Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
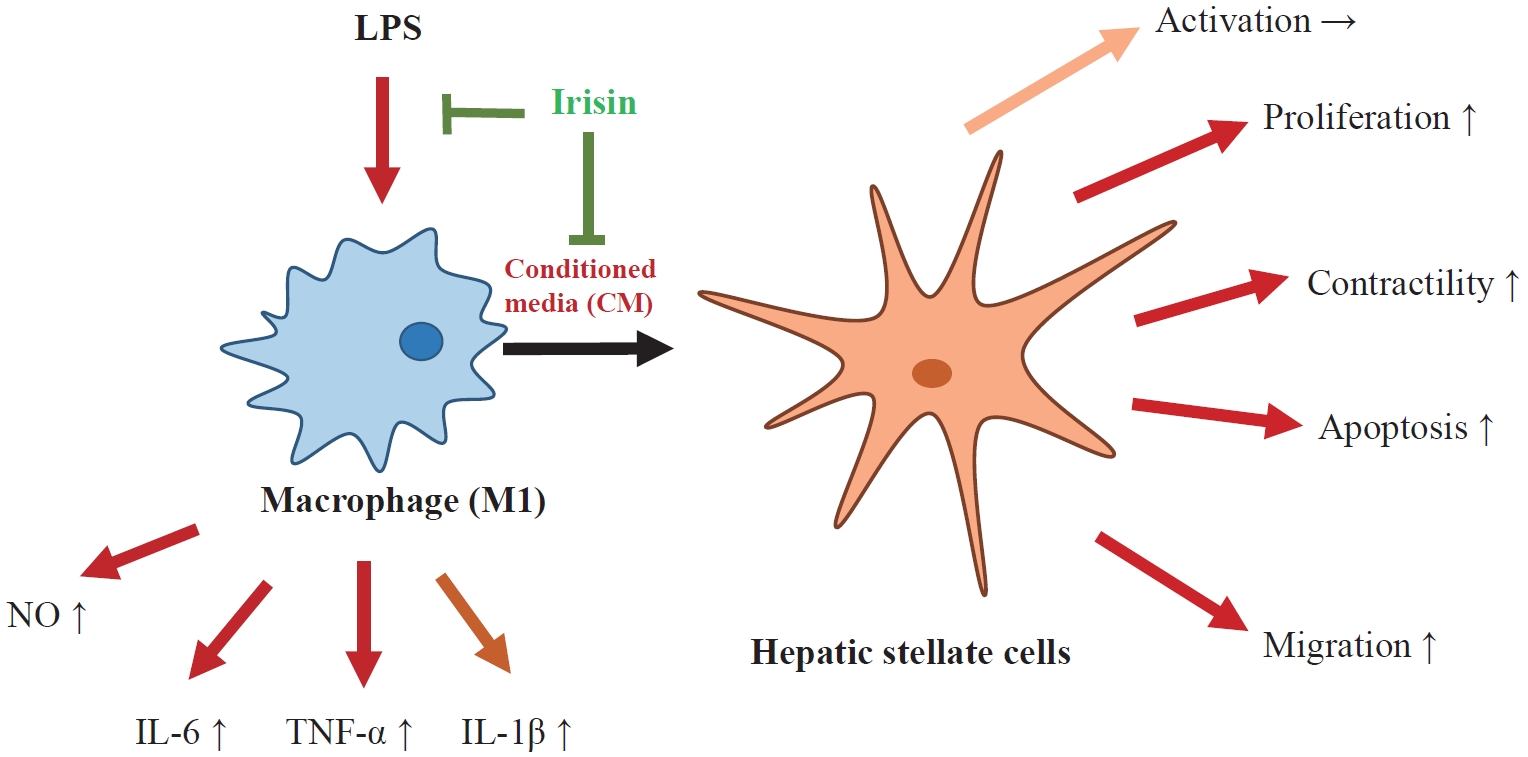
- The Effects of Irisin on the Interaction between Hepatic Stellate Cell and Macrophage in Liver Fibrosis
- Dinh Vinh Do, So Young Park, Giang Thi Nguyen, Dae Hee Choi, Eun-Hee Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(4):620-629. Published online July 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1412
- 4,523 View
- 197 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are the central players interacting with multiple cell types in liver fibrosis. The crosstalk between HSCs and macrophages has recently become clearer. Irisin, an exercise-responsive myokine, was known to have a potentially protective role in liver and renal fibrosis, especially in connection with stellate cells. This study investigated the effects of irisin on the interaction between HSCs and macrophages.
Methods
Tamm-Horsfall protein-1 (THP-1) human monocytes were differentiated into macrophages, polarized into the inflammatory M1 phenotype with lipopolysaccharide. Lieming Xu-2 (LX-2) cells, human HSCs, were treated with conditioned media (CM) from M1 macrophages, with or without recombinant irisin. HSCs responses to CM from M1 macrophages were evaluated regarding activation, proliferation, wound healing, trans-well migration, contractility, and related signaling pathway.
Results
CM from M1 macrophages significantly promoted HSC proliferation, wound healing, transwell migration, and contractility, but not activation of HSCs. Irisin co-treatment attenuated these responses of HSCs to CM. However, CM and irisin treatment did not induce any changes in HSC activation. Further, irisin co-treatment alleviated CM-induced increase of phopho-protein kinase B (pAKT), matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1).
Conclusion
These findings suggested that irisin may play a protective role in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis, especially when working in the crosstalk between HSCs and macrophages. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Matrix metalloproteinases induce extracellular matrix degradation through various pathways to alleviate hepatic fibrosis
Liang Shan, Fengling Wang, Dandan Zhai, Xiangyun Meng, Jianjun Liu, Xiongwen Lv
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 161: 114472. CrossRef - Potential role of irisin in digestive system diseases
Yueming Zhang, Linxian Zhao, Huan Gao, Jinghui Zhai, Yanqing Song
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 166: 115347. CrossRef - The effect of sarcopenia and serum myokines on prognosis and survival in cirrhotic patients: a multicenter cross-sectional study
Salih Boga, Abdullah Emre Yildirim, Enver Ucbilek, Ali Riza Koksal, Sevil Tokdemir Sisman, Ibrahim Durak, Ilker Sen, Beril Dogu, Erdinc Serin, Ayse Bolat Ucbilek, Makbule Ozge Yildirim, Sukru Mehmet Erturk, Huseyin Alkim, Canan Alkim
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2022; 34(12): 1261. CrossRef
- Matrix metalloproteinases induce extracellular matrix degradation through various pathways to alleviate hepatic fibrosis

- Endocrine Research
- Irisin Regulates the Functions of Hepatic Stellate Cells
- Hanh Nguyen Dong, So Young Park, Cong Thuc Le, Dae-Hee Choi, Eun-Hee Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):647-655. Published online September 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.658

- 6,481 View
- 180 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are known to play a fundamental role in the progression of liver fibrosis. Once HSCs are activated, they are involved in proliferation, migration, and contractility which are characteristics of liver fibrogenesis. Recent studies have shown that irisin, a myokine secreted during physical exercise, has a protective effect in various metabolic diseases, especially in renal fibrosis. However, whether irisin is involved in HSC activation and other processes associated with liver fibrosis has not yet been investigated. In this study, we reveal the role of irisin in HSC activation as well as in proliferation, migration, and contractile properties of HSCs in vitro.
Methods
LX-2 cells, immortalized human HSCs, were treated with transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1), a core regulator of HSC fibrosis, with or without irisin, and markers of the aforementioned processes were analyzed. Further, an inflammatory response was stimulated with TGF-β1 and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in combination with irisin and the expression of cytokines was measured.
Results
Recombinant irisin significantly suppressed the expression of TGF-β1-stimulated fibrosis markers including alpha-smooth muscle actin and collagen type 1 alpha 1 and prevented the TGF-β1-induced proliferation, migration, and contractility of LX-2 cells. Additionally, irisin ameliorated the production of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-1β induced by TGF-β1 and LPS treatments.
Conclusion
These findings suggested that irisin potently improved the progression of hepatic fibrosis by regulating HSC activation, proliferation, migration, contractility, and HSC-mediated production of inflammatory cytokine. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Potential role of irisin in digestive system diseases
Yueming Zhang, Linxian Zhao, Huan Gao, Jinghui Zhai, Yanqing Song
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 166: 115347. CrossRef - Potential role of irisin in lung diseases and advances in research
Hongna Dong, Xuejiao Lv, Peng Gao, Yuqiu Hao
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Stem bark of Fraxinus rhynchophylla ameliorates the severity of pancreatic fibrosis by regulating the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway
Ji-Won Choi, Joon Yeon Shin, Ziqi Zhou, Dong-Uk Kim, Bitna Kweon, Hyuncheol Oh, Youn-Chul Kim, Ho-Joon Song, Gi-Sang Bae, Sung-Joo Park
Journal of Investigative Medicine.2022; 70(5): 1285. CrossRef - Circadian rhythms and cancers: the intrinsic links and therapeutic potentials
Li Zhou, Zhe Zhang, Edouard Nice, Canhua Huang, Wei Zhang, Yong Tang
Journal of Hematology & Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Kinsenoside alleviates inflammation and fibrosis in experimental NASH mice by suppressing the NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway
Yan-fang Deng, Qian-qian Xu, Tian-qi Chen, Jia-xiong Ming, Ya-fen Wang, Li-na Mao, Jia-jun Zhou, Wei-guang Sun, Qun Zhou, Hong Ren, Yong-hui Zhang
Phytomedicine.2022; 104: 154241. CrossRef - The potential role of FNDC5/irisin in various liver diseases: awakening the sleeping beauties
Xiaoyu Wang, Lihong Mao, Chaoqun Li, Yangyang Hui, Zihan Yu, Mingyu Sun, Yifan Li, Gaoyue Guo, Wanting Yang, Binxin Cui, Xiaofei Fan, Chao Sun
Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Irisin on the Interaction between Hepatic Stellate Cell and Macrophage in Liver Fibrosis
Dinh Vinh Do, So Young Park, Giang Thi Nguyen, Dae Hee Choi, Eun-Hee Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 620. CrossRef - Hepatic Steatosis Contributes to the Development of Muscle Atrophy via Inter-Organ Crosstalk
Kenneth Pasmans, Michiel E. Adriaens, Peter Olinga, Ramon Langen, Sander S. Rensen, Frank G. Schaap, Steven W. M. Olde Damink, Florian Caiment, Luc J. C. van Loon, Ellen E. Blaak, Ruth C. R. Meex
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Physiopathology of Lifestyle Interventions in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
David Carneros, Guillermo López-Lluch, Matilde Bustos
Nutrients.2020; 12(11): 3472. CrossRef
- Potential role of irisin in digestive system diseases

- Clinical Study
- Association between Circulating Irisin and C-Reactive Protein Levels: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Elham Eslampour, Farzad Ebrahimzadeh, Amir Abbasnezhad, Mohammad Zeinali Khosroshahi, Razieh Choghakhori, Omid Asbaghi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(2):140-149. Published online June 24, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.2.140
- 4,481 View
- 53 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Although previous studies have demonstrated that irisin plays an anti-inflammatory role in the body, conflicting results have been reported regarding the correlation between serum levels of irisin and C-reactive protein (CRP). The present meta-analysis was conducted to further investigate the correlation between irisin and CRP levels.
Methods We systematically searched PubMed, the Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Embase, SCOPUS, and Ovid to retrieve studies assessing the correlation between irisin and CRP levels. Meta-analyses were performed using a random-effects model, and the
I 2 index was used to evaluate heterogeneity.Results Of the 428 studies that were initially found, 14 studies with 2,530 participants met the inclusion criteria for the meta-analysis. The pooled effect size was calculated as 0.052 (95% confidence interval, −0.047 to 0.152;
P =0.302). Subgroup analyses identified s ignificant, positive, but weak correlations between CRP and irisin levels in cohort studies, studies conducted among healthy participants, studies in which the male-to-female ratio was less than 1, in overweight or obese subjects, and in studies with a sample size of at least 100 participants.Conclusion The present meta-analysis found no overall significant correlation between irisin and CRP levels, although a significant positive correlation was found in overweight or obese subjects. Well-designed studies are needed to verify the results of the present meta-analysis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Zinc Supplementation in Individuals with Prediabetes and type 2 Diabetes: a GRADE-Assessed Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-analysis
Matin Nazari, Mahlagha Nikbaf-Shandiz, Fereshteh Pashayee-Khamene, Reza Bagheri, Kian Goudarzi, Navid Vahid Hosseinnia, Sina Dolatshahi, Hossein Salehi Omran, Niusha Amirani, Damoon Ashtary-larky, Omid Asbaghi, Matin Ghanavati
Biological Trace Element Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Irisin reduces inflammatory signaling pathways in inflammation-mediated metabolic syndrome
John J. Slate-Romano, Naohiro Yano, Ting C. Zhao
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2022; 552: 111676. CrossRef - Circulating Irisin Levels in Patients with Chronic Plaque Psoriasis
Francesca Ambrogio, Lorenzo Sanesi, Angela Oranger, Chiara Barlusconi, Manuela Dicarlo, Patrizia Pignataro, Roberta Zerlotin, Paolo Romita, Elvira Favoino, Gerardo Cazzato, Nicoletta Cassano, Gino Antonio Vena, Caterina Foti, Maria Grano
Biomolecules.2022; 12(8): 1096. CrossRef - Fibronectin type III domain-containing 5 in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases: a promising biomarker and therapeutic target
Xin Zhang, Can Hu, Hai-ming Wu, Zhen-guo Ma, Qi-zhu Tang
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.2021; 42(9): 1390. CrossRef - Progress and Challenges in the Biology of FNDC5 and Irisin
Steffen Maak, Frode Norheim, Christian A Drevon, Harold P Erickson
Endocrine Reviews.2021; 42(4): 436. CrossRef - L-arginine supplementation to mitigate cardiovascular effects of walking outside in the context of traffic-related air pollution in participants with elevated blood pressure: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Hongyu Li, Qisijing Liu, Zhiyong Zou, Qiao Chen, Wanzhou Wang, Andrea A. Baccarelli, Furong Deng, Xinbiao Guo, Shaowei Wu
Environment International.2021; 156: 106631. CrossRef - “Association between dietary inflammatory index (DII) and risk of irritable bowel syndrome: a case-control study”
Elham Eslampour, Koroush Ghanadi, Vahideh Aghamohammadi, Alireza Moayed Kazemi, Rasool Mohammadi, Farhad Vahid, Amir Abbasnezhad
Nutrition Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Roles and Mechanisms of Irisin in Attenuating Pathological Features of Osteoarthritis
Xiangfen Li, Xiaofang Zhu, Hongle Wu, Thomas E. Van Dyke, Xiaoyang Xu, Elise F. Morgan, Wenyu Fu, Chuanju Liu, Qisheng Tu, Dingming Huang, Jake Chen
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Irisin, interleukin-33 and interleukin-37 in patients with ischemic heart disease and obesity
Yuliia Kovalova, Nataliia Sukhonos, Valeriia Brek, Kateryna Smolianyk
Medicinski casopis.2021; 55(3): 87. CrossRef - Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid therapy due to pregnant intrahepatic cholestasis on chemerin and irisin levels
Krzysztof Dąbrowski, Rafał Kierach, Beniamin O. Grabarek, Dariusz Boroń, Michał Kukla
Dermatologic Therapy.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of royal jelly and tocotrienol‐rich fraction on impaired glycemic control and inflammation through irisin in obese rats
Pardis Irandoost, Naimeh Mesri Alamdari, Atoosa Saidpour, Farzad Shidfar, Neda Roshanravan, Mohammad Asghari Jafarabadi, Farnaz Farsi, Nazanin Asghari Hanjani, Mohammadreza Vafa
Journal of Food Biochemistry.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID-19: Could Irisin Become the Handyman Myokine of the 21st Century?
Alessia Catalano
Coronaviruses.2020; 1(1): 32. CrossRef - Effect of l-arginine supplementation on C-reactive protein and other inflammatory biomarkers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Behzad Nazarian, Ezatollah Fazeli Moghadam, Omid Asbaghi, Mohammad Zeinali Khosroshahi, Razieh Choghakhori, Amir Abbasnezhad
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2019; 47: 102226. CrossRef - The effect of green tea on C-reactive protein and biomarkers of oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Omid Asbaghi, Faezeh Fouladvand, Michael J. Gonzalez, Vahideh Aghamohammadi, Razieh Choghakhori, Amir Abbasnezhad
Complementary Therapies in Medicine.2019; 46: 210. CrossRef
- Zinc Supplementation in Individuals with Prediabetes and type 2 Diabetes: a GRADE-Assessed Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-analysis

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Novel Molecules Regulating Energy Homeostasis: Physiology and Regulation by Macronutrient Intake and Weight Loss
- Anna Gavrieli, Christos S. Mantzoros
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(3):361-372. Published online July 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.3.361
- 4,520 View
- 48 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Excess energy intake, without a compensatory increase of energy expenditure, leads to obesity. Several molecules are involved in energy homeostasis regulation and new ones are being discovered constantly. Appetite regulating hormones such as ghrelin, peptide tyrosine-tyrosine and amylin or incretins such as the gastric inhibitory polypeptide have been studied extensively while other molecules such as fibroblast growth factor 21, chemerin, irisin, secreted frizzle-related protein-4, total bile acids, and heme oxygenase-1 have been linked to energy homeostasis regulation more recently and the specific role of each one of them has not been fully elucidated. This mini review focuses on the above mentioned molecules and discusses them in relation to their regulation by the macronutrient composition of the diet as well as diet-induced weight loss.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extracts of Dunkelfelder Grape Seeds and Peel Increase the Metabolic Rate and Reduce Fat Deposition in Mice Maintained on a High-Fat Diet
Chenlu Yang, Xuelin Tian, Yulei Han, Xueqing Shi, Hua Wang, Hua Li
Foods.2023; 12(17): 3251. CrossRef - Insulin Resistance and Glucose Metabolism during Infection
Borros Arneth
Endocrines.2023; 4(4): 685. CrossRef - CMKLR1 senses chemerin/resolvin E1 to control adipose thermogenesis and modulate metabolic homeostasis
Zewei Zhao, Siqi Liu, Bingxiu Qian, Lin Zhou, Jianglin Shi, Junxi Liu, Lin Xu, Zhonghan Yang
Fundamental Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dissecting biological activities of fibroblast growth factor receptors by the coiled-coil-mediated oligomerization of FGF1
Natalia Porebska, Marta Pozniak, Mateusz Adam Krzyscik, Agata Knapik, Aleksandra Czyrek, Marika Kucinska, Kamil Jastrzebski, Malgorzata Zakrzewska, Jacek Otlewski, Lukasz Opalinski
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2021; 180: 470. CrossRef - Oral Semaglutide, the First Ingestible Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist: Could It Be a Magic Bullet for Type 2 Diabetes?
Hwi Seung Kim, Chang Hee Jung
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(18): 9936. CrossRef - Serum interleukin 15 in anorexia nervosa: Comparison to normal weight and obese girls
Wojciech Roczniak, Agata Mikołajczak-Będkowska, Elżbieta Świętochowska, Zofia Ostrowska, Katarzyna Ziora, Sylwia Balcerowicz, Karolina Górska-Flak, Magdalena Milan, Joanna Oświęcimska
The World Journal of Biological Psychiatry.2020; 21(3): 203. CrossRef - Physiology of energy homeostasis: Models, actors, challenges and the glucoadipostatic loop
Didier Chapelot, Keyne Charlot
Metabolism.2019; 92: 11. CrossRef - Correlates of zinc finger BED domain-containing protein 3 and ghrelin in metabolic syndrome patients with and without prediabetes
Rawan AbuZayed, Nailya Bulatova, Violet Kasabri, Maysa Suyagh, Lana Halaseh, Sundus AlAlawi
Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Pharmacotherapy of obesity: Available medications and drugs under investigation
Eleni Pilitsi, Olivia M. Farr, Stergios A. Polyzos, Nikolaos Perakakis, Eric Nolen-Doerr, Aimilia-Eirini Papathanasiou, Christos S. Mantzoros
Metabolism.2019; 92: 170. CrossRef - Link between chemerin, central obesity, and parameters of the Metabolic Syndrome: findings from a longitudinal study in obese children participating in a lifestyle intervention
Petra Niklowitz, Juliane Rothermel, Nina Lass, Andre Barth, Thomas Reinehr
International Journal of Obesity.2018; 42(10): 1743. CrossRef - The relationship between the leptin/ghrelin ratio and meals with various macronutrient contents in men with different nutritional status: a randomized crossover study
Edyta Adamska-Patruno, Lucyna Ostrowska, Joanna Goscik, Barbara Pietraszewska, Adam Kretowski, Maria Gorska
Nutrition Journal.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The Science of Obesity Management: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement
George A Bray, William E Heisel, Ashkan Afshin, Michael D Jensen, William H Dietz, Michael Long, Robert F Kushner, Stephen R Daniels, Thomas A Wadden, Adam G Tsai, Frank B Hu, John M Jakicic, Donna H Ryan, Bruce M Wolfe, Thomas H Inge
Endocrine Reviews.2018; 39(2): 79. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Weight loss technology for people with treated type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial
Kuat Oshakbayev, Bibazhar Dukenbayeva, Gulnar Togizbayeva, Aigul Durmanova, Meruyert Gazaliyeva, Abdul Sabir, Aliya Issa, Alisher Idrisov
Nutrition & Metabolism.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Salivary, gingival crevicular fluid and serum levels of ghrelin and chemerin in patients with periodontitis and overweight
H. F. R. Jentsch, N. Arnold, V. Richter, J. Deschner, T. Kantyka, S. Eick
Journal of Periodontal Research.2017; 52(6): 1050. CrossRef
- Extracts of Dunkelfelder Grape Seeds and Peel Increase the Metabolic Rate and Reduce Fat Deposition in Mice Maintained on a High-Fat Diet


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



