Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Calcium & bone metabolism
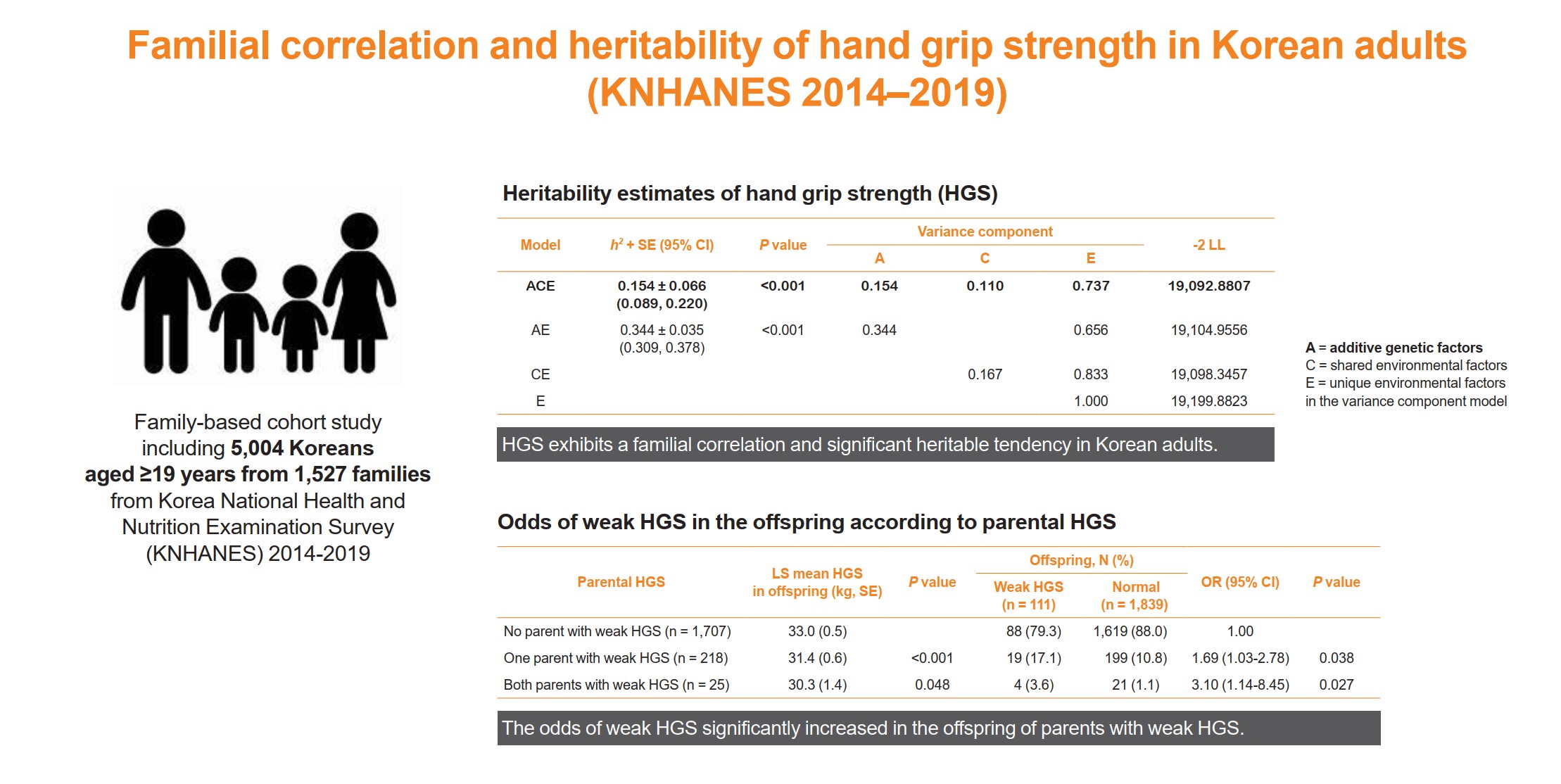
- Familial Correlation and Heritability of Hand Grip Strength in Korean Adults (Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2014 to 2019)
- Seong Hee Ahn, Eun Byeol Park, Seongha Seo, Yongin Cho, Da Hea Seo, So Hun Kim, Young Ju Suh, Seongbin Hong
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):709-719. Published online November 7, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1740
- 1,183 View
- 47 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The onset and progression of sarcopenia are highly variable among individuals owing to genetic and environmental factors. However, there are a limited number of studies measuring the heritability of muscle strength in large numbers of parent-adult offspring pairs. We aimed to investigate the familial correlation and heritability of hand grip strength (HGS) among Korean adults.
Methods
This family-based cohort study on data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2014 to 2019) included 5,004 Koreans aged ≥19 years from 1,527 families. HGS was measured using a digital grip strength dynamometer. Familial correlations of HGS were calculated in different pairs of relatives. Variance component methods were used to estimate heritability.
Results
The heritability estimate of HGS among Korean adults was 0.154 (standard error, 0.066). Correlation coefficient estimates for HGS between parent-offspring, sibling, and spouse pairs were significant at 0.07, 0.10, and 0.23 (P<0.001, P=0.041, and P<0.001, respectively). The total variance in the HGS phenotype was explained by additive genetic (15.4%), shared environmental (11.0%), and unique environmental (73.6%) influences. The odds of weak HGS significantly increased in the offspring of parents with weak HGS (odds ratio [OR], 1.69–3.10; P=0.027–0.038), especially in daughters (OR, 2.04–4.64; P=0.029–0.034).
Conclusion
HGS exhibits a familial correlation and significant heritable tendency in Korean adults. Therefore, Asian adults, especially women, who have parents with weak HGS, need to pay special attention to their muscle health with the help of healthy environmental stimuli.

- Calcium & bone metabolism
- Higher Plasma Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1 Is Associated with Lower Risk for Sarcopenia in Older Asian Adults
- Sunghwan Ji, Kyunggon Kim, So Jeong Park, Jin Young Lee, Hee-Won Jung, Hyun Ju Yoo, Il-Young Jang, Eunju Lee, Ji Yeon Baek, Beom-Jun Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):701-708. Published online October 18, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1783

- 1,672 View
- 76 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Despite the protective effects of stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1) in stimulating muscle regeneration shown in experimental research, there is a lack of clinical studies linking circulating SDF-1 concentrations with muscle phenotypes. In order to elucidate the role of SDF-1 as a potential biomarker reflecting human muscle health, we investigated the association of plasma SDF-1 levels with sarcopenia in older adults.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 97 community-dwelling participants who underwent a comprehensive geriatric assessment at a tertiary hospital in South Korea. Sarcopenia was defined by specific cutoff values applicable to the Asian population, whereas plasma SDF-1 levels were determined using an enzyme immunoassay.
Results
After accounting for sex, age, and body mass index, participants with sarcopenia and low muscle mass exhibited plasma SDF-1 levels that were 21.8% and 18.3% lower than those without these conditions, respectively (P=0.008 and P=0.009, respectively). Consistently, higher plasma SDF-1 levels exhibited a significant correlation with higher skeletal muscle mass index (SMI) and gait speed (both P=0.043), and the risk of sarcopenia and low muscle mass decreased by 58% and 55% per standard deviation increase in plasma SDF-1 levels, respectively (P=0.045 and P=0.030, respectively). Furthermore, participants in the highest SDF-1 tertile exhibited significantly higher SMI compared to those in the lowest tertile (P=0.012).
Conclusion
These findings clinically corroborate earlier experimental discoveries highlighting the muscle anabolic effects of SDF- 1 and support the potential role of circulating SDF-1 as a biomarker reflecting human muscle health in older adults.

- Miscellaneous
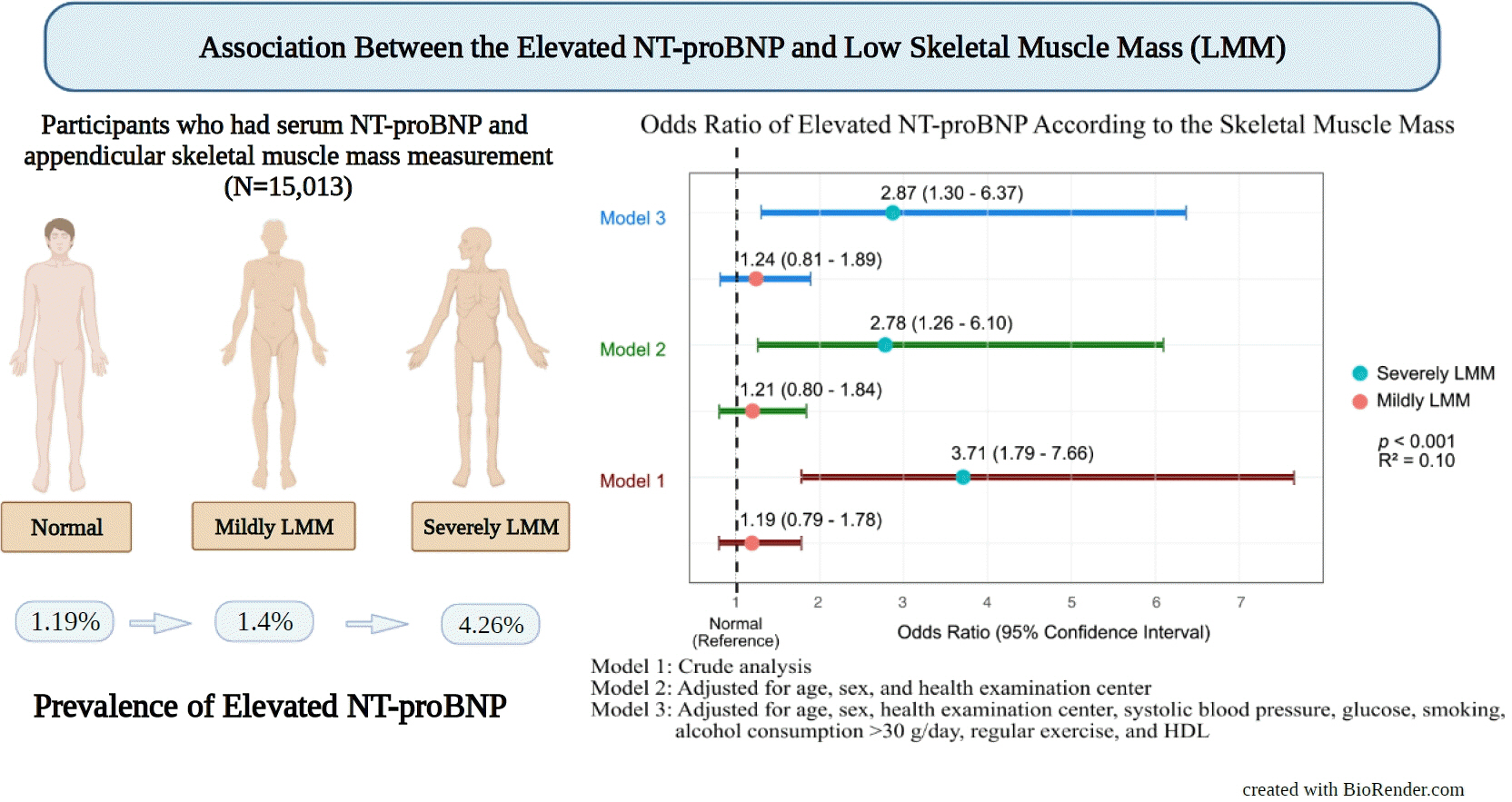
- Association between N-Terminal Prohormone Brain Natriuretic Peptide and Decreased Skeletal Muscle Mass in a Healthy Adult Population: A Cross-Sectional Study
- Tae Kyung Yoo, Marie Yung-Chen Wu, Moon Soo Kim, Mi-Yeon Lee, Yong-Taek Lee, Kyung Jae Yoon, Chul-Hyun Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):269-276. Published online March 13, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1588
- 1,801 View
- 76 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Although an inverse association between the N-terminal prohormone brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and obesity exists, only few major studies have assessed the association between NT-proBNP levels and skeletal muscle mass in asymptomatic healthy adults. Therefore, this cross-sectional study was conducted.
Methods
We assessed participants who underwent health examinations at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital in South Korea from January 2012 to December 2019. Appendicular skeletal muscle mass was measured using a bioelectrical impedance analyzer, and the skeletal muscle mass index (SMI) was calculated. Participants were divided into the control, mildly low skeletal muscle mass (LMM) (−2 standard deviation [SD] < SMI ≤−1 [SD]), and severely LMM groups (SD ≤−2) based on their SMI. The association between elevated NT-proBNP level (≥125 pg/mL) and skeletal muscle mass was assessed using multivariable logistic regression analysis with adjustment for confounding factors.
Results
This study enrolled 15,013 participants (mean age, 37.52±9.52; men, 54.24%; control, n=12,827; mildly LMM, n=1,998; severely LMM, n=188). Prevalence of elevated NT-proBNP was higher in mildly and severely LMM groups than in the control group (control, 1.19%; mildly LMM, 1.4%; severely LMM, 4.26%; P=0.001). The adjusted odds ratio (OR) of elevated NT-proBNP was significantly higher in severely LMM (OR, 2.87; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.3 to 6.37) than in control (OR, 1.00; reference) or mildly LMM groups (OR, 1.24; 95% CI, 0.81 to 1.89).
Conclusion
Our results showed that NT-proBNP elevation were more prevalent in participants with LMM. In addition, our study showed an association between skeletal muscle mass and NT-proBNP level in a relatively young and healthy adult population.

- Miscellaneous
- DN200434 Inhibits Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Prevents Neointima Formation in Mice after Carotid Artery Ligation
- Sudeep Kumar, Jonghwa Jin, Hyeon Young Park, Mi-Jin Kim, Jungwook Chin, Sungwoo Lee, Jina Kim, Jung-Guk Kim, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Keun-Gyu Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(5):800-809. Published online September 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1462

- 3,015 View
- 200 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Excessive proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), which contributes to the development of occlusive vascular diseases, requires elevated mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation to meet the increased requirements for energy and anabolic precursors. Therefore, therapeutic strategies based on blockade of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation are considered promising for treatment of occlusive vascular diseases. Here, we investigated whether DN200434, an orally available estrogen receptor-related gamma inverse agonist, inhibits proliferation and migration of VSMCs and neointima formation by suppressing mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation.
Methods
VSMCs were isolated from the thoracic aortas of 4-week-old Sprague-Dawley rats. Oxidative phosphorylation and the cell cycle were analyzed in fetal bovine serum (FBS)- or platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-stimulated VSMCs using a Seahorse XF-24 analyzer and flow cytometry, respectively. A model of neointimal hyperplasia was generated by ligating the left common carotid artery in male C57BL/6J mice.
Results
DN200434 inhibited mitochondrial respiration and mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 activity and consequently suppressed FBS- or PDGF-stimulated proliferation and migration of VSMCs and cell cycle progression. Furthermore, DN200434 reduced carotid artery ligation-induced neointima formation in mice.
Conclusion
Our data suggest that DN200434 is a therapeutic option to prevent the progression of atherosclerosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Jatrorrhizine inhibits Piezo1 activation and reduces vascular inflammation in endothelial cells
Tianying Hong, Xianmei Pan, Han Xu, Zhijuan Zheng, Lizhen Wen, Jing Li, Mingfeng Xia
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 163: 114755. CrossRef
- Jatrorrhizine inhibits Piezo1 activation and reduces vascular inflammation in endothelial cells

Review Article
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
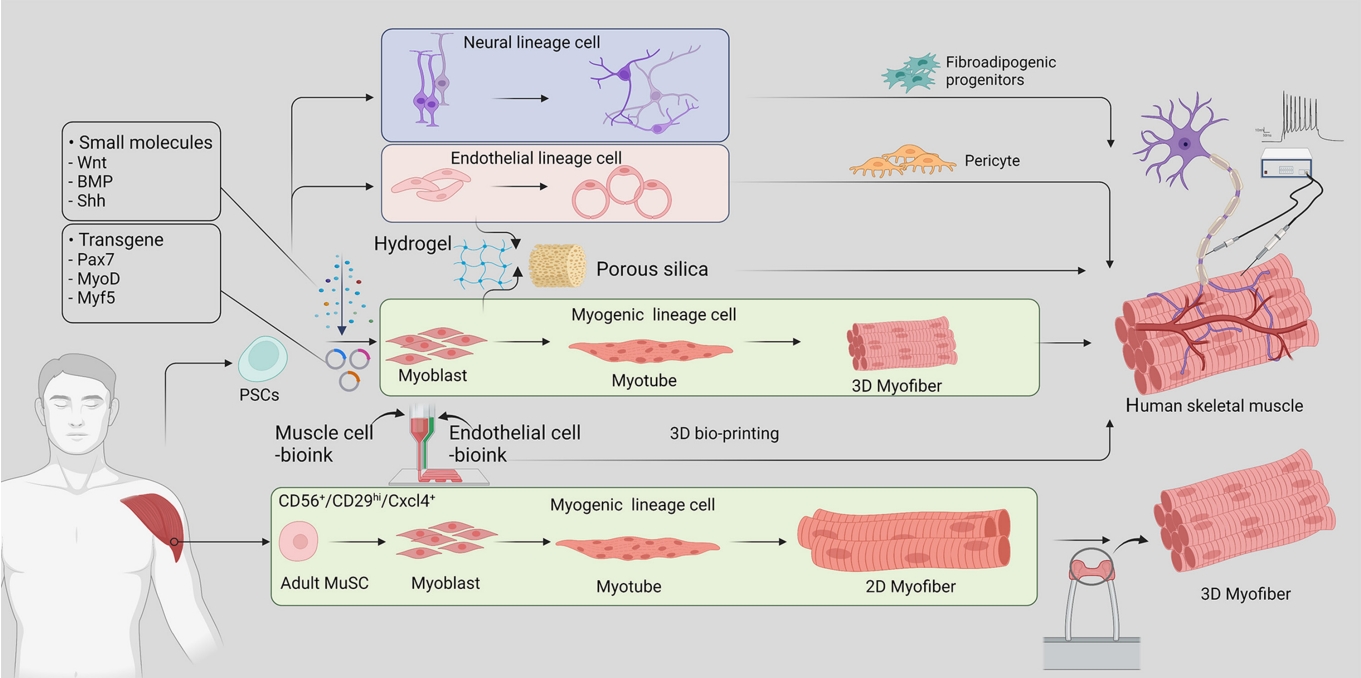
- Human Tissue-Engineered Skeletal Muscle: A Tool for Metabolic Research
- Ji-Hoon Kim, Seung-Min Yu, Jang Won Son
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):408-414. Published online June 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.302
- 3,975 View
- 162 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Skeletal muscle is now regarded as an endocrine organ based on its secretion of myokines and exerkines, which, in response to metabolic stimuli, regulate the crosstalk between the skeletal muscle and other metabolic organs in terms of systemic energy homeostasis. This conceptual basis of skeletal muscle as a metabolically active organ has provided insights into the potential role of physical inactivity and conditions altering muscle quality and quantity in the development of multiple metabolic disorders, including insulin resistance, obesity, and diabetes. Therefore, it is important to understand human muscle physiology more deeply in relation to the pathophysiology of metabolic diseases. Since monolayer cell lines or animal models used in conventional research differ from the pathophysiological features of the human body, there is increasing need for more physiologically relevant in vitro models of human skeletal muscle. Here, we introduce recent studies on in vitro models of human skeletal muscle generated from adult myogenic progenitors or pluripotent stem cells and summarize recent progress in the development of three-dimensional (3D) bioartificial muscle, which mimics the physiological complexity of native skeletal muscle tissue in terms of maturation and functionality. We then discuss the future of skeletal muscle 3D-organoid culture technology in the field of metabolic research for studying pathological mechanisms and developing personalized therapeutic strategies.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Human‐based new approach methodologies to accelerate advances in nutrition research
Manuela Cassotta, Danila Cianciosi, Maria Elexpuru‐Zabaleta, Inaki Elio Pascual, Sandra Sumallo Cano, Francesca Giampieri, Maurizio Battino
Food Frontiers.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Key indicators of beef safety and quality as important aspects of conservation
S. V. Furman, I. M. Sokulskyi, D. V. Lisohurska, O. V. Lisohurska, B. V. Gutyj
Ukrainian Journal of Veterinary and Agricultural Sciences.2024; 7(1): 68. CrossRef
- Human‐based new approach methodologies to accelerate advances in nutrition research

Brief Report
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
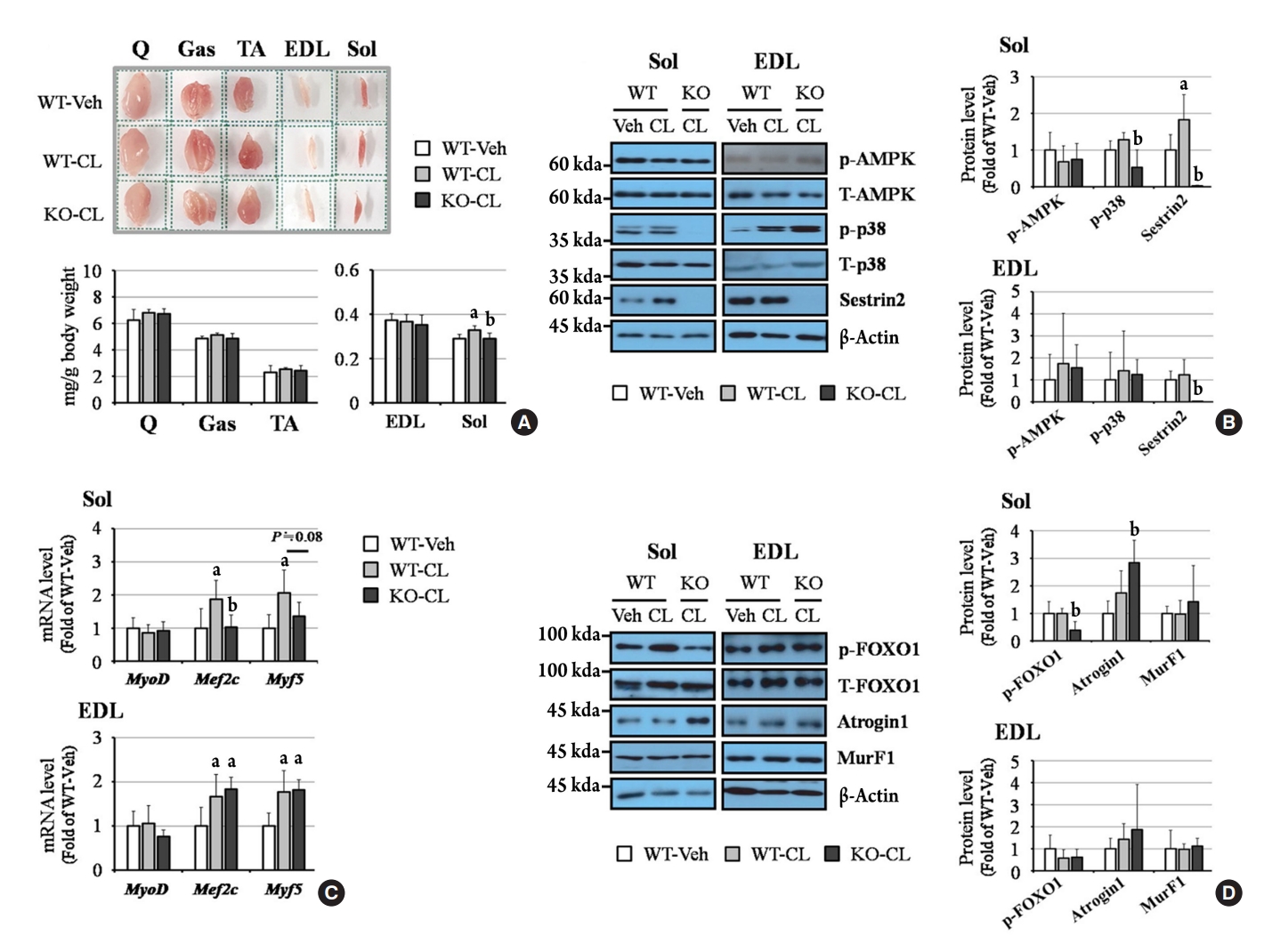
- Sestrin2 Regulates Beneficial β3-Adrenergic Receptor-Mediated Effects Observed in Inguinal White Adipose Tissue and Soleus Muscle
- Min Jeong Park, Joo Won Kim, Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hwan-Jin Hwang, Hye Jin Yoo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):552-557. Published online June 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1421
- 2,623 View
- 106 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Sestrin2, a well-known adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) regulator, plays a protective role against metabolic stress. The β3-adrenergic receptor (β3AR) induces fat browning and inhibits muscle atrophy in an AMPK-dependent manner. However, no prior research has examined the relationship of sestrin2 with β3AR in body composition changes. In this study, CL 316,243 (CL), a β3AR agonist, was administered to wild-type and sestrin2-knockout (KO) mice for 2 weeks, and fat and muscle tissues were harvested. CL induced AMPK phosphorylation, expression of brown-fat markers, and mitochondrial biogenesis, which resulted in the reduction of lipid droplet size in inguinal white adipose tissue (iWAT). These effects were not observed in sestrin2-KO mice. In CL-treated soleus muscle, sestrin2-KO was related to decreased myogenic gene expression and increased levels of muscle atrophy-related molecules. Our results suggest that sestrin2 is associated with beneficial β3AR-mediated changes in body composition, especially in iWAT and in the soleus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sestrin2 levels in patients with anxiety and depression myocardial infarction was up-regulated and suppressed inflammation and ferroptosis by LKB1-mediated AMPK activation
Yufeng Qian, Lian Chen, Beibei Gao, Xianhua Ye
Clinical and Experimental Hypertension.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sestrin2 in diabetes and diabetic complications
Xiaodan Zhang, Zirui Luo, Jiahong Li, Yaxuan Lin, Yu Li, Wangen Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Sestrin2 levels in patients with anxiety and depression myocardial infarction was up-regulated and suppressed inflammation and ferroptosis by LKB1-mediated AMPK activation

Original Articles
- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
- Decreased Serum Level of Sclerostin in Older Adults with Sarcopenia
- Seong Hee Ahn, Hee-Won Jung, Eunju Lee, Ji Yeon Baek, Il-Young Jang, So Jeong Park, Jin Young Lee, Eunah Choi, Yun Sun Lee, Seongbin Hong, Beom-Jun Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):487-496. Published online May 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1428
- 3,135 View
- 141 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
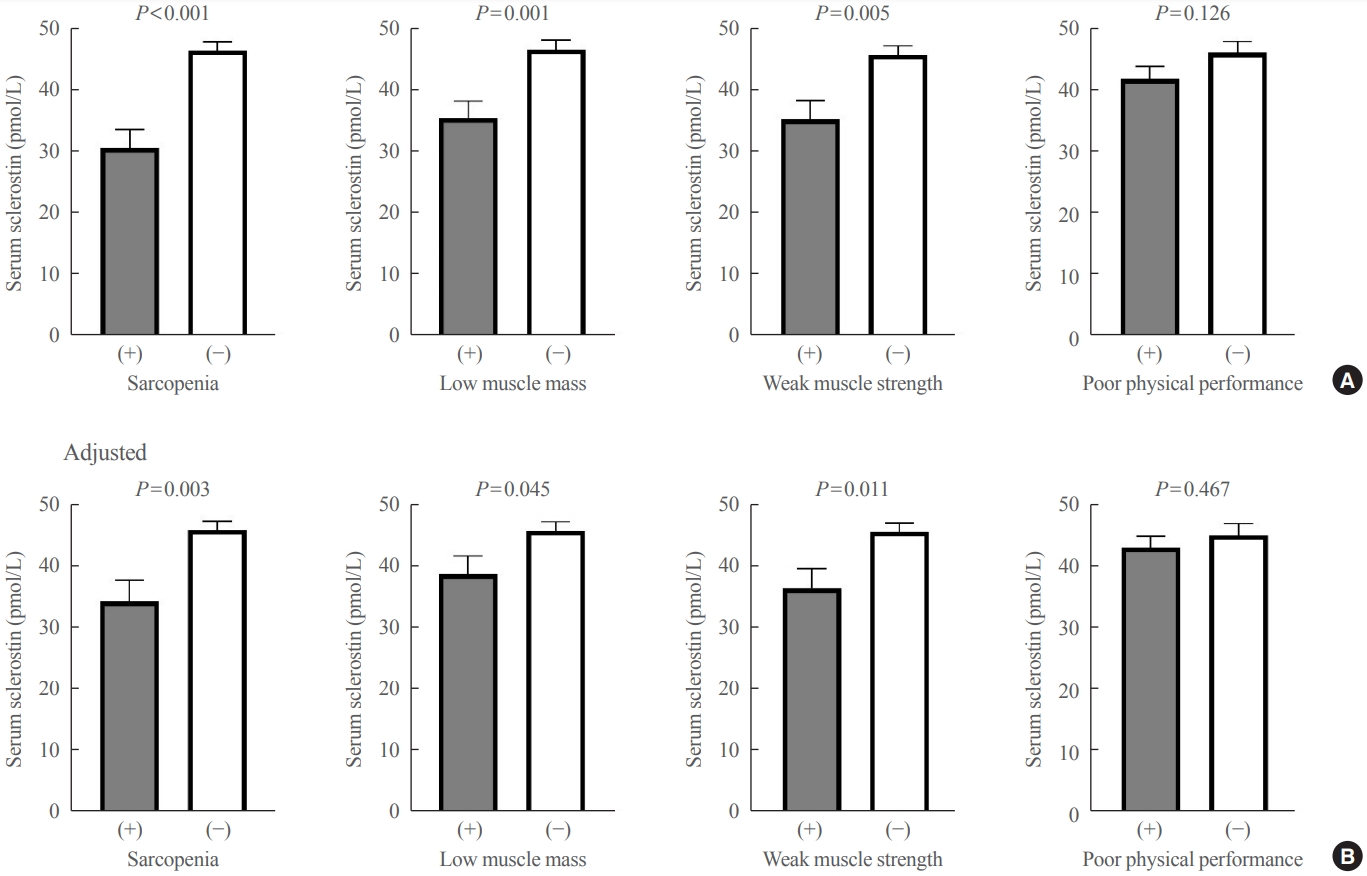
Although muscles and bones interact with each other through various secretory factors, the role of sclerostin, an osteocyte-secreted factor, on muscle metabolism has not been well studied. We investigated the levels of serum sclerostin in Korean older adults with sarcopenia.
Methods
Blood samples were collected from 129 participants who underwent evaluation of muscle mass and function in an outpatient geriatric clinic of a teaching hospital. Sarcopenia and related parameters were determined using cutoff values for the Asian population. Serum sclerostin levels were measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Results
The mean age of the participants was 69.6 years, and 20 participants (15.5%) were classified as having sarcopenia. After adjusting for age, sex, and body mass index, serum sclerostin levels were significantly lower in participants with sarcopenia, low muscle mass, or weak muscle strength (P=0.003 to 0.045). Serum sclerostin levels were positively associated with skeletal muscle index and grip strength after adjusting for confounders (P=0.001 and P=0.003), whereas sarcopenic phenotype score showed a negative association (P=0.006). These increases in muscle mass and strength were also dose dependent as serum sclerostin levels increased (P for trends=0.003 and P for trends=0.015). Higher serum sclerostin levels were associated with lower odds ratio (ORs) for sarcopenia, low muscle mass, and weak muscle strength after adjusting for confounders (OR, 0.27 to 0.50; P<0.001 to 0.025).
Conclusion
Higher serum sclerostin levels were associated with a lower risk of sarcopenia, low muscle mass, and weak muscle strength in Korean older adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mechanism and physical activities in bone-skeletal muscle crosstalk
Zhonghan Zhao, Kai Yan, Qiao Guan, Qiang Guo, Can Zhao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Musculoskeletal disorders and coronary artery disease —promising molecular markers: literature review
Viktoria N. Karetnikova, Anastasiya G. Neeshpapa, Evgenia I. Carpova, Olga L. Barbarash
CardioSomatics.2024; 15(1): 55. CrossRef - Determinants of bone mass in older adults with normal- and overweight derived from the crosstalk with muscle and adipose tissue
Carina O. Walowski, Catrin Herpich, Janna Enderle, Wiebke Braun, Marcus Both, Mario Hasler, Manfred J. Müller, Kristina Norman, Anja Bosy-Westphal
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of the Osteocyte in Musculoskeletal Disease
Anika Shimonty, Lynda F. Bonewald, Fabrizio Pin
Current Osteoporosis Reports.2023; 21(3): 303. CrossRef - The role of sclerostin in lipid and glucose metabolism disorders
Hewen Jiang, Dijie Li, Ying Han, Nanxi Li, Xiaohui Tao, Jin Liu, Zongkang Zhang, Yuanyuan Yu, Luyao Wang, Sifan Yu, Ning Zhang, Huan Xiao, Xin Yang, Yihao Zhang, Ge Zhang, Bao-Ting Zhang
Biochemical Pharmacology.2023; 215: 115694. CrossRef - Cytokines and exosomal miRNAs in skeletal muscle–adipose crosstalk
Liu Guo, Menchus Quan, Weijun Pang, Yulong Yin, Fengna Li
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 34(10): 666. CrossRef - Sclerostin: clinical insights in muscle–bone crosstalk
Antimo Moretti, Giovanni Iolascon
Journal of International Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-sclerostin antibodies: a new frontier in fragility fractures treatment
Giovanni Iolascon, Sara Liguori, Marco Paoletta, Giuseppe Toro, Antimo Moretti
Therapeutic Advances in Musculoskeletal Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sclerostin as a Putative Myokine in Sarcopenia
Hyon-Seung Yi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 430. CrossRef - Organokines, Sarcopenia, and Metabolic Repercussions: The Vicious Cycle and the Interplay with Exercise
Giulia Minniti, Letícia Maria Pescinini-Salzedas, Guilherme Almeida dos Santos Minniti, Lucas Fornari Laurindo, Sandra Maria Barbalho, Renata Vargas Sinatora, Lance Alan Sloan, Rafael Santos de Argollo Haber, Adriano Cressoni Araújo, Karina Quesada, Jesse
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(21): 13452. CrossRef
- Mechanism and physical activities in bone-skeletal muscle crosstalk

- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
- Association between Elevated Plasma Homocysteine and Low Skeletal Muscle Mass in Asymptomatic Adults
- Jae-Hyeong Choi, Jin-Woo Seo, Mi-Yeon Lee, Yong-Taek Lee, Kyung Jae Yoon, Chul-Hyun Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):333-343. Published online February 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1202
- 7,908 View
- 187 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
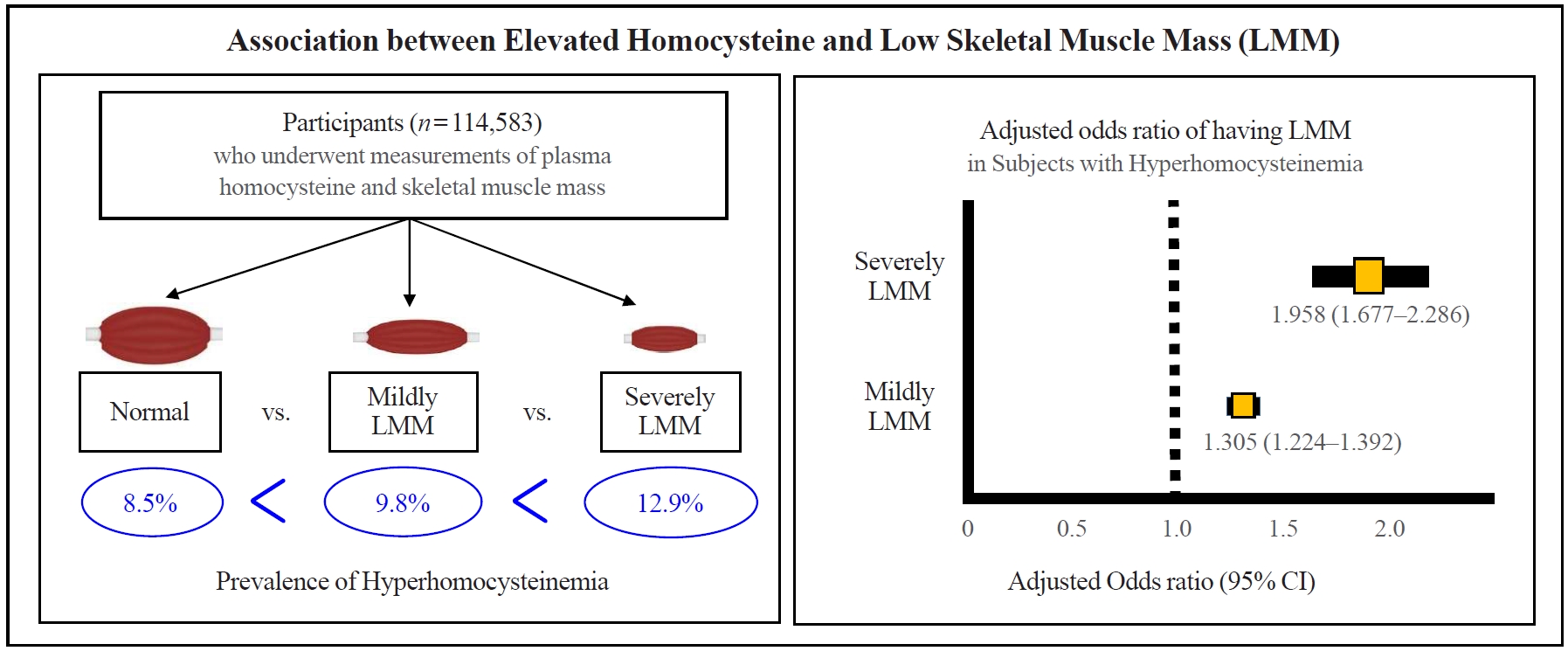
Homocysteine has been drawing attention with a closed linkage with skeletal muscle. However, the association of hyperhomocysteinemia with decreased skeletal muscle mass remains unclear. We aimed to investigate the association of hyperhomocysteinemia with low skeletal muscle mass (LMM) in asymptomatic adults.
Methods
This was a cross-sectional study of 114,583 community-dwelling adults without cancer, stroke, or cardiovascular diseases who underwent measurements of plasma homocysteine and body composition analysis from 2012 to 2018. Hyperhomocysteinemia was defined as >15 μmol/L. Skeletal muscle mass index (SMI) was calculated based on appendicular muscle mass (kg)/height (m)2. Participants were classified into three groups based on SMI: “normal,” “mildly low,” and “severely low.”
Results
The prevalence of hyperhomocysteinemia was the highest in subjects with severely LMM (12.9%), followed by those with mildly LMM (9.8%), and those with normal muscle mass (8.5%) (P for trend <0.001). In a multivariable logistic regression model, hyperhomocysteinemia was significantly associated with having a mildly LMM (odds ratio [OR], 1.305; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.224 to 1.392) and severely LMM (OR, 1.958; 95% CI, 1.667 to 2.286), respectively. One unit increment of log-transformed homocysteine was associated with 1.360 and 2.169 times higher risk of having mildly LMM and severely LMM, respectively.
Conclusion
We demonstrated that elevated homocysteine has an independent association with LMM in asymptomatic adults, supporting that hyperhomocysteinemia itself can be a risk for decline in skeletal musculature. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The role of the mitochondrial trans-sulfuration in cerebro-cardio renal dysfunction during trisomy down syndrome
Sathnur Pushpakumar, Mahavir Singh, Utpal Sen, N. Tyagi, Suresh C. Tyagi
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2024; 479(4): 825. CrossRef - Association of vitamins B1 and B2 intake with early-onset sarcopenia in the general adult population of the US: a cross-sectional study of NHANES data from 2011 to 2018
Sha Yang, Zhenyu Dong, Jiaqi Zhao, Lijia Yuan, Yao Xiao, Xing Luo, Zhuyang Zhao, Xia Kang, Kanglai Tang, Ming Chen, Liu Feng
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Triglyceride-Glucose Index with the Risk of Hyperhomocysteinemia Among Chinese Male Bus Drivers: A Longitudinal Study
Juan Xiong, Yanxia Wu, Lingling Huang, Xujuan Zheng
International Journal of General Medicine.2023; Volume 16: 2857. CrossRef - Relationship between hyperhomocysteinemia and coexisting obesity with low skeletal muscle mass in asymptomatic adult population
Tae Kyung Yoo, Hye Chang Rhim, Yong-Taek Lee, Kyung Jae Yoon, Chul-Hyun Park
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Causal effects of homocysteine levels on the components of sarcopenia: A two-sample mendelian randomization study
Hongwei Yu, Gan Luo, Tianwei Sun, Qiong Tang
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between serum homocysteine and sarcopenia among hospitalized older Chinese adults: a cross-sectional study
Bing Lu, Lingyu Shen, Haiqiong Zhu, Ling Xi, Wei Wang, Xiaojun Ouyang
BMC Geriatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- The role of the mitochondrial trans-sulfuration in cerebro-cardio renal dysfunction during trisomy down syndrome

Review Article
- Miscellaneous
- Quality Matters as Much as Quantity of Skeletal Muscle: Clinical Implications of Myosteatosis in Cardiometabolic Health
- Hong-Kyu Kim, Chul-Hee Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1161-1174. Published online December 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1348

- 6,391 View
- 283 Download
- 26 Web of Science
- 29 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Although age-related changes in skeletal muscles are closely associated with decreases in muscle strength and functional decline, their associations with cardiometabolic diseases in the literature are inconsistent. Such inconsistency could be explained by the fact that muscle quality—which is closely associated with fatty infiltration of the muscle (i.e., myosteatosis)—is as important as muscle quantity in cardiometabolic health. However, muscle quality has been less explored compared with muscle mass. Moreover, the standard definition of myosteatosis and its assessment methods have not been established yet. Recently, some techniques using single axial computed tomography (CT) images have been introduced and utilized in many studies, as the mass and quality of abdominal muscles could be measured opportunistically on abdominal CT scans obtained during routine clinical care. Yet, the mechanisms by which myosteatosis affect metabolic and cardiovascular health remain largely unknown. In this review, we explore the recent advances in the assessment of myosteatosis and its changes associated with aging. We also review the recent literature on the clinical implication of myosteatosis by focusing on metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Finally, we discuss the challenges and unanswered questions that need addressing to set myosteatosis as a therapeutic target for the prevention or treatment of cardiometabolic diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A CT-based Deep Learning Model for Predicting Subsequent Fracture Risk in Patients with Hip Fracture
Yisak Kim, Young-Gon Kim, Jung-Wee Park, Byung Woo Kim, Youmin Shin, Sung Hye Kong, Jung Hee Kim, Young-Kyun Lee, Sang Wan Kim, Chan Soo Shin
Radiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Myosteatosis is associated with poor survival after kidney transplantation: a large retrospective cohort validation
Jie Chen, Yue Li, Chengjie Li, Turun Song
Abdominal Radiology.2024; 49(4): 1210. CrossRef - Fatty infiltration of gastrocnemius–soleus muscle complex: Considerations for myosteatosis rehabilitation
Catherine Hatzantonis, Lalith Satkunam, Karyne N. Rabey, Jennifer C. Hocking, Anne M. R. Agur
Journal of Anatomy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Muscle attenuation, not skeletal muscle index, is an independent prognostic factor for survival in gastric cancer patients with overweight and obesity
Cheng-Le Zhuang, Hao-Fan Wu, Hao-Jie Jiang, Feng-Min Zhang, Han-Ping Shi, Zhen Yu, Xian Shen, Xiao-Lei Chen, Su-Lin Wang
Nutrition.2024; 122: 112391. CrossRef - Myosteatosis is associated with coronary artery calcification in patients with type 2 diabetes
Fu-Peng Liu, Mu-Jie Guo, Qing Yang, Yan-Ying Li, Yan-Gang Wang, Mei Zhang
World Journal of Diabetes.2024; 15(3): 429. CrossRef - Unlocking liver health: Can tackling myosteatosis spark remission in metabolic dysfunction‐associated steatotic liver disease?
Guillaume Henin, Audrey Loumaye, Louise Deldicque, Isabelle A. Leclercq, Nicolas Lanthier
Liver International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of serum gamma-glutamyl transferase with myosteatosis assessed by muscle quality mapping using abdominal computed tomography
Han Na Jung, Yun Kyung Cho, Hwi Seung Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Clinical Imaging.2023; 93: 4. CrossRef - Increased visceral fat area to skeletal muscle mass ratio is positively associated with the risk of cardiometabolic diseases in a Chinese natural population: A cross‐sectional study
Shi Zhang, Yaping Huang, Jing Li, Xincheng Wang, Xiaohe Wang, Minying Zhang, Yanju Zhang, Meiyang Du, Jingna Lin, Chunjun Li
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between hypertension and myosteatosis evaluated by abdominal computed tomography
Han Na Jung, Yun Kyung Cho, Hwi Seung Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Woo Je Lee, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Hypertension Research.2023; 46(4): 845. CrossRef - Epidemiological, mechanistic, and practical bases for assessment of cardiorespiratory fitness and muscle status in adults in healthcare settings
Jaime A. Gallo-Villegas, Juan C. Calderón
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2023; 123(5): 945. CrossRef - Muscle fat infiltration in chronic kidney disease: a marker related to muscle quality, muscle strength and sarcopenia
Carla Maria Avesani, Aline Miroski de Abreu, Heitor S. Ribeiro, Torkel B. Brismar, Peter Stenvinkel, Alice Sabatino, Bengt Lindholm
Journal of Nephrology.2023; 36(3): 895. CrossRef - IDF2022-1139 Association Between Dyslipidemia And Myosteatosis Using Visual Muscular Quality Map In Computed Tomography
H.S. Kim, H.N. Jung, Y.K. Cho, E.H. Kim, M.J. Lee, W.J. Lee, J.Y. Park, H.K. Kim, C.H. Jung
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 197: 110467. CrossRef - The role of skeletal muscle mass on cardiovascular disease risk: an emerging role on modulating lipid profile
Evangelia Damigou, Matina Kouvari, Demosthenes Panagiotakos
Current Opinion in Cardiology.2023; 38(4): 352. CrossRef - Reference values for low muscle mass and myosteatosis using tomographic muscle measurements in living kidney donors
Lisa B. Westenberg, Marcel Zorgdrager, Tim D. A. Swaab, Marco van Londen, Stephan J. L. Bakker, Henri G. D. Leuvenink, Alain R. Viddeleer, Robert A. Pol
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between sarcopenic obesity and poor muscle quality based on muscle quality map and abdominal computed tomography
Yun Kyung Cho, Han Na Jung, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Joong‐Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee, Hong‐Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Obesity.2023; 31(6): 1547. CrossRef - Increase in skeletal muscular adiposity and cognitive decline in a biracial cohort of older men and women
Caterina Rosano, Anne Newman, Adam Santanasto, Xiaonan Zhu, Bret Goodpaster, Iva Miljkovic
Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.2023; 71(9): 2759. CrossRef - Evaluation of Paraspinal Muscle Degeneration on Pain Relief after Percutaneous Epidural Adhesiolysis in Patients with Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Disease
Misun Kang, Shin Hyung Kim, Minju Jo, Hyun Eom Jung, Jungbin Bae, Hee Jung Kim
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1118. CrossRef - Sarcopenic obesity and its relation with muscle quality and mortality in patients on chronic hemodialysis
Alice Sabatino, Carla Maria Avesani, Giuseppe Regolisti, Marianna Adinolfi, Giuseppe Benigno, Marco Delsante, Enrico Fiaccadori, Ilaria Gandolfini
Clinical Nutrition.2023; 42(8): 1359. CrossRef - Association between computed tomography‐assessed sarcopenia and mortality in patients with anti‐neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody‐associated vasculitis
Sung Soo Ahn, Yong‐Beom Park, Sang‐Won Lee
International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases.2023; 26(9): 1704. CrossRef - Association Between Insulin Resistance and Myosteatosis Measured by Abdominal Computed Tomography
Myung Jin Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Han Na Jung, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Chang Hee Jung, Joong-Yeol Park, Hong-Kyu Kim, Woo Je Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(12): 3100. CrossRef - Association of Visceral Fat Obesity, Sarcopenia, and Myosteatosis with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease without Obesity
Hong-Kyu Kim, Sung-Jin Bae, Min Jung Lee, Eun Hee Kim, Hana Park, Hwi Seung Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee, Jaewon Choe
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 987. CrossRef - Different computed tomography parameters for defining myosteatosis in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
Wenyi Zhang, Jing Tang, Huiyu Tang, Lingling Xie, Jing Wang, Jinhui Wu, Ming Yang
Clinical Nutrition.2023; 42(12): 2414. CrossRef - All you need to know about sarcopenia: a short guide for an internal medicine physician in questions and answers
G. R. Bikbavova, M. A. Livzan, D. V. Tikhonravova
Bulletin of Siberian Medicine.2023; 22(3): 88. CrossRef - Muscle Fat Content Is Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis in Chinese Adults
W. Guo, X. Zhao, D. Cheng, X. Liang, M. Miao, X. Li, J. Lu, N. Xu, Shuang Hu, Qun Zhang
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2023; 27(11): 960. CrossRef - Body Composition Evaluation and Clinical Markers of Cardiometabolic Risk in Patients with Phenylketonuria
Luis M. Luengo-Pérez, Mercedes Fernández-Bueso, Ana Ambrojo, Marta Guijarro, Ana Cristina Ferreira, Luís Pereira-da-Silva, André Moreira-Rosário, Ana Faria, Conceição Calhau, Anne Daly, Anita MacDonald, Júlio César Rocha
Nutrients.2023; 15(24): 5133. CrossRef - Assessment of Muscle Quantity, Quality and Function
Bo Kyung Koo
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2022; 31(1): 9. CrossRef - Influence of cross‐sectional area and fat infiltration of paraspinal muscles on analgesic efficacy of epidural steroid injection in elderly patients
Hee Jung Kim, Miribi Rho, Kyung Bong Yoon, Minju Jo, Dong Woo Lee, Shin Hyung Kim
Pain Practice.2022; 22(7): 621. CrossRef - Sarcopenia, Obesity, Sarcopenic Obesity and Risk of Poor Nutritional Status in Polish Community-Dwelling Older People Aged 60 Years and Over
Marika Murawiak, Roma Krzymińska-Siemaszko, Aleksandra Kaluźniak-Szymanowska, Marta Lewandowicz, Sławomir Tobis, Katarzyna Wieczorowska-Tobis, Ewa Deskur-Śmielecka
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2889. CrossRef - Metabolic mechanisms for and treatment of NAFLD or NASH occurring after liver transplantation
Amedeo Lonardo, Alessandro Mantovani, Salvatore Petta, Amedeo Carraro, Christopher D. Byrne, Giovanni Targher
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2022; 18(10): 638. CrossRef
- A CT-based Deep Learning Model for Predicting Subsequent Fracture Risk in Patients with Hip Fracture

Original Articles
- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
- Comparison of Two DXA Systems, Hologic Horizon W and GE Lunar Prodigy, for Assessing Body Composition in Healthy Korean Adults
- Seung Shin Park, Soo Lim, Hoyoun Kim, Kyoung Min Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1219-1231. Published online December 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1274
- 4,325 View
- 149 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
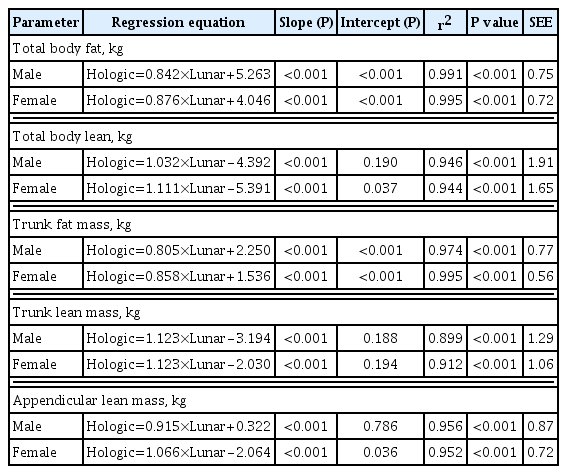
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is the most widely used method for evaluating muscle masses. The aim of this study was to investigate the agreement between muscle mass values assessed by two different DXA systems.
Methods
Forty healthy participants (20 men, 20 women; age range, 23 to 71 years) were enrolled. Total and regional body compositional values for fat and lean masses were measured consecutively with two DXA machines, Hologic Horizon and GE Lunar Prodigy. Appendicular lean mass (ALM) was calculated as the sum of the lean mass of four limbs.
Results
In both sexes, the ALM values measured by the GE Lunar Prodigy (24.8±4.3 kg in men, 15.8±2.9 kg in women) were significantly higher than those assessed by Hologic Horizon (23.0±4.0 kg in men, 14.8±3.2 kg in women). Furthermore, BMI values or body fat (%), either extremely higher or lower levels, contributed greater differences between two systems. Bland-Altman analyses revealed a significant bias between ALM values assessed by the two systems. Linear regression analyses were performed to develop equations to adjust for systematic differences (men: Horizon ALM [kg]=0.915×Lunar Prodigy ALM [kg]+0.322, R2=0.956; women: Horizon ALM [kg]=1.066×Lunar Prodigy ALM [kg]–2.064, R2=0.952).
Conclusion
Although measurements of body composition including muscle mass by the two DXA systems correlated strongly, significant differences were observed. Calibration equations should enable mutual conversion between different DXA systems. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Total and regional appendicular skeletal muscle mass prediction from dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry body composition models
Cassidy McCarthy, Grant M. Tinsley, Anja Bosy-Westphal, Manfred J. Müller, John Shepherd, Dympna Gallagher, Steven B. Heymsfield
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross-Calibration of iDXA and pQCT Scanners at Rural and Urban Research Sites in The Gambia, West Africa
Mícheál Ó Breasail, Ramatoulie Janha, Ayse Zengin, Camille Pearse, Landing Jarjou, Ann Prentice, Kate A. Ward
Calcified Tissue International.2023; 112(5): 573. CrossRef - Estimation of Absolute and Relative Body Fat Content Using Noninvasive Surrogates: Can DXA Be Bypassed?
David J. Greenblatt, Christopher D. Bruno, Jerold S. Harmatz, Bess Dawson‐Hughes, Qingchen Zhang, Chunhui Li, Christina R. Chow
The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Total and regional appendicular skeletal muscle mass prediction from dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry body composition models

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Musclin Is Related to Insulin Resistance and Body Composition, but Not to Body Mass Index or Cardiorespiratory Capacity in Adults
- Yeliana L. Sánchez, Manuela Yepes-Calderón, Luis Valbuena, Andrés F. Milán, María C. Trillos-Almanza, Sergio Granados, Miguel Peña, Mauricio Estrada-Castrillón, Juan C. Aristizábal, Raúl Narvez-Sanchez, Jaime Gallo-Villegas, Juan C. Calderón
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1055-1068. Published online October 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1104
- 5,044 View
- 137 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We studied whether musclin function in humans is related to glycemic control, body composition, and cardiorespiratory capacity.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was performed in sedentary adults with or without metabolic syndrome (MS). Serum musclin was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Insulin resistance (IR) was evaluated by the homeostatic model assessment (HOMA-IR). Body composition was determined by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and muscle composition by measuring carnosine in the thigh, a surrogate of fiber types, through proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Cardiorespiratory capacity was assessed through direct ergospirometry.
Results
The control (n=29) and MS (n=61) groups were comparable in age (51.5±6.5 years old vs. 50.7±6.1 years old), sex (72.4% vs. 70.5% women), total lean mass (58.5%±7.4% vs. 57.3%±6.8%), and peak oxygen consumption (VOpeak) (31.0±5.8 mL O2./kg.min vs. 29.2±6.3 mL O2/kg.min). Individuals with MS had higher body mass index (BMI) (30.6±4.0 kg/m2 vs. 27.4± 3.6 kg/m2), HOMA-IR (3.5 [95% confidence interval, CI, 2.9 to 4.6] vs. 1.7 [95% CI, 1.1 to 2.0]), and musclin (206.7 pg/mL [95% CI, 122.7 to 387.8] vs. 111.1 pg/mL [95% CI, 63.2 to 218.5]) values than controls (P˂0.05). Musclin showed a significant relationship with HOMA-IR (β=0.23; 95% CI, 0.12 to 0.33; P˂0.01), but not with VOpeak, in multiple linear regression models adjusted for age, sex, fat mass, lean mass, and physical activity. Musclin was significantly associated with insulin, glycemia, visceral fat, and regional muscle mass, but not with BMI, VCO2peak, maximum heart rate, maximum time of work, or carnosine.
Conclusion
In humans, musclin positively correlates with insulinemia, IR, and a body composition profile with high visceral adiposity and lean mass, but low body fat percentage. Musclin is not related to BMI or cardiorespiratory capacity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Musclin Mitigates the Attachment of HUVECs to THP-1 Monocytes in Hyperlipidemic Conditions through PPARα/HO-1-Mediated Attenuation of Inflammation
Wonjun Cho, Heeseung Oh, Sung Woo Choi, A. M. Abd El-Aty, Fatma Yeşilyurt, Ji Hoon Jeong, Tae Woo Jung
Inflammation.2024; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Glucose restriction enhances oxidative fiber formation: A multi-omic signal network involving AMPK and CaMK2
Kaiyi Zhang, Ning Xie, Huaqiong Ye, Jiakun Miao, Boce Xia, Yu Yang, Huanqi Peng, Shuang Xu, Tianwen Wu, Cong Tao, Jinxue Ruan, Yanfang Wang, Shulin Yang
iScience.2024; 27(1): 108590. CrossRef - Myokines: metabolic regulation in obesity and type 2 diabetes
Zhi-Tian Chen, Zhi-Xuan Weng, Jiandie D Lin, Zhuo-Xian Meng
Life Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiological, mechanistic, and practical bases for assessment of cardiorespiratory fitness and muscle status in adults in healthcare settings
Jaime A. Gallo-Villegas, Juan C. Calderón
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2023; 123(5): 945. CrossRef - Serum Levels of Myonectin Are Lower in Adults with Metabolic Syndrome and Are Negatively Correlated with Android Fat Mass
Jorge L. Petro, María Carolina Fragozo-Ramos, Andrés F. Milán, Juan C. Aristizabal, Jaime A. Gallo-Villegas, Juan C. Calderón
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(8): 6874. CrossRef - The correlation of serum musclin with diabetic nephropathy
Jie Zhang, Jing Shi, Zengguang Cheng, Wenchao Hu
Cytokine.2023; 167: 156211. CrossRef - Efficacy of high-intensity interval- or continuous aerobic-training on insulin resistance and muscle function in adults with metabolic syndrome: a clinical trial
Jaime Gallo-Villegas, Leonardo A. Castro-Valencia, Laura Pérez, Daniel Restrepo, Oscar Guerrero, Sergio Cardona, Yeliana L. Sánchez, Manuela Yepes-Calderón, Luis H. Valbuena, Miguel Peña, Andrés F. Milán, Maria C. Trillos-Almanza, Sergio Granados, Juan C.
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2022; 122(2): 331. CrossRef - Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species (RONS) and Cytokines—Myokines Involved in Glucose Uptake and Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle
Paola Llanos, Jesus Palomero
Cells.2022; 11(24): 4008. CrossRef
- Musclin Mitigates the Attachment of HUVECs to THP-1 Monocytes in Hyperlipidemic Conditions through PPARα/HO-1-Mediated Attenuation of Inflammation

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Differences in Abdominal Body Composition According to Glycemic Status: An Inverse Probability Treatment Weighting Analysis
- Seungbong Han, Young-Jee Jeon, Gyung-Min Park, Tae Young Lee, Soon Eun Park, Gyeongseok Yu, Byung Ju Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):855-864. Published online August 11, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1086
- 3,196 View
- 110 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
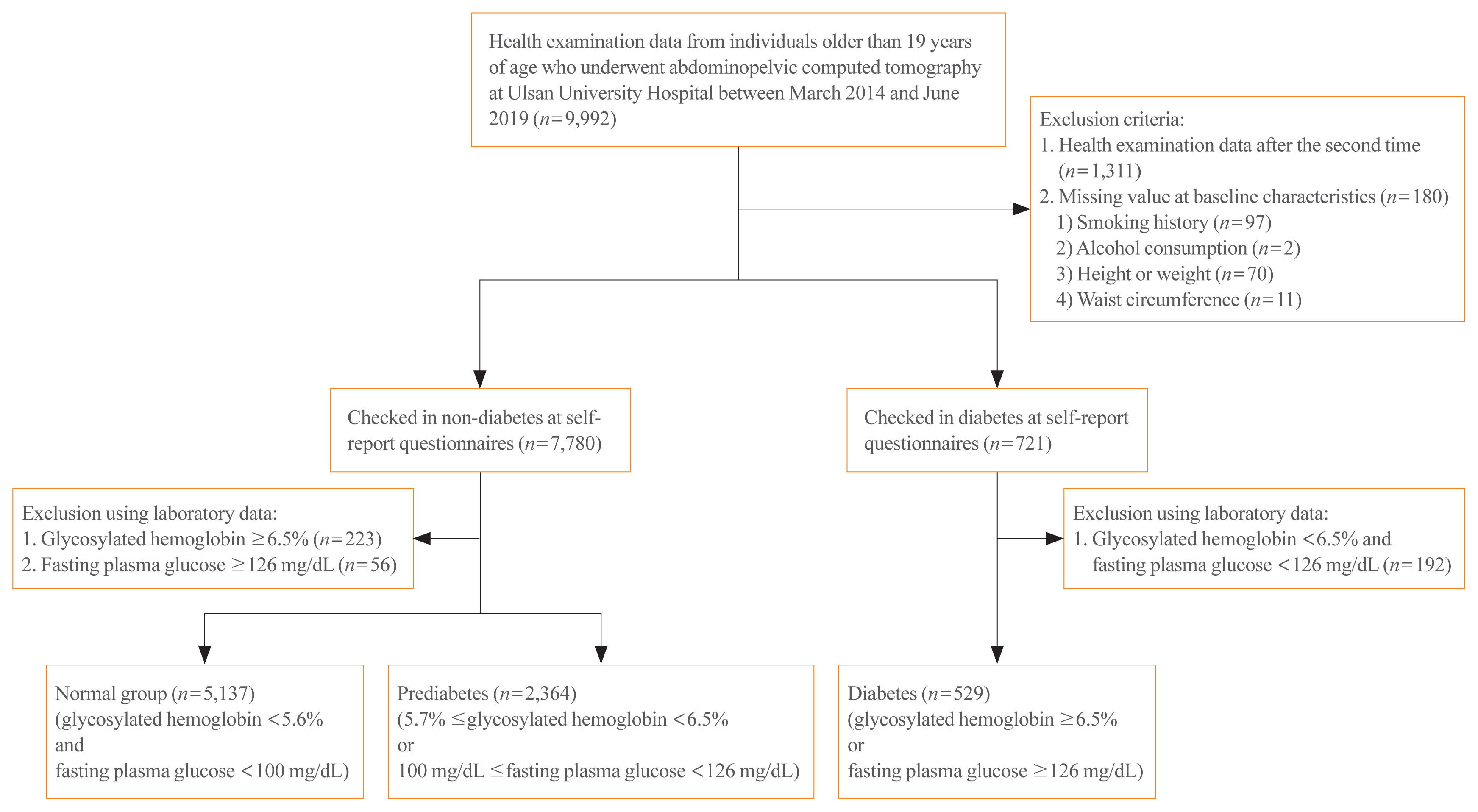
Several studies have reported that abdominal fat and muscle changes occur in diabetic patients. However, there are few studies about such changes among prediabetic patients. In this study, we evaluated the differences in abdominal fat and muscles based on abdominopelvic computed tomography in prediabetic and diabetic subjects compared to normal subjects.
Methods
We performed a cross-sectional study using health examination data from March 2014 to June 2019 at Ulsan University Hospital and classified subjects into normal, prediabetic, and diabetic groups. We analyzed the body mass index corrected area of intra-abdominal components among the three groups using inverse probability treatment weighting (IPTW) analysis.
Results
Overall, 8,030 subjects were enrolled; 5,137 (64.0%), 2,364 (29.4%), and 529 (6.6%) subjects were included in the normal, prediabetic, and diabetic groups, respectively. After IPTW adjustment of baseline characteristics, there were significant differences in log visceral adipose tissue index (VATI; 1.22±0.64 cm2/[kg/m2] vs. 1.30±0.63 cm2/[kg/m2] vs. 1.47±0.64 cm2/[kg/m2], P<0.001) and low-attenuation muscle index (LAMI; 1.02±0.36 cm2/[kg/m2] vs. 1.03±0.36 cm2/[kg/m2] vs. 1.09±0.36 cm2/[kg/m2], P<0.001) among the normal, prediabetic, and diabetic groups. Prediabetic subjects had higher log VATI (estimated coefficient= 0.082, P<0.001), and diabetic subjects had higher log VATI (estimated coefficient=0.248, P<0.001) and LAMI (estimated coefficient=0.078, P<0.001) compared to normal subjects.
Conclusion
Considering that VATI and LAMI represented visceral fat and lipid-rich skeletal muscle volumes, respectively, visceral obesity was identified in both prediabetic and diabetic subjects compared to normal subjects in this study. However, intra-muscular fat infiltration was observed in diabetic subjects only. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Testosterone is associated with abdominal body composition derived from computed tomography: a large cross sectional study
Seungbong Han, Young-Jee Jeon, Tae Young Lee, Gyung-Min Park, Sungchan Park, Seong Cheol Kim
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Testosterone is associated with abdominal body composition derived from computed tomography: a large cross sectional study

Review Article
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Exercise/Resistance Training and Muscle Stem Cells
- So-ichiro Fukada, Ayasa Nakamura
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):737-744. Published online August 10, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.401
- 5,226 View
- 259 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
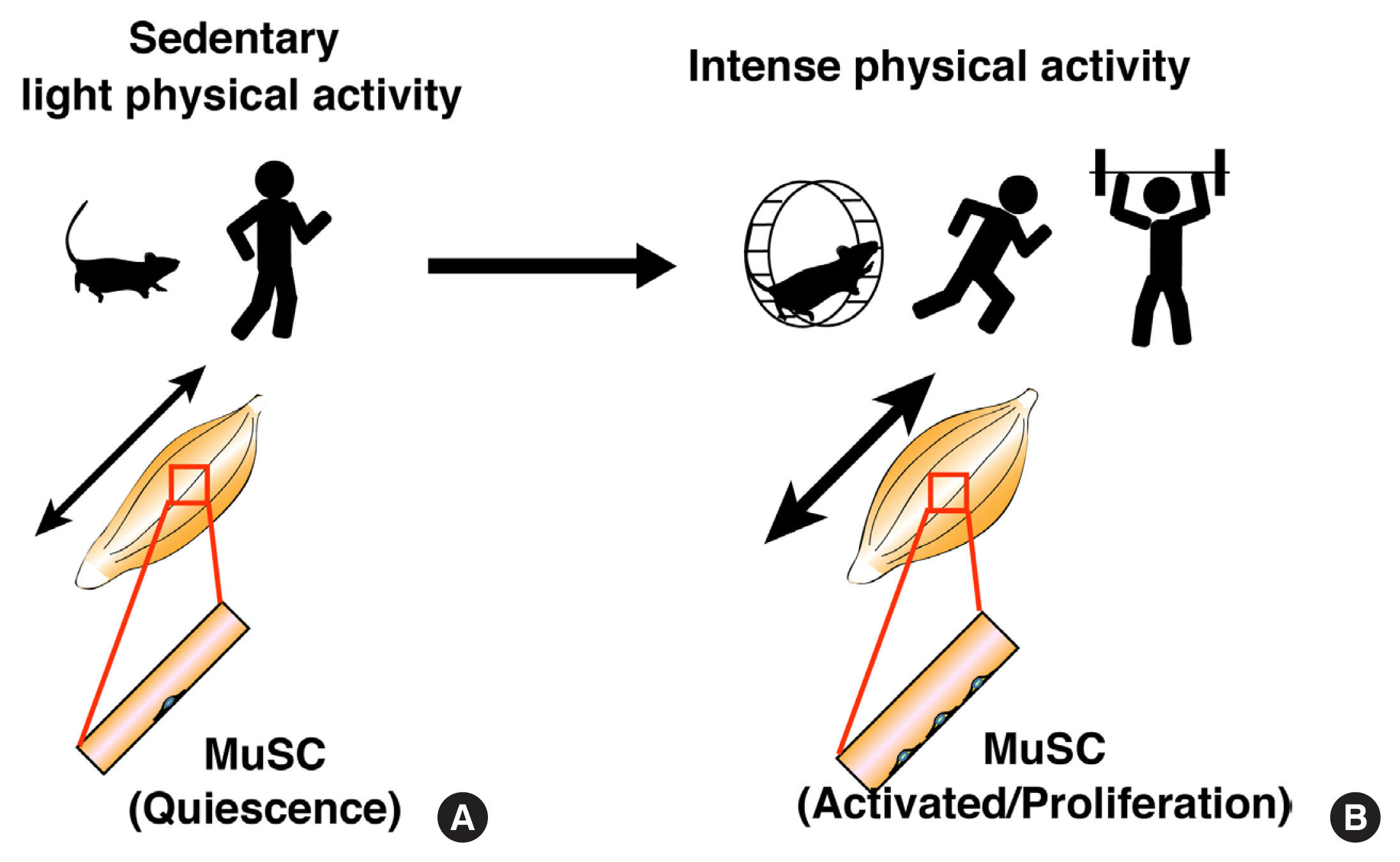
ePub - Skeletal muscle has attracted attention as endocrine organ, because exercise-dependent cytokines called myokines/exerkines are released from skeletal muscle and are involved in systemic functions. While, local mechanical loading to skeletal muscle by exercise or resistance training alters myofiber type and size and myonuclear number. Skeletal muscle-resident stem cells, known as muscle satellite cells (MuSCs), are responsible for the increased number of myonuclei. Under steady conditions, MuSCs are maintained in a mitotically quiescent state but exit from that state and start to proliferate in response to high physical activity. Alterations in MuSC behavior occur when myofibers are damaged, but the lethal damage to myofibers does not seem to evoke mechanical loading-dependent MuSC activation and proliferation. Given that MuSCs proliferate without damage, it is unclear how the different behaviors of MuSCs are controlled by different physical activities. Recent studies demonstrated that myonuclear number reflects the size of myofibers; hence, it is crucial to know the properties of MuSCs and the mechanism of myonuclear accretion by MuSCs. In addition, the elucidation of mechanical load-dependent changes in muscle resident cells, including MuSCs, will be necessary for the discovery of new myokines/exerkines and understating skeletal muscle diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Control of muscle satellite cell function by specific exercise‐induced cytokines and their applications in muscle maintenance
Qian Guo, Qing Luo, Guanbin Song
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2024; 15(2): 466. CrossRef - Resistance exercise preconditioning prevents disuse muscle atrophy by inhibiting apoptosis and protein degradation via SESN2 in C57BL/6J mice
Yating Huang, Chenxin Jiang, Xiuru Li, Sujuan Liu, Yanmei Niu, Li Fu
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2024; 1870(4): 167111. CrossRef - Anthropometric, muscle and serum myokine levels effects of physical exercise with an online platform in female patients with obesity
David Primo, Olatz Izaola, Juan Jose Lopez Gomez, Daniel de Luis
Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición.2023; 70(7): 484. CrossRef - Anthropometric, muscle and serum myokine levels effects of physical exercise with an online platform in female patients with obesity
David Primo, Olatz Izaola, Juan Jose Lopez Gomez, Daniel de Luis
Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición (English ed.).2023; 70(7): 484. CrossRef - The muscle stem cell niche at a glance
Margaret Hung, Hsiao-Fan Lo, Grace E. L. Jones, Robert S. Krauss
Journal of Cell Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise Therapy for People With Sarcopenic Obesity: Myokines and Adipokines as Effective Actors
Hamed Alizadeh Pahlavani
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms of exercise contributing to tissue regeneration
Jibao Chen, Ren Zhou, Ye Feng, Lin Cheng
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Control of muscle satellite cell function by specific exercise‐induced cytokines and their applications in muscle maintenance

Original Article
- Adrenal Gland
- Aldosterone Inhibits In Vitro Myogenesis by Increasing Intracellular Oxidative Stress via Mineralocorticoid Receptor
- Jin Young Lee, Da Ae Kim, Eunah Choi, Yun Sun Lee, So Jeong Park, Beom-Jun Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):865-874. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1108

- 4,254 View
- 111 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Despite clinical evidence indicating poor muscle health in subjects with primary aldosteronism (PA), it is still unclear whether the role of aldosterone in muscle metabolism is direct or mediated indirectly via factors, such as electrolyte imbalance or impaired glucose uptake. As one approach to clarify this issue, we investigated the effect of aldosterone on in vitro myogenesis and the potential mechanism explaining it.
Methods
Myogenesis was induced in mouse C2C12 myoblasts with 2% horse serum. Immunofluorescence, quantitative reversetranscription polymerase chain reaction, Western blot, viability, and migration analyses were performed for experimental research.
Results
Recombinant aldosterone treatment suppressed muscle differentiation from mouse C2C12 myoblasts in a dose-dependent manner, and consistently reduced the expression of myogenic differentiation markers. Furthermore, aldosterone significantly increased intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in myotubes, and treatment with N-acetyl cysteine, a potent biological thiol antioxidant, reversed the decrease of myotube area, myotube area per myotube, nucleus number per myotube, and fusion index due to aldosterone through decreasing oxidative stress. A binding enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay confirmed that mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) interacted with aldosterone in C2C12 myoblasts, while eplerenone, an MR inhibitor, blocked aldosterone-stimulated intracellular ROS generation during myogenesis and markedly attenuated the suppression of in vitro myogenesis by aldosterone.
Conclusion
These findings support the hypothesis that hypersecretion of aldosterone, like PA, directly contributes to muscular deterioration and suggest that antioxidants and/or MR antagonists could be effective therapeutic options to reduce the risk of sarcopenia in these patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Molecular mechanisms underlying sarcopenia in heart failure
Cody A. Rutledge
The Journal of Cardiovascular Aging.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) skeletal muscle: A transcriptomic perspective of cortisol action
Jorge E. Aedo, Rodrigo Zuloaga, Daniela Aravena-Canales, Alfredo Molina, Juan Antonio Valdés
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of 11-Deoxycorticosterone in the Transcriptomic Response to Stress in Rainbow Trout Skeletal Muscle
Rodrigo Zuloaga, Daniela Aravena-Canales, Jorge Eduardo Aedo, Cesar Osorio-Fuentealba, Alfredo Molina, Juan Antonio Valdés
Genes.2023; 14(2): 512. CrossRef - Heart Failure Medication and Muscle Wasting
Yasuhiro Izumiya
Circulation Journal.2023; 88(1): 20. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Endocrine Society Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Primary Aldosteronism
Jeonghoon Ha, Jung Hwan Park, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Kyong Yeun Jung, Jeongmin Lee, Jong Han Choi, Seung Hun Lee, Namki Hong, Jung Soo Lim, Byung Kwan Park, Jung-Han Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Jooyoung Cho, Mi-kyung Kim, Choon Hee Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 597. CrossRef - Higher Plasma Stromal Cell-Derived Factor 1 Is Associated with Lower Risk for Sarcopenia in Older Asian Adults
Sunghwan Ji, Kyunggon Kim, So Jeong Park, Jin Young Lee, Hee-Won Jung, Hyun Ju Yoo, Il-Young Jang, Eunju Lee, Ji Yeon Baek, Beom-Jun Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 701. CrossRef - The Role of Aldosterone in OSA and OSA-Related Hypertension
Yi Wang, Chuan Xiang Li, Ying Ni Lin, Li Yue Zhang, Shi Qi Li, Liu Zhang, Ya Ru Yan, Fang Ying Lu, Ning Li, Qing Yun Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Daiji Kawanami, Yuichi Takashi, Yoshimi Muta, Naoki Oda, Dai Nagata, Hiroyuki Takahashi, Makito Tanabe
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Molecular mechanisms underlying sarcopenia in heart failure

Review Article
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Receptor-Mediated Muscle Homeostasis as a Target for Sarcopenia Therapeutics
- Jong Hyeon Yoon, Ki-Sun Kwon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):478-490. Published online June 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1081
- 8,822 View
- 334 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
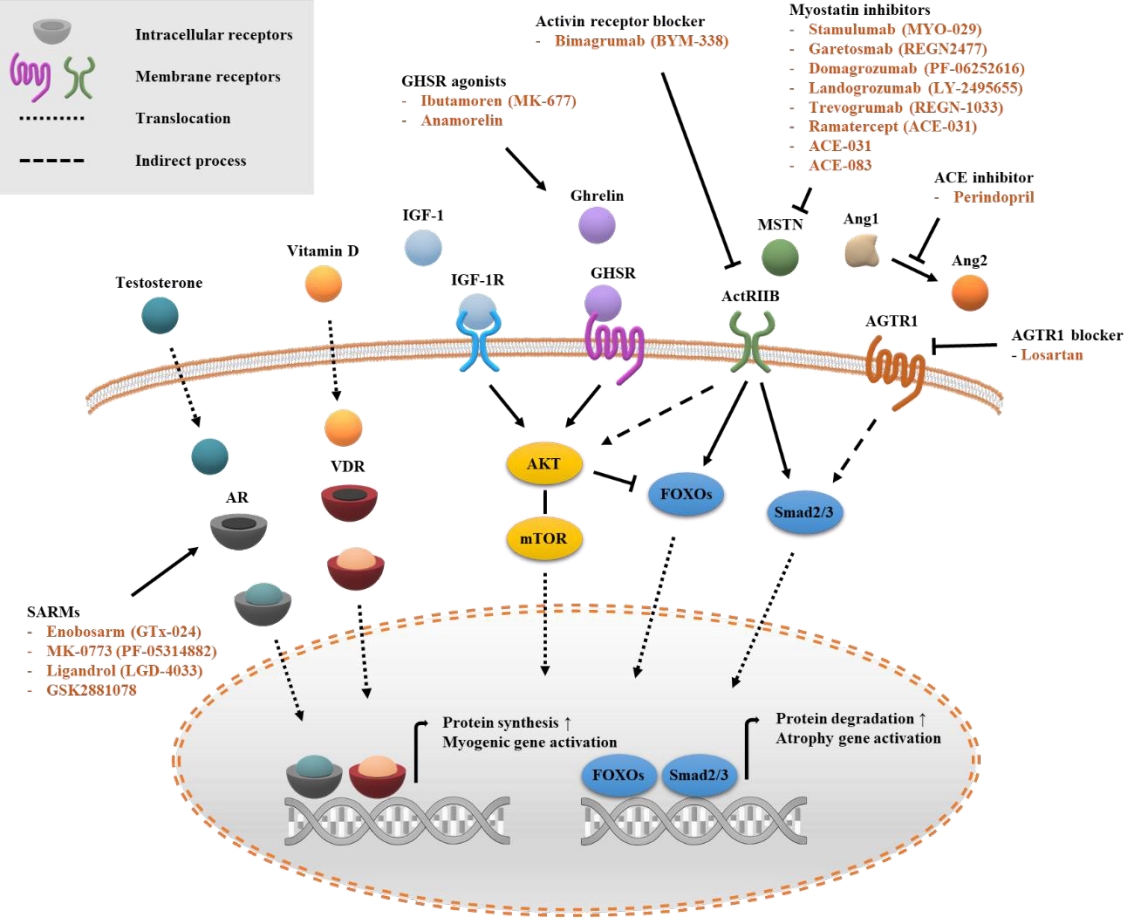
ePub - Sarcopenia is a disease characterized by age-related decline of skeletal muscle mass and function. The molecular mechanisms of the pathophysiology of sarcopenia form a complex network due to the involvement of multiple interconnected signaling pathways. Therefore, signaling receptors are major targets in pharmacological strategies in general. To provide a rationale for pharmacological interventions for sarcopenia, we herein describe several druggable signaling receptors based on their role in skeletal muscle homeostasis and changes in their activity with aging. A brief overview is presented of the efficacy of corresponding drug candidates under clinical trials. Strategies targeting the androgen receptor, vitamin D receptor, Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor, and ghrelin receptor primarily focus on promoting anabolic action using natural ligands or mimetics. Strategies involving activin receptors and angiotensin receptors focus on inhibiting catabolic action. This review may help to select specific targets or combinations of targets in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Current Landscape of Pharmacotherapies for Sarcopenia
Gulistan Bahat, Serdar Ozkok
Drugs & Aging.2024; 41(2): 83. CrossRef - Associations of micronutrient dietary patterns with sarcopenia among US adults: a population-based study
Yining Liu, Xiangliang Liu, Linnan Duan, Yixin Zhao, Yuwei He, Wei Li, Jiuwei Cui
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Vitamin D Level on Sarcopenia in Elderly People: A Critical Review
Saniya Khan, Sunil Kumar, Sourya Acharya, Anil Wanjari
Journal of Health and Allied Sciences NU.2023; 13(04): 453. CrossRef - Novel Potential Targets for Function-Promoting Therapies: Orphan Nuclear Receptors, Anti-inflammatory Drugs, Troponin Activators, Mas Receptor Agonists, and Urolithin A
Waly Dioh, Vihang Narkar, Anurag Singh, Fady Malik, Luigi Ferrucci, Cendrine Tourette, Jean Mariani, Rob van Maanen, Roger A Fielding, Lewis A Lipsitz
The Journals of Gerontology: Series A.2023; 78(Supplement): 44. CrossRef - Alverine citrate promotes myogenic differentiation and ameliorates muscle atrophy
Jong Hyeon Yoon, Seung-Min Lee, Younglang Lee, Min Ju Kim, Jae Won Yang, Jeong Yi Choi, Ju Yeon Kwak, Kwang-Pyo Lee, Yong Ryoul Yang, Ki-Sun Kwon
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2022; 586: 157. CrossRef - Adeno-associated virus-mediated expression of an inactive CaMKIIβ mutant enhances muscle mass and strength in mice
Takahiro Eguchi, Yuji Yamanashi
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2022; 589: 192. CrossRef - Gastric Mobility and Gastrointestinal Hormones in Older Patients with Sarcopenia
Hsien-Hao Huang, Tse-Yao Wang, Shan-Fan Yao, Pei-Ying Lin, Julia Chia-Yu Chang, Li-Ning Peng, Liang-Kung Chen, David Hung-Tsang Yen
Nutrients.2022; 14(9): 1897. CrossRef - Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Intensive Care Unit-Acquired Weakness and Sarcopenia
Marcela Kanova, Pavel Kohout
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(15): 8396. CrossRef
- The Current Landscape of Pharmacotherapies for Sarcopenia


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



