora Psaltopoulou, Dimitrios G. Goulis, Eleni Anastasiou
Endocrine.2023; 82(2): 250. CrossRef - Association between the triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a second analysis based on data from a prospective cohort study
Yun You, Haofei Hu, Changchun Cao, Yong Han, Jie Tang, Weihua Zhao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of early standardized management on the growth trajectory of offspring with gestational diabetes mellitus at 0–5 years old: a preliminary longitudinal study
Bingbing Guo, Jingjing Pei, Yin Xu, Yajie Wang, Xinye Jiang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Benefits Of Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Pregnancy
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 472. CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications
Joon Ho Moon, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 3. CrossRef - Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 552. CrossRef - Maternal Gestational Diabetes Influences DNA Methylation in the Serotonin System in the Human Placenta
Jae Yen Song, Kyung Eun Lee, Eun Jeong Byeon, Jieun Choi, Sa Jin Kim, Jae Eun Shin
Life.2022; 12(11): 1869. CrossRef - Fetal Abdominal Obesity Detected At 24 to 28 Weeks of Gestation Persists Until Delivery Despite Management of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:547-57)
Kyung-Soo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 966. CrossRef
- Relationships between triglyceride-glucose index and incident gestational diabetes mellitus: a prospective cohort study of a Korean population using publicly available data

- Clinical Study
- The Prevalence and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Adults with Disabilities in Korea
- Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):552-561. Published online July 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.653
- 8,055 View
- 186 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
People with disabilities are at risk of secondary conditions such as diabetes. The aim of this study was to evaluate the prevalence and risk of type 2 diabetes in South Korea, especially among people with all types of disabilities.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional study using data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service, with two disabilityfree controls matched for each participant with disabilities by age and sex. Information regarding the type, severity and grade of disabilities was obtained based on the National Disability Registry. Diagnosis of type 2 diabetes was defined according to the following criteria: presence of International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification codes E11, E12, E13, or E14 and claims for at least one oral anti-diabetic agent or insulin at baseline, or fasting glucose level ≥126 mg/dL.
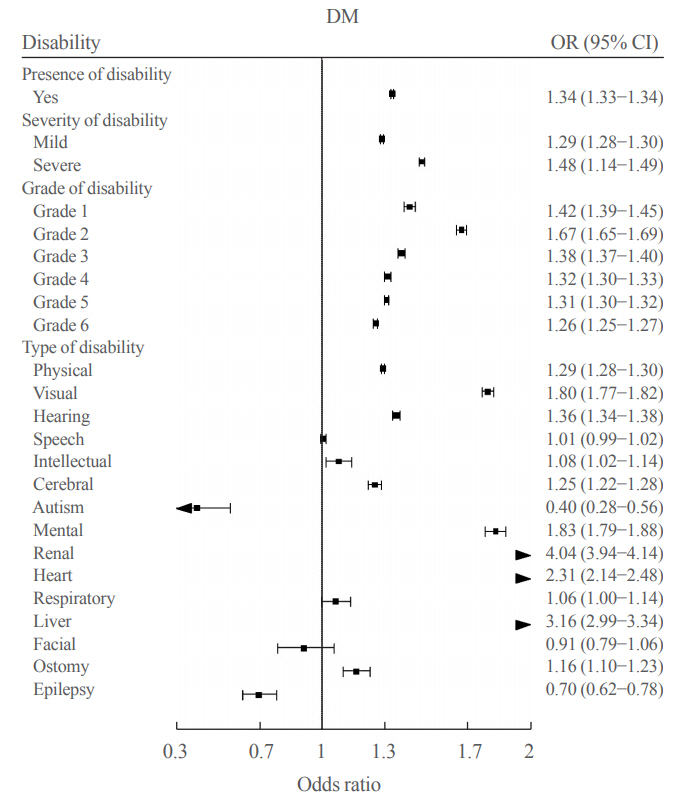
Results
We included 1,297,806 participants with disabilities and 2,943,719 control. Out of 4,241,525 participants, 841,990 (19.9%) were diagnosed with diabetes. The prevalence of diabetes was higher in the disability group compared with individuals without disabilities (23.1% vs. 18.4%). The odds of having diabetes was higher in the disability group compared with the control group (adjusted odds ratio, 1.34; 95% confidence interval, 1.33 to 1.34). The results showed higher prevalence of diabetes in the mildly disabled group (23.2%) than in the severely disabled group (22.7%).
Conclusion
The prevalence and risk of diabetes were higher in people with disabilities compared with the general population. Physicians and public health authorities should focus on people with disabilities for proper diabetes management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Widening disparities in the national prevalence of diabetes mellitus for people with disabilities in South Korea
I. Hwang, S.Y. Kim, Y.Y. Kim, J.H. Park
Public Health.2024; 226: 173. CrossRef - Bipolar disorder and the risk of cardiometabolic diseases, heart failure, and all-cause mortality: a population-based matched cohort study in South Korea
You-Bin Lee, Hyewon Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Dongwoo Kang, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim, Hong Jin Jeon, Kyu Yeon Hur
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychotic Disorders and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases, and All-Cause Mortality: A Population-Based Matched Cohort Study
You-Bin Lee, Hyewon Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Dongwoo Kang, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim, Hong Jin Jeon, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 122. CrossRef - Pathways linking health literacy to self-care in diabetic patients with physical disabilities: A moderated mediation model
Hye Jin Nam, Ju Young Yoon, Wen-Jun Tu
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(3): e0299971. CrossRef - Dysphagia Requiring Medical Attention in Parkinson’s Disease: A Korean Population-Based Study
Seungwoo Cha, Won Kee Chang, Hee-Mun Cho, Kyungdo Han, Nam-Jong Paik, Sohyun Kwon, Won-Seok Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Disparities in diabetes-related avoidable hospitalization among diabetes patients with disability using a nationwide cohort study
Hin Moi Youn, Dong-Woo Choi, Sung-In Jang, Eun-Cheol Park
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Disability type–specific mortality patterns and life expectancy among disabled people in South Korea using 10-year combined data between 2008 and 2017
Jinwook Bahk, Hee-Yeon Kang, Young-Ho Khang
Preventive Medicine Reports.2022; 29: 101958. CrossRef - Cholecystectomy reduces the risk of myocardial and cerebral infarction in patients with gallstone-related infection
Seon Mee Park, Hyun Jung Kim, Tae Uk Kang, Heather Swan, Hyeong Sik Ahn
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Nationwide trends in the incidence of tuberculosis among people with disabilities in Korea:
a nationwide serial cross-sectional study
Jinsoo Min, So Young Kim, Jong Eun Park, Yeon Yong Kim, Jong Hyock Park
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022098. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to impaired fasting glucose and future risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Eun Sil Koh, Oak-Kee Hong, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 175: 108799. CrossRef - Diabetes in People with Disabilities: a Call for Action
Inha Jung, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2021; 3(4): 82. CrossRef
- Widening disparities in the national prevalence of diabetes mellitus for people with disabilities in South Korea

- Clinical Study
- Epidemiology and Prognosis of Pheochromocytoma/Paraganglioma in Korea: A Nationwide Study Based on the National Health Insurance Service
- Jung Hee Kim, Hyemi Moon, Junghyun Noh, Juneyoung Lee, Sin Gon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):157-164. Published online March 19, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.157
- 7,234 View
- 172 Download
- 26 Web of Science
- 24 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas (PPGLs) are rare endocrine tumors originating from chromaffin cells. PPGLs are associated with a high mortality rate and several complications. To date, no epidemiological studies have been conducted on PPGLs in Asia. This study aimed to investigate the epidemiology and prognosis of PPGLs in Korea using nationwide data.
Methods Using the National Health Insurance Service Database, subjects with a principal diagnosis of PPGLs on two or more occasions between 2003 and 2014 who satisfied the operational definition of PPGLs were included. Incidence, prevalence, complications, metastasis, and mortality were investigated.
Results In total, 1048 subjects with a mean age of 47.6±16.1 years were included. There was no sex preponderance. The overall prevalence of PPGLs was 2.13 per 100,000 persons, and the overall age-standardized incidence rate was 0.18 per 100,000 person-years. Malignant PPGLs accounted for 17.7% (185 of 1,048) of cases, and 94 subjects exhibited metastasis at the time of diagnosis. Among initially non-metastatic PPGLs, 9.5% (nine of 954) eventually metastasized after a mean duration of 78.1±41.4 months. The 5-year survival rates for non-metastatic and metastatic PPGLs at diagnosis were 97% and 84%, respectively. Multivariable Cox regression models adjusted for covariates showed that metastatic PPGLs were associated with a 2.40-fold higher risk of mortality than non-metastatic PPGLs (95% confidence interval, 1.38 to 4.17;
P =0.002).Conclusion PPGLs are rare in Korea, and the prognosis of these endocrine tumors varies depending on whether they are benign or malignant. This epidemiological study paves the way for further research on PPGLs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Management of Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas: A Guide for the Clinician
Sona Sharma, Lauren Fishbein
Endocrine Practice.2023; 29(12): 999. CrossRef - Pheochromocytoma: a changing perspective and current concepts
Andreas Kiriakopoulos, Periklis Giannakis, Evangelos Menenakos
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Image-Guided Precision Medicine in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas
Gildas Gabiache, Charline Zadro, Laura Rozenblum, Delphine Vezzosi, Céline Mouly, Matthieu Thoulouzan, Rosine Guimbaud, Philippe Otal, Lawrence Dierickx, Hervé Rousseau, Christopher Trepanier, Laurent Dercle, Fatima-Zohra Mokrane
Cancers.2023; 15(18): 4666. CrossRef - Trends in the incidence of adrenocortical carcinoma and pheochromocytoma/paraganglioma in Taiwan
Chung-Hsin Tsai, Tun-Sung Huang, Shih-Ping Cheng
Formosan Journal of Surgery.2023; 56(5): 147. CrossRef - An open-label, single-arm, multi-center, phase II clinical trial of single-dose [131I]meta-iodobenzylguanidine therapy for patients with refractory pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma
Anri Inaki, Tohru Shiga, Yoshito Tsushima, Megumi Jinguji, Hiroshi Wakabayashi, Daiki Kayano, Norihito Akatani, Takafumi Yamase, Yuji Kunita, Satoru Watanabe, Tomo Hiromasa, Hiroshi Mori, Kenji Hirata, Shiro Watanabe, Tetsuya Higuchi, Hiroyasu Tomonaga, S
Annals of Nuclear Medicine.2022; 36(3): 267. CrossRef - Pheochromocytomas and Abdominal Paragangliomas: A Practical Guidance
Jan Calissendorff, Carl Christofer Juhlin, Irina Bancos, Henrik Falhammar
Cancers.2022; 14(4): 917. CrossRef - Characteristics of Intraoperative Hemodynamic Instability in Postoperatively Diagnosed Pheochromocytoma and Sympathetic Paraganglioma Patients
Jung Hee Kim, Hyung-Chul Lee, Su-jin Kim, Kyu Eun Lee, Kyeong Cheon Jung
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Change of Computed Tomography-Based Body Composition after Adrenalectomy in Patients with Pheochromocytoma
Yousun Ko, Heeryoel Jeong, Seungwoo Khang, Jeongjin Lee, Kyung Won Kim, Beom-Jun Kim
Cancers.2022; 14(8): 1967. CrossRef - Systematic Review: Incidence of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma Over 70 Years
Abdul Rahman Al Subhi, Veronica Boyle, Marianne S Elston
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidence and risk factors for myocardial injury after laparoscopic adrenalectomy for pheochromocytoma: A retrospective cohort study
Ling Lan, Qian Shu, Chunhua Yu, Lijian Pei, Yuelun Zhang, Li Xu, Yuguang Huang
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics of Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas with Negative Catecholamines
Lin Zhao, Xiaoran Zhang, Xu Meng, Ting Zhang, Hua Fan, Qiongyu Zhang, Yecheng Liu, Xianliang Zhou, Huadong Zhu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(19): 5583. CrossRef - A midline ectopic paraganglioma
Christina SANT FOURNIER, Matthias FARRUGIA, Kimberley PACE, Christian CAMENZULI, Alexander R. ATTARD
Chirurgia.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-Selective Alpha-Blockers Provide More Stable Intraoperative Hemodynamic Control Compared with Selective Alpha1-Blockers in Patients with Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study with a Propensity Score-Matched Ana
Yang Yang, Jie Zhang, Liqun Fang, Xue Jia, Wensheng Zhang
Drug Design, Development and Therapy.2022; Volume 16: 3599. CrossRef - Incidence and Clinical Presentation of Pheochromocytoma and Sympathetic Paraganglioma: A Population-based Study
Andreas Ebbehoj, Kirstine Stochholm, Sarah Forslund Jacobsen, Christian Trolle, Peter Jepsen, Maciej Grzegorz Robaczyk, Åse Krogh Rasmussen, Ulla Feldt-Rasmussen, Reimar Wernich Thomsen, Esben Søndergaard, Per Løgstrup Poulsen
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 106(5): e2251. CrossRef - Determinants of anxiety and depression among pheochromocytoma patients
Siming Jia, Chengbai Li, Zhuqing Lei, Qiang Xia, Yuqing Jiang
Medicine.2021; 100(3): e24335. CrossRef - Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma with negative results for urinary metanephrines show higher risks for metastatic diseases
Akiyuki Kawashima, Masakatsu Sone, Nobuya Inagaki, Kentaro Okamoto, Mika Tsuiki, Shoichiro Izawa, Michio Otsuki, Shintaro Okamura, Takamasa Ichijo, Takuyuki Katabami, Yoshiyu Takeda, Takanobu Yoshimoto, Mitsuhide Naruse, Akiyo Tanabe
Endocrine.2021; 74(1): 155. CrossRef - Diagnosis for Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: A Joint Position Statement of the Korean Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma Task Force
Eu Jeong Ku, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Chang Ho Ahn, Kyung Ae Lee, Seung Hun Lee, You-Bin Lee, Kyeong Hye Park, Yun Mi Choi, Namki Hong, A Ram Hong, Sang-Wook Kang, Byung Kwan Park, Moon-Woo Seong, Myungshin Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Chan
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(2): 322. CrossRef - Clinical Presentation and Perioperative Management of Pheochromocytomas and Paragangliomas: A 4-Decade Experience
Thomas Uslar, Ignacio F San Francisco, Roberto Olmos, Stefano Macchiavelo, Alvaro Zuñiga, Pablo Rojas, Marcelo Garrido, Alvaro Huete, Gonzalo P Mendez, Ignacio Cortinez, José Tomás Zemelman, Joaquín Cifuentes, Fernando Castro, Daniela Olivari, José Miguel
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Pheochromocytoma
Zhonghua Liu, Junsheng Ma, Camilo Jimenez, Miao Zhang
American Journal of Surgical Pathology.2021; 45(9): 1155. CrossRef - Perioperative hemodynamic instability in pheochromocytoma and sympathetic paraganglioma patients
Jung Hee Kim, Hyung-Chul Lee, Su-jin Kim, Soo Bin Yoon, Sung Hye Kong, Hyeong Won Yu, Young Jun Chai, June Young Choi, Kyu Eun Lee, Kwang-Woong Lee, Seung-Kee Min, Chan Soo Shin, Kyu Joo Park
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in the Nociception Level Index During Surgical Resection of Paragangliomas: A Case Report
Rita Saynhalath, Umar H. Khan, Gijo Alex, Joseph T. Murphy, Peter Szmuk
A&A Practice.2021; 15(11): e01542. CrossRef - Hypertension Cure and Reducing Pill Burden after Adrenalectomy for Endocrine Hypertension of Adrenal Origin: A Comparative Study from an Asian and UK Cohort
Kee Y Ngiam, Ciaran Durand, Titus C Vasciuc, Chia H Tai, Raluca Orpean, Fiona Eatock, Mehak Mahipal, Tan W Boon
World Journal of Endocrine Surgery.2021; 13(1): 9. CrossRef - A Brief Overview of the Epidemiology of Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma in Korea
Yun Mi Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 95. CrossRef
- Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Metabolic Syndrome and Insulin Resistance Syndrome among Infertile Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study from Central Vietnam
- Minh Tam Le, Vu Quoc Huy Nguyen, Quang Vinh Truong, Dinh Duong Le, Viet Nguyen Sa Le, Ngoc Thanh Cao
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(4):447-458. Published online November 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.4.447
- 4,278 View
- 76 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most common endocrinopathies among reproductive-age women. Its metabolic features often overlap with those associated with metabolic syndrome (MS) and insulin resistance syndrome (IRS). The objective of this study was to determine the prevalence and predictors of MS and IRS in infertile Vietnamese women with PCOS.
Methods A cross-sectional study was conducted at a tertiary fertility centre at Hue University Hospital from June 2016 to November 2017. A total of 441 infertile women diagnosed with PCOS based on the revised 2003 Rotterdam consensus criteria were enrolled. MS and IRS were defined based on the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/American Heart Association Adult Treatment Panel III 2005 and American College of Endocrinology IRS 2003 criteria, respectively. Complete clinical and biochemical measurements of 318 women were available for analysis. Independent predictors of MS and IRS were identified using multivariate logistic regression.
Results The overall prevalence of MS and IRS in women with PCOS was 10.4% and 27.0%, respectively. We identified older age (>30 years) and obesity as independent predictors of MS and IRS. Elevated anti-Müllerian hormone levels increased the risk of IRS, but not that of MS.
Conclusion MS and IRS are prevalent disorders among infertile Vietnamese women with PCOS. PCOS is not solely a reproductive problem. Screening and early intervention for MS and/or IRS based on anthropometric, metabolic, and reproductive hormone risk factors should be an integral part of fertility care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Role of the tripartite motif‐containing (TRIM) family of proteins in insulin resistance and related disorders
Jianrong Chen, Xianjie Feng, Xu Zhou, Yong Li
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(1): 3. CrossRef - Effect of pharmacological interventions on lipid profiles and C‐reactive protein in polycystic ovary syndrome: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Mohammed A. Abdalla, Najeeb Shah, Harshal Deshmukh, Amirhossein Sahebkar, Linda Östlundh, Rami H. Al‐Rifai, Stephen L. Atkin, Thozhukat Sathyapalan
Clinical Endocrinology.2022; 96(4): 443. CrossRef - A Cross-Sectional Study of Serum Ferritin Levels in Vietnamese Adults with Metabolic Syndrome
Thua Nguyen Tran, Huu Dang Tran, Thanh Tung Tran-Huu, Duc Minh Tran, Quang Nhat Tran
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 1517. CrossRef - The effects of metformin on clinical features, endocrine and metabolic profiles of infertile women with polycystic ovary syndrome
Sa Le Viet
Journal of Clinical Medicine- Hue Central Hospital.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Uric acid metabolism in polycystic ovary syndrome
Yan-Nan Liu, Hai Luo, Xuan Che, Hui Peng, Ming Li, Ke-Xuan Liu
Clinica Chimica Acta.2021; 517: 74. CrossRef - PREVALENCE OF METABOLIC SYNDROME AND INSULIN RESISTANCE AMONG PCOS WOMEN ATTENDING TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL IN NORTH INDIAN POPULATION.
Anita R Bhatia, Peyir Bagra, Jyotsna Suri, Rajni Dawar
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2021; : 35. CrossRef - “Obesity and Insulin Resistance” Is the Component of the Metabolic Syndrome Most Strongly Associated with Oxidative Stress
Grzegorz K. Jakubiak, Kamila Osadnik, Mateusz Lejawa, Tadeusz Osadnik, Marcin Goławski, Piotr Lewandowski, Natalia Pawlas
Antioxidants.2021; 11(1): 79. CrossRef - Correlation between serum AMH levels and cardiometabolic indices in PCOS women
Subarna Mitra, GautomK Saharia, SaubhagyaK Jena
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 25(6): 545. CrossRef - Predicting Risk of Insulin Resistance in a Chinese Population with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Designing and Testing a New Predictive Nomogram
Feng Jiang, Ke Wei, Wenjun Lyu, Chuyan Wu
BioMed Research International.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Association of the Genetic Polymorphisms rs6259 and rs727428 of the SHBG Gene with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Risk: A Meta-Analysis
Xihong Liao, Shujun Cao
Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers.2020; 24(8): 492. CrossRef - The relationship between glomerular filtration rate, and metabolic and inflammatory parameters in obese and non-obese patients with polycystic ovary syndrome
Mustafa Can, Cevdet Duran, Ibrahim Guney, Halis Elmas, Mehmet Ayhan, Said Sami Erdem
Clínica e Investigación en Arteriosclerosis.2020; 32(6): 256. CrossRef - Effect of Central Obesity and Hyperandrogenism on Selected Inflammatory Markers in Patients with PCOS: A WHtR-Matched Case-Control Study
Małgorzata Kałużna, Magdalena Człapka-Matyasik, Katarzyna Wachowiak-Ochmańska, Jerzy Moczko, Jolanta Kaczmarek, Adam Janicki, Katarzyna Piątek, Marek Ruchała, Katarzyna Ziemnicka
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(9): 3024. CrossRef - The relationship between glomerular filtration rate, and metabolic and inflammatory parameters in obese and non-obese patients with polycystic ovary syndrome
Mustafa Can, Cevdet Duran, Ibrahim Guney, Halis Elmas, Mehmet Ayhan, Said Sami Erdem
Clínica e Investigación en Arteriosclerosis (English Edition).2020; 32(6): 256. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia involvement in the development of polycystic ovary syndrome
Qi Liu, Yuan-jie Xie, Li-hua Qu, Meng-xia Zhang, Zhong-cheng Mo
Taiwanese Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.2019; 58(4): 447. CrossRef
- Role of the tripartite motif‐containing (TRIM) family of proteins in insulin resistance and related disorders

- Thyroid
- Prevalence and Annual Incidence of Thyroid Disease in Korea from 2006 to 2015: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- Hyemi Kwon, Jin-hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Jung-Hwan Cho, Da Young Lee, Ji Min Han, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(2):260-267. Published online June 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.2.260
- 6,314 View
- 128 Download
- 36 Web of Science
- 37 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background The incidence of thyroid nodules has increased worldwide in recent years. Thyroid dysfunction is a potential risk factor for hypercholesterolemia, cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, arrhythmia, and neuropsychiatric disease. This study investigated the prevalence and annual incidence of thyroid nodules, hypothyroidism, and hyperthyroidism in Koreans.
Methods In this nationwide population-based cohort study, 51,834,660 subjects were included using the National Health Information database from 2006 to 2015, after the exclusion of subjects with thyroid cancer.
Results The prevalence in Korea in 2015 of thyroid nodules, hypothyroidism in patients taking thyroid hormone, and hyperthyroidism in patients undergoing treatment was 15.82/1,000 population, 15.94/1,000 population, and 2.76/1,000 population, respectively. All these diseases were more prevalent among women than among men. The number of incident cases of these three thyroid diseases steadily increased from 2006 to 2012, and then decreased through 2015. The incidence of thyroid nodules, hypothyroidism treated with thyroid hormone, and treated hyperthyroidism was 6.79/1,000 population, 1.76/1,000 population, and 0.55/1,000 population, respectively, in Korea in 2015. The use of methimazole continuously increased, from 33% of total antithyroid drug prescriptions in 2006 to 74.4% in 2015, and it became the most frequently prescribed antithyroid drug in Korea. In contrast, the use of propylthiouracil continuously decreased.
Conclusion This was the first nationwide study of the prevalence and annual incidence of thyroid nodules, hypothyroidism, and hyperthyroidism to take into account recent changes and to include the current status of patients receiving treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- New-onset atrial fibrillation in seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: association with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs treatment
Hyung Woo Kim, Minkyung Han, Inkyung Jung, Sung Soo Ahn
Rheumatology.2024; 63(3): 630. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer Among Young Adults in South Korea
Hyemi Kwon, Kyung-Do Han, Sun Joon Moon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(3): e1095. CrossRef - Endocrine and metabolic comorbidities in primary cicatricial alopecia: A nationwide population‐based study
Da‐Ae Yu, Seong Rae Kim, Soo Ick Cho, Ohsang Kwon
The Journal of Dermatology.2024; 51(3): 429. CrossRef - Risk of non-thyroidal autoimmune diseases in patients with Graves’ disease: a nationwide retrospective cohort study
Seo Young Sohn, Jiyeon Ahn, Min Kyung Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee, Ji-Won Kwon, Ji-Min Kweon, Ju-Yeun Lee
Rheumatology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer Risk in Graves Disease with Radioactive131I Treatment: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Kyeong Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Kyoung Jin Kim, Eyun Song, Ji Hee Yu, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim
Journal of Nuclear Medicine.2024; : jnumed.123.266531. CrossRef - Long-term effect of thyrotropin-binding inhibitor immunoglobulin on atrial fibrillation in euthyroid patients
Jung-Chi Hsu, Kang-Chih Fan, Ting-Chuan Wang, Shu-Lin Chuang, Ying-Ting Chao, Ting-Tse Lin, Kuan-Chih Huang, Lian-Yu Lin, Lung-Chun Lin
Endocrine Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Myotonic dystrophy type 1 in South Korea: a comprehensive analysis of cancer and comorbidity risks
Incheol Seo, Jin-Mo Park
Neurological Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of ITM2A rs1751094 polymorphism on X chromosome in Korean pediatric patients with autoimmune thyroid disease
Won K. Cho, In‐Cheol Baek, Sung E. Kim, Mirae Kim, Tai‐Gyu Kim, Byung‐Kyu Suh
Immunity, Inflammation and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Preoperative Risk Stratification of Follicular-patterned Thyroid Lesions on Core Needle Biopsy by Histologic Subtyping and RAS Variant-specific Immunohistochemistry
Meejeong Kim, Sora Jeon, Chan Kwon Jung
Endocrine Pathology.2023; 34(2): 247. CrossRef - Cancer and Mortality Risks of Graves’ Disease in South Korea Based on National Data from 2010 to 2019
Young Ju Choi, Kyungdo Han, Won Kyoung Cho, Min Ho Jung, Byung-Kyu Suh
Clinical Epidemiology.2023; Volume 15: 535. CrossRef - Acromegaly and the long-term fracture risk of the vertebra and hip: a national cohort study
Hyemi Kwon, Kyung-Do Han, Bong-Sung Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Osteoporosis International.2023; 34(9): 1591. CrossRef - Association of Thyroid Hormone Medication Adherence With Risk of Dementia
Saemi Han, Seogsong Jeong, Seulggie Choi, Sun Jae Park, Kyae Hyung Kim, Gyeongsil Lee, Yoosun Cho, Joung Sik Son, Sang Min Park
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 109(1): e225. CrossRef - Increased risk of incident gout in patients with hyperthyroidism: a nationwide retrospective cohort study
Ju-Yeun Lee, So-Yeon Park, Seo Young Sohn
Rheumatology International.2023; 44(3): 451. CrossRef - The Current Status of Hyperthyroidism in Korea
Hyemi Kwon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 392. CrossRef - Prevalence, Treatment Status, and Comorbidities of Hyperthyroidism in Korea from 2003 to 2018: A Nationwide Population Study
Hwa Young Ahn, Sun Wook Cho, Mi Young Lee, Young Joo Park, Bon Seok Koo, Hang-Seok Chang, Ka Hee Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 436. CrossRef - Comprehensive analysis of chemokine gene polymorphisms in Korean children with autoimmune thyroid disease
Chungwoo Shin, In-Cheol Baek, Won Kyoung Cho, Tai-Gyu Kim, Byung-Kyu Suh
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of the status of treatment of benign thyroid diseases — a public health problem aggravated in the COVID-19 pandemic era
Giulianno Molina Melo, Antonio José Gonçalves, Fernando Walder, Carolina Ferraz, Murilo Catafesta Neves, Marcio Abrahão, Onivaldo Cervantes
Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology.2022; 88(6): 982. CrossRef - Graves’ disease and the risk of Parkinson’s disease: a Korean population-based study
Yoon Young Cho, Bongseong Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Jinyoung Youn, Ji Oh Mok, Chul-Hee Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Kyungdo Han, Tae Hyuk Kim
Brain Communications.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Graves’ Disease and the Risk of End-Stage Renal Disease: A Korean Population-Based Study
Yoon Young Cho, Bongseong Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Hye Ryoun Jang, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chan-Hee Jung, Jae Hyeon Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Kyungdo Han, Tae Hyuk Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 281. CrossRef - Incidence of hypothyroidism after treatment for breast cancer: A Korean population-based study
Jongmoo Park, Choongrak Kim, Yongkan Ki, Wontaek Kim, Jiho Nam, Donghyun Kim, Dahl Park, Hosang Jeon, Dong Woon Kim, Ji Hyeon Joo, Claudio Andaloro
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(6): e0269893. CrossRef - Genome-wide association study of hyperthyroidism based on electronic medical record from Taiwan
Ting-Yuan Liu, Wen-Ling Liao, Tzu-Yuan Wang, Chia-Jung Chan, Jan-Gowth Chang, Yu-Chia Chen, Hsing-Fang Lu, Hsien-Hui Yang, Shih-Yin Chen, Fuu-Jen Tsai
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Graves’ disease, its treatments, and the risk of atrial fibrillation: A Korean population-based study
Yoon Young Cho, Bongseong Kim, Dughyun Choi, Chul-Hee Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Jee Soo Kim, Seung-Jung Park, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung, Kyungdo Han, Tae Hyuk Kim
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of autoimmune diseases in recurrent aphthous ulcer patients: A nationwide population study
Young Chan Lee, Su Jin Jeong, Young‐Gyu Eun, Ran Song, In‐Hwan Oh
Oral Diseases.2021; 27(6): 1443. CrossRef - Hyperthyroidism Prevalence in China After Universal Salt Iodization
Chuyuan Wang, Yongze Li, Di Teng, Xiaoguang Shi, Jianming Ba, Bing Chen, Jianling Du, Lanjie He, Xiaoyang Lai, Yanbo Li, Haiyi Chi, Eryuan Liao, Chao Liu, Libin Liu, Guijun Qin, Yingfen Qin, Huibiao Quan, Bingyin Shi, Hui Sun, Xulei Tang, Nanwei Tong, Gui
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comorbidity network analysis related to obesity in middle-aged and older adults: findings from Korean population-based survey data
Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
Epidemiology and Health.2021; 43: e2021018. CrossRef - Prevalence of Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism and its Correlation with Serum Antithyroglobulin among patients in Kirkuk-Iraq
Sabah Mohammed Salih, Wijdan Abdullameer Kamel, Mohammed Talat Abbas, Kasim Sakran Abass
Journal Of Advanced Pharmacy Education And Research.2021; 11(2): 57. CrossRef - A nationwide study of patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance with a 10-year follow-up in South Korea
Ka-Won Kang, Ji Eun Song, Byung-Hyun Lee, Min Ji Jeon, Eun Sang Yu, Dae Sik Kim, Se Ryeon Lee, Hwa Jung Sung, Chul Won Choi, Yong Park, Byung Soo Kim
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidence and Mortality of Myocardial Infarction and Stroke in Patients with Hyperthyroidism: A Nationwide Cohort Study in Korea
Hyun Jung Kim, Taeuk Kang, Min Ji Kang, Hyeong Sik Ahn, Seo Young Sohn
Thyroid.2020; 30(7): 955. CrossRef - Vitamin D supplementation does not prevent the recurrence of Graves’ disease
Yoon Young Cho, Yun Jae Chung
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Binding and Activity of Tetrabromobisphenol A Mono-Ether Structural Analogs to Thyroid Hormone Transport Proteins and Receptors
Xiao-Min Ren, Linlin Yao, Qiao Xue, Jianbo Shi, Qinghua Zhang, Pu Wang, Jianjie Fu, Aiqian Zhang, Guangbo Qu, Guibin Jiang
Environmental Health Perspectives.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome and its components in Chinese patients with a range of thyroid-stimulating hormone concentrations
Kun Tang, Qiao Zhang, Nian-chun Peng, Miao Zhang, Shu-jing Xu, Hong Li, Ying Hu, Chun-ju Xue, Li-xin Shi
Journal of International Medical Research.2020; 48(11): 030006052096687. CrossRef - The Association of Overt and Subclinical Hyperthyroidism with the Risk of Cardiovascular Events and Cardiovascular Mortality: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Cohort Studies
Seo Young Sohn, Eunyoung Lee, Min Kyung Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(4): 786. CrossRef - Prevalence of Thyroid Disease in Patients Surgically Treated for Pituitary Disease
Kim, Cho, Ku, Jung, Moon, Kim, Shin, Kim, Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(8): 1142. CrossRef - Association of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone and Thyroid Hormones with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Euthyroid Children and Adolescents Aged 10–18 Years: A Population-Based Study
Cheol Gyu Ma, Young Suk Shim
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Weight change is significantly associated with risk of thyroid cancer: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Hyemi Kwon, Kyung-Do Han, Cheol-Young Park
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the relationship of subclinical hypothyroidism with metabolic syndrome and its components in adolescents: a population-based study
Min-Kyung Lee, Yoo Mee Kim, Seo-Young Sohn, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Young Jun Won, Se Hwa Kim
Endocrine.2019; 65(3): 608. CrossRef - Autoimmune thyroiditis and central serous chorioretinopathy may have a relation
Brijesh Takkar, Harsha Saxena, Anubha Rathi, Rekha Singh
Medical Hypotheses.2018; 121: 180. CrossRef
- New-onset atrial fibrillation in seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: association with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs treatment

- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Reference Range and Prevalence of Thyroid Dysfunction in the Korean Population: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013 to 2015
- Won Gu Kim, Won Bae Kim, Gyeongji Woo, Hyejin Kim, Yumi Cho, Tae Yong Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Myung-Hee Shin, Jin Woo Park, Hai-Lin Park, Kyungwon Oh, Jae Hoon Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(1):106-114. Published online January 23, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.1.106
- Correction in: Endocrinol Metab 2023;38(3):357
- 7,905 View
- 201 Download
- 71 Web of Science
- 79 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background No nationwide epidemiological study evaluating the prevalence of subclinical and overt forms of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism has yet been conducted in Korea. This study aimed to evaluate the reference range of serum thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and the national prevalence of thyroid dysfunctions in Korea.
Methods Nation-wide cross-sectional data were analyzed from a representative sample of the civilian, non-institutionalized Korean population (
n =6,564) who underwent blood testing for thyroid function and anti-thyroid peroxidase antibody (TPOAb) as part of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI (2013 to 2015).Results The reference interval of serum TSH in the Korean reference population was 0.62 to 6.68 mIU/L. Based on this reference interval, the prevalence of overt and subclinical hypothyroidism was 0.73% (males 0.40%, females 1.10%) and 3.10% (males 2.26%, females 4.04%), respectively. The prevalence of hypothyroidism increased with age until the age group between 50 to 59 years. Positive TPOAb were found in 7.30% of subjects (males 4.33%, females 10.62%). The prevalence of overt and subclinical hypothyroidism TPOAb-positive subjects was 5.16% and 10.88%, respectively. The prevalence of overt and subclinical hyperthyroidism was 0.54% (males 0.30%, females 0.81%) and 2.98% (males 2.43%, females, 3.59%), respectively.
Conclusion The Serum TSH reference levels in the Korean population were higher than the corresponding levels in Western countries. Differences were found in the prevalence of hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism according to age, sex, and TPOAb positivity. This study provides important baseline information for understanding patterns of thyroid dysfunction and diseases in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Deciphering the roles of triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) on cardiac electrical remodeling in clinical and experimental hypothyroidism
Oscar Casis, Leire Echeazarra, Beatriz Sáenz-Díez, Mónica Gallego
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry.2024; 80(1): 1. CrossRef - The Impact of Physical Activity on Thyroid Health: Insights From Representative Data in Korea
Jeongmin Lee, Han-Sang Baek, Kwanhoon Jo, Min-Hee Kim, Jung Min Lee, Sang Ah Chang, Dong-Jun Lim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Subclinical thyroid dysfunction and chronic kidney disease: a nationwide population-based study
Hye Jeong Kim, Sang Joon Park, Hyeong Kyu Park, Dong Won Byun, Kyoil Suh, Myung Hi Yoo
BMC Nephrology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between iodine intake and metabolic syndrome in euthyroid adult in an iodine-replete area: a nationwide population-based study
Hye Jeong Kim, Suyeon Park, Sang Joon Park, Hyeong Kyu Park, Dong Won Byun, Kyoil Suh, Myung Hi Yoo
Endocrine Journal.2023; 70(4): 393. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Patients with Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Hyun Kyung Chung, Eu Jeong Ku, Won Sang Yoo, Yea Eun Kang, Kyeong Jin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Tae-Yong Kim, Young Joo Park, Chang Ho Ahn, Jee Hee Yoon, Eun Kyung Lee, Jong Min Lee, Eui Dal Jung, Jae Hoon Chung, Yun Jae Chung, Won Bae Kim, Ka Hee Yi, Ho-Cheol Ka
International Journal of Thyroidology.2023; 16(1): 32. CrossRef - The Current Status of Hyperthyroidism in Korea
Hyemi Kwon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 392. CrossRef - Management of Subclinical Hypothyroidism: A Focus on Proven Health Effects in the 2023 Korean Thyroid Association Guidelines
Eu Jeong Ku, Won Sang Yoo, Hyun Kyung Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 381. CrossRef - Association between shift work and the risk of hypothyroidism in adult male workers in Korea: a cohort study
Seonghyeon Kwon, Yesung Lee, Eunhye Seo, Daehoon Kim, Jaehong Lee, Youshik Jeong, Jihoon Kim, Jinsook Jeong, Woncheol Lee
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Depressão e hipotireoidismo: Uma revisão sistemática
Eduarda Silva Souza, Rosangela Soares Chriguer, Maria Cristina Mazzaia
Revista Portuguesa de Investigação Comportamental e Social.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Results from Eight Different Reagents and Assay-Specific Korean Reference Interval for Subclinical Hypothyroidism Treatment
Won Sang Yoo, Sollip Kim, Young Joo Park, Sang Hoon Song, Kyunghoon Lee, Eun Kyung Lee, Jehoon Lee, Ho-Young Lee, Yun Jae Chung, Hyun Kyung Chung, Jin Chul Paeng, Minje Han, Ho-Cheol Kang
International Journal of Thyroidology.2023; 16(2): 166. CrossRef - Comparison of Five Different Criteria for Diagnosis of Subclinical Hypothyroidism in a Large-Scale Chinese Population
Yan-song Zheng, Sheng-yong Dong, Yan Gong, Jia-hong Wang, Fei Wang, Qiang Zeng
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of thyroid autoimmunity with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in euthyroid middle‐aged subjects: A population‐based study
Hye Jeong Kim, Sang Joon Park, Hyeong Kyu Park, Dong Won Byun, Kyoil Suh, Myung Hi Yoo
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 37(8): 1617. CrossRef - Heart Failure and Stroke Risks in Users of Liothyronine With or Without Levothyroxine Compared with Levothyroxine Alone: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis
Wook Yi, Bo Hyun Kim, Mijin Kim, Jinmi Kim, Myungsoo Im, Soree Ryang, Eun Heui Kim, Yun Kyung Jeon, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim
Thyroid.2022; 32(7): 764. CrossRef - Association of free thyroxine with obstructive lung pattern in euthyroid middle-aged subjects: A population-based study
Hye Jeong Kim, Sang Joon Park, Hyeong Kyu Park, Dong Won Byun, Kyoil Suh, Myung Hi Yoo, Dong Keon Yon
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(7): e0270126. CrossRef - Long working hours and the risk of hypothyroidism in healthy Korean workers: a cohort study
Yesung Lee, Woncheol Lee, Hyoung-Ryoul Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022104. CrossRef - Association of breastfeeding with thyroid function and autoimmunity in postmenopausal women
Sung-Woo Kim, Ji-Hyun Lee, Ho-Sang Shon, Eonju Jeon, Tae-Yong Kim
Endocrine.2021; 71(1): 130. CrossRef - Distributions of serum thyroid-stimulating hormone in 2020 thyroid disease-free adults from areas with different iodine levels: a cross-sectional survey in China
B. Ren, S. Wan, L. Liu, M. Qu, H. Wu, H. Shen
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2021; 44(5): 1001. CrossRef - Low Thyroid-stimulating Hormone Levels Are Associated With Annoying Tinnitus in Adult Women: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
So Young Kim, Chanyang Min, Hyung-Jong Kim, Hyo Geun Choi
Otology & Neurotology.2021; 42(4): e408. CrossRef - Risk of All-Cause Mortality in Levothyroxine-Treated Hypothyroid Patients: A Nationwide Korean Cohort Study
Seo Young Sohn, Gi Hyeon Seo, Jae Hoon Chung
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Decreased Expression of Ileal Thyroid Hormone Transporters in a Hypothyroid Patient: A Case Report
Chae Won Chung, Eun Young Mo, Gyung Seo Jung, Yoo Hyung Kim, Sun Wook Cho, Do Joon Park, Jeong Mo Bae, Young Joo Park
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 20th anniversary: accomplishments and future directions
Kyungwon Oh, Yoonjung Kim, Sanghui Kweon, Soyeon Kim, Sungha Yun, Suyeon Park, Yeon-Kyeng Lee, Youngtaek Kim, Ok Park, Eun Kyeong Jeong
Epidemiology and Health.2021; 43: e2021025. CrossRef - Association between triglyceride-glucose index and thyroid function in euthyroid adults: The Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey 2015
Wonsuk Choi, Ji Yong Park, A. Ram Hong, Jee Hee Yoon, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sun Young Lee
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(7): e0254630. CrossRef - Association between Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Incident Hypertension in Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Jean Kim, Narut Prasitlumkum, Sandeep Randhawa, Dipanjan Banerjee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(15): 3318. CrossRef - Sex Difference in the Association between Sleep Duration and Thyroid Disease among South Korean Adults
Jeong Hyun Ahn, Jin Young Nam, Soojin Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(3): 337. CrossRef - The Association between the Dietary Inflammatory Index and Thyroid Function in U.S. Adult Males
Nuozhou Liu, Fang Ma, Ying Feng, Xue Ma
Nutrients.2021; 13(10): 3330. CrossRef - T4+T3 Combination Therapy: An Unsolved Problem of Increasing Magnitude and Complexity
Wilmar M. Wiersinga
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 938. CrossRef - Association between thyroid hormones and insulin resistance indices based on the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Yun Mi Choi, Min Kyung Kim, Mi Kyung Kwak, Dooman Kim, Eun-Gyoung Hong
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Implication of thyroid function in periodontitis: a nationwide population-based study
Eyun Song, Min Jeong Park, Jung A. Kim, Eun Roh, Ji Hee Yu, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between thyroid hormone and components of metabolic syndrome in euthyroid Korean adults
Kyung A. Shin, Eun Jae Kim
Medicine.2021; 100(51): e28409. CrossRef - Association between Serum Free Thyroxine and Anemia in Euthyroid Adults: A Nationwide Study
Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Hyungi Lee, Min Hee Jang, Jeong Mi Kim, Eun Heui Kim, Yun Kyung Jeon, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 106. CrossRef - Unmet Clinical Needs in the Treatment of Patients with Thyroid Cancer
Won Bae Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 14. CrossRef - Long Work Hours Are Associated with Hypothyroidism: A Cross-Sectional Study with Population-Representative Data
Young Ki Lee, Dong-eun Lee, Yul Hwangbo, You Jin Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim, Eun Kyung Lee
Thyroid.2020; 30(10): 1432. CrossRef - Subclinical thyroid dysfunction, bone mineral density, and osteoporosis in a middle-aged Korean population
K. Lee, S. Lim, H. Park, H.Y. Woo, Y. Chang, E. Sung, H.S. Jung, K.E. Yun, C.W. Kim, S. Ryu, M.J. Kwon
Osteoporosis International.2020; 31(3): 547. CrossRef - Update on Thyroid Hormone Levels and Thyroid Dysfunction in the Korean Population Based on Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI (2013 to 2015)
Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 7. CrossRef - Assessment of the relationship between knee ultrasound and clinical symptoms in patients with thyroid dysfunction
Bo Young Kim, Sung-Soo Kim, Hyeong Kyu Park, Hyun-Sook Kim
Journal of International Medical Research.2020; 48(1): 030006051989770. CrossRef - Association between urinary sodium levels and iodine status in Korea
Jonghwa Ahn, Jang Ho Lee, Jiwoo Lee, Ji Yeon Baek, Eyun Song, Hye-Seon Oh, Mijin Kim, Suyeon Park, Min Ji Jeon, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Gu Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2020; 35(2): 392. CrossRef - Association of Thyroid Status with Health-Related Quality of Life in Korean Older Adults
Minjung Han, Seulggie Choi, Sarang Kim, Ahryoung Ko, Joung Sik Son, Sang Min Park
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2020; 41(1): 38. CrossRef - High neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with relapse in Graves’ disease after antithyroid drug therapy
Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Min Hee Jang, Jeong Mi Kim, Eun Heui Kim, Yun Kyung Jeon, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim
Endocrine.2020; 67(2): 406. CrossRef - Sex differences in subclinical hypothyroidism and associations with metabolic risk factors: a health examination-based study in mainland China
Li Jiang, Jinman Du, Weizhu Wu, Jianjiang Fang, Jufang Wang, Jinhua Ding
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Serum Free Thyroxine and Anemia in Euthyroid Adults: A Nationwide Study (Endocrinol Metab 2020;35:106-14, Mijin Kim et al.)
Mijin Kim, Bo Hyun Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(3): 669. CrossRef - Urinary Iodine Concentration and Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies in the Korean Population Using Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI
Myung-Chul Chang
International Journal of Thyroidology.2020; 13(2): 155. CrossRef - Recent Issues Related to Thyroid Disease in Pregnancy
Jae Hoon Chung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2020; 13(2): 85. CrossRef - Epidemiology of thyroid disorders in the Lifelines Cohort Study (the Netherlands)
Hanneke J. C. M. Wouters, Sandra N. Slagter, Anneke C. Muller Kobold, Melanie M. van der Klauw, Bruce H. R. Wolffenbuttel, Silvia Naitza
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(11): e0242795. CrossRef - Hipertiroidi Hastalarında Tedavi Öncesi ve Sonrası Trombosit/Lenfosit ve Nötrofil/Lenfosit Oranlarının Değerlendirilmesi
Çiğdem CİNDOĞLU, Mehmet GÜLER, Mehmet Ali EREN, Tevfik SABUNCU
Harran Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi.2020; 17(1): 104. CrossRef - Association between Sleep Duration and Subclinical Thyroid Dysfunction Based on Nationally Representative Data
Woojun Kim, Jeongmin Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Kwanghoon Jo, Dong-Jun Lim, Jung-Min Lee, Sang-Ah Chang, Moo-Il Kang, Min-Hee Kim
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(11): 2010. CrossRef - High Normal Range of Free Thyroxine is Associated with Decreased Triglycerides and with Increased High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Based on Population Representative Data
Jeongmin Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Kwanhoon Jo, Dong-Jun Lim, Jung-Min Lee, Sang-Ah Chang, Moo-Il Kang, Min-Hee Kim
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(6): 758. CrossRef - Association High-Iodine-Containing Seaweed Soup Consumption after Birth and Subclinical Hypothyroidism in Korean Women: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey IV (2013–2015)
Hyunsam Kim, Ha Ni Lee, Jeonghoon Ha
International Journal of Thyroidology.2019; 12(2): 105. CrossRef - Reference Range and Sociodemographic Characteristics of TSH among Reproductive Age Women in Rural China
Qiang Su, Shikun Zhang, Mei Hu, Qiaomei Wang, Na Liu, Haiping Shen, Yiping Zhang, Man Zhang
Biological Trace Element Research.2019; 189(2): 336. CrossRef - Prevalence of Thyroid Disease in Patients Surgically Treated for Pituitary Disease
Kim, Cho, Ku, Jung, Moon, Kim, Shin, Kim, Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(8): 1142. CrossRef - Thyroid Dysfunction in Patients with Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody–associated Vasculitis: A Monocentric Retrospective Study
JAE YEON KIM, YONG-BEOM PARK, SANG-WON LEE
The Journal of Rheumatology.2019; 46(9): 1248. CrossRef - Thyroid dysfunction in patients with suspected or documented supraventricular tachyarrhythmia
Hye Bin Gwag, Ji Eun Jun, Youngjun Park, Seong Soo Lee, Seung-Jung Park, June Soo Kim, Kyoung-Min Park, Young Keun On
International Journal of Arrhythmia.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Iodine Nutrition Status and Thyroid Disease-Related Hormone in Korean Adults: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI (2013–2015)
Kim, Kwon, Kim, Hong, Park
Nutrients.2019; 11(11): 2757. CrossRef - Thyroid-stimulating hormone levels in the normal range and incident type 2 diabetes mellitus
T. I. de Vries, L. J. Kappelle, Y. van der Graaf, H. W. de Valk, G. J. de Borst, H. M. Nathoe, F. L. J. Visseren, Jan Westerink
Acta Diabetologica.2019; 56(4): 431. CrossRef - The Association between Low Vitamin D Status and Autoimmune Thyroid Disease in Korean Premenopausal Women: The 6th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2013–2014
Choon-Young Kim, Yeon Ji Lee, Ji-Ho Choi, Soo Yeon Lee, Hye Young Lee, Da Hye Jeong, Yeon Jun Choi
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2019; 40(5): 323. CrossRef - Associations between urine iodine and allergic diseases in the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2015: A STROBE-compliant article
Young Bok Lee, Ji hyun Lee, Min Ji Kang, Dong Soo Yu, Kyung Do Han, Yong Gyu Park
Phytomedicine.2019; 62: 152937. CrossRef - The Relationship between Thyroid Function and Different Obesity Phenotypes in Korean Euthyroid Adults
Jeong Mi Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Hyungi Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Mijin Kim, Jong Ho Kim, Yun Kyung Jeon, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, Yong Ki Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 867. CrossRef - Sex-Dependent Association between Weight Change and Thyroid Dysfunction: Population-Level Analysis Using the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eyun Song, Jonghwa Ahn, Hye-Seon Oh, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Tae Yong Kim
European Thyroid Journal.2019; 8(4): 202. CrossRef - Subclinical Hypothyroidism: is it Really Subclinical with Aging?
Robin Gourmelon, Sandrine Donadio-Andréi, Karim Chikh, Muriel Rabilloud, Elisabetta Kuczewski, Anne-Sophie Gauchez, Anne Charrié, Pierre-Yves Brard, Raphaëlle Andréani, Jean-Cyril Bourre, Christine Waterlot, Domitille Guédel, Anne Mayer, Emmanuel Disse, C
Aging and disease.2019; 10(3): 520. CrossRef - Serum thyroid‐stimulating hormone levels and smoking status: Data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI
Suyeon Park, Won Gu Kim, Min Ji Jeon, Mijin Kim, Hye‐Seon Oh, Minkyu Han, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2018; 88(6): 969. CrossRef - Sex-specific genetic influence on thyroid-stimulating hormone and free thyroxine levels, and interactions between measurements: KNHANES 2013–2015
Young Ki Lee, Dong Yeob Shin, Hyejung Shin, Eun Jig Lee, Silvia Naitza
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(11): e0207446. CrossRef - Ten Years of the Korean Thyroid Association: Achievement and Future
Young Joo Park, Young Shin Song, Ka Hee Yi
International Journal of Thyroidology.2018; 11(1): 1. CrossRef - Association between diffuse lymphocytic infiltration and papillary thyroid cancer aggressiveness according to the presence of thyroid peroxidase antibody and BRAFV600E mutation
Young Ki Lee, Kyeong Hye Park, Se Hee Park, Kwang Joon Kim, Dong Yeob Shin, Kee Hyun Nam, Woong Youn Chung, Eun Jig Lee
Head & Neck.2018; 40(10): 2271. CrossRef - Prevalence and Annual Incidence of Thyroid Disease in Korea from 2006 to 2015: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Hyemi Kwon, Jin-hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Jung-Hwan Cho, Da Young Lee, Ji Min Han, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(2): 260. CrossRef - Evaluation of Thyroid Hormone Levels and Urinary Iodine Concentrations in Koreans Based on the Data from Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI (2013 to 2015)
Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(2): 160. CrossRef - Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone Reference Ranges in the First Trimester of Pregnancy in an Iodine-Sufficient Country
Carmen Castillo, Nicole Lustig, Paula Margozzini, Andrea Gomez, María Paulina Rojas, Santiago Muzzo, Lorena Mosso
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(4): 466. CrossRef - Male-specific association between subclinical hypothyroidism and the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease estimated by hepatic steatosis index: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013 to 2015
Jeongmin Lee, Jeonghoon Ha, Kwanhoon Jo, Dong-Jun Lim, Jung-Min Lee, Sang-Ah Chang, Moo-Il Kang, Bong-Yun Cha, Min-Hee Kim
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Sex differences in risk factors for subclinical hypothyroidism
Jeonghoon Ha, Jeongmin Lee, Kwanhoon Jo, Dong-Jun Lim, Moo Il Kang, Bong Yun Cha, Min-Hee Kim
Endocrine Connections.2018; 7(4): 511. CrossRef - Associations of Urinary Cotinine-Verified Active and Passive Smoking with Thyroid Function: Analysis of Population-Based Nationally Representative Data
Jihun Kang, Eunhee Kong, Jongsoon Choi
Thyroid.2018; 28(5): 583. CrossRef - Establishment of Korean Thyroid Association-10 Years of Development in Internal Medicine
Jae Hoon Chung
International Journal of Thyroidology.2018; 11(1): 7. CrossRef - Association between subclinical thyroid dysfunction and depressive symptoms in the Korean adult population: The 2014 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jae Won Hong, Jung Hyun Noh, Dong-Jun Kim, Osama Ali Abulseoud
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(8): e0202258. CrossRef - Association Between Thyroid Dysfunction and Lipid Profiles Differs According to Age and Sex: Results from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hye-Seon Oh, Hyemi Kwon, Jonghwa Ahn, Eyun Song, Suyeon Park, Mijin Kim, Minkyu Han, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Eun-Jung Rhee, Tae Yong Kim
Thyroid.2018; 28(7): 849. CrossRef - The Relationship between Subclinical Thyroid Disease and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Score in Koreans
Hee Joong Lim, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, Young Ju Suh
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2017; 32(10): 1626. CrossRef - Changes in standardized mortality rates from thyroid cancer in Korea between 1985 and 2015: Analysis of Korean national data
Yun Mi Choi, Won Gu Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Minkyu Han, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Sang Mo Hong, Eun‐Gyoung Hong, Won Bae Kim
Cancer.2017; 123(24): 4808. CrossRef - Response: Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Reference Range and Prevalence of Thyroid Dysfunction in the Korean Population: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013 to 2015 (Endocrinol Metab 2017;32:106-14, Won Gu Kim et al.)
Won Gu Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(2): 304. CrossRef - Excessive Iodine Intake and Thyrotropin Reference Interval: Data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Mijin Kim, Suyeon Park, Hye-Seon Oh, Minkyu Han, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
Thyroid.2017; 27(7): 967. CrossRef - Subclinical thyroid dysfunction and risk of carotid atherosclerosis
Hosu Kim, Tae Hyuk Kim, Hye In Kim, So Young Park, Young Nam Kim, Seonwoo Kim, Min-Ji Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee, Yong-Ki Min, Jae Hoon Chung, Mira Kang, Sun Wook Kim, Tatsuo Shimosawa
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(7): e0182090. CrossRef - Letter: Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Reference Range and Prevalence of Thyroid Dysfunction in the Korean Population: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013 to 2015 (Endocrinol Metab 2017;32:106-14, Won Gu Kim et al.)
Young Ki Lee, Dong Yeob Shin
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(2): 302. CrossRef - Vitamin D deficiency affects thyroid autoimmunity and dysfunction in iodine-replete area: Korea national health and nutrition examination survey
Mijin Kim, Eyun Song, Hye-Seon Oh, Suyeon Park, Hyemi Kwon, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Won Bae Kim, Young Kee Shong, Tae Yong Kim
Endocrine.2017; 58(2): 332. CrossRef - Viral Hepatitis in South Korea
Stella C Pak, Yaseen Alastal, Zubair Khan, Umar Darr
Euroasian Journal of Hepato-Gastroenterology.2017; 7(2): 163. CrossRef
- Deciphering the roles of triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) on cardiac electrical remodeling in clinical and experimental hypothyroidism

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Trends in the Diabetes Epidemic in Korea
- Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(2):142-146. Published online June 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.2.142
- 4,950 View
- 46 Download
- 66 Web of Science
- 78 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Diabetes mellitus is a leading cause of mortality and increased disability-adjusted life years worldwide. In Korea, the prevalence of diabetes increased from 8.6% to 11.0% in 2001 to 2013 and the prevalence of adult obesity, which is the most important risk factor of diabetes, increased from 29.2% to 31.8% during the same period. There has been a dramatic increase in the number of obese Koreans with diabetes in recent decades and the prevalence of diabetes in people aged 40 years and older also increased in 2001 to 2013. Nevertheless, the mean age at the first diagnosis of diabetes was very similar for men in 2005 and 2013, while the mean age for women decreased slightly. There is an inverse linear relationship between body mass index and age at the diagnosis of diabetes among those who are newly diagnosed. Accordingly, the prevalence of diabetes is increasingly shifting to younger individuals and those who are obese. Therefore, public efforts should focus on healthy lifestyle changes, primary prevention measures, screening for the early detection of diabetes, and long-term management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cluster analysis based on fasting and postprandial plasma glucose and insulin concentrations
Miguel Altuve, Erika Severeyn
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Smoking behavior change and the risk of pneumonia hospitalization among smokers with diabetes mellitus
Dong-Woo Han, Wonyoung Jung, Kyu Na Lee, Kyungdo Han, Sei Won Lee, Dong Wook Shin
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Teneligliptin on HbA1c levels, Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Time in Range and Glycemic Variability in Elderly Patients with T2DM (TEDDY Study)
Ji Cheol Bae, Soo Heon Kwak, Hyun Jin Kim, Sang-Yong Kim, You-Cheol Hwang, Sunghwan Suh, Bok Jin Hyun, Ji Eun Cha, Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 81. CrossRef - Rising Incidence of Diabetes in Young Adults in South Korea: A National Cohort Study
Hyun Ho Choi, Giwoong Choi, Hojun Yoon, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 803. CrossRef - Differences in health behavior and nutrient intake status between diabetes-aware and unaware Korean adults based on the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey 2016–18 data: A cross-sectional study
Anshul Sharma, Chen Lulu, Kee-Ho Song, Hae-Jeung Lee
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride glucose (TyG) index as a predictor of incident type 2 diabetes among nonobese adults: a 12-year longitudinal study of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study cohort
Byoungjin Park, Hye Sun Lee, Yong-Jae Lee
Translational Research.2021; 228: 42. CrossRef - Did Sejong the Great have ankylosing spondylitis? The oldest documented case of ankylosing spondylitis
JiHwan Lee
International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases.2021; 24(2): 203. CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2020: An Appraisal of Current Status
Chan-Hee Jung, Jang Won Son, Shinae Kang, Won Jun Kim, Hun-Sung Kim, Hae Soon Kim, Mihae Seo, Hye-Jung Shin, Seong-Su Lee, Su Jin Jeong, Yongin Cho, Seung Jin Han, Hyang Mi Jang, Mira Rho, Shinbi Lee, Mihyun Koo, Been Yoo, Jung-Wha Moon, Hye Young Lee, Ja
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 1. CrossRef - Association between living alone and incident type 2 diabetes among middle-aged individuals in Korea: a nationwide cohort study
Ga Eun Nam, Wonsock Kim, Kyungdo Han, Jin-Hyung Jung, Byoungduck Han, Jinwook Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Kyung Hwan Cho, Yong Gyu Park, Seon Mee Kim
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - White Blood Cell Count as a Predictor of Incident Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among Non-Obese Adults: A Longitudinal 10-Year Analysis of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Jae-Min Park, Hye Sun Lee, Ju-Young Park, Dong-Hyuk Jung, Ji-Won Lee
Journal of Inflammation Research.2021; Volume 14: 1235. CrossRef - A 9-Year Comparison of Dementia Prevalence in Korea: Results of NaSDEK 2008 and 2017
Seung Wan Suh, You Joung Kim, Kyung Phil Kwak, Kiwon Kim, Moon-Doo Kim, Byung-Soo Kim, Bong Jo Kim, Shin Gyeom Kim, Jeong Lan Kim, Tae Hui Kim, Seok Woo Moon, Kyung Won Park, Jong-Il Park, Joon Hyuk Park, Jae Nam Bae, Jiyeong Seo, Su Jeong Seong, Sang Joo
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2021; 81(2): 821. CrossRef - Trends of Diabetes and Prediabetes Prevalence among Korean Adolescents From 2007 to 2018
Ji Hyun Kim, Jung Sub Lim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Breast Cancer Statistics in Korea, 2018
Sang Yull Kang, Sae Byul Lee, Yoo Seok Kim, Zisun Kim, Hyun Yul Kim, Hee Jeong Kim, Sungmin Park, Soo Youn Bae, Kwanghyun Yoon, Se Kyung Lee, Kyu-Won Jung, Jaihong Han, Hyun Jo Youn
Journal of Breast Cancer.2021; 24(2): 123. CrossRef - Longitudinal Changes in Clinical Features, Management, and Outcomes of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. A Nationwide Cohort Study
Sung Woo Moon, Song Yee Kim, Man Pyo Chung, Hongseok Yoo, Sung Hwan Jeong, Dong Soon Kim, Jin Woo Song, Hong Lyeol Lee, Sun Mi Choi, Young Whan Kim, Yong Hyun Kim, Choon-Sik Park, Sung-Woo Park, Jong Sun Park, Yangjin Jegal, Jongmin Lee, Soo-Taek Uh, Tae-
Annals of the American Thoracic Society.2021; 18(5): 780. CrossRef - Association between Inflammatory Markers and Glycemic Control in Korean Diabetic Patients
Min Kang, Seok-Joon Sohn
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2021; 46(3): 247. CrossRef - Associations between obesity, weight change and decreased renal function in Korean type 2 diabetic patients: a longitudinal follow-up study
Bo-Yeon Kim, Dug-Hyun Choi, Chan-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok, Chul-Hee Kim
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Estrogen in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Clinical and Preclinical Data
Monica De Paoli, Geoff H. Werstuck
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2020; 44(5): 448. CrossRef - Site-specific cancer risk in patients with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide population-based cohort study in Korea
Suk Kyeong Kim, Ju-Young Jang, Dong-Lim Kim, Young A Rhyu, Suh Eun Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyungdo Han, Kee-Ho Song
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2020; 35(3): 641. CrossRef - Alteration of Microbiome Profile by D-Allulose in Amelioration of High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice
Youngji Han, Haryung Park, Bo-Ra Choi, Yosep Ji, Eun-Young Kwon, Myung-Sook Choi
Nutrients.2020; 12(2): 352. CrossRef - Type 2 diabetes: epidemiological changes at Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social—associated with complications in Mexico
Jessie N. Zurita-Cruz, Leticia Manuel-Apolinar, María Luisa Arellano-Flores, Alejandro Gutierrez-Gonzalez, Aleida de Jesús Rivera-Hernández, Rosa Angélica Carranza-Muleiro, Víctor Hugo Borja-Aburto, Nelly Cisneros-González
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2020; 40(2): 178. CrossRef - Effects of Particulate Respirator Use on Cardiopulmonary Function in Elderly Women: a Quasi-Experimental Study
Youn-Hee Lim, Woosung Kim, Yumi Choi, Hwan-Cheol Kim, Geunjoo Na, Hyoung-Ryoul Kim, Yun-Chul Hong
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - GLP‑1 receptor agonist on cardiovascular complications of diabetes mellitus
Fengjun Liu, Yanhua Kong
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasma sphingomyelins increase in pre-diabetic Korean men with abdominal obesity
Seung-Soon Im, Hyeon Young Park, Jong Cheol Shon, In-Sung Chung, Ho Chan Cho, Kwang-Hyeon Liu, Dae-Kyu Song, Kyoung Heon Kim
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(3): e0213285. CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2018: An Appraisal of Current Status
Bo-Yeon Kim, Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyuk Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Jung Hwan Park, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kyu Chang Won, Dae Jung Kim, Kyong Soo Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 487. CrossRef - Analysis of diabetes quality assessment findings and future directions for the appropriate management of diabetes in Korea
Yu Jin Kim, Suk Chon, Seungjoon Oh, Jeong-taek Woo, Sung Woon Kim, Sang Youl Rhee
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2019; 34(1): 125. CrossRef - Diabetes and the Risk of Infection: A National Cohort Study
Eun Jin Kim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Young Hwa Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 804. CrossRef - Age-specific diabetes risk by the number of metabolic syndrome components: a Korean nationwide cohort study
Min-Kyung Lee, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in real-life practice for hepatocellular carcinoma patients in the Republic of Korea over a 12-year period: A nationwide random sample study
Beom Kyung Kim, Do Young Kim, Kwang-Hyub Han, Jinsil Seong, Jung Weon Lee
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(10): e0223678. CrossRef - Association between continuity of care and type 2 diabetes development among patients with thyroid disorder
Sang Ah Lee, Dong-Woo Choi, Junhyun Kwon, Doo Woong Lee, Eun-Cheol Park
Medicine.2019; 98(52): e18537. CrossRef - Association of C-Reactive Protein with Risk of Developing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and Role of Obesity and Hypertension: A Large Population-Based Korean Cohort Study
Suganya Kanmani, Minji Kwon, Moon-Kyung Shin, Mi Kyung Kim
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Egg consumption is associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes in middle-aged and older men
Jieul Lee, Jihye Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2018; 12(5): 396. CrossRef - Diabetes, Frequency of Exercise, and Mortality Over 12 Years: Analysis of the National Health Insurance Service-Health Screening (NHIS-HEALS) Database
Woo Young Shin, Taehee Lee, Da-Hye Jeon, Hyeon Chang Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology of liver cancer in South Korea
Bo Hyun Kim, Joong-Won Park
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2018; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Letter: Clinical Characteristics of People with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes between 2015 and 2016: Difference by Age and Body Mass Index (Diabetes Metab J 2018;42:137-46)
Ah Reum Khang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(3): 249. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of Panax ginseng berry extract on glycemic control: A 12-wk randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled clinical trial
Han Seok Choi, Sunmi Kim, Min Jung Kim, Myung-Sunny Kim, Juewon Kim, Chan-Woong Park, Daebang Seo, Song Seok Shin, Sang Woo Oh
Journal of Ginseng Research.2018; 42(1): 90. CrossRef - Response: Clinical Characteristics of People with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes between 2015 and 2016: Difference by Age and Body Mass Index (Diabetes Metab J2018;42:137-46)
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Sungrae Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(3): 251. CrossRef - Prediction of Type 2 Diabetes Remission after Bariatric or Metabolic Surgery
Ji Yeon Park
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2018; 27(4): 213. CrossRef - Waist‐to‐calf circumstance ratio is an independent predictor of hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes
Eun Yeong Choe, Yong‐ho Lee, Young Ju Choi, Byung Wook Huh, Byung‐Wan Lee, Soo‐Kyung Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Bong‐Soo Cha, Eun Jig Lee, Kap Bum Huh, Zobair M Younossi
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2018; 33(5): 1082. CrossRef - Prevalence of Comorbidities among Patients with Diabetes
Suyoung Kim, Eun-Hee Nah, Seon Cho
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2018; 43(3): 237. CrossRef - Risk of new-onset diabetes among patients treated with statins according to hypertension and gender: Results from a nationwide health-screening cohort
Sang-Eun Lee, Ji Min Sung, In-Jeong Cho, Hyeon Chang Kim, Hyuk-Jae Chang, Lamberto Manzoli
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(4): e0195459. CrossRef - Outcomes of living donor kidney transplantation in diabetic patients: age and sex matched comparison with non-diabetic patients
Chung Hee Baek, Hyosang Kim, Seung Don Baek, Mun Jang, Wonhak Kim, Won Seok Yang, Duck Jong Han, Su-Kil Park
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2018; 33(2): 356. CrossRef - An Analysis of The Morbidity and Mortality of Diabetes Mellitus in a Forensic Context
Chong Zhou, Roger W. Byard
Journal of Forensic Sciences.2018; 63(4): 1149. CrossRef - Favorable glycemic response after pancreatoduodenectomy in both patients with pancreatic cancer and patients with non-pancreatic cancer
Seo Young Sohn, Eun Kyung Lee, Sung-Sik Han, You Jin Lee, Yul Hwangbo, Young Hwa Kang, Seung Duk Lee, Seong Hoon Kim, Sang Myung Woo, Woo Jin Lee, Eun Kyung Hong, Sang-Jae Park
Medicine.2018; 97(18): e0590. CrossRef - Comparison of Open and Laparoscopic Gastrectomy in Elderly Patients
Su Mi Kim, Ho Geun Youn, Ji Yeong An, Yoon Young Choi, Sung Hoon Noh, Seung Jong Oh, Tae Sung Sohn, Sung Kim
Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2018; 22(5): 785. CrossRef - Development and Validation of the Korean Diabetes Risk Score: A 10-Year National Cohort Study
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Yong-ho Lee, Sun Ok Song, Jae-woo Lee, Dong Wook Kim, Kyung-hee Cho, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(5): 402. CrossRef - Trends in diabetes prevalence among Korean adults based on Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys III–VI
Jae-woo Lee, Hee-Taik Kang, Hyoung-Ji Lim, Byoungjin Park
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 138: 57. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of People with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes between 2015 and 2016: Difference by Age and Body Mass Index
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Cheol Young Park, In Kyung Jeong, Hyun Jin Kim, Sang-Yong Kim, Won Jun Kim, Ji Sung Yoon, In Joo Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Sungrae Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(2): 137. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatocellular carcinoma in a hepatitis B virus-endemic area
Chang Hwi Yoon, Young-Joo Jin, Jin Woo Lee
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2018; 30(9): 1090. CrossRef - Prediction of Diabetes Remission after Bariatric or Metabolic Surgery
Ji Yeon Park
Journal of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery.2018; 7(1): 22. CrossRef - Incidence and predictors of type 2 diabetes among Koreans: A 12-year follow up of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Seung Jin Han, Hae Jin Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Kwan Woo Lee, Nam H. Cho
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2017; 123: 173. CrossRef - Glycated Hemoglobin and All-Cause Mortality in Korean Type 2 Diabetes
Mi Suk An, Sun A Kim, Jun-Ho Lee, Seong-Woo Choi, Min-Ho Shin
Chonnam Medical Journal.2017; 53(3): 223. CrossRef - Analysis and comparison of the cost-effectiveness of statins according to the baseline low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level in Korea
Y. J. Jeong, H. Kim, S. J. Baik, T. M. Kim, S. J. Yang, S.-H. Lee, J.-H. Cho, H. Lee, H. W. Yim, I. Y. Choi, K.-H. Yoon, H.-S. Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2017; 42(3): 292. CrossRef - Governmental or Social Support of Bariatric Surgery in the Asia-Pacific Region
Jisun Lim, Young Hye Cho, Hiroshi Yamamoto, Alvin Eng, Tania Markovic, Kyoung Kon Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2017; 26(1): 10. CrossRef - Application of the 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Cholesterol Guideline to the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys from 1998 to 2012
Young Shin Song, Tae Jung Oh, Kyoung Min Kim, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang, Kyong Soo Park, Soo Lim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(1): 38. CrossRef - The differences in the incidence of diabetes mellitus and prediabetes according to the type of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors prescribed in Korean patients
Tong Min Kim, Hyunah Kim, Yoo Jin Jeong, Sun Jung Baik, So Jung Yang, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, In Young Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon, Hun-Sung Kim
Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety.2017; 26(10): 1156. CrossRef - The Effect and Safety of Dapagliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Single-Institution Pharmacovigilance Review
Hyung Woo Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hee Sim Han, Eun Jeong Shin, Jin Hee Baek, Hyun-Joo Han, Young Min Cho, Kwi Suk Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2017; 18(4): 275. CrossRef - Optimal glycemic target level for colon cancer patients with diabetes
Shin Jun Lee, Jae Hyun Kim, Seun Ja Park, So Young Ock, Su Kyoung Kwon, Young Sik Choi, Bu Kyung Kim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2017; 124: 66. CrossRef - Physician-Directed Diabetes Education without a Medication Change and Associated Patient Outcomes
Hun-Sung Kim, Hyunah Kim, Hae-Kyung Yang, Eun Young Lee, Yoo Jin Jeong, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Seo Yeon Baik, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, In Young Choi, Hyeon Woo Yim, Bong-Yun Cha
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(3): 187. CrossRef - Does Weight Gain Associated with Thiazolidinedione Use Negatively Affect Cardiometabolic Health?
Ki Dong Ko, Kyoung Kon Kim, Kyu Rae Lee
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2017; 26(2): 102. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics and Outcome of Acute Heart Failure in Korea: Results from the Korean Acute Heart Failure Registry (KorAHF)
Sang Eun Lee, Hae-Young Lee, Hyun-Jai Cho, Won-Seok Choe, Hokon Kim, Jin Oh Choi, Eun-Seok Jeon, Min-Seok Kim, Jae-Joong Kim, Kyung-Kuk Hwang, Shung Chull Chae, Sang Hong Baek, Seok-Min Kang, Dong-Ju Choi, Byung-Su Yoo, Kye Hun Kim, Hyun-Young Park, Myeon
Korean Circulation Journal.2017; 47(3): 341. CrossRef - Factors that could explain the increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes among adults in a Canadian province: a critical review and analysis
Véronique Thibault, Mathieu Bélanger, Emilie LeBlanc, Lise Babin, Stuart Halpine, Beverly Greene, Michelina Mancuso
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Waist-Height Ratio with Diabetes Risk: A 4-Year Longitudinal Retrospective Study
Yoon Jeong Son, Jihyun Kim, Hye-Jeong Park, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(1): 127. CrossRef - Social Networking Services-Based Communicative Care for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
Hun-Sung Kim, Yoo Jeong, Sun Baik, So Yang, Tong Kim, Hyunah Kim, Hyunyong Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Cho, In-Young Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon
Applied Clinical Informatics.2016; 07(03): 899. CrossRef - Relative and combined effects of socioeconomic status and diabetes on mortality
Nam Hoon Kim, Tae Joon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Dong Seop Choi, Yousung Park, Sin Gon Kim
Medicine.2016; 95(30): e4403. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Diagnostic Strategies for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Jong Chul Won, Tae Sun Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(2): 230. CrossRef - Patterns of Diagnosis and Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes in Women with a History of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Mi Jin Choi, Chae Weon Chung
Perspectives in Nursing Science.2016; 13(1): 17. CrossRef - Mortality and causes of death in a national sample of type 2 diabetic patients in Korea from 2002 to 2013
Yu Mi Kang, Ye-Jee Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee, Chang Hee Jung
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Health Performance and Challenges in Korea: a Review of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013
Yo Han Lee, Seok-Jun Yoon, Arim Kim, Hyeyoung Seo, Seulki Ko
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2016; 31(Suppl 2): S114. CrossRef - Pharmacological Management of Obesity in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: An Update
Eun Ju Lee, Tae Nyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Obesity.2016; 25(3): 121. CrossRef - Current status of managing diabetes mellitus in Korea
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(5): 845. CrossRef - Hyperglycemia at presentation is associated with in hospital mortality in non-diabetic patient with organophosphate poisoning
Jeong Mi Moon, Byeong Jo Chun, Yong Soo Cho
Clinical Toxicology.2016; 54(3): 252. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Web-Based Interventions for Managing Diabetes in Korea
Jee Young Joo
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2016; 34(12): 587. CrossRef - Hypoglycemia and Health Costs
Yong-ho Lee, Gyuri Kim, Eun Seok Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2016; 17(1): 11. CrossRef - Letter: Characterization of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes according to Body Mass Index: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2007 to 2011 (Endocrinol Metab 2015;30:514-21, Dong-Hwa Lee et al.)
Eun-Hee Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(2): 345. CrossRef - Gender-Specific Associations between Socioeconomic Status and Psychological Factors and Metabolic Syndrome in the Korean Population: Findings from the 2013 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Kyoung Im Cho, Bo Hyun Kim, Hyung Gon Je, Jae Sik Jang, Yong Hyun Park
BioMed Research International.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Need for Diabetes Prevention Study
Ja Young Jeon, Dae Jung Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2015; 16(3): 161. CrossRef - Diabetes in Asians
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(3): 263. CrossRef - Epidemiologic Characteristics of Dyslipidemia in Korea
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2015; 4(2): 93. CrossRef
- Cluster analysis based on fasting and postprandial plasma glucose and insulin concentrations

- Thyroid
- Risk of Malignancy in Thyroid Incidentalomas Identified by Fluorodeoxyglucose-Positron Emission Tomography
- A Reum Chun, Hye Min Jo, Seoung Ho Lee, Hong Woo Chun, Jung Mi Park, Kyu Jin Kim, Chan Hee Jung, Ji Oh Mok, Sung Koo Kang, Chul Hee Kim, Bo Yeon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(1):71-77. Published online March 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.1.71
- 4,085 View
- 43 Download
- 28 Web of Science
- 26 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Thyroid incidentalomas detected by 2-deoxy-2-18F-fluoro-D-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18F-FDG PET/CT) have been reported in 1% to 4% of the population, with a risk of malignancy of 27.8% to 74%. We performed a retrospective review of FDG-avid thyroid incidentalomas in cancer screening subjects and patients with nonthyroid cancer. The risk of malignancy in thyroid incidentaloma and its association with the maximal standardized uptake value (SUVmax) in 18F-FDG PET/CT were evaluated to define the predictor variables in assessing risk of malignancy.
Methods A total of 2,584 subjects underwent 18F-FDG PET/CT for metastatic evaluation or cancer screening from January 2005 to January 2010. Among them, 36 subjects with FDG-avid thyroid incidentalomas underwent further diagnostic evaluation (thyroid ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration cytology [FNAC] or surgical resection). We retrospectively reviewed the database of these subjects.
Results Of the 2,584 subjects who underwent 18F-FDG PET/CT (319 for cancer screening and 2,265 for metastatic evaluation), 52 (2.0%) were identified as having FDG-avid thyroid incidentaloma and cytologic diagnosis was obtained by FNAC in 36 subjects. Of the subjects, 15 were proven to have malignant disease: 13 by FNAC and two by surgical resection. The positive predictive value of malignancy in FDG-avid thyroid incidentaloma was 41.7%. Median SUVmax was higher in malignancy than in benign lesions (4.7 [interquartile range (IQR), 3.4 to 6.0] vs. 2.8 [IQR, 2.6 to 4.0],
P =0.001).Conclusion Thyroid incidentalomas found on 18F-FDG PET/CT have a high risk of malignancy, with a positive predictive value of 41.7%. FDG-avid thyroid incidentalomas with higher SUVmax tended to be malignant.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Incidental 68Ga-DOTATATE uptake in thyroid nodules: Is guideline-directed management still appropriate?
Kyla Wright, Jason C. Fisher, Gary D. Rothberger, Jason D. Prescott, John D. Allendorf, Kepal Patel, Insoo Suh
Surgery.2024; 175(1): 228. CrossRef - Prediction of Malignant Thyroid Nodules Using 18F-FDG PET/CT–Based Radiomics Features in Thyroid Incidentalomas
Woo Seog Ko, Seong-Jang Kim
Clinical Nuclear Medicine.2023; 48(6): 497. CrossRef - KSNM60 in Nuclear Endocrinology: from the Beginning to the Future
Chae Moon Hong, Young Jin Jeong, Hae Won Kim, Byeong-Cheol Ahn
Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.2022; 56(1): 17. CrossRef - The value of 99mTc-MIBI scan in the detection of malignancy potential of hypermetabolic thyroid incidentalomas of 18F-FDG PET/CT
G. Tatar, G. Alçın, Ö. Erol Fenercioglu, E. Beyhan, H.Y. Barut, N. Ergül, T.F. Çermik
Médecine Nucléaire.2022; 46(3): 139. CrossRef - Diagnosis of thyroid nodules
Erik K Alexander, Edmund S Cibas
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2022; 10(7): 533. CrossRef - PET/CT Variants and Pitfalls in Head and Neck Cancers Including Thyroid Cancer
Jasna Mihailovic, Ronan P. Killeen, John A. Duignan
Seminars in Nuclear Medicine.2021; 51(5): 419. CrossRef - Characteristics of malignant thyroid lesions on [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)-Positron emission tomography (PET)/Computed tomography (CT)
Hatem Nasr, Hussein Farghaly, Abdullah Alqarni, Seham Al-Salem, Mohamed Sayed
European Journal of Radiology Open.2021; 8: 100373. CrossRef - Focal Thyroid Incidentalomas on 18F-FDG PET/CT: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Prevalence, Risk of Malignancy and Inconclusive Fine Needle Aspiration
J. F. de Leijer, M. J. H. Metman, A. van der Hoorn, A. H. Brouwers, S. Kruijff, B. M. van Hemel, T. P. Links, H. E. Westerlaan
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Thyroid incidentaloma: next to be neglected or investigated?
S.I. Rybakov
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2021; 17(4): 361. CrossRef - Metastatic renal cell carcinoma in the thyroid gland
Mark M. Cruz, Gregory S. Schmidt, Jeptha T. Johnson, Thanh D. Hoang, Mohamed K. M. Shakir
Clinical Case Reports.2020; 8(11): 2302. CrossRef - Clinical significance of thyroid incidentalomas detected on fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography scan (PETomas): An Indian experience
AVSAnil Kumar, Gaurav Datta, Harkirat Singh, ParthaBrata Mukherjee, Shashindran Vangal
World Journal of Nuclear Medicine.2019; 18(3): 273. CrossRef - Risk of Malignancy in FDG‐Avid Thyroid Incidentalomas on PET/CT: A Prospective Study
Chadi Nimeh Abdel‐Halim, Tine Rosenberg, Kristine Bjørndal, Anders Rørbæk Madsen, John Jakobsen, Helle Døssing, Mette Bay, Anders Thomassen, Anne Lerberg Nielsen, Christian Godballe
World Journal of Surgery.2019; 43(10): 2454. CrossRef - Is TI-RADS classification and Score Modified Method of thyroid nodules can be effective for evaluation of Thyroid Incidentalomas on FDG PET-CT imaging
Kara Pelin Ozcan, Koc Zehra Pinar, Balci Yüksel, Arpaci Rabia Bozdogan
Open Journal of Thyroid Research.2019; 2(1): 005. CrossRef - Hounsfield unit value has null effect on thyroid nodules at 18F-FDG PET/CT scans
Filiz Eksi Haydardedeoglu, Gulay Simsek Bagir, Nese Torun, Emrah Kocer, Mehmet Reyhan, Melek Eda Ertorer
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 62(4): 460. CrossRef - Utility of 18F-FDG-PET/CT in patients suspected of paraneoplastic neurological syndrome: importance of risk classification
F. J. Pena Pardo, A. M. García Vicente, M. Amo-Salas, J. F. López-Fidalgo, J. A. Garrido Robles, J. Á. de Ayala Fernández, P. del Saz Saucedo, M. Muñoz Pasadas, A. Soriano Castrejón
Clinical and Translational Oncology.2017; 19(1): 111. CrossRef - Unusual Soft Tissue Uptake of F-18 Sodium Fluoride in Three Patients Undergoing F-18 NaF PET/CT Bone Scans for Prostate Cancer
Andrew S. Hawkins, Brandon A. Howard
Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.2017; 51(3): 274. CrossRef - Molecular imaging of advanced thyroid cancer: iodinated radiotracers and beyond
Prasanna Santhanam, Lilja B. Solnes, Steven P. Rowe
Medical Oncology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The assessment of incidental thyroid lesions on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomogrophy: A single centre experience
Efnan Algin, Aytug Uner, Umit Ozgur Akdemir, Ozge Gumusay, Ozlem Kapucu, Ahmet Ozet
Journal of Oncological Sciences.2017; 3(2): 57. CrossRef - Cytological evaluation by fine needle aspiration biopsy of incidental focal increased fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in thyroid on positron emission tomography scan
Yanchun Li, Min Cui, Nami Azar, Dean Nakamoto, Claire W. Michael
Diagnostic Cytopathology.2017; 45(6): 501. CrossRef - [18F]FDG-PET/CT texture analysis in thyroid incidentalomas: preliminary results
M. Sollini, L. Cozzi, G. Pepe, L. Antunovic, A. Lania, L. Di Tommaso, P. Magnoni, P. A. Erba, M. Kirienko
European Journal of Hybrid Imaging.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of PET diagnosed thyroid incidentalomas in British Columbia Canada: Critical importance of the PET report
Jordan Wong, Kaidi Liu, Celia Siu, Steven Jones, Marlise Sovka, Don Wilson, Sam M. Wiseman
The American Journal of Surgery.2017; 213(5): 950. CrossRef - Incidental hypermetabolic PET positive lesions in thyroid and pituitary glands in a patient with lung cancer: A case of two uncommon findings in a single patient
Pratima Nayak, Kyaw Soe, Mona Natwa, Taha Sachak, Ming Jin, Norman L. Lehman, Fadi Nabhan
Journal of Clinical and Translational Endocrinology: Case Reports.2016; 2: 10. CrossRef - The incidence of 18F-FDG PET/CT thyroid incidentalomas andthe prevalence of malignancy: a prospective study
Mine ŞENCAN EREN, Özhan ÖZDOĞAN, Arzu GEDİK, Mehmet CEYLAN, Merih GÜRAY DURAK, Mustafa SEÇİL, Mehmet Ali KOÇDOR, Abdurrahman ÇÖMLEKÇİ, Hatice DURAK
TURKISH JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES.2016; 46: 840. CrossRef - Should the Prevalence of Incidental Thyroid Cancer Determine the Extent of Surgery in Multinodular Goiter?
Krzysztof Kaliszewski, Marta Strutyńska-Karpińska, Agnieszka Zubkiewicz-Kucharska, Beata Wojtczak, Paweł Domosławski, Waldemar Balcerzak, Tadeusz Łukieńczuk, Zdzisław Forkasiewicz, Pei-Yi Chu
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(12): e0168654. CrossRef - The incidence of thyroid cancer in focal hypermetabolic thyroid lesions
Martin Barrio, Johannes Czernin, Michael W. Yeh, Miguel F. Palma Diaz, Pawan Gupta, Martin Allen-Auerbach, Christiaan Schiepers, Ken Herrmann
Nuclear Medicine Communications.2016; 37(12): 1290. CrossRef - Incidental Detection of Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma in 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT Imaging
Sait Sager, Betül Vatankulu, Lebriz Uslu, Kerim Sönmezoglu
Journal of Nuclear Medicine Technology.2016; 44(3): 199. CrossRef
- Incidental 68Ga-DOTATATE uptake in thyroid nodules: Is guideline-directed management still appropriate?

- Thyroid
- Incidence and Prevalence of Overt Hypothyroidism and Causative Diseases in Korea as Determined Using Claims Data Provided by the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service
- Gi Hyeon Seo, Jae Hoon Chung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(3):288-296. Published online January 5, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.3.288
- 3,758 View
- 44 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The incidence and prevalence of overt hypothyroidism have been reported to be 2 to 4/1,000 population/year and 8 to 13/1,000 population, respectively, in foreign countries. As there has been no nationwide survey to obtain data in Korea, the present study investigated the incidence and prevalence of overt hypothyroidism in Korea using claims data provided by the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. The proportions of causative diseases for hypothyroidism were also analyzed.
Methods This study was retrospectively performed with 541,969 Korean patients (92,832 men and 449,137 women), with overt hypothyroidism, treated with thyroid hormone between 2008 and 2012.
Results The incidence of overt hypothyroidism in Korea was 2.26/1,000 population/year (0.78 in men and 3.72 in women), and the prevalence was 14.28/1,000 population (4.40 in men and 24.03 in women). When patients with thyroid cancer were excluded, the incidence was 1.56/1,000 population/year (0.54 in men and 2.57 in women). The incidence increased with age, with peaks in and after the late 60s in men and in the early 50s in women. The prevalence peaked in the early 70s in men and in the late 50s in women.
Conclusion This is a report of the first nationwide investigation of the incidence and prevalence of overt hypothyroidism in Korea, although it is limited to patients treated with thyroid hormone.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of Thyroid Hormone Medication Adherence With Risk of Dementia
Saemi Han, Seogsong Jeong, Seulggie Choi, Sun Jae Park, Kyae Hyung Kim, Gyeongsil Lee, Yoosun Cho, Joung Sik Son, Sang Min Park
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 109(1): e225. CrossRef - The impact of the micronutrient iodine in health and diseases
Ma. Cecilia Opazo, Irenice Coronado-Arrázola, Omar P. Vallejos, Rodrigo Moreno-Reyes, Carlos Fardella, Lorena Mosso, Alexis M. Kalergis, Susan M. Bueno, Claudia A. Riedel
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2022; 62(6): 1466. CrossRef - Hypothyroidism risk associated with rheumatoid arthritis
Chung-Ming Huang, Fung-Chang Sung, Hsuan-Ju Chen, Che-Chen Lin, Cheng-Li Lin, Po-Hao Huang
Medicine.2022; 101(1): e28487. CrossRef - Risk of All-Cause Mortality in Levothyroxine-Treated Hypothyroid Patients: A Nationwide Korean Cohort Study
Seo Young Sohn, Gi Hyeon Seo, Jae Hoon Chung
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Update on Thyroid Hormone Levels and Thyroid Dysfunction in the Korean Population Based on Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI (2013 to 2015)
Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 7. CrossRef - Treatment of hypothyroidism using Korean medicine: 2 case reports
Hyongjun Kim, Sun-Young Moon, Kyungsun Han, Jun-Hwan Lee, Jong Hwan Im, Sungha Kim, Jeong-Eun Yoo
Medicine.2020; 99(18): e19737. CrossRef - Genotype association of IP6K3 gene with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis in Algerian population (Aures region)
Warda Kherrour, Dean Kalicanin, Luka Brčić, Leila Hambaba, Mouloud Yahia, Souheyla Benbia, Vesna Boraska Perica
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of Thyroid Disease in Patients Surgically Treated for Pituitary Disease
Kim, Cho, Ku, Jung, Moon, Kim, Shin, Kim, Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(8): 1142. CrossRef - Medical Big Data Is Not Yet Available: Why We Need Realism Rather than Exaggeration
Hun-Sung Kim, Dai-Jin Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(4): 349. CrossRef - Evaluation of Thyroid Hormone Levels and Urinary Iodine Concentrations in Koreans Based on the Data from Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI (2013 to 2015)
Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(2): 160. CrossRef - Prevalence and Annual Incidence of Thyroid Disease in Korea from 2006 to 2015: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Hyemi Kwon, Jin-hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Jung-Hwan Cho, Da Young Lee, Ji Min Han, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(2): 260. CrossRef - Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Reference Range and Prevalence of Thyroid Dysfunction in the Korean Population: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013 to 2015
Won Gu Kim, Won Bae Kim, Gyeongji Woo, Hyejin Kim, Yumi Cho, Tae Yong Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Myung-Hee Shin, Jin Woo Park, Hai-Lin Park, Kyungwon Oh, Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 106. CrossRef - The relationship of 19 functional polymorphisms in iodothyronine deiodinase and psychological well-being in hypothyroid patients
Yoon Young Cho, Hye Jeong Kim, Hye Won Jang, Tae Hyuk Kim, Chang-Seok Ki, Sun Wook Kim, Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrine.2017; 57(1): 115. CrossRef - Concomitant Thyroid Disorders and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Literature Review
Toru Shizuma
BioMed Research International.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Hypothyroidism among SLE patients: Case–control study
Abdulla Watad, Naim Mahroum, Aaron Whitby, Smadar Gertel, Doron Comaneshter, Arnon D. Cohen, Howard Amital
Autoimmunity Reviews.2016; 15(5): 484. CrossRef
- Association of Thyroid Hormone Medication Adherence With Risk of Dementia

- Thyroid
- Prevalence and Risk Factors of Subclinical Thyroid Disease
- Ye An Kim, Young Joo Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(1):20-29. Published online March 14, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.1.20
- 6,601 View
- 81 Download
- 69 Web of Science
- 70 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Subclinical thyroid disease is defined biochemically by an abnormal thyrotropin (TSH) level and normal serum-free thyroxine level. The prevalence of this condition varies according to the reference range for TSH and geographic or demographic factors. Recently, several studies, including our community-based cohort studies, have reported on the incidence of subclinical thyroid disease in Korea. Using these studies, we reviewed the prevalence and risk factors of subclinical thyroid disease, focusing on subclinical hypothyroidism.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Appropriateness of Levothyroxine Prescription: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
Ivan Nicolas Ayala, Cristian Soto Jacome, David Toro-Tobon, Elizabeth Golembiewski, Andrea Garcia-Bautista, Jessica Hidalgo, Sandra Cordova-Madera, Raghda Al Anbari, Jessica Sohn R, Naykky Singh Ospina, Spyridoula Maraka, Marina Joseph, Juan P Brito
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(2): e765. CrossRef - Changes in thyroid function and evolution of subclinical thyroid disease in older men
Stephanie Y. Tan, S. A. Paul Chubb, Leon Flicker, Osvaldo P. Almeida, Jonathan Golledge, Graeme J. Hankey, Bu B. Yeap
Clinical Endocrinology.2024; 100(2): 170. CrossRef - Subclinical thyroid dysfunction and the risk of incident atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Hasveer Singh, Mariam Z. Shahid, Stephanie L. Harrison, Deirdre A. Lane, Gregory Y. H. Lip, Sunil Jit R. J. Logantha, Gaetano Santulli
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(1): e0296413. CrossRef - Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Clinical Outcomes After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Meta-Analysis
Song Peng Ang, Jia Ee Chia, Vikash Jaiswal, Dhrubajyoti Bandyopadhyay, Jose Iglesias, Gautham Varun Krishna Mohan, Sudarshan Gautam, Thazin Win, Tushar Kumar, Abbas Iqbal, Tong Hong Chia, Wilbert Aronow
Current Problems in Cardiology.2023; 48(8): 101719. CrossRef - Preliminary observation of thyroid function changes in subclinical thyroid diseases
Hua-Xin Wang, Wen-Yu Gao, Yang Yang, Yun-Feng Li, Yan Zhang, Xin-Yi Zhang, Yu-Xia Li
Technology and Health Care.2023; 31(5): 1715. CrossRef - Cardiovascular outcomes in subclinical thyroid disease: an update
Matthew D. Ettleson
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2023; 30(5): 218. CrossRef - Effects of whole seaweed consumption on humans: current evidence from randomized-controlled intervention trials, knowledge gaps, and limitations
João P. Trigo, Marie Palmnäs-Bédard, Mar Vall-Llosera Juanola, Ingrid Undeland
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The correlation of lipid profile with subclinical and overt hypothyroidism: A cross-sectional study from Syria
Fatima Tarboush, Mohammad Alsultan, Zaynab Alourfi
Medicine.2023; 102(37): e34959. CrossRef - Autoimmune thyroid status in subclinical thyroid disorders in patients attending a tertiary care center in Nepal: a hospital-based cross-sectional study
Vijay Kumar Sharma, Apeksha Niraula, Eans Tara Tuladhar, Aseem Bhattarai, Mithileshwer Raut, Raju Kumar Dubey, Sujata Baidya, Naresh Parajuli
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of low dose thyroid replacement therapy in patients with episodic migraine and subclinical hypothyroidism: A randomised placebo-controlled trial
Priya Dev, T.T. Favas, Rishab Jaiswal, Mareena Cyriac, Vijaya Nath Mishra, Abhishek Pathak
Cephalalgia.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Global Longitudinal Strain in Subclinical Hypothyroid Patients With Heart Failure
Nismat Javed, Vibha Hayagreev, Angel DeLaCruz, Muhammad Saad, Amandeep Singh, Timothy Vittorio
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship Between Thyroid Hormonal Status in Patients with a Hypothyroid Form of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis and Iodine Concentrations in Drinking Water
Olha Kasiyan, Halyna Tkachenko, Natalia Kurhaluk, Svitlana Yurchenko, Alek Manenko
Biological Trace Element Research.2022; 200(1): 59. CrossRef - Androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer and the risk of thyroid diseases
Jui‐Ming Liu, Yu‐Tang Chen, Chun‐Te Wu, Wen‐Lin Hsu, Ren‐Jun Hsu
The Prostate.2022; 82(7): 809. CrossRef - Subclinical hypothyroidism in women’s health: from pre- to post-menopause
Anna Capozzi, Giovanni Scambia, Stefano Lello
Gynecological Endocrinology.2022; 38(5): 357. CrossRef - Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Cognitive Impairment
Jung-Min Pyun, Young Ho Park, SangYun Kim
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2022; 88(2): 757. CrossRef - Rosuvastatin potentiates the thyrotropin‐lowering effect of metformin in men with non‐autoimmune subclinical hypothyroidism and prediabetes
Robert Krysiak, Karolina Kowalcze, Bogusław Okopień
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2022; 47(12): 2030. CrossRef - Natural history of subclinical hypothyroidism and prognostic factors for the development of overt hypothyroidism: Tehran Thyroid Study (TTS)
A. Amouzegar, M. Dehghani, H. Abdi, L. Mehran, S. Masoumi, F. Azizi
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2022; 45(12): 2353. CrossRef - Interplay between cardiovascular and thyroid dysfunctions: A review of clinical implications and management strategies
Sanyal Debmalya, Ray Saumitra, Malhi Harshveer Singh
Endocrine Regulations.2022; 56(4): 311. CrossRef - Routine Measurement of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone in Patients Presenting With Third-Degree Atrioventricular Block: Do We Really Need It?
Muhammad Faisal, Zubair Mumtaz, Abdul Mueed, Sajid Ali, Haseeb H Raza, Samra Khan, Sayeda Salma, Mustajab Mujtaba, Musa Karim, Faisal Qadir
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Update of hypothyroidism and its management in Unani medicine
Md. Anzar Alam, Mohd Aleemuddin Quamri, Ghulamuddin Sofi, Shabnam Ansari
Journal of Basic and Clinical Physiology and Pharmacology.2021; 32(2): 1. CrossRef - Endemik guatrın dünü, bugünü ve yarını
Yılmaz SEZGİN
Turkish Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2021; 15(1): 1. CrossRef - Prognosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma in relation to preoperative subclinical hypothyroidism
SY Kang, HR Ahn, HJ Youn, SH Jung
The Annals of The Royal College of Surgeons of England.2021; 103(5): 367. CrossRef - Stroke in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Pictorial Overview of the Pathoetiology
Saeideh Aghayari Sheikh Neshin, Shima Shahjouei, Eric Koza, Isabel Friedenberg, Faezeh Khodadadi, Mirna Sabra, Firas Kobeissy, Saeed Ansari, Georgios Tsivgoulis, Jiang Li, Vida Abedi, Donna M. Wolk, Ramin Zand
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Higher hepatic sterol-binding protein-2 gene expression and serum triglyceride level in methimazole induced subclinical hypothyroid animal model
Marie Saghaeian Jazi, Mohammad Mostakhdem Hashemi, Abbas Nezhadebrahimi, Azadreza Mansourian
Comparative Clinical Pathology.2021; 30(4): 627. CrossRef - Subclinical Hypothyroidism: Prevalence, Health Impact, and Treatment Landscape
Won Sang Yoo, Hyun Kyung Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 500. CrossRef - Thyroid Function and Nutrient Status in the Athlete
D. Enette Larson-Meyer, Demetre E. Gostas
Current Sports Medicine Reports.2020; 19(2): 84. CrossRef - Seasonal effects on resting energy expenditure are dependent on age and percent body fat
Duong Duc Pham, Jeong Hun Lee, Ki Hwan Hong, Youn Joo Jung, Sung Jin Kim, Chae Hun Leem
Clinical Nutrition.2020; 39(4): 1276. CrossRef - Subclinical hypothyroidism
Chelsea Simon, Emily Weidman-Evans, Sarah Allen
JAAPA.2020; 33(5): 21. CrossRef - Clinical and subclinical maternal hypothyroidism and their effects on neurodevelopment, behavior and cognition
Alice Batistuzzo, Miriam Oliveira Ribeiro
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 64(1): 89. CrossRef - Protective effect of a polyherbal bioactive fraction in propylthiouracil-induced thyroid toxicity in ratsby modulation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axes
Sneha Singh, Vandana Panda, Sudhamani S., Payal Dande
Toxicology Reports.2020; 7: 730. CrossRef - Subclinical Hypothyroidism Affects the Long-Term Outcomes of Patients Who Undergo Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Surgery but Not Heart Valve Surgery
Hana Kim, Sung Hye Kong, Jae Hoon Moon, Sang Yoon Kim, Kay-Hyun Park, Jun Sung Kim, Joong Haeng Choh, Young Joo Park, Cheong Lim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 308. CrossRef - Serum FT4 / FT3 Ratio, a Predictive Biochemical Marker for Subclinical Hypothyroidism in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
Venkat Siddarth Chagamreddy, Malligai Elancheran, Murugavel K
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2020; 9(33): 2319. CrossRef - Importance of thyroid-stimulating hormone levels in liver disease
Hyun Jin Kim
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 33(9): 1133. CrossRef - Does Hypothyroidism Increase Complications, Lengths of Stay, Readmissions, and Costs Following Primary 1- to 2-Level Lumbar Fusion?
Rushabh M. Vakharia, Joseph O. Ehiorobo, Bilal Mahmood, Martin W. Roche, Michael A. Mont, Afshin E. Razi
Clinical Spine Surgery: A Spine Publication.2020; 33(10): E559. CrossRef - Acute psychosis in patients with subclinical hyperthyroidism
Sohei Kimoto, Kazuhiko Yamamuro, Toshifumi Kishimoto
Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences.2019; 73(6): 348. CrossRef - Screening for thyroid dysfunction and treatment of screen-detected thyroid dysfunction in asymptomatic, community-dwelling adults: a systematic review
Francesca Reyes Domingo, Marc T. Avey, Marion Doull
Systematic Reviews.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between subclinical hypothyroidism and metabolic disorders: A retrospective chart review study in an emerging university hospital
Khaled Aldossari, Sameer Al‐Ghamdi, Jamaan Al‐Zahrani, Anwar Al Jammah, Bader Alanazi, Abdulilah Al‐Briek, Mohammad Alanazi
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation of Vitamin D Levels and Metabolic Parameters in Patients With Subclinical Hyperthyroidism
Müge Keskin, Esra Ademoğlu, Arzu Or Koca, Derun Taner Ertugrul
Ankara Medical Journal.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Reference Range and Sociodemographic Characteristics of TSH among Reproductive Age Women in Rural China
Qiang Su, Shikun Zhang, Mei Hu, Qiaomei Wang, Na Liu, Haiping Shen, Yiping Zhang, Man Zhang
Biological Trace Element Research.2019; 189(2): 336. CrossRef - Subklinik Hipotiroiditli Çocuklarda Ağız Sağlığı Durumunun Değerlendirilmesi
Nuray TÜLOĞLU, Tuğçe KALİÇOĞLU, Birgül KIREL
Journal of Biotechnology and Strategic Health Research.2019; 3(3): 237. CrossRef - Association High-Iodine-Containing Seaweed Soup Consumption after Birth and Subclinical Hypothyroidism in Korean Women: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey IV (2013–2015)
Hyunsam Kim, Ha Ni Lee, Jeonghoon Ha
International Journal of Thyroidology.2019; 12(2): 105. CrossRef - Graves Disease in Central Ghana: Clinical Characteristics and Associated Factors
Osei Sarfo-Kantanka, Fred Stephen Sarfo, Eunice Oparebea Ansah, Ishmael Kyei
Clinical Medicine Insights: Endocrinology and Diabetes.2018; 11: 117955141875907. CrossRef - Sex differences in risk factors for subclinical hypothyroidism
Jeonghoon Ha, Jeongmin Lee, Kwanhoon Jo, Dong-Jun Lim, Moo Il Kang, Bong Yun Cha, Min-Hee Kim
Endocrine Connections.2018; 7(4): 511. CrossRef - Age-sex disparities and sub-clinical hypothyroidism among patients in Tikur Anbesa Specialized Hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Habtamu Azene Tekle, Tesfahun Molla Bobe, Efrata Girma Tufa, Fithamlak Bisetegen Solomon
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Subclinical Hypothyroidism and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies
Shinje Moon, Min Joo Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Hyung Joon Yoo, Young Joo Park
Thyroid.2018; 28(9): 1101. CrossRef - Age- and gender-specific reference intervals of TSH and free T4 in an iodine-replete area: Data from Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey IV (2013–2015)
So Young Park, Hae In Kim, Hyun-Kyung Oh, Tae Hyuk Kim, Hye Won Jang, Jae Hoon Chung, Myung-Hee Shin, Sun Wook Kim, Sun Y Lee
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(2): e0190738. CrossRef - Helicobacter pylori-induced autoimmune thyroiditis: is the pathogenic link concluded or still a hypothesis?
Santhanamari Thiyagarajan, Anil M.R. Saini, Jamal Alruwaili
Reviews in Medical Microbiology.2018; 29(2): 64. CrossRef - Evaluation of Thyroid Hormone Levels and Urinary Iodine Concentrations in Koreans Based on the Data from Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VI (2013 to 2015)
Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(2): 160. CrossRef - Transcriptome Network Analysis Reveals Aging-Related Mitochondrial and Proteasomal Dysfunction and Immune Activation in Human Thyroid
Byuri Angela Cho, Seong-Keun Yoo, Young Shin Song, Su-jin Kim, Kyu Eun Lee, Minho Shong, Young Joo Park, Jeong-Sun Seo
Thyroid.2018; 28(5): 656. CrossRef - Relation of Subclinical Hypothyroidism is Associated With Cardiovascular Events and All-Cause Mortality in Adults With High Cardiovascular Risk
Shinje Moon, Sung Hye Kong, Hoon Sung Choi, Yul Hwangbo, Moon-Kyu Lee, Jae Hoon Moon, Hak Chul Jang, Nam Han Cho, Young Joo Park
The American Journal of Cardiology.2018; 122(4): 571. CrossRef - Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Coronary Revascularization After Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
Sung Hye Kong, Ji Won Yoon, Sang Yoon Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Kay-Hyun Park, Joong Haeng Choh, Young Joo Park, Cheong Lim
The American Journal of Cardiology.2018; 122(11): 1862. CrossRef - A Case of Subclinical Hyperthyroidism Treatment with Herbal Medicine
Dong-eun Jin, Seok-woo Kim, Hyeon-cheo Shin
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine.2018; 39(4): 831. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Risk in Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Mariana Dobrescu, Diana Păun, Daniel Grigorie, Cătălina Poiană
Internal Medicine.2018; 15(3): 51. CrossRef - Association between thyroid autoimmunity and Helicobacter pylori infection
Yun Mi Choi, Tae Yong Kim, Eui Young Kim, Eun Kyung Jang, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(2): 309. CrossRef - Effect of Marijuana Use on Thyroid Function and Autoimmunity
Sonali Malhotra, Rubina A. Heptulla, Peter Homel, Roja Motaghedi
Thyroid.2017; 27(2): 167. CrossRef - Insidious danger in childhood era's: subclinical hypothyroidism
Ayşegül Alpcan, Ayça Törel Ergür, Serkan Tursun
Ortadoğu Tıp Dergisi.2017; 9(1): 34. CrossRef - Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Reference Range and Prevalence of Thyroid Dysfunction in the Korean Population: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013 to 2015
Won Gu Kim, Won Bae Kim, Gyeongji Woo, Hyejin Kim, Yumi Cho, Tae Yong Kim, Sun Wook Kim, Myung-Hee Shin, Jin Woo Park, Hai-Lin Park, Kyungwon Oh, Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 106. CrossRef - Thyroid diseases and risk of non-thyroidal pathology
R I Glushakov, E V Kozyrko, I V Sobolev, S A Ermolova, O V Vlaseva, A A Kuzin, N I Tapilskaya
Kazan medical journal.2017; 98(1): 77. CrossRef - Hipertiroidismo
M. Toni, J. Pineda, E. Anda, J.C. Galofré
Medicine - Programa de Formación Médica Continuada Acreditado.2016; 12(13): 731. CrossRef - Subclinical Hypothyroidism in Childhood Cancer Survivors
Hyun Joo Lee, Seung Min Hahn, Song Lee Jin, Yoon Jung Shin, Sun Hee Kim, Yoon Sun Lee, Hyo Sun Kim, Chuhl Joo Lyu, Jung Woo Han
Yonsei Medical Journal.2016; 57(4): 915. CrossRef - Comparison of universal screening with targeted high-risk case finding for diagnosis of thyroid disorders
Sima Nazarpour, Fahimeh Ramezani Tehrani, Masoumeh Simbar, Maryam Tohidi, Hamid AlaviMajd, Fereidoun Azizi
European Journal of Endocrinology.2016; 174(1): 77. CrossRef - Association of low baseline free thyroxin levels with progression of coronary artery calcification over 4 years in euthyroid subjects: the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Hye‐Jeong Park, Jihyun Kim, Eun Jin Han, Se Eun Park, Cheol‐Young Park, Won‐Young Lee, Ki‐Won Oh, Sung‐Woo Park, Eun‐Jung Rhee
Clinical Endocrinology.2016; 84(6): 889. CrossRef - Distinct Features of Nonthyroidal Illness in Critically Ill Patients With Infectious Diseases
Woo Kyung Lee, Sena Hwang, Daham Kim, Seul Gi Lee, Seonhyang Jeong, Mi-Youn Seol, Hyunji Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Dong Yeop Shin, Woong Youn Chung, Eun Jig Lee, Jandee Lee, Young Suk Jo
Medicine.2016; 95(14): e3346. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef - Reference interval for thyrotropin in a ultrasonography screened Korean population
Mijin Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Soo Han Kim, Yunkyoung Lee, Su-yeon Park, Hyung-don Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Yun Mi Choi, Eun Kyung Jang, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Young Kee Shong, Won Bae Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2015; 30(3): 335. CrossRef - Incidence and Prevalence of Overt Hypothyroidism and Causative Diseases in Korea as Determined Using Claims Data Provided by the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service
Gi Hyeon Seo, Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(3): 288. CrossRef - Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Cardiovascular Disease
Sunghwan Suh, Duk Kyu Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(3): 246. CrossRef - Bone Health and Clinical Results after Hip Fracture Surgery in Patients with Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Ki-Choul Kim, Young-Kyun Lee, You Jin Lee, Yong-Chan Ha, Kyung-Hoi Koo
Journal of Bone Metabolism.2014; 21(3): 213. CrossRef - Subclinical Thyroid Dysfunction in the Elderly
Ki Dong Ko
Journal of the Korean Geriatrics Society.2014; 18(3): 111. CrossRef - Subclinical hypothyroidism in addition to common risk scores for prediction of cardiovascular disease: a 10-year community-based cohort study
Tae Hyuk Kim, Hoon Sung Choi, Ji Cheol Bae, Jae Hoon Moon, Hyung-Kwan Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Soo Lim, Do Joon Park, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Moon-Kyu Lee, Nam H Cho, Young Joo Park
European Journal of Endocrinology.2014; 171(5): 649. CrossRef
- Appropriateness of Levothyroxine Prescription: A Multicenter Retrospective Study


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



