Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- The Emerging Importance of Mitochondria in White Adipocytes: Neither Last nor Least
- Juan Cai, Fenfen Wang, Mengle Shao
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):493-503. Published online October 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1813
- 1,912 View
- 92 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
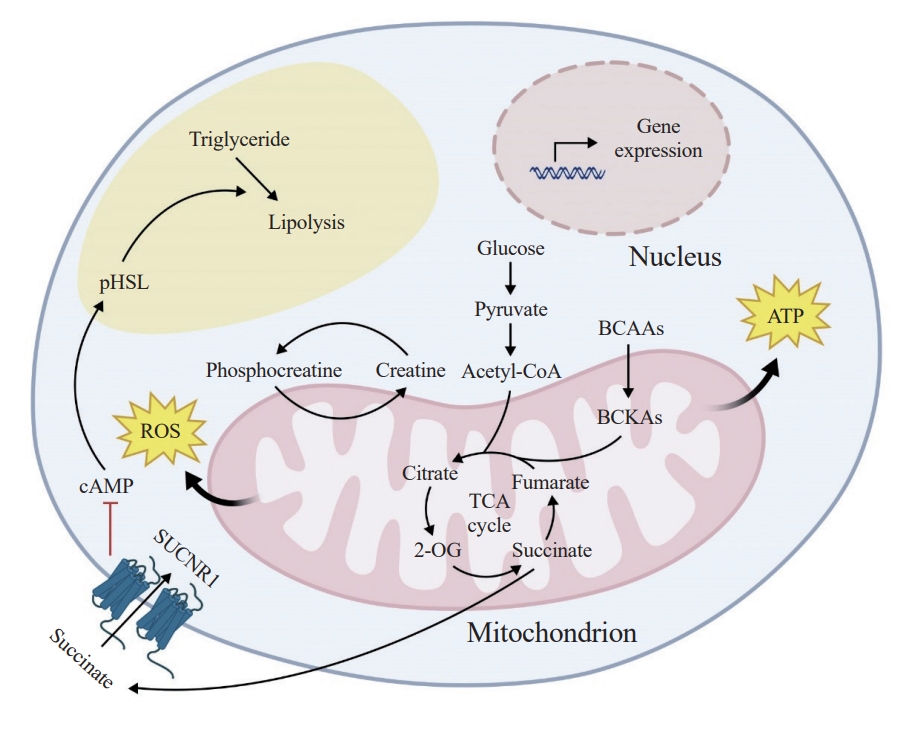
ePub - The growing recognition of mitochondria’s crucial role in the regulation of white adipose tissue remodeling and energy balance underscores its significance. The marked metabolic diversity of mitochondria provides the molecular and cellular foundation for enabling adipose tissue plasticity in response to various metabolic cues. Effective control of mitochondrial function at the cellular level, not only in thermogenic brown and beige adipocytes but also in energy-storing white adipocytes, exerts a profound influence on adipose homeostasis. Furthermore, mitochondria play a pivotal role in intercellular communication within adipose tissue via production of metabolites with signaling properties. A more comprehensive understanding of mitochondrial regulation within white adipocytes will empower the development of targeted and efficacious strategies to enhance adipose function, leading to advancements in overall metabolic health.

- Miscellaneous
- Quality Matters as Much as Quantity of Skeletal Muscle: Clinical Implications of Myosteatosis in Cardiometabolic Health
- Hong-Kyu Kim, Chul-Hee Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(6):1161-1174. Published online December 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1348

- 6,390 View
- 283 Download
- 26 Web of Science
- 29 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Although age-related changes in skeletal muscles are closely associated with decreases in muscle strength and functional decline, their associations with cardiometabolic diseases in the literature are inconsistent. Such inconsistency could be explained by the fact that muscle quality—which is closely associated with fatty infiltration of the muscle (i.e., myosteatosis)—is as important as muscle quantity in cardiometabolic health. However, muscle quality has been less explored compared with muscle mass. Moreover, the standard definition of myosteatosis and its assessment methods have not been established yet. Recently, some techniques using single axial computed tomography (CT) images have been introduced and utilized in many studies, as the mass and quality of abdominal muscles could be measured opportunistically on abdominal CT scans obtained during routine clinical care. Yet, the mechanisms by which myosteatosis affect metabolic and cardiovascular health remain largely unknown. In this review, we explore the recent advances in the assessment of myosteatosis and its changes associated with aging. We also review the recent literature on the clinical implication of myosteatosis by focusing on metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Finally, we discuss the challenges and unanswered questions that need addressing to set myosteatosis as a therapeutic target for the prevention or treatment of cardiometabolic diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A CT-based Deep Learning Model for Predicting Subsequent Fracture Risk in Patients with Hip Fracture
Yisak Kim, Young-Gon Kim, Jung-Wee Park, Byung Woo Kim, Youmin Shin, Sung Hye Kong, Jung Hee Kim, Young-Kyun Lee, Sang Wan Kim, Chan Soo Shin
Radiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Myosteatosis is associated with poor survival after kidney transplantation: a large retrospective cohort validation
Jie Chen, Yue Li, Chengjie Li, Turun Song
Abdominal Radiology.2024; 49(4): 1210. CrossRef - Fatty infiltration of gastrocnemius–soleus muscle complex: Considerations for myosteatosis rehabilitation
Catherine Hatzantonis, Lalith Satkunam, Karyne N. Rabey, Jennifer C. Hocking, Anne M. R. Agur
Journal of Anatomy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Muscle attenuation, not skeletal muscle index, is an independent prognostic factor for survival in gastric cancer patients with overweight and obesity
Cheng-Le Zhuang, Hao-Fan Wu, Hao-Jie Jiang, Feng-Min Zhang, Han-Ping Shi, Zhen Yu, Xian Shen, Xiao-Lei Chen, Su-Lin Wang
Nutrition.2024; 122: 112391. CrossRef - Myosteatosis is associated with coronary artery calcification in patients with type 2 diabetes
Fu-Peng Liu, Mu-Jie Guo, Qing Yang, Yan-Ying Li, Yan-Gang Wang, Mei Zhang
World Journal of Diabetes.2024; 15(3): 429. CrossRef - Unlocking liver health: Can tackling myosteatosis spark remission in metabolic dysfunction‐associated steatotic liver disease?
Guillaume Henin, Audrey Loumaye, Louise Deldicque, Isabelle A. Leclercq, Nicolas Lanthier
Liver International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of serum gamma-glutamyl transferase with myosteatosis assessed by muscle quality mapping using abdominal computed tomography
Han Na Jung, Yun Kyung Cho, Hwi Seung Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Clinical Imaging.2023; 93: 4. CrossRef - Increased visceral fat area to skeletal muscle mass ratio is positively associated with the risk of cardiometabolic diseases in a Chinese natural population: A cross‐sectional study
Shi Zhang, Yaping Huang, Jing Li, Xincheng Wang, Xiaohe Wang, Minying Zhang, Yanju Zhang, Meiyang Du, Jingna Lin, Chunjun Li
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between hypertension and myosteatosis evaluated by abdominal computed tomography
Han Na Jung, Yun Kyung Cho, Hwi Seung Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Woo Je Lee, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Hypertension Research.2023; 46(4): 845. CrossRef - Epidemiological, mechanistic, and practical bases for assessment of cardiorespiratory fitness and muscle status in adults in healthcare settings
Jaime A. Gallo-Villegas, Juan C. Calderón
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2023; 123(5): 945. CrossRef - Muscle fat infiltration in chronic kidney disease: a marker related to muscle quality, muscle strength and sarcopenia
Carla Maria Avesani, Aline Miroski de Abreu, Heitor S. Ribeiro, Torkel B. Brismar, Peter Stenvinkel, Alice Sabatino, Bengt Lindholm
Journal of Nephrology.2023; 36(3): 895. CrossRef - IDF2022-1139 Association Between Dyslipidemia And Myosteatosis Using Visual Muscular Quality Map In Computed Tomography
H.S. Kim, H.N. Jung, Y.K. Cho, E.H. Kim, M.J. Lee, W.J. Lee, J.Y. Park, H.K. Kim, C.H. Jung
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 197: 110467. CrossRef - The role of skeletal muscle mass on cardiovascular disease risk: an emerging role on modulating lipid profile
Evangelia Damigou, Matina Kouvari, Demosthenes Panagiotakos
Current Opinion in Cardiology.2023; 38(4): 352. CrossRef - Reference values for low muscle mass and myosteatosis using tomographic muscle measurements in living kidney donors
Lisa B. Westenberg, Marcel Zorgdrager, Tim D. A. Swaab, Marco van Londen, Stephan J. L. Bakker, Henri G. D. Leuvenink, Alain R. Viddeleer, Robert A. Pol
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between sarcopenic obesity and poor muscle quality based on muscle quality map and abdominal computed tomography
Yun Kyung Cho, Han Na Jung, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Joong‐Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee, Hong‐Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Obesity.2023; 31(6): 1547. CrossRef - Increase in skeletal muscular adiposity and cognitive decline in a biracial cohort of older men and women
Caterina Rosano, Anne Newman, Adam Santanasto, Xiaonan Zhu, Bret Goodpaster, Iva Miljkovic
Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.2023; 71(9): 2759. CrossRef - Evaluation of Paraspinal Muscle Degeneration on Pain Relief after Percutaneous Epidural Adhesiolysis in Patients with Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Disease
Misun Kang, Shin Hyung Kim, Minju Jo, Hyun Eom Jung, Jungbin Bae, Hee Jung Kim
Medicina.2023; 59(6): 1118. CrossRef - Sarcopenic obesity and its relation with muscle quality and mortality in patients on chronic hemodialysis
Alice Sabatino, Carla Maria Avesani, Giuseppe Regolisti, Marianna Adinolfi, Giuseppe Benigno, Marco Delsante, Enrico Fiaccadori, Ilaria Gandolfini
Clinical Nutrition.2023; 42(8): 1359. CrossRef - Association between computed tomography‐assessed sarcopenia and mortality in patients with anti‐neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody‐associated vasculitis
Sung Soo Ahn, Yong‐Beom Park, Sang‐Won Lee
International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases.2023; 26(9): 1704. CrossRef - Association Between Insulin Resistance and Myosteatosis Measured by Abdominal Computed Tomography
Myung Jin Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Han Na Jung, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Chang Hee Jung, Joong-Yeol Park, Hong-Kyu Kim, Woo Je Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(12): 3100. CrossRef - Association of Visceral Fat Obesity, Sarcopenia, and Myosteatosis with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease without Obesity
Hong-Kyu Kim, Sung-Jin Bae, Min Jung Lee, Eun Hee Kim, Hana Park, Hwi Seung Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee, Jaewon Choe
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 987. CrossRef - Different computed tomography parameters for defining myosteatosis in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
Wenyi Zhang, Jing Tang, Huiyu Tang, Lingling Xie, Jing Wang, Jinhui Wu, Ming Yang
Clinical Nutrition.2023; 42(12): 2414. CrossRef - All you need to know about sarcopenia: a short guide for an internal medicine physician in questions and answers
G. R. Bikbavova, M. A. Livzan, D. V. Tikhonravova
Bulletin of Siberian Medicine.2023; 22(3): 88. CrossRef - Muscle Fat Content Is Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis in Chinese Adults
W. Guo, X. Zhao, D. Cheng, X. Liang, M. Miao, X. Li, J. Lu, N. Xu, Shuang Hu, Qun Zhang
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2023; 27(11): 960. CrossRef - Body Composition Evaluation and Clinical Markers of Cardiometabolic Risk in Patients with Phenylketonuria
Luis M. Luengo-Pérez, Mercedes Fernández-Bueso, Ana Ambrojo, Marta Guijarro, Ana Cristina Ferreira, Luís Pereira-da-Silva, André Moreira-Rosário, Ana Faria, Conceição Calhau, Anne Daly, Anita MacDonald, Júlio César Rocha
Nutrients.2023; 15(24): 5133. CrossRef - Assessment of Muscle Quantity, Quality and Function
Bo Kyung Koo
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2022; 31(1): 9. CrossRef - Influence of cross‐sectional area and fat infiltration of paraspinal muscles on analgesic efficacy of epidural steroid injection in elderly patients
Hee Jung Kim, Miribi Rho, Kyung Bong Yoon, Minju Jo, Dong Woo Lee, Shin Hyung Kim
Pain Practice.2022; 22(7): 621. CrossRef - Sarcopenia, Obesity, Sarcopenic Obesity and Risk of Poor Nutritional Status in Polish Community-Dwelling Older People Aged 60 Years and Over
Marika Murawiak, Roma Krzymińska-Siemaszko, Aleksandra Kaluźniak-Szymanowska, Marta Lewandowicz, Sławomir Tobis, Katarzyna Wieczorowska-Tobis, Ewa Deskur-Śmielecka
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2889. CrossRef - Metabolic mechanisms for and treatment of NAFLD or NASH occurring after liver transplantation
Amedeo Lonardo, Alessandro Mantovani, Salvatore Petta, Amedeo Carraro, Christopher D. Byrne, Giovanni Targher
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2022; 18(10): 638. CrossRef
- A CT-based Deep Learning Model for Predicting Subsequent Fracture Risk in Patients with Hip Fracture

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Normal Weight and Obesity
- Norbert Stefan
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):487-493. Published online August 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.301
- 9,061 View
- 437 Download
- 31 Web of Science
- 30 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
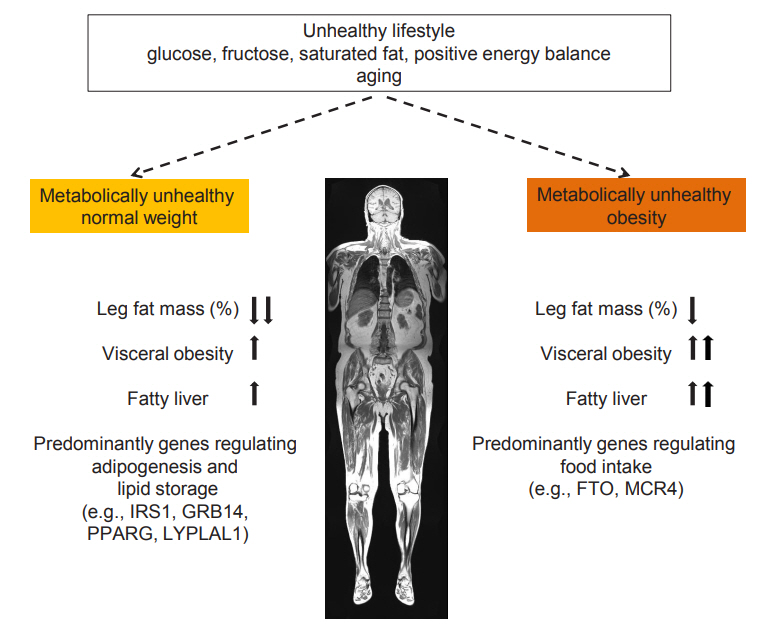
ePub - Increased fat mass is an established risk factor for the cardiometabolic diseases type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (CVD) and is associated with increased risk of all-cause and CVD mortality. However, also very low fat mass associates with such an increased risk. Whether impaired metabolic health, characterized by hypertension, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and subclinical inflammation, may explain part of the elevated risk of cardiometabolic diseases that is found in many subjects with very low fat mass, as it does in many obese subjects, is unknown. An important pathomechanism of impaired metabolic health is disproportionate fat distribution. In this article the risk of cardiometabolic diseases and mortality in subjects with metabolically healthy and unhealthy normal weight and obesity is summarized. Furthermore, the change of metabolic health during a longer period of follow-up and its impact on cardiometabolic diseases is being discussed. Finally, the implementation of the concept of metabolic health in daily clinical practice is being highlighted.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Phenotyping obesity: A focus on metabolically healthy obesity and metabolically unhealthy normal weight
Rachel Agius, Nikolai P. Pace, Stephen Fava
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing verum and sham acupoint catgut embedding for adults with obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Jin-huan Yue, Xiao-ling Li, Yu-ying Zhang, Guan-hu Yang, Jeffrey Zhong-xue Mah, Ang Li, Wei-wei Zhao, Yu-lin Wang, Qin-hong Zhang, Jia-qi Huang
Medicine.2024; 103(4): e36653. CrossRef - Association between Weight Change and Incidence of Dyslipidemia in Young Adults: A Retrospective Cohort Study of Korean Male Soldiers
Joon-Young Yoon, Won Ju Park, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Cheol-Kyu Park, Wonsuk Choi
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2024; 33(1): 36. CrossRef - Metabolically Healthy Obesity: An Eye-opener
Purushothaman Padmanabhan, Nagendram Dinakaran, Somnath Verma, S Keerthana
Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Endoscopy Practice.2023; 3(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of metabolic health and obesity on all-cause death and CVD incidence in Korean adults: a retrospective cohort study
Ye-Seul Kim, Sang-Jun Shin, Yonghwan Kim, Joungyoun Kim, Hee-Taik Kang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Coffee and metabolic phenotypes: A cross-sectional analysis of the Japan multi-institutional collaborative cohort (J-MICC) study
Takeshi Watanabe, Kokichi Arisawa, Tien Van Nguyen, Masashi Ishizu, Sakurako Katsuura-Kamano, Asahi Hishida, Takashi Tamura, Yasufumi Kato, Rieko Okada, Rie Ibusuki, Chihaya Koriyama, Sadao Suzuki, Takahiro Otani, Teruhide Koyama, Satomi Tomida, Kiyonori
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2023; 33(3): 620. CrossRef - Metabolically unhealthy phenotype in adults with normal weight: Is cardiometabolic health worse off when compared to adults with obesity?
Myong-Won Seo, Joon Young Kim
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2023; 17(2): 116. CrossRef - Association between metabolic obesity phenotypes and multiple myeloma hospitalization burden: A national retrospective study
Yue Zhang, Xiude Fan, Chunhui Zhao, Zinuo Yuan, Yiping Cheng, Yafei Wu, Junming Han, Zhongshang Yuan, Yuanfei Zhao, Keke Lu
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolically healthy obesity: Misleading phrase or healthy phenotype?
Cem Tanriover, Sidar Copur, Abduzhappar Gaipov, Batu Ozlusen, Rustu E. Akcan, Masanari Kuwabara, Mads Hornum, Daniel H. Van Raalte, Mehmet Kanbay
European Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 111: 5. CrossRef - Prevalence of combined metabolic health and weight status by various diagnosis criteria and association with cardiometabolic disease in Korean adults
Myong-Won Seo, Jung-Min Lee, Hyun Chul Jung
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2023; 17(2): 137. CrossRef - Precision medicine in complex diseases—Molecular subgrouping for improved prediction and treatment stratification
Åsa Johansson, Ole A. Andreassen, Søren Brunak, Paul W. Franks, Harald Hedman, Ruth J. F. Loos, Benjamin Meder, Erik Melén, Craig E. Wheelock, Bo Jacobsson
Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 294(4): 378. CrossRef - Lipid droplet biogenesis and functions in health and disease
Armella Zadoorian, Ximing Du, Hongyuan Yang
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2023; 19(8): 443. CrossRef - Molecular Mechanisms for the Vicious Cycle between Insulin Resistance and the Inflammatory Response in Obesity
Dariusz Szukiewicz
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(12): 9818. CrossRef - Insulin Resistance Is the Main Characteristic of Metabolically Unhealthy Obesity (MUO) Associated with NASH in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery
Sophia M. Schmitz, Sebastian Storms, Alexander Koch, Christine Stier, Andreas Kroh, Karl P. Rheinwalt, Sandra Schipper, Karim Hamesch, Tom F. Ulmer, Ulf P. Neumann, Patrick H. Alizai
Biomedicines.2023; 11(6): 1595. CrossRef - Hyperleptinemia as a marker of various phenotypes of obesity and overweight in women with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus
L. V. Kondrateva, Yu. N. Gorbunova, T. A. Panafidina, T. V. Popkova
Rheumatology Science and Practice.2023; 61(3): 339. CrossRef - Predictable Representation of Metabolic Synthesis Pathways of Vitamins and Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Obese Adults
A. V. Shestopalov, L. A. Ganenko, I. M. Kolesnikova, T. V. Grigoryeva, I. Yu. Vasilyev, Yu. L. Naboka, N. I. Volkova, O. V. Borisenko, S. A. Roumiantsev
Journal of Evolutionary Biochemistry and Physiology.2023; 59(5): 1510. CrossRef - Metabolically unhealthy individuals, either with obesity or not, have a higher risk of critical coronavirus disease 2019 outcomes than metabolically healthy individuals without obesity
Nam Hoon Kim, Kyeong Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim
Metabolism.2022; 128: 154894. CrossRef - Associations between obesity, metabolic syndrome, and endometrial cancer risk in East Asian women
Boyoung Park
Journal of Gynecologic Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin and cancer: a tangled web
Brooks P. Leitner, Stephan Siebel, Ngozi D. Akingbesote, Xinyi Zhang, Rachel J. Perry
Biochemical Journal.2022; 479(5): 583. CrossRef - Relationships Between Metabolic Body Composition Status and Rapid Kidney Function Decline in a Community-Based Population: A Prospective Observational Study
Shao-Chi Chu, Po-Hsi Wang, Kuan-Ying Lu, Chia-Chun Ko, Yun-Hsuan She, Chin-Chan Lee, I-Wen Wu, Chiao-Yin Sun, Heng-Jung Hsu, Heng-Chih Pan
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dissecting the clinical relevance of polygenic risk score for obesity—a cross-sectional, longitudinal analysis
Eun Kyung Choe, Manu Shivakumar, Seung Mi Lee, Anurag Verma, Dokyoon Kim
International Journal of Obesity.2022; 46(9): 1686. CrossRef - Metabolic and Obesity Phenotype Trajectories in Taiwanese Medical Personnel
Hsin-Yun Chang, Jer-Hao Chang, Yin-Fan Chang, Chih-Hsing Wu, Yi-Ching Yang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(13): 8184. CrossRef - Sex Differences in Cardiovascular Impact of Early Metabolic Impairment: Interplay between Dysbiosis and Adipose Inflammation
Haneen S. Dwaib, Ibrahim AlZaim, Ghina Ajouz, Ali H. Eid, Ahmed El-Yazbi
Molecular Pharmacology.2022; 102(1): 60. CrossRef - Reduced leukocyte mitochondrial copy number in metabolic syndrome and metabolically healthy obesity
Rachel Agius, Nikolai Paul Pace, Stephen Fava
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in BMI and physical activity from youth to adulthood distinguish normal-weight, metabolically obese adults from those who remain healthy
A. Viitasalo, K. Pahkala, T. Lehtimäki, JSA. Viikari, TH. Tammelin, O. Raitakari, TO. Kilpeläinen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathogenesis, Murine Models, and Clinical Implications of Metabolically Healthy Obesity
Yun Kyung Cho, Yoo La Lee, Chang Hee Jung
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(17): 9614. CrossRef - Metabolically healthy obesity: it is time to consider its dynamic changes
Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(4): 123. CrossRef - Obesity as a Risk Factor for Breast Cancer—The Role of miRNA
Karolina Hanusek, Jakub Karczmarski, Anna Litwiniuk, Katarzyna Urbańska, Filip Ambrozkiewicz, Andrzej Kwiatkowski, Lidia Martyńska, Anita Domańska, Wojciech Bik, Agnieszka Paziewska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(24): 15683. CrossRef - Propensity Score–Matching Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG) vs. Gastric Bypass (RYGB) in Patients ≥ 60 Years
Omar Thaher, Stefanie Wolf, Martin Hukauf, Christine Stroh
Obesity Surgery.2021; 31(6): 2682. CrossRef - Associations between obesity, metabolic health, and the risk of breast cancer in East Asian women
Boyoung Park, Soyeoun Kim, Hayoung Kim, Chihwan Cha, Min Sung Chung
British Journal of Cancer.2021; 125(12): 1718. CrossRef
- Phenotyping obesity: A focus on metabolically healthy obesity and metabolically unhealthy normal weight

- Clinical Study
- Metabolic Health Is More Important than Obesity in the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A 4-Year Retrospective Study
- Min-Kyung Lee, Eun-Jung Rhee, Min Chul Kim, Byung Sub Moon, Jeong In Lee, Young Seok Song, Eun Na Han, Hyo Sun Lee, Yoonjeong Son, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(4):522-530. Published online December 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.4.522
- 4,457 View
- 61 Download
- 23 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The aim of this study is to compare the risk for future development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) according to different status of metabolic health and obesity.
Methods A total of 3,045 subjects without NAFLD and diabetes at baseline were followed for 4 years. Subjects were categorized into four groups according to the following baseline metabolic health and obesity statuses: metabolically healthy, non-obese (MHNO); metabolically healthy, obese (MHO); metabolically unhealthy, non-obese (MUHNO); and metabolically unhealthy, obese (MUHO). Being metabolically healthy was defined as having fewer than two of the following five components: high blood pressure, high fasting blood glucose, high triglyceride, low high density lipoprotein cholesterol, and being in the highest decile of the homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance index. Obesity was defined as a body mass index >25 kg/m2. The presence of NAFLD was assessed by ultrasonography.
Results The proportions of subjects included in the MHNO, MHO, MUHNO, and MUHO groups were 71.4%, 9.8%, 13.0%, and 5.8%, respectively. The proportions of subjects who developed NAFLD were 10.5%, 31.4%, 23.2%, and 42% in the MHNO, MHO, MUHNO, and MUHO groups, respectively. The risk for developing NAFLD was highest in subjects who were metabolically unhealthy both at baseline and after 4 years compared with subjects who were consistently metabolically healthy during the follow-up period (odds ratio, 2.862). Using the MHNO group as reference, the odds ratios for the MHO, MUHNO, and MUHO groups were 1.731, 1.877, and 2.501, respectively.
Conclusion The risk for NAFLD was lower in MHO subjects than in MUNO subjects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Increased metabolic variability in Korean patients with new onset bipolar disorder: a nationwide cohort study
Ji Hyun Baek, Kyungdo Han, Hyewon Kim, Kyojin Yang, Hong Jin Jeon
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Increased risk of incident atrial fibrillation in young adults with mental disorders: A nationwide population-based study
Hyun Jin Ahn, So-Ryoung Lee, Eue-Keun Choi, Nan Young Bae, Hyo-Jeong Ahn, Soonil Kwon, Seung-Woo Lee, Kyung-Do Han, Seil Oh, Gregory Y.H. Lip
Heart Rhythm.2023; 20(3): 365. CrossRef - Association between Sarcopenic Obesity Status and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Fibrosis
Wolhwa Song, Sung Hwan Yoo, Jinsun Jang, Su Jung Baik, Byoung Kwon Lee, Hyun Woong Lee, Jong Suk Park
Gut and Liver.2023; 17(1): 130. CrossRef - The impact of metabolic health on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). A single center experience
Anna Boulouta, Ioanna Aggeletopoulou, Stavros Kanaloupitis, Efthymios P Tsounis, Vasileios Issaris, Konstantinos Papantoniou, Anastasios Apostolos, Paraskevas Tsaplaris, Ploutarchos Pastras, Christos Sotiropoulos, Aggeliki Tsintoni, Georgia Diamantopoulou
Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology.2022; 46(5): 101896. CrossRef - Lean non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (Lean-NAFLD) and the development of metabolic syndrome: a retrospective study
Wenting Wang, Jianping Ren, Wenzhao Zhou, Jinyu Huang, Guomin Wu, Fenfang Yang, Shuang Yuan, Juan Fang, Jing Liu, Yao Jin, Haiyang Qi, Yuyang Miao, Yanna Le, Cenhong Ge, Xiantao Qiu, JinJing Wang, Ping Huang, Zixin Liu, Sheng Wang
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolically healthy obesity and risk of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease severity independent of visceral fat
Tsung‐Po Chen, Wen‐Yuan Lin, Chien‐Hsieh Chiang, Ting‐Hsin Shen, Kuo‐Chin Huang, Kuen‐Cheh Yang
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 36(10): 2903. CrossRef - Increased metabolic variability is associated with newly diagnosed depression: A nationwide cohort study
Ji Hyun Baek, Dong Wook Shin, Maurizio Fava, David Mischoulon, Hyewon Kim, Mi Jin Park, Eun Ji Kim, Kyung-Do Han, Hong Jin Jeon
Journal of Affective Disorders.2021; 294: 786. CrossRef - The expression signatures in liver and adipose tissue from obese Göttingen Minipigs reveal a predisposition for healthy fat accumulation
Susanna Cirera, Emirhan Taşöz, Mette Juul Jacobsen, Camilla Schumacher-Petersen, Berit Østergaard Christoffersen, Rikke Kaae Kirk, Trine Pagh Ludvigsen, Henning Hvid, Henrik Duelund Pedersen, Lisbeth Høier Olsen, Merete Fredholm
Nutrition & Diabetes.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of obesity and metabolic health status in the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A United Kingdom population-based cohort study using the health improvement network (THIN)
A. Vusirikala, T. Thomas, N. Bhala, A. A. Tahrani, G. N. Thomas, K. Nirantharakumar
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in non‐obese populations: Meta‐analytic assessment of its prevalence, genetic, metabolic, and histological profiles
Zi Yuan Zou, Vincent Wai‐Sun Wong, Jian Gao Fan
Journal of Digestive Diseases.2020; 21(7): 372. CrossRef - Ultrasound-Diagnosed Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Independently Predicts a Higher Risk of Developing Diabetes Mellitus in Nonoverweight Individuals
Liang Wang
Academic Radiology.2019; 26(7): 863. CrossRef - Blood Pressure and Development of Cardiovascular Disease in Koreans With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Eun Sil Koh, Eun Sook Kim, Min-Kyung Lee, Ga Eun Nam, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Hypertension.2019; 73(2): 319. CrossRef - Understanding the association of polycystic ovary syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Nicolás Salva-Pastor, Norberto C. Chávez-Tapia, Misael Uribe, Natalia Nuño-Lámbarri
The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.2019; 194: 105445. CrossRef - Weight change and mortality and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with new-onset diabetes mellitus: a nationwide cohort study
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Eun Sil Koh, Eun Sook Kim, Min-Kyung Lee, Ga Eun Nam, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Longitudinal analysis of risk of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease in adulthood
Daniel J. Cuthbertson, Emily Brown, Juha Koskinen, Costan G. Magnussen, Nina Hutri‐Kähönen, Matthew Sabin, Päivi Tossavainen, Eero Jokinen, Tomi Laitinen, Jorma Viikari, Olli T. Raitakari, Markus Juonala
Liver International.2019; 39(6): 1147. CrossRef - Associations of Variability in Blood Pressure, Glucose and Cholesterol Concentrations, and Body Mass Index With Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes in the General Population
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Yong-Moon Park, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Gunseog Kang, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hwan Lee
Circulation.2018; 138(23): 2627. CrossRef - The effects of metabolic status on non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease‐related outcomes, beyond the presence of obesity
Javier Ampuero, Rocío Aller, Rocío Gallego‐Durán, Jesus M. Banales, Javier Crespo, Carmelo García‐Monzón, María Jesús Pareja, Eduardo Vilar‐Gómez, Juan Caballería, Desamparados Escudero‐García, Judith Gomez‐Camarero, José Luis Calleja, Mercedes Latorre, A
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2018; 48(11-12): 1260. CrossRef - Dissecting the relationship between obesity and hyperinsulinemia: Role of insulin secretion and insulin clearance
Mee Kyoung Kim, Gerald M. Reaven, Sun H. Kim
Obesity.2017; 25(2): 378. CrossRef - The Effects of Exercise on Abdominal Fat and Liver Enzymes in Pediatric Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Katherine González-Ruiz, Robinson Ramírez-Vélez, Jorge Enrique Correa-Bautista, Mark D. Peterson, Antonio García-Hermoso
Childhood Obesity.2017; 13(4): 272. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Based on Analyses from the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Eun-Jung Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2017; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Emerging Burden in Cardiometabolic and Renal Diseases
Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(6): 430. CrossRef - Predictive Value of Triglyceride Glucose Index for the Risk of Incident Diabetes: A 4-Year Retrospective Longitudinal Study
Da Young Lee, Eun Seo Lee, Ji Hyun Kim, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee, Fernando Guerrero-Romero
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(9): e0163465. CrossRef - Lean, but not healthy
Cherlyn Ding, Zhiling Chan, Faidon Magkos
Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition & Metabolic Care.2016; 19(6): 408. CrossRef
- Increased metabolic variability in Korean patients with new onset bipolar disorder: a nationwide cohort study

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Comparison of Serum Adipocytokine Levels according to Metabolic Health and Obesity Status
- Tae Hoon Lee, Won Seon Jeon, Ki Joong Han, Shin Yeoung Lee, Nam Hee Kim, Hyun Beom Chae, Choel Min Jang, Kyung Mo Yoo, Hae Jung Park, Min Kyung Lee, Se Eun Park, Hyung Geun Oh, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(2):185-194. Published online June 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.2.185
- 4,622 View
- 34 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Metabolic health is an emerging concept that is highly correlated with various metabolic complications, and adipocytokines have been causally linked to a wide range of metabolic diseases. Thus, this study compared serum adipocytokine levels according to metabolic health and obesity status.
Methods Four hundred and fifty-six nondiabetic subjects (mean age, 40.5 years) were categorized into four groups according to metabolic health and obesity status: metabolically healthy nonobese (MHNO), metabolically healthy obese (MHO), metabolically unhealthy nonobese (MUHNO), and metabolically unhealthy obese (MUHO). Being metabolically healthy was defined as the presence of fewer than two of the following five metabolic abnormalities: high blood pressure, high fasting blood glucose, high triglyceride, low high density lipoprotein cholesterol, and being in the highest decile of the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance index. Obesity status was assessed using body mass index (BMI), with obesity defined as a BMI higher than 25 kg/m2. Levels of serum interleukin-6 (IL-6), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), and adipocyte fatty acid binding protein (A-FABP) were also evaluated.
Results Of the 456 subjects, 247 (54.2%) were in the MHNO group, 66 (14.5%) were in the MHO group, 66 (14.5%) were in the MUHNO group, and 77 (16.9%) were in the MUHO group. There were no significant differences in IL-6 or MCP-1 levels among the groups, but levels of TNF-α and A-FABP were significantly higher in the MUHNO group compared to the MHNO group.
Conclusion High TNF-α and A-FABP levels are significantly associated with metabolically unhealthiness in nonobese Korean individuals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Differences in the levels of inflammatory markers between metabolically healthy obese and other obesity phenotypes in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Zhouli Su, Ljupcho Efremov, Rafael Mikolajczyk
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024; 34(2): 251. CrossRef - Relationship between the thrombospondin-1/Toll-like receptor 4 (TSP1/TLR4) pathway and vitamin D levels in obese and normal weight subjects with different metabolic phenotypes
Eman Y. Khairy, Azza Saad
The Journal of Physiological Sciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Pattern of Adiponectin, Osteocalcin, Irisin, FGF-21, and MCP-1 According to the Body Size Phenotype: Could They Be Markers of Metabolic Health in Mexican-Mestizo Middle-Aged Women?
Lourdes Balcázar-Hernandez, Lourdes Basurto, Leticia Manuel-Apolinar, Sara Vega-García, Norma Basurto-Acevedo, Carlos Martínez-Murillo, Rosalinda Sánchez-Arenas
Metabolites.2021; 11(11): 771. CrossRef - Exploring Therapeutic Targets to Reverse or Prevent the Transition from Metabolically Healthy to Unhealthy Obesity
Tenzin D. Dagpo, Christopher J. Nolan, Viviane Delghingaro-Augusto
Cells.2020; 9(7): 1596. CrossRef - Poor Vitamin D Status in Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients and Its Correlation with Leptin and TNF-α
Qiuzhen WANG, Aiguo MA, Tianlin GAO, Yufeng LIU, Lisheng REN, Lei HAN, Boyang WEI, Qian LIU, Chunjiang DONG, Yuze MU, Duo LI, Frans J KOK, Evert G SCHOUTEN
Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology.2019; 65(5): 390. CrossRef - Metabolic Health—The Role of Adipo-Myokines
Christine Graf, Nina Ferrari
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(24): 6159. CrossRef - Does the Metabolically Healthy Obese Phenotype Protect Adults with Class III Obesity from Biochemical Alterations Related to Bone Metabolism?
Ligiane Marques Loureiro, Suzane Lessa, Rodrigo Mendes, Sílvia Pereira, Carlos José Saboya, Andrea Ramalho
Nutrients.2019; 11(9): 2125. CrossRef - Being Metabolically Healthy, the Most Responsible Factor for Vascular Health
Eun-Jung Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(1): 19. CrossRef - Association between Serum Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Concentration and Obesity-related Factors in Health Screen Examinees
Ji Yeon Lee, Byoung Kuk Jang, Min Kyung Song, Hye Soon Kim, Mi-Kyung Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2017; 26(3): 188. CrossRef - Kofaktoren und Komorbiditäten bei Necrobiosis lipoidica – Analyse der deutschen DRG‐Daten von 2012
Finja Jockenhöfer, Knut Kröger, Joachim Klode, Regina Renner, Cornelia Erfurt‐Berge, Joachim Dissemond
JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft.2016; 14(3): 277. CrossRef - The relationship between serum fatty-acid binding protein 4 level and lung function in Korean subjects with normal ventilatory function
Hye-Jeong Park, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Seong Yong Lim, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
BMC Pulmonary Medicine.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Cofactors and comorbidities of necrobiosis lipoidica: analysis of the German DRG data from 2012
Finja Jockenhöfer, Knut Kröger, Joachim Klode, Regina Renner, Cornelia Erfurt‐Berge, Joachim Dissemond
JDDG: Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft.2016; 14(3): 277. CrossRef - Response: Comparison of Serum Adipocytokine Levels according to Metabolic Health and Obesity Status (Endocrinol Metab2015;30:185-94, Tae Hoon Lee et al.)
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(3): 416. CrossRef - Letter: Comparison of Serum Adipocytokine Levels according to Metabolic Health and Obesity Status (Endocrinol Metab2015;30:185-94, Tae Hoon Lee et al.)
Mikyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(3): 414. CrossRef - Adipokine Profiles and Metabolic Health
Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(2): 175. CrossRef
- Differences in the levels of inflammatory markers between metabolically healthy obese and other obesity phenotypes in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



