Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Hypothalamic AMP-Activated Protein Kinase as a Whole-Body Energy Sensor and Regulator
- Se Hee Min, Do Kyeong Song, Chan Hee Lee, Eun Roh, Min-Seon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):1-11. Published online February 14, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2024.1922
- 1,721 View
- 61 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
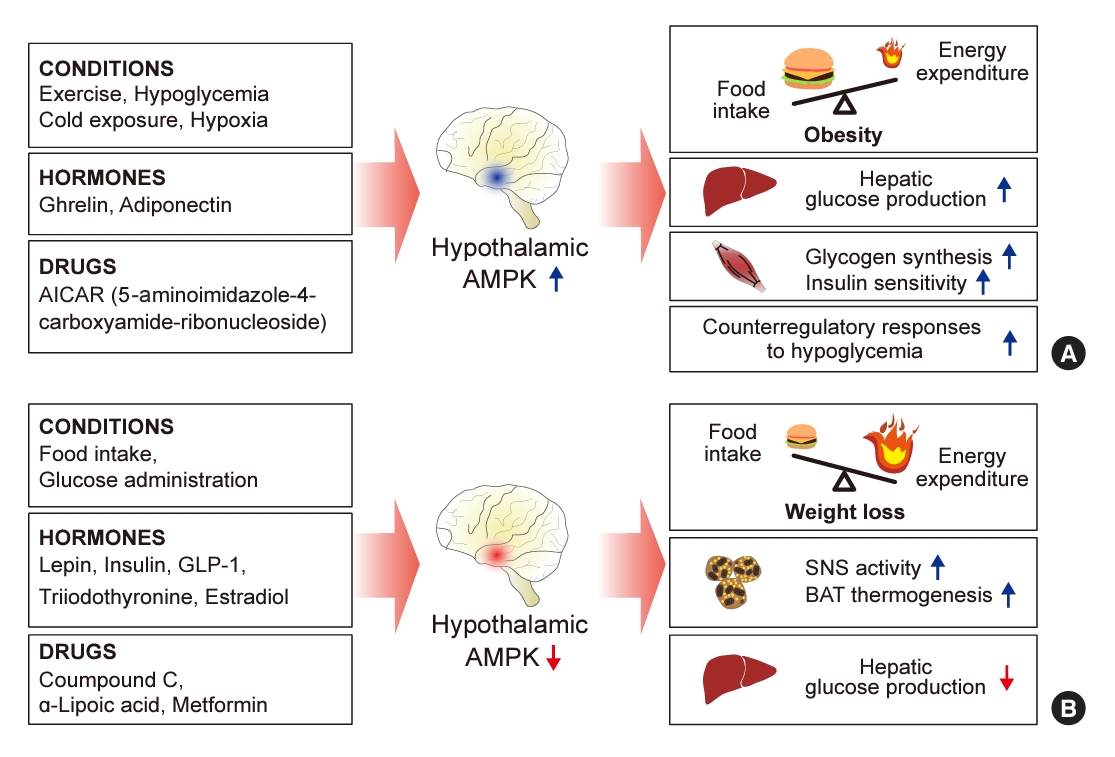
ePub - 5´-Adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a cellular energy sensor, is an essential enzyme that helps cells maintain stable energy levels during metabolic stress. The hypothalamus is pivotal in regulating energy balance within the body. Certain neurons in the hypothalamus are sensitive to fluctuations in food availability and energy stores, triggering adaptive responses to preserve systemic energy equilibrium. AMPK, expressed in these hypothalamic neurons, is instrumental in these regulatory processes. Hypothalamic AMPK activity is modulated by key metabolic hormones. Anorexigenic hormones, including leptin, insulin, and glucagon-like peptide 1, suppress hypothalamic AMPK activity, whereas the hunger hormone ghrelin activates it. These hormonal influences on hypothalamic AMPK activity are central to their roles in controlling food consumption and energy expenditure. Additionally, hypothalamic AMPK activity responds to variations in glucose concentrations. It becomes active during hypoglycemia but is deactivated when glucose is introduced directly into the hypothalamus. These shifts in AMPK activity within hypothalamic neurons are critical for maintaining glucose balance. Considering the vital function of hypothalamic AMPK in the regulation of overall energy and glucose balance, developing chemical agents that target the hypothalamus to modulate AMPK activity presents a promising therapeutic approach for metabolic conditions such as obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus.

- Miscellaneous
- Toward Systems-Level Metabolic Analysis in Endocrine Disorders and Cancer
- Aliya Lakhani, Da Hyun Kang, Yea Eun Kang, Junyoung O. Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(6):619-630. Published online November 21, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1814
- 2,341 View
- 106 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
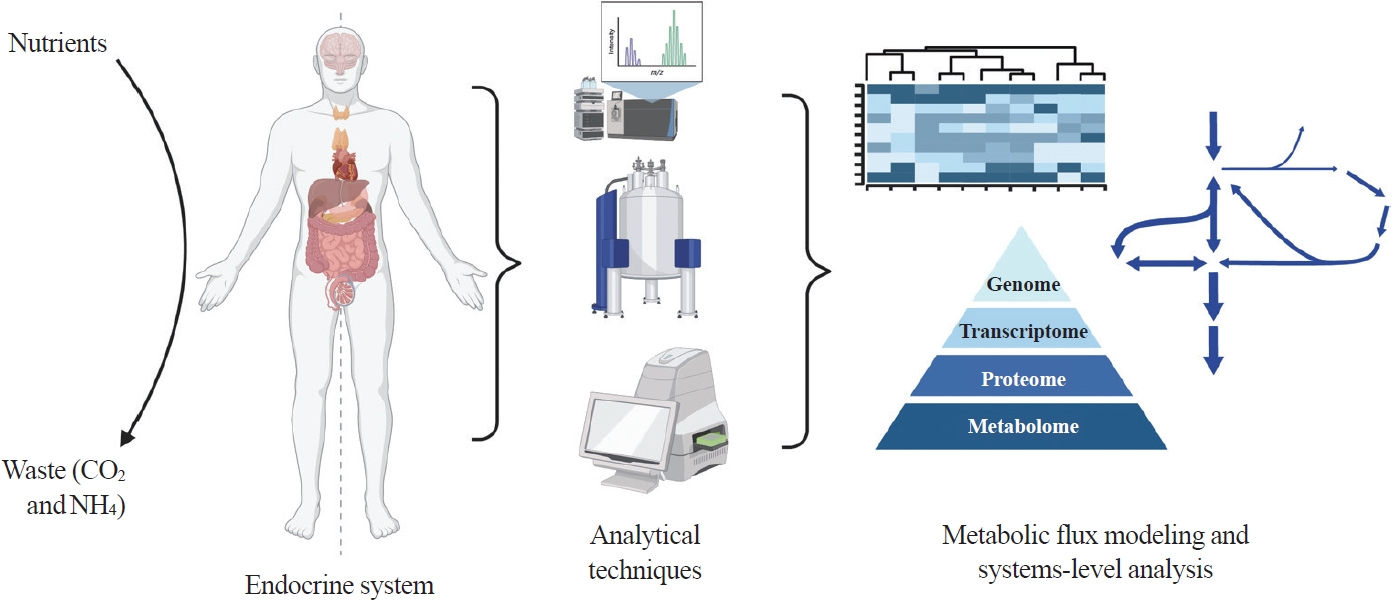
ePub - Metabolism is a dynamic network of biochemical reactions that support systemic homeostasis amidst changing nutritional, environmental, and physical activity factors. The circulatory system facilitates metabolite exchange among organs, while the endocrine system finely tunes metabolism through hormone release. Endocrine disorders like obesity, diabetes, and Cushing’s syndrome disrupt this balance, contributing to systemic inflammation and global health burdens. They accompany metabolic changes on multiple levels from molecular interactions to individual organs to the whole body. Understanding how metabolic fluxes relate to endocrine disorders illuminates the underlying dysregulation. Cancer is increasingly considered a systemic disorder because it not only affects cells in localized tumors but also the whole body, especially in metastasis. In tumorigenesis, cancer-specific mutations and nutrient availability in the tumor microenvironment reprogram cellular metabolism to meet increased energy and biosynthesis needs. Cancer cachexia results in metabolic changes to other organs like muscle, adipose tissue, and liver. This review explores the interplay between the endocrine system and systems-level metabolism in health and disease. We highlight metabolic fluxes in conditions like obesity, diabetes, Cushing’s syndrome, and cancers. Recent advances in metabolomics, fluxomics, and systems biology promise new insights into dynamic metabolism, offering potential biomarkers, therapeutic targets, and personalized medicine.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial: Tumor metabolism and programmed cell death
Dan-Lan Pu, Qi-Nan Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Editorial: Tumor metabolism and programmed cell death

- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Association between Serum Amyloid A Levels and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Ting Liu, Meng Li, Chunying Cui, Jielin Zhou
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(3):315-327. Published online June 7, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1621
- 2,058 View
- 102 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To date, consistent data have not been reported on the association between serum amyloid A (SAA) levels and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The purpose of this study was to systematically summarize their relationship.
Methods
Databases including PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, Web of Science, and MEDLINE were searched until August 2021. Cross-sectional and case-control studies were included.
Results
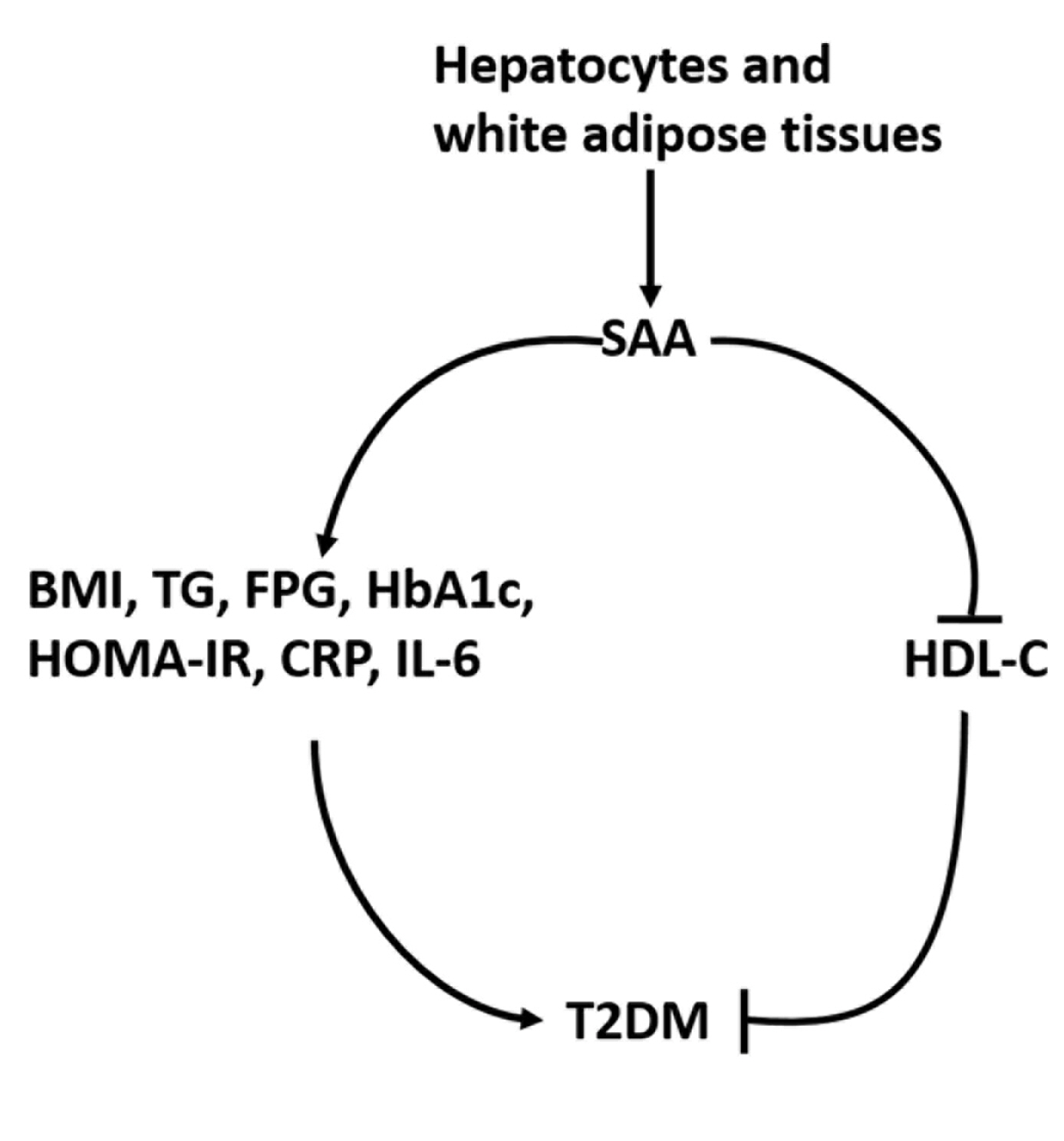
Twenty-one studies with 1,780 cases and 2,070 controls were identified. SAA levels were significantly higher in T2DM patients than in healthy groups (standardized mean difference [SMD], 0.68; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.39 to 0.98). A subgroup analysis showed that the mean age of participants and the continent that participants were from were related to differences in SAA levels between cases and controls. Furthermore, in T2DM patients, SAA levels were positively associated with body mass index (r=0.34; 95% CI, 0.03 to 0.66), triglycerides (r=0.12; 95% CI, 0.01 to 0.24), fasting plasma glucose (r=0.26; 95% CI, 0.07 to 0.45), hemoglobin A1c (r=0.24; 95% CI, 0.16 to 0.33), homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance (r=0.22; 95% CI, 0.10 to 0.34), C-reactive protein (r=0.77; 95% CI, 0.62 to 0.91), and interleukin-6 (r=0.42; 95% CI, 0.31 to 0.54), but negatively linked with highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol (r=–0.23; 95% CI, –0.44 to –0.03).
Conclusion
The meta-analysis suggests that high SAA levels may be associated with the presence of T2DM, as well as lipid metabolism homeostasis and the inflammatory response. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Correlation between insulin resistance and the rate of neutrophils-lymphocytes, monocytes-lymphocytes, platelets-lymphocytes in type 2 diabetic patients
Yuanyuan Zhang, Huaizhen Liu
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Functions of High-Density Lipoprotein in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Damien Denimal
Antioxidants.2023; 13(1): 57. CrossRef
- Correlation between insulin resistance and the rate of neutrophils-lymphocytes, monocytes-lymphocytes, platelets-lymphocytes in type 2 diabetic patients

- Miscellaneous
- Brown Adipose Tissue: Activation and Metabolism in Humans
- Imane Hachemi, Mueez U-Din
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(2):214-222. Published online March 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1659
- 5,784 View
- 432 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
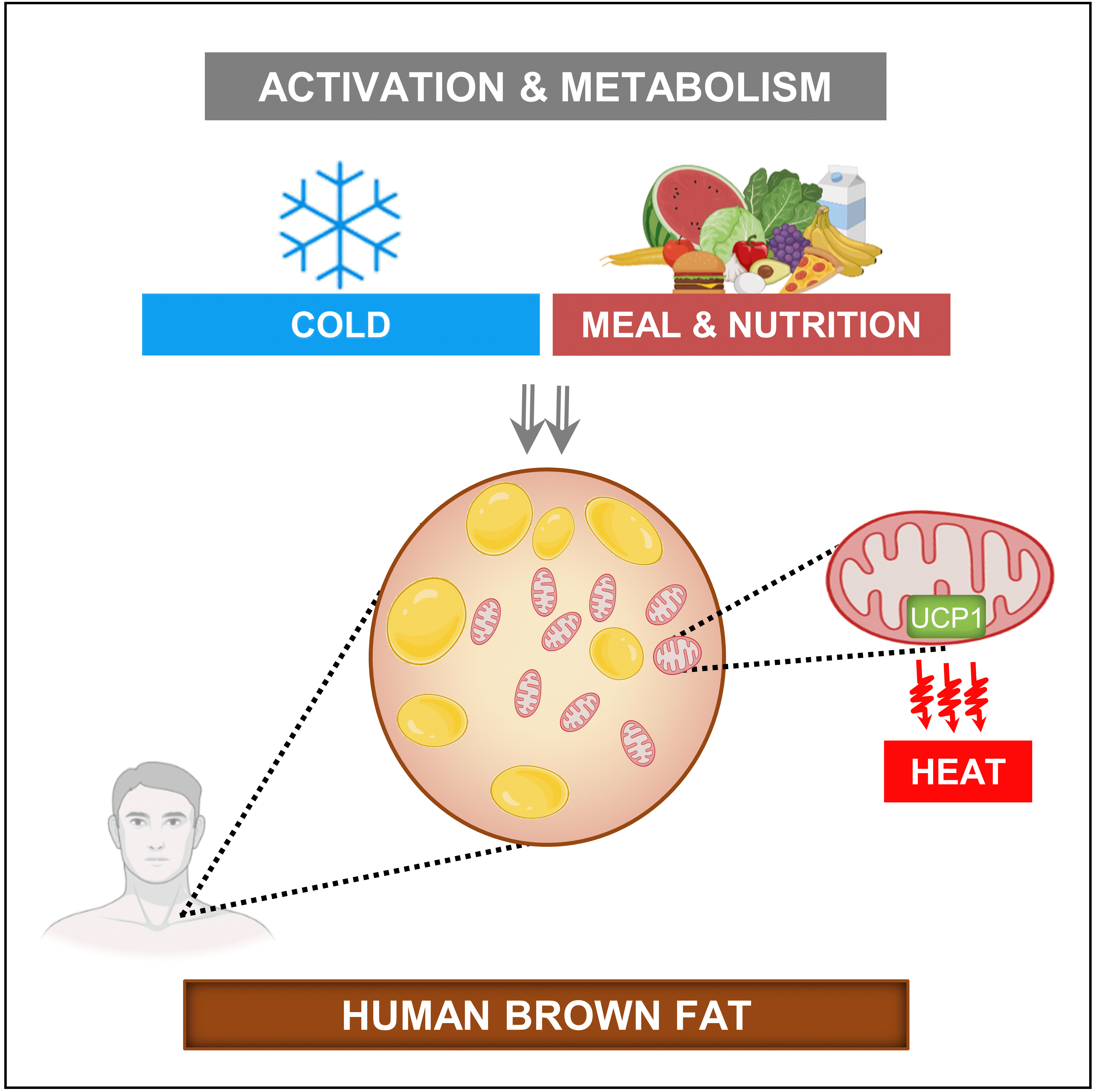
ePub - Brown adipose tissue (BAT) is a thermogenic organ contributing to non-shivering thermogenesis. BAT becomes active under cold stress via sympathetic nervous system activation. However, recent evidence has suggested that BAT may also be active at thermoneutrality and in a postprandial state. BAT has superior energy dissipation capacity compared to white adipose tissue (WAT) and muscles. Thus, it has been proposed that the recruitment and activation of additional BAT may increase the overall energy-expending capacity in humans, potentially improving current whole-body weight management strategies. Nutrition plays a central role in obesity and weight management. Thus, this review discusses human studies describing BAT hyper-metabolism after dietary interventions. Nutritional agents that can potentially recruit brown adipocytes via the process of BAT-WAT transdifferentiation are also discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Spermidine activates adipose tissue thermogenesis through autophagy and fibroblast growth factor 21
Yinhua Ni, Liujie Zheng, Liqian Zhang, Jiamin Li, Yuxiang Pan, Haimei Du, Zhaorong Wang, Zhengwei Fu
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2024; 125: 109569. CrossRef - A natural sustained-intestinal release formulation of red chili pepper extracted capsaicinoids (Capsifen®) safely modulates energy balance and endurance performance: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study
N. Roopashree, Das S. Syam, I. M. Krishnakumar, K. N. Mala, Bradley S. Fleenor, Jestin Thomas
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - MRI Methods to Visualize and Quantify Adipose Tissue in Health and Disease
Katerina Nikiforaki, Kostas Marias
Biomedicines.2023; 11(12): 3179. CrossRef
- Spermidine activates adipose tissue thermogenesis through autophagy and fibroblast growth factor 21

- Thyroid
- Metabolite Changes during the Transition from Hyperthyroidism to Euthyroidism in Patients with Graves’ Disease
- Ho Yeop Lee, Byeong Chang Sim, Ha Thi Nga, Ji Sun Moon, Jingwen Tian, Nguyen Thi Linh, Sang Hyeon Ju, Dong Wook Choi, Daiki Setoyama, Hyon-Seung Yi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(6):891-900. Published online December 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1590
- 2,440 View
- 253 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
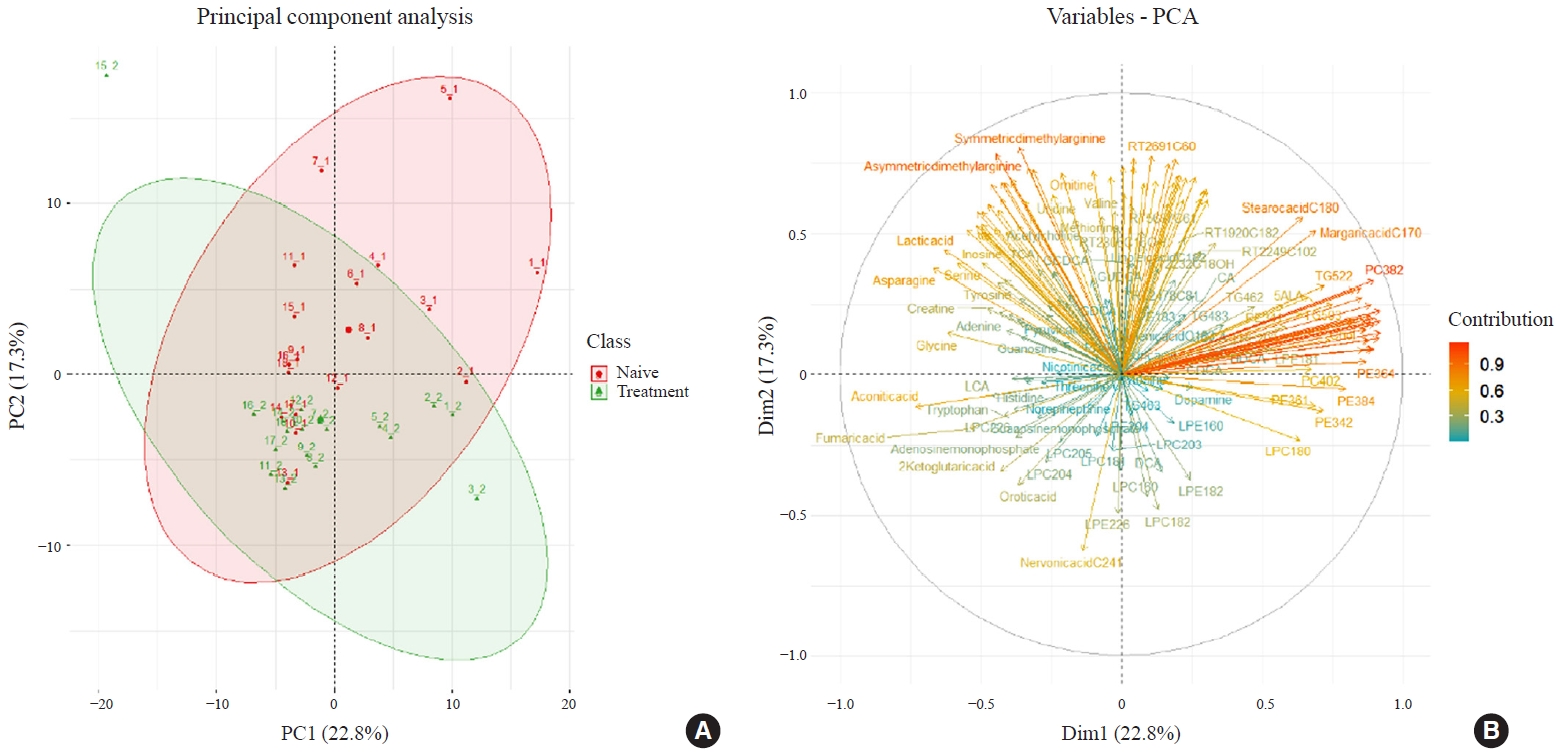
An excess of thyroid hormones in Graves’ disease (GD) has profound effects on systemic energy metabolism that are currently partially understood. In this study, we aimed to provide a comprehensive understanding of the metabolite changes that occur when patients with GD transition from hyperthyroidism to euthyroidism with methimazole treatment.
Methods
Eighteen patients (mean age, 38.6±14.7 years; 66.7% female) with newly diagnosed or relapsed GD attending the endocrinology outpatient clinics in a single institution were recruited between January 2019 and July 2020. All subjects were treated with methimazole to achieve euthyroidism. We explored metabolomics by performing liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of plasma samples of these patients and then performed multivariate statistical analysis of the metabolomics data.
Results
Two hundred metabolites were measured before and after 12 weeks of methimazole treatment in patients with GD. The levels of 61 metabolites, including palmitic acid (C16:0) and oleic acid (C18:1), were elevated in methimazole-naïve patients with GD, and these levels were decreased by methimazole treatment. The levels of another 15 metabolites, including glycine and creatinine, were increased after recovery of euthyroidism upon methimazole treatment in patients with GD. Pathway analysis of metabolomics data showed that hyperthyroidism was closely related to aminoacyl-transfer ribonucleic acid biosynthesis and branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis pathways.
Conclusion
In this study, significant variations of plasma metabolomic patterns that occur during the transition from hyperthyroidism to euthyroidism were detected in patients with GD via untargeted metabolomics analysis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations of serum keratin 1 with thyroid function and immunity in Graves’ disease
Chao-Wen Cheng, Wen-Fang Fang, Jiunn-Diann Lin, Appuwawadu Mestri Nipun Lakshitha de Silva
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(11): e0289345. CrossRef
- Associations of serum keratin 1 with thyroid function and immunity in Graves’ disease

- Thyroid
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Repeated Low High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer: A Nationwide Population- Based Study in Korea
- Jinyoung Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):303-311. Published online April 6, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1332

- 4,516 View
- 152 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) plays an important role in the reverse cholesterol transport pathway and prevents atherosclerosis-mediated disease. It has also been suggested that HDL-C may be a protective factor against cancer. However, an inverse correlation between HDL-C and cancer has not been established, and few studies have explored thyroid cancer.
Methods
The study participants received health checkups provided by the Korean National Health Insurance Service from 2009 to 2013 and were followed until 2019. Considering the variability of serum HDL-C level, low HDL-C level was analyzed by grouping based on four consecutive health checkups. The data analysis was performed using univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression models.
Results
A total of 3,134,278 total study participants, thyroid cancer occurred in 16,129. In the crude model, the hazard ratios for the association between repeatedly measured low HDL-C levels and thyroid cancer were 1.243, 1.404, 1.486, and 1.680 (P for trend <0.01), respectively, which were significant even after adjusting for age, sex, lifestyle factors, and metabolic diseases. The subgroup analysis revealed that low HDL-C levels likely had a greater impact on the group of patients with central obesity (P for interaction= 0.062), high blood pressure (P for interaction=0.057), impaired fasting glucose (P for interaction=0.051), and hyperlipidemia (P for interaction=0.126).
Conclusion
Repeatedly measured low HDL-C levels can be considered a risk factor for cancer as well as vascular disease. Low HDL-C levels were associated with the risk of thyroid cancer, and this correlation was stronger in a metabolically unhealthy population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between total cholesterol levels and all-cause mortality among newly diagnosed patients with cancer
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, So Hyun Cho, Rosa Oh, Ji Yoon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between organophosphate flame retardant exposure and lipid metabolism: data from the 2013–2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Fu-Jen Cheng, Kai-Fan Tsai, Kuo-Chen Huang, Chia-Te Kung, Wan-Ting Huang, Huey-Ling You, Shau-Hsuan Li, Chin-Chou Wang, Wen-Chin Lee, Hsiu-Yung Pan
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Low serum total cholesterol levels predict inferior prognosis of patients with POEMS syndrome
Jue Zhang, Ting Zhang, Ye Yao, Xuxing Shen, Yuanyuan Jin, Run Zhang, Lijuan Chen
Discover Oncology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipoprotein alterations in endocrine disorders - a review of the recent developments in the field
Michal Olejarz, Ewelina Szczepanek-Parulska, Marek Ruchala
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Carbohydrate, Lipid, and Apolipoprotein Biomarkers in Blood and Risk of Thyroid Cancer: Findings from the AMORIS Cohort
Xue Xiao, Yi Huang, Fetemeh Sadeghi, Maria Feychting, Niklas Hammar, Fang Fang, Zhe Zhang, Qianwei Liu
Cancers.2023; 15(2): 520. CrossRef - Altered serum lipid levels are associated with prognosis of diffuse large B cell lymphoma and influenced by utility of rituximab
Fei Wang, Luo Lu, HuiJuan Chen, Yanhua Yue, Yanting Sun, Feng Yan, Bai He, Rongrong Lin, Weiying Gu
Annals of Hematology.2023; 102(2): 393. CrossRef - Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and carcinogenesis
Meijuan Tan, Shijie Yang, Xiequn Xu
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 34(5): 303. CrossRef - Low Serum Cholesterol Level Is a Significant Prognostic Factor That Improves CLL-IPI in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia
Rui Gao, Kaixin Du, Jinhua Liang, Yi Xia, Jiazhu Wu, Yue Li, Bihui Pan, Li Wang, Jianyong Li, Wei Xu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(8): 7396. CrossRef - Do metabolic factors increase the risk of thyroid cancer? a Mendelian randomization study
Weiwei Liang, FangFang Sun
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of causal association between differentiated thyroid cancer and disordered serum lipid profile: a Mendelian randomization study
Qiang Ma, Yu Li, Lijuan An, Liang Guo, Xiaokang Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk factors and diagnostic prediction models for papillary thyroid carcinoma
Xiaowen Zhang, Yuyang Ze, Jianfeng Sang, Xianbiao Shi, Yan Bi, Shanmei Shen, Xinlin Zhang, Dalong Zhu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Exposure to multiple trace elements and thyroid cancer risk in Chinese adults: A case-control study
Jia-liu He, Hua-bing Wu, Wen-lei Hu, Jian-jun Liu, Qian Zhang, Wei Xiao, Ming-jun Hu, Ming Wu, Fen Huang
International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health.2022; 246: 114049. CrossRef
- Association between total cholesterol levels and all-cause mortality among newly diagnosed patients with cancer

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- The Influence of Obesity and Metabolic Health on Vascular Health
- Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):1-8. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.101
- 6,793 View
- 296 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The prevalence of obesity is rapidly increasing worldwide. Obesity should not be understood only as the accumulation of fat in the body, but instead as a phenomenon that exerts different effects on our health according to the place of fat deposition and its stability. Obesity is the starting point of most metabolic diseases, such as diabetes, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, sleep apnea, and eventually cardiovascular disease. There are different kinds of obesity, ranging from simple obesity to sarcopenic obesity. The main purpose of intervening to address obesity is to decrease the ultimate consequence of obesity—namely, cardiovascular disease. The main mechanism through which obesity, especially abdominal obesity, increases cardiovascular risk is the obesity-induced derangement of metabolic health, leading to the development of metabolic diseases such as diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and metabolic syndrome, which are the main initiators of vascular damage. In this review, I discuss the influence of various types of obesity on the risk of metabolic diseases, and how these diseases increase cardiovascular disease risk.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
Nam Hoon Kim, Ji Yoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim
European Heart Journal - Cardiovascular Pharmacotherapy.2024; 10(2): 118. CrossRef - Severity of abdominal obesity and cardiometabolic diseases in US adults
S. Wang, S. Shi, Y. Huang, H. Huang, V.W. Zhong
Public Health.2024; 227: 154. CrossRef - Anti-obesity effects of fucoidan from
Sargassum thunbergii in adipocytes and high fat diet induced obese mice through inhibiting adipogenic specific transcription factor
Hyo-Geun Lee, H.H.A.C.K. Jayawardhana, Fengqi Yang, D.P. Nagahawaththa, N.M. Liyanage, Kyung-Mo Song, Yun-Sang Choi, Seung-Hong Lee, You-Jin Jeon, Min-Cheol Kang
Food Science and Human Wellness.2024; 13(3): 1608. CrossRef - Association of a High Healthy Eating Index Diet with Long-Term Visceral Fat Loss in a Large Longitudinal Study
Sunmin Park
Nutrients.2024; 16(4): 534. CrossRef - Ancistrocladus tectorius Extract Inhibits Obesity by Promoting Thermogenesis and Mitochondrial Dynamics in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice
Minju Kim, Jin Hyub Paik, Hwa Lee, Min Ji Kim, Sang Mi Eum, Soo Yong Kim, Sangho Choi, Ho-Yong Park, Hye Gwang Jeong, Tae-Sook Jeong
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3743. CrossRef - Biological Activity Evaluation of Olive, Grape, and Fig at Various Mixing Ratios
Chan-Hwi Lee, So-Young Lee, Ae-Jung Kim
Asian Journal of Beauty and Cosmetology.2024; 22(1): 91. CrossRef - Investigation and Comparison of Maternal Pre-Pregnancy Body Mass Index Coupled with Gestational Weight Gain on Maternal–Fetal Complications Based on US and Chinese Guidelines: A Retrospective Study
Wan-Ju Kung, Hsin-Yi Kuo, Ching-Feng Chang, Yeong-Hwa Zen, Ching-Chiang Lin
Reproductive Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mechanistic insights into dietary (poly)phenols and vascular dysfunction-related diseases using multi-omics and integrative approaches: Machine learning as a next challenge in nutrition research
Dragan Milenkovic, Tatjana Ruskovska
Molecular Aspects of Medicine.2023; 89: 101101. CrossRef - Pharmacological Support for the Treatment of Obesity—Present and Future
Marcin Kosmalski, Kacper Deska, Bartłomiej Bąk, Monika Różycka-Kosmalska, Tadeusz Pietras
Healthcare.2023; 11(3): 433. CrossRef - Prioritizing obesity treatment: expanding the role of cardiologists to improve cardiovascular health and outcomes
Donna H. Ryan, John E. Deanfield, Stephan Jacob
Cardiovascular Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 12(1): e0279. CrossRef - Adipopenia is associated with osteoporosis in community-dwelling non-underweight adults independent of sarcopenia
Seunghyun Lee, Kyoungmyoung Ko, Sungjae Shin, Hye Sun Park, Namki Hong, Yumie Rhee
Archives of Osteoporosis.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Design, synthesis and evaluation of 2-pyrimidinylindole derivatives as anti-obesity agents by regulating lipid metabolism
Shi-Yao Guo, Li-Yuan Wei, Bing-Bing Song, Yu-Tao Hu, Zhi Jiang, Dan-Dan Zhao, Yao-Hao Xu, Yu-Wei Lin, Shu-Min Xu, Shuo-Bin Chen, Zhi-Shu Huang
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2023; 260: 115729. CrossRef - Short-Term L-Citrulline Supplementation Does Not Affect Blood Pressure, Pulse Wave Reflection, or Arterial Stiffness at Rest and during Isometric Exercise in Older Males
Andrea Tryfonos, Filippos Christodoulou, George M. Pamboris, Stephanos Christodoulides, Anastasios A. Theodorou
Sports.2023; 11(9): 177. CrossRef - Skinfold Thickness as a Cardiometabolic Risk Predictor in Sedentary and Active Adult Populations
Sughey González-Torres, Luis Miguel Anaya-Esparza, Gabriel Fermín Trigueros del Valle, Edgar Alfonso Rivera-León, Zuamí Villagrán, Sergio Sánchez-Enríquez
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(9): 1326. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance in Adults: A before and after Pandemic Lockdown Longitudinal Study
Ángel Arturo López-González, Bárbara Altisench Jané, Luis Masmiquel Comas, Sebastiana Arroyo Bote, Hilda María González San Miguel, José Ignacio Ramírez Manent
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2795. CrossRef - Fenofibrate enhances lipid deposition via modulating PPARγ, SREBP-1c, and gut microbiota in ob/ob mice fed a high-fat diet
Ying Zhang, Xiu-Bin Jia, Yun-Chao Liu, Wen-Qian Yu, Yan-Hong Si, Shou-Dong Guo
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictive Roles of Basal Metabolic Rate and Body Water Distribution in Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity: The link to Carbohydrates
Lizheng Guan, Tiantian Li, Xuan Wang, Kang Yu, Rong Xiao, Yuandi Xi
Nutrients.2022; 14(19): 3911. CrossRef - Metabolic risk factors in patients with comorbidity in Ufa primary health care
O.V. Molchanova, A.V. Mamaeva, A.R. Dunayeva, Z.A. Lust, E.M. Faskhetdinova, R.N. Shepel, D.O. Orlov, L.M. Zhamalov, G.F. Andreeva, O.M. Drapkina
Profilakticheskaya meditsina.2022; 25(9): 39. CrossRef - Assessment of Vitamin D Levels in Relation to Statin Therapy in Elderly Hypertensive Patients with Comorbidities
Kinga-Ilona Nyulas, Zsuzsánna Simon-Szabó, Zoltán Preg, Sándor Pál, Arundhati Sharma, Tünde Pál, Márta Germán-Salló, Enikő Nemes-Nagy
Journal of Interdisciplinary Medicine.2022; 7(4): 88. CrossRef
- Associations of omega-3 fatty acids vs. fenofibrate with adverse cardiovascular outcomes in people with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Homeostatic Regulation of Glucose Metabolism by the Central Nervous System
- Jong Han Choi, Min-Seon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):9-25. Published online February 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1364

- 5,408 View
- 348 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Evidence for involvement of the central nervous system (CNS) in the regulation of glucose metabolism dates back to the 19th century, although the majority of the research on glucose metabolism has focused on the peripheral metabolic organs. Due to recent advances in neuroscience, it has now become clear that the CNS is indeed vital for maintaining glucose homeostasis. To achieve normoglycemia, specific populations of neurons and glia in the hypothalamus sense changes in the blood concentrations of glucose and of glucoregulatory hormones such as insulin, leptin, glucagon-like peptide 1, and glucagon. This information is integrated and transmitted to other areas of the brain where it eventually modulates various processes in glucose metabolism (i.e., hepatic glucose production, glucose uptake in the brown adipose tissue and skeletal muscle, pancreatic insulin and glucagon secretion, renal glucose reabsorption, etc.). Errors in these processes lead to hyper- or hypoglycemia. We here review the current understanding of the brain regulation of glucose metabolism.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sympathetic nerve-enteroendocrine L cell communication modulates GLP-1 release, brain glucose utilization, and cognitive function
Wenran Ren, Jianhui Chen, Wenjing Wang, Qingqing Li, Xia Yin, Guanglei Zhuang, Hong Zhou, Wenwen Zeng
Neuron.2024; 112(6): 972. CrossRef - Hypothalamic astrocyte NAD+ salvage pathway mediates the coupling of dietary fat overconsumption in a mouse model of obesity
Jae Woo Park, Se Eun Park, Wuhyun Koh, Won Hee Jang, Jong Han Choi, Eun Roh, Gil Myoung Kang, Seong Jun Kim, Hyo Sun Lim, Chae Beom Park, So Yeon Jeong, Sang Yun Moon, Chan Hee Lee, Sang Yeob Kim, Hyung Jin Choi, Se Hee Min, C. Justin Lee, Min-Seon Kim
Nature Communications.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of metformin and electrical pulses in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells
Praveen Sahu, Ignacio G. Camarillo, Raji Sundararajan
Exploration of Targeted Anti-tumor Therapy.2024; 5(1): 54. CrossRef - Redox imbalance and metabolic defects in the context of Alzheimer disease
Fabio Di Domenico, Chiara Lanzillotta, Marzia Perluigi
FEBS Letters.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity-associated microglial inflammatory activation paradoxically improves glucose tolerance
John D. Douglass, Kelly M. Ness, Martin Valdearcos, Alice Wyse-Jackson, Mauricio D. Dorfman, Jeremy M. Frey, Rachael D. Fasnacht, Olivia D. Santiago, Anzela Niraula, Jineta Banerjee, Megan Robblee, Suneil K. Koliwad, Joshua P. Thaler
Cell Metabolism.2023; 35(9): 1613. CrossRef - Phenotypic screening using waveform analysis of synchronized calcium oscillations in primary cortical cultures
Richi Sakaguchi, Saki Nakamura, Hiroyuki Iha, Masaki Tanaka, Ming Tatt Lee
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(4): e0271782. CrossRef - Effects of Escitalopram on the Functional Neural Circuits in an Animal Model of Adolescent Depression
Se Jong Oh, Namhun Lee, Kyung Rok Nam, Kyung Jun Kang, Sang Jin Han, Jae Yong Choi
Molecular Imaging and Biology.2023; 25(4): 735. CrossRef - A Survey of Deep Learning for Alzheimer’s Disease
Qinghua Zhou, Jiaji Wang, Xiang Yu, Shuihua Wang, Yudong Zhang
Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction.2023; 5(2): 611. CrossRef - Potassium channels in behavioral brain disorders. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential: A narrative review
Kazi Asraful Alam, Pernille Svalastoga, Aurora Martinez, Jeffrey Colm Glennon, Jan Haavik
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews.2023; 152: 105301. CrossRef - Knockout of Nur77 Leads to Amino Acid, Lipid, and Glucose Metabolism Disorders in Zebrafish
Yang Xu, Juanjuan Tian, Qi Kang, Hang Yuan, Chengdong Liu, Zhehui Li, Jie Liu, Mingyu Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the POMC System on Glucose Homeostasis and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Obesity and Diabetes
Dan Yang, Xintong Hou, Guimei Yang, Mengnan Li, Jian Zhang, Minmin Han, Yi Zhang, Yunfeng Liu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 2939. CrossRef
- Sympathetic nerve-enteroendocrine L cell communication modulates GLP-1 release, brain glucose utilization, and cognitive function

- Adrenal Gland
- Metabolic Subtyping of Adrenal Tumors: Prospective Multi-Center Cohort Study in Korea
- Eu Jeong Ku, Chaelin Lee, Jaeyoon Shim, Sihoon Lee, Kyoung-Ah Kim, Sang Wan Kim, Yumie Rhee, Hyo-Jeong Kim, Jung Soo Lim, Choon Hee Chung, Sung Wan Chun, Soon-Jib Yoo, Ohk-Hyun Ryu, Ho Chan Cho, A Ram Hong, Chang Ho Ahn, Jung Hee Kim, Man Ho Choi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1131-1141. Published online October 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1149
- 4,998 View
- 208 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
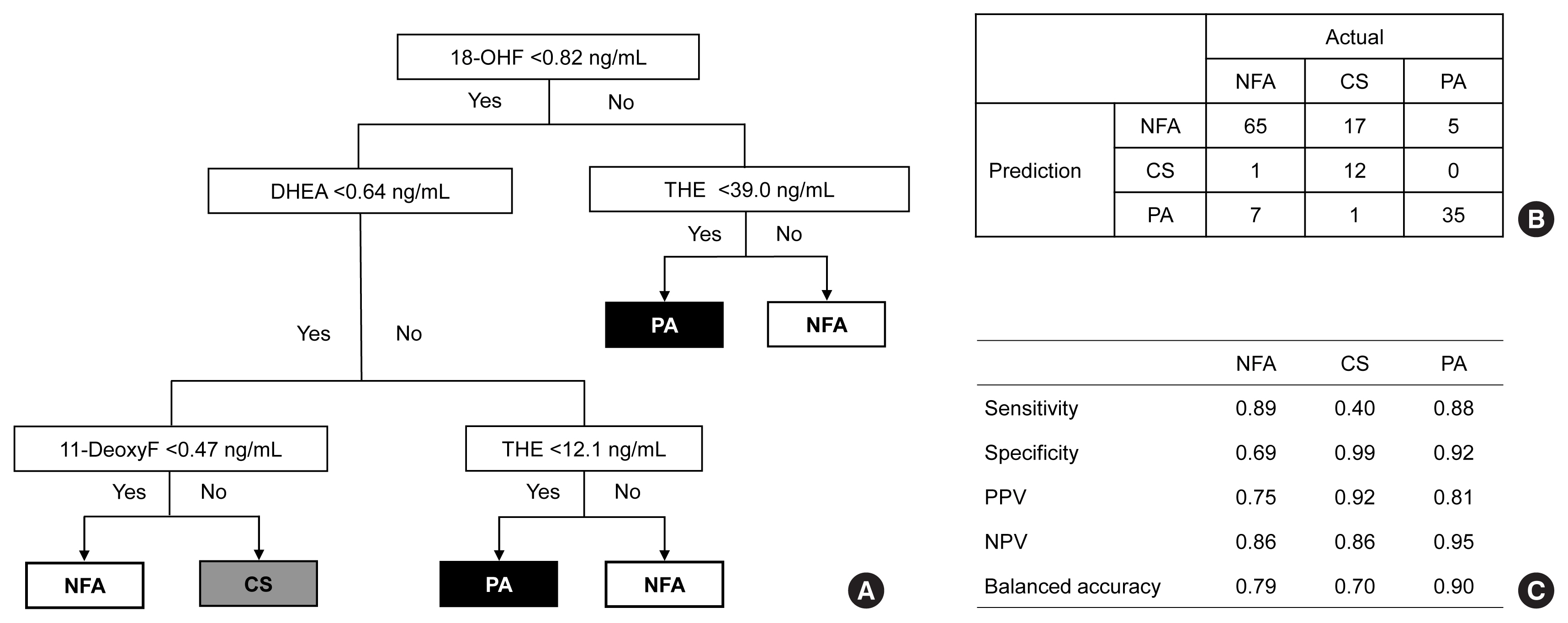
ePub - Background
Conventional diagnostic approaches for adrenal tumors require multi-step processes, including imaging studies and dynamic hormone tests. Therefore, this study aimed to discriminate adrenal tumors from a single blood sample based on the combination of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and machine learning algorithms in serum profiling of adrenal steroids.
Methods
The LC-MS-based steroid profiling was applied to serum samples obtained from patients with nonfunctioning adenoma (NFA, n=73), Cushing’s syndrome (CS, n=30), and primary aldosteronism (PA, n=40) in a prospective multicenter study of adrenal disease. The decision tree (DT), random forest (RF), and extreme gradient boost (XGBoost) were performed to categorize the subtypes of adrenal tumors.
Results
The CS group showed higher serum levels of 11-deoxycortisol than the NFA group, and increased levels of tetrahydrocortisone (THE), 20α-dihydrocortisol, and 6β-hydroxycortisol were found in the PA group. However, the CS group showed lower levels of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and its sulfate derivative (DHEA-S) than both the NFA and PA groups. Patients with PA expressed higher serum 18-hydroxycortisol and DHEA but lower THE than NFA patients. The balanced accuracies of DT, RF, and XGBoost for classifying each type were 78%, 96%, and 97%, respectively. In receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis for CS, XGBoost, and RF showed a significantly greater diagnostic power than the DT. However, in ROC analysis for PA, only RF exhibited better diagnostic performance than DT.
Conclusion
The combination of LC-MS-based steroid profiling with machine learning algorithms could be a promising one-step diagnostic approach for the classification of adrenal tumor subtypes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treating Primary Aldosteronism-Induced Hypertension: Novel Approaches and Future Outlooks
Nathan Mullen, James Curneen, Padraig T Donlon, Punit Prakash, Irina Bancos, Mark Gurnell, Michael C Dennedy
Endocrine Reviews.2024; 45(1): 125. CrossRef - Steroid profiling in adrenal disease
Danni Mu, Dandan Sun, Xia Qian, Xiaoli Ma, Ling Qiu, Xinqi Cheng, Songlin Yu
Clinica Chimica Acta.2024; 553: 117749. CrossRef - Serum and hair steroid profiles in patients with nonfunctioning pituitary adenoma undergoing surgery: A prospective observational study
Seung Shin Park, Yong Hwy Kim, Ho Kang, Chang Ho Ahn, Dong Jun Byun, Man Ho Choi, Jung Hee Kim
The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.2023; 230: 106276. CrossRef - Recent Updates on the Management of Adrenal Incidentalomas
Seung Shin Park, Jung Hee Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 373. CrossRef - LC-MS based simultaneous profiling of adrenal hormones of steroids, catecholamines, and metanephrines
Jongsung Noh, Chaelin Lee, Jung Hee Kim, Seung Woon Myung, Man Ho Choi
Journal of Lipid Research.2023; 64(11): 100453. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Endocrine Society Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Primary Aldosteronism
Jeonghoon Ha, Jung Hwan Park, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Kyong Yeun Jung, Jeongmin Lee, Jong Han Choi, Seung Hun Lee, Namki Hong, Jung Soo Lim, Byung Kwan Park, Jung-Han Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Jooyoung Cho, Mi-kyung Kim, Choon Hee Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 597. CrossRef - Toward Systems-Level Metabolic Analysis in Endocrine Disorders and Cancer
Aliya Lakhani, Da Hyun Kang, Yea Eun Kang, Junyoung O. Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 619. CrossRef - Prevalence and Characteristics of Adrenal Tumors in an Unselected Screening Population
Ying Jing, Jinbo Hu, Rong Luo, Yun Mao, Zhixiao Luo, Mingjun Zhang, Jun Yang, Ying Song, Zhengping Feng, Zhihong Wang, Qingfeng Cheng, Linqiang Ma, Yi Yang, Li Zhong, Zhipeng Du, Yue Wang, Ting Luo, Wenwen He, Yue Sun, Fajin Lv, Qifu Li, Shumin Yang
Annals of Internal Medicine.2022; 175(10): 1383. CrossRef
- Treating Primary Aldosteronism-Induced Hypertension: Novel Approaches and Future Outlooks

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Role of TRPV4 Channel in Human White Adipocytes Metabolic Activity
- Julio C. Sánchez, Aníbal Valencia-Vásquez, Andrés M. García
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):997-1006. Published online October 14, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1167

- 3,579 View
- 122 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Intracellular calcium (Ca2+) homeostasis plays an essential role in adipocyte metabolism and its alteration is associated with obesity and related disorders. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) channels are an important Ca2+ pathway in adipocytes and their activity is regulated by metabolic mediators such as insulin. In this study, we evaluated the role of TRPV4 channels in metabolic activity and adipokine secretion in human white adipocytes.
Methods
Human white adipocytes were freshly cultured and the effects of the activation and inhibition of TRPV4 channels on lipolysis, glucose uptake, lactate production, and leptin and adiponectin secretion were evaluated.
Results
Under basal and isoproterenol-stimulated conditions, TRPV4 activation by GSK1016709A decreased lipolysis whereas HC067047, an antagonist, increased lipolysis. The activation of TRPV4 resulted in increased glucose uptake and lactate production under both basal conditions and insulin-stimulated conditions; in contrast HC067047 decreased both parameters. Leptin production was increased, and adiponectin production was diminished by TRPV4 activation and its inhibition had the opposite effect.
Conclusion
Our results suggested that TRPV4 channels are metabolic mediators involved in proadipogenic processes and glucose metabolism in adipocyte biology. TRPV4 channels could be a potential pharmacological target to treat metabolic disorders. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Obesity, bone marrow adiposity, and leukemia: Time to act
Vijay Kumar, John H. Stewart
Obesity Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - TRP channels associated with macrophages as targets for the treatment of obese asthma
Wenzhao Zhu, Dinxi Bai, Wenting Ji, Jing Gao
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Multidisciplinary Advances Address the Challenges in Developing Drugs against Transient Receptor Potential Channels to Treat Metabolic Disorders
Yibing Wang
ChemMedChem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Ion channels regulate energy homeostasis and the progression of metabolic disorders: Novel mechanisms and pharmacology of their modulators
Wenyi Wu, Jianan Zheng, Ru Wang, Yibing Wang
Biochemical Pharmacology.2023; 218: 115863. CrossRef - Potential lipolytic regulators derived from natural products as effective approaches to treat obesity
Xi-Ding Yang, Xing-Cheng Ge, Si-Yi Jiang, Yong-Yu Yang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Adipokines: Deciphering the cardiovascular signature of adipose tissue
Joseph C. Galley, Shubhnita Singh, Wanessa M.C. Awata, Juliano V. Alves, Thiago Bruder-Nascimento
Biochemical Pharmacology.2022; 206: 115324. CrossRef
- Obesity, bone marrow adiposity, and leukemia: Time to act

- Obesity and Metabolism
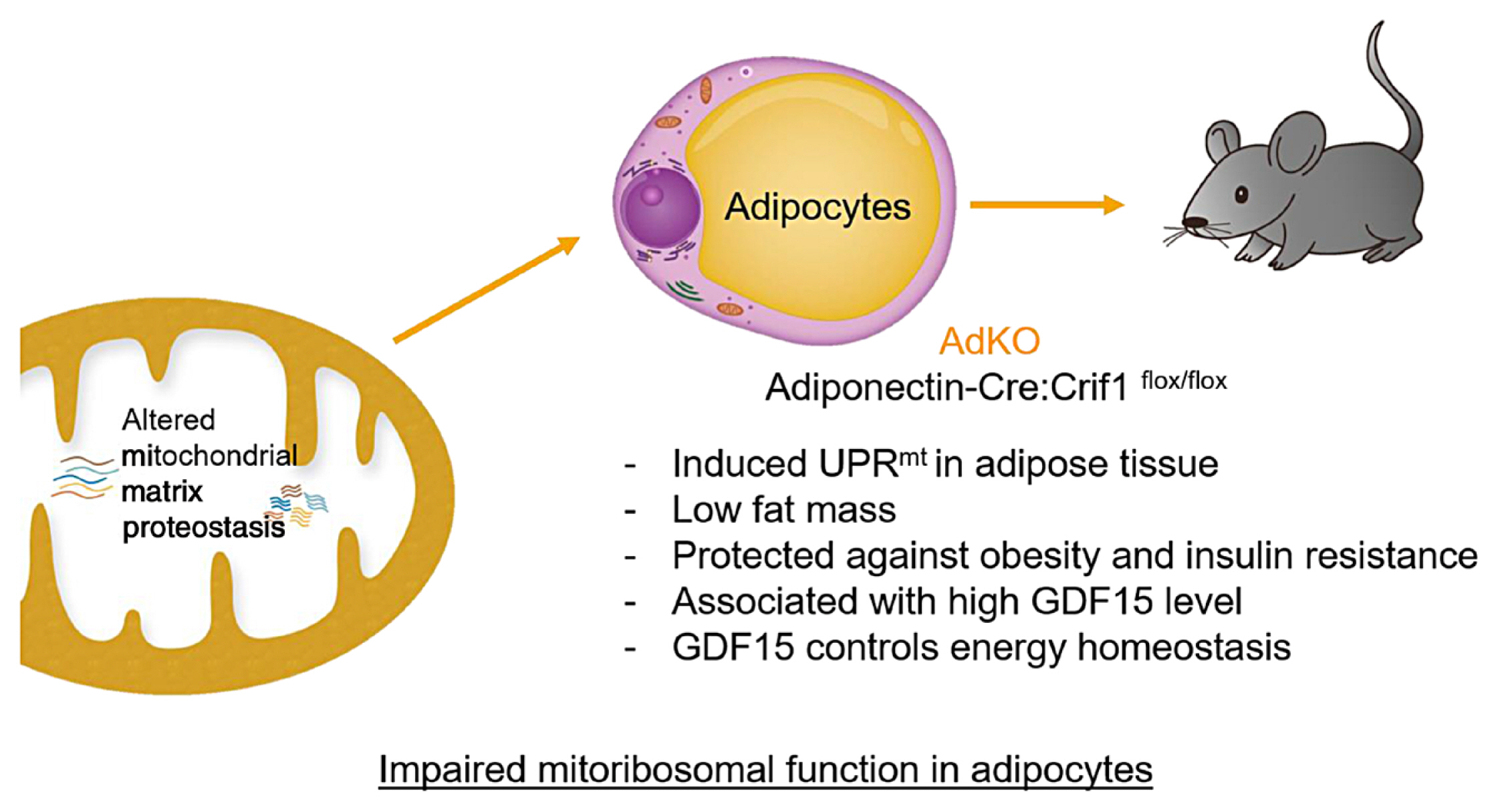
- Cellular and Intercellular Homeostasis in Adipose Tissue with Mitochondria-Specific Stress
- Min Jeong Choi, Saet-Byel Jung, Joon Young Chang, Minho Shong
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(1):1-11. Published online February 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.956
- 5,394 View
- 226 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Paracrine interactions are imperative for the maintenance of adipose tissue intercellular homeostasis, and intracellular organelle dysfunction results in local and systemic alterations in metabolic homeostasis. It is currently accepted that mitochondrial proteotoxic stress activates the mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) in vitro and in vivo. The induction of mitochondrial chaperones and proteases during the UPRmt is a key cell-autonomous mechanism of mitochondrial quality control. The UPRmt also affects systemic metabolism through the secretion of cell non-autonomous peptides and cytokines (hereafter, metabokines). Mitochondrial function in adipose tissue plays a pivotal role in whole-body metabolism and human diseases. Despite continuing interest in the role of the UPRmt and quality control pathways of mitochondria in energy metabolism, studies on the roles of the UPRmt and metabokines in white adipose tissue are relatively sparse. Here, we describe the role of the UPRmt in adipose tissue, including adipocytes and resident macrophages, and the interactive roles of cell non-autonomous metabokines, particularly growth differentiation factor 15, in local adipose cellular homeostasis and systemic energy metabolism.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mitochondrial stress-induced GFRAL signaling controls diurnal food intake and anxiety-like behavior
Carla Igual Gil, Bethany M Coull, Wenke Jonas, Rachel N Lippert, Susanne Klaus, Mario Ost
Life Science Alliance.2022; 5(11): e202201495. CrossRef - Stress-induced FGF21 and GDF15 in obesity and obesity resistance
Susanne Keipert, Mario Ost
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 32(11): 904. CrossRef
- Mitochondrial stress-induced GFRAL signaling controls diurnal food intake and anxiety-like behavior

- Miscellaneous
- Systems Biology: A Multi-Omics Integration Approach to Metabolism and the Microbiome
- Jang Won Son, Saeed Shoaie, Sunjae Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):507-514. Published online September 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.303

- 6,512 View
- 287 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The complex and dynamic nature of human physiology, as exemplified by metabolism, has often been overlooked due to the lack of quantitative and systems approaches. Recently, systems biology approaches have pushed the boundaries of our current understanding of complex biochemical, physiological, and environmental interactions, enabling proactive medicine in the near future. From this perspective, we review how state-of-the-art computational modelling of human metabolism, i.e., genome-scale metabolic modelling, could be used to identify the metabolic footprints of diseases, to guide the design of personalized treatments, and to estimate the microbiome contributions to host metabolism. These state-of-the-art models can serve as a scaffold for integrating multi-omics data, thereby enabling the identification of signatures of dysregulated metabolism by systems approaches. For example, increased plasma mannose levels due to decreased uptake in the liver have been identified as a potential biomarker of early insulin resistance by multi-omics approaches. In addition, we also review the emerging axis of human physiology and the human microbiome, discussing its contribution to host metabolism and quantitative approaches to study its variations in individuals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Innovative Therapeutic Approaches in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: When Knowing Your Patient Is Key
Marta Alonso-Peña, Maria Del Barrio, Ana Peleteiro-Vigil, Carolina Jimenez-Gonzalez, Alvaro Santos-Laso, Maria Teresa Arias-Loste, Paula Iruzubieta, Javier Crespo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(13): 10718. CrossRef - Oxymatrine Alleviates High-Fat-High-Fructose-Induced Fatty Liver in Rats: Understanding the Molecular Mechanism Through an Untargeted Metabonomics Study
Huan Li, Chang Wang, Qing Wang, Xuehua Liu, Juanjuan Zhang, He Zhang, Wenjie Fei, Hang Zhao, Luping Ren
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 4013. CrossRef - Research progress on inosine monophosphate deposition mechanism in chicken muscle
Zengwen Huang, Juan Zhang, Yaling Gu, Zhengyun Cai, Xiaofang Feng, Chaoyun Yang, Guosheng Xin
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2022; 62(4): 1062. CrossRef - Advances in Microbiome-Derived Solutions and Methodologies Are Founding a New Era in Skin Health and Care
Audrey Gueniche, Olivier Perin, Amina Bouslimani, Leslie Landemaine, Namita Misra, Sylvie Cupferman, Luc Aguilar, Cécile Clavaud, Tarun Chopra, Ahmad Khodr
Pathogens.2022; 11(2): 121. CrossRef - Multi-omics research strategies in ischemic stroke: A multidimensional perspective
Wentao Li, Chongyu Shao, Huifen Zhou, Haixia Du, Haiyang Chen, Haitong Wan, Yu He
Ageing Research Reviews.2022; 81: 101730. CrossRef - Combating Childhood Infections in LMICs: evaluating the contribution of Big Data Big data, biomarkers and proteomics: informing childhood diarrhoeal disease management in Low- and Middle-Income Countries
Karen H. Keddy, Senjuti Saha, Iruka N. Okeke, John Bosco Kalule, Farah Naz Qamar, Samuel Kariuki
EBioMedicine.2021; 73: 103668. CrossRef
- Innovative Therapeutic Approaches in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: When Knowing Your Patient Is Key

- Endocrine Research
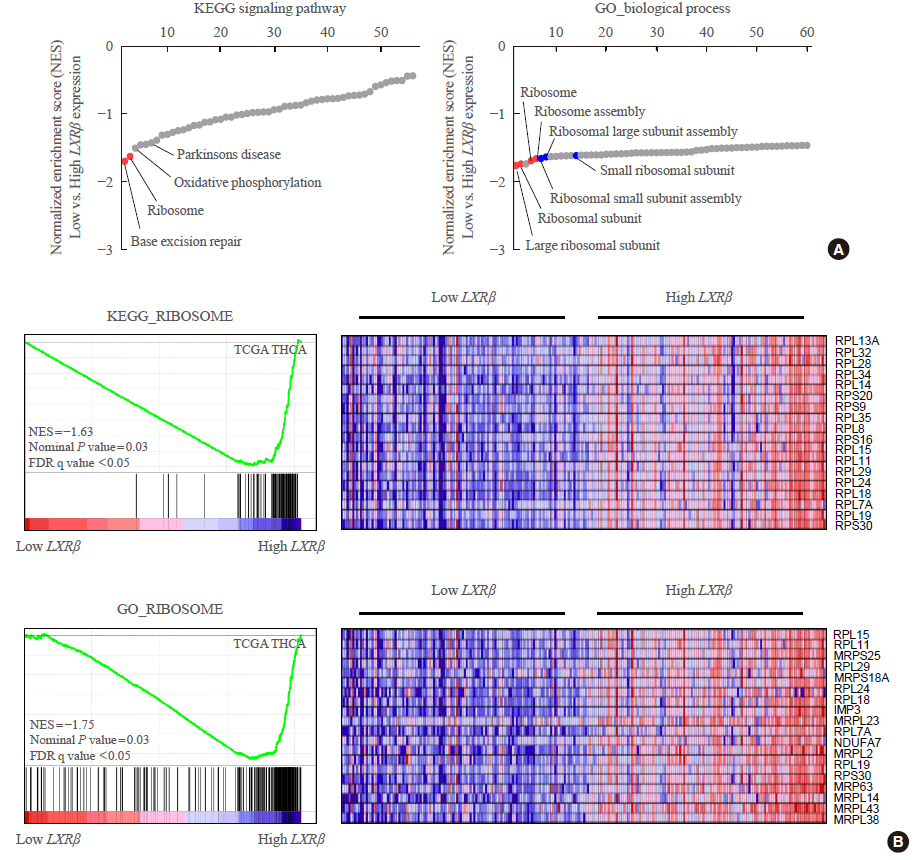
- Liver X Receptor β Related to Tumor Progression and Ribosome Gene Expression in Papillary Thyroid Cancer
- Seonhyang Jeong, In-Kyu Kim, Hyunji Kim, Moon Jung Choi, Jandee Lee, Young Suk Jo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):656-668. Published online August 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.667
- 6,521 View
- 131 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Intracellular lipid deposition has been reported in thyroid glands in obese animal and human. To understand the regulatory mechanism of lipid metabolism in thyroid cancer, we investigated the expression status of liver X receptor (LXR) and analyzed its clinicopathological characteristics and molecular biological features.
Methods
Expression status of LXR and its transcriptional targets in human cancers were analyzed using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). The gene-sets related to high LXRβ expression was investigated by gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) using Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) signaling pathways and gene ontology biologic process. Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction was performed in thyroid cancer samples using our validation cohort.
Results
In contrast to low expression of LXRα, LXRβ was highly expressed in thyroid cancer compared to the other types of human cancers. High LXRβ expression was correlated with the expression of LXRβ transcriptional targets genes, such as apolipoprotein C1 (APOC1), APOC2, apolipoprotein E (APOE), ATP binding cassette subfamily G member 8 (ABCG8), sterol regulatory elementbinding protein 1c (SREBP1c), and SPOT14. Furthermore, High LXRβ expression group indicated poor clinicopathological characteristics and aggressive molecular biological features independently from the drive mutation status. Mechanistically, high LXRβ expression was coordinately related to ribosome-related gene sets.
Conclusion
The mechanistic link between LXRβ and ribosomal activity will be addressed to develop new diagnostic and therapeutic targets in thyroid cancers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- ApoC1 promotes glioma metastasis by enhancing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and activating the STAT3 pathway
Rui Liang, Guofeng Zhang, Wenhua Xu, Weibing Liu, Youjia Tang
Neurological Research.2023; 45(3): 268. CrossRef - The Novel RXR Agonist MSU-42011 Differentially Regulates Gene Expression in Mammary Tumors of MMTV-Neu Mice
Lyndsey A. Reich, Ana S. Leal, Edmund Ellsworth, Karen T. Liby
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(5): 4298. CrossRef - The Role of Apolipoproteins in the Commonest Cancers: A Review
Nour M. Darwish, Mooza Kh. Al-Hail, Youssef Mohamed, Rafif Al Saady, Sara Mohsen, Amna Zar, Layla Al-Mansoori, Shona Pedersen
Cancers.2023; 15(23): 5565. CrossRef - Apolipoproteins: New players in cancers
Yingcheng He, Jianrui Chen, Yanbing Ma, Hongping Chen
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Simultaneous Expression of Long Non-Coding RNA FAL1 and Extracellular Matrix Protein 1 Defines Tumour Behaviour in Young Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Seonhyang Jeong, Seul-Gi Lee, Hyunji Kim, Gibbeum Lee, Sunmi Park, In-Kyu Kim, Jandee Lee, Young-Suk Jo
Cancers.2021; 13(13): 3223. CrossRef - Using BioPAX-Parser (BiP) to enrich lists of genes or proteins with pathway data
Giuseppe Agapito, Mario Cannataro
BMC Bioinformatics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive Analysis of Prognostic Alternative Splicing Signature Reveals Recurrence Predictor for Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Mian Liu, Rooh Afza Khushbu, Pei Chen, Hui-Yu Hu, Neng Tang, Deng-jie Ou-yang, Bo Wei, Ya-xin Zhao, Peng Huang, Shi Chang
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Reprogramming of Thyroid Cancer Cells and Crosstalk in Their Microenvironment
Lisha Bao, Tong Xu, Xixuan Lu, Ping Huang, Zongfu Pan, Minghua Ge
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cooperative Subtype Switch of Thyroid Hormone Receptor and Nuclear Receptor Corepressor Related Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Seonhyang Jeong, Seul Gi Lee, Hyunji Kim, Gibbeum Lee, Sunmi Park, In-Kyu Kim, Jandee Lee, Young Suk Jo
International Journal of Thyroidology.2021; 14(2): 152. CrossRef
- ApoC1 promotes glioma metastasis by enhancing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and activating the STAT3 pathway

- Miscellaneous
- Machine Learning Applications in Endocrinology and Metabolism Research: An Overview
- Namki Hong, Heajeong Park, Yumie Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):71-84. Published online March 19, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.71
- 15,434 View
- 203 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Machine learning (ML) applications have received extensive attention in endocrinology research during the last decade. This review summarizes the basic concepts of ML and certain research topics in endocrinology and metabolism where ML principles have been actively deployed. Relevant studies are discussed to provide an overview of the methodology, main findings, and limitations of ML, with the goal of stimulating insights into future research directions. Clear, testable study hypotheses stem from unmet clinical needs, and the management of data quality (beyond a focus on quantity alone), open collaboration between clinical experts and ML engineers, the development of interpretable high-performance ML models beyond the black-box nature of some algorithms, and a creative environment are the core prerequisites for the foreseeable changes expected to be brought about by ML and artificial intelligence in the field of endocrinology and metabolism, with actual improvements in clinical practice beyond hype. Of note, endocrinologists will continue to play a central role in these developments as domain experts who can properly generate, refine, analyze, and interpret data with a combination of clinical expertise and scientific rigor.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Artificial Intelligence for Predicting and Diagnosing Complications of Diabetes
Jingtong Huang, Andrea M. Yeung, David G. Armstrong, Ashley N. Battarbee, Jorge Cuadros, Juan C. Espinoza, Samantha Kleinberg, Nestoras Mathioudakis, Mark A. Swerdlow, David C. Klonoff
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2023; 17(1): 224. CrossRef - Expressions of Cushing’s syndrome in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1
William F. Simonds
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of machine learning and artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and classification of polycystic ovarian syndrome: a systematic review
Francisco J. Barrera, Ethan D.L. Brown, Amanda Rojo, Javier Obeso, Hiram Plata, Eddy P. Lincango, Nancy Terry, René Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, Janet E. Hall, Skand Shekhar
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of rituximab effect on modified Rodnan skin score in systemic sclerosis: a machine-learning analysis of the DesiReS trial
Satoshi Ebata, Koji Oba, Kosuke Kashiwabara, Keiko Ueda, Yukari Uemura, Takeyuki Watadani, Takemichi Fukasawa, Shunsuke Miura, Asako Yoshizaki-Ogawa, Asano Yoshihide, Ayumi Yoshizaki, Shinichi Sato
Rheumatology.2022; 61(11): 4364. CrossRef - Automating and improving cardiovascular disease prediction using Machine learning and EMR data features from a regional healthcare system
Qi Li, Alina Campan, Ai Ren, Wael E. Eid
International Journal of Medical Informatics.2022; 163: 104786. CrossRef - An Interactive Online App for Predicting Diabetes via Machine Learning from Environment-Polluting Chemical Exposure Data
Rosy Oh, Hong Kyu Lee, Youngmi Kim Pak, Man-Suk Oh
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(10): 5800. CrossRef - Ensemble blood glucose prediction in diabetes mellitus: A review
M.Z. Wadghiri, A. Idri, Touria El Idrissi, Hajar Hakkoum
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2022; 147: 105674. CrossRef - The maze runner: navigating through basic kinetics to AI models of human metabolism pathology
Arina V. Martyshina, Oksana M. Tilinova, Anastasia A. Simanova, Olga S. Knyazeva, Irina V. Dokukina
Procedia Computer Science.2022; 213: 271. CrossRef - Applications of Machine Learning in Bone and Mineral Research
Sung Hye Kong, Chan Soo Shin
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 928. CrossRef - Facial Recognition Intensity in Disease Diagnosis Using Automatic Facial Recognition
Danning Wu, Shi Chen, Yuelun Zhang, Huabing Zhang, Qing Wang, Jianqiang Li, Yibo Fu, Shirui Wang, Hongbo Yang, Hanze Du, Huijuan Zhu, Hui Pan, Zhen Shen
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2021; 11(11): 1172. CrossRef - The Application of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Pituitary Adenomas
Congxin Dai, Bowen Sun, Renzhi Wang, Jun Kang
Frontiers in Oncology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Real World Data and Artificial Intelligence in Diabetology
Kwang Joon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 140. CrossRef - A Novel Detection Framework for Detecting Abnormal Human Behavior
Chengfei Wu, Zixuan Cheng, Yi-Zhang Jiang
Mathematical Problems in Engineering.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef
- Artificial Intelligence for Predicting and Diagnosing Complications of Diabetes

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Recent Progress on Branched-Chain Amino Acids in Obesity, Diabetes, and Beyond
- Md Abu Bakkar Siddik, Andrew C. Shin
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(3):234-246. Published online September 26, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.3.234
- 11,586 View
- 251 Download
- 78 Web of Science
- 76 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) are essential amino acids that are not synthesized in our body; thus, they need to be obtained from food. They have shown to provide many physiological and metabolic benefits such as stimulation of pancreatic insulin secretion, milk production, adipogenesis, and enhanced immune function, among others, mainly mediated by mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway. After identified as a reliable marker of obesity and type 2 diabetes in recent years, an increasing number of studies have surfaced implicating BCAAs in the pathophysiology of other diseases such as cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and even neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer's disease. Here we discuss the most recent progress and review studies highlighting both correlational and potentially causative role of BCAAs in the development of these disorders. Although we are just beginning to understand the intricate relationships between BCAAs and some of the most prevalent chronic diseases, current findings raise a possibility that they are linked by a similar putative mechanism.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- First trimester metabolomics 1H-NMR study of the urinary profile predicts gestational diabetes mellitus development in obese women
Cristina Piras, Isabella Neri, Roberta Pintus, Antonio Noto, Elisabetta Petrella, Francesca Monari, Angelica Dessì, Vassilios Fanos, Luigi Atzori, Fabio Facchinetti
The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine.2024; 35(25): 8275. CrossRef - Branched‐Chain Amino Acid Accumulation Fuels the Senescence‐Associated Secretory Phenotype
Yaosi Liang, Christopher Pan, Tao Yin, Lu Wang, Xia Gao, Ergang Wang, Holly Quang, De Huang, Lianmei Tan, Kun Xiang, Yu Wang, Peter B. Alexander, Qi‐Jing Li, Tso‐Pang Yao, Zhao Zhang, Xiao‐Fan Wang
Advanced Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Deficiency of BCAT2-mediated branched-chain amino acid catabolism promotes colorectal cancer development
Zi-Ran Kang, Shanshan Jiang, Ji-Xuan Han, Yaqi Gao, Yile Xie, Jinxian Chen, Qiang Liu, Jun Yu, Xin Zhao, Jie Hong, Haoyan Chen, Ying-Xuan Chen, Huimin Chen, Jing-Yuan Fang
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2024; 1870(2): 166941. CrossRef - Microbiome metabolite quantification methods enabling insights into human health and disease
Jarrod Roach, Rohit Mital, Jacob J. Haffner, Nathan Colwell, Randy Coats, Horvey M. Palacios, Zongyuan Liu, Joseane L.P. Godinho, Monica Ness, Thilini Peramuna, Laura-Isobel McCall
Methods.2024; 222: 81. CrossRef - Branched-chain amino acids promote occurrence and development of cardiovascular disease dependent on triglyceride metabolism via activation of the mTOR/SREBP-1/betatrophin pathway
Jie Zhang, Ziyu Liu, Yaojun Ni, Yang Yu, Fei Guo, Yanwen Lu, Xiaoqing Wang, Hairong Hao, Shayan Li, Pan Wei, Weinan Yu, Wen Hu
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2024; 584: 112164. CrossRef - Heat stress reduces brown adipose tissue activity by exacerbating mitochondrial damage in type 2 diabetic mice
Penghua Lai, Linlin Zhang, Yan Qiu, Jie Ren, Xue Sun, Ting Zhang, Liuyi Wang, Sijie Cheng, Sijia Liu, Hongli Zhuang, Daiwei Lu, Shaoliang Zhang, Huiqing Liang, Shaodong Chen
Journal of Thermal Biology.2024; 119: 103799. CrossRef - Unraveling Adipose Tissue Dysfunction: Molecular Mechanisms, Novel Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Targets for Liver Fat Deposition
Marta Lopez-Yus, Carlos Hörndler, Sofia Borlan, Vanesa Bernal-Monterde, Jose M. Arbones-Mainar
Cells.2024; 13(5): 380. CrossRef - Microbial production of branched chain amino acids: Advances and perspectives
Yanan Hao, Xuewei Pan, Jiajia You, Guomin Li, Meijuan Xu, Zhiming Rao
Bioresource Technology.2024; 397: 130502. CrossRef - Maintenance of the branched-chain amino acid transporter LAT1 counteracts myotube atrophy following chemotherapy
Stephen Mora, Olasunkanmi A. J. Adegoke
American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology.2024; 326(3): C866. CrossRef - Metabolic Signatures Elucidate the Effect of Body Mass Index on Type 2 Diabetes
Qiuling Dong, Sidra Sidra, Christian Gieger, Rui Wang-Sattler, Wolfgang Rathmann, Cornelia Prehn, Jerzy Adamski, Wolfgang Koenig, Annette Peters, Harald Grallert, Sapna Sharma
Metabolites.2023; 13(2): 227. CrossRef - The Preventive Effect of Exercise and Oral Branched-Chain Amino Acid Supplementation on Obesity-Induced Brain Changes in Ldlr−/−.Leiden Mice
Klara J. Lohkamp, Anita M. van den Hoek, Gemma Solé-Guardia, Maria Lisovets, Talissa Alves Hoffmann, Konstantina Velanaki, Bram Geenen, Vivienne Verweij, Martine C. Morrison, Robert Kleemann, Maximilian Wiesmann, Amanda J. Kiliaan
Nutrients.2023; 15(7): 1716. CrossRef - The Crosstalk between Gut Microbiota and White Adipose Tissue Mitochondria in Obesity
Luca Colangeli, David Israel Escobar Marcillo, Valeria Simonelli, Egidio Iorio, Tommaso Rinaldi, Paolo Sbraccia, Paola Fortini, Valeria Guglielmi
Nutrients.2023; 15(7): 1723. CrossRef - Prebiotic and Probiotic Modulation of the Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis in Depression
Daniel E. Radford-Smith, Daniel C. Anthony
Nutrients.2023; 15(8): 1880. CrossRef - Machine learning model to predict obesity using gut metabolite and brain microstructure data
Vadim Osadchiy, Roshan Bal, Emeran A. Mayer, Rama Kunapuli, Tien Dong, Priten Vora, Danny Petrasek, Cathy Liu, Jean Stains, Arpana Gupta
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin Resistance and Impaired Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism in Alzheimer’s Disease
Rui Liu, Lei Zhang, Hao You
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2023; 93(3): 847. CrossRef - Obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: connections in epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatments
Rexiati Ruze, Tiantong Liu, Xi Zou, Jianlu Song, Yuan Chen, Ruiyuan Xu, Xinpeng Yin, Qiang Xu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Crosstalk between arginine, glutamine, and the branched chain amino acid metabolism in the tumor microenvironment
Tanner J. Wetzel, Sheila C. Erfan, Lucas D. Figueroa, Leighton M. Wheeler, Elitsa A. Ananieva
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Stachydrine, N‐acetylornithine and trimethylamine N‐oxide levels as candidate milk biomarkers of maternal consumption of an obesogenic diet during lactation
Pedro Castillo, Ondrej Kuda, Jan Kopecky, Catalina Amadora Pomar, Andreu Palou, Mariona Palou, Catalina Picó
BioFactors.2023; 49(5): 1022. CrossRef - Biofunctionalization of natural extracts, trends in biological activity and kinetic release
Abraham Osiris Martínez-Olivo, Víctor Manuel Zamora-Gasga, Luis Medina-Torres, Alejandro Pérez-Larios, Sonia Guadalupe Sáyago-Ayerdi, Jorge Alberto Sánchez-Burgos
Advances in Colloid and Interface Science.2023; 318: 102938. CrossRef - Muscle Traits, Sarcopenia, and Sarcopenic Obesity: A Vitamin D Mendelian Randomization Study
Joshua P. Sutherland, Ang Zhou, Elina Hyppönen
Nutrients.2023; 15(12): 2703. CrossRef - Bioactive Ingredients in Traditional Fermented Food Condiments: Emerging Products for Prevention and Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
Alphonse Laya, Honoré Wangso, Iva Fernandes, Raphaël Djakba, Joana Oliveira, Eugenia Carvalho, Wen yi Kang
Journal of Food Quality.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Sex related differences in muscle health and metabolism in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Mariëlle P.K.J. Engelen, Sarah K. Kirschner, Kimberly S. Coyle, David Argyelan, Gabriel Neal, Srinivasan Dasarathy, Nicolaas E.P. Deutz
Clinical Nutrition.2023; 42(9): 1737. CrossRef - Depiction of Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) in Diabetes with a Focus on Diabetic Microvascular Complications
Daniela Maria Tanase, Evelina Maria Gosav, Tina Botoc, Mariana Floria, Claudia Cristina Tarniceriu, Minela Aida Maranduca, Anca Haisan, Andrei Ionut Cucu, Ciprian Rezus, Claudia Florida Costea
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(18): 6053. CrossRef - Genetic and Lifestyle-Related Factors Influencing Serum Hyper-Propionylcarnitine Concentrations and Their Association with Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Yong-Hwa Lee, Sunmin Park
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(21): 15810. CrossRef -
Relationship between Components, Intestinal Microbiota, and Mechanism of Hypoglycemic Effect of the Saggy Ink Cap Medicinal Mushroom (Coprinus Comatus, Agaricomycetes): A Review
Wei Wang, Min Sun, Jinyan Yu, Xumin Ma, Chunchao Han
International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms.2023; 25(12): 81. CrossRef - High-protein diet with excess leucine prevents inactivity-induced insulin resistance in women
Alessandro Mangogna, Filippo Giorgio Di Girolamo, Nicola Fiotti, Pierandrea Vinci, Matteo Landolfo, Filippo Mearelli, Gianni Biolo
Clinical Nutrition.2023; 42(12): 2578. CrossRef - Exploring the functional roles of small-molecule metabolites in disease research: Recent advancements in metabolomics
Aolei Tan, Xiaoxiao Ma
Chinese Chemical Letters.2023; : 109276. CrossRef - Toward Systems-Level Metabolic Analysis in Endocrine Disorders and Cancer
Aliya Lakhani, Da Hyun Kang, Yea Eun Kang, Junyoung O. Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 619. CrossRef - Dietary intake of branched-chain amino acids in relation to general and abdominal obesity
Farzaneh Asoudeh, Asma Salari-Moghaddam, Ammar Hassanzadeh Keshteli, Ahmad Esmaillzadeh, Peyman Adibi
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity.2022; 27(4): 1303. CrossRef - Tea polyphenol – gut microbiota interactions: hints on improving the metabolic syndrome in a multi-element and multi-target manner
Hui Ma, Yaozhong Hu, Bowei Zhang, Zeping Shao, Eugeni Roura, Shuo Wang
Food Science and Human Wellness.2022; 11(1): 11. CrossRef - Exogenous isoleucine can confer browning resistance on fresh-cut potato by suppressing polyphenol oxidase activity and improving the antioxidant capacity
Zan Meng, Tong Wang, Aman Ullah Malik, Qingguo Wang
Postharvest Biology and Technology.2022; 184: 111772. CrossRef - Impact of thermal treatment and fermentation by lactic acid bacteria on sorghum metabolite changes, their antioxidant and antidiabetic activities
Fred Kwame Ofosu, Fazle Elahi, Eric Banan-Mwine Daliri, Sang-Ik Han, Deog-Hwan Oh
Food Bioscience.2022; 45: 101502. CrossRef - Infant intakes of human milk branched chain amino acids are negatively associated with infant growth and influenced by maternal body mass index
Jessica L. Saben, Clark R. Sims, Lindsay Pack, Renny Lan, Elisabet Børsheim, Aline Andres
Pediatric Obesity.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) Surgery during High Liquid Sucrose Diet Leads to Gut Microbiota-Related Systematic Alterations
Laimdota Zizmare, Christina N. Boyle, Sabrina Buss, Sandrine Louis, Laura Kuebler, Ketki Mulay, Ralf Krüger, Lara Steinhauer, Isabelle Mack, Manuel Rodriguez Gomez, Kristina Herfert, Yvonne Ritze, Christoph Trautwein
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(3): 1126. CrossRef - Omics Analyses of Intestinal Microbiota and Hypothalamus Clock Genes in Circadian Disturbance Model Mice Fed with Green Tea Polyphenols
Yuting Zhang, Lu Cheng, Yanan Liu, Ruilin Zhang, Zufang Wu, Kejun Cheng, Xin Zhang
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.2022; 70(6): 1890. CrossRef - Age, Sex, Body Mass Index, Diet and Menopause Related Metabolites in a Large Homogeneous Alpine Cohort
Vinicius Verri Hernandes, Nikola Dordevic, Essi Marjatta Hantikainen, Baldur Bragi Sigurdsson, Sigurður Vidir Smárason, Vanessa Garcia-Larsen, Martin Gögele, Giulia Caprioli, Ilaria Bozzolan, Peter P. Pramstaller, Johannes Rainer
Metabolites.2022; 12(3): 205. CrossRef - α-ketoisocaproic acid promotes ER stress through impairment of autophagy, thereby provoking lipid accumulation and insulin resistance in murine preadipocytes
Tae Jun Park, Seung Yeon Park, Hyun Jung Lee, A.M. Abd El-Aty, Ji Hoon Jeong, Tae Woo Jung
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2022; 603: 109. CrossRef - The associations of serum valine with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease
Yong-lan Xiong, Joseph Therriault, Shu-jiang Ren, Xiao-jun Jing, Hua Zhang
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research.2022; 34(8): 1807. CrossRef - The Critical Role of the Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) Catabolism-Regulating Enzymes, Branched-Chain Aminotransferase (BCAT) and Branched-Chain α-Keto Acid Dehydrogenase (BCKD), in Human Pathophysiology
Aikaterini Dimou, Vasilis Tsimihodimos, Eleni Bairaktari
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(7): 4022. CrossRef - Obesity, exercise training, and BCAA supplementation: All that glitters (may not be) gold
Stephen J. Carter, Emily B. Long, Cydne A. Perry
Obesity.2022; 30(6): 1139. CrossRef - Effects of serum branched-chain amino acids on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and subsequent cardiovascular disease
Fei Guo, Rui Chen, Linghui Kong, Pan Wei, Ziyu Liu, Xiaoqing Wang, Hairong Hao, Yanwen Lu, Wen Hu
Hepatology International.2022; 16(6): 1424. CrossRef - Advances in multi-omics study of biomarkers of glycolipid metabolism disorder
Xinyi Fang, Runyu Miao, Jiahua Wei, Haoran Wu, Jiaxing Tian
Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal.2022; 20: 5935. CrossRef - Targeted Metabolomics Revealed a Sex-Dependent Signature for Metabolic Syndrome in the Mexican Population
Berenice Palacios-González, Guadalupe León-Reyes, Berenice Rivera-Paredez, Isabel Ibarra-González, Marcela Vela-Amieva, Yvonne N. Flores, Samuel Canizales-Quinteros, Jorge Salmerón, Rafael Velázquez-Cruz
Nutrients.2022; 14(18): 3678. CrossRef - Case report: NAFLD and maple syrup urine disease: Is there an interplay between branched-chain amino acids and fructose consumption?
Helena Moreira-Silva, Sandra Ferreira, Manuela Almeida, Isabel Gonçalves, Maria Augusta Cipriano, J. R. Vizcaíno, Ermelinda Santos-Silva, Esmeralda Gomes-Martins
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A self-assembled leucine polymer sensitizes leukemic stem cells to chemotherapy by inhibiting autophagy in acute myeloid leukemia
Xi Xu, Jian Wang, Tong Tong, Wenwen Zhang, Jin Wang, Weiwei Ma, Shunqing Wang, Dunhua Zhou, Jun Wu, Linjia Jiang, Meng Zhao
Haematologica.2022; 107(10): 2344. CrossRef - Effect of dietary protein content shift on aging in elderly rats by comprehensive quantitative score and metabolomics analysis
Wenxuan Zheng, Ruiding Li, Yang Zhou, Fengcui Shi, Yao Song, Yanting Liao, Fan Zhou, Xiaohua Zheng, Jingwen Lv, Quanyang Li
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Caloric restriction improves glycaemic control without reducing plasma branched-chain amino acids or keto-acids in obese men
M. H. Sayda, M. H. Abdul Aziz, N. Gharahdaghi, D. J. Wilkinson, P. L. Greenhaff, B. E. Phillips, K. Smith, I. Idris, P. J. Atherton
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietary Protein and Amino Acid Deficiency Inhibit Pancreatic Digestive Enzyme mRNA Translation by Multiple Mechanisms
Maria Dolors Sans, Stephen J. Crozier, Nancy L. Vogel, Louis G. D’Alecy, John A. Williams
Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 11(1): 99. CrossRef - Isoleucine increases muscle mass through promoting myogenesis and intramyocellular fat deposition
Shuge Liu, Yunmei Sun, Rui Zhao, Yingqian Wang, Wanrong Zhang, Weijun Pang
Food & Function.2021; 12(1): 144. CrossRef - Serum metabolomics study of women with different annual decline rates of anti-Müllerian hormone: an untargeted gas chromatography–mass spectrometry-based study
Nazanin Moslehi, Parvin Mirmiran, Rezvan Marzbani, Hassan Rezadoost, Mehdi Mirzaie, Fereidoun Azizi, Fahimeh Ramezani Tehrani
Human Reproduction.2021; 36(3): 721. CrossRef - Amino acid sensing pathway: A major check point in the pathogenesis of obesity and COVID‐19
Aradhana Mariam Philips, Nooruddin Khan
Obesity Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The chemical mechanisms of the enzymes in the branched-chain amino acids biosynthetic pathway and their applications
Yan-Fei Liang, Zi-Xian Long, Ya-Jian Zhang, Cai-Yun Luo, Le-Tian Yan, Wen-Yun Gao, Heng Li
Biochimie.2021; 184: 72. CrossRef - Plasma Metabolomic Profiling in 1391 Subjects with Overweight and Obesity from the SPHERE Study
Gianfranco Frigerio, Chiara Favero, Diego Savino, Rosa Mercadante, Benedetta Albetti, Laura Dioni, Luisella Vigna, Valentina Bollati, Angela Cecilia Pesatori, Silvia Fustinoni
Metabolites.2021; 11(4): 194. CrossRef - Sarcopenic Obesity and Amino Acids: Concord Health and Ageing in Men Project
David G Le Couteur, David J Handelsman, Fiona Stanaway, Louise M Waite, Fiona M Blyth, Vasi Naganathan, Robert G Cumming, Vasant Hirani, Rafael de Cabo
The Journals of Gerontology: Series A.2021; 76(6): 1000. CrossRef - Metabolic signatures of greater body size and their associations with risk of colorectal and endometrial cancers in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition
Nathalie Kliemann, Vivian Viallon, Neil Murphy, Rebecca J. Beeken, Joseph A. Rothwell, Sabina Rinaldi, Nada Assi, Eline H. van Roekel, Julie A. Schmidt, Kristin Benjaminsen Borch, Claudia Agnoli, Ann H. Rosendahl, Hanna Sartor, José María Huerta, Anne Tjø
BMC Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasma Amino Acids and Residual Hypertriglyceridemia in Diabetic Patients Under Statins: Two Independent Cross-Sectional Hospital-Based Cohorts
Shuang Wang, Yun-Feng Cao, Xiao-Yu Sun, Mo Hong, Zhong-Ze Fang, Hui-Huan Luo, Huan Sun, Ping Yang
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of Metabolic Phenotypes in Young Adults with Obesity by 1H NMR Metabolomics of Blood Serum
Khin Thandar Htun, Jie Pan, Duanghathai Pasanta, Montree Tungjai, Chatchanok Udomtanakunchai, Sirirat Chancharunee, Siriprapa Kaewjaeng, Hong Joo Kim, Jakrapong Kaewkhao, Suchart Kothan
Life.2021; 11(6): 574. CrossRef - A Metabolic Pattern in Healthy Subjects Given a Single Dose of Metformin: A Metabolomics Approach
Lina A. Dahabiyeh, Muhammad Mujammami, Tawfiq Arafat, Hicham Benabdelkamel, Assim A. Alfadda, Anas M. Abdel Rahman
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Branched-chain Amino Acids: Catabolism in Skeletal Muscle and Implications for Muscle and Whole-body Metabolism
Gagandeep Mann, Stephen Mora, Glory Madu, Olasunkanmi A. J. Adegoke
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of TBX15 as an adipose master trans regulator of abdominal obesity genes
David Z. Pan, Zong Miao, Caroline Comenho, Sandhya Rajkumar, Amogha Koka, Seung Hyuk T. Lee, Marcus Alvarez, Dorota Kaminska, Arthur Ko, Janet S. Sinsheimer, Karen L. Mohlke, Nicholas Mancuso, Linda Liliana Muñoz-Hernandez, Miguel Herrera-Hernandez, Maria
Genome Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Antidiabetic Effect of Noodles Containing Fermented Lettuce Extracts
Soon Yeon Jeong, Eunjin Kim, Ming Zhang, Yun-Seong Lee, Byeongjun Ji, Sun-Hee Lee, Yu Eun Cheong, Soon-Il Yun, Young-Soo Kim, Kyoung Heon Kim, Min Sun Kim, Hyun Soo Chun, Sooah Kim
Metabolites.2021; 11(8): 520. CrossRef - Targeted and Untargeted Mass Spectrometry Reveals the Impact of High-Fat Diet on Peripheral Amino Acid Regulation in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease
Amelia L. Taylor, Don E. Davis, Simona G. Codreanu, Fiona E. Harrison, Stacy D. Sherrod, John A. McLean
Journal of Proteome Research.2021; 20(9): 4405. CrossRef - The Association of 9 Amino Acids With Cardiovascular Events in Finnish Men in a 12-Year Follow-up Study
Raimo Jauhiainen, Jagadish Vangipurapu, Annamaria Laakso, Teemu Kuulasmaa, Johanna Kuusisto, Markku Laakso
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 106(12): 3448. CrossRef - Serum Metabolite Profile Associated with Sex-Dependent Visceral Adiposity Index and Low Bone Mineral Density in a Mexican Population
Berenice Palacios-González, Guadalupe León-Reyes, Berenice Rivera-Paredez, Isabel Ibarra-González, Marcela Vela-Amieva, Yvonne N. Flores, Samuel Canizales-Quinteros, Jorge Salmerón, Rafael Velázquez-Cruz
Metabolites.2021; 11(9): 604. CrossRef - Branched chain amino acids—friend or foe in the control of energy substrate turnover and insulin sensitivity?
Elżbieta Supruniuk, Ewa Żebrowska, Adrian Chabowski
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2021; : 1. CrossRef - Diet Effects on Cerebrospinal Fluid Amino Acids Levels in Adults with Normal Cognition and Mild Cognitive Impairment
Kate J. Russin, K. Sreekumaran Nair, Thomas J. Montine, Laura D. Baker, Suzanne Craft
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2021; 84(2): 843. CrossRef - QSHY Granules Promote White Adipose Tissue Browning and Correct BCAAs Metabolic Disorder in NAFLD Mice
Binbin Zhang, Mingzhu Ni, Xiaojing Li, Qiaohong Liu, Yiyang Hu, Yu Zhao
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 4241. CrossRef - The Changes in Endogenous Metabolites in Hyperlipidemic Rats Treated with Herbal Mixture Containing Lemon, Apple Cider, Garlic, Ginger, and Honey
Azliana Abu Bakar Sajak, Azrina Azlan, Faridah Abas, Hazilawati Hamzah
Nutrients.2021; 13(10): 3573. CrossRef - Integration of Transcriptome and Metabolome Provides Unique Insights to Pathways Associated With Obese Breast Cancer Patients
Mohammed A. Hassan, Kaltoom Al-Sakkaf, Mohammed Razeeth Shait Mohammed, Ashraf Dallol, Jaudah Al-Maghrabi, Alia Aldahlawi, Sawsan Ashoor, Mabrouka Maamra, Jiannis Ragoussis, Wei Wu, Mohammad Imran Khan, Abdulrahman L. Al-Malki, Hani Choudhry
Frontiers in Oncology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Omics Biomarkers in Obesity: Novel Etiological Insights and Targets for Precision Prevention
Krasimira Aleksandrova, Caue Egea Rodrigues, Anna Floegel, Wolfgang Ahrens
Current Obesity Reports.2020; 9(3): 219. CrossRef - Why Are Branched-Chain Amino Acids Increased in Starvation and Diabetes?
Milan Holeček
Nutrients.2020; 12(10): 3087. CrossRef - Differential gene signature in adipose tissue depots of growth hormone transgenic mice
Silvana Duran‐Ortiz, Jonathan A. Young, Adam Jara, Elizabeth A. Jensen, Reetobrata Basu, Edward O. List, Yanrong Qian, John J. Kopchick, Darlene E. Berryman
Journal of Neuroendocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Role of Serum Amino Acids in Head and Neck Cancer
Gabriella Cadoni, Luca Giraldi, Carlo Chiarla, Jacopo Gervasoni, Silvia Persichilli, Aniello Primiano, Stefano Settimi, Jacopo Galli, Gaetano Paludetti, Dario Arzani, Stefania Boccia, Ivo Giovannini, Giovanni Almadori, Leigh A. Madden
Disease Markers.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Lipid changes in the metabolome of a single case study with maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) after five days of improved diet adherence of controlled branched-chain amino acids (BCAA)
Teresa D. Douglas, L. Kristin Newby, Julie Eckstrand, Douglas Wixted, Rani H. Singh
Molecular Genetics and Metabolism Reports.2020; 25: 100651. CrossRef - Branched chain amino acids, aging and age-related health
David G. Le Couteur, Samantha M. Solon-Biet, Victoria C. Cogger, Rosilene Ribeiro, Rafael de Cabo, David Raubenheimer, Gregory J. Cooney, Stephen J. Simpson
Ageing Research Reviews.2020; 64: 101198. CrossRef - Branched-chain ketoacid overload inhibits insulin action in the muscle
Dipsikha Biswas, Khoi T. Dao, Angella Mercer, Andrew M. Cowie, Luke Duffley, Yassine El Hiani, Petra C. Kienesberger, Thomas Pulinilkunnil
Journal of Biological Chemistry.2020; 295(46): 15597. CrossRef
- First trimester metabolomics 1H-NMR study of the urinary profile predicts gestational diabetes mellitus development in obese women


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



