Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Hypothalamus and pituitary gland
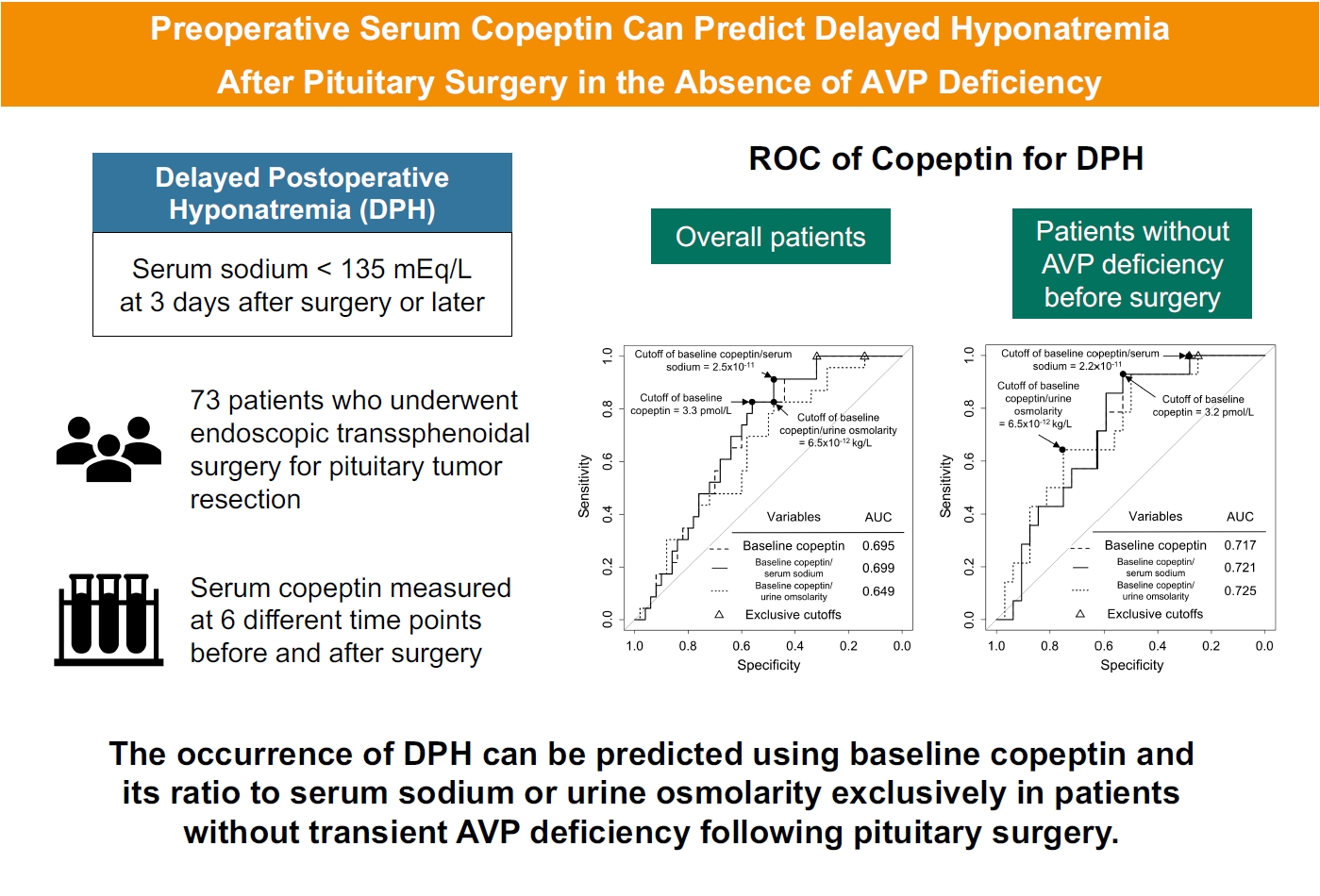
- Preoperative Serum Copeptin Can Predict Delayed Hyponatremia after Pituitary Surgery in the Absence of Arginine Vasopressin Deficiency
- Ho Kang, Seung Shin Park, Yoo Hyung Kim, Hwan Sub Lim, Mi-Kyeong Lee, Kyoung-Ryul Lee, Jung Hee Kim, Yong Hwy Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2024;39(1):164-175. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1792
- 1,020 View
- 47 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Delayed postoperative hyponatremia (DPH) is the most common cause of readmission after pituitary surgery. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the cutoff values of serum copeptin and determine the optimal timing for copeptin measurement for the prediction of the occurrence of DPH in patients who undergo endoscopic transsphenoidal approach (eTSA) surgery and tumor resection.
Methods
This was a prospective observational study of 73 patients who underwent eTSA surgery for pituitary or stalk lesions. Copeptin levels were measured before surgery, 1 hour after extubation, and on postoperative days 1, 2, 7, and 90.
Results
Among 73 patients, 23 patients (31.5%) developed DPH. The baseline ratio of copeptin to serum sodium level showed the highest predictive performance (area under the curve [AUROC], 0.699), and its optimal cutoff to maximize Youden’s index was 2.5×10–11, with a sensitivity of 91.3% and negative predictive value of 92.0%. No significant predictors were identified for patients with transient arginine vasopressin (AVP) deficiency. However, for patients without transient AVP deficiency, the copeptin-to-urine osmolarity ratio at baseline demonstrated the highest predictive performance (AUROC, 0.725). An optimal cutoff of 6.5×10–12 maximized Youden’s index, with a sensitivity of 92.9% and a negative predictive value of 94.1%.
Conclusion
The occurrence of DPH can be predicted using baseline copeptin and its ratio with serum sodium or urine osmolarity only in patients without transient AVP deficiency after pituitary surgery.

- Clinical Study
- Prevalence of Hyponatremia in Hypothyroid Patients during Radioactive 131I Ablation for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Single Institution Experience
- Juan Carlo P. Dayrit, Elaine C. Cunanan, Sjoberg A. Kho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(3):410-415. Published online August 17, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.3.410
- 3,427 View
- 34 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Hyponatremia developing in hypothyroid patients has been encountered in clinical practice; however, its prevalence has not been well established.
Methods Thirty patients diagnosed with differentiated thyroid cancer, rendered hypothyroid after surgery and levothyroxine withdrawal, and who are for radioactive iodine (RAI) ablation were included. Serum sodium concentrations were measured twice, at the time of admission for RAI ablation, and before discharge after increased oral fluid intake. The outcome measures were to determine the prevalence of hyponatremia among hypothyroid patients prior to RAI ablation and after oral hydration post-RAI, and to correlate the serum sodium levels pre-RAI and post-RAI with thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) concentration and age.
Results Thirty patients were included, with ages from 23 to 65 years old (median, 40). Two patients (6.7%) were hyponatremic prior to RAI ablation, and eight patients (26.7%) had mild hyponatremia (130 to 134 mEq/L) after RAI and hydration. There was no significant correlation between TSH levels and serum sodium levels prior to or after RAI. There was also no significant correlation between pre- and post-RAI sodium concentration and age.
Conclusions The prevalence of hyponatremia pre-RAI was 6.7%, and 26.7% post-RAI. No significant correlation was noted between TSH concentration and age on pre- or post-RAI sodium concentrations. Routine measurement of serum sodium post-RAI/isolation is still not advised. Measurement of sodium post-RAI may be considered in patients who are elderly, with comorbid conditions or on medications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is there a causal relationship between hypothyroidism and hyponatremia?
Julie Chen
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Endocrinopathy-induced euvolemic hyponatremia
Talia Diker-Cohen, Benaya Rozen-Zvi, Dana Yelin, Amit Akirov, Eyal Robenshtok, Anat Gafter-Gvili, Daniel Shepshelovich
Internal and Emergency Medicine.2018; 13(5): 679. CrossRef
- Is there a causal relationship between hypothyroidism and hyponatremia?

- Thyroid
- Hyponatremia after Thyroid Hormone Withdrawal in a Patient with Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Hyo Jin Jo, Yong Hyun Kim, Dong Hyun Shin, Mi Jeoung Kim, Sang Jin Lee, Dong Ok Jeon, Sung Gyu Im, Sun Kyung Jang, Jin Young Choi
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(1):77-82. Published online March 14, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.1.77
- 4,191 View
- 42 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Hyponatremia is an electrolyte abnormality commonly found in clinical practice. It is important to diagnose the underlying etiology of the hyponatremia and correct it appropriately because severe hyponatremia can cause serious complications and substantially increase the risk of mortality. Although hypothyroidism is known to be a cause of hyponatremia, it is rare that hyponatremia occurs in relation to hypothyroidism induced by thyroid hormone withdrawal in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. We report a case of a 76-year-old woman with papillary thyroid carcinoma presenting with severe hyponatremia related to hypothyroidism induced by thyroid hormone withdrawal for radio-active iodine whole-body scanning, who was treated by thyroid hormone replacement and hydration. Considering that the incidence of differentiated thyroid cancer is rapidly increasing, physicians should be aware that, although uncommon, hyponatremia can occur in patients undergoing radioiodine therapy or diagnostic testing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of preparation method for radioactive iodine therapy on serum electrolytes
Noriko Takata, Masao Miyagawa, Tomohisa Okada, Naoto Kawaguchi, Yutaka Fujimoto, Yoshihiro Kouchi, Shintaro Tsuruoka, Kotaro Uwatsu, Teruhito Kido
Japanese Journal of Radiology.2023; 41(11): 1247. CrossRef - MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: Hypothyroidism-associated hyponatremia: mechanisms, implications and treatment
G Liamis, T D Filippatos, A Liontos, M S Elisaf
European Journal of Endocrinology.2017; 176(1): R15. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef - Parathyroid hormone-related protein serves as a prognostic indicator in oral squamous cell carcinoma
Zhongjing Lv, Xiangbing Wu, Wei Cao, ZongZe Shen, Lizhen Wang, FuRong Xie, JianJun Zhang, Tong Ji, Ming Yan, WanTao Chen
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Hyponatremia and the Thyroid: Causality or Association?
Kevin Pantalone, Betul Hatipoglu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2014; 4(1): 32. CrossRef
- Effect of preparation method for radioactive iodine therapy on serum electrolytes

- A Case of Giant Cell Granulomatous Hypophysitis with Recurrent Hypoosmolar Hyponatremia.
- Yun Hyeong Lee, Yong Bum Kim, Ju Hee Lee, Kyoung Hye Jeong, Min Kyeong Kim, Kyu Sang Song, Young Suk Jo
- Endocrinol Metab. 2010;25(4):347-353. Published online December 1, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2010.25.4.347
- 2,038 View
- 24 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 39-year-old woman presented with a 20 day history of recurrent hypoosmolar hyponatremia. Because her volume status seemed to be normal, the most suspected causes of her hyponatremia were adrenal insufficiency and hypothyroidism. Endocrinologic examination, including a combined pituitary function test, showed TSH and ACTH deficiency without GH deficiency, and hyperprolactinemia was also present. Sella MRI showed a pituitary mass, stalk thickening and loss of the normal neurohypophysial hyperintense signal on the T1 weighted image. Pathologic exam demonstrated granulomatous lesions and Langhans' multinucleated giant cells with inflammatory cell infiltration. After high dose methylprednisolone pulse therapy (1 g/day for 3 days) with subsequent prednisolone and levothyoxine replacement, there was no more recurrence of the hyponatremia. The sella MRI on the 6th month showed decreased mass size, narrowed stalk thickening and the reappearance of the normal neurohyphophysial hyperintense signal. She is currently in a good general condition and is receiving hormone replacement therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Primary Granulomatous Hypophysitis Presenting with Panhypopituitarism and Central Diabetes Insipidus
Hyun Jin Oh, Ji Young Mok, Ji Eun Kim, Sung Bae Cho, Sang Ah Chang, Ji Hyun Kim, Jung Min Lee
Korean Journal of Medicine.2015; 88(5): 581. CrossRef - Idiopathic granulomatous hypophysitis: a systematic review of 82 cases in the literature
Benjamin H. M. Hunn, William G. Martin, Steven Simpson, Catriona A. Mclean
Pituitary.2014; 17(4): 357. CrossRef
- Primary Granulomatous Hypophysitis Presenting with Panhypopituitarism and Central Diabetes Insipidus

- A Case of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Syndrome Complicated with Tuberculous Meningitis Refractory to Antituberculosis Drugs.
- Ju Hee Oh, Sang Pil Yun, So Young Lee, Yeo Kyung Lee, Young Sun Jung, Soo Kyung Kim, Sung Kwan Hong, Seok Won Park, Yong Wook Cho
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007;22(3):210-214. Published online June 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.3.210
- 1,570 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone is the most common cause of hyponatremia in hospitalized patients. It is defined as retention of water, loss of sodium and inappropriately concentrated urine in euvolemic patients with normal renal and adrenal function. A 26-year old male was admitted due to weight loss and fever that he had experienced for the previous 1 month. The chest X-ray and CT scan of lung showed about 2.5x1.2 cm lymph node enlargement at the left hilum and multiple lymph node enlargements. Thoracoscopic biopsy revealed tuberculosis. During treatment with antituberculosis drugs, the serum sodium was 125 mEq/L, the serum osmolality was 263 mOsm/kg, the urine osmolality was 577 mOsm/kg, and the urine sodium concentration was 177 mEq/L. He was treated by fluid restriction and hypertonic saline infusion, but he did not improve. Brain CT scan showed tuberculous meningitis with hydrocephalus. He fully recovered after undergoing ventriculoperitoneal shunt. We report here on a case of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone syndrome complicated by tuberculous meningitis that was refractory to antituberculosis drugs.

- Rhabdomyolysis Associated with Hyponatremia.
- Kyoung Wook Lee, Seong Bin Hong, Seung Baik Han, Bon Ju Jeong, Hwi Ra Park, Eun Sil Kim, Dong Hyo Hyun, Moon Suk Nam, Yong Seong Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2003;18(3):306-310. Published online June 1, 2003
- 1,185 View
- 26 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hyponatremia is a frequent condition of body fluid and electrolyte imbalance encountered in clinical practice. However, rhabdomyolysis has rarely been reported in association with hyponatremia. We experienced a 56-year-old woman who had developed symptomatic hyponatremia after prolonged nausea and subsequent rhabdomyolysis. Hyponatremia was probably mediated by hypersecretion of antidiuretic hormones.The woman had developed severe hypotonic hyponatremia with an alternation in mental status after suffering from severe nausea and vomiting for x months/years. She recovered with intensive supportive therapy, including hypertonic saline administration. One day after hospitalization, she complained of thigh pains; furthermore her serum creatine phosphokinase level had increased. She was treated with alkaline diuresis. Renal failure or compartment syndrome did not complicate the clinical course. The patient was discharged and returned to her normal daily activities. The possibility of rhabdomyolysis should be considered in patients with acute hyponatremia who have developed muscle pain.

- A Case of Cerebral Salt Wasting Syndrome associated with Tuberculous Meningitis.
- Seung Hyuk Rho, Ji Yong Choi, Taek Man Nam, Hyeon Kyu Kim, Seong Jin Lee, In Kyung Jeong, Eun Gyung Hong, Cheol Soo Choi, Doo Man Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Sung Hee Ihm, Moon Gi Choi, Hyung Joon Yoo, Sung Woo Park, Hyoung Cheol Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2002;17(5):698-704. Published online October 1, 2002
- 1,252 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hyponatremia in patients with central nervous system disorders is suggestive of the syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH), and volume restriction is recommended for its correction. However, if volume depletion is present in a situation otherwise compatible with SIADH, cerebral salt wasting syndrome (CSWS) should be considered as the cause of the hyponatremia to avoid hypovolemic shock that may be induced by the standard management of SIADH, i.e. volume restriction. We present a case of a 17-year-old male patient with CSWS associated with tuberculous meningitis. The clinical feature of the patient comprised hyponatremia, excessive natriuresis, polyuria, and hypovolemia. Following the administration of saline and fludrocortisone, natriuresis and polyuria were decreased, and the hyponatremia improved

- A Case of Cerebral salt Wasting Syndrome with Pseudomonas Meningitis after Removal of Pituitary Adenoma.
- Dong Yoon Kim, Byung Yi Ahn, Duk Soo Cho, Se Hwa Kim, Kwi Wan Kim, Jong Phil Eun
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1997;12(4):609-613. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,048 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Hyponatremia is frequently seen in intracranial hemorrhagic patients and has been often attributed to inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone. But in recent years, a number of studies have shown that hyponatremia in many patients with intracranial disease may actually be caused by cerebral salt wasting (CSW) syndrome and circulating Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) are probably involved. This report describes a patient who developed bacterial meningites caused by pseudomonas aeruginosa and CSW syndrome after removal of pituitary adenoma. CSW syndrome resolved by fluid and salt replacement after 4 months.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



