Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Thyroid
- Association between Thyroid Function and Heart Rate Monitored by Wearable Devices in Patients with Hypothyroidism
- Ki-Hun Kim, Juhui Lee, Chang Ho Ahn, Hyeong Won Yu, June Young Choi, Ho-Young Lee, Won Woo Lee, Jae Hoon Moon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):1121-1130. Published online October 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1216
- 5,403 View
- 157 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
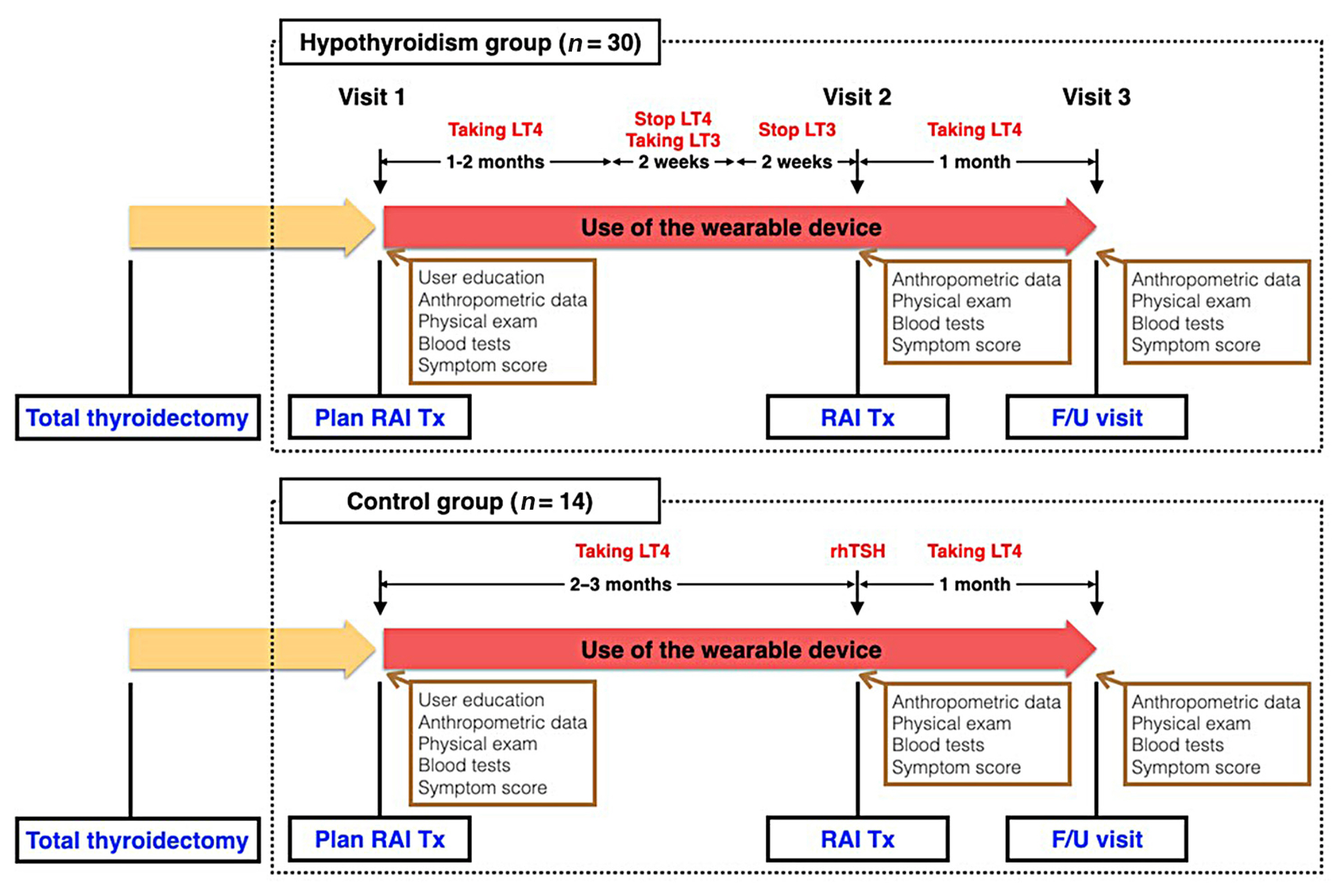
Heart rate (HR) monitored by a wearable device (WD) has demonstrated its clinical feasibility for thyrotoxicosis subjects. However, the association of HR monitored by wearables with hypothyroidism has not been examined. We assessed the association between serum thyroid hormone concentration and three WD-HR parameters in hypothyroid subjects.
Methods
Forty-four subjects scheduled for radioactive iodine therapy (RAI Tx) after thyroid cancer surgery were included. Thirty subjects were prepared for RAI Tx by thyroid hormone withdrawal (hypothyroidism group) and 14 subjects by recombinant human thyrotropin (control group). Three WD-HR parameters were calculated from the HR data collected during rest, during sleep, and from 2:00 AM to 6:00 AM, respectively. We analyzed the changes in conventionally measured resting HR (On-site rHR) and WDHR parameters relative to thyroid hormone levels.
Results
Serum free thyroxine (T4) levels, On-site rHR, and WD-HR parameters were lower in the hypothyroid group than in the control group at the time of RAI Tx. WD-HR parameters also reflected minute changes in free T4 levels. A decrease in On-site rHR and WD-HR parameters by one standard deviation (On-site rHR, approximately 12 bpm; WD-HR parameters, approximately 8 bpm) was associated with a 0.2 ng/dL decrease in free T4 levels (P<0.01) and a 2-fold increase of the odds ratio of hypothyroidism (P<0.01). WD-HR parameters displayed a better goodness-of-fit measure (lower quasi-information criterion value) than On-site rHR in predicting the hypothyroidism.
Conclusion
This study identified WD-HR parameters as informative and easy-to-measure biomarkers to predict hypothyroidism. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Application of wearables for remote monitoring of oncology patients: A scoping review
Katharina Cloß, Marlo Verket, Dirk Müller-Wieland, Nikolaus Marx, Katharina Schuett, Edgar Jost, Martina Crysandt, Fabian Beier, Tim H Brümmendorf, Guido Kobbe, Julia Brandts, Malte Jacobsen
DIGITAL HEALTH.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Thyroid hormone action during GABAergic neuron maturation: The quest for mechanisms
Sabine Richard, Juan Ren, Frédéric Flamant
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A machine learning-assisted system to predict thyrotoxicosis using patients’ heart rate monitoring data: a retrospective cohort study
Kyubo Shin, Jongchan Kim, Jaemin Park, Tae Jung Oh, Sung Hye Kong, Chang Ho Ahn, Joon Ho Moon, Min Joo Kim, Jae Hoon Moon
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Application of wearables for remote monitoring of oncology patients: A scoping review

- Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland
- Heart Rate Variability in Postoperative Patients with Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenoma
- Jeonghoon Ha, Hansang Baek, Chaiho Jeong, Minsoo Yeo, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Ki-Hyun Baek, Moo Il Kang, Dong-Jun Lim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):678-687. Published online June 10, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.978
- 4,531 View
- 108 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
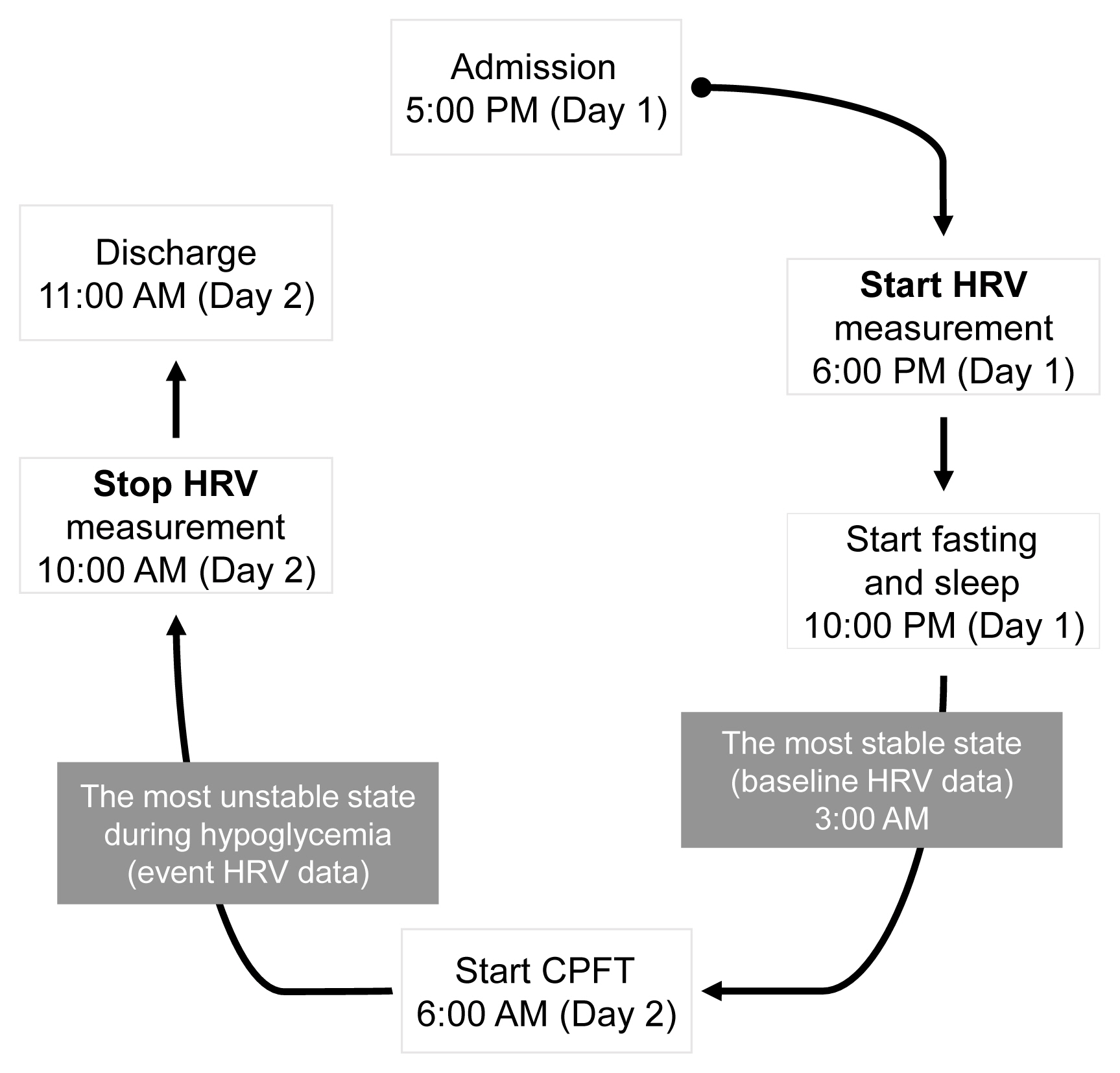
Decreased heart rate variability (HRV) has been reported to be associated with cardiac autonomic dysfunction. Hypopituitarism in nonfunctioning pituitary adenoma (NFPA) is often linked to increased cardiovascular mortality. We therefore hypothesized that postoperative NFPA patients with hormone deficiency have an elevated risk of HRV alterations indicating cardiac autonomic dysfunction.
Methods
A total of 22 patients with NFPA were enrolled in the study. Between 3 and 6 months after surgery, a combined pituitary function test (CPFT) was performed, and HRV was measured. The period of sleep before the CPFT was deemed the most stable period, and the hypoglycemic period that occurred during the CPFT was defined as the most unstable period. Changes in HRV parameters in stable and unstable periods were observed and compared depending on the status of hormone deficiencies.
Results
In patients with adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) deficiency with other pituitary hormone deficiencies, the low frequency to high frequency ratio, which represents overall autonomic function and is increased in the disease state, was higher (P=0.005). Additionally, the standard deviation of the normal-to-normal interval, which decreases in the autonomic dysfunction state, was lower (P=0.030) during the hypoglycemic period. In panhypopituitarism, the low frequency to high frequency ratio during the hypoglycemic period was increased (P=0.007).
Conclusion
HRV analysis during CPFT enables estimation of cardiac autonomic dysfunction in patients with NFPA who develop ACTH deficiency with other pituitary hormone deficiencies or panhypopituitarism after surgery. These patients may require a preemptive assessment of cardiovascular risk. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Heart Rate Variability in Subjects with Severe Allergic Background Undergoing COVID-19 Vaccination
Maria Bernadette Cilona, Filippo D’Amico, Chiara Asperti, Giuseppe Alvise Ramirez, Stefano Turi, Giovanni Benanti, Shai Marc Bohane, Serena Nannipieri, Rosa Labanca, Matteo Gervasini, Federica Russetti, Naomi Viapiana, Martina Lezzi, Giovanni Landoni, Lor
Vaccines.2023; 11(3): 567. CrossRef - Pituitary Diseases and COVID-19 Outcomes in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Jeonghoon Ha, Kyoung Min Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(14): 4799. CrossRef - Effect of a 16-Session Qigong Program in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Survivors: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Keyla Vargas-Román, Emilia I. De la Fuente-Solana, Jonathan Cortés-Martín, Juan Carlos Sánchez-García, Christian J. González-Vargas, Lourdes Díaz-Rodríguez
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(12): 3421. CrossRef
- Heart Rate Variability in Subjects with Severe Allergic Background Undergoing COVID-19 Vaccination


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



